Fibromuscular Dysplasia and Intracranial Aneurysms: A Narrative Review of a Dangerous and Underestimated Association
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Proportion of Ruptured and Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms in Patients with FMD
- -
- Multivessel FMD (OR 3.99, 95% CI [2.89–5.57], p < 0.001)
- -
- Multifocal FMD (OR 1.91, 95% CI [1.26–2.98], p = 0.003)
3.2. Prevalence of FMD in Patients with SAH
3.3. Features of Intracranial Aneurysms
- 1.
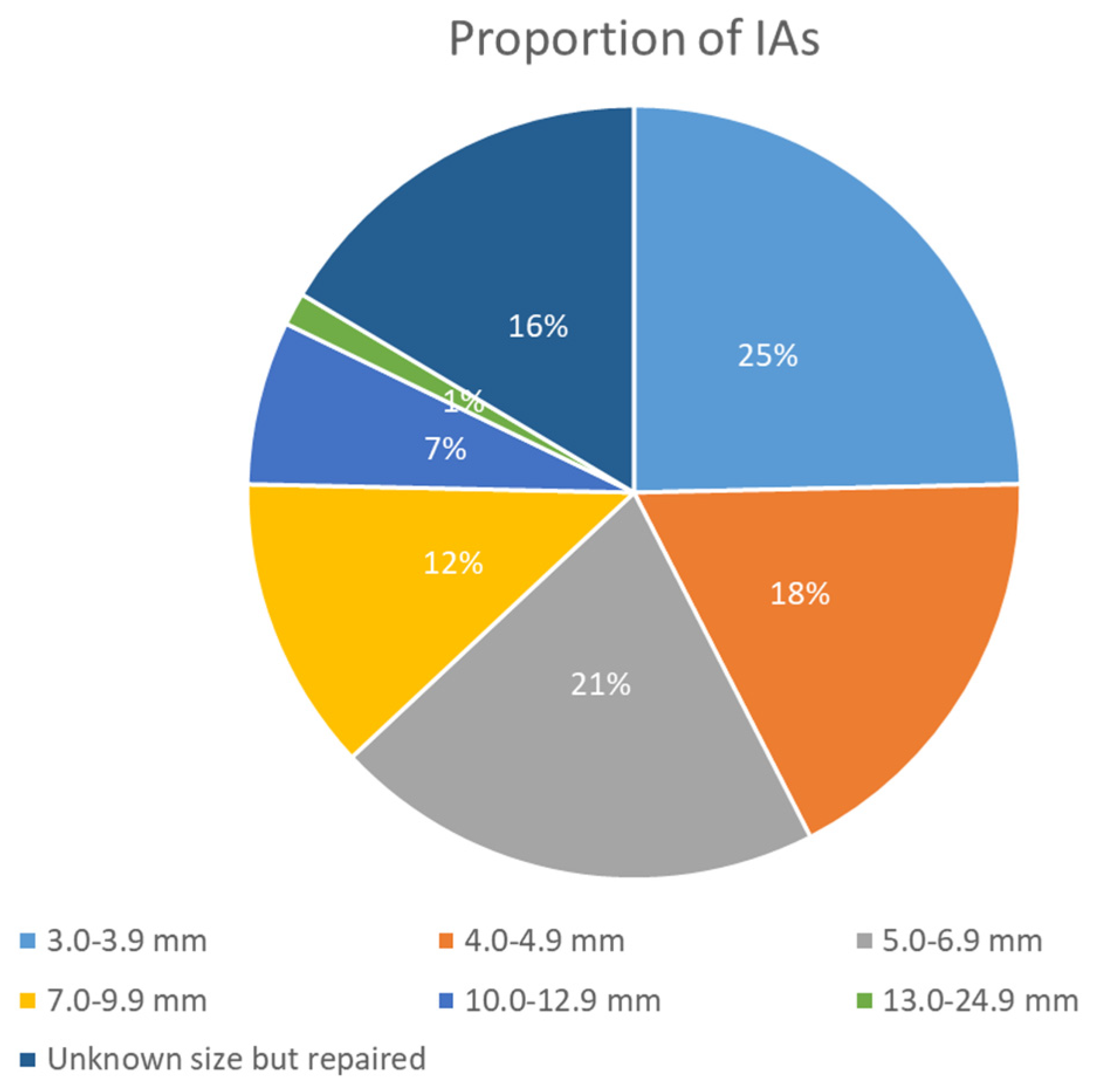
- Size of Aneurysms: 56/128 (43.2%) aneurysms were ≥5 mm, i.e., at high risk of rupture, illustrating a higher risk profile compared to general population findings. The sizes were categorized as in Figure 1.
- 2.
- Location of Aneurysms: The distribution of IAs was notable, with a significant number located in areas typically associated with higher risks of rupture. A substantial 41% of the identified intracranial aneurysms were located in the intradural segments of the ICA, which is considered a high-risk area, along with 12% in the posterior communicating artery and 9% in posterior circulation arteries.
- 3.
- Multiplicity: Many patients presented with multiple IAs, indicating a possible underlying susceptibility linked to the pathophysiology of FMD. The median number of aneurysms per patient was 1, but some had as many as 8 intracranial aneurysms.
3.4. Treatment Issues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRF | Case Report Form |
| CTA | Computed Tomography Angiography |
| DSA | Digital Subtraction Angiography |
| FMD | FibroMuscular Dysplasia |
| IA | Intracranial Aneurysm |
| ICA | Internal Carotid Artery |
| MIP | Maximum Intensity Projections |
| MPR | Multiplanar Reconstruction |
| MRA | Magnetic Resonance Angiography |
| SAH | Subarachnoid Hemorrhage |
| UIA | Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm |
| VA | Vertebral Artery |
References
- Gornik, H.L.; Persu, A.; Adlam, D.; Aparicio, L.S.; Azizi, M.; Boulanger, M.; Bruno, R.M.; De Leeuw, P.; Fendrikova-Mahlay, N.; Froehlich, J.; et al. Working Group ‘Hypertension and the Kidney’ of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and the Society for Vascular Medicine (SVM). First international consensus on the diagnosis and management of fibromuscular dysplasia. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 229–252, Erratum in J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 1098. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000002100. Erratum in J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1932. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000002978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappaccogli, M.; Di Monaco, S.; Warchoł-Celińska, E.; Lorthioir, A.; Amar, L.; Aparicio, L.S.; Beauloye, C.; Bruno, R.M.; Chenu, P.; De Leeuw, P.; et al. European/International FMD Registry and Initiative (FEIRI), and the Working Group ‘Hypertension and the Kidney’ of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). The European/International Fibromuscular Dysplasia Registry and Initiative (FEIRI)-clinical Phenotypes and Their Predictors Based on a Cohort of 1000 Patients. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedde, M.; Stoenoiu, M.S.; Persu, A.; Pascarella, R. Neurovascular Involvement in Fibromuscular Dysplasia: A Clue for Reappraisal of Old Classifications. Eur. J. Neurol. 2025, 32, e70143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedde, M.; Stoenoiu, M.S.; Persu, A.; Pascarella, R. Fibromuscular dysplasia: Challenges for the current classification. Neurol. Sci. 2025, 46, 6149–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedde, M.; Stoenoiu, M.S.; Persu, A.; Pascarella, R. Carotid Web: An Update Focusing on Its Relationship with Fibromuscular Dysplasia and Therapeutic Strategy. J. Stroke 2025, 27, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedde, M.; Stoenoiu, M.S.; Persu, A.; Pascarella, R. Fibromuscular dysplasia: A single name for several imaging patterns. Neurol. Sci. 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.C.; Gewertz, B.L.; Bove, E.L.; Sottiurai, V.; Fry, W.J. Arterial fibrodysplasia. Histopathologic character and current etiologic concepts. Arch. Surg. 1975, 110, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, A.G.; Anderson, R.E. Angiographic spectrum of cervical and intracranial fibromuscular dysplasia. Stroke 1977, 8, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettinger, K.L.; Soderstrom, C.E. Pathogenetic profile of TIA before 55. A three-year investigation. J. Neurol. Sci. 1978, 36, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloft, H.J.; Kallmes, D.F.; Kallmes, M.H.; Goldstein, J.H.; Jensen, M.E.; Dion, J.E. Prevalence of cerebral aneurysms in patients with fibromuscular dysplasia: A reassessment. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 88, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.C., Jr.; Lechter, A.; DeBakey, M.E. Surgical treatment of fibromuscular disease of the carotid arteries. Arch. Surg. 1968, 96, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manelfe, C.; Clarisse, J.; Fredy, D.; Andre, J.M.; Crouzet, G. Fibromuscular dysplasia of the cervico-cephalic arteries. J. Neuroradiol. 1974, 1, 149–231. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, J.C.; Fry, W.J.; Seeger, J.F.; Hoffman, G.L.; Gabrielsen, T.O. Extracranial internal carotid and vertebral artery fibrodysplasia. Arch. Surg. 1974, 109, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesen, C.A.; Elliott, B.M. Fibromuscular dysplasia of the carotid arteries. Am. J. Surg. 1986, 151, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, P.; Albat, B.; Thevenet, A. Fibromuscular dysplasia of the internal carotid artery: Long-term surgical results. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1993, 34, 465–472. [Google Scholar]
- Śliwczyński, A.; Jewczak, M.; Dorobek, M.; Furlepa, K.; Gołębiak, I.; Skibińska, E.; Sarzyńska-Długosz, I. An Analysis of the Incidence and Cost of Intracranial Aneurysm and Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Treatment between 2013 and 2021. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laukka, D.; Kivelev, J.; Rahi, M.; Vahlberg, T.; Paturi, J.; Rinne, J.; Hirvonen, J. Detection Rates and Trends of Asymptomatic Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms from 2005 to 2019. Neurosurgery 2024, 94, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian-Dodov, D.; Gornik, H.L.; Gu, X.; Froehlich, J.; Bacharach, J.M.; Chi, Y.W.; Gray, B.H.; Jaff, M.R.; Kim, E.S.; Mace, P.; et al. Dissection and Aneurysm in Patients with Fibromuscular Dysplasia: Findings from the U.S. Registry for FMD. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, J.W.; Sealove, B.A. Diagnosis, management, and future developments of fibromuscular dysplasia. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 53, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkel, G.J.; Djibuti, M.; Algra, A.; van Gijn, J. Prevalence and risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: A systematic review. Stroke 1998, 29, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plouin, P.F.; Baguet, J.P.; Thony, F.; Ormezzano, O.; Azarine, A.; Silhol, F.; Oppenheim, C.; Bouhanick, B.; Boyer, L.; Persu, A.; et al. High Prevalence of Multiple Arterial Bed Lesions in Patients with Fibromuscular Dysplasia: The ARCADIA Registry (Assessment of Renal and Cervical Artery Dysplasia). Hypertension 2017, 70, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warchol-Celinska, E.; Prejbisz, A.; Dobrowolski, P.; Klisiewicz, A.; Kadziela, J.; Florczak, E.; Michalowska, I.; Jozwik-Plebanek, K.; Kabat, M.; Kwiatek, P.; et al. Systematic and Multidisciplinary Evaluation of Fibromuscular Dysplasia Patients Reveals High Prevalence of Previously Undetected Fibromuscular Dysplasia Lesions and Affects Clinical Decisions: The ARCADIA-POL Study. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claassen, J.; Park, S. Spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet 2022, 400, 846–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatlo, B.; Fung, C.; Stienen, M.N.; Fathi, A.R.; Fandino, J.; Smoll, N.R.; Zumofen, D.; Daniel, R.T.; Burkhardt, J.K.; Bervini, D.; et al. Incidence and Outcome of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: The Swiss Study on Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (Swiss SOS). Stroke 2021, 52, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, A.M.; Reed, S.D.; Curtis, L.H.; Alexander, M.J.; Villani, J.J.; Schulman, K.A. Characteristics of nontraumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage in the United States in 2003. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahood, W.; Rizvi, A.A.; Alexander, A.Y.; Yolcu, Y.U.; Lanzino, G.; Brinjikji, W.; Rabinstein, A.A. Trends in Admissions and Outcomes for Treatment of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in the United States. Neurocrit. Care 2022, 37, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Hoffman, H.; Anikpezie, N.; Philip, K.; Wee, C.; Choudhry, R.; Albright, K.C.; Masoud, H.; Beutler, T.; Schmidt, E.; et al. Trends in the Incidence of Spontaneous Subarachnoid Hemorrhages in the United States, 2007-2017. Neurology 2023, 100, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuurbier, C.C.M.; Molenberg, R.; Mensing, L.A.; Wermer, M.J.; Juvela, S.; Lindgren, A.E.; Jääskeläinen, J.E.; Koivisto, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Uyttenboogaart, M.; et al. Sex Difference and Rupture Rate of Intracranial Aneurysms: An Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2022, 53, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.B.; Vik, A.; Romundstad, P.R.; Sandvei, M.S. Risk Factors for Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in a Prospective Population-Based Study. Stroke 2019, 50, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebers, D.O.; Whisnant, J.P.; Huston, J., 3rd; Meissner, I.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Piepgras, D.G.; Forbes, G.S.; Thielen, K.; Nichols, D.; O’Fallon, W.M.; et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 2003, 362, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UCAS Japan Investigators. The natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in a Japanese cohort. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greving, J.P.; Wermer, M.J.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Morita, A.; Juvela, S.; Yonekura, M.; Ishibashi, T.; Torner, J.C.; Nakayama, T.; Rinkel, G.J.; et al. Development of the PHASES score for prediction of risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: A pooled analysis of six prospective cohort studies. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonobe, M.; Yamazaki, T.; Yonekura, M.; Kikuchi, H. Small unruptured intracranial aneurysm verification study: SUAVe study, Japan. Stroke 2010, 41, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.D.; Huston, J., 3rd; Layton, K.F.; Piepgras, D.G.; Brown, R.D., Jr. Intracranial aneurysm enlargement on serial magnetic resonance angiography: Frequency and risk factors. Stroke 2009, 40, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, S.; Hadeishi, H.; Suzuki, A.; Yasui, N.; Nishimura, H. Incidence and risk factors for the growth of unruptured cerebral aneurysms: Observation using serial computerized tomography angiography. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 101, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lather, H.D.; Gornik, H.L.; Olin, J.W.; Gu, X.; Heidt, S.T.; Kim, E.S.H.; Kadian-Dodov, D.; Sharma, A.; Gray, B.; Jaff, M.R.; et al. Prevalence of Intracranial Aneurysm in Women with Fibromuscular Dysplasia: A Report from the US Registry for Fibromuscular Dysplasia. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkel, G.J.E.; Algra, A. Long-term outcomes of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlak, M.H.M.; Algra, A.; Brandenburg, R.; Rinkel, G.J.E. Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, M.T.; Hurtado, C.; Jiang, B.; Campos, J.K.; Huang, J.; Tamargo, R.J.; Lin, L.M.; Coon, A.L.; Colby, G.P. Safety Assessment of Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms in Patients with Fibromuscular Dysplasia. Interv. Neurol. 2018, 7, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Fujimoto, T.; Pouleur, A.C.; Vancraeynest, D.; Wang, J.; Zen, K.; Stoenoiu, M.S.; Persu, A. Characteristics of Asian patients with Fibromuscular Dysplasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertens. Res. 2025, 48, 2184–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacina, S.; Grassi, M.; Zedde, M.; Zini, A.; Bersano, A.; Gandolfo, C.; Silvestrelli, G.; Baracchini, C.; Cerrato, P.; Lodigiani, C.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients with Cervical Artery Dissection and Fibromuscular Dysplasia. Stroke 2021, 52, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volovici, V.; Verploegh, I.S.; Satoer, D.; Vrancken Peeters, N.J.M.C.; Sadigh, Y.; Vergouwen, M.D.I.; Schouten, J.W.; Bruggeman, G.; Pisica, D.; Yildirim, G.; et al. Outcomes Associated with Intracranial Aneurysm Treatments Reported as Safe, Effective, or Durable: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2331798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zedde, M.; Sette, M.D.; Quatrale, R.; Causin, F.; Pascarella, R. Intracranial vessel wall lesions on MRI: Anatomical and pathological issues. Neurol. Sci. 2025, 46, 4851–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinkel, G.J.E.; Ruigrok, Y.M.; Krings, T.; Etminan, N.; Vergouwen, M.D.I. Advances in screening and management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Lancet Neurol. 2025, 24, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, M.K.; Ruigrok, Y.M. Genetics of Intracranial Aneurysms. Stroke 2021, 52, 3004–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Category | Clefts et al. [10] | Kadian-Dodov et al. [18] | Warchol-Celinska et al. 2020 [22] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Patients (N) | 498 (Meta-Analysis), 117 (Institutional Series) | 921 | 232 |
| Gender of Patients | 85% Female (Meta-Analysis) | 93.5% Female, 6.5% Male | 17.2% men, 82.8% women |
| Age | Range 4 to 83 years | Mean 52.2 ± 13.4 years | Mean 42.7 ± 15.7 years |
| Patients with Intracranial Aneurysms (N) | 108 (Meta-Analysis); 28 (Institutional Series) | 43 (21.5% of patients with aneurysms) | 29 (12.5%) |
| Gender of Patients with Intracranial Aneurysms | 25 Males, 103 Females (Meta-Analysis) | 39 Females (90.7%), 4 Males (9.3%) | Not specified |
| Age of Patients with Intracranial Aneurysms | Mean age 60 years (Institutional Series) | Not specified | Not specified |
| Location of Aneurysms |
|
| specific locations not detailed |
| Rate of Multiple Aneurysms | 21% (in patients with FMD and aneurysms) | Not specified in the study | Not specified |
| Size of Aneurysms | Not specified in the study | Not specified in the study | Not specified |
| Rate of SAH at Presentation | 22 patients presented with symptoms, including 19 with SAH (Institutional Series) | 8.4% of patients with aneurysms had a history of SAH | 29/730 (4.0) in multifocal FMD group and 1/281 (0.4) in focal FMD group |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zedde, M.; Stoenoiu, M.S.; Persu, A.; Pascarella, R. Fibromuscular Dysplasia and Intracranial Aneurysms: A Narrative Review of a Dangerous and Underestimated Association. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8080. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228080
Zedde M, Stoenoiu MS, Persu A, Pascarella R. Fibromuscular Dysplasia and Intracranial Aneurysms: A Narrative Review of a Dangerous and Underestimated Association. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8080. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228080
Chicago/Turabian StyleZedde, Marialuisa, Maria Simona Stoenoiu, Alexandre Persu, and Rosario Pascarella. 2025. "Fibromuscular Dysplasia and Intracranial Aneurysms: A Narrative Review of a Dangerous and Underestimated Association" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8080. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228080
APA StyleZedde, M., Stoenoiu, M. S., Persu, A., & Pascarella, R. (2025). Fibromuscular Dysplasia and Intracranial Aneurysms: A Narrative Review of a Dangerous and Underestimated Association. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8080. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228080





