Associations Between Halitosis and Craniofacial Morphology, Salivary Biochemical Parameters, and Mouth Breathing in Adult Patients with Malocclusion: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects, Eligibility Criteria and Ethics
- (1)
- active dental caries or periodontitis (probing depth ≥ 4 mm or bleeding on probing),
- (2)
- poor oral hygiene (plaque control record ≥ 30%),
- (3)
- smoking habit,
- (4)
- (5)
- history of psychiatric or neurological disorders,
- (6)
- congenital craniofacial anomalies or multiple tooth agenesis,
- (7)
- history of orthodontic treatment, and
- (8)
- nasal obstruction or allergic rhinitis affecting habitual breathing patterns, meaning participants with active symptoms at the time of examination were excluded to avoid confounding effects of ongoing airway blockage.
2.2. Halitosis Assessment and Group Classification
2.3. Evaluation of Craniofacial Morphology
2.4. Salivary Parameters
2.5. Assessment of Mouth Breathing
2.6. Sample Size Calculation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Normality Assessment and Sex-Based Exploratory Comparison
3.2. Comparison Between Halitosis-Positive and Halitosis-Negative Groups
3.3. Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
3.4. Association Between Mouth Breathing and Halitosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seerangaiyan, K.; Jüch, F.; Winkel, E.G. Tongue coating: Its characteristics and role in intra-oral halitosis and general health—A review. J. Breath Res. 2018, 12, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krespi, Y.P.; Shrime, M.G.; Kacker, A. The relationship between oral malodor and volatile sulfur compound–producing bacteria. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 135, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Kho, H.-S.; Chung, S.-C.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y. The relationship between volatile sulfur compounds and major halitosis-inducing factors. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Sakanaka, A.; Lamont, R.J.; Amano, A.; Kuboniwa, M. Interspecies metabolite transfer fuels the methionine metabolism of Fusobacterium nucleatum to stimulate volatile methyl mercaptan production. mSystems 2024, 9, e00764-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, A.; Zaitsu, T.; Ueno, M.; Kawaguchi, Y. Characterization of oral bacteria in the tongue coating of patients with halitosis using 16S rRNA analysis. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2020, 78, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, N.; Fujimoto, A.; Yoneda, M.; Watanabe, T.; Hirofuji, T.; Hanioka, T. Resting salivary flow independently associated with oral malodor. BMC Oral Health 2016, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, M.; Zhu, C.; Feng, X.-P. Relationship of tongue coating microbiome on volatile sulfur compounds in healthy and halitosis adults. J. Breath Res. 2019, 14, 016005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaesu, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Naito, M.; Watanabe, T.; Shimazu, A.; Yatabe, N.; Yoneda, M.; Hirofuji, T.; Hanioka, T. Novel oral biomarkers predicting oral malodor. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020, 130, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navazesh, M. Methods for collecting saliva. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 694, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kado, I.; Kunimatsu, R.; Yoshimi, Y.; Medina, C.C.; Yamada, S.; Tanimoto, K. Surveillance of Salivary Properties of Pre-Orthodontic Patients in Relation to Age and Sex. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Ortiz, A.d.C.; Carvalho, T.S.; Fideles, S.O.M.; Araújo, T.T.; Moraes, S.M.; Buzalaf, N.R.; Reis, F.N. Saliva as a diagnostic tool for dental caries, periodontal disease and cancer: Is there a need for more biomarkers? Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nieuw Amerongen, A.; Bolscher, J.G.M.; Veerman, E.C.I. Salivary Proteins: Protective and Diagnostic Value in Cariology? Caries Res. 2004, 38, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, S.; Tandon, S.; Satyamoorthy, K. Salivary Proteins and Early Childhood Caries: A Gel Electrophoretic Analysis. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2010, 1, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enerbäck, H.; Lingström, P.; Möller, M.; Nylén, C.; Ödman Bresin, C.; Östman Ros, I.; Westerlund, A. Validation of Caries Risk Assessment Methods in Orthodontic Patients. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 158, 92–101.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomar-Vercher, S.; Simón-Soro, A.; Montiel-Company, J.M.; Almerich-Silla, J.M.; Mira, A. Stimulated and unstimulated saliva samples have significantly different bacterial profiles. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.K.; Johnson, D.A.; Dodds, M.W.J.; Sakai, S.; Rugh, J.D.; Hatch, J.P. Association of salivary flow rates with maximal bite force. J. Dent. Res. 2000, 79, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, L.; Daraqel, B.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y. Effects of mouth breathing on maxillofacial and airway development in children and adolescents with different cervical vertebral maturation stages: A cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zheng, L.; Huang, X.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y. Effects of mouth breathing on facial skeletal development in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinho, H.A.; Furtado, I.A.; Silva, F.S.; Torrent, J.U. Cephalometric evaluation of children with allergic rhinitis and mouth breathing. Acta Medica Port. 2015, 28, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feștilă, D.; Ciobotaru, C.D.; Suciu, T.; Olteanu, C.D.; Ghergie, M. Oral breathing effects on malocclusions and mandibular posture: Complex consequences on dentofacial development in pediatric orthodontics. Children 2025, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, F.C.P.; Enoki, C.; Feres, M.F.N.; Valera, F.C.P.; Anselmo-Lima, W.T.; Matsumoto, M.A.N. Breathing mode influence in craniofacial development. Rev. Bras. Otorrinolaringol. 2005, 71, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasson, J.M.D.; Magnani, M.B.B.A.; Nouer, D.F.; Vieira de Siqueira, V.C.; Lunardi, N. Comparative Cephalometric Study Between Nasal and Predominantly Mouth Breathers. Bras. Otorrinolaringol. 2006, 72, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettergren-Wijk, L.; Forsberg, C.-M.; Linder-Aronson, S. Changes in Dentofacial Morphology after Adeno-/Tonsillectomy in Young Children with OSA—A 5-Year Follow-Up Study. Eur. J. Orthod. 2006, 28, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakor, S.F.; Enlow, D.H.; Pontes, P.; De Biase, N.G. Craniofacial Growth Variations in Nasal-Breathing, Oral-Breathing, and Tracheotomized Children. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 140, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.K.; Baniasad, N.; Asadi, E.; Nadafpour, N. Effect of malocclusion severity on oral health and its correlation with socioeconomical status in Iranian adolescents. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, Ș.-D.; Suciu, I.; Albu, C.-C.; Dragomirescu, A.-O.; Ionescu, E. Impact of malocclusions on periodontopathogenic bacterial load and progression of periodontal disease: A quantitative analysis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Riveiro, P.; Obregón-Rodríguez, N.; Piñeiro-Lamas, M.; Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Smyth-Chamosa, E.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.M. The Dental Aesthetic Index and Its Association with Dental Caries, Dental Plaque and Socio-Demographic Variables in Schoolchildren Aged 12 and 15 Years. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, Y.; Kunimatsu, R.; Kado, I.; Yoshimi, Y.; Yamada, S.; Ogasawara, T.; Tanimoto, K. Maxillofacial Morphology as a Predictive Factor for Caries Risk in Orthodontic Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhao, T.; Qin, D.; Hua, F.; He, H. The Impact of Mouth Breathing on Dentofacial Development: A Concise Review. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 929165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurfluh, M.A.; van Waes, H.J.M.; Filippi, A. The influence of fixed orthodontic appliances on halitosis. Schweiz. Monatsschr Zahnmed. 2013, 123, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grippaudo, C.; Paolantonio, E.G.; Antonini, G.; Saulle, R.; La Torre, G.; Deli, R. Association between oral habits, mouth breathing and malocclusion. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2016, 36, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsironi, K.; Mylonopoulou, I.M.; Pandis, N.; Vassilopoulos, S.; Sifakakis, I.; Papaioannou, W. The effect of mastic mouthwash on halitosis and oral hygiene in orthodontic patients: A randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Orthod. 2023, 45, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, N.; Shimpo, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Sekiya, T.; Tomonari, H. Effects of 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride mouthwash on halitosis and tongue microbiota in patients undergoing orthodontic treatment: A double-blind randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, M.; McCulloch, C.A. Measurement of oral malodor: Current methods and future prospects. J. Periodontol. 1992, 63, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadamio, J.; Van Tournout, M.; Teughels, W.; Dekeyser, C.; Coucke, W.; Quirynen, M. Efficacy of different mouthrinse formulations in reducing oral malodour: A randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013, 40, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Wang, J. Distribution of various maxilla-mandibular positions and cephalometric comparison in Chinese skeletal class II malocclusions. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2020, 21, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, M.; Tanaka, H.; Sakurai, A.; Otagiri, H.; Karasawa, I.; Yamada, S.-I.; Kurita, H. Exploration of correlation of oral hygiene and condition with influenza infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, A.; Yamada, S.; Karasawa, I.; Kondo, E.; Kurita, H. Accuracy of a salivary examination kit for the screening of periodontal disease in a group medical check-up. Medicine 2021, 100, e24539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T.; Fushida, S.; Wada, M.; Gonda, T.; Hatta, K.; Kuboniwa, M.; Wada, A.; Hashimoto, S.; Hatanaka, H.; Higashi, M.; et al. Effectiveness of a Salivary Testing System to Screen for Periodontal Disease: The NOSE Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harari, D.; Redlich, M.; Miri, S.; Hamud, T.; Gross, M. The effect of mouth breathing versus nasal breathing on dentofacial and craniofacial development in orthodontic patients. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, M.; Sano, S.; Kato, H.; Arakawa, K.; Arai, M. Proposal for a screening questionnaire for detecting habitual mouth breathing, based on a mouth-breathing habit score. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Moura Milanesi, J.; Berwig, L.C.; Marquezan, M.; Schuch, L.H.; de Moraes, A.B.; da Silva, A.M.T.; Corrêa, E.C.R. Variables associated with mouth breathing diagnosis in children based on a multidisciplinary assessment. CoDAS 2018, 30, e20170071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farronato, M.; Lanteri, V.; Fama, A.; Maspero, C. Correlation between malocclusion and allergic rhinitis in pediatric patients: A systematic review. Children 2020, 7, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.B. How Many Subjects Does It Take to Do a Regression Analysis? Multivar. Behav. Res. 1991, 26, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlovsky, A.; Gordon, D.; Gelernter, I.; Loesche, W.J.; Rosenberg, M. Correlation between the BANA Test and Oral Malodor Parameters. J. Dent. Res. 1994, 73, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazor, C.E.; Mitchell, P.M.; Lee, A.M.; Stokes, L.N.; Loesche, W.J.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Paster, B.J. Diversity of Bacterial Populations on the Tongue Dorsa of Patients with Halitosis and Healthy Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, C.-Y.; Jiang, J.-H. Effects of fixed orthodontic brackets on oral malodor: A systematic review and meta-analysis according to the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses guidelines. Medicine 2018, 97, e0233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kado, I.; Hisatsune, J.; Tsuruda, K.; Tanimoto, K.; Sugai, M. The Impact of Fixed Orthodontic Appliances on Oral Microbiome Dynamics in Japanese Patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjar, A.A.; Hassan, S.M.; Alyafi, R.A.; Alawady, S.A.; Alghamdi, M.H.; Baik, K.M. Self-perceived halitosis among young adults undergoing orthodontic treatment. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2022, 20, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, K.A.; Yusuf, H.; Vassallo, P. Editorial: The WHO Global Oral Health Action Plan 2023–2030. Community Dent Health 2023, 40, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, Y.; Yamamoto, J.-I.; Kanzaki, H.; Shimpo, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kobayashi, F.; Nishida, T.; Mizokami, K.; Katayama, M.; Sekiya, T.; et al. Association Between Severity of Malocclusion and Parameters of Oral Functions in Permanent Dentition with Various Malocclusion: Case-Control Study. Clin. Investig. Orthod. 2023, 82, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
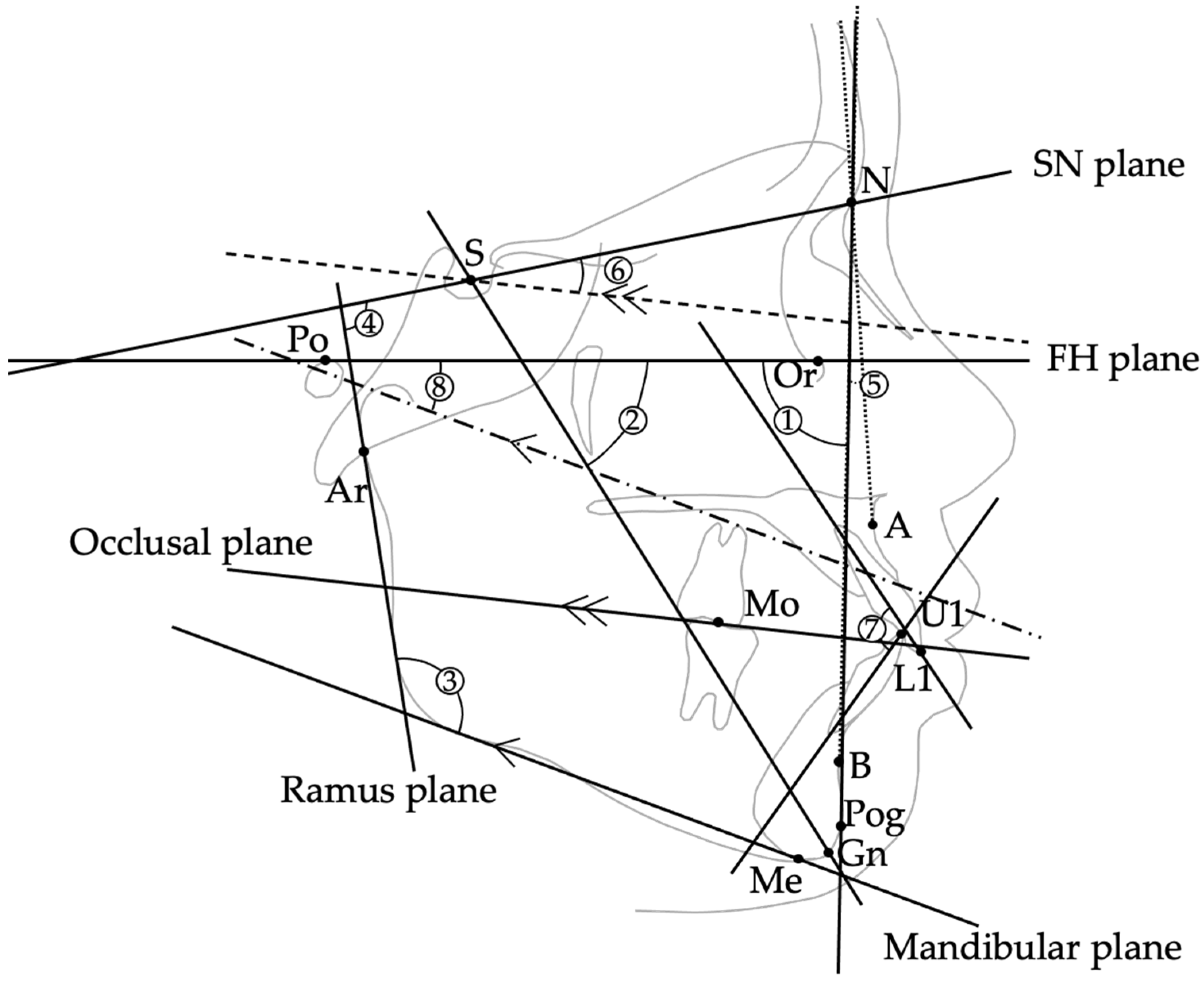
| Item | Definition | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| (Landmarks/Points) | ||
| S (Sella) | Center of the sella turcica | — |
| N (Nasion) | Most anterior point of the frontonasal suture | — |
| Ar (Articulare) | Point of intersection between the posterior border of the mandibular ramus and the cranial base (typically at the intersection of the posterior ramus contour and the basion–sella line) | — |
| Or (Orbitale) | Lowest point on the infraorbital rim | — |
| Po (Porion) | Highest point on the external auditory meatus | — |
| A-Point | Deepest point on the anterior contour of the maxilla | — |
| B-Point | Deepest point on the anterior contour of the mandible | — |
| Pog (Pogonion) | Point on the midsagittal outline of the mandibular symphysis that is tangent to a line perpendicular to the mandibular plane | — |
| Gn (Gnathion) | Point where the bisector of the angle formed by the N–Pog line and the mandibular plane intersects the mandibular symphysis in the midsagittal plane | — |
| Me (Menton) | Lowest point on the mandibular symphysis | — |
| U1/L1 | Incisal edge of the maxillary/mandibular central incisor | — |
| Mo | Central point of upper/lower first molar occlusal contact | — |
| (Reference Planes) | ||
| FH plane (Po–Or) | Plane connecting Porion and Orbitale | — |
| SN plane (S–N) | Plane connecting Sella and Nasion | — |
| Ramus plane | Tangent drawn from Articulare (Ar) along the posterior border of the mandibular ramus | — |
| Mandibular plane | Tangent drawn from Menton (Me) along the lower border of the mandible | — |
| Occlusal plane | Plane connecting midpoint of U1–L1 and Mo | — |
| (Cephalometric Measurements ①–⑧) | ||
| ① Facial angle | Angle between FH plane and N–Pog line | ° |
| ② Y-axis | Angle between S–Gn and FH plane | ° |
| ③ Gonial angle | Angle between mandibular plane and ramus plane | ° |
| ④ Ramus plane to SN | Angle between ramus plane and SN plane | ° |
| ⑤ ANB | Angle formed by A–N–B | ° |
| ⑥ Occlusal plane to SN | Angle between occlusal plane and SN plane | ° |
| ⑦ Interincisal angle | Angle between long axes of U1 and L1 | ° |
| ⑧ FMA | Angle between mandibular plane and FH plane | ° |
| (Dental Model Measurements ⑨–⑩) | ||
| ⑨ Overjet | Horizontal overlap of U1 over L1 (measured on dental models with a digital caliper) | mm |
| ⑩ Overbite | Vertical overlap of U1 over L1 (measured on dental models with a digital caliper) | mm |
| Variable | Halitosis-Positive Group Mean/Median ± SD or (IQR) | Halitosis-Negative Group Mean/Median ± SD or (IQR) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facial angle (°) | 86.96 ± 4.59 | 87.84 ± 4.78 | 0.17 a |
| Y-axis (°) | 63.98 ± 4.65 | 63.37 ± 4.83 | 0.28 a |
| Gonial angle (°) | 122.3 ± 6.1 | 121.9 ± 6.4 | 0.61 a |
| Ramus plane to SN (°) | 124.8 (122.0–128.4) | 126.4 (122.7–129.7) | 0.096 U |
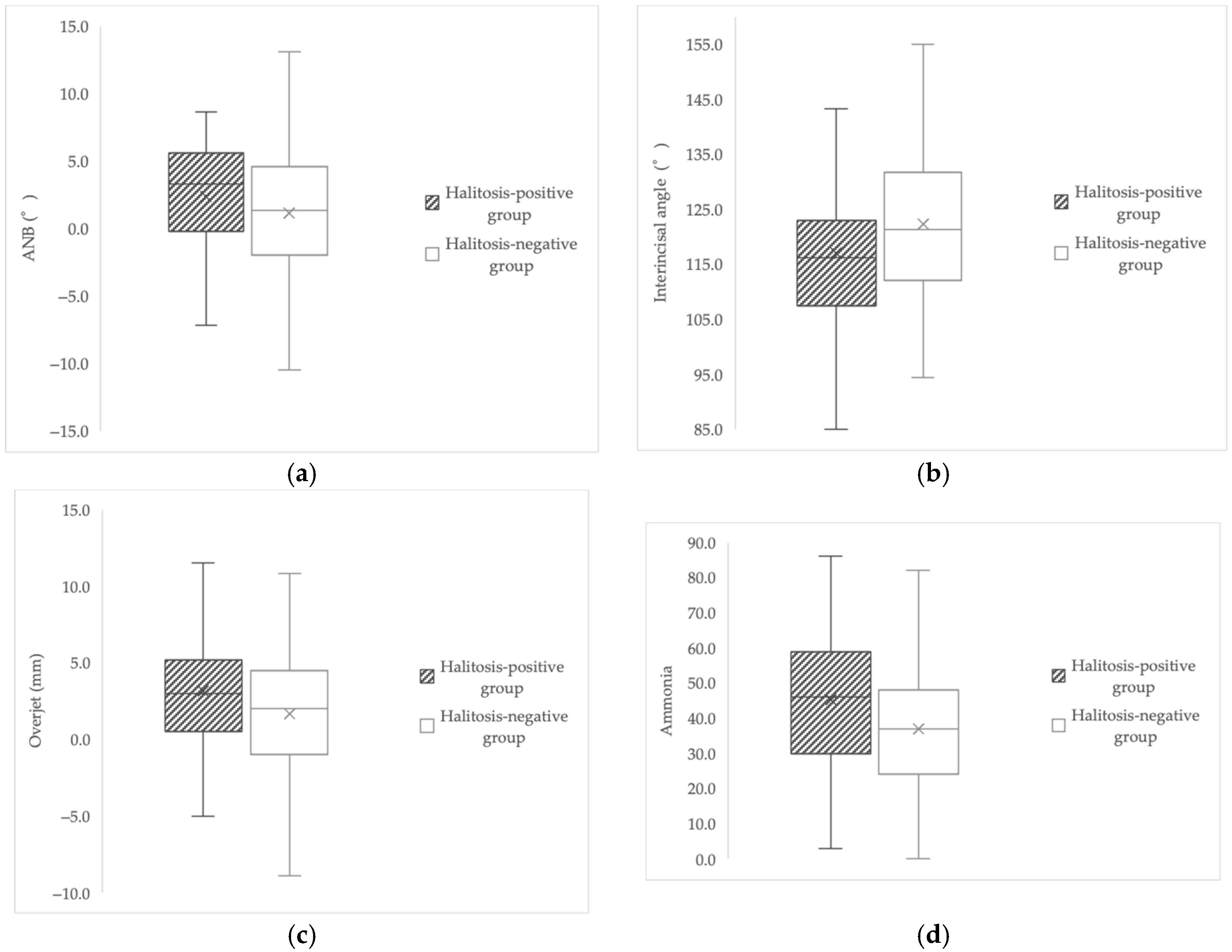
| ANB (°) | 3.3 (−0.2–5.5) | 1.3 (−2.0–4.6) | 0.037 U |
| Occlusal plane to SN (°) | 16.7 ± 5.1 | 17.4 ± 5.3 | 0.42 a |
| Interincisal angle (°) | 117.07 ± 14.85 | 122.25 ± 12.66 | 0.009 a |
| FMA (°) | 27.3 ± 5.0 | 27.0 ± 4.9 | 0.64 ᵃ |
| Overjet (mm) | 3.00 (0.50–5.10) | 2.00 (−1.00–4.50) | 0.034 a |
| Overbite (mm) | 2.00 (0.10–3.45) | 2.50 (0.00–3.10) | 0.27 U |
| Salivary leukocytes | 70.0 (51.5–82.0) | 64.0 (46.5–78.0) | >0.05 U |
| Salivary protein | 47.0 (36.0–55.5) | 43.0 (33.0–54.0) | >0.05 U |
| Ammonia | 45.16 ± 18.84 | 36.93 ± 17.12 | 0.001 a |
| Stimulated salivary flow rate (g/2 min) | 6.20 (4.30–7.20) | 6.10 (4.85–7.30) | >0.05 U |
| Predictor | β (Unstandardized) | p-Value | 95% CI (Lower) | 95% CI (Upper) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interincisal angle (°) | −4.57 | 0.019 | −8.37 | −0.77 | Smaller angle (greater proclination) → higher VSC (significant) |
| Gonial angle (°) | 11.26 | 0.063 | −0.61 | 23.13 | Trend (not significant) |
| FMA (°) | −20.89 | 0.061 | −42.77 | 0.99 | Trend (not significant) |
| Overjet (mm) | 12.44 | 0.085 | −1.75 | 26.63 | Trend (not significant) |
| Ramus plane to SN (°) | −6.85 | 0.194 | −17.22 | 3.51 | Not significant |
| ANB (°) | 10.69 | 0.225 | −6.62 | 28.00 | Not significant |
| Facial angle (°) | 12.59 | 0.390 | −16.21 | 41.40 | Not significant |
| Y-axis (°) | 15.93 | 0.340 | −16.88 | 48.74 | Not significant |
| Occlusal plane to SN (°) | 4.43 | 0.469 | −7.59 | 16.44 | Not significant |
| Overbite (mm) | 3.13 | 0.741 | −15.50 | 21.76 | Not significant |
| Stimulated salivary flow rate (Saxon) | 2.89 | 0.776 | −17.06 | 22.84 | Not significant |
| Salivary leukocytes | 0.46 | 0.647 | −1.51 | 2.42 | Not significant |
| Salivary protein | −0.56 | 0.717 | −3.60 | 2.48 | Not significant |
| Salivary ammonia | 0.75 | 0.577 | −1.90 | 3.41 | Not significant |
| Variable | Halitosis (+) | Halitosis (−) | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouth breathing present | 53 | 47 | 4.68 | 2.62–8.38 | <0.001 |
| Mouth breathing absent | 26 | 108 | Reference | — | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kikuchi, K.; Shimpo, Y.; Sekiya, T.; Shiina, N.; Kiwada, M.; Inaba, S.; Nomura, Y.; Tomonari, H. Associations Between Halitosis and Craniofacial Morphology, Salivary Biochemical Parameters, and Mouth Breathing in Adult Patients with Malocclusion: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238293
Kikuchi K, Shimpo Y, Sekiya T, Shiina N, Kiwada M, Inaba S, Nomura Y, Tomonari H. Associations Between Halitosis and Craniofacial Morphology, Salivary Biochemical Parameters, and Mouth Breathing in Adult Patients with Malocclusion: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(23):8293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238293
Chicago/Turabian StyleKikuchi, Koh, Yudai Shimpo, Toshiko Sekiya, Natsuki Shiina, Mami Kiwada, Sakurako Inaba, Yoshiaki Nomura, and Hiroshi Tomonari. 2025. "Associations Between Halitosis and Craniofacial Morphology, Salivary Biochemical Parameters, and Mouth Breathing in Adult Patients with Malocclusion: A Cross-Sectional Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 23: 8293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238293
APA StyleKikuchi, K., Shimpo, Y., Sekiya, T., Shiina, N., Kiwada, M., Inaba, S., Nomura, Y., & Tomonari, H. (2025). Associations Between Halitosis and Craniofacial Morphology, Salivary Biochemical Parameters, and Mouth Breathing in Adult Patients with Malocclusion: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(23), 8293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238293








