Barriers, Facilitators, and a Proposed Model of Care for Implementation of Upper Limb Distributed Practice Approaches for Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design and Setting
2.2.1. Phase One
2.2.2. Phase Two
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Case Series Data Review (Phase One)
2.3.2. Identification of Implementation Strategies and Outcomes (Phase Two)
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Data
3.2. Case Series Data Review (Phase One)
3.3. Identification of Implementation Strategies and Outcomes (Phase Two)
3.3.1. Barriers
3.3.2. Facilitators
3.3.3. Implementation Outcomes
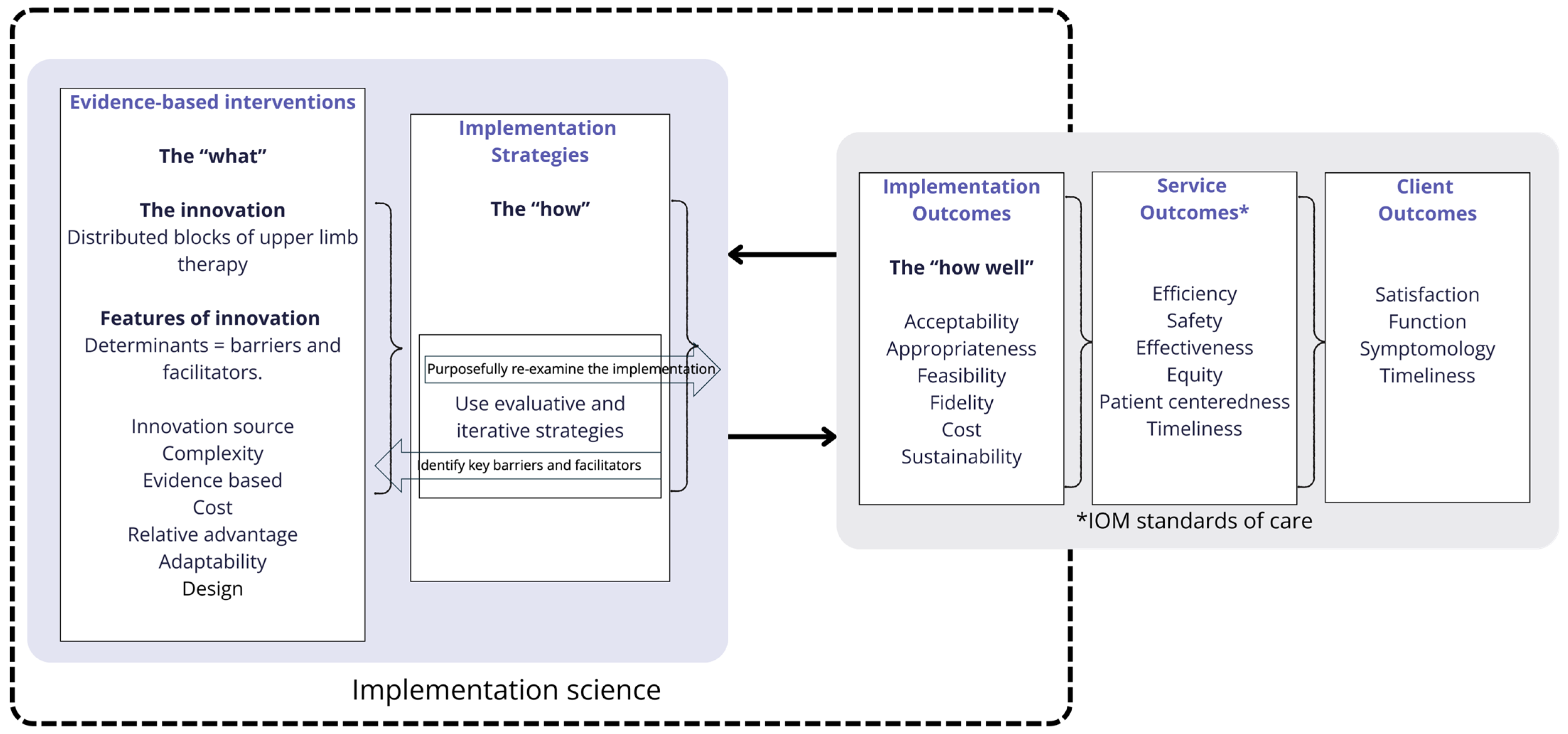
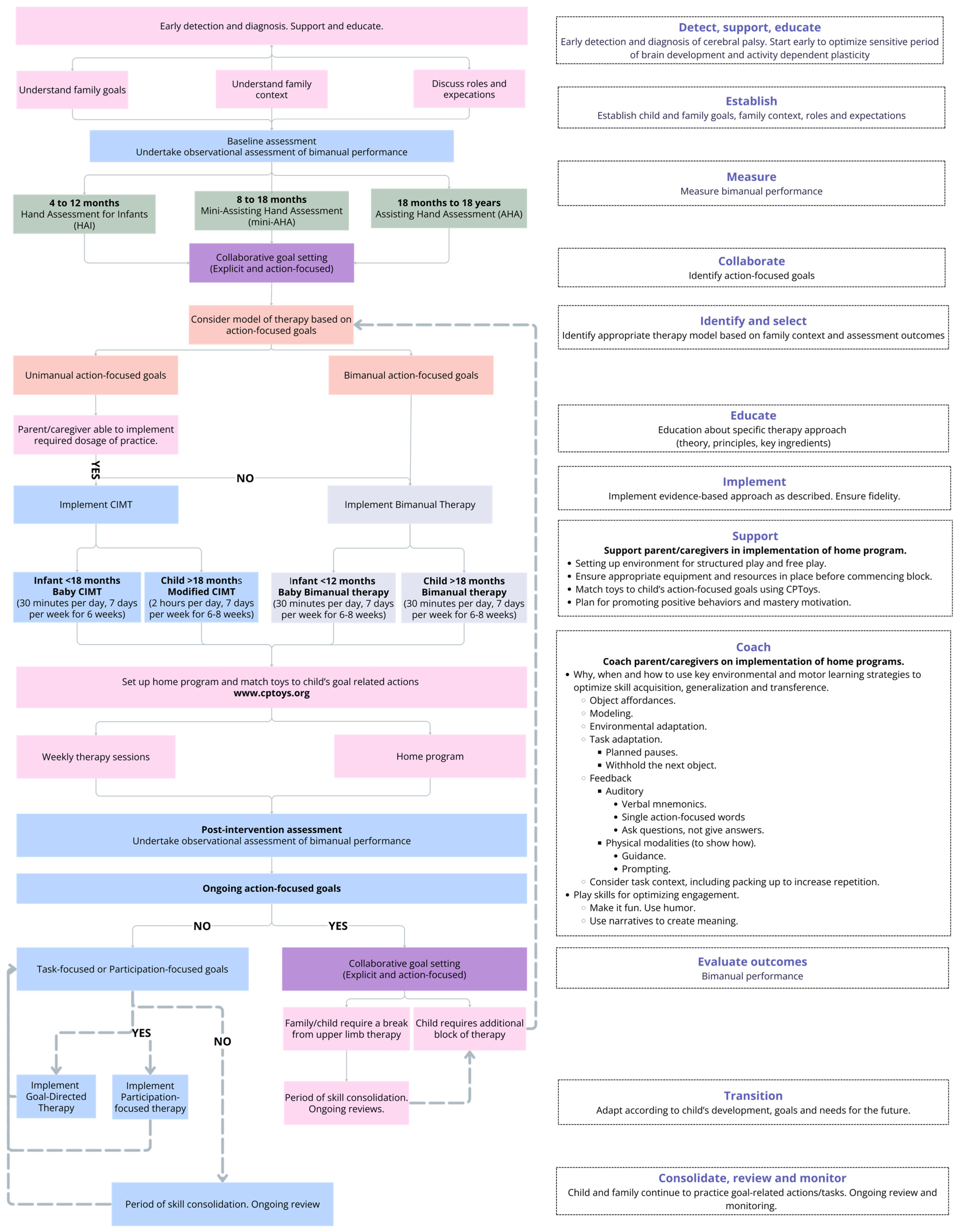
3.4. Development of a Proposed Model of Care (MOC) for Upper Limb Therapy
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Practical Applications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Report of the Australian Cerebral Palsy Register, Birth Years 1995–2016, January 2023. Available online: https://cpregister.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/2023-ACPR-Report.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- Centorame, D.; Rawicki, B.; Hennel, S.; Hoare, B. Upper Limb Onabotulinumtoxin A Injections in Children Under 2 Years with Cerebral Palsy: A Retrospective Chart Review. J. Child Neurol. 2022, 37, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordstrand, L.; Eliasson, A.-C.; Holmefur, M. Longitudinal Development of Hand Function in Children with Unilateral Spastic Cerebral Palsy Aged 18 Months to 12 Years. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klevberg, G.L.; Jahnsen, R.; Elkjær, S.; Zucknick, M. Hand Use Development in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmefur, M.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Bergstrom, J.; Eliasson, A.-C. Longitudinal Development of Hand Function in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmefur, M.; Kits, A.; Bergström, J.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Flodmark, O.; Forssberg, H.; Eliasson, A.-C. Neuroradiology Can Predict the Development of Hand Function in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2013, 27, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakzewski, L.; Greaves, S.; Eliasson, A.C.; Wallen, M.; Novak, I.; Ware, R.S.; Heathcock, J.; Maitre, N.; Boyd, R. Early developmental trajectories of the impaired hand in infants with unilateral cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2025; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friel, K.M.; Williams, P.T.J.A.; Serradj, N.; Chakrabarty, S.; Martin, J.H. Activity-Based Therapies for Repair of the Corticospinal System Injured during Development. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleim, J.; Jones, T. Principles of Experience-Dependent Neural Plasticity: Implications for Rehabilitation After Brain Damage. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2008, 51, S225–S239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boychuck, Z.; Andersen, J.; Bussières, A.; Fehlings, D.; Kirton, A.; Li, P.; Oskoui, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Shevell, M.; Snider, L.; et al. International Expert Recommendations of Clinical Features to Prompt Referral for Diagnostic Assessment of Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klevberg, G.L.; Elvrum, A.G.; Zucknick, M.; Elkjær, S.; Østensjø, S.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Kjeken, I.; Jahnsen, R. Development of Bimanual Performance in Young Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, A.; Nordstrand, L.; Backheden, M.; Holmefur, M. Longitudinal Development of Hand Use in Children with Unilateral Spastic Cerebral Palsy from 18 Months to 18 Years. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023, 65, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoare, B.; Greaves, S. Unimanual versus Bimanual Therapy in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: Same, Same, but Different. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 10, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, A.; Webster, K.E.; Bhopti, A.; Carey, L.; Hoare, B. Are They Really Motor Learning Therapies? A Scoping Review of Evidence-Based, Task-Focused Models of Upper Limb Therapy for Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2023, 45, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakzewski, L.; Ziviani, J.; Boyd, R.N. Efficacy of Upper Limb Therapies for Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Meta-Analysis. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e175–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.M.; Schneider, J.A.; Chinnan, A.; Charles, J.R. Efficacy of a Hand–Arm Bimanual Intensive Therapy (HABIT) in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Control Trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, B.; Imms, C.; Villanueva, E.; Rawicki, H.B.; Matyas, T.; Carey, L. Intensive Therapy Following Upper Limb Botulinum Toxin A Injection in Young Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, A.-C.; Shaw, K.; Berg, E.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L. An Ecological Approach of Constraint Induced Movement Therapy for 2–3-Year-Old Children: A Randomized Control Trial. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 2820–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallen, M.; Ziviani, J.; Naylor, O.; Evans, R.; Novak, I.; Herbert, R.D. Modified Constraint-induced Therapy for Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, I.; Cusick, A.; Lannin, N. Occupational Therapy Home Programs for Cerebral Palsy: Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Pediatrics 2009, 124, e606–e614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamudot, R.; Parush, S.; Rigbi, A.; Horovitz, R.; Gross-Tsur, V. Effectiveness of Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy Compared with Bimanual Therapy Home Programs for Infants with Hemiplegia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2018, 72, 7206205010p1–7206205010p9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulf, G.; Schmidt, R.A. Variability of Practice and Implicit Motor Learning. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1997, 23, 987–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Shea, C.H. Effect of Practice on Effector Independence. J. Mot. Behav. 2003, 35, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleyenheuft, Y.; Ebner-Karestinos, D.; Surana, B.; Paradis, J.; Sidiropoulos, A.; Renders, A.; Friel, K.M.; Brandao, M.; Rameckers, E.; Gordon, A.M. Intensive Upper- and Lower-Extremity Training for Children with Bilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Quasi-Randomized Trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Fahey, M.; Finch-Edmondson, M.; Galea, C.; Hines, A.; Langdon, K.; Namara, M.M.; Paton, M.C.B.; Popat, H.; et al. State of the Evidence Traffic Lights 2019: Systematic Review of Interventions for Preventing and Treating Children with Cerebral Palsy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, B.J.; Wallen, M.A.; Thorley, M.N.; Jackman, M.L.; Carey, L.M.; Imms, C. Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, CD004149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, B. Constraint Therapy, the Panacea for Unilateral Cerebral Palsy? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.; Shierk, A.; Alfonso, A.J.; Yeatts, P.; DeJong, T.L.; Clegg, N.J.; Baldwin, D.; Delgado, M.R. Improved Hand Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy with Repeat Doses of Group Based Hybrid Pediatric Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy. Disabilities 2022, 2, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluca, S.C.; Ramey, S.L.; Trucks, M.R.; Wallace, D.A. Multiple Treatments of Pediatric Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (PCIMT): A Clinical Cohort Study. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2015, 69, 6906180010p1–6906180010p9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, J.R.; Gordon, A.M. A Repeated Course of Constraint-induced Movement Therapy Results in Further Improvement. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, A.-C.; Nordstrand, L.; Ek, L.; Lennartsson, F.; Sjöstrand, L.; Tedroff, K.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L. The Effectiveness of Baby-CIMT in Infants Younger than 12 Months with Clinical Signs of Unilateral-Cerebral Palsy; an Explorative Study with Randomized Design. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 72, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klevberg, G.L.; Zucknick, M.; Jahnsen, R.; Eliasson, A.-C. Development of Hand Use with and Without Intensive Training Among Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy in Scandinavia. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2023, 26, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, I.; Mcintyre, S.; Morgan, C.; Campbell, L.; Dark, L.; Morton, N.; Stumbles, E.; Wilson, S.; Goldsmith, S. A Systematic Review of Interventions for Children with Cerebral Palsy: State of the Evidence. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 885–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordstrand, L.; Eliasson, A.-C. Six Years After a Modified Constraint Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT) Program-What Happens When the Children Have Become Young Adults? Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2013, 33, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, C.J. Observational research methods. Research design II: Cohort, cross sectional, and case-control studies. Emerg. Med. J. 2003, 20, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, L.; Wolfenden, L. Research Note: Designing Implementation Trials in Physiotherapy. J. Physiother. 2022, 68, 210–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, A.-C.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Rösblad, B.; Beckung, E.; Arner, M.; Öhrvall, A.-M.; Rosenbaum, P. The Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) for Children with Cerebral Palsy: Scale Development and Evidence of Validity and Reliability. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Ek, L.; Sicola, E.; Sjöstrand, L.; Guzzetta, A.; Sgandurra, G.; Cioni, G.; Eliasson, A.-C. Development of the Hand Assessment for Infants: Evidence of Internal Scale Validity. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, S.; Imms, C.; Dodd, K.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L. Development of the Mini-Assisting Hand Assessment: Evidence for Content and Internal Scale Validity. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmefur, M.M.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L. Psychometric Properties of a Revised Version of the Assisting Hand Assessment (Kids-AHA 5.0). Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damschroder, L.J.; Reardon, C.M.; Widerquist, M.A.O.; Lowery, J. The Updated Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research Based on User Feedback. Implement. Sci. 2022, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, E.K.; Landsverk, J.; Aarons, G.; Chambers, D.; Glisson, C.; Mittman, B. Implementation Research in Mental Health Services: An Emerging Science with Conceptual, Methodological, and Training Challenges. Adm. Policy Ment. Health Ment. Health Serv. Res. 2009, 36, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltz, T.J.; Powell, B.J.; Matthieu, M.M.; Damschroder, L.J.; Chinman, M.J.; Smith, J.L.; Proctor, E.K.; Kirchner, J.E. Use of Concept Mapping to Characterize Relationships among Implementation Strategies and Assess Their Feasibility and Importance: Results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) Study. Implement. Sci. 2015, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signal, N.; Gomes, E.; Olsen, S.; Alder, G. Enhancing the Reporting Quality of Rehabilitation Interventions through an Extension of the Template for Intervention Description and Replication (TIDieR): The TIDieR-Rehab Checklist and Supplementary Manual. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e084320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Clinical Innovation, Implementation Team, Clinical Redesign and Implementation Portfolio. ACI (2013). Understanding the Process to Implement a Model of Care—An ACI Framework. Agency for Clinical Innovation. Available online: https://www.aci.health.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0009/194715/HS13-036_ImplementationFramework_D5-ck2.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Davidson, P.; Halcomb, E.; Hickman, L.; Phillips, J.; Graham, B. Beyond the Rhetoric: What Do We Mean by a “Model of Care”? Aust. J. Adv. Nurs. 2006, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.M.; Burns, K.E.; Adhikari, N.K.; Kho, M.E.; Meade, M.O.; Cook, D.J. The Design and Interpretation of Pilot Trials in Clinical Research in Critical Care. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, S69–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPToys.org. Available online: https://www.cptoys.org (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Proctor, E.; Silmere, H.; Raghavan, R.; Hovmand, P.; Aarons, G.; Bunger, A.; Griffey, R.; Hensley, M. Outcomes for Implementation Research: Conceptual Distinctions, Measurement Challenges, and Research Agenda. Adm. Policy Ment. Health Ment. Health Serv. Res. 2011, 38, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, P.; Gorter, J.W. The ‘F-words’ in childhood disability: I swear this is how we should think! Child Care Health Dev. 2012, 38, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, A.-C. What Can Be Learned from Reporting No-treatment Effect of Distribution of Upper Limb Training? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, S.; Hoare, B. Upper Limb Therapy for Infants and Young Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Clinical Framework. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.; Fetters, L.; Adde, L.; Badawi, N.; Bancale, A.; Boyd, R.N.; Chorna, O.; Cioni, G.; Damiano, D.L.; Darrah, J.; et al. Early Intervention for Children Aged 0 to 2 Years with or at High Risk of Cerebral Palsy: International Clinical Practice Guideline Based on Systematic Reviews. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 846–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Disability Insurance Agency. “What Is the NDIS?”. 2022. Available online: https://www.ndis.gov.au/understanding/what-ndis (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Ives, Y. What Is “Coaching”? An Exploration of Conflicting Paradigms. Int. J. Evid. Based Coach. Mentor. 2008, 6, 100–113. [Google Scholar]
- Valvano, J. Activity-Focused Motor Interventions for Children with Neurological Conditions. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2004, 24, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, C.; Novak, I.; Dale, R.C.; Badawi, N. Optimising Motor Learning in Infants at High Risk of Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study. BMC Pediatr. 2015, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoare, B.J.; Imms, C.; Rawicki, H.B.; Carey, L. Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy or Bimanual Occupational Therapy Following Injection of Botulinum Toxin-A to Improve Bimanual Performance in Young Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Randomised Controlled Trial Methods Paper. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, A.-C.; Sjöstrand, L.; Ek, L.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Tedroff, K. Efficacy of Baby-CIMT: Study Protocol for a Randomised Controlled Trial on Infants below Age 12 Months, with Clinical Signs of Unilateral CP. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerstein, R.; Hoffman, M.B.; Rand, Y.; Jensen, M.R.; Tzuriel, D.; Hoffmann, D.B. Learning to Learn: Mediated Learning Experiences and Instrumental Enrichment. Spec. Serv. Sch. 1986, 3, 49–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.T.; Bedell, G. Motor Skill Acquisition Frame of Reference. In Frames of Reference for Pediatric Occupational Therapy; Hinojosa, J., Kramer, P., Eds.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1999; Volume 2, pp. 401–429. [Google Scholar]
- Meichenbaum, D. Cognitive-Behavior Modification, an Integrative Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer Science + Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, E.J. Exploratory Behavior in the Development of Perceiving, Acting, and the Acquiring of Knowledge. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1988, 39, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastos, M.; Miller, K.; Eliasson, A.C.; Imms, C. Goal-Directed Training: Linking Theories of Treatment to Clinical Practice for Improved Functional Activities in Daily Life. Clin. Rehabil. 2007, 21, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelen, E.; Smith, L.B. Dynamic Systems: Exploring Paradigms for Change. In A Dynamic Systems Approach to the Development of Cognition and Action; Thelen, E., Smith, L.B., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 45–69. [Google Scholar]
- Law, M. Family-Centred Functional Therapy for Children with Cerebral Palsy: An Emerging Practice Model; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, A.; Webster, K.E.; Bhopti, A.; Hoare, B. Development and Content Validation of the Upper Limb-Motor Learning Strategy Tool for Cerebral Palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2024, 46, 5624–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
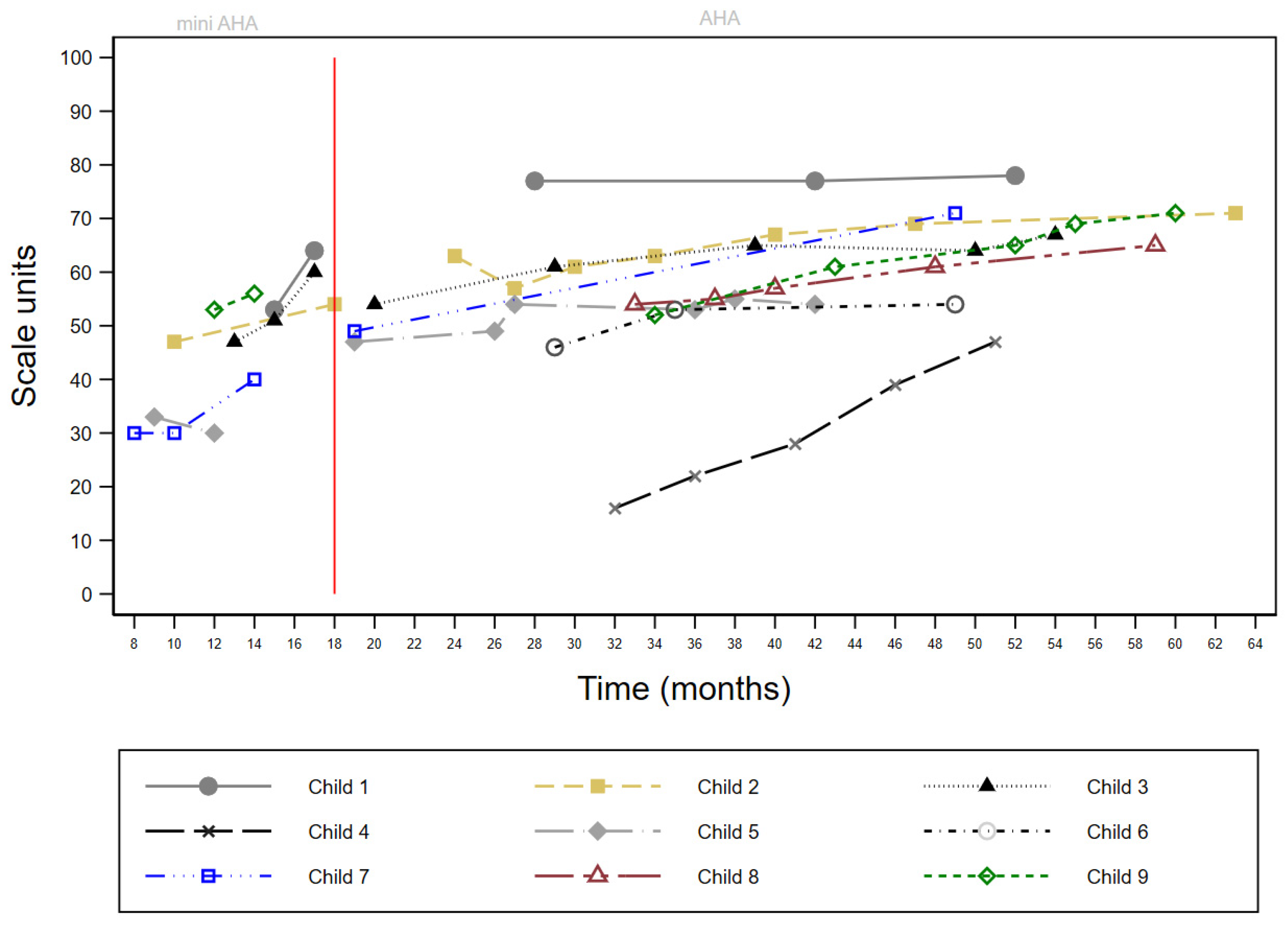
| Child | Sex | MACS | More-Affected Side | Age at 1st Contact (Months) | First Block | Initial HAI Units | CIMT Total Blocks | BIM Total Blocks | Total Blocks | Initial Mini-AHA Units | Final Mini-AHA Units | Change Mini-AHA Units | Initial AHA Units | Final AHA Units | Change AHA Units | Transition to GDT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 1 | L | 15 | BIM | - | 0 | 2 | 2 | 53 | 64 | 11 | 77 | 78 | 1 | 2 yrs 5 mths |
| 2 | F | 1 | L | 7 | BIM | 7 months EaHS: R 24 EaHS: L 7 BoHM: 53 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 47 | 54 | 7 | 57 | 71 | 14 | 2 yrs 9 mths |
| 3 | M | 2 | R | 12 | CIMT | 12 months EaHS: R 12 EaHS: L 24 BoHM: 60 | 1 | 8 | 9 | 47 | 60 | 13 | 54 | 67 | 13 | 4 yrs 2 mths |
| 4 | M | 2 | R | 5 | CIMT | 10 months EaHS: R 24 EaHS: L 5 BoHM: 48 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 23 | - | - | 16 | 47 | 31 | 4 yrs 3 mths |
| 5 | M | 2 | R | 9 | CIMT | - | 1 | 5 | 6 | 33 | 30 | −3 | 47 | 55 | 8 | * |
| 6 | M | 2 | L | 6 | CIMT | 7 months EaHS: R 20 EaHS: L 4 BoHM: 42 | 1 | 7 | 8 | - | - | - | 46 | 54 | 8 | 3 yrs |
| 7 | F | 2 | R | 7 | CIMT | - | 3 | 4 | 7 | 30 | 40 | 10 | 49 | 71 | 22 | 4 yrs 1 mth |
| 8 | M | 2 | R | 33 | BIM | - | 0 | 3 | 3 | - | - | - | 54 | 65 | 11 | 4 yrs 1 mth |
| 9 | M | 2 | R | 12 | CIMT | - | 1 | 6 | 7 | 53 | 56 | 3 | 52 | 71 | 19 | 4 yrs 4 mths |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taylor, E.; Greaves, S.; Hoare, B. Barriers, Facilitators, and a Proposed Model of Care for Implementation of Upper Limb Distributed Practice Approaches for Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030924
Taylor E, Greaves S, Hoare B. Barriers, Facilitators, and a Proposed Model of Care for Implementation of Upper Limb Distributed Practice Approaches for Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(3):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030924
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaylor, Emma, Susan Greaves, and Brian Hoare. 2025. "Barriers, Facilitators, and a Proposed Model of Care for Implementation of Upper Limb Distributed Practice Approaches for Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 3: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030924
APA StyleTaylor, E., Greaves, S., & Hoare, B. (2025). Barriers, Facilitators, and a Proposed Model of Care for Implementation of Upper Limb Distributed Practice Approaches for Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(3), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030924






