Ultrasound Elastography and Tonometry as Predictive Tools for Capsular Contracture After Breast Implant Surgery: Over a 12-Month Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
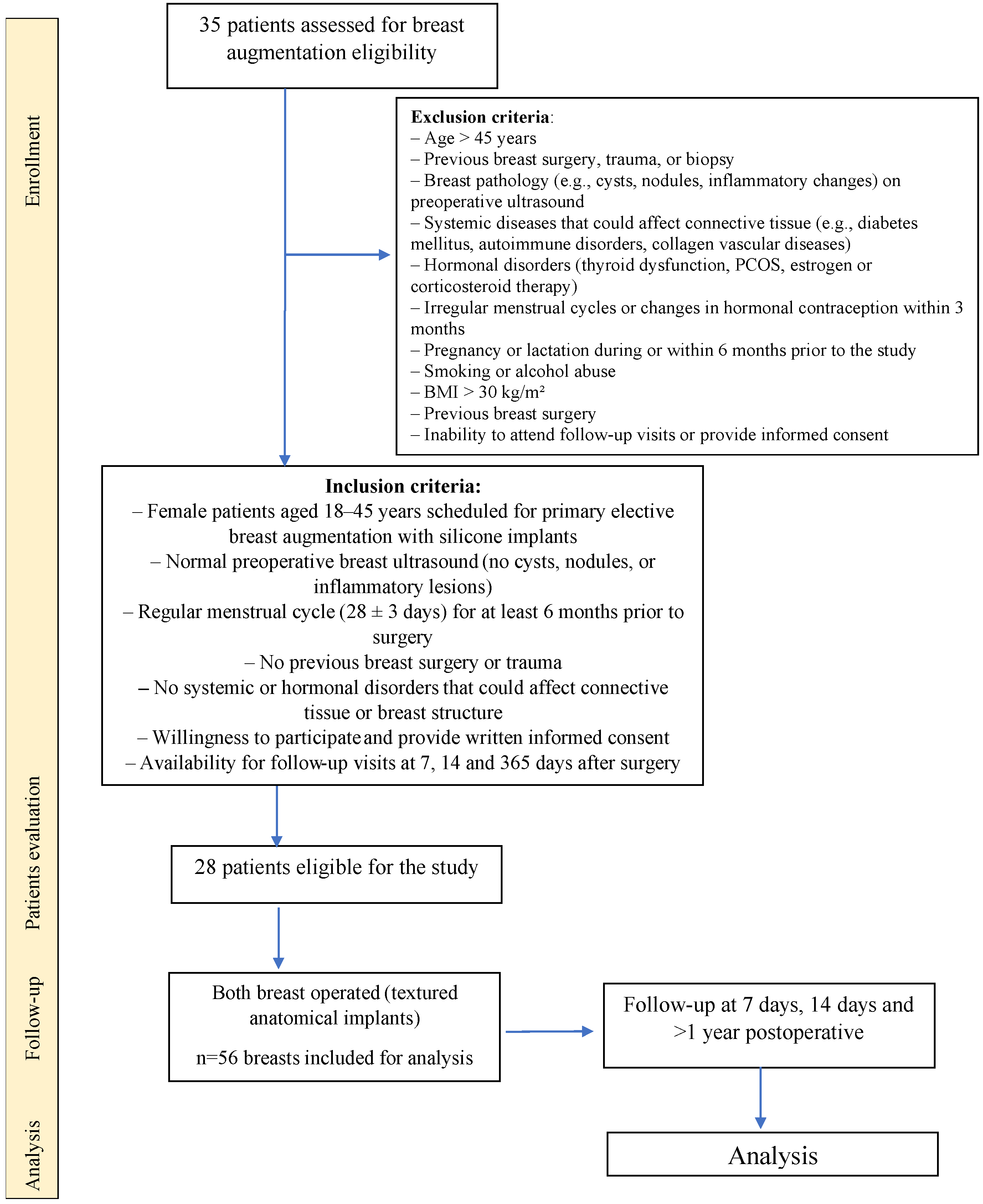
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Study Protocol
2.3. Clinical Assessment
2.4. Tonometric Assessment
2.5. Elastographic Assessment
2.6. Surgical Technique
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SWE | Shear-wave Elastography |
| SE | Strain Elastography |
| CC | Capsular contracture |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
References
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons®. Plastic Surgery Statistic Report 2024—Cosmetic Procedure Trends. Available online: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/news/statistics/2024/plastic-surgery-statistics-report-2024.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- 2020 Plastic Surgery Statistics Report. Plastic Surgery 2020. Available online: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/news/plastic-surgery-statistics?sub=2020+Plastic+Surgery+Statistics (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Mohebali, K.; Wixtrom, R.N. Breast Implant Engineering and Performance. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 6S–11S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.H.; Garza, R.; Povoski, S.P. A Review of the Use of Silicone Implants in Breast Surgery. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices 2016, 13, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, P.; Papas, A.; Hedén, P. Is Rotation a Concern with Anatomical Breast Implants? A Statistical Analysis of Factors Predisposing to Rotation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Xue, E.Y.; Sangiovanni, C.; Therattil, P.J.; Lee, E.S. Breast Massage, Implant Displacement, and Prevention of Capsular Contracture After Breast Augmentation with Implants: A Review of the Literature. Eplasty 2017, 17, e41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.R.; Chien, P.N.; Trinh, X.-T.; Nam, S.-Y.; Heo, C.-Y. Comparison of Formation of Capsule Among Different Breast Silicone Implants. In Vivo 2022, 36, 2756–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagani, A.; Aitzetmüller, M.M.; Larcher, L. A Forgotten Entity Following Breast Implant Contracture: Does Baker Need a Change? Arch. Plast. Surg. 2022, 49, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, J.M.; Perry, T.; Ren, C.D.; Nofrey, B.; Teitelbaum, S.; Van Epps, D.E. Histological Characterization of Human Breast Implant Capsules. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2015, 39, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahavi, A.; Sklair, M.L.; Ad-El, D.D. Capsular Contracture of the Breast: Working Towards a Better Classification Using Clinical and Radiologic Assessment. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2006, 57, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allergan, Inc. Directions for Use: Natrelle Silicone-Filled Breast Implants and Natrelle Inspira Breast Implants. Available online: https://www.rxabbvie.com/pdf/natrelle-siliconeimplants_dfu.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Newman, A.N.; Davison, S.P. Effect of Keller Funnel on the Rate of Capsular Contracture in Periareolar Breast Augmentation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2018, 6, e1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, S.L.; Bulan, E.J.; Venturi, M.L. Breast Augmentation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 188S–196S; discussion 197S–198S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Mu, D.; Luan, J. Capsular Contracture Rate After Breast Augmentation with Periareolar Versus Other Two (Inframammary and Transaxillary) Incisions: A Meta-Analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2018, 42, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreml, S.; Heine, N.; Eisenmann-Klein, M.; Prantl, L. Bacterial Colonization Is of Major Relevance for High-Grade Capsular Contracture after Augmentation Mammaplasty. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2007, 59, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajdic, D.; Zoghbi, Y.; Gerth, D.; Panthaki, Z.J.; Thaller, S. The Relationship of Bacterial Biofilms and Capsular Contracture in Breast Implants. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2016, 36, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsnell, J.D.; Searle, A.E.; Harris, P.A. Intra-Operative Techniques to Reduce the Risk of Capsular Contracture in Patients Undergoing Aesthetic Breast Augmentation—A Review. Surgeon 2017, 15, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabeg, R.; Jakirlic, M.; Karabeg, A.; Crnogorac, D.; Aslani, I. The New Method of Pocket Forming for Breast Implant Placement in Augmentation Mammaplasty: Dual Plane Subfascial. Med. Arch. 2019, 73, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeberg, A.; Sørensen, J.A. The Impact of Breast Implant Location on the Risk of Capsular Contraction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 77, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, P.; Cheema, M.; Hedén, P.; Agko, M.; Quattrini Li, A.; Avvedimento, S. Do Not Fear an Implant’s Shape: A Single Surgeon’s Experience of Over 1200 Round and Shaped Textured Implants in Primary Breast Augmentation. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2018, 38, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforza, M.; Kul, Z.; Saghir, R.; Saghir, N.; Okhiria, R.; Okhiria, T.; Sidhu, M. Predicting the Expansion of the Lower Pole of the Breast Following Smooth Breast Implant Augmentation: A Novel Shear Wave Elastography Study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2023, 84, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, R.-G.; Helgiu, A.; Cimpean, A.-M.; Ichim, C.; Todor, S.B.; Iliescu-Glaja, M.; Bodea, I.C.; Crainiceanu, Z.P. Assessing Fat Grafting in Breast Surgery: A Narrative Review of Evaluation Techniques. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Faria Castro Fleury, E. Why Is the Baker Classification Inadequate for Classifying Silicone Implant Fibrous Capsules? Cureus 2024, 16, e55776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, S.L.; Baker, J.L. Classification of Capsular Contracture after Prosthetic Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 96, 1119–1123; discussion 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.S.; Sullivan, J.; Tenenbaum, M.M.; Broderick, K.B.; Myckatyn, T.M. Toward a Consensus Aproach for Assessing Capsular Contracture Severity and Progression: A Systematic Review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 153, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.; Hösl, V.; von Fraunberg, S.; Jung, F.; Prantl, L. Ultrasound Elastography for the Detection of Capsular Fibrosis in Breast Implants: First Results. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2021, 77, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfob, A.; Golatta, M. Breast Elastography—Ready for Prime Time? Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 943–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, R.G.; Engel, A.; Kim, S.; Tran, P.; De Silvestri, A. Improved Breast 2D SWE Algorithm to Eliminate False-Negative Cases. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, R.G. The Role of Sonoelastography in Breast Lesions. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2018, 39, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A.; Cosgrove, D.O.; Doré, C.J.; Schäfer, F.K.W.; Svensson, W.E.; Hooley, R.J.; Ohlinger, R.; Mendelson, E.B.; Balu-Maestro, C.; Locatelli, M.; et al. Shear-Wave Elastography Improves the Specificity of Breast US: The BE1 Multinational Study of 939 Masses. Radiology 2012, 262, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzymski, P.; Skórzewska, A.; Opala, T. Changes in Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography Properties of Normal Breast during Menstrual Cycle. Clin. Exp. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 38, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Togawa, R.; Pfob, A.; Büsch, C.; Fastner, S.; Gomez, C.; Goncalo, M.; Hennigs, A.; Killinger, K.; Nees, J.; Riedel, F.; et al. Intra- and Interobserver Reliability of Shear Wave Elastography in Breast Cancer Diagnosis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2024, 43, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantl, L.; Englbrecht, M.A.; Schoeneich, M.; Kuehlmann, B.; Jung, E.M.; Kubale, R. Semiquantitative Measurements of Capsular Contracture with Elastography—First Results in Correlation to Baker Score. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2014, 58, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimabukuro, M.; Ishii, N.; Ko, T.; Ohta, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Kishi, K. False-Positive Diagnoses of Damaged Breast Implants on Imaging: A Report of Two Cases. Gland. Surg. 2023, 12, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Zuniga, S.; Ziade, N.V.; Zambrano, J.C. Ultrasound Criteria and Baker Scale for Breast Implant Capsular Contracture Diagnosis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffenach, L.; Heintz, D.; Villette, C.; Cosentino, C.; Funfschilling, D.; Bodin, F.; Bahlouli, N.; Chatelin, S. Ultrasonic Elastography for the Prevention of Breast Implant Rupture: Detection of an Increase with Stiffness over Implantation Time. J. Biomech. 2024, 163, 111955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, C.; Mazzocchi, M.; Scuderi, N. Mammary Compliance: An Objective Measurement of Capsular Contracture. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2004, 28, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wen, W.; He, Y.; Wei, T.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dong, F.; et al. Evaluation of Standard Breast Ultrasonography by Adding Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography: A Prospective, Multicenter Trial. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, F.W.-F.; Ghai, S.; Moshonov, H.; Kahn, H.; Brennan, C.; Dua, H.; Crystal, P. Diagnostic Performance of Quantitative Shear Wave Elastography in the Evaluation of Solid Breast Masses: Determination of the Most Discriminatory Parameter. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 203, W328–W336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, H.; Celik, M.; Warm, M.; Thangarajah, F.; Vogel-Minea, C.; Malter, W.; Pisek, A.; Eichler, C. Sonographic Assessment of Breast Implants Using Strain Elastography and Shear Wave Elastography in an Animal Model. Anticancer Res. 2024, 44, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantl, L.; Pöppl, N.; Horvat, N.; Heine, N.; Eisenmann-Klein, M. Serologic and Histologic Findings in Patients with Capsular Contracture after Breast Augmentation with Smooth Silicone Gel Implants: Is Serum Hyaluronan a Potential Predictor? Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2005, 29, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, Y.; Yokota, I.; Itsukage, S.; Nakatsukasa, K.; Sakaguchi, K.; Taguchi, T.; Numajiri, T. Evaluation of the Severity of Capsular Contracture Using Elastography after Breast Implant Reconstruction. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2017, 66, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. Wound Healing: Cellular Mechanisms and Pathological Outcomes. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacka, A.; Dobaczewski, M.; Frangogiannis, N.G. TGF-β Signaling in Fibrosis. Growth Factors 2011, 29, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoberleitner, I.; Lackner, M.; Coraça-Huber, D.C.; Augustin, A.; Imsirovic, A.; Sigl, S.; Wolfram, D. SMI-Capsular Fibrosis and Biofilm Dynamics: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Antimicrobial Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, B.; Di Napoli, A.; Curigliano, G.; Veronesi, P.; Pileri, S.; Martelli, M.; De Vita, R.; Felici, N.; Cirillo, P.; Bernardi, C.; et al. Clinical Recommendations for Diagnosis and Treatment According to Current Updated Knowledge on BIA-ALCL. Breast 2022, 66, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flugstad, N.A.; Pozner, J.N.; Baxter, R.A.; Creasman, C.; Egrari, S.; Martin, S.; Messa, C.A.; Oliva, A.; Schlesinger, S.L.; Kortesis, B.G. Does Implant Insertion with a Funnel Decrease Capsular Contracture? A Preliminary Report. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2016, 36, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.D.; Yi, M.-H.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, Y.; Choi, Y.; Oh, S.-H. The Effect of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A on Capsule Formation around Silicone Implants: The in Vivo and in Vitro Study. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Health and Human Services, U.F.& D. Administration. Breast Implants—Certain Labeling Recommendations to Improve Patient Communication. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/breast-implants-certain-labeling-recommendations-improve-patient-communication (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Expert Panel on Breast Imaging; Chetlen, A.; Niell, B.L.; Brown, A.; Baskies, A.M.; Battaglia, T.; Chen, A.; Jochelson, M.S.; Klein, K.A.; Malak, S.F.; et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Breast Implant Evaluation: 2023 Update. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2023, 20, S329–S350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|
| Before surgery (V1) | 625.0 ± 159.6 |
| On postoperative day 7 (V2) | 1021.0 ± 238.2 |
| On postoperative day 14 (V3) | 979.0 ± 244.2 |
| >1 year after surgery (V4) | 765.6 ± 142.8 |
| V1 Preoperative | V2 Day 7 Postoperative | V3 Day 14 Postoperative | V4 >1 Year Postoperative | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | |||||
| Adipose Tissue | LQ | 4.7 ± 2.3 | 12.0 ± 7.6 * | 11.7 ± 6.2 * | 7.7 ± 4.6 * |
| UQ | 7.8 ± 4.3 | 11.9 ± 4.7 * | 10.5 ± 5.1 * | 7.6 ± 4.2 | |
| OQ | 6.7 ± 3.8 | 14.6 ± 6.3 * | 13.4 ± 6.5 * | 10.5 ± 5.7 * | |
| IQ | 7.7 ± 5.1 | 12.9 ± 5.4 * | 15.0 ± 7.7 * | 9.1 ± 4.0 * | |
| Fascia | UQ | 9.2 ± 4.5 | 13.3 ± 4.9 * | 13.2 ± 5.8 * | 11.2 ± 4.7 * |
| IQ | 12.0 ± 7.3 | 22.8 ± 11.8 * | 20.5 ± 6.3 * | 13.2 ± 4.4 | |
| Muscle | UQ | 9.4 ± 5.2 | 14.5 ± 5.8 * | 15.9 ± 7.3 * | 11.4 ± 5.7 * |
| IQ | 10.6 ± 5.5 | 22.8 ± 11.8 * | 21.8 ± 7.4 * | 14.4 ± 4.8 | |
| Glandular Tissue | LQ | 5.8 ± 3.0 | 14.3 ± 6.9 * | 12.1 ± 7.9 * | 9.0 ± 4.3 * |
| UQ | 8.7 ± 3.7 | 12.9 ± 4.7 * | 12.6 ± 6.0 * | 8.5 ± 3.7 | |
| OQ | 9.5 ± 12.9 | 15.0 ± 6.7 * | 14.4 ± 5.9 * | 11.7 ± 5.9 * | |
| IQ | 8.4 ± 4.2 | 16.1 ± 6.9 * | 16.5 ± 6.6 * | 11.3 ± 4.4 * | |
| Peri-implant region (capsule) | LQ | - | 23.7 ± 7.7 | 22.4 ± 6.7 | 15.1 ± 4.8 |
| UQ | - | 19.6 ± 5.5 | 18.3 ± 6.1 | 13.4 ± 5.0 | |
| OQ | - | 25.5 ± 8.9 | 22.5 ± 7.5 | 17.7 ± 6.4 | |
| IQ | - | 25.4 ± 8.7 | 23.5 ± 6.6 | 15.7 ± 4.9 | |
| Baker Scale | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Late Postoperative Elastography to Endpoint Baker Scale (V4) | Early Postoperative Elastography to Endpoint Baker Scale | |||
| V4 | V2 | V3 | ||
| Adipose Tissue | LQ | Rs = 0.01 p = 0.883 CI = (−0.361, 0.413) | Rs = 0.093 p = 0.652 CI = (−0.306, 0.463) | Rs = 0.348 p = 0.082 CI = (−0.046, 0.710) |
| UQ | Rs = 0.06 p = 0.846 CI = (−0.421, 0.353) | Rs = −0.105 p = 0.609 CI = (−0.473, 0.294) | Rs = 0.241 p = 0.236 CI = (−0.158, 0.618) | |
| OQ | Rs = 0.02 p = 0.730 CI = (−0.325, 0.446) | Rs = −0.040 p = 0.845 CI = (−0.421, 0.352) | Rs = 0.376 p = 0.058 CI = (0.001, 0.665) | |
| IQ | Rs = 0.46 p = 0.014 CI = (0.109, 0.729) | Rs = −0.145 p = 0.481 CI = (−0.504, 0.257) | Rs = 0.235 p = 0.249 CI = (−0.197, 0.602) | |
| Fascia | UQ | Rs = 0.10 p = 0.512 CI = (−0.267, 0.496) | Rs = 0.377 p = 0.058 CI = (−0.012, 0.667) | Rs = 0.199 p = 0.329 CI = (−0.199, 0.544) |
| IQ | Rs = 0.28 p = 0.042 CI = (−0.018, 0.663) | Rs = −0.138 p = 0.501 CI = (−0.499, 0.263) | Rs = 0.316 p = 0.116 CI = (−0.102, 0.678) | |
| Muscle | UQ | Rs = −0.01 p = 0.938 CI = (−0.401, 0.374) | Rs = 0.388 p = 0.050 CI = (0.001, 0.674) | Rs = 0.070 p = 0.734 CI = (−0.348, 0.454) |
| IQ | Rs = 0.25 p = 0.184 CI = (−0.132, 0.595) | Rs = −0.131 p = 0.524 CI = (−0.493, 0.270) | Rs = 0.248 p = 0.221 CI = (−0.178, 0.655) | |
| Glandular Tissue | LQ | Rs = 0.12 p = 0.612 CI = (−0.295, 0.473) | Rs = 0.305 p = 0.130 CI = (−0.093, 0.619) | Rs = 0.321 p = 0.110 CI = (−0.181, 0.716) |
| UQ | Rs = 0.08 p = 0.964 CI = (−0.395, 0.379) | Rs = 0.168 p = 0.411 CI = (−0.234, 0.522) | Rs = 0.182 p = 0.374 CI = (−0.259, 0.572) | |
| OQ | Rs = 0.05 p = 0.892 CI = (−0.363, 0.411) | Rs = 0.008 p = 0.970 CI = (−0.381, 0.394) | Rs = 0.436 p = 0.026 CI = (0.088, 0.686) | |
| IQ | Rs = 0.18 p = 0.134 CI = (−0.097, 0.617) | Rs = −0.136 p = 0.508 CI = (−0.497, 0.265) | Rs = 0.303 p = 0.132 CI = (−0.178, 0.710) | |
| Peri-implant region | LQ | Rs = 0.08 p = 0.754 CI = (−0.331, 0.441) | Rs = 0.063 p = 0.759 CI = (−0.332, 0.440) | Rs = 0.121 p = 0.557 CI = (−0.276, 0.492) |
| UQ | Rs = −0.06 p = 0.370 CI = (−0.533, 0.220) | Rs = 0.089 p = 0.665 CI = (−0.309, 0.461) | Rs = 0.016 p = 0.939 CI = (−0.372, 0.386) | |
| OQ | Rs = −0.08 p = 0.370 CI = (−0.644, 0.520) | Rs = −0.211 p = 0.301 CI = (−0.553, 0.192) | Rs = 0.218 p = 0.284 CI = (−0.271, 0.637) | |
| IQ | Rs = 0.33 p = 0.047 CI = (−0.013, 0.667) | Rs = −0.101 p = 0.625 CI = (−0.470, 0.298) | Rs = 0.308 p = 0.125 CI = (−0.160, 0.693) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubasik, M.; Rzymska, A.; Pięta, B.; Rzymski, P. Ultrasound Elastography and Tonometry as Predictive Tools for Capsular Contracture After Breast Implant Surgery: Over a 12-Month Prospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228084
Kubasik M, Rzymska A, Pięta B, Rzymski P. Ultrasound Elastography and Tonometry as Predictive Tools for Capsular Contracture After Breast Implant Surgery: Over a 12-Month Prospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228084
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubasik, Mikołaj, Alicja Rzymska, Beata Pięta, and Paweł Rzymski. 2025. "Ultrasound Elastography and Tonometry as Predictive Tools for Capsular Contracture After Breast Implant Surgery: Over a 12-Month Prospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228084
APA StyleKubasik, M., Rzymska, A., Pięta, B., & Rzymski, P. (2025). Ultrasound Elastography and Tonometry as Predictive Tools for Capsular Contracture After Breast Implant Surgery: Over a 12-Month Prospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228084







