Peri-Eyebrow Incision: A Practical and Aesthetic Solution for Forehead Lipoma Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
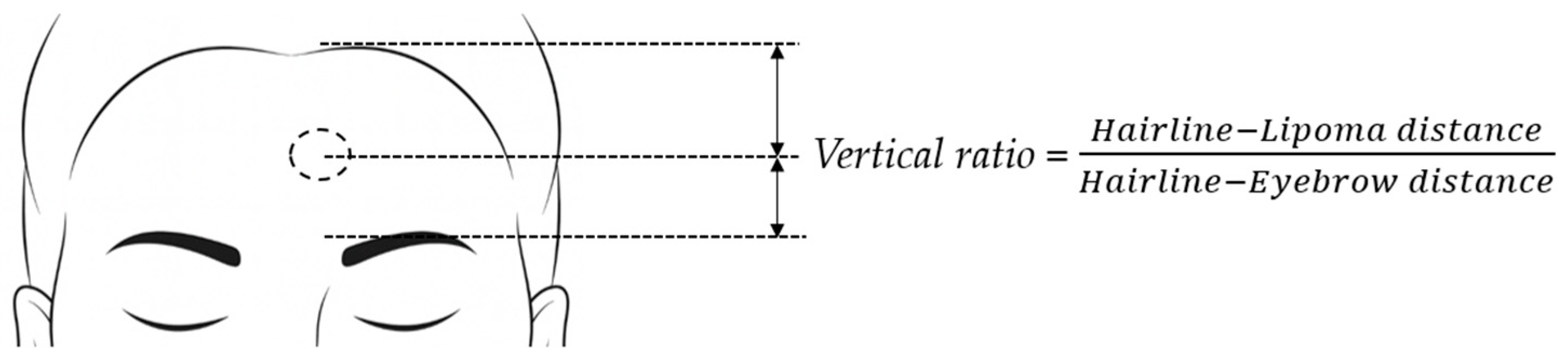
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Operation Technique
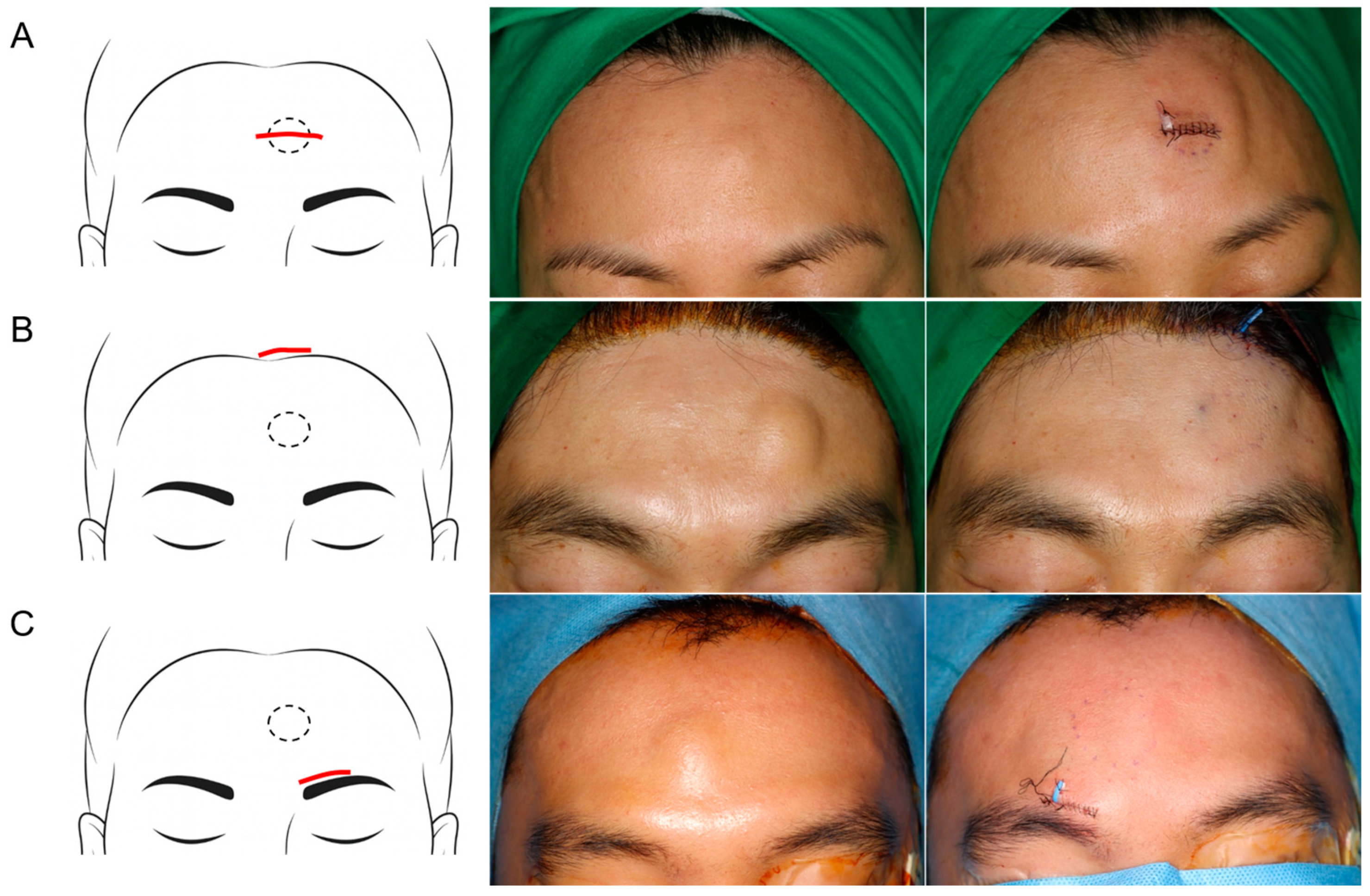
2.4.1. Direct Transcutaneous Incision
2.4.2. Hairline Incision
2.4.3. Peri-Eyebrow Incision
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Selection
3.2. Patient Characteristics
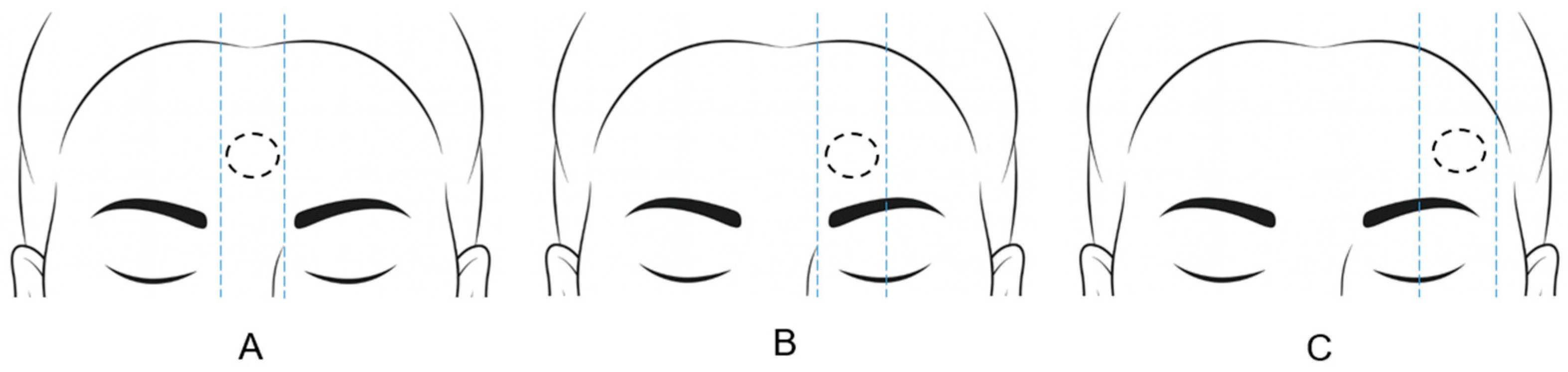
3.3. Lipoma Location
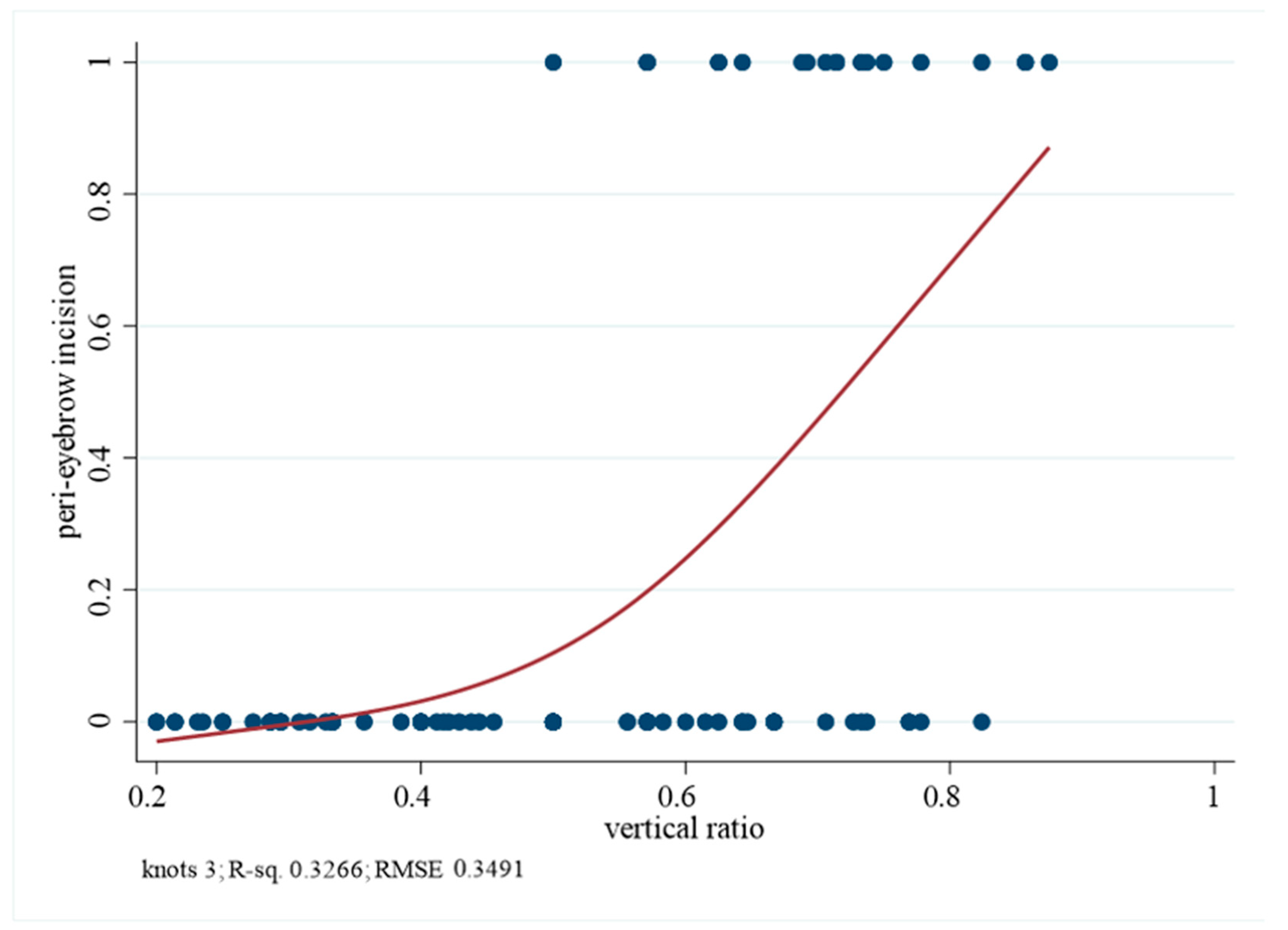
3.4. Vertical Ratio and Incision Selection
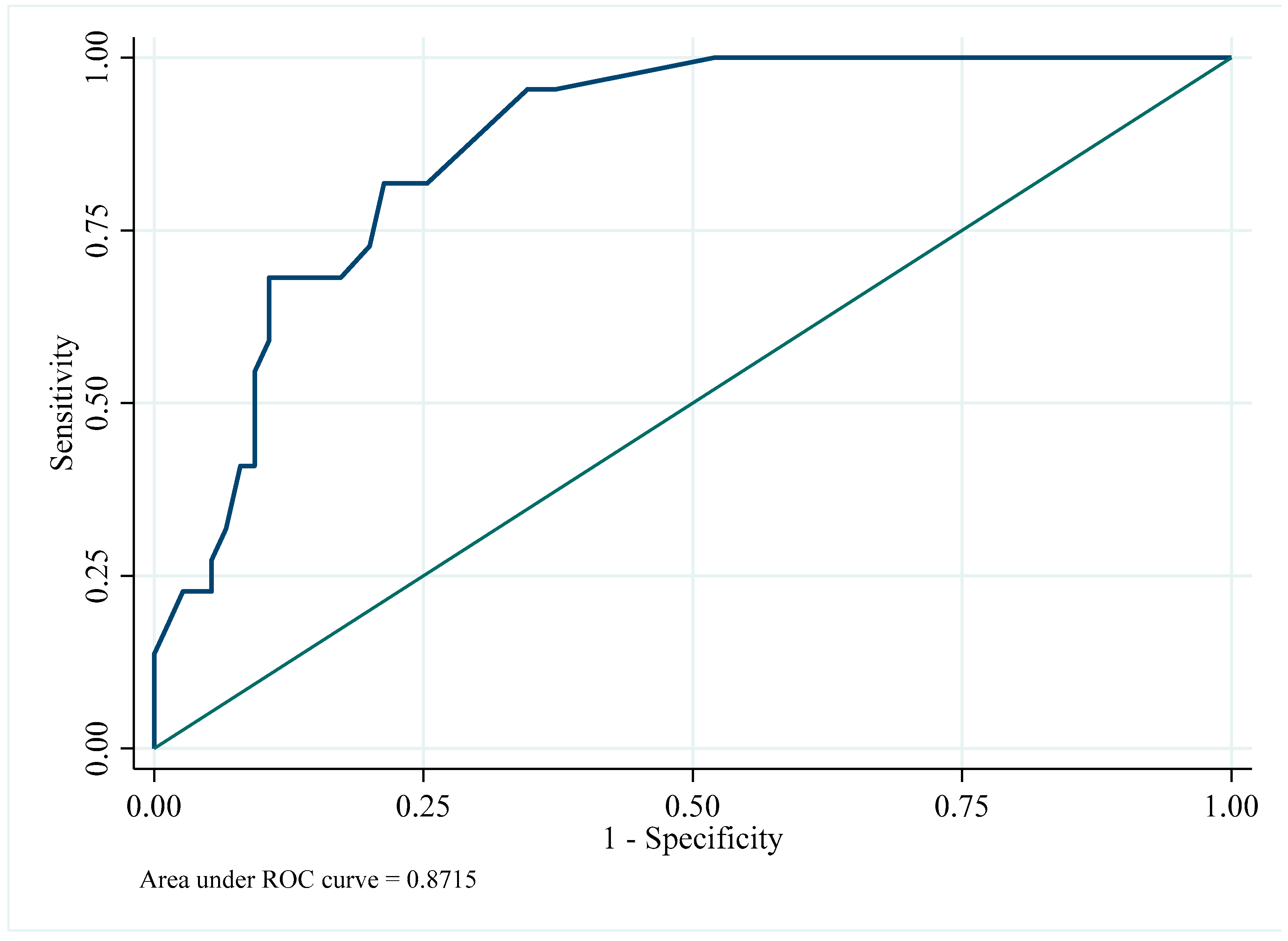
3.5. Multivariate Analysis and Internal Validation
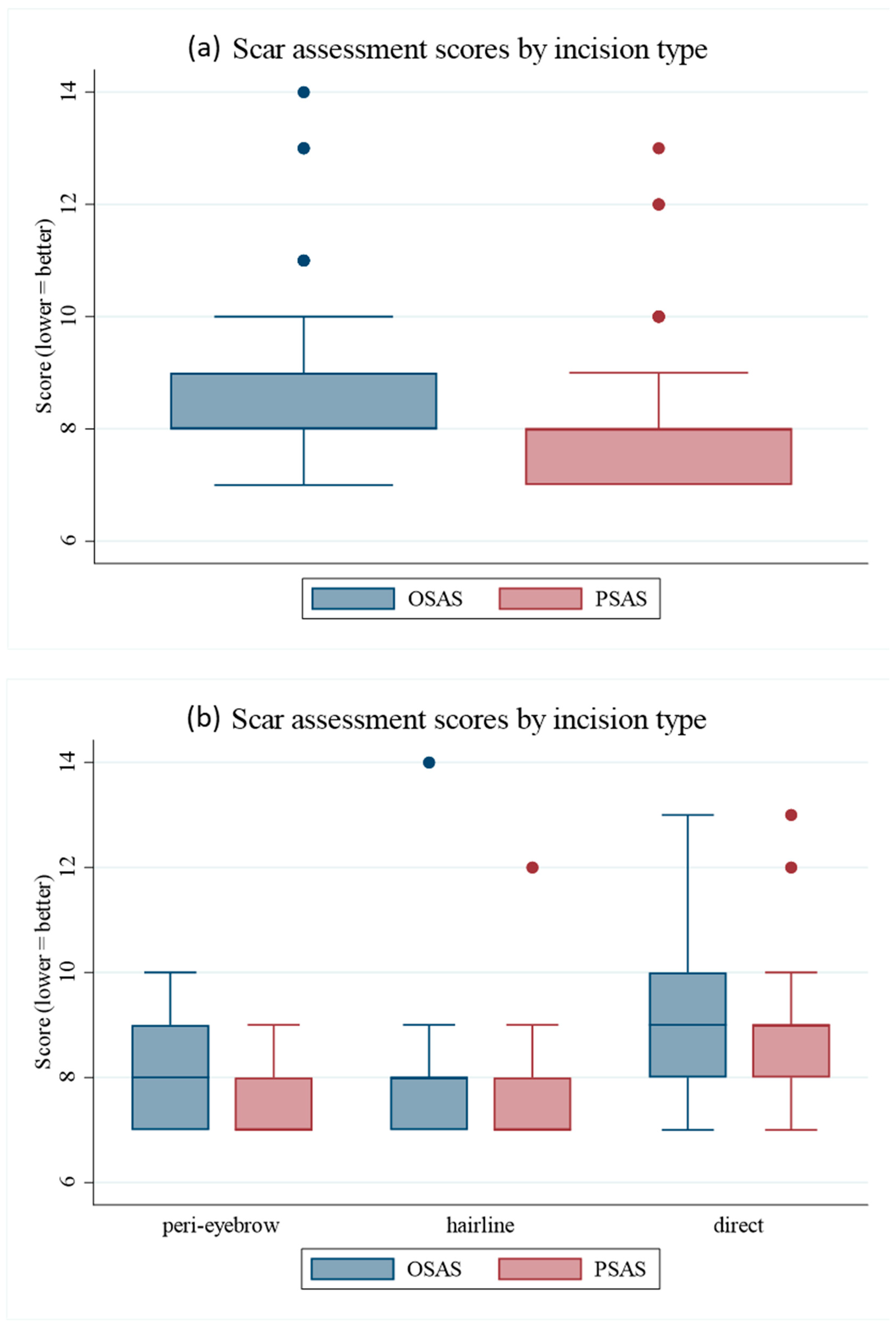
3.6. Scar Outcomes
3.7. Complications
4. Discussion
4.1. Overall Safety and Cosmetic Outcomes
4.2. Advantages of the Peri-Eyebrow Approach
4.3. Predictive Validation and Clinical Correlation
4.4. Location-Specific Considerations
4.5. Clinical Implications and Novelty
4.6. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| ORs | Odd ratios |
| OSAS | Observer Scar Assessment Scales |
| PSAS | Patient Scar Assessment Scales |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| RSTL | Resting skin tension lines |
References
- Salam, G.A. Lipoma excision. Am. Fam. Physician 2002, 65, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fattah, A. ‘Scarless’ removal of forehead lipomas. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2012, 94, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Nam, K.; Roh, M.R.; Chung, K.Y.; Oh, B.H. Advantages of a hairline incision for the excision of forehead lipomas. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, e60–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, K. Clinical characteristics of the forehead lipoma. Arch. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 15, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Funayama, E.; Minakawa, H.; Oyama, A. Forehead lipoma resection via a small remote incision using a surgical raspatory. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 56, 458–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, N.G.; Kim, Y.H. Minimal one-third incision and four-step (MOTIF) excision method for lipoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4331250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.N.; Ha, A.S.; Chen, E.; Davidson, D. Lipomatous soft-tissue tumors. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 26, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Lee, J.H. The diagnostic accuracy of depth prediction for lipomas by preoperative imaging with distribution according to anatomical site in Korea: A retrospective analysis. Arch. Craniofacial Surg. 2025, 26, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Peri-Eyebrow (n = 22) | Hairline (n = 38) | Direct (n = 37) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y), mean ± SD | 44.9 ± 11.6 | 45.0 ± 13.1 | 43.9 ± 14.2 | 0.982 |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.984 | |||
| Male | 13 (59.1) | 22 (57.9) | 21 (56.8) | |
| Female | 9 (40.9) | 16 (42.1) | 16 (43.2) | |
| Mass location, n (%) | 0.001 2 | |||
| Midline | 5 (22.7) | 9 (23.7) | 9 (24.3) | |
| Median | 17 (77.3) | 12 (31.6) | 15 (40.5) | |
| Lateral | 0 (0.0) | 17 (44.7) | 13 (35.1) | |
| Hairline–lipoma distance (cm), mean ± SD | 5.4 ± 1.1 | 3.0 ± 1.3 | 3.9 ± 1.6 | <0.001 (a > c > b) |
| Eyebrow-lipoma distance (cm), mean ± SD | 2.3 ± 0.8 | 4.0 ± 1.2 | 3.6 ± 1.4 | <0.001 (a < b, c) |
| Vertical ratio (lipoma–eyebrow/hairline–eyebrow), mean ± SD | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | <0.001 (a > c > b) |
| Mass size (cm), mean ± SD | ||||
| Long axis | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 0.664 |
| Short axis | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.7 | 0.496 |
| Incision length (cm), mean ± SD | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 2.2 ± 1.0 | 0.004 (b > a, c) |
| Location | Peri-Eyebrow (n = 22) | Hairline (n = 38) | Direct (n = 37) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midline | 5 (22.7%) | 9 (23.7%) | 9 (24.3%) | |
| Median | 17 (77.3%) | 12 (31.6%) | 15 (40.5%) | |
| Lateral | 0 (0.0%) | 17 (44.7%) | 13 (35.1%) | <0.001 1 |
| Analysis | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Logistic regression (per 0.1-unit increase) | 3.15 (1.85–5.36) | <0.001 |
| Logistic regression (cut-off 0.615, categorical) | 16.59 (4.92–55.99) | <0.001 |
| Analysis | Variable | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multivariate logistic regression 1 | Vertical ratio (per 0.1-unit increase) | 3.32 (1.71–6.42) | <0.001 |
| Mass location—median (vs. midline) | 3.91 (0.75–20.40) | 0.105 | |
| Mass size (long axis, cm) | 0.59 (0.19–1.78) | 0.349 | |
| Age (y) | 1.00 (0.94–1.06) | 0.989 | |
| Sex—female (vs. male) | 0.44 (0.11–1.81) | 0.259 | |
| Bootstrap validation (1000 iterations) 2 | Cut-off value | 0.62 (0.53–0.71) | - |
| AUC | 0.80 (0.73–0.88) | - |
| Peri-Eyebrow (n = 22) | Hairline (n = 38) | Direct (n = 37) | p-Value 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSAS | 8.1 ± 0.9 | 8.0 ± 1.2 | 9.1 ± 1.5 | <0.001 |
| PSAS | 7.5 ± 0.6 | 7.5 ± 1.0 | 8.7 ± 1.3 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.W.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, J.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, K.S. Peri-Eyebrow Incision: A Practical and Aesthetic Solution for Forehead Lipoma Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238460
Kim DW, Lee HJ, Kim SH, Choi JH, Hwang JH, Kim KS. Peri-Eyebrow Incision: A Practical and Aesthetic Solution for Forehead Lipoma Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(23):8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238460
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dong Wan, Ho Jun Lee, Seung Hyun Kim, Jun Ho Choi, Jae Ha Hwang, and Kwang Seog Kim. 2025. "Peri-Eyebrow Incision: A Practical and Aesthetic Solution for Forehead Lipoma Surgery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 23: 8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238460
APA StyleKim, D. W., Lee, H. J., Kim, S. H., Choi, J. H., Hwang, J. H., & Kim, K. S. (2025). Peri-Eyebrow Incision: A Practical and Aesthetic Solution for Forehead Lipoma Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(23), 8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238460







