A Cross-Sectional Study of Word Recognition and Cognitive Function in Older Adults with Hearing Loss Using a Standardized Neuropsychological Battery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
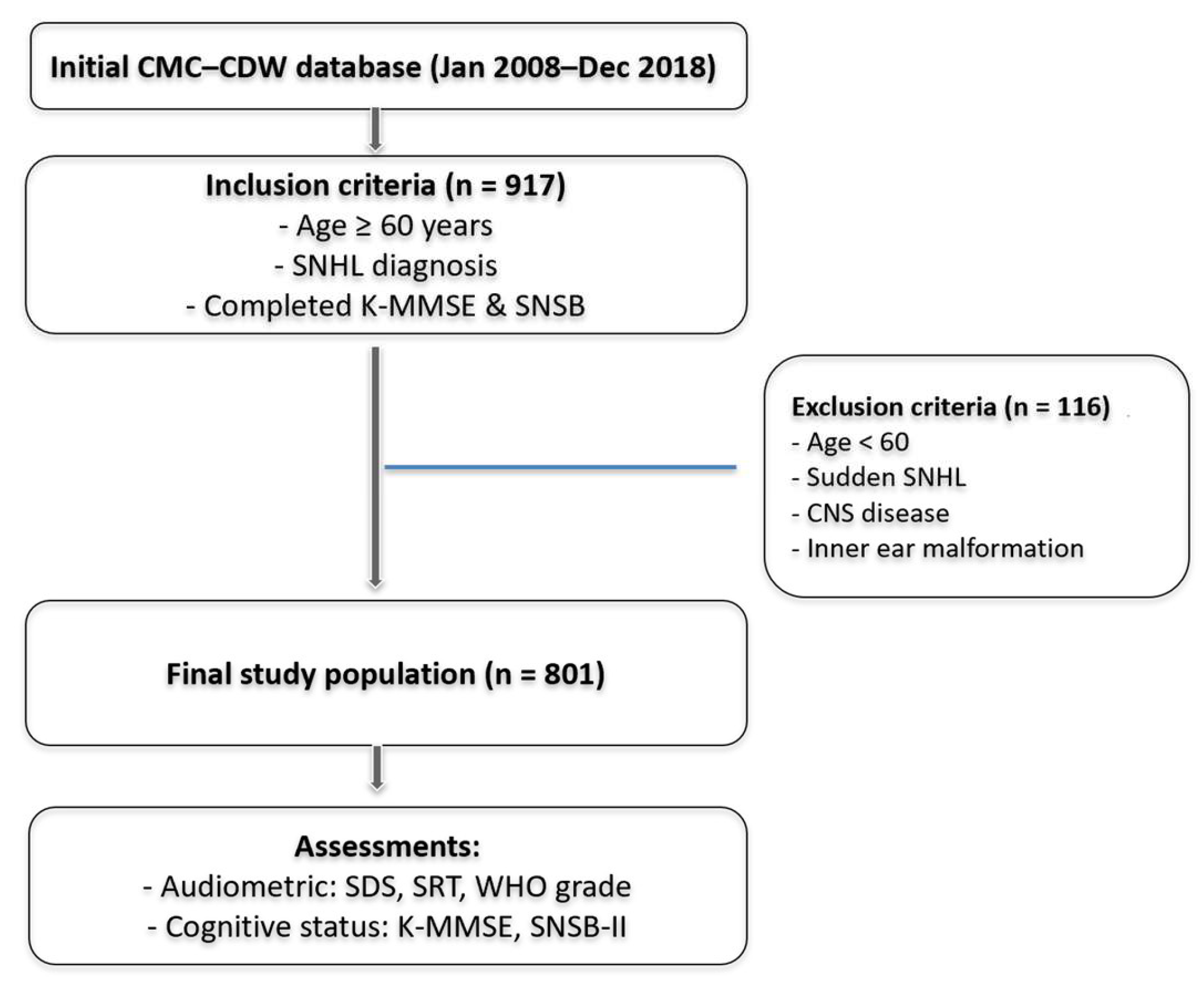
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Audiometric Measurements
2.3. Assessment of Cognitive Function
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
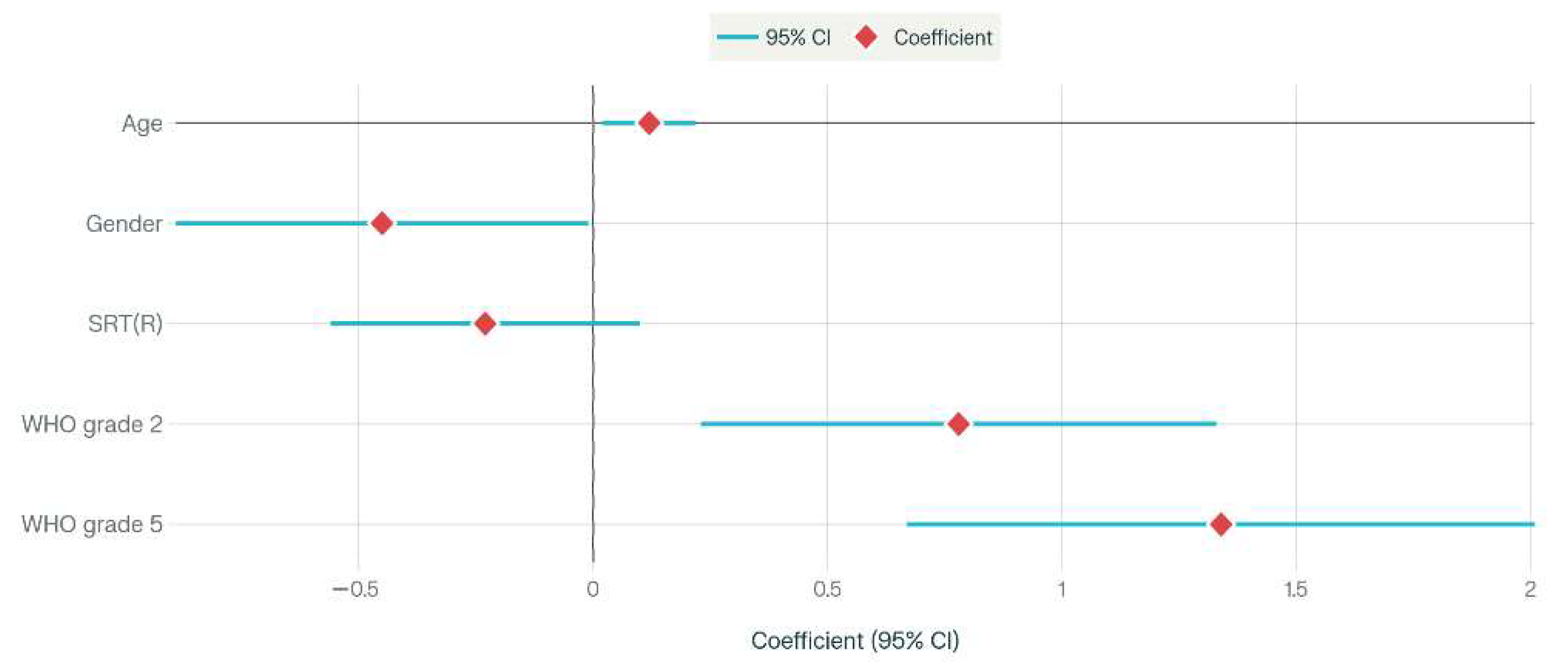
3. Results
Group Comparisons by Hearing Loss Severity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, F.R.; Yaffe, K.; Xia, J.; Xue, Q.L.; Harris, T.B.; Purchase-Helzner, E.; Satterfield, S.; Ayonayon, H.N.; Ferrucci, L.; Simonsick, E.M. Hearing loss and cognitive decline in older adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, D. Age-Related Hearing Loss and Cognitive Decline: You Haven’t Heard the Half of It. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slade, K.; Plack, C.J.; Nuttall, H.E. The Effects of Age-Related Hearing Loss on the Brain and Cognitive Function. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, T.D.; Lad, M.; Kumar, S.; Holmes, E.; McMurray, B.; Maguire, E.A.; Billig, A.J.; Sedley, W. How Can Hearing Loss Cause Dementia? Neuron 2020, 108, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, M.; Bryce, R.; Albanese, E.; Wimo, A.; Ribeiro, W.; Ferri, C.P. The global prevalence of dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2013, 9, 63–75.e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.R.; Ferrucci, L.; Metter, E.J.; An, Y.; Zonderman, A.B.; Resnick, S.M. Hearing loss and cognition in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Neuropsychology 2011, 25, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, B.; Schneider, J.; McMahon, C.M.; Teber, E.; Leeder, S.R.; Mitchell, P. Severity of age-related hearing loss is associated with impaired activities of daily living. Age Ageing 2012, 41, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, A.; Scarpa, A.; Di Girolamo, S.; De Luca, P.; Cassandro, C.; Viola, P.; Ricciardiello, F.; Greco, A.; Vincentiis, M.; Ralli, M.; et al. Hearing Loss and Cognitive Impairment: Epidemiology, Common Pathophysiological Findings, and Treatment Considerations. Life 2021, 11, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição Santos de Oliveira, D.; Gomes-Filho, I.S.; Araújo, E.M.; Xavier Ramos, M.S.; Freitas Coelho, J.M.; Marques, A.A.; Hintz, A.M.; Firmino Rabelo, D.; Figueiredo, A.; da Cruz, S.S. Association between hearing loss and cognitive decline in the elderly: A systematic review with meta-analysis study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuesse, T.; Steenken, R.; Neher, T.; Holube, I. Exploring the Link Between Cognitive Abilities and Speech Recognition in the Elderly Under Different Listening Conditions. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlauch, R.S.; Carney, E. Clinical Strategies for Sampling Word Recognition Performance. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. JSLHR 2018, 61, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humes, L.E.; Dubno, J.R.; Gordon-Salant, S.; Lister, J.J.; Cacace, A.T.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Gates, G.A.; Wilson, R.H.; Wingfield, A. Central presbycusis: A review and evaluation of the evidence. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2012, 23, 635–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.W.; Beom, I.G.; Cho, J.Y.; Son, H.R. Accuracy of Korean-Mini-Mental Status Examination Based on Seoul Neuro-Psychological Screening Battery II Results. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2016, 37, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.J.; Yang, D.W. The Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery (SNSB) for Comprehensive Neuropsychological Assessment. Dement. Neurocognitive Disord. 2023, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.R.; Metter, E.J.; O’Brien, R.J.; Resnick, S.M.; Zonderman, A.B.; Ferrucci, L. Hearing loss and incident dementia. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.W. Frequencies of Korean Syllables and the Distribution of Syllables of PB Word List. Korean J. Otorhinolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2003, 46, 737–741. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.J. Reliability of Speech Recognition Threshold Test Using the Korean Standard Bisyllabic Word List for Adults in Comparison with Conventional Hahm’s List. Korean J. Otorhinolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2012, 55, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhoo, J.H.; Kim, K.W.; Huh, Y.; Lee, S.B.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.J.; Choi, E.A.; Han, C.; Choo, I.H.; Youn, J.C.; et al. Prevalence of dementia and its subtypes in an elderly urban korean population: Results from the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health And Aging (KLoSHA). Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2008, 26, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humes, L.E. The World Health Organization’s hearing-impairment grading system: An evaluation for unaided communication in age-related hearing loss. Int. J. Audiol. 2019, 58, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludden, T.M.; Beal, S.L.; Sheiner, L.B. Comparison of the Akaike Information Criterion, the Schwarz criterion and the F test as guides to model selection. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1994, 22, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, M.; Min, J.; Yao, M.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Yuan, J. Effect of hearing loss on cognitive function in patients with mild cognitive impairment: A prospective, randomized, and controlled study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 934921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Liang, T.; Liu, D.; Qiu, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y. Sensorineural hearing loss and cognitive impairment: Three hypotheses. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1368232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berns, M.P.; Nunez, G.M.; Zhang, X.; Chavan, A.; Zemlianova, K.; Mowery, T.M.; Yao, J.D. Auditory decision-making deficits after permanent noise-induced hearing loss. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peelle, J.E.; Wingfield, A. The Neural Consequences of Age-Related Hearing Loss. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.C.; Proctor, D.; Soni, J.; Pikett, L.; Livingston, G.; Lewis, G.; Schilder, A.; Bamiou, D.; Mandavia, R.; Omar, R.; et al. Adult-onset hearing loss and incident cognitive impairment and dementia—A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 98, 102346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, H. Memory loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoub, T.R.; deToledo-Morrell, L.; Stebbins, G.T.; Leurgans, S.; Bennett, D.A.; Shah, R.C. Hippocampal disconnection contributes to memory dysfunction in individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10041–10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanon Zotin, M.C.; Sveikata, L.; Viswanathan, A.; Yilmaz, P. Cerebral small vessel disease and vascular cognitive impairment: From diagnosis to management. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2021, 34, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, T.; Lee, E.; Park, S.W.; Yeo, N.Y.; Kim, Y.J. Hearing loss and the risk of dementia: A longitudinal analysis of the Korean National Health Insurance Service Senior Cohort. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2025, 104, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, R.V.; Johnsrude, I.S. A review of causal mechanisms underlying the link between age-related hearing loss and cognitive decline. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 23, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deal, J.A.; Betz, J.; Yaffe, K.; Harris, T.; Purchase-Helzner, E.; Satterfield, S.; Pratt, S.; Govil, N.; Simonsick, E.M.; Lin, F.R. Hearing Impairment and Incident Dementia and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: The Health ABC Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iva, P.; Fielding, J.; Clough, M.; White, O.; Godic, B.; Martin, R.; Rajan, R. Speech Discrimination Tasks: A Sensitive Sensory and Cognitive Measure in Early and Mild Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 604991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, H.A.; Sharma, A. Cortical Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Function in Early-Stage, Mild-Moderate Hearing Loss: Evidence of Neurocognitive Benefit From Hearing Aid Use. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Sugiura, S.; Nishita, Y.; Saji, N.; Sone, M.; Ueda, H. Age-related hearing loss and cognitive decline—The potential mechanisms linking the two. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, C.J.; Yusuf, A.; Wilson, D.E.; Peelle, J.E.; Davis, M.H.; Johnsrude, I.S. Effortful listening: The processing of degraded speech depends critically on attention. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14010–14021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Lan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Noise exposure, hearing loss and cognitive impairment: A cross-sectional study based on an occupational health surveillance cohort in China. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1455340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Połtyn-Zaradna, K.; Pazdro-Zastawny, K.; Szcześniak, D.; Basiak-Rasała, A.; Wołyniec, M.; Zatońska, K.; Zatoński, T. Age-related hearing loss associated with cognitive impairment in the Polish cohort of the PURE study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2025, 17, 1540803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Liu, K.Y.; Costafreda, S.G.; Selbæk, G.; Alladi, S.; Ames, D.; Banerjee, S.; Burns, A.; Brayne, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2024 report of the Lancet standing Commission. Lancet 2024, 404, 572–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döge, J.; Hackenberg, B.; Beutel, M.E.; Otten, D.; Wild, P.S.; Chalabi, J.; Matthias, C.; Bahr-Hamm, K. Hearing Loss and Its Relation to Loneliness and Depression-A Population-Based Cohort Study. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Chern, A.; Golub, J.S. Age-Related Hearing Loss and the Development of Cognitive Impairment and Late-Life Depression: A Scoping Overview. Semin. Hear. 2021, 42, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardone, R.; Battista, P.; Panza, F.; Lozupone, M.; Griseta, C.; Castellana, F.; Capozzo, R.; Ruccia, M.; Resta, E.; Seripa, D.; et al. The Age-Related Central Auditory Processing Disorder: Silent Impairment of the Cognitive Ear. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakody, D.M.P.; Friedland, P.L.; Martins, R.N.; Sohrabi, H.R. Impact of Aging on the Auditory System and Related Cognitive Functions: A Narrative Review. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolt, E.; Giroud, N. Neural encoding of linguistic speech cues is unaffected by cognitive decline, but decreases with increasing hearing impairment. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Ho, S.H.; Hong, Y.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, K.H.; Kim, S.; Wang, M.J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, R.E.Y.; Yang, D.W.; et al. The Effect of Hearing Loss on Cognitive Function in Subjective Cognitive Decline. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2022, 51, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Hou, J.; Nan, H.; Yue, A.; Chu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L. Relationship between hearing impairment and dementia and cognitive function: A Mendelian randomization study. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.S.; Oh, E.S.; Reed, N.S.; Lin, F.R.; Deal, J.A. Hearing Loss and Cognition: What We Know and Where We Need to Go. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 769405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.Y.; Shim, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Yoon, S.W.; Joo, E.J. Is cognitive function in adults with hearing impairment improved by the use of hearing AIDS? Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 4, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.; Zhao, G.; Xu, X.; Su, S.; Xie, X. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive impairment and dementia: An umbrella review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1241224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Cao, G.; Duan, Y.; Yan, S.; Yan, M.; Yin, P.; Jiang, H. Gender Differences in the Association Between Hearing Loss and Cognitive Function. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2020, 35, 1533317519871167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.S.; Yu, L.; Lamar, M.; Schneider, J.A.; Boyle, P.A.; Bennett, D.A. Education and cognitive reserve in old age. Neurology 2019, 92, e1041–e1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Li, S.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. The impact of education and occupation on cognitive impairment: A cross-sectional study in China. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1435626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total Patients (n = 801) | |
|---|---|
| Age | 77.10 ± 9.77 |
| Sex (M:F) | 313 (39.1%)/488 (60.9%) |
| SRT (right) | 39.69 ± 24.91 |
| WHO classification (right) | |
| Normal | 303 (37.8%) |
| Mild | 240 (30.0%) |
| Moderate | 149 (18.6%) |
| Severe | 22 (2.7%) |
| Profound | 87 (10.9%) |
| SRT (left) | 41.44 ± 26.71 |
| WHO classification (left) | |
| Normal | 296 (37.0%) |
| Mild | 228 (28.5%) |
| Moderate | 149 (18.6%) |
| Severe | 19 (2.4%) |
| Profound | 109 (13.6%) |
| SDS (right) | 73.35 ± 29.92 |
| SDS (left) | 71.23 ± 31.79 |
| Education (years) | 10.74 ± 5.24 |
| K-MMSE | 25.14 ± 4.33 |
| CDR | |
| 0 | 70 (8.7%) |
| 0.5 | 632 (78.9%) |
| 1.0 | 72 (9.0%) |
| 2.0 | 26 (3.2%) |
| 3.0 | 1 (0.1%) |
| Dementia | |
| Normal | 205 (25.6%) |
| MCI | 438 (54.7%) |
| Mild dementia | 115 (14.4%) |
| Moderate to severe | 43 (5.3%) |
| Normal (n = 240, 30.0%) | Mild (n = 234, 29.2%) | Moderate (n = 165, 20.6%) | Severe (n = 29, 3.6%) | Profound (n = 133, 16.6%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 71.56 ± 9.76 | 77.39 ± 7.65 | 79.60 ± 9.02 | 83.41 ± 6.64 | 82.11 ± 9.74 | <0.001 |
| Sex (M:F) | 83:157 (34.6%:65.4%) | 78:156 (33.3%:66.7%) | 61:104 (37.0%:63.0%) | 19:10 (65.5%:34.5%) | 72:61 (54.1%:45.9%) | <0.001 |
| SRT_R | 18.77 ± 4.65 | 32.49 ± 6.31 | 45.07 ± 10.07 | 60.34 ± 13.22 | 78.94 ± 30.31 | <0.001 |
| SRT_L | 18.63 ± 4.60 | 32.29 ± 6.91 | 46.24 ± 9.06 | 60.52 ± 15.60 | 88.56 ± 24.67 | <0.001 |
| SDS_R | 96.71 ± 6.10 | 82.90 ± 13.20 | 66.24 ± 17.53 | 57.07 ± 20.03 | 26.80 ± 33.54 | <0.001 |
| SDS_L | 95.99 ± 10.20 | 83.15 ± 11.74 | 64.43 ± 17.35 | 56.41 ± 22.77 | 17.24 ± 28.26 | <0.001 |
| Education (years) | 11.71 ± 4.88 | 10.31 ± 5.44 | 10.04 ± 5.37 | 11.24 ± 5.42 | 10.48 ± 5.12 | 0.010 |
| K-MMSE | 26.43 ± 3.78 | 25.23 ± 4.27 | 24.51 ± 4.25 | 23.86 ± 4.64 | 23.73 ± 4.77 | <0.001 |
| CDR | 0.002 | |||||
| 0 | 34 (14.2%) | 17 (7.3%) | 9 (5.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | 10 (7.5%) | |
| 0.5 | 188 (78.3%) | 190 (81.2%) | 134 (81.2%) | 26 (89.7%) | 94 (70.7%) | |
| 1.0 | 14 (5.8%) | 18 (7.7%) | 18 (10.9%) | 1 (3.4%) | 21 (15.8%) | |
| 2.0 | 3 (1.3%) | 9 (3.8%) | 4 (2.4%) | 2 (6.9%) | 8 (6.0%) | |
| 3.0 | 1 (0.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Cognition status | <0.001 | |||||
| Normal | 82 (34.2%) | 69 (29.5%) | 29 (17.6%) | 2 (17.3%) | 23 (25.6%) | |
| MCI | 125 (52.1%) | 120 (51.3%) | 106 (64.2%) | 20 (50.4%) | 67 (54.7%) | |
| Mild dementia | 27 (11.3%) | 34 (14.5%) | 20 (12.1%) | 4 (22.6%) | 30 (14.4%) | |
| Moderate to severe | 6 (2.5%) | 11 (4.7%) | 10 (6.0%) | 3 (9.1%) | 13 (5.3%) |
| Normal (n = 205, 25.6%) | MCI (n = 438, 54.7%) | Mild (n = 115, 14.4%) | Moderate to Severe (n = 43, 5.3%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 71.98 ± 9.93 | 77.69 ± 9.16 | 81.23 ± 8.05 | 84.49 ± 7.50 | <0.001 |
| Sex (M:F) | 52:153 (25.4%:74.6%) | 187:251 (42.7%:57.3%) | 56:59 (48.7%:51.3%) | 18:25 (41.9%:58.1%) | <0.001 |
| SRT_R | 30.68 ± 20.88 | 41.06 ± 24.12 | 44.96 ± 27.16 | 54.65 ± 30.46 | <0.001 |
| SRT_L | 34.68 ± 24.43 | 41.26 ± 25.49 | 50.35 ± 30.58 | 51.58 ± 29.15 | <0.001 |
| WHO classification | <0.001 | ||||
| Normal | 82 (40.0%) | 125 (28.5%) | 27 (23.5%) | 6 (14.0%) | |
| Mild | 69 (33.7%) | 120 (27.4%) | 34 (29.6%) | 11 (25.6%) | |
| Moderate | 29 (14.1%) | 106 (24.2%) | 20 (17.4%) | 0 (23.3%) | |
| Severe | 2 (1.0%) | 20 (4.6%) | 4 (3.5%) | 3 (7.0%) | |
| Profound | 23 (11.2%) | 67 (15.3%) | 30 (26.1%) | 13 (30.2%) | |
| SDS_R | 84.44 ± 24.54 | 71.91 ± 29.13 | 66.50 ± 32.18 | 53.58 ± 36.55 | <0.001 |
| SDS_L | 81.14 ± 28.24 | 70.64 ± 30.46 | 61.32 ± 36.30 | 56.47 ± 34.12 | <0.001 |
| Education (years) | 10.89 ± 5.38 | 10.70 ± 5.03 | 10.77 ± 5.70 | 10.34 ± 5.54 | 0.929 |
| K-MMSE | 27.67 ± 2.52 | 25.70 ± 3.37 | 21.64 ± 3.96 | 16.81 ± 5.19 | <0.001 |
| CDR | <0.001 | ||||
| 0 | 52 (25.4%) | 18 (4.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| 0.5 | 152 (74.1%) | 413 (94.3%) | 67 (58.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| 1.0 | 1 (0.5%) | 5 (1.1%) | 46 (40.0%) | 20 (46.5%) | |
| 2.0 | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (0.5%) | 2 (1.7%) | 22 (51.2%) | |
| 3.0 | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.3%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.J.; Kong, T.H.; Park, K.H. A Cross-Sectional Study of Word Recognition and Cognitive Function in Older Adults with Hearing Loss Using a Standardized Neuropsychological Battery. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7897. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227897
Lee HJ, Kong TH, Park KH. A Cross-Sectional Study of Word Recognition and Cognitive Function in Older Adults with Hearing Loss Using a Standardized Neuropsychological Battery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):7897. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227897
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyun Jin, Tae Hoon Kong, and Kyoung Ho Park. 2025. "A Cross-Sectional Study of Word Recognition and Cognitive Function in Older Adults with Hearing Loss Using a Standardized Neuropsychological Battery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 7897. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227897
APA StyleLee, H. J., Kong, T. H., & Park, K. H. (2025). A Cross-Sectional Study of Word Recognition and Cognitive Function in Older Adults with Hearing Loss Using a Standardized Neuropsychological Battery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 7897. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227897






