Evolving Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bibliographic Strategy
3. Classification
4. Pathophysiology
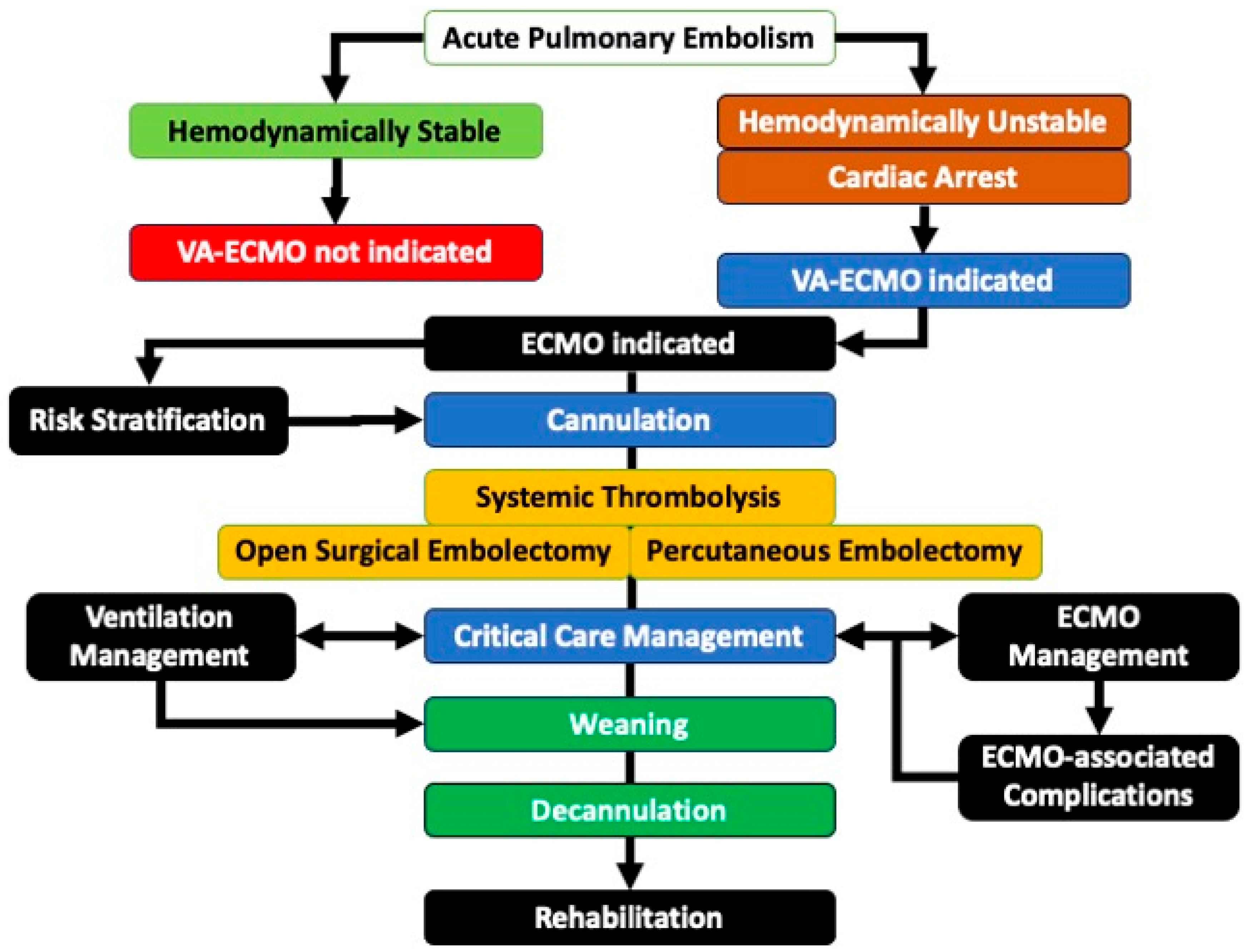
5. Evidence-Based Guidelines and Risk Stratification for ECMO in APE
6. Goals of and Implementation Strategies for ECMO Care in APE
7. Complications of ECMO
8. Management
9. Weaning and Decannulation
10. Outcomes
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APE | acute pulmonary embolism |
| ECMO | extra-corporal membrane oxygenation |
| VA-ECMO | veno-arterial extra-corporal membrane oxygenation |
References
- Wendelboe, A.M.; Raskob, G.E. Global Burden of Thrombosis: Epidemiologic Aspects. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.; Hobohm, L.; Ebner, M.; Kresoja, K.P.; Münzel, T.; Konstantinides, S.V.; Lankeit, M. Trends in thrombolytic treatment and outcomes of acute pulmonary embolism in Germany. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.A.; Molsberry, R.; Cuttica, M.J.; Desai, K.R.; Schimmel, D.R.; Khan, S.S. Time trends in pulmonary embolism mortality rates in the United States, 1999 to 2018. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.-J.; Harjola, V.-P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS) The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar]
- Chopard, R.; Behr, J.; Vidoni, C.; Ecarnot, F.; Meneveau, N. An Update on the Management of Acute High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, R.; McDermott, G.; Diaz, L. Massive Pulmonary Embolism as a Cause of Cardiac Arrest: Navigating Unknowns in Life After Death. Cureus 2020, 12, e8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucher, N.; Rossi, E.; De Rosa, M.; Goldhaber, S.Z. Massive pulmonary embolism. Circulation 2006, 113, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kürkciyan, I.; Meron, G.; Sterz, F.; Janata, K.; Domanovits, H.; Holzer, M.; Berzlanovich, A.; Bankl, H.C.; Laggner, A.N. Pulmonary embolism as a cause of cardiac arrest: Presentation and outcome. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuma, M.; Nakamura, M.; Nakanishi, N.; Miyahara, Y.; Tanabe, N.; Yamada, N.; Kuriyama, T.; Kunieda, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Nakano, T. Inferior vena cava filter is a new additional therapeutic option to reduce mortality from acute pulmonary embolism. Circ. J. 2004, 68, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kasper, W.; Konstantinides, S.; Geibel, A.; Olschewski, M.; Heinrich, F.; Grosser, K.D.; Rauber, K.; Iversen, S.; Redecker, M.; Kienast, J. Management strategies and determinants of outcome in acute major pulmonary embolism: Results of a multicenter registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1997, 30, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, D.; Lobo, J.L.; Otero, R.; Monreal, M.; Yusen, R.D. Prognostic significance of multidetector computed tomography in normotensive patients with pulmonary embolism: Rationale, methodology and reproducibility for the PROTECT study. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2012, 34, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, C.V.; Schreiber, D.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Slattery, D.; Fanikos, J.; O’Neil, B.J.; Thompson, J.R.; Hiestand, B.; Briese, B.A.; Pendleton, R.C.; et al. Clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients diagnosed with acute pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: Initial report of EMPEROR (Multicenter Emergency Medicine Pulmonary Embolism in the Real World Registry). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casazza, F.; Becattini, C.; Bongarzoni, A.; Cuccia, C.; Roncon, L.; Favretto, G.; Zonzin, P.; Pignataro, L.; Agnelli, G. Clinical features and short term outcomes of patients with acute pulmonary embolism. The Italian Pulmonary Embolism Registry (IPER). Thromb. Res. 2012, 130, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Pugliese, S.; Sethi, S.S.; Parikh, S.A.; Goldberg, J.; Alkhafan, F.; Vitarello, C.; Rosenfield, K.; Lookstein, R.; Keeling, B. Contemporary management and outcomes of patients with high-risk pulmonary embolism. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.; Giordano, N.; Zheng, H.; Parry, B.A.; Barnes, G.D.; Heresi, G.A.; Jaber, W.; Wood, T.; Todoran, T.; Courtney, D.M.; et al. EXPRESS: A Multidisciplinary Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (PERT)—Experience from a national multicenter consortium. Pulm. Circ. 2019, 9, 2045894018824563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.E. Major pulmonary embolism: Review of a pathophysiologic approach to the golden hour of hemodynamically significant pulmonary embolism. Chest 2002, 121, 877–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, J.B.; Giri, J.; Kobayashi, T.; Ruel, M.; Mittnacht, A.J.; Rivera-Lebron, B.; DeAnda, A., Jr.; Moriarty, J.M.; MacGillivray, T.E.; American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; et al. Surgical management and mechanical circulatory support in high-risk pulmonary embolisms: Historical context, current status, and future directions: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 147, e628–e647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaff, M.R.; McMurtry, M.S.; Archer, S.L.; Cushman, M.; Goldenberg, N.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Jenkins, J.S.; Kline, J.A.; Michaels, A.D.; Thistlethwaite, P. Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011, 123, 1788–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, X.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, C. Assessment of the Bova score for risk stratification of acute normotensive pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb. Res. 2020, 193, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.; Beule, J.; Balzer, J.; Dippold, W. Modified Bova score for risk stratification and short-term outcome in acute pulmonary embolism. Neth. J. Med. 2015, 73, 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, D.; Lobo, J.L.; Fernandez-Golfin, C.; Portillo, A.K.; Nieto, R.; Lankeit, M.; Konstantinides, S.; Prandoni, P.; Muriel, A.; Yusen, R.D. Effectiveness of prognosticating pulmonary embolism using the ESC algorithm and the Bova score. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanni, S.; Nazerian, P.; Pepe, G.; Baioni, M.; Risso, M.; Grifoni, G.; Viviani, G.; Grifoni, S. Comparison of two prognostic models for acute pulmonary embolism: Clinical vs. right ventricular dysfunction-guided approach. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.J.; Assad, A.P.L.; Alves, J.L., Jr.; Jardim, C.; de Souza, R. Pulmonary embolism and gas exchange. Respiration 2019, 98, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhaber, S.Z.; Visani, L.; De Rosa, M. Acute pulmonary embolism: Clinical outcomes in the International Cooperative Pulmonary Embolism Registry (ICOPER). Lancet 1999, 353, 1386–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, M. Acute pulmonary embolism 1: Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and diagnosis. Heart 2001, 85, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smulders, Y.M. Pathophysiology and treatment of haemodynamic instability in acute pulmonary embolism: The pivotal role of pulmonary vasoconstriction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 48, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Nieto, O.R.; Gómez-Oropeza, I.; Quintero-Leyra, A.; Kammar-García, A.; Zamarrón-López, É.I.; Soto-Estrada, M.; Morgado-Villaseñor, L.A.; Meza-Comparán, H.D. Hemodynamic and respiratory support in pulmonary embolism: A narrative review. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1123793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, N.; Stephens, K.; Ball, E.; Crandall, C.; Ouchi, K.; Unruh, M.; Kamdar, N.; Myaskovsky, L. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Cardiac Arrest: Does Age Matter? Crit. Care Med. 2023, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.S.C.; Tonna, J.E.; Nanjayya, V.; Nixon, P.; Abrams, D.C.; Raman, L.; Bernard, S.; Finney, S.J.; Grunau, B.; Youngquist, S.T. Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation in adults. Interim guideline consensus statement from the extracorporeal life support organization. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearon, C.; Akl, E.A.; Comerota, A.J.; Prandoni, P.; Bounameaux, H.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Nelson, M.E.; Wells, P.S.; Gould, M.K.; Dentali, F.; et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012, 141, e419S–e496S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Torbicki, A.; Agnelli, G.; Danchin, N.; Fitzmaurice, D.; Galiè, N.; Gibbs, J.S.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Kucher, N.; et al. 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 3033–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, J.; Sista, A.K.; Weinberg, I.; Kearon, C.; Kumbhani, D.J.; Desai, N.D.; Piazza, G.; Gladwin, M.T.; Chatterjee, S.; Kobayashi, T. Interventional therapies for acute pulmonary embolism: Current status and principles for the development of novel evidence: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, e774–e801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Quinlan, D.J.; Agnelli, G.; Eikelboom, J.W. Thrombolysis compared with heparin for the initial treatment of pulmonary embolism: A meta-analysis of the randomized controlled trials. Circulation 2004, 110, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.T.; Gould, M.K.; Louie, J.D.; Rosenberg, J.K.; Sze, D.Y.; Hofmann, L.V. Catheter-directed therapy for the treatment of massive pulmonary embolism: Systematic review and meta-analysis of modern techniques. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leacche, M.; Unic, D.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Rawn, J.D.; Aranki, S.F.; Couper, G.S.; Mihaljevic, T.; Rizzo, R.J.; Cohn, L.H.; Aklog, L. Modern surgical treatment of massive pulmonary embolism: Results in 47 consecutive patients after rapid diagnosis and aggressive surgical approach. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2005, 129, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, R.; Shekar, K.; MacLaren, G.; Schmidt, M.; Pellegrino, V.; Meyns, B.; Haft, J.; Vercaemst, L.; Pappalardo, F.; Bermudez, C. ELSO interim guidelines for venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in adult cardiac patients. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-C.; Huang, K.-Y.; Yao, C.-W.; Wu, C.-F.; Liang, S.-J.; Li, C.-H.; Tu, C.-Y.; Chen, H.-J. The modified SAVE score: Predicting survival using urgent veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation within 24 hours of arrival at the emergency department. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, S.; Caliskan, K.; Soliman, O.; Muslem, R.; Guven, G.; van Thiel, R.J.; Struijs, A.; Gommers, D.; Zijlstra, F.; Bakker, J. A novel mortality risk score predicting intensive care mortality in cardiogenic shock patients treated with veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J. Crit. Care 2020, 55, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, R.; Laurencet, M.; Assouline, B.; De Charrière, A.; Banfi, C.; Bendjelid, K. Can VA-ECMO Be Used as an Adequate Treatment in Massive Pulmonary Embolism? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubron, C.; Cheng, A.C.; Pilcher, D.; Leong, T.; Magrin, G.; Cooper, D.J.; Scheinkestel, C.; Pellegrino, V. Factors associated with outcomes of patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support: A 5-year cohort study. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO). ELSO Registry. Available online: https://www.elso.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Kim, D.H.; Cho, W.H.; Son, J.; Lee, S.K.; Yeo, H.J. Catastrophic Mechanical Complications of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Asaio J. 2021, 67, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. ELSO Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Extracorporeal Life Support; ELSO: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2017; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Fior, G.; Colon, Z.F.V.; Peek, G.J.; Fraser, J.F. Mechanical ventilation during ECMO: Lessons from clinical trials and future prospects. Sem. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 43, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aissaoui, N.; Luyt, C.-E.; Leprince, P.; Trouillet, J.-L.; Léger, P.; Pavie, A.; Diebold, B.; Chastre, J.; Combes, A. Predictors of successful extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) weaning after assistance for refractory cardiogenic shock. Intens. Care Med. 2011, 37, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, L.M.; Seoane, L.; Diez, M.; Vila, R.C.B.; Furmento, J.F.; Vrancic, M.; Aissaoui, N. Multiparameters associated to successful weaning from VA ECMO in adult patients with cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Card. Anesth. 2023, 26, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, D.; Slutsky, A.S.; Combes, A. Extracorporeal life support for adults with respiratory failure and related indications: A review. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2019, 322, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Pellegrino, V.; Combes, A.; Scheinkestel, C.; Cooper, D.J.; Hodgson, C. Mechanical ventilation during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappalardo, F.; Pieri, M.; Corada, B.A.; Ajello, S.; Melisurgo, G.; De Bonis, M.; Zangrillo, A. Timing and strategy for weaning from venoarterial ECMO are complex issues. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2015, 29, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aissaoui, N.; Brehm, C.; El-Banayosy, A.; Combes, A. Weaning strategy from veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). In Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation-Advances in Therapy; Firstenberg, M.S., Ed.; InTech Online Publishers: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ortuno, S.; Delmas, C.; Diehl, J.-L.; Bailleul, C.; Lancelot, A.; Naili, M.; Cholley, B.; Pirracchio, R.; Aissaoui, N. Weaning from veno-arterial extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation: Which strategy to use? Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 8, E1–E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aso, S.; Matsui, H.; Fushimi, K.; Yasunaga, H. In-hospital mortality and successful weaning from venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: Analysis of 5,263 patients using a national inpatient database in Japan. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastan, A.J.; Dege, A.; Mohr, M.; Doll, N.; Falk, V.; Walther, T.; Mohr, F.W. Early and late outcomes of 517 consecutive adult patients treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for refractory postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 139, 302–311.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sertic, F.; Chavez, L.; Diagne, D.; Richards, T.; Wald, J.; Acker, M.; Birati, E.; Rame, E.; Bermudez, C. Predictors of in-hospital mortality and midterm outcomes of patients successfully weaned from venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 161, 666–678.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisdas, T.; Beutel, G.; Warnecke, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Kuehn, C.; Haverich, A.; Teebken, O.E. Vascular complications in patients undergoing femoral cannulation for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stulak, J.M.; Dearani, J.A.; Burkhart, H.M.; Barnes, R.D.; Scott, P.D.; Schears, G.J. ECMO cannulation controversies and complications. Semin. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2009, 13, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellenc, Q.; Girault, A.; Roussel, A.; Aguir, S.; Cerceau, P.; Longrois, D.; Mal, H.; Mordant, P.; Castier, Y. Preclosing of the femoral artery allows total percutaneous venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and prevents groin wound infection after lung transplantation. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac Surg. 2020, 58, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmakis, I.T.; Sagoschen, I.; Barco, S.; Keller, K.; Valerio, L.; Wild, J.; Giannakoulas, G.; Piazza, G.; Konstantinides, S.V.; Hobohm, L. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation and Reperfusion Strategies in High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism Hospitalizations. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 52, e512–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Hachamovitch, R.; Kittleson, M.; Patel, J.; Arabia, F.; Moriguchi, J.; Esmailian, F.; Azarbal, B. Complications of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for treatment of cardiogenic shock and cardiac arrest: A meta-analysis of 1,866 adult patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 97, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Holena, D.; McCunn, M.; Kohl, B.; Sarani, B. A review of the fundamental principles and evidence base in the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in critically ill adult patients. J. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 26, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuff, H.; Zochios, V.; Vuylsteke, A. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in acute massive pulmonary embolism: A systematic review. Perfusion 2015, 30, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldetti, L.; Beneduce, A.; Cianfanelli, L.; Falasconi, G.; Pannone, L.; Moroni, F.; Venuti, A.; Sacchi, S.; Gramegna, M.; Pazzanese, V. Use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in high-risk acute pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Artif. Organs 2021, 45, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, T.J.; Choi, J.H.; Maynes, E.J.; Wood, C.T.; D’Antonio, N.D.; Mellado, M.; West, F.M.; Galanis, T.; Gonsalves, C.F.; Marhefka, G.D. Outcomes of extracorporeal life support for the treatment of acute massive pulmonary embolism: A systematic review. Resuscitation 2020, 146, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, M.; Metge, A.; Martelin, A.; Giroudon, C.; Lanier Demma, J.; Koffel, C.; Fornier, W.; Chiari, P.; Fellahi, J.L.; Obadia, J.F. Efficacy and safety of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for high-risk pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vasc. Med. 2020, 25, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood-Scott, J.; Gordon, M.; Vender, R.; Pettigrew, S.; Desai, P.; Marchetti, N.; Mamary, A.J.; Panaro, J.; Cohen, G.; Bashir, R. Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in massive pulmonary embolism-related cardiac arrest: A systematic review. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, M.; Mandigers, L.; Miranda, D.D.R.; Rietdijk, W.J.; Binnekade, J.M.; Knijn, D.C.; Lagrand, W.K.; den Uil, C.A.; Henriques, J.P.; Vlaar, A.P. Survival of patients with acute pulmonary embolism treated with venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Crit. Care 2021, 64, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaso, E.R.; Pan, J.A.; Salerno, M.; Kadl, A.; Aldridge, C.; Haskal, Z.J.; Kennedy, J.L.; Mazimba, S.; Mihalek, A.D.; Teman, N.R. Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for acute massive pulmonary embolism: A meta-analysis and call to action. J. Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 2022, 15, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopard, R.; Nielsen, P.; Ius, F.; Cebotari, S.; Ecarnot, F.; Pilichowski, H.; Schmidt, M.; Kjaergaard, B.; Sousa-Casasnovas, I.; Ghoreishi, M.; et al. Optimal reperfusion strategy in acute high-risk pulmonary embolism requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boey, J.J.E.; Dhundi, U.; Ling, R.R.; Chiew, J.K.; Fong, N.C.; Chen, Y.; Hobohm, L.; Nair, P.; Lorusso, R.; MacLaren, G.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Pulmonary Embolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xiang, M.; Wu, L.; He, M.; Zhu, H. Survival after venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for acute high-risk Pulmonary Embolism: A meta-analysis of comparative studies. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2025, 41, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashtish, N.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Karnib, M.; Zanath, E.; Mitchell, S.; Di Felice, C.; Zacharias, M.; Oliveira, G.H.; Medalion, B.; Lytle, F. Causes and predictors of 30-day readmissions in patients with cardiogenic shock requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support. Intern. J. Artif. Organs 2020, 43, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuqali, A.; Goyal, A.; Acharya, P.; Mastoris, I.; Dalia, T.; Chan, W.-C.; Sauer, A.; Haglund, N.; Vidic, A.; Abicht, T. Thirty-day readmissions among patients with cardiogenic shock who underwent extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support in the United States: Insights from the nationwide readmissions database. Am. Heart J. Plus Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2022, 13, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gigorro, R.; Renes-Carreño, E.; Pérez-Vela, J.; Marin-Mateos, H.; Gutierrez, J.; Corres-Peiretti, M.; Delgado, J.; Pérez-de la Sota, E.; Cortina-Romero, J.; Montejo-González, J. Mechanical support with venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO-VA): Short-term and long-term prognosis after a successful weaning. Med. Intensiv. 2017, 41, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadlbauer, A.; Philipp, A.; Blecha, S.; Lubnow, M.; Lunz, D.; Li, J.; Terrazas, A.; Schmid, C.; Lange, T.J.; Camboni, D. Long-term follow-up and quality of life in patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for pulmonary embolism and cardiogenic shock. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi, F.; Lebreton, G.; Bréchot, N.; Hekimian, G.; Nieszkowska, A.; Trouillet, J.-L.; Luyt, C.-E.; Leprince, P.; Chastre, J.; Combes, A. Life-threatening massive pulmonary embolism rescued by venoarterial-extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Absolute | Relative |
|---|---|
| Patient refusal | Advanced age |
| Advanced stage of cancer | Immunosuppressed patients or on pharmacological immunosuppression |
| Non-survivable intra-cerebral hemorrhage Non-survivable cerebral herniation Intractable intracranial hypertension | Injurious ventilator settings > 7 days |
| Irreversible destruction of the lung parenchyma | Right-heart failure |
| Contraindications to lung transplantation | Hematologic malignancies |
| SAPS II score ≥ 60 points | |
| SOFA score > 12 points | |
| PRESERVE score ≥ 5 points | |
| RESP score ≤ −2 points | |
| PRESET score ≥ 6 points | |
| Active do not attempt resuscitation status |
| Cardiogenic Shock | Cardiac Arrest |
|---|---|
| Aortic valve incompetence | Older than 70 years old |
| End-stage heart failure | Unwitnessed arrest |
| Severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) | An interval from cardiopulmonary arrest to first CPR of greater than 5 min |
| End-stage liver failure | Observed initial rhythm does not conform to Ventricular Fibrillation (VF), paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia, or pulseless electrical activity (PEA) |
| End-stage renal failure (ESRD) | Presence of recurrent VF |
| Terminal or irreversible illness | Intermittent return of spontaneous circulation |
| Modified SAVE Score | Predicted Mortality | SOFARV Score | Predicted Mortality |
|---|---|---|---|
| >5 | 25% | 0–1 | 0% |
| 1 to 5 | 43% | 2–3 | 6% |
| −4 to 0 | 58% | 4–5 | 20% |
| −9 to −5 | 70% | 6–7 | 22% |
| ≤−10 | 72% | 8–9 | 33% |
| Patient | ||
|---|---|---|
| System | Mechanisms | Complication |
| Inflammatory |
Activated coagulation cascade, Activated complement systems, Activated endothelial cells, activated leukocytes, Activated platelets |
Microcirculatory thrombosis Microcirculatory dysfunction Aseptic parenchymal inflammation |
| Coagulation | Thrombocytopenia, Platelet dysfunction, Acquired von Willebrand syndrome, Hemolysis, Enhanced fibrinolysis | Bleeding Thrombosis End-organ malperfusion |
| Gastrointestinal Tract | Dysfunctional gastrointestinal barrier | Bacterial translocation and endotoxin release |
| Renal | Hypotension, Hypoxia, Ischemia–reperfusion injury, Parenchymal ischemia | Acute kidney injury Dialysis |
| Pulmonary |
LV overload, Systemic inflammatory response, Hemodynamic changes parenchymal ischemia, lung congestion due to altered ventricular filling, ischemia–reperfusion injury | Pulmonary injury, pulmonary congestion |
| Limb | Mechanical obstruction, In situ thrombosis, Distal embolism | Acute arterial ischemia Acute Compartment syndrome Acute DVT Phlegmasia Thrombo-embolism |
| Neurologic | Hypotension, Hypoxia, Bleeding, Thrombosis, Parenchymal ischemia, Ischemia–reperfusion injury | Intracranial hemorrhage Acute ischemic stroke New-onset seizure activity Cerebral edema Intracranial hypertension Hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy |
| Device related | ||
| Circuit: | Incorrect connections; clamped tubing | Poor Flow Blood Loss Air embolism Hypoxia |
| Oxygenator | Perforations or leaks, Blood cell trauma | Air embolism Hemolysis |
| Sweep Gas Flow | Flow too high or too low | Abnormal gas exchange |
| Pump | Leak, Malfunction | Hemorrhage Thrombosis Poor Flow Hypoxia |
| Cannulation related | Vessel injury, Vessel obstruction | Thrombus Ischemia Macro- and micro-embolism |
| Cannulas | Misplacement, Size mismatch, Displacement | Reduced Flow Thrombus Bleeding |
| Heat Exchanger | Heating/cooling malfunction | Hypothermia/hyperthermia |
| Monitoring Devices | Malfunction | Poor Flow Hypoxia |
| Hemodynamic Stability | Present |
|---|---|
| Vasoactive, inotropic support | Minimal |
| Pulse pressure | >10 mm Hg |
| Mean arterial pressure | >65 mm Hg |
| Echocardiographic imaging | Satisfactory RV and LV function |
| PaO2 with an FiO2 of 21% | >60 mmHg |
| ECMO flow | 3–4 L per min |
| Sweep gas flow | 1 L per min |
| Acute respiratory distress syndrome | No clinical or radiological signs |
| Parameters are Associated with Successful Weaning | |
| Aortic velocity time interval (VTI) | ≥10 cm |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction | >25% |
| Lateral mitral annulus peak systolic velocity | >6 cm/s |
| Parameters are associated with failure of weaning | |
| Pre-existing ischemic heart disease | Present |
| Pre-wean test left ventricular ejection fraction | ≤25% |
| Post-wean test left ventricular ejection fraction | ≤40% |
| Post-wean test systolic blood pressure | ≤120 mmHg |
| Duration of ECMO support | >7 days |
| Author | Year | Reference | Study Type | Number of Studies | Number of Patients | ECMO | No ECMO | Mean ECMO Duration (Days) | Complication | Successful Wean | ECMO Survival | No ECMO Survival |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yusuff | 2015 | [62] | SR | 19 | 69 | 69 | none | 5 | 23% | NR | 70% | none |
| Baldetti | 2020 | [63] | SR/MA | 21 | 416 | 416 | none | 2 | 25% | 69% | 59% | none |
| O’Malley | 2020 | [64] | SR | 50 | 99 | 99 | none | 3 | 23% | NR | 88% | none |
| Pozzi | 2020 | [65] | SR/MA | 16 | 533 | 533 | none | 3 | 19% | 68% | 50% | none |
| Harwood Scott | 2021 | [66] | SR | 77 | 301 | 301 | none | NR | 7% | 85% | 61% | none |
| Karami | 2021 | [67] | MA | 20 | 1947 | 1138 | 809 | NR | NR | NR | 57% | 65% |
| Kaso | 2022 | [68] | MA | 11 | 791 | 270 | 521 | 4 | NR | NR | 54% | 60% |
| Chopard | 2022 | [69] | SR/MA | 17 | 327 | 106 | 221 | NR | 22% | NR | 77% | 57% |
| Boey | 2023 | [70] | SR/MA | 39 | 1,177,998 | 6409 | 1,171,589 | 4 | 51% | NR | 45% | 81% |
| Yang | 2025 | [71] | MA | 10 | 2846 | 1181 | 1685 | NR | NR | NR | 67% | 65% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hart, J.P.; Davies, M.G. Evolving Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation—A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228004
Hart JP, Davies MG. Evolving Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation—A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228004
Chicago/Turabian StyleHart, Joseph P., and Mark G. Davies. 2025. "Evolving Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation—A Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228004
APA StyleHart, J. P., & Davies, M. G. (2025). Evolving Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation—A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228004







