Cochlear Implantation in Children with Inner Ear Malformations: Auditory Outcomes, Safety and the Role of Anatomical Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
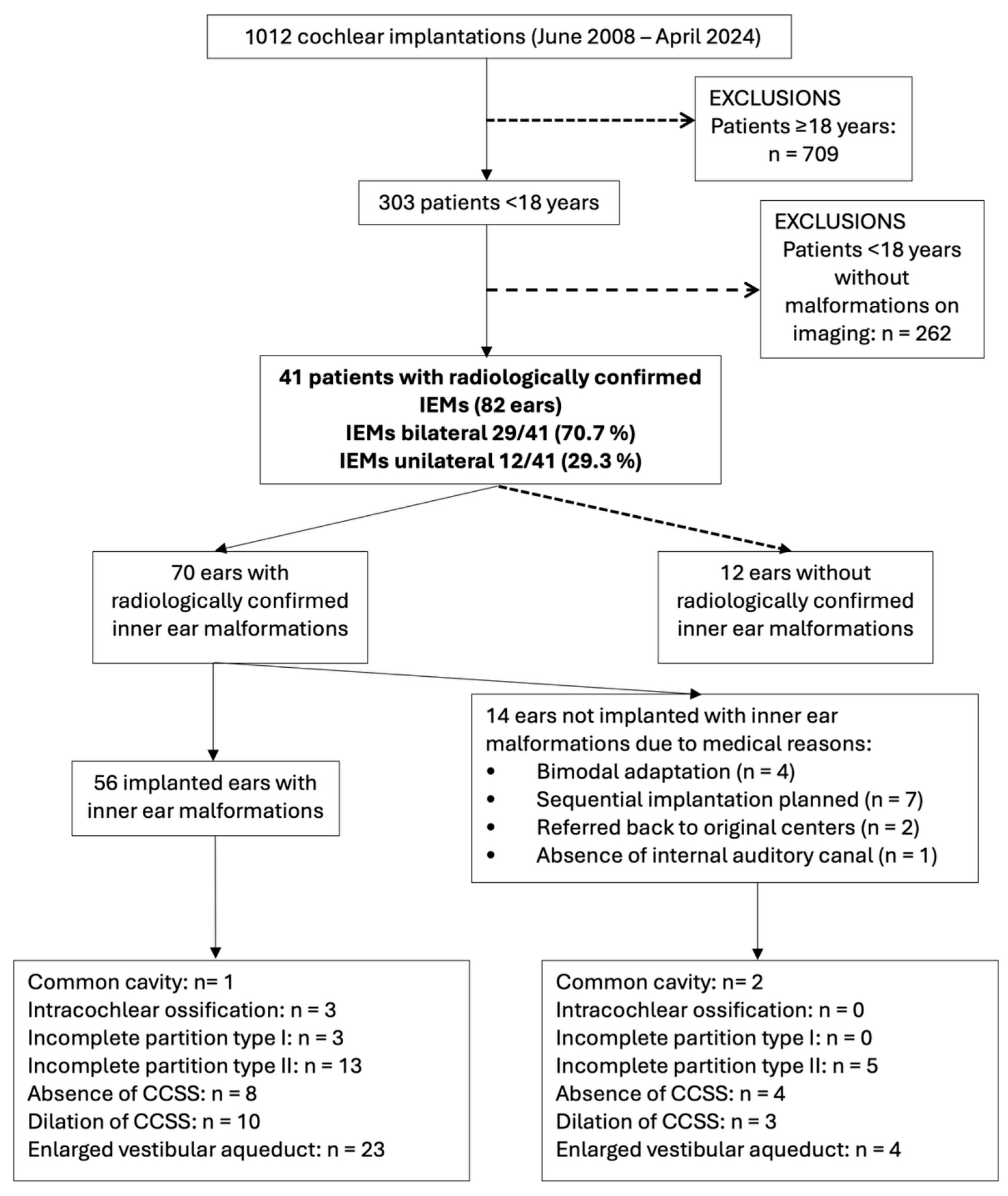
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Classification of IEMs
2.3. Data and Outcome Measures
2.4. Data Handling and Missing Values
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Inner Ear Malformations (Sennaroğlu Classification)
3.3. Device and Electrode Selection
3.4. INCAV-Derived Severity Score Distribution
3.5. Associated Risk Factors
3.6. Postoperative Complications
3.7. Surgical and Postoperative Data
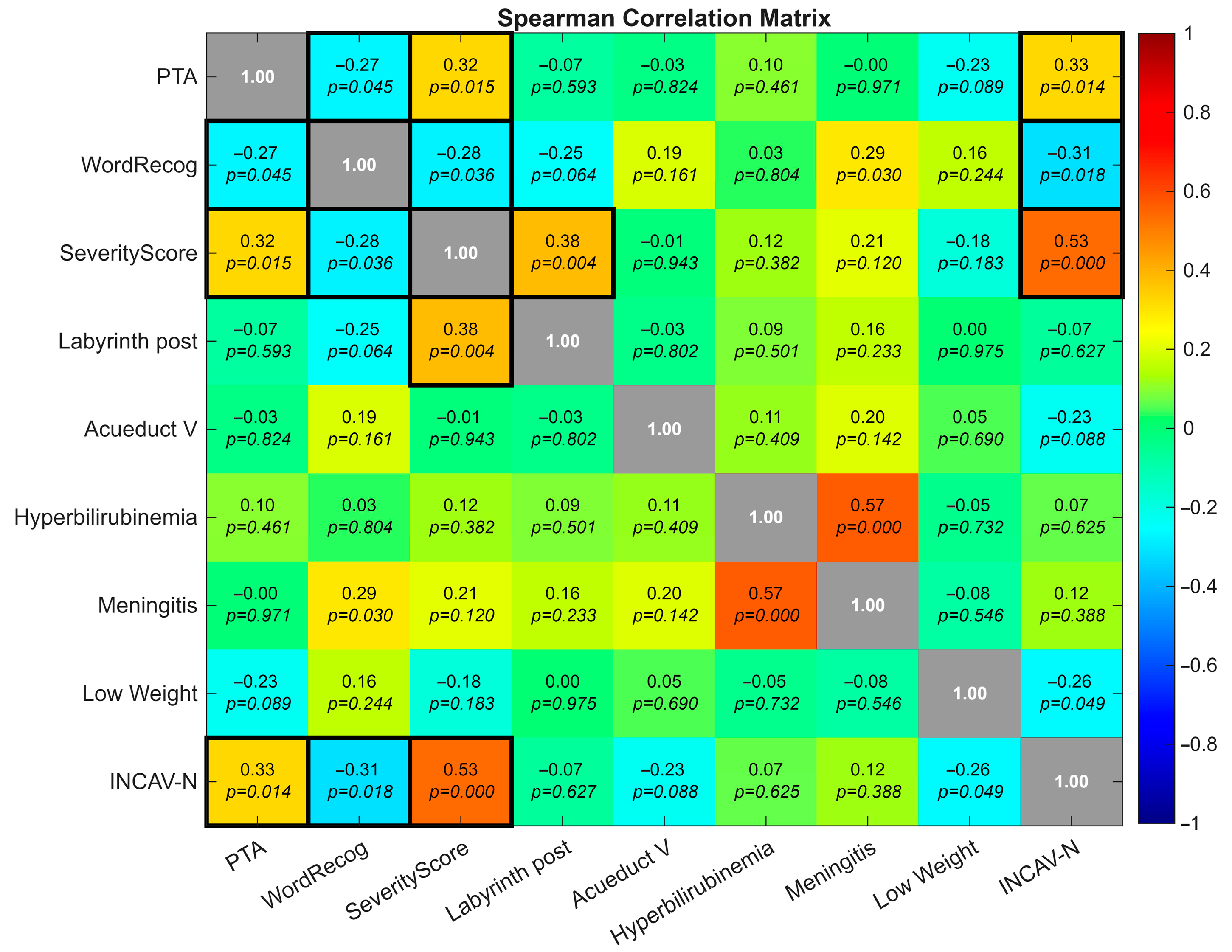
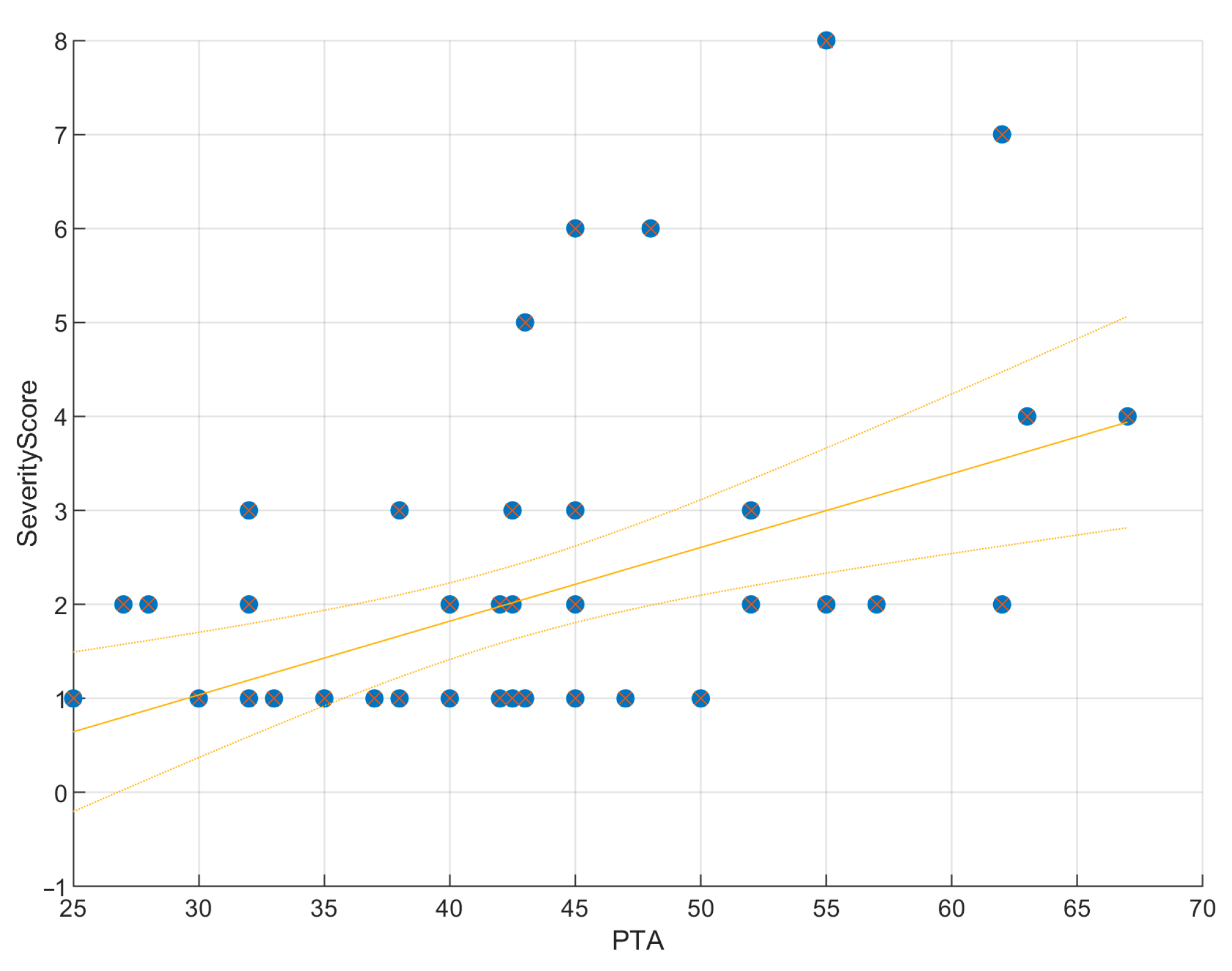
3.7.1. Correlation Analyses
3.7.2. Regression Analyses
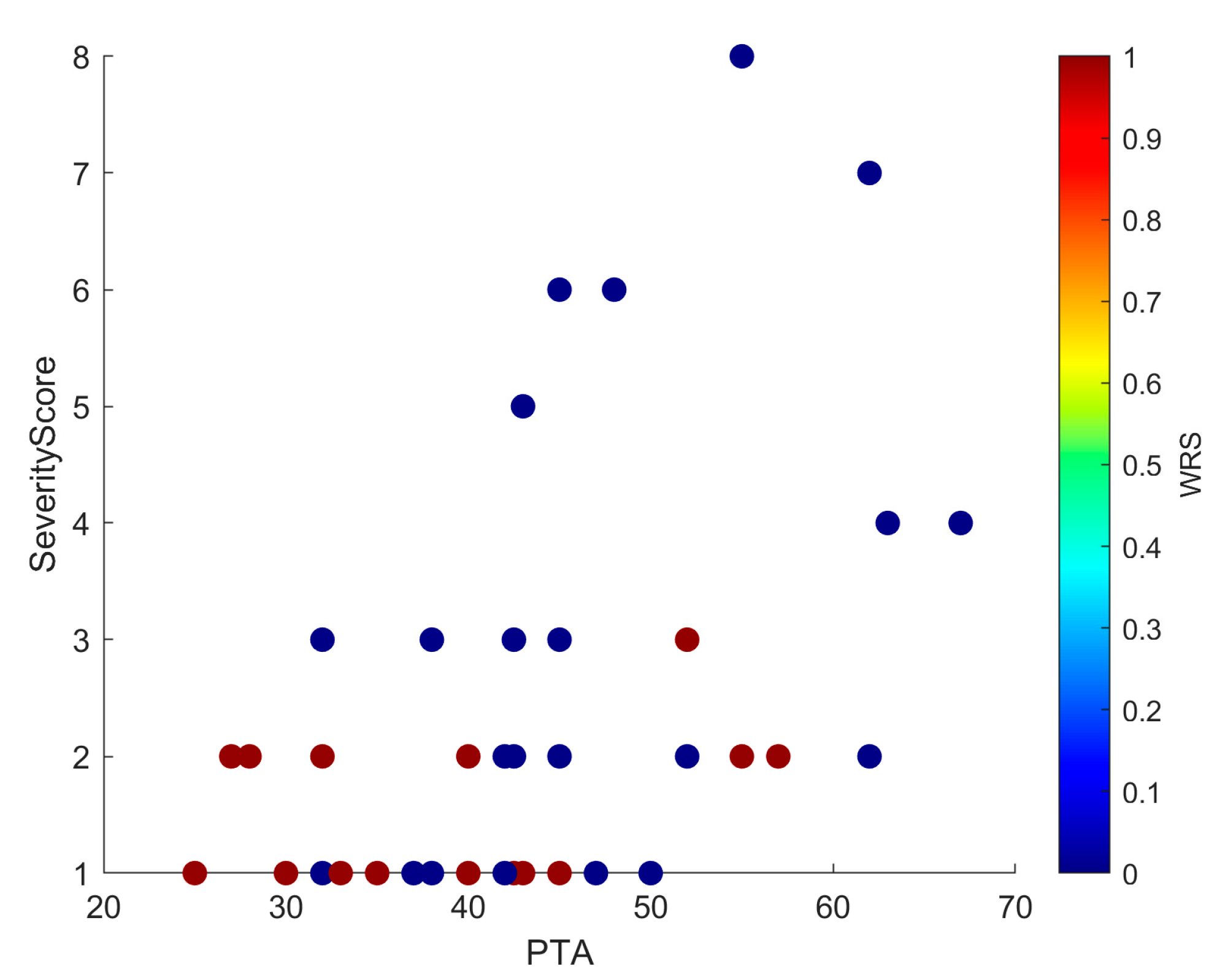
3.7.3. Exploratory Multivariate Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Safety and Complications
4.2. Auditory and Linguistic Outcomes
4.3. Toward Objective Stratification: INCAV and Severity Scoring
4.4. Cochlear Nerve Status
4.5. Risk Factors and Genetic Influences
4.6. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| ABR | Auditory Brainstem Response |
| CAP | Categories of Auditory Performance |
| CI | Cochlear Implantation |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| EVA | Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct |
| IEM | Inner Ear Malformation |
| INCAV | Internal Auditory Canal, Nerve, Cochlea, Aqueduct, Vestibule (classification system) |
| IP | Incomplete Partition |
| IP-I | Incomplete Partition Type I |
| IP-II | Incomplete Partition Type II |
| LBW | Low Birth Weight |
| MANOVA | Multivariate Analysis of Variance |
| NICU | Neonatal Intensive Care Unit |
| NAMES | Nottingham Auditory Milestones |
| PTA | Pure-Tone Average |
| SE | Standard Error |
| SLI | Specific Language Impairment |
| WRS | Word Recognition Score |
References
- Sennaroglu, L.; Saatci, I. A New Classification for Cochleovestibular Malformations. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 2230–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshi, A.; Farhadi, M.; Ajalloueyan, M.; Rajati, M.; Hashemi, S.B.; Ghasemi, M.M.; Emamdjomeh, H.; Asghari, A.; Mohseni, M.; Mohebbi, S.; et al. Cochlear Implantation in Children with Inner Ear Malformation: A Multicenter Study on Auditory Performance and Speech Production Outcomes. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 132, 109901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manrique, M.; Ramos, Á.; De Paula Vernetta, C.; Gil-Carcedo, E.; Lassaletta, L.; Sanchez-Cuadrado, I.; Espinosa, J.M.; Batuecas, Á.; Cenjor, C.; Lavilla, M.J.; et al. Guía clínica sobre implantes cocleares. Acta Otorrinolaringológica Española 2019, 70, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackler, R.K.; Luxfor, W.M.; House, W.F. Congenital Malformations of the Inner Ear: A Classification Based on Embryogenesis. Laryngoscope 1987, 97, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennaroğlu, L.; Bajin, M.D. Classification and Current Management of Inner Ear Malformations. Balk. Med. J. 2017, 34, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibelli, Z.H.; Isayeva, L.; Koc, A.M.; Catli, T.; Adibelli, H.; Olgun, L. The New Classification System for Inner Ear Malformations: The INCAV System. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2017, 137, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdaman, M.N.; Herrmann, B.S.; Curtin, H.D.; Van Beek-King, J.; Lee, D.J. Cochlear Implantation in Children with Anomalous Cochleovestibular Anatomy: A Systematic Review. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 146, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P.; Hsu, C. Common Clinical Features of Children with Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct and Mondini Dysplasia. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, A.; Abdelsamad, Y.; Salamah, M.; Alenzi, S.; Badr, K.M.; Alghamdi, S.; Alsanosi, A. Cochlear Implantation in Adults and Pediatrics with Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct: A Systematic Review on the Surgical Findings and Patients’ Performance. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 5497–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forli, F.; Lazzerini, F.; Auletta, G.; Bruschini, L.; Berrettini, S. Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct and Mondini Malformation: Audiological, Clinical, Radiologic and Genetic Features. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 278, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archbold, S.; Lutman, M.E.; Marshall, D.H. Categories of Auditory Performance. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. Suppl. 1995, 166, 312–314. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, G.; Kitterick, P.T.; Ramirez-Inscoe, J. Development and Validation of the Nottingham Auditory Milestones (NAMES) Profile for Deaf Children under 2 Years Old, Using Cochlear Implants. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2018, 19, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cardenas, M.; Marrero Aguiar, V. Cuaderno de Logoaudiometría; UNED: Madrid, Spain, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Farhood, Z.; Nguyen, S.A.; Miller, S.C.; Holcomb, M.A.; Meyer, T.A.; Rizk, A.H.G. Cochlear Implantation in Inner Ear Malformations: Systematic Review of Speech Perception Outcomes and Intraoperative Findings. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bille, J.; Fink-Jensen, V.; Ovesen, T. Outcome of Cochlear Implantation in Children with Cochlear Malformations. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, B.; Cesur, S.; Sahin, A.; Binnetoglu, A.; Ciprut, A.; Batman, C. Outcomes of Cochlear Implantation in Children with Inner Ear Malformations. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 2397–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbeih, F.; Bouzaher, M.H.; Appachi, S.; Schwartz, S.; Cohen, M.S.; Carvalho, D.; Yoon, P.; Liu, Y.-C.C.; Anne, S. Safety of Cochlear Implantation in Children 12 Months or Younger: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 167, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papsin, B.C. Cochlear implantation in children with anomalous cochleovestibular anatomy. Laryngoscope 2005, 115 Pt 2 (Suppl. S106), 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chao, X.; Wang, R.; Luo, J.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Hu, F.; Xu, L. Long-Term Auditory and Speech Outcomes of Cochlear Implantation in Children with IP-I Malformation. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 2120–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennaroglu, L. Cochlear Implantation in Inner Ear Malformations—A Review Article. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2010, 11, 4–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birman, C.S.; Powell, H.R.; Gibson, W.P.; Elliott, E.J. Cochlear implant outcomes in cochlear nerve aplasia and hypoplasia. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaiah, A.; Lee, D.; Lenes-Voit, F.; Sweeney, M.; Kutz, W.; Isaacson, B.; Roland, P.; Lee, K.H. Clinical Outcomes Following Cochlear Implantation in Children with Inner Ear Anomalies. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 93, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, N.M.; Kim, F.M.; Ryan, M.E.; Tournis, E.; Yaras, S. Pediatric cochlear implantation of children with eighth nerve deficiency. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 76, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, A.E.; Hildebrand, M.S.; Schaefer, A.M.; Smith, R.J. Genetic Hearing Loss Overview. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarotto, T.; Blázquez-Gamero, D.; Delforge, M.-L.; Foulon, I.; Luck, S.; Modrow, S.; Leruez-Ville, M. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: A Narrative Review of the Issues in Screening and Management from a Panel of European Experts. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
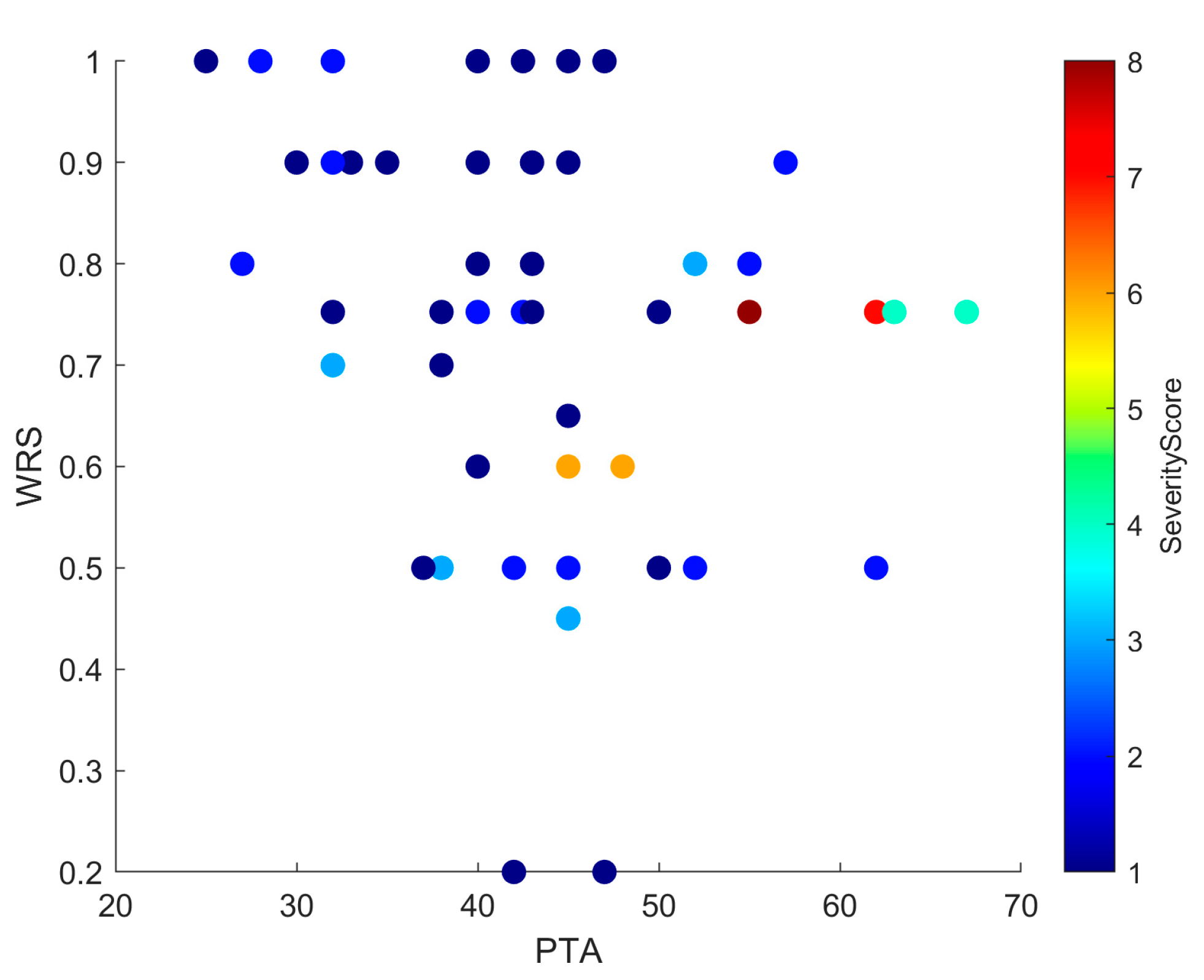
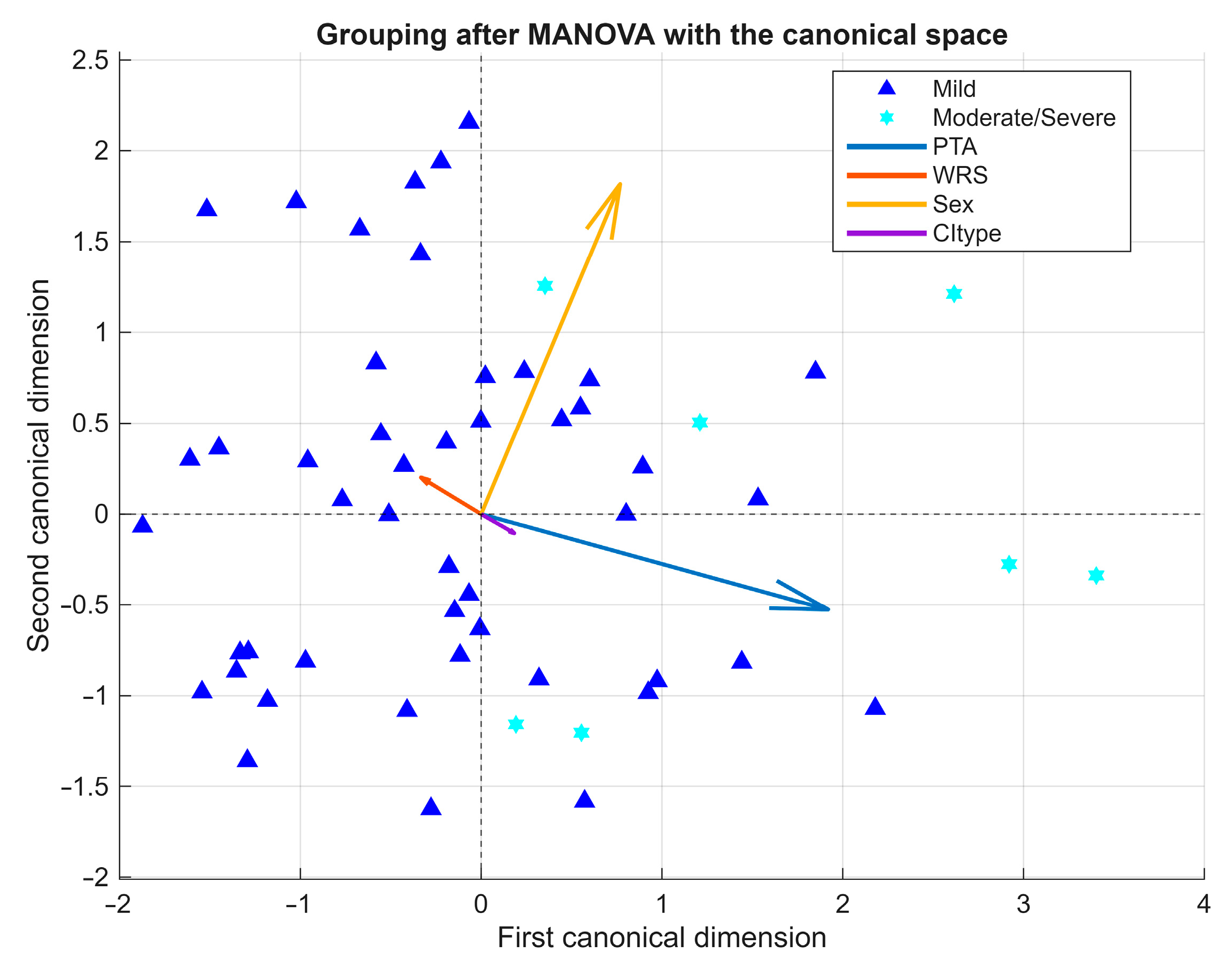
| Structure | Category | n | % of Total Malformed Ears |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cochlea | Normal morphology | 55 | 61.4 |
| Cochlea | Incomplete partition type II | 18 | 21.95 |
| Cochlea | Incomplete partition type I | 3 | 3.66 |
| Cochlea | Common cavity | 3 | 3.66 |
| Cochlea | Intracochlear ossification | 3 | 3.66 |
| Posterior labyrinth | Normal | 57 | 64.3 |
| Posterior labyrinth | Dilated semicircular canals | 13 | 15.85 |
| Posterior labyrinth | Absence of semicircular canals | 12 | 14.63 |
| Vestibular aqueduct | Normal | 55 | 61.4 |
| Vestibular aqueduct | Enlarged vestibular aqueduct | 27 | 32.93 |
| INCAV Code | Total Ears n (%) | % Implanted Within Malformation | % Non-Implanted Within Malformation | Internal Auditory Canal (I) | Cochlear Nerve (N) | Cochlea (C) | Vestibular Aqueduct (A) | Vestibule (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I0 N0 C0 A1 V0 | 15 (18.3) | 13 (86.7) | 2 (13.3) | normal | normal | normal | EVA | normal |
| I0 N0 C0 A0 V1 | 14 (17.1) | 12 (85.7) | 2 (14.3) | normal | normal | normal | normal | SSCC malformation |
| I0 N2 C0 A0 V0 | 6 (7.3) | 6 (100) | 0 | normal | hypoplasia | normal | normal | normal |
| I0 N0 C1 A0 V0 | 5 (6.1) | 4 (80) | 1 (20) | normal | normal | IP type II | normal | normal |
| I0 N0 C1 A0 V1 | 3 (3.7) | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) | normal | normal | IP type II | normal | SSCC malformation |
| I2 N0 C5 A0 V5 | 3 (3.7) | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | narrow | normal | CC | normal | CC |
| I0 N0 C1 A1 V2 | 3 (3.7) | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) | normal | normal | IP type II | EVA | dilated |
| I3 N2 C1 A0 V1 | 2 (2.4) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | atresia | hypoplasia | IP type II | normal | SSCC malformation |
| I1 N0 C0 A0 V0 | 2 (2.4) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | enlarged | normal | normal | normal | normal |
| I2 N2 C0 A1 V1 | 2 (2.4) | 2 (100) | 0 | narrow | hypoplasia | normal | EVA | SSCC malformation |
| I2 N2 C0 A0 V0 | 2 (2.4) | 2 (100) | 0 | narrow | hypoplasia | normal | normal | normal |
| I0 N0 C0 A1 V2 | 2 (2.4) | 1 (50) | 1 (50) | normal | normal | normal | EVA | dilated |
| I0 N0 C1 A1 V0 | 2 (2.4) | 2 (100) | 0 | normal | normal | IP type II | EVA | normal |
| I0 N0 C4 A0 V2 | 2 (2.4) | 2 (100) | 0 | normal | normal | IP type I | normal | dilated |
| I2 N0 C0 A0 V0 | 1 (1.2) | 1 (100) | 0 | narrow | normal | normal | normal | normal |
| I0 N0 C0 A0 V1 | 1 (1.2) | 0 | 1 (100) | normal | normal | normal | normal | SSCC malformation |
| I0 N0 C4 A1 V4 | 1 (1.2) | 1 (100) | 0 | normal | normal | IP type I | EVA | IP type I |
| I0 N0 C1 A0 V2 | 1 (1.2) | 1 (100) | 0 | normal | normal | IP type II | normal | dilated |
| I0 N0 C0 A1 V1 | 1 (1.2) | 1 (100) | 0 | normal | normal | normal | EVA | SSCC malformation |
| I0 N0 C0 A0 V2 | 1 (1.2) | 0 | 1 (100) | normal | normal | normal | normal | dilated |
| I0 N0 C1 A1 V1 | 1 (1.2) | 1 (100) | 0 | normal | normal | IP type II | EVA | SSCC malformation |
| Risk Factor | n, (%) | Mean PTA (dB HL) | Mean WRS (%) at 65 dB HL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic alterations | 18 (22%) | 47 | 76 |
| SLI | 24 (29%) | 44 | 74 |
| NICU Stay | 18 (22%) | 46 | 69 |
| Low birth weight | 8 (9.8%) | 48 | 65 |
| CMV | 6 (7.3%) | 37 | 74 |
| Prematurity | 4 (5%) | 42 | 50 |
| Meningitis | 3 (3.7%) | 42 | 20 |
| Hyperbilirubinemia | 1 (1.2%) | 38 | 0 |
| Alteration | Frequency | Percentage (%) | PTA Mean (dB HL) | WRS Mean (%) at 65 dB HL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC26A4 mutation | 4 | 4.88 | 44 | 70 |
| CHARGE syndrome | 4 | 4.88 | 62 | 0 |
| GJB2/GJB6 compound heterozygous mutations | 2 | 2.44 | 38 | 0 |
| DIABLO (c.592C>T) variant | 2 | 2.44 | 47 | 80 |
| Down syndrome | 2 | 2.44 | 65 | 0 |
| GJB2 mutation | 2 | 2.44 | N/A | N/A |
| Spinocerebellar ataxia and XYY syndrome | 2 | 2.44 | 43 | 50 |
| Epilepsy (unspecified genetic form) | 4 | 2.44 | 32 | 0 |
| Usher syndrome type II | 2 | 2.44 | 32 | 90 |
| Complication | n (%) |
|---|---|
| No complications | 50 (89.3 %) |
| Cerebrospinal fluid gusher | 2 (3.6 %) |
| Reimplantation | 2 (3.6 %) |
| Subperiosteal abscess | 1 (1.8 %) |
| Transient peripheral facial paralysis | 1 (1.8 %) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-García, M.; Alonso-González, C.; Ropero-Romero, F.; Berrocal-Postigo, E.; Aguilar-Vera, F.J.; Gago-Torres, C.; Andrés-Ustárroz, L.; Lazo-Maestre, M.; Callejón-Leblic, M.A.; Sánchez-Gómez, S. Cochlear Implantation in Children with Inner Ear Malformations: Auditory Outcomes, Safety and the Role of Anatomical Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8245. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228245
González-García M, Alonso-González C, Ropero-Romero F, Berrocal-Postigo E, Aguilar-Vera FJ, Gago-Torres C, Andrés-Ustárroz L, Lazo-Maestre M, Callejón-Leblic MA, Sánchez-Gómez S. Cochlear Implantation in Children with Inner Ear Malformations: Auditory Outcomes, Safety and the Role of Anatomical Severity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8245. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228245
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-García, Miriam, Cristina Alonso-González, Francisco Ropero-Romero, Estefanía Berrocal-Postigo, Francisco Javier Aguilar-Vera, Concepción Gago-Torres, Leyre Andrés-Ustárroz, Manuel Lazo-Maestre, M. Amparo Callejón-Leblic, and Serafín Sánchez-Gómez. 2025. "Cochlear Implantation in Children with Inner Ear Malformations: Auditory Outcomes, Safety and the Role of Anatomical Severity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8245. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228245
APA StyleGonzález-García, M., Alonso-González, C., Ropero-Romero, F., Berrocal-Postigo, E., Aguilar-Vera, F. J., Gago-Torres, C., Andrés-Ustárroz, L., Lazo-Maestre, M., Callejón-Leblic, M. A., & Sánchez-Gómez, S. (2025). Cochlear Implantation in Children with Inner Ear Malformations: Auditory Outcomes, Safety and the Role of Anatomical Severity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8245. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228245








