Surgical Outcomes and Complications of Distal Nasal Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Data Collection Process
2.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
2.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Results
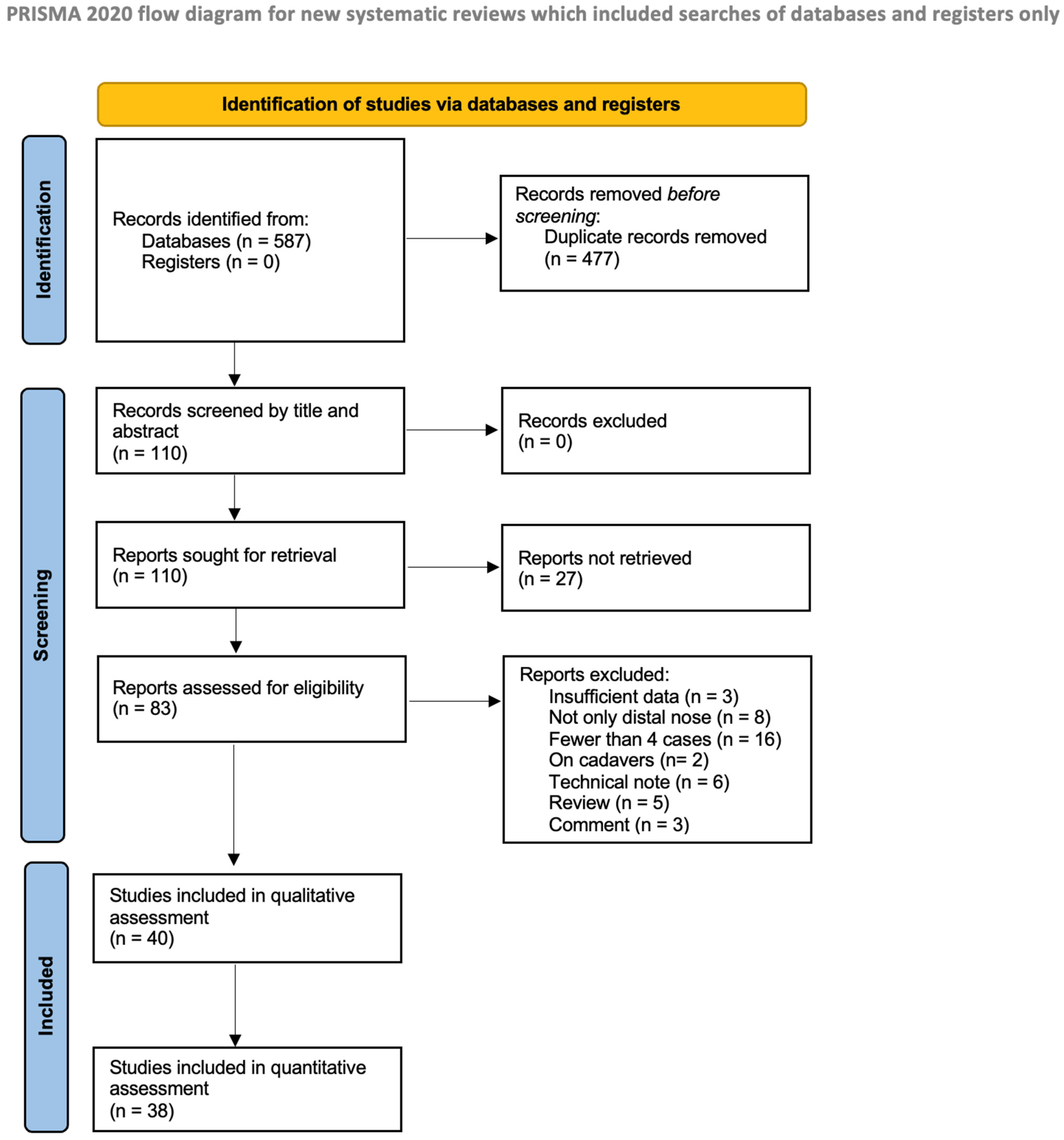
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
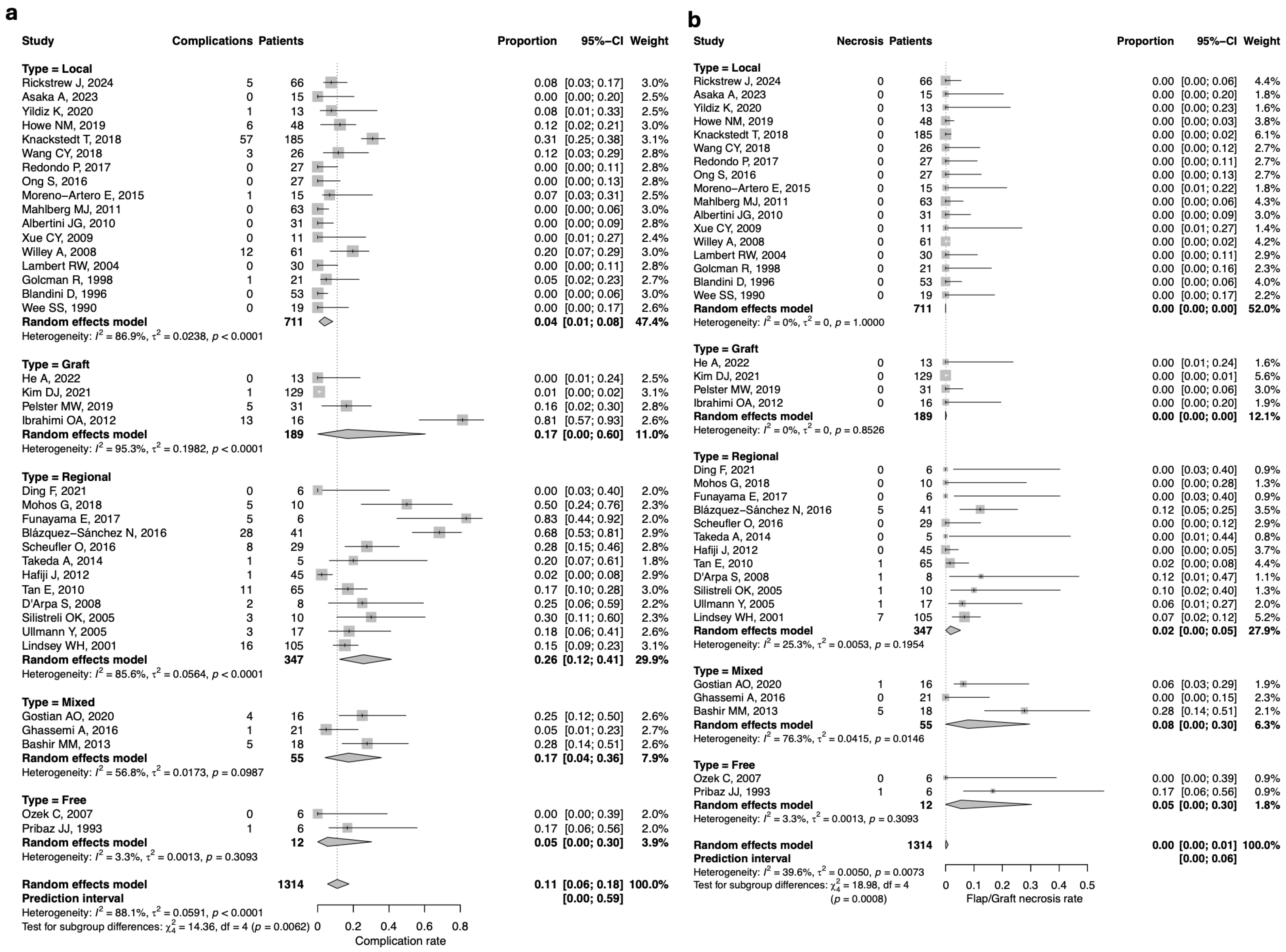
3.3. Study Results
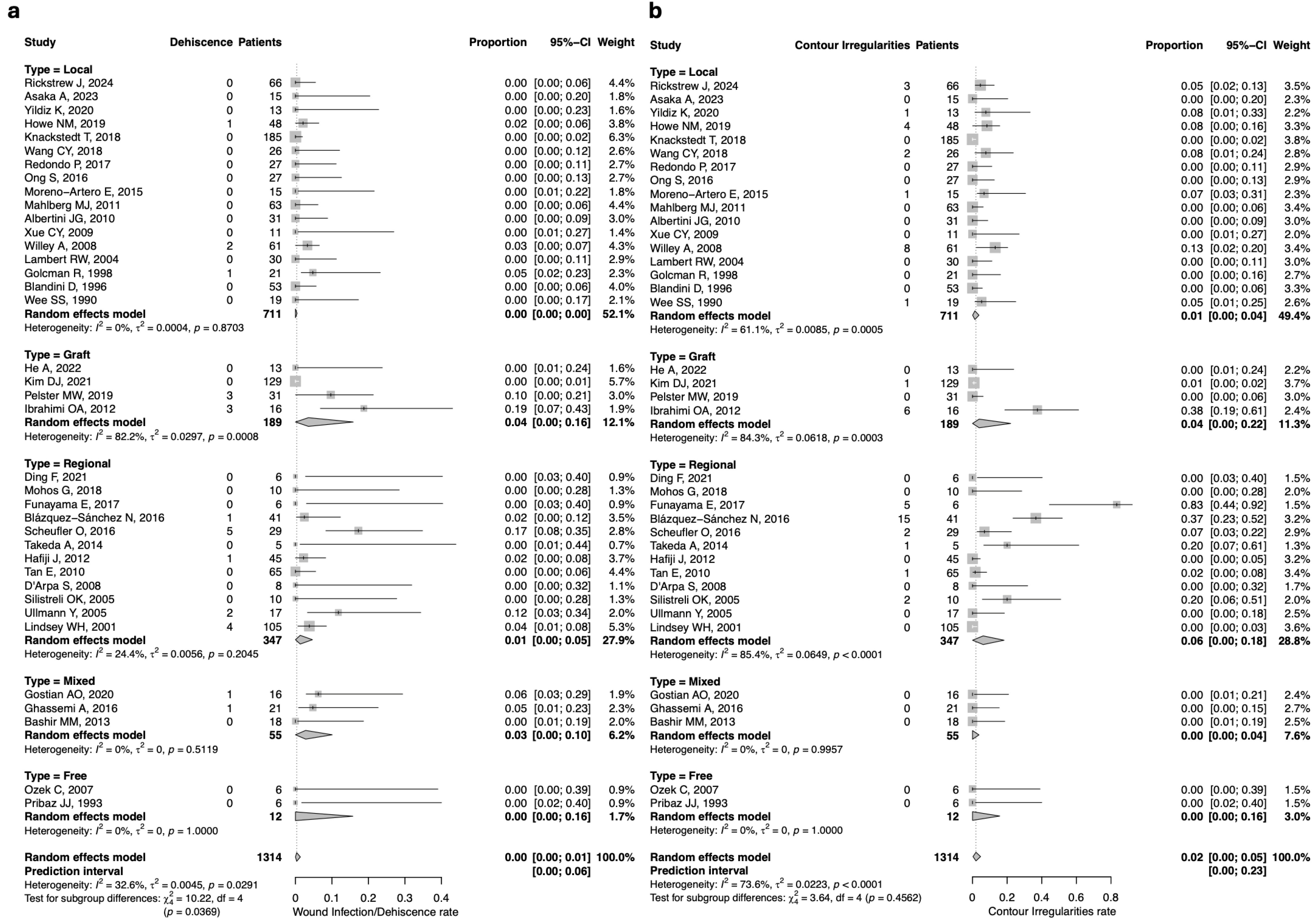
3.4. Complication Rate
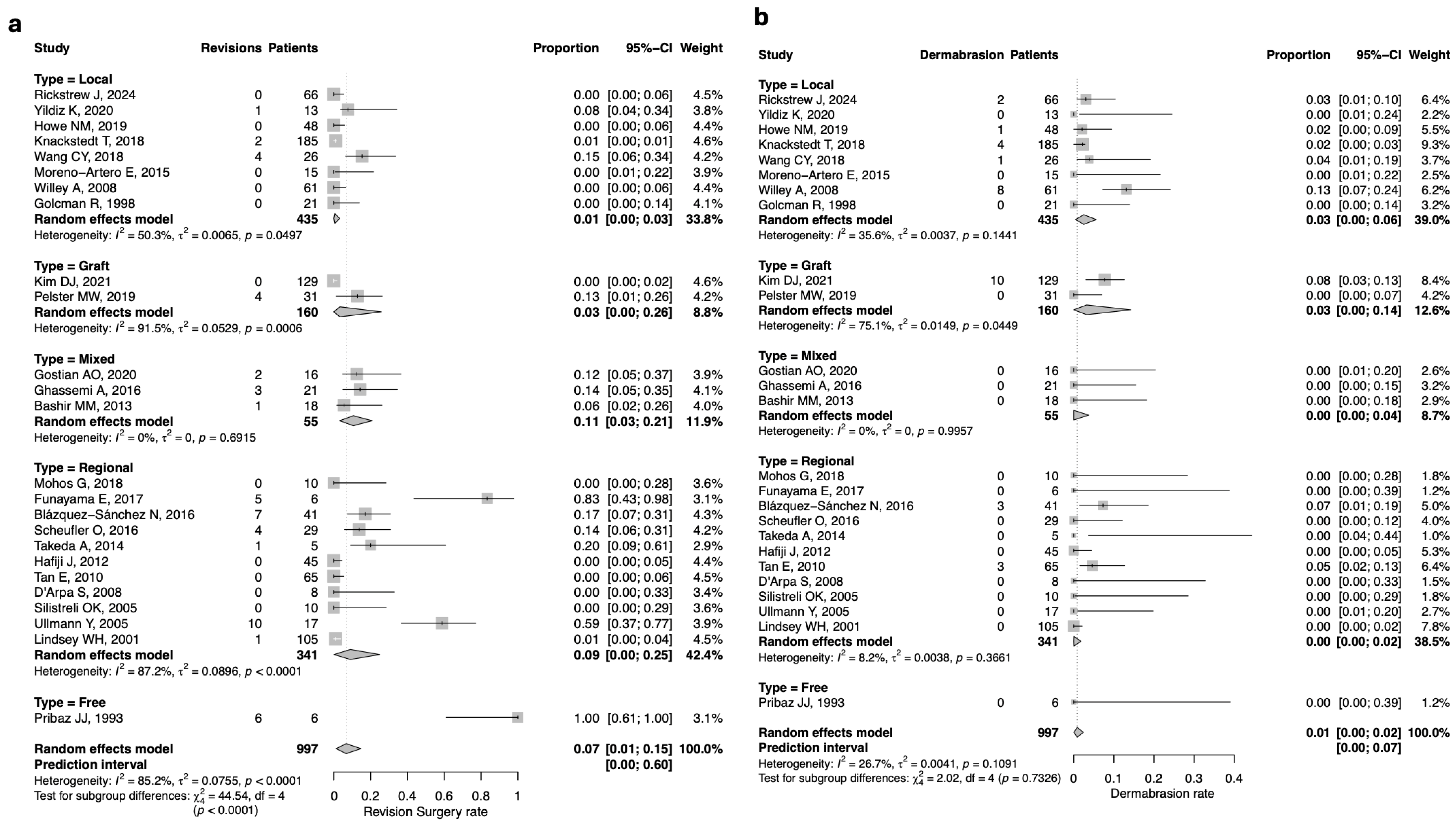
3.5. Revision Surgery
3.6. Aesthetic Outcomes
3.7. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burget, G.C.; Menick, F.J. Nasal support and lining: The marriage of beauty and blood supply. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1989, 84, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burget, G.C.; Menick, F.J. The subunit principle in nasal reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1985, 76, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burget, G.C.; Menick, F.J. Nasal reconstruction: Seeking a fourth dimension. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1986, 78, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, P.; Ballantyne, D.L., Jr. Skin Grafts. In Plastic Surgery; McCarthy, J.G., Ed.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990; Volume 1, pp. 221–274. [Google Scholar]
- Redondo, P.; Bernad, I.; Moreno, E.; Ivars, M. Elongated Dorsal Nasal Flap to Reconstruct Large Defects of the Nose. Dermatol. Surg. 2017, 43, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, T.; Kadakia, S.; Saman, M.; Habal, M.B.; Kohlert, S.; Sokoya, M.; Ducic, Y.; Wood-Smith, D. The Paramedian forehead flap for nasal reconstruction: From antiquity to present. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 30, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.; Ratner, D. Composite and free cartilage grafting. Dermatol. Clin. 2005, 23, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilinsky, I.; Farber, N.; Haik, J.; Weissman, O.; Friedman, T.; Winkler, E. The hatchet and bilobed flaps revisited: Shedding new light on traditional concepts. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2012, 11, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, Y.; Ishida, S.; Mineda, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Nagasaka, S.; Yamasaki, H.; Hashimoto, I. Lateral Nasal Artery Perforator Flap for Nasal Reconstruction: Clinical Applications and Risk Factors Associated with Nasal Deformities. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 88, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, T.E.; Dzubow, L.M. Conchal bowl skin grafting in nasal tip reconstruction: Clinical and histologic evaluation. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1995, 33, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, J.O. Modifying the Burow’s triangles of traditional transposition flaps for the repair of adjacent nasal defects. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 63, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cason, R.W.; Shammas, R.L.; Pyfer, B.J.; Glener, A.D.; Marcus, J.R.; Cook, J.L. Cutaneous Reconstruction of the Nasal Distal Third: Alternative Local Flaps for a Complex Region. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2021, 9, e3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerci, F.B.; Dellatorre, G. Paramedian forehead flap combined with hinge flap for nasal tip reconstruction. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2016, 91 (Suppl. S1), 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eley, K.A.; Pleat, J.M.; Wall, S.A. Reconstruction of a congenital nasal deformity using skin tags as a chondrocutaneous composite graft. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2009, 20, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, M. The radial forearm flap as a pedicled flap for resurfacing a scarred nose. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1994, 32, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Yoshimatsu, H.; Tashiro, K.; Hara, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Narushima, M.; Koshima, I. Reconstruction of a full-thickness, complex nasal defect that includes the nasal septum using a free, thin superficial inferior epigastric artery flap. Microsurgery 2016, 36, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, B.J.; Tolkachjov, S.N. “West by East-West”: Combination repair of wide or multiple distal nasal defects. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 1270–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliano, J.; Abelenda, M.P.; Navarrete, J.; Bazzano, C. East-West Flap After Mohs Micrographic Surgery. Colgajo este-oeste después de la cirugía micrográfica de Mohs. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 110, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.; Martins, S.; Cebotari, M.; Coelho, L. Paramedian Frontal Flap Reconstruction for Nasal Defect Following an Accidental Amputation. Cureus 2024, 16, e61167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poerink, J.G.; Kon, M.; van Minnen, L.P. Brachydactyly, anonychia and a deformed nasal tip in a 16-year-old girl: A case report. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2011, 64, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, K.; Rudolph, C.; Cotofana, S.; Goebeler, M.; Weyandt, G. Large Nasal Defects with Exposed Cartilage: The Folded Transposition Flap as an Innovative Alternative to the Paramedian Forehead Flap. Dermatology 2018, 234, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schopper, C.; Maria Valesky, E.; Kaufmann, R.; Meissner, M. Single-Pedicled Myocutaneous Flap of the Nose: A Case Study with Scar Quality Assessment. Open Dermatol. J. 2014, 8, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarzani, R.; Negosanti, L.; Marchetti, C.; Cipriani, R. Microvascular reconstruction of the columella using a small radial forearm free flap: A case report. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2009, 32, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swick, M.; Behshad, R.; Demer, A.M.; Maher, I.A. Repair of a Large Distal Nose Defect. Dermatol. Surg. 2022, 48, 679–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaena, M.L.H.T.; Alessio, C.G.; Sicalo, K.; de Olveira Brito Queiroz, F.; de Souza Albuquerque, R.R.; da Silva, D.R.L. A New Two-Staged Method for Total Columellar Reconstruction. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, R.L.; Seelaus, R.; Robinson, B.R. Subtotal Nasal Reconstruction Using a Custom 3-Dimensional Porous Polyethylene Construct. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahern, R.W.; Lawrence, N. The Peng flap: Reviewed and refined. Dermatol. Surg. 2008, 34, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, R.E.; Meleca, J.; Vidimos, A.; Fritz, M.A. Free vascularized fascia lata flap for total columella reconstruction. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 43, 103226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justiniano, H.; Edwards, J.; Eisen, D.B. Paramedian forehead flap thinning using a flexible razor blade. Dermatol. Online J. 2009, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaria, A.M. Birhombic flap, a modified bilobed flap, for repair of nasal defect. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, e357–e362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.R.; Griner, N.; Cook, T.A. The precise midline forehead flap as a musculocutaneous flap. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1988, 114, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaria, A.M. The medial based bi- or trilobed flap for repair of distal alar defects. Dermatology 2013, 227, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, G.D. Reconstruction of the nasal infratip, columella, and soft triangle. Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40 (Suppl. S9), S53–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidian Jahromi, A.; Horen, S.R.; Konofaos, P. Implications of Free Temporoparietal Fascial Flap Reconstruction in the Pediatric Population. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2021, 32, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quatela, V.C.; Leake, D.S.; Sabini, P. Surgical management of concavities of the distal nose. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. 2004, 12, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinciullo, C. Reconstructing the nasal dorsum. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171 (Suppl. S2), 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavod, M.B.; Zavod, M.B.; Goldman, G.D. The dorsal nasal flap. Dermatol. Clin. 2005, 23, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, W.; Salmon, P.; Hafiji, J. Reply to: “The bilobed flap versus the AIRNS flap for repair of distal nose defects”. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, E.B.; Zitelli, J.A. The bilobed flap versus the AIRNS flap for repair of distal nose defects. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 684–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, C.; Kent, R.A.; Finzi, E. Laterally Based Island Pedicle Flap Reconstruction of Distal Nasal Defects. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiröz, A.; Yildiz, T.F.; Öner, M.B.; Ercan, A.; Karatan, B.; Kömürcü, H. Use of Dorsal Nasal Flap in Combination with Nasolabial Perforator Propeller Flap for Reconstruction of Nasal Skin Defects of Medium to Large Size; A Simpler Alternative to Frontal Flap. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2021, 32, 2292–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friduss, M.; Dagum, P.; Mandych, A.; Reppucci, A. Forehead flap in nasal reconstruction. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly-Sell, M.; Hollmig, S.T.; Cook, J. The superiorly based bilobed flap for nasal reconstruction. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selçuk, C.T.; Durgun, M.; Özalp, B.; Bozkurt, M. Cartilage-supported paramedian forehead flaps for reconstruction of full-thickness nasal defects. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2013, 24, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, Y.C.; Chang, C.S.; Zelken, J. Aesthetic Refinements in Forehead Flap Reconstruction of the Asian Nose. Plast. Surg. 2017, 25, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribuffo, D.; Serratore, F.; Cigna, E.; Sorvillo, V.; Guerra, M.; Bucher, S.; Scuderi, N. Nasal reconstruction with the two stages vs three stages forehead flap. A three centres experience over ten years. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, C.I.; Chang, C.S.; Chen, H.C.; Yang, S.Y.; Chang, S.Y.; Hsiao, Y.C. A Novel T-Shaped Design of the Forehead Flap in Columella Reconstruction: T-Shaped Design of the Forehead Flap. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2025, 94, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, H.; You, J.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, R.; Tian, L.; Fan, F. A Decade’s Experience: A Sound Framework as the Foundation to Nasal Reconstruction. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2018, 29, 2032–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daurade, M.; Sigaux, N.; Gleizal, A.; Breton, P.; Chauvel-Picard, J.; Pierrefeu, A. Posterior auricular artery helix root free flap-part I: Radio-anatomical study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 51, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Kim, D.W. Modification of the Zitelli bilobed flap: A comparison of flap dynamics in human cadavers. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2006, 8, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Fan, F.; Wang, H.; You, J. Nasal Reconstruction and Repair of Secondary Nasal Deformities Following Treatment of Nasal Hemangiomas. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2017, 28, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantine, F.C.; Lee, M.R.; Sinno, S.; Thornton, J.F. Reconstruction of the nasal soft triangle subunit. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 131, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goleman, R.; Speranzim, M.B.; Goleman, B. The Bilobed Island Flap in Nasal Ala Reconstruction. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1998, 51, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandini, D.; Tremolada, C.; Beretta, M.; Mascetti, M. Use of a versatile axial dorsonasal musculocutaneous flap in repair of the nasal lobule. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1996, 98, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pribaz, J.J.; Falco, N. Nasal reconstruction with auricular microvascular transplant. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1993, 31, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, S.S.; Hruza, G.J.; Mustoe, T.A. Refinements of nasalis myocutaneous flap. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1990, 25, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickstrew, J.; Neill, B.C.; Downing, M.; Cappel, J.A.; Tolkachjov, S.N. Nasal tip rotation flap for reconstruction of surgical defects on the distal nose. Int. J. Dermatol. 2024, 63, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaka, A.; Kyutoku, S.; Nuri, T.; Sakuraba, M.; Ueda, K. Modified trilobed transposition flap for a distal nasal defect. J. Dermatol. 2023, 50, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Yu, J.; Liu, N.; Ye, X. Reconstruction of Distal Nasal Defects with a Large Postauricular Skin-Fat-Fascia Composite Graft. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 88, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Huang, C.; Sun, D.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, J.; Jin, R.; Luo, X. Combination of Extended Paramedian Forehead Flap and Laser Hair Removal in the Reconstruction of Distal Nasal Defect. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2021, 86 (Suppl. S2), S293–S298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Makdisi, J.; Regan, C.; Chen, P.C.; Chao, E.; Rotunda, A.M. Reconstruction of Distal Nasal Defects Using Free Cartilage Batten Grafting with Secondary Intention Healing: A Retrospective Case Series of 129 Patients. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gostian, A.-O.; Balk, M.; Stegmann, A.; Iro, H.; Wurm, J. Full-thickness skin grafts and quilting sutures for the reconstruction of internal nasal lining. Facial Plast. Surg. 2020, 36, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, K.; Gorgulu, T.; Yesiloglu, N.; Kelahmetoglu, O.; Camli, M.F.; Canter, H.I. Hybrid reconstruction of distal nasal defects. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelster, M.W.; Gibbons, M.S.; Patel, P.M.; Behshad, R.; Semchyshyn, N.; Maher, I.A. Aesthetic outcomes of nasal Burow’s grafts with interdomal sutures after Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, N.M.; Chen, D.L.; Holmes, T.E. Crescentic modification to island pedicle rotation flaps for defects of the distal nose. Dermatol. Surg. 2019, 45, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knackstedt, T.; Knackstedt, R.W.; Couto, R.; Gastman, B. Malignant Melanoma: Diagnostic and Management Update. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 202e–216e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohos, G.; Kocsis, Á.; Erős, G.; Korponyai, C.; Varga, Á.; Bende, B.; Varga, J. Reconstruction of Alar-Perialar Defects with a Combined Subcutaneous and Cutaneous Pedicled Rotation-Advancement Nasolabial Flap. J. Investig. Surg. 2019, 33, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Armbrecht, E.S.; Burkemper, N.M.; Glaser, D.A.; Maher, I.A. Bending the arc of the trilobed flap through external interlobe angle inequality. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 44, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funayama, E.; Yamamoto, Y.; Furukawa, H.; Murao, N.; Shichinohe, R.; Yamao, T.; Hayashi, T.; Oyama, A. Full-thickness entire nasal alar reconstruction using a forehead flap in Asians: No cartilaginous infrastructural lining is necessary. Journal of Craniofacial Surg. 2017, 28, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez-Sánchez, N.; Fernández-Canedo, I.; Repiso-Jiménez, J.B.; Rivas-Ruiz, F.; de Troya-Martín, M. Usefulness of the paramedian forehead flap in nasal reconstructive surgery: A retrospective series of 41 patients. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas (Engl. Ed.) 2016, 107, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, A.; Ahmed, S.S.; Ghanepur, H.; Modabber, A. Three-layer reconstruction of lower third nasal defects using forehead flap, reversed nasolabial flap, and auricular cartilage. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.; Mortimer, N.J.; Salmon, P.J. Utility of the quadrilobe flap for repairing defects of the nasal tip. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2016, 57, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheufler Oliver, M.D. Variations in Frontonasal Flap Design for Single-Stage Reconstruction of the Nasal Tip. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 1032e–1042e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Artero, E.; Redondo, P. Colgajo en espiral logarítmica para defectos circulares u ovalados en superficie lateral y ala nasal. Una serie de 15 casos. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015, 106, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, A.; Akimoto, M.; Park, K.; Kounoike, N.; Shimakura, Y.; Nemoto, M.; Uchinuma, E. Single-Stage Reconstruction of a Full-Thickness Alar Defect Using a Folded Nasolabial Flap Combined with a Redundant Skin Turnover Flap. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 25, 2144–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.M.; Khan, B.A.; Abbas, M.; Khan, F.A. Outcome of Modified Turn-In Flaps for the Lining with Primary Cartilage Support in Nasal Reconstruction. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2013, 24, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiji, J.; Salmon, P.; Hussain, W. The AIRNS Flap: An Alternative to the Bilobed Flap for the Repair of Defects of the Distal Nose. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahimi, O.A.; Campbell, T.; Youker, S.; Eisen, D.B. Nonanatomic free cartilage batten grafting with second intention healing for defects on the distal nose. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2012, 11, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Mahlberg, M.J.; Leach, B.C.; Cook, J. The Spiral Flap for Nasal Alar Reconstruction: Our Experience with 63 Patients. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, J.G.; Hansen, J.P. Trilobed Flap Reconstruction for Distal Nasal Skin Defects. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Mortimer, N.J.; Hussain, W.; Salmon, P.J. The Nasal Sidewall Rotation Flap: A Workhorse Flap for Small Defects of the Distal Nose. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36, 1563–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.Y.; Li, L.; Guo, L.L.; Li, J.H.; Xing, X. The bilobed flap for reconstruction of distal nasal defect in Asians. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2009, 33, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arpa, S.; Cordova, A.; Pirrello, R.; Moschella, F. Free style facial artery perforator flap for one stage reconstruction of the nasal ala. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2009, 62, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willey, A.; Papadopoulos, D.J.; Swanson, N.A.; Lee, K.K. Modified single-sling myocutaneous island pedicle flap: Series of 61 reconstructions. Dermatol. Surg. 2008, 34, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozek, C.; Gurler, T.; Uckan, A.; Bilkay, U. Reconstruction of the distal third of the nose with composite ear-helix free flap. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2007, 58, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silistreli, O.K.; Demirdöver, C.; Ayhan, M.; Oztan, Y.; Görgü, M.; Ulusal, B.G. Prefabricated nasolabial flap for reconstruction of full-thickness distal nasal defects. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, Y.; Fodor, L.; Shoshani, O.; Rissin, Y.; Eldor, L.; Egozi, D.; Ramon, Y. A novel approach to the use of the paramedian forehead flap for nasal reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 115, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.W.; Dzubow, L.M. A dorsal nasal advancement flap for off-midline defects. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 50, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, W.H. Reliability of the melolabial flap for alar reconstruction. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2001, 3, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.G.; Baskin, J.Z. Improving outcomes of locoregional flaps: An emphasis on anatomy and basic science. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006, 14, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Pribaz, J.R.; Pribaz, J.J. Nasal reconstruction with local flaps: A simple algorithm for management of small defects. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 130e–139e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | Design | Country | Department | Surgeon | Years | No Patients (Male) | Mean Age (Range) | Aetiology | Type of Cutaneous Reconstruction | Defect Location | Defect Depth | Mean Defect Size (Range) | Operation Stages | Mean Follow Up Time (Range) | Recurrence Rate | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rickstrew J, 2024 [58] | RSP | Texas, USA | Dermatology | Two | 2018–2022 | 66 (46) | 68.2 | 53: BCC; 11: SCC; 1: melanoma in situ; 1: desmoplastic trichoepithelioma | Nasal tip rotation flap | 29: tip: 29: ala; 5: soft triangle; 3: tip | N/A | 1.2 cm (0.7–1.9) | 1 | N/A | N/A | Complications and revisions needed |
| Asaka A, 2023 [59] | RSP | Japan | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 2013–2019 | 15 (6) | 68.9 (51–86) | 10: BCC; 2: keratocanthosis; 1: nevus cell; 1: trichoblastoma; 1: angioleiomyoma | Modified trilobed flap | 12: tip; 2: tip and left triangle; 1: tip and columella | N/A | 1.5 × 1.4 cm (1.1 × 1.1–2 × 2) | 1 | 15.6 mo | 0 | Complications, patients’ satisfaction, tip’s symmetry |
| He A, 2022 [60] | RSP | China | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 2017–2019 | 13 (9) | 50 (37–68) | Trauma or tumour | Postauricular skin-fat-fascia composite graft | N/A | Partial thickness | 2.45 cm (2–2.9) | 1 | (3–14) mo | N/A | Complications and aesthetic results |
| Ding F, 2021 [61] | RSP | China | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 2016–2018 | 6 (0) | (4–24) | Benign skin tumours | Extended forehead flap | 2: tip; 1: columella; 1: ala; 2: multiunit | N/A | 1.5 × 2–11 × 10 cm (with the right palpebral and the cheek involved) | 2 (3 weeks) | 9–17 mo | N/A | Surgical and laser complications |
| Kim DJ, 2021 [62] | RSP | California, USA | Dermatology | Single and senior | 2011–2018 | 129 | 70 * (33–97) | N/A | Free cartilage batten grafting (FCBG) flap | Ala | 112: superficial; 14: extended to cartilage; 2: full thickness | 0.8 cm2 * (0.15–11.1) | 1 | 9 w | 0 | Complications, alar rim retraction, healed skin surface contour and aesthetic results |
| Gostian AO, 2020 [63] | RSP | Germany | Otolaryngology | N/A | 2016–2018 | 16 (9) | 68 (40–91) | 9: BCC; 6: SCC; 1: trauma | Skin graft + extended forehead flap | Ala (14: multiunit) | Full thickness | N/A | 3 (2nd: 5.4 w; 3rd: 10.5 w) | 18.4 mo (3–35) | N/A | Complications |
| Yildiz K, 2020 [64] | N/A | Turkey | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N//A | 2011–2016 | 13 (8) | 61 (42–85) | 11: BCC; 2: infection | Lateral nasal artery perforator flap | Ala (6: multiunit) | Full thickness | 2.8 cm2 (1.8–3.4) | 1 | 22 mo (9–48) | N/A | Complications and revisions needed |
| Pelster MW, 2019 [65] | RSP | Texas, USA | Dermatology | Single | 2013–2017 | 31 (11) | 75.6 | Skin tumour | Skin graft | Tip | N/A | 1.8 ± 03 cm | 1 | 15 w | N/A | Complications and aesthetic results |
| Howe NM, 2019 [66] | RSP | Philadelphia, USA | Dermatology | Single and senior | 2009–2017 | 48 (23) | 67 * (41–92) | 42: BCC; 6: SCC | Crescentic island pedicle rotation flap | 18: lower nasal sidewall; 16: tip; 14: ala | N/A | 1.29 cm2 (0.25–3.8) | 1 | 6 mo (1–23) | N/A | Complications and revisions needed |
| Knackstedt T, 2018 [67] | RSP | Ohio, USA | Dermatology | N/A | 2009–2016 | 185 (89) 111(56) vs. 74 (33) | 71.0 vs. 69.2 | 162: BCC; 21: BCC; 2: other | Bilobed vs. trilobed flap | 28: inferior nasal dorsum; 19: inferior nasal sidewall; 54: supratip; 41: tip/infratip; 43: ala | N/A | 1.36 cm2 vs. 1.32 cm2 | 1 | 63.5 d vs. 69.6 d | N/A | Flap design, complications and revisions needed |
| Mohos G, 2018 [68] | N/A | Hungary | Dermatology | N/A | N/A | 10 (6) | 77 (66–84) | BCC | Nasolabial flap | Ala | N/A | 1.8 × 1.8–2.6 × 2.9 cm | 1 | 7.5 mo (5–15) | N/A | Complication, aesthetic results and patients’ satisfaction |
| Wang CY, 2018 [69] | RSP | Missouri, USA | Dermatology | N/A | 2013–2014 | 26 | N/A | N/A | Trilobed flap | N/A | N/A | 1.46 × 1.12 cm | 1 | 90 d | N/A | Complications, alar symmetry and aesthetic results |
| Funayama E, 2017 [70] | RSP | Japan | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 1996–2013 | 6 (6) | 65.3 (53–77) | 4: BCC; 1: SCC; 1: recurrent pleomorphic adenoma | Paramedian forehead flap | Ala | Full thickness | N/A | 2 (2–3 w) | 37 mo | N/A | Complications and aesthetic results |
| Redondo P, 2017 [5] | RSP | Spain | Dermatology | Single | 2004–2015 | 27 816) | 62.8 (44–88) | 19: BCC; 6: SCC; 2: lentigo maligna | Dorsal nasal flap | N/A | N/A | 2.4 cm * (1.5 × 2.1–3.2 × 3.7) | 1 | 12 mo–11 y | 0 | Complications and patients’ satisfaction |
| Blázquez-Sánchez N, 2016 [71] | RSP | Spain | Dermatology | N/A | 2004–2011 | 41 (29) | 67 (41–85) | 35: BCC; 4: SCC; 1: lentigo maligna; 1: trigeminal trophic ulcer | Paramedian forehead flap | 21: tip; 10: ala; 8: lower dorsum, lateral wall of the nose | 32: superficial; 9: full thickness | 2.16 cm (1.5–4) | 2 | 70.9 mo (±23.3) | N/A | Complications, secondary procedures, and cosmetic results |
| Ghassemi A, 2016 [72] | N/A | Germany | Maxillofacial surgery | N/A | Since 2010 | 21 (12) | 59.8 (43–84) | BCC | Reverse subcutaneous pedicled nasolabial flap + paramedian forehead (for coverage) flap | Ala | Full thickness | N/A | 3 (2nd: 2 w; 3rd: 3–5 w) | 1 y | 5 | Complications, aesthetic and function results |
| Lu X, 2016 [52] | RSP | China | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 2010–2015 | 34 (16) | 18 (5–36) | Haemangiomas | 28: forehead; 5: nasolabial; 1: medial upper arm tube flap | 2: lower dorsum; 5: ala; 2: tip; 25: two or more subunits | N/A | N/A | All 1 except the medial upper arm tube flap: 2 (2 w) | 12–36 mo | N/A | Complications, aesthetic and function results |
| Ong S, 2016 [73] | N/A | New Zealand | Dermatology | N/A | Past 3 years | 27 | 64.4 | Tumour | Quadrilobed flap | 18: tip; 5: ala; 2: lower nasal sidewall; 2: infratip | N/A | (0.7 × 0.5–3.0 × 1.0) cm | 1 | N/A | N/A | Complications and revisions needed |
| Scheufler O, 2016 [74] | RSP | Switzerland | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | Single | 2009–2015 | 29 (13) | 73 (48–95) | N/A | Frontonasal flap (standard vs. extent) | Tip | N/A | 2 cm (1.6–2.4) | 1 | 8.4 mo | N/A | Complications and aesthetic results |
| Moreno-Artero E, 2015 [75] | N/A | Spain | Dermatology | N/A | 2011–2015 | 15 (10) | 57 (31–84) | 12: BCC; 3: SCC | Spiral flap | Ala | N/A | 1 cm (0.8–1.3) | 1 | N/A | Complications, aesthetic and functional results | |
| Takeda A, 2014 [76] | RSP | Japan | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | N/A | 5 (3) | 78 (72–82) | 4: BCC, 1: SCC | Nasolabial flap | Ala | Full thickness | 1.9 × 1.7 cm (1.6 × 1.6–2.3 × 1.9) | 1 | 32 mo (17–36) | 0 | Complications, aesthetic results revisions needed, patients’ satisfaction |
| Bashir MM, 2013 [77] | N/A | Pakistan | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 2007–2011 | 18 (6) | 35 (12–24) | Trauma | Modified nasal turn-in flap + forehead flap (for coverage) | Columella, tip, soft triangles, and alae and extending partially to the dorsum and paired side wall | Full thickness | N/A | 2 (3 weeks) | N/A | N/A | Airway patency and alar rim contour |
| Constantine FC, 2013 [53] | RSP | Texas, USA | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | Single and senior | 1995–2010 | 14 (3) | 61 (46–78) | N/A | 9: nasolabial flap; 3: paramedian forehead flap; 2: skin graft | Soft triangle | 2: only external skin; 9: external skin + soft tissue; 3: full thickness | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Complications and revisions needed |
| Hafiji J, 2012 [78] | N/A | UK, New Zealand | Dermatology | N/A | Since 2011 | 45 (25) | 70 (41–88) | N/A | Advancement and inferior rotation of the nasal sidewall (AIRNS) flap | The overwhelming majority of cases involved the nasal tip or the lower nasal dorsum | N/A | 1.2 × 1.2 cm | 1 | N/A | N/A | Complications and aesthetic results |
| Ibrahimi OA, 2012 [79] | RSP | Connecticut, USA | Dermatology | N/A | N/A | 16 | N/A | N/A | Free cartilage batten grafting | Ala | N/A | N/A | 1 | N/A | N/A | Complications, aesthetic and functional results |
| Mahlberg MJ, 2011 [80] | RSP | South Carolina, USA | Dermatology | N/A | 2006–2011 | 63 (30) | 65 * (27–96) | 57: BCC; 4: SCC; 1: Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma; 1: hidradenoma | Spiral flap | Ala | Partial thickness | 1.0 cm (0.5–1.5) | 1 | Minimum 3 mo | N/A | Complications and revisions needed |
| Albertini JG, 2010 [81] | RSP | Utah, USA | Dermatology | N/A | 2005–2008 | 31 (19) | N/A | Tumour | Trilobed flap | 20: tip; 10: ala; 1: dorsum | N/A | 1.6 cm | 1 | 7 mo | N/A | Complications, alar symmetry and aesthetic results |
| Tan E, 2010 [82] | RSP | New Zealand | Dermatology | N/A | 2004–2008 | 65 (19) | 60.5 (39–86) | N/A | Nasal sidewall rotation flap | 70: tip; 3: lower sidewall; 1: lower dorsum; 1: ala | N/A | 1.1 × 1.0 cm (0.4–2.0) | 1 | Minimum 1 y | N/A | Complications and revisions needed |
| Xue CY, 2009 [83] | RSP | China | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 2003–2007 | 11 (5) | 57 (42–76) | 7: BCC; 2: SCC; 2: nevus cell | Bilobed flap | 4: tip; 4: ala; 3: soft triangle | N/A | 1.38 × 1.38 cm (1.2 × 1.2–1.6 × 1.6) | 1 | 6 mo (1–24) | 0 | Complications and aesthetic results |
| D’Arpa S, 2008 [84] | RSP | Italy | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 2004–2007 | 8 | 73 (42–89) | 7: BCC; 1: SCC | Nasolabial perforator flap | Ala | Partial thickness | N/A | 1 | 16 mo (3–31) | N/A | Flap design, complications and aesthetic results |
| Willey A, 2008 [85] | N/A | Georgia, USA | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 2006–2007 | 61 (31) | 69 (32–72) | 47: BCC; 9: SCC; 3: melanoma; 1: Merckel cell carcinoma | Single-sling myocutaneous island pedicle flap | 41: tip; 18: ala; 3: lower sidewall | N/A | 0.6–2.8 cm | 1 | N/A | N/A | Complications, aesthetic and functional results |
| Ozek C, 2007 [86] | N/A | Turkey | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 1997–2005 | 6 (6) | 52 (41–62) | 4: BCC; 2: SCC | Ear helix free flap | 2: ala + columella; 2: ala; 1: tip + ala; 1: columella | Full thickness | 3.2 × 2.7 cm (2.9 × 2.5–3.6 × 3.0) | 1 | N/A | N/A | Complications, aesthetic results and patients’ satisfaction |
| Silistreli OK, 2005 [87] | RSP | Turkey | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 2000–2002 | 10 (5) | 53.8 (15–78) | 5: BCC; 1: metatypical cancer; 3: trauma; 1: congenital nevus | Nasolabial flap | 5: ala; 3: columella; 1: tip | Full thickness | 1.8 × 1.3 cm (1.1 × 1.0–2.5 × 1.5) | 2 (2 w) | 25 mo (18–31) | N/A | Complications and revisions needed |
| Ullmann Y, 2005 [88] | N/A | Israel | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 2002–2003 | 17 (6) | (46–84) | BCC/SCC | Paramedian forehead flap | N/A | 3: full thickness | (1.8–3.6 cm) | 2 (2–3 w) | N/A | N/A | Complications, aesthetic results and revisions needed |
| Lambert RW, 2004 [89] | N/A | Pennsylvania, USA | Dermatology | N/A | N/A | 30 | N/A | N/A | Dorsal nasal advancement flap | Tip | N/A | 0.5 × 2.0 cm | 1 | N/A | N/A | Complications and aesthetic results |
| Lindsey WH, 2001 [90] | RSP | Virginia, USA | Otolaryngology | Single | Dating back 41⁄2 years | 105 | N/A | Tumour | Nasolabial flap | Ala | 17: full thickness | N/A | 1 | Minimum 6 mo | N/A | Complications and revisions needed |
| Goleman R, 1998 [54] | N/A | Brazil | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | N/A | 21 (9) | 62.71 (25–83) | 19: BCC; 1: SCC; 1: actinic keratosis | Bilobed island flap | Ala | 19: partial thickness; 2: full thickness | 1.6 × 1.7 cm (1.1 × 1.2–2.1 × 2) | 1 | N/A | N/A | Flap design and complications |
| Blandini D, 1996 [55] | N/A | Italy | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 17 y | 53 (21) | 65.7 (49–97) | 35: BCC; 13: SCC; 5: pigmented lesion | Axial sliding dorsal nasal flap | Ala | N/A | 1 × 1 cm- entire lobular | 1 | 47.3 mo (3 mo–17 y) | N/A | Complications |
| Pribaz JJ, 1993 [56] | RSP | Massachusetts, USA | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | N/A | 1985–1992 | 6 (2) | 43 (7–76) | 2: BCC; 2: AVM; 1: sarcoma; 1: huma bite | Auricular free flap | 3: ala; 2: columella; 1: two or more subunits | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Complications and revisions needed |
| Wee SS, 1990 [57] | N/A | Missouri, USA | Dermatology | Senior and single | 3 y | 19 (8) | (30–76) | 18: BCC; 1: lentigo maligna | Nasalis myocutaneous island flap | Ala | N/A | 1 × 0.9–4 × 3.5 cm | 1 | 1 mo–2.5 y | 0 | Complications and aesthetic results |
| Author, Year | Type of Cutaneous Reconstruction | No Patients | Complications | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tot | Flap/Graft Necrosis | Wound Infection/Dehiscence | Alar Notching | Contour Irregularities/Contraction | Nasal Valve Collapse/Obstruction | Pincushion/Trapdoor | Others | |||
| Rickstrew J, 2024 [58] | Nasal tip rotation flap | 66 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Asaka A, 2023 [59] | Modified trilobed flap | 15 | 0 | |||||||
| He A, 2022 [60] | Postauricular skin-fat-fascia composite graft | 13 | 0 | |||||||
| Ding F, 2021 [61] | Extended forehead flap | 6 | 0 | |||||||
| Kim DJ, 2021 [62] | Free cartilage batten grafting (FCBG) flap | 129 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gostian AO, 2020 [63] | Skin graft + extended forehead flap | 16 | 4 | 1 (partial) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1: pain; 1: perforation of nasal septum |
| Yildiz K, 2020 [64] | Lateral nasal artery perforator flap | 13 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pelster MW, 2019 [65] | Skin graft | 31 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 (temporary) | 0 | 1: bleeding |
| Howe NM, 2019 [66] | Crescentic island pedicle rotation flap | 48 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Knackstedt T, 2018 [67] | Bilobed vs. trilobed flap | 185 | 57 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 44 | 10: erythema; |
| Mohos G, 2018 [68] | Nasolabial flap | 10 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3: sweeling; 2: erythema |
| Wang CY, 2018 [69] | Trilobed flap | 26 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Funayama E, 2017 [70] | Paramedian forehead flap | 6 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Redondo P, 2017 [5] | Dorsal nasal flap | 27 | 0 | |||||||
| Blázquez-Sánchez N, 2016 [71] | Paramedian forehead flap | 41 | 28 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 8: transposition of forehead hair with the flap |
| Ghassemi A, 2016 [72] | Reverse subcutaneous pedicled nasolabial flap + paramedian forehead flap | 21 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Lu X, 2016 [52] | 28: forehead; 5: nasolabial; 1: medial upper arm tube flap | 34 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1: swelling |
| Ong S, 2016 [73] | Quadrilobed flap | 27 | 0 | |||||||
| Scheufler O, 2016 [74] | Frontonasal flap (standard vs. extent) | 29 | 8 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1: haematoma |
| Moreno-Artero E, 2015 [75] | Spiral flap | 15 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Takeda A, 2014 [76] | Nasolabial flap | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bashir MM, 2013 [77] | Modified nasal turn-in flap + forehead flap (for coverage) | 18 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Constantine FC, 2013 [53] | 9: nasolabial flap; 3: paramedian forehead flap; 2: skin graft | 14 | N/A | |||||||
| Hafiji J, 2012 [78] | Advancement and inferior rotation of the nasal sidewall (AIRNS) flap | 45 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ibrahimi OA, 2012 [79] | Free cartilage batten grafting | 16 | 13 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2: pain |
| Mahlberg MJ, 2011 [80] | Spiral flap | 63 | 0 | |||||||
| Albertini JG, 2010 [81] | Trilobed flap | 31 (19) | 0 | |||||||
| Tan E, 2010 [82] | Nasal sidewall rotation flap | 65 (19) | 11 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 9: swelling |
| Xue CY, 2009 [83] | Bilobed flap | 11 (5) | 0 | |||||||
| D’Arpa S, 2008 [84] | Nasolabial perforator flap | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Willey A, 2008 [85] | Single-sling myocutaneous island pedicle flap | 61 (31) | 12 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 1: haemorrhage |
| Ozek C, 2007 [86] | Ear helix free flap | 6 (6) | 0 | |||||||
| Silistreli OK, 2005 [87] | Nasolabial flap | 10 (5) | 3 | 1 (partial) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ullmann Y, 2005 [88] | Paramedian forehead flap | 17 (6) | 3 | 1 (partial) | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Lambert RW, 2004 [89] | Dorsal nasal advancement flap | 30 | 0 | |||||||
| Lindsey WH, 2001 [90] | Nasolabial flap | 105 | 16 | 7 (partial) | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4: haematoma |
| Golcman R, 1998 [54] | Bilobed island flap | 21 (9) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Blandini D, 1996 [55] | Axial sliding dorsal nasal flap | 53 (21) | 0 | |||||||
| Pribaz JJ, 1993 [56] | Auricular free flap | 6 (2) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wee SS, 1990 [57] | Nasalis myocutaneous island flap | 19 | 0 | |||||||
| Author, Year | Type of Cutaneous Reconstruction | No Patients | Complications | Revision Surgery | Dermabrasion | Intralesional Corticosteroid Injection | Laser | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rickstrew J, 2024 [58] | Nasal tip rotation flap | 66 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| Kim DJ, 2021 [62] | Free cartilage batten grafting (FCBG) flap | 129 | 1 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| Gostian AO, 2020 [63] | Skin graft + extended forehead flap | 16 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Yildiz K, 2020 [64] | Lateral nasal artery perforator flap | 13 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Flap debulking |
| Pelster MW, 2019 [65] | Skin graft | 31 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Howe NM, 2019 [66] | Crescentic island pedicle rotation flap | 48 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | |
| Knackstedt T, 2018 [67] | Bilobed vs. trilobed flap | 185 | 57 | 2 | 4 | 44 | 10 | |
| Mohos G, 2018 [68] | Nasolabial flap | 10 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Wang CY, 2018 [69] | Trilobed flap | 26 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Funayama E, 2017 [70] | Paramedian forehead flap | 6 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Flap debulking |
| Blázquez-Sánchez N, 2016 [71] | Paramedian forehead flap | 41 | 28 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 0 | Flap debulking and hair removal |
| Ghassemi A, 2016 [72] | Reverse subcutaneous pedicled nasolabial flap + paramedian forehead flap | 21 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Lu X, 2016 [52] | 28: forehead; 5: nasolabial; 1: medial upper arm tube flap | 34 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Scheufler O, 2016 [74] | Frontonasal flap (standard vs. extent) | 29 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2: flap debulking; 1: haematoma evacuation; 1: scar revision |
| Moreno-Artero E, 2015 [75] | Spiral flap | 15 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Takeda A, 2014 [76] | Nasolabial flap | 5 | 1 | 1 (minor) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bashir MM, 2013 [77] | Modified nasal turn-in flap + forehead flap (for coverage) | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Constantine FC, 2013 [53] | 9: nasolabial flap; 3: paramedian forehead flap; 2: skin graft | 14 | N/A | 3 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 3 required revisions with subsequent resurfacing, 2 required resurfacing alone. |
| Hafiji J, 2012 [78] | Advancement and inferior rotation of the nasal sidewall (AIRNS) flap | 45 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ibrahimi OA, 2012 [79] | Free cartilage batten grafting | 16 | 13 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Tan E, 2010 [82] | Nasal sidewall rotation flap | 65 (19) | 11 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 0 | |
| D’Arpa S, 2008 [84] | Nasolabial perforator flap | 8 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Willey A, 2008 [85] | Single-sling myocutaneous island pedicle flap | 61 (31) | 12 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | |
| Silistreli OK, 2005 [87] | Nasolabial flap | 10 (5) | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ullmann Y, 2005 [88] | Paramedian forehead flap | 17 (6) | 3 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 patients require 2 revision surgeries each, while 7 patients required 1 revision surgery each |
| Lindsey WH, 2001 [90] | Nasolabial flap | 105 | 16 | 1 | 0 | 15 | 0 | |
| Goleman R, 1998 [54] | Bilobed island flap | 21 (9) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pribaz JJ, 1993 [56] | Auricular free flap | 6 (2) | 1 | 6 (minor) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Author, Year | Type of Cutaneous Reconstruction | Aesthetic Results |
|---|---|---|
| Rickstrew J, 2024 [58] | Nasal tip rotation flap | N/A |
| Asaka A, 2023 [59] | Modified trilobed flap | Good colour and texture all |
| He A, 2022 [60] | Postauricular skin-fat-fascia composite graft | Favourable |
| Ding F, 2021 [61] | Extended forehead flap | Good colour and texture all |
| Kim DJ, 2021 [62] | Free cartilage batten grafting (FCBG) flap | 18: poor; 40: good; 40: very good; 31: excellent |
| Gostian AO, 2020 [63] | Skin graft + extended forehead flap | N/A |
| Yildiz K, 2020 [64] | Lateral nasal artery perforator flap | N/A |
| Mohos G, 2018 [68] | Nasolabial flap | All satisfied |
| Pelster MW, 2019 [65] | Skin graft | All satisfied |
| Howe NM, 2019 [66] | Crescentic island pedicle rotation flap | N/A |
| Knackstedt T, 2018 [67] | Bilobed vs. trilobed flap | N/A |
| Wang CY, 2018 [69] | Trilobed flap | Excellent-very good |
| Redondo P, 2017 [5] | Dorsal nasal flap | Good |
| Funayama E, 2017 [70] | Paramedian forehead flap | 4: excellent, 1: good, 1: fair |
| Lu X, 2016 [52] | 28: forehead; 5: nasolabial; 1: medial upper arm tube flap | Forehead: excellent; Nasolabial: satisfying, shape, colour, texture was excellent; Upper arm tube flap: survived but bloated |
| Blázquez-Sánchez N, 2016 [71] | Paramedian forehead flap | 4: unacceptable; 19: acceptable; 18: excellent |
| Ghassemi A, 2016 68] | Reverse subcutaneous pedicled nasolabial flap + paramedian forehead (for coverage) flap | 19: satisfied; 2: unsatisfied |
| Ong S, 2016 [73] | Quadrilobed flap | N/A |
| Scheufler O, 2016 [74] | Frontonasal flap (standard vs. extent) | 28: good, excellent |
| Moreno-Artero E, 2015 [75] | Spiral flap | Adequate |
| Takeda A, 2014 [76] | Nasolabial flap | Acceptable |
| Bashir MM, 2013 [77] | Modified nasal turn-in flap + forehead flap | 3: satisfactory; 9: just satisfactory; 6: unsatisfactory |
| Constantine FC, 2013 [53] | 9: nasolabial flap; 3: paramedian forehead flap; 2: skin graft | N/A |
| Hafiji J, 2012 [78] | Advancement and inferior rotation of the nasal sidewall (AIRNS) flap | Good or excellent |
| Mahlberg MJ, 2011 [80] | Spiral flap | N/A |
| Ibrahimi OA, 2012 [79] | Free cartilage batten grafting | 7: excellent, 6: very good, 3: good |
| Albertini JG, 2010 [81] | Trilobed flap | 0.84 (range 0–3) |
| Tan E, 2010 [82] | Nasal sidewall rotation flap | N/A |
| Xue CY, 2009 [83] | Bilobed flap | Excellent |
| D’Arpa S, 2008 [84] | Nasolabial perforator flap | All satisfied |
| Willey A, 2008 [85] | Single-sling myocutaneous island pedicle flap | High aesthetic goals were achieved |
| Ozek C, 2007 [86] | Ear helix free flap | Good colour match |
| Silistreli OK, 2005 [87] | Nasolabial flap | N/A |
| Ullmann Y, 2005 [88] | Paramedian forehead flap | All satisfied |
| Lambert RW, 2004 [89] | Dorsal nasal advancement flap | Good outstanding |
| Lindsey WH, 2001 [90] | Nasolabial flap | N/A |
| Goleman R, 1998 [54] | Bilobed island flap | N/A |
| Blandini D, 1996 [55] | Axial sliding dorsal nasal flap | N/A |
| Pribaz JJ, 1993 [56] | Auricular free flap | N/A |
| Wee SS, 1990 [57] | Nasalis myocutaneous island flap | Excellent |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salzano, G.; Scocca, V.; Romano, A.; Vaira, L.A.; Lechien, J.R.; Maglitto, F.; Petrocelli, M.; Dell'Aversana Orabona, G. Surgical Outcomes and Complications of Distal Nasal Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227983
Salzano G, Scocca V, Romano A, Vaira LA, Lechien JR, Maglitto F, Petrocelli M, Dell'Aversana Orabona G. Surgical Outcomes and Complications of Distal Nasal Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):7983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227983
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalzano, Giovanni, Veronica Scocca, Antonio Romano, Luigi Angelo Vaira, Jerome R. Lechien, Fabio Maglitto, Marzia Petrocelli, and Giovanni Dell'Aversana Orabona. 2025. "Surgical Outcomes and Complications of Distal Nasal Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 7983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227983
APA StyleSalzano, G., Scocca, V., Romano, A., Vaira, L. A., Lechien, J. R., Maglitto, F., Petrocelli, M., & Dell'Aversana Orabona, G. (2025). Surgical Outcomes and Complications of Distal Nasal Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 7983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227983