Targeted Neonatal Echocardiography in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: A Framework for Screening and Management of Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
Framework Development
- Identification of the at-risk population for screening;
- Definition and echocardiographic grading of cPH severity;
- Follow-up strategies and the role of additional biomarkers;
- Pharmacological and non-pharmacological management strategies.
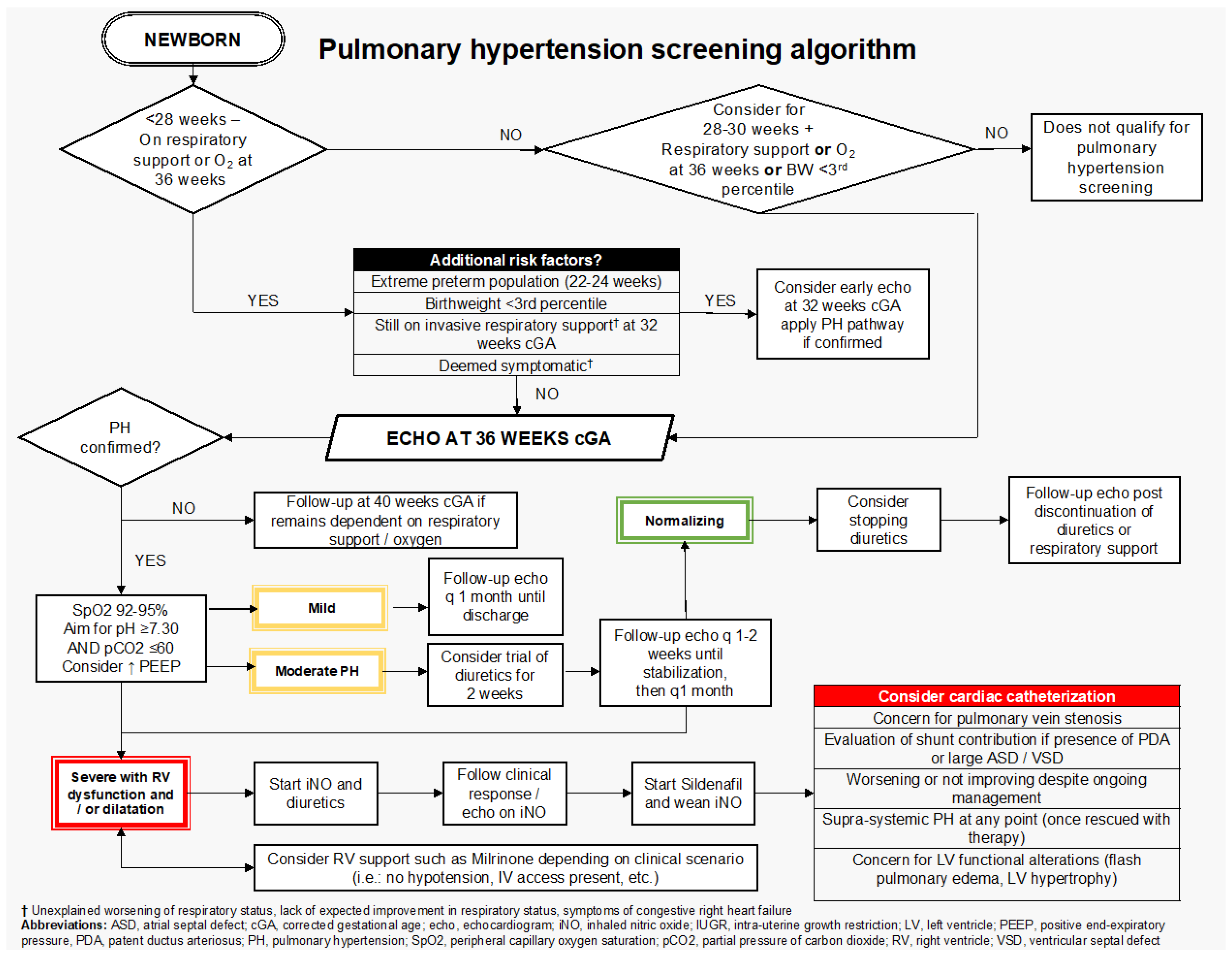
2. Targeted Population for Screening
3. Echocardiographic Markers of cPH and Definition
4. Grading PH Severity via Echocardiography
5. Echocardiographic Follow-Up
6. Biomarkers for cPH Screening
7. cPH Management
7.1. Non-Pharmacological Management
7.1.1. Respiratory Management
7.1.2. Airway Lesions Screening
7.1.3. Reflux and Aspiration Management
7.1.4. Nutrition
7.2. Pharmacological Management
7.3. Systemic Hypertension
8. Indications for Cardiac Catheterization
9. Limitations
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Li, B.; Qu, S.S.; Li, L.X.; Zhou, N.; Liu, N.; Wei, B. Risk factors and clinical outcomes of pulmonary hypertension associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely premature infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2024, 59, 3117–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abman, S.H.; Hansmann, G.; Archer, S.L.; Ivy, D.D.; Adatia, I.; Chung, W.K.; Hanna, B.D.; Rosenzweig, E.B.; Raj, J.U.; Cornfield, D.; et al. Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension: Guidelines From the American Heart Association and American Thoracic Society. Circulation 2015, 132, 2037–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, U.; Feinstein, J.A.; Adatia, I.; Austin, E.D.; Mullen, M.P.; Hopper, R.K.; Hanna, B.; Romer, L.; Keller, R.L.; Fineman, J.; et al. Evaluation and Management of Pulmonary Hypertension in Children with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. J. Pediatr. 2017, 188, 24–34.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, T.R.; Kim, J.H. A systematic review and meta-analysis to revise the Fenton growth chart for preterm infants. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mourani, P.M.; Sontag, M.K.; Younoszai, A.; Miller, J.I.; Kinsella, J.P.; Baker, C.D.; Poindexter, B.B.; Ingram, D.A.; Abman, S.H. Early pulmonary vascular disease in preterm infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jone, P.N.; Ivy, D.D. Echocardiography in pediatric pulmonary hypertension. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jone, P.N.; Schäfer, M.; Li, L.; Craft, M.; Ivy, D.D.; Kutty, S. Right Atrial Deformation in Predicting Outcomes in Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, e006250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.E.; Braun, H.; Goldblatt, A.; Liberthson, R.; Weyman, A.E. Interventricular septal configuration as a predictor of right ventricular systolic hypertension in children: A cross-sectional echocardiographic study. Circulation 1983, 68, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.; Weismann, C.G. Left Ventricular End-Systolic Eccentricity Index for Assessment of Pulmonary Hypertension in Infants. Echocardiography 2016, 33, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, A.H.; Reyes, M.; Rios, D.R.; Giesinger, R.E.; Jetton, J.G.; Bischoff, A.R.; McNamara, P.J. Safety, Feasibility, and Impact of Enalapril on Cardiorespiratory Physiology and Health in Preterm Infants with Systemic Hypertension and Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderlaan, R.D.; Rome, J.; Hirsch, R.; Ivy, D.; Caldarone, C.A. Pulmonary vein stenosis: Treatment and challenges. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 161, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Berkelhamer, S.; Lakshminrusimha, S. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Matern. Health Neonatol. Perinatol. 2015, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malloy, K.W.; Austin, E.D. Pulmonary hypertension in the child with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 3546–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilgendorff, A.; Apitz, C.; Bonnet, D.; Hansmann, G. Pulmonary hypertension associated with acute or chronic lung diseases in the preterm and term neonate and infant. The European Paediatric Pulmonary Vascular Disease Network, endorsed by ISHLT and DGPK. Heart 2016, 102 (Suppl. 2), ii49–ii56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansmann, G.; Sallmon, H.; Roehr, C.C.; Kourembanas, S.; Austin, E.D.; Koestenberger, M.; European Pediatric Pulmonary Vascular Disease Network (EPPVDN). Pulmonary hypertension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkelhamer, S.K.; Mestan, K.K.; Steinhorn, R. An update on the diagnosis and management of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)-associated pulmonary hypertension. Semin. Perinatol. 2018, 42, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, P.; Lakshminrusimha, S. Oxygen therapy in preterm infants with pulmonary hypertension. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 25, 101070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentle, S.J.; Travers, C.P.; Nakhmani, A.; Indic, P.; Carlo, W.A.; Ambalavanan, N. Intermittent Hypoxemia and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia with Pulmonary Hypertension in Preterm Infants. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, P.T.; Levin, J.; Leeman, K.T.; Mullen, M.P.; Hansmann, G.; Kourembanas, S. Diagnosis and management of pulmonary hypertension in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 27, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, K.; Jensen, E.A.; Alexiou, S.; Munson, D.; Zhang, H. Ventilation Strategies in Severe Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Neoreviews 2020, 21, e226–e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.A.; Zhang, H.; Feng, R.; Dysart, K.; Nilan, K.; Munson, D.A.; Kirpalani, H. Individualising care in severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A series of N-of-1 trials comparing transpyloric and gastric feeding. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2020, 105, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.Y.; Bai, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.C. Gastroesophageal Reflux Poses a Potential Risk for Late Complications of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: A Prospective Cohort Study. Chest 2020, 158, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, M.C.; Cornfield, D.N. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Then, Now, and Next. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2020, 33, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baczynski, M.; Kelly, E.; McNamara, P.J.; Shah, P.S.; Jain, A. Short and long-term outcomes of chronic pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants managed using a standardized algorithm. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Ibarra Rios, D.; Joye, S.; Baczynski, M.; Rios, D.; Giesinger, R.E.; McNamara, P.J.; Jain, A. Cardiopulmonary physiological effects of diuretic therapy in preterm infants with chronic pulmonary hypertension. J. Perinatol. 2023, 43, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ó Briain, E.; Byrne, A.O.; Dowling, J.; Kiernan, J.; Carlo Rio Lynch, J.; Alomairi, L.; Coyle, L.; Mulkerrin, L.; Mockler, D.; Fitzgerald, G.; et al. Diuretics use in the management of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants: A systematic review. Acta Paediatr. 2024, 113, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abman, S.H.; Kinsella, J.P.; Rosenzweig, E.B.; Krishnan, U.; Kulik, T.; Mullen, M.; Wessel, D.L.; Steinhorn, R.; Adatia, I.; Hanna, B.; et al. Food and Drug Administration warning against the use of sildenafil for the treatment of pediatric pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionne, J.M.; Abitbol, C.L.; Flynn, J.T. Hypertension in infancy: Diagnosis, management and outcome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2012, 27, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Hernandez, M.E.; Bischoff, A.R.; Giesinger, R.E.; Rios, D.R.; Stanford, A.H.; McNamara, P.J. Echocardiography Assessment of Left Ventricular Function in Extremely Preterm Infants, Born at Less Than 28 Weeks’ Gestation, With Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Systemic Hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2024, 37, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, A.; Krishnamurthy, M.B.; Clark, M.; Menahem, S. ACE inhibition for severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia-an approach based on physiology. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PH Severity | |
| No PH | Right Ventricular systolic pressure less than 1/3 systemic pressure by tricuspid regurgitant jet (TRJ) or other metric (VSD, PDA); septal position round; LV eccentricity index less than 1.3; no RV hypertrophy; normal RV size and function |
| Definition of pulmonary hypertension mPAP > 20 mmHg (pulmonary insufficiency jet) sPAP > 40 mmHg (TRJ > 35 mmHg; VSD/PDA gradient) Concerns of pulmonary hypertension PAAT/RVET less than 0.25 (RVET/PAAT greater than 4) Eccentricity index greater than 1.3 Septal flattening at peak systole D-RV/D-LV greater than 1.00 Inter-atrial or post-tricuspid shunt with a right-to-left directionality Signs of pulmonary venous stenosis | |
| Mild | RV systolic pressure 1/3–1/2 systemic pressure; septal flattening in systole, RV function normal |
| Moderate | RVSP ½–2/3 systemic pressure; septum flattening in systole, RVH or dilatation, RV with altered function (TAPSE 6.5 to 8 mm; FAC: 20–30%):
|
| Severe | RV systolic pressure greater than 2/3 systemic pressure; If present, shunt (inter-atrial, post-tricuspid) with predominant R-L gradient, septal bowing, RVH, severe RV dysfunction, RV dilatation. Dilated right atrium and dilated inferior vena cava are also evidence of RA hypertension and RV diastolic dysfunction. Some concerning signs for severe alteration of RV function,
|
| Domain | Key Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Respiratory Management | Target SaO2 92–95%; Maintain pH ≥ 7.30 and PaCO2 ≤ 60 mmHg; Consider higher PEEP; Use higher tidal volumes (8–12 mL/kg) and lower rates; Baseline sleep oximetry before discharge. |
| Airway Lesion Screening | Evaluate for vocal cord dysfunction, tracheomalacia, bronchomalacia, and stenosis; Refer to ENT if airway involvement is suspected; Involve cardiac anesthesia for bronchoscopy. |
| Reflux and Aspiration Management | Assess for GER and aspiration; Initiate treatment as needed based on local protocols to reduce further lung injury and optimize respiratory status. |
| Nutrition | Provide 130–150 kcal/kg/day; Monitor growth closely Involve a neonatal dietitian Individualize care due to a lack of standardized nutritional guidelines |
| Pharmacological Management | Trial of diuretics at 36 weeks PMA in moderate to severe cPH after stabilization; Monitor electrolytes if >1 week; Consider iNO and sildenafil in severe cases with RV dysfunction; Use vasodilators under specialist guidance (neonatal hemodynamics and pediatric cardiology). |
| Cardiac Catheterization | Indicated for suspected pulmonary vein stenosis, significant shunting, or lack of improvement; Consider if supra-systemic PH or LV dysfunction present; Cardiac anesthesia is recommended for procedural support. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hébert, A.; Villeneuve, A.; Lapointe, A.; Drolet, C.; Nouraeyan, N.; Bensouda, B.; Michel-Macias, C.; Wazneh, L.; Zeid, M.; Brief, F.; et al. Targeted Neonatal Echocardiography in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: A Framework for Screening and Management of Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228161
Hébert A, Villeneuve A, Lapointe A, Drolet C, Nouraeyan N, Bensouda B, Michel-Macias C, Wazneh L, Zeid M, Brief F, et al. Targeted Neonatal Echocardiography in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: A Framework for Screening and Management of Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228161
Chicago/Turabian StyleHébert, Audrey, Andréanne Villeneuve, Anie Lapointe, Christine Drolet, Nina Nouraeyan, Brahim Bensouda, Carolina Michel-Macias, Laila Wazneh, Marco Zeid, Floriane Brief, and et al. 2025. "Targeted Neonatal Echocardiography in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: A Framework for Screening and Management of Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228161
APA StyleHébert, A., Villeneuve, A., Lapointe, A., Drolet, C., Nouraeyan, N., Bensouda, B., Michel-Macias, C., Wazneh, L., Zeid, M., Brief, F., & Altit, G. (2025). Targeted Neonatal Echocardiography in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: A Framework for Screening and Management of Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228161







