Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Swallowed Topical Corticosteroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
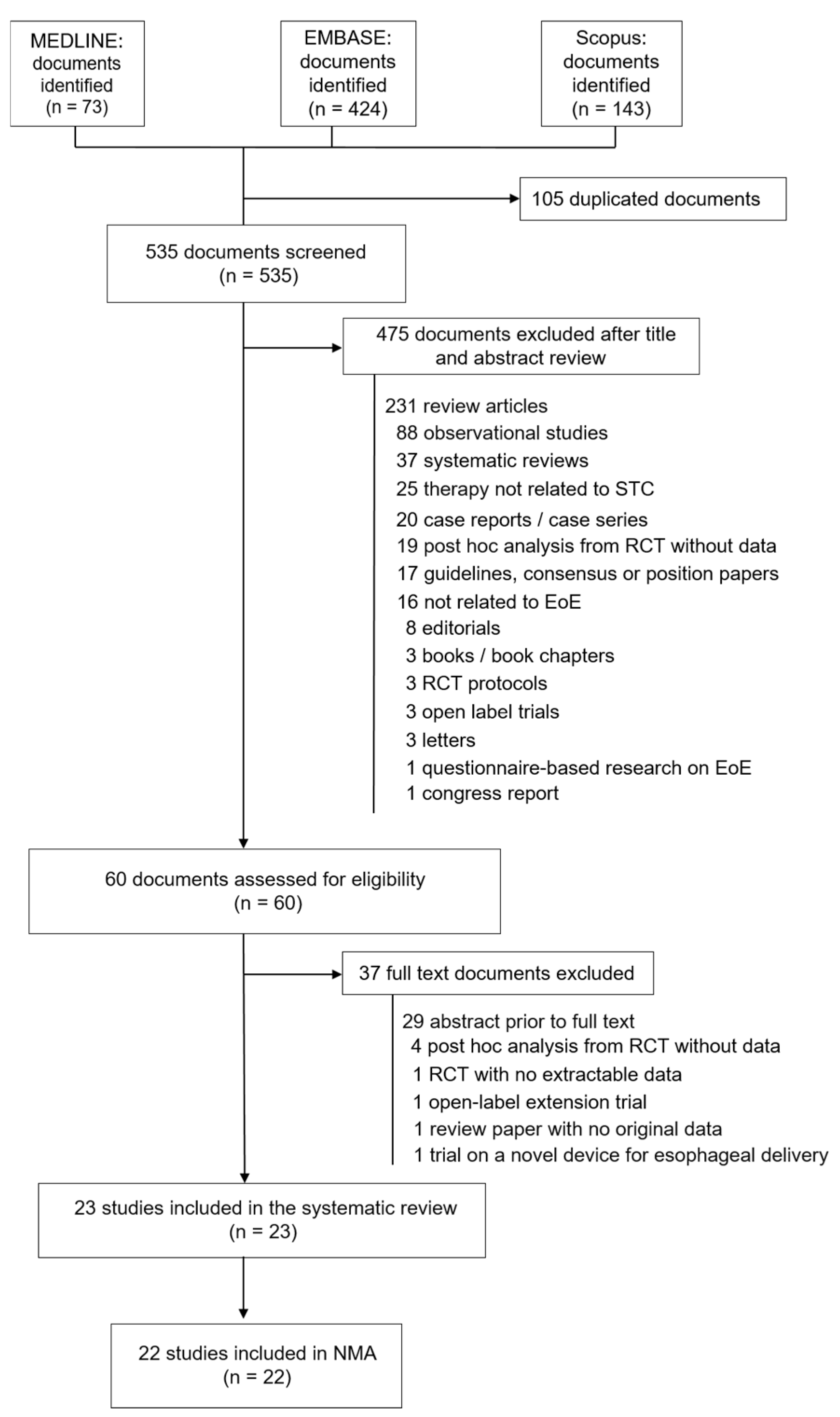
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Definition of Outcome Measures
- -
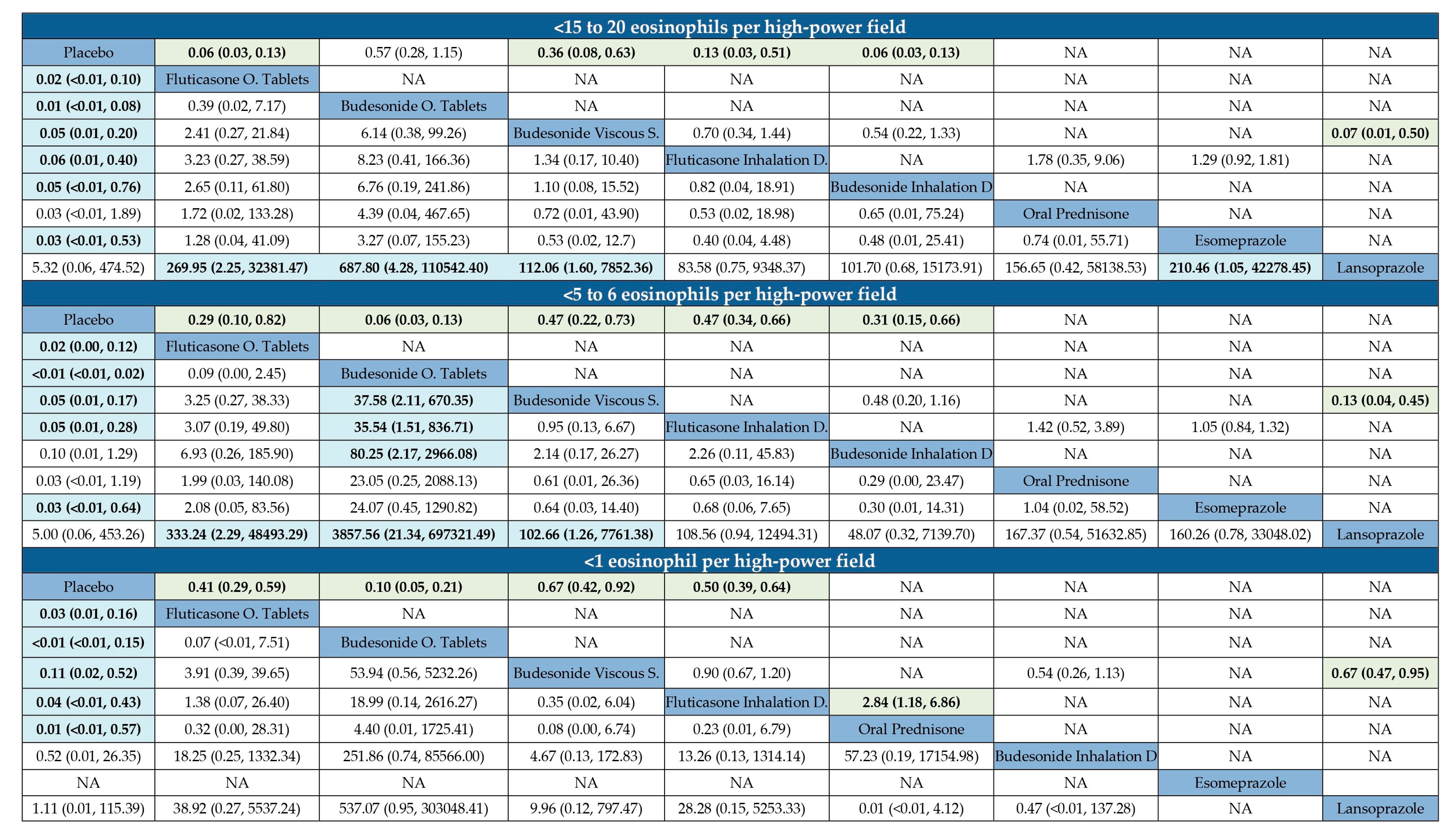
- Histological remission, assessed using several peak cut-off points of eosinophil counts: (a) a peak eosinophil count (PEC) of <15 or <20 eosinophils per high-power field (hpf), which is below the diagnostic infiltration threshold defined for EoE [3,28] and is recommended as the histological remission criterion for regular clinical practice [14]; (b) a PEC of <5 to <6 eos/hpf (histological remission criteria defined by the regulatory European Medicines Agency [EMS] and Food and Drug Administration [FDA] [29], respectively); and (c) the deep histological remission of <1 eos/hpf.
- -
- Clinical improvement, as measured with either validated (the Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ) [30], the EoE activity index (EesAI) [31], or the 2-week or 30-day versions of the Mayo Dysphagia Questionnaire (MDQ) [32,33]) or non-validated scores (Dysphagia Symptom Score or DSS [34], Watson Dysphagia Scale [35], or a 0-to-10 numeric rating scale (NRS)).
- -
- Changes induced by therapy in endoscopic features measured by the eosinophilic esophagitis endoscopic scoring system (EREFS system) [36].
- -
- Histopathological changes in grade (severity) and stage (extent), all measured by the EoE histologic scoring system or EoEHSS [37].
- -
- Quality of life, measured using the EoE-QoL-A questionnaire [38].
- -
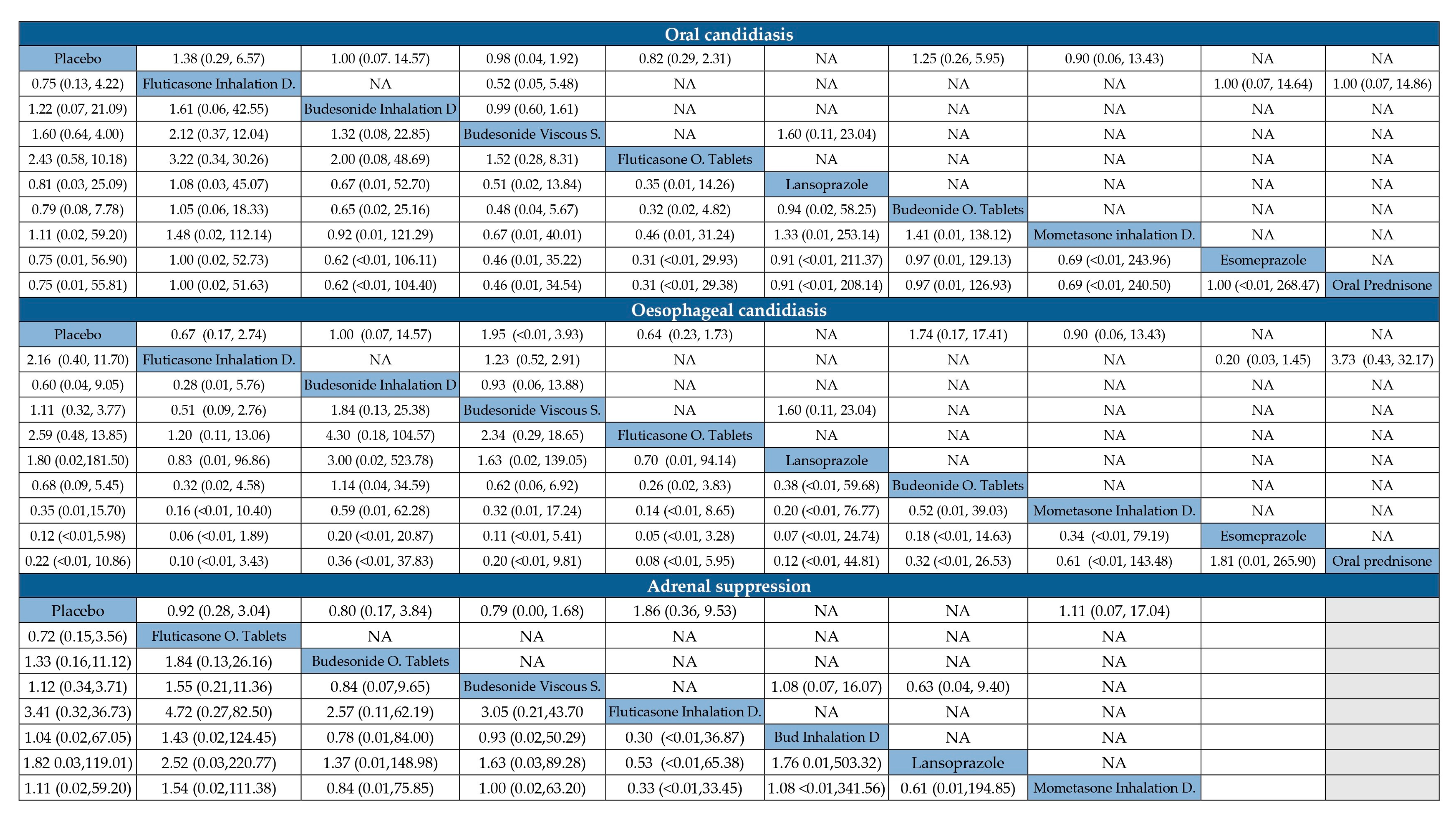
- Adverse events, including oral or pharyngeal candidiasis, esophageal candidiasis, and adrenal suppression.
2.4. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Certainty of Evidence
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Risk of Bias and GRADE
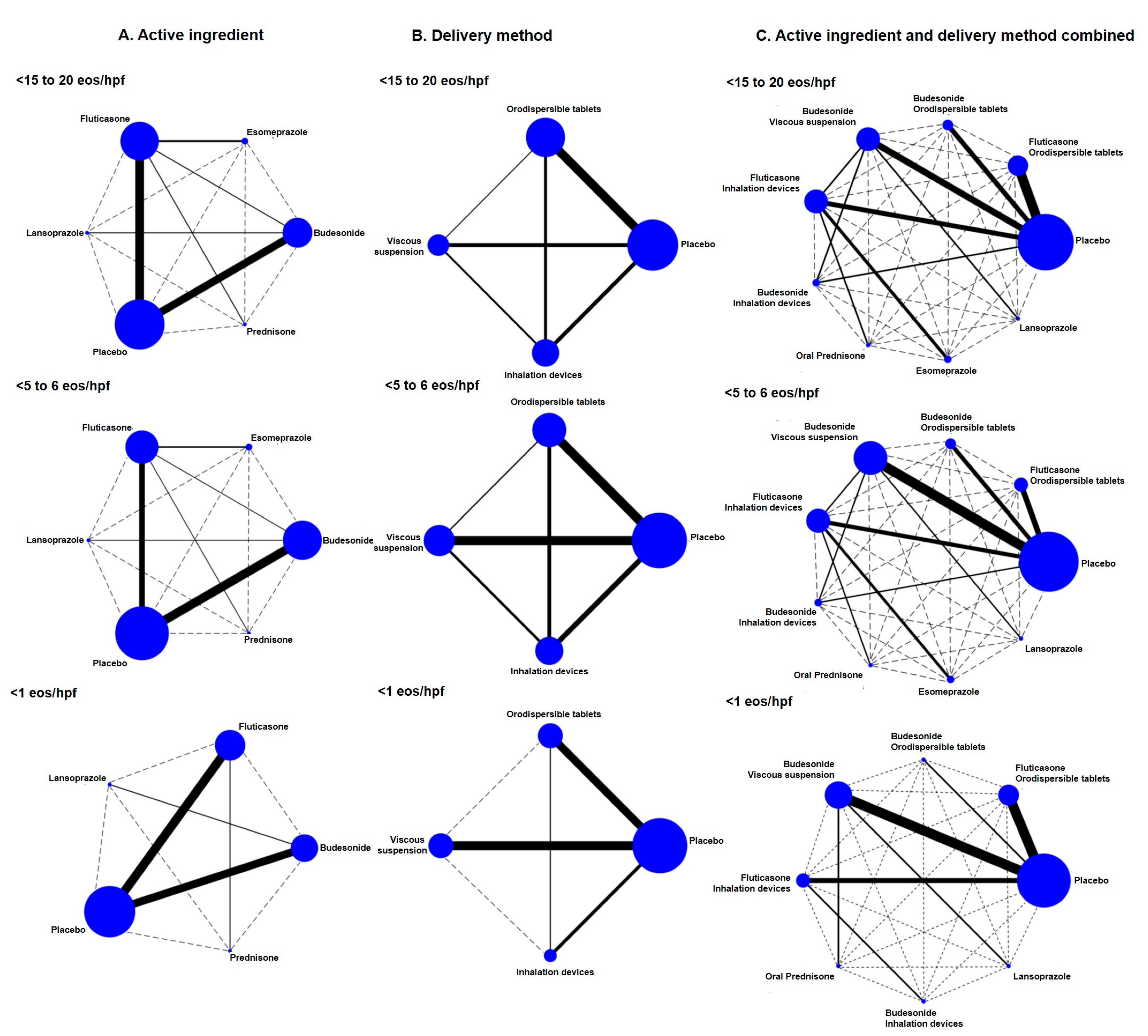
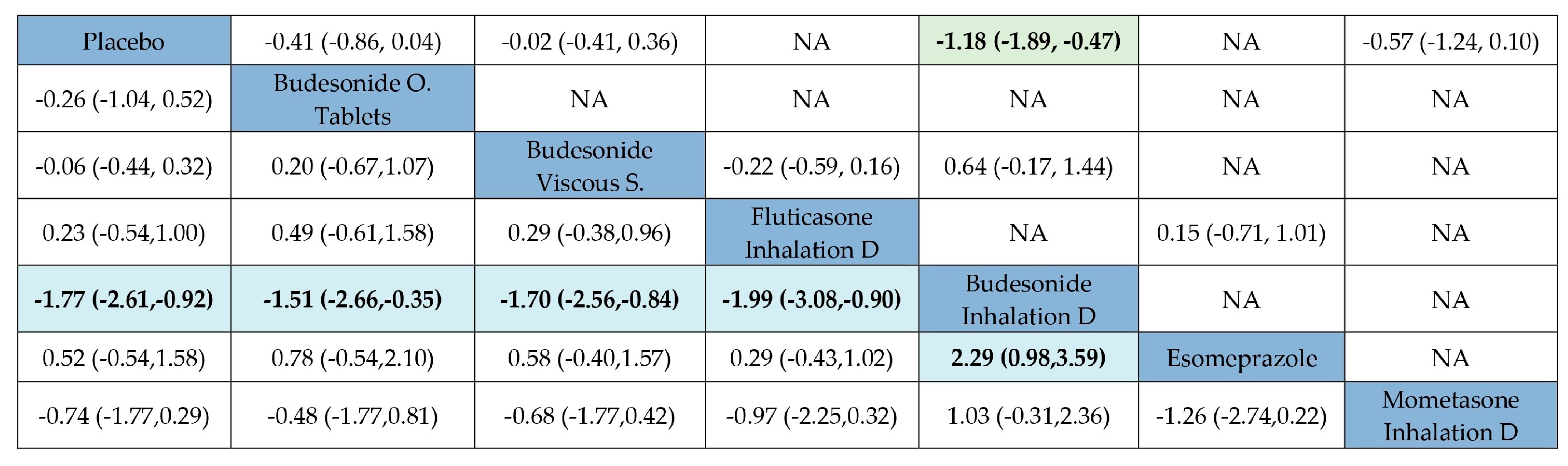
3.3. Failure to Induce Histological Remission in EoE
3.4. Effectiveness to Induce Symptomatic Improvement in EoE
3.5. Failure to Achieve Endoscopic Improvement of Active EoE
3.6. Efficacy According to Rankograms and SUCRA Values
3.7. Adverse Events of Treatment to Induce Active EoE Remission
3.8. Sensitivity Analysis and Publication Bias
3.9. Maintenance of EoE in Remission
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EoE | Eosinophilic esophagitis |
| Eos | eosinophils |
| EREFS | Eosinophilic esophagitis endoscopic scoring system |
| hpf | High-power field |
| NA | Not applicable/Not available |
| NMA | Network meta-analysis |
| MD | Mean differences |
| PEC | Peak eosinophil count |
| PPI | Proton pump inhibitor |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| RR | Risk ratio |
| STC | Swallowed topical corticosteroid |
| SUCRA | Surface under the cumulative ranking curve |
References
- Arias, Á.; Lucendo, A.J. Molecular basis and cellular mechanisms of eosinophilic esophagitis for the clinical practice. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.; Falk, G.W. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, Á.; Von Arnim, U.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Bussmann, C.; Dias, J.A.; Bove, M.; González-Cervera, J.; Larsson, H.; et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: Evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Muir, A.B.; Katzka, D.A.; Shah, S.C.; Sauer, B.G.; Aceves, S.S.; Furuta, G.T.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 120, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhofer, C.; Kavallar, A.M.; Aldrian, D.; Lindner, A.K.; Müller, T.; Vogel, G.F. Efficacy of elimination diets in eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 2197–2210.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J. Dietary therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis: Chances and limitations in the clinical practice. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 14, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Arias, A.; Molina-Infante, J. Efficacy of Proton Pump Inhibitor Drugs for Inducing Clinical and Histologic Remission in Patients With Symptomatic Esophageal Eosinophilia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 13–22.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Casabona, S.; Guagnozzi, D.; Savarino, E.; Perelló, A.; Guardiola-Arévalo, A.; Barrio, J.; Pérez-Martínez, I.; Krarup, A.L.; Alcedo, J.; et al. Efficacy of proton pump inhibitor therapy for eosinophilic oesophagitis in 630 patients: Results from the EoE connect registry. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.-X.; Lu, Y.; Li, T.; Gong, B. A meta-analysis of efficacy of topical steroids in eosinophilic esophagitis: From the perspective of histologic, clinical, and endoscopic outcome. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 44, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Collins, M.H.; Hirano, I.; Chehade, M.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Spergel, J.M.; Aceves, S.; Sun, X.; et al. Dupilumab in Adults and Adolescents with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwood, S.E.; Smyrk, T.C.; Demeester, T.R.; Jones, J.B. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. A distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1993, 38, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Spichtin, H.P.; Bernoulli, R.; Loosli, J.; Vögtlin, J. Idiopathic eosinophilic esophagitis: A frequently overlooked disease with typical clinical aspects and discrete endoscopic findings. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 1994, 124, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J. Eosinophilic oesophagitis: Current evidence-based diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 41, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Dellon, E.S.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Chehade, M.; Collins, M.H.; Feagan, B.G.; Furuta, G.T.; Gupta, S.K.; Hirano, I.; et al. Development of a core outcome set for therapeutic studies in eosinophilic esophagitis (COREOS). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 149, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rank, M.A.; Sharaf, R.N.; Furuta, G.T.; Aceves, S.S.; Greenhawt, M.; Spergel, J.M.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Dellon, E.S.; AGA Institute. Technical review on the management of eosinophilic esophagitis: A report from the AGA institute and the joint task force on allergy-immunology practice parameters. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 124, 424–440.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Navarro, P.; Casabona-Francés, S.; Savarino, E.V.; Amorena, E.; Pérez-Martínez, I.; Guagnozzi, D.; Blas-Jhon, L.; Betoré, E.; Guardiola-Arévalo, A.; et al. Swallowed topical corticosteroids for eosinophilic esophagitis: Utilization and real-world efficacy from the EoE CONNECT registry. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2024, 12, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faubion, W.A.; Perrault, J.; Burgart, L.J.; Zein, N.N.; Clawson, M.; Freese, D.K. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with inhaled corticosteroids. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1998, 27, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamarit-Sebastian, S.; Ferrer-Soler, F.M.; Lucendo, A.J. Current options and investigational drugs for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2022, 31, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Pascual-Turrion, J.M.; Navarro, M.; Comas, C.; Castillo, P.; Letrán, A.; Caballero, M.T.; Larrauri, J. Endoscopic, bioptic, and manometric findings in eosinophilic esophagitis before and after steroid therapy: A case series. Endoscopy 2007, 39, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves, S.S.; Bastian, J.F.; Newbury, R.O.; Dohil, R. Oral viscous budesonide: A potential new therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis in children. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Rubenstein, J.H.; Dellon, E.S.; Worthing, N.; Stefanadis, Z.; Chang, J.W. Variability in Practices of Compounding Budesonide for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 1336–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konikoff, M.R.; Noel, R.J.; Blanchard, C.; Kirby, C.; Jameson, S.C.; Buckmeier, B.K.; Akers, R.; Cohen, M.B.; Collins, M.H.; Assa’ad, A.H.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fluticasone propionate for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipka, S.; Kumar, A.; Miladinovic, B.; Richter, J.E. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: Comparative effectiveness of topical steroids vs. PPIs for the treatment of the spectrum of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokkas, T.; Niv, Y.; Malfertheiner, P. A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials on the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Adults and Children. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 55, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visaggi, P.; Barberio, B.; Del Corso, G.; de Bortoli, N.; Black, C.J.; Ford, A.C.; Savarino, E. Comparison of drugs for active eosinophilic oesophagitis: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Gut 2023, 72, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, T.; Cumpston, M.L.T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3 (Updated February 2022); Cochrane: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dellon, E.S.; Liacouras, C.A.; Molina-Infante, J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.M.; Zevit, N.; Spechler, S.J.; Attwood, S.E.; Straumann, A.; Aceves, S.S.; et al. Updated International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1022–1033.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Developing Drugs for Treatment Guidance for Industry; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020.
- Dellon, E.S.; Irani, A.-M.; Hill, M.R.; Hirano, I. Development and field testing of a novel patient-reported outcome measure of dysphagia in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Straumann, A.; Panczak, R.; Coslovsky, M.; Kuehni, C.E.; Maurer, E.; Haas, N.A.; Romero, Y.; Hirano, I.; Alexander, J.A.; et al. Development and validation of a symptom-based activity index for adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1255–1266.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grudell, A.B.M.; Alexander, J.A.; Enders, F.B.; Pacifico, R.; Fredericksen, M.; Wise, J.L.; Iii, G.R.L.; Arora, A.; Zais, T.; Talley, N.J.; et al. Validation of the Mayo Dysphagia Questionnaire. Dis. Esophagus 2007, 20, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElhiney, J.; Lohse, M.R.; Arora, A.S.; Peloquin, J.M.; Geno, D.M.; Kuntz, M.M.; Enders, F.B.; Fredericksen, M.; Abdalla, A.A.; Khan, Y.; et al. The Mayo Dysphagia Questionnaire-30: Documentation of reliability and validity of a tool for interventional trials in adults with esophageal disease. Dysphagia 2010, 25, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Conus, S.; Degen, L.; Frei, C.; Bussmann, C.; Beglinger, C.; Schoepfer, A.; Simon, H. Long-term budesonide maintenance treatment is partially effective for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 400–409.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albinsson, S.; Tuomi, L.; Wennerås, C.; Larsson, H. Validation of the Swedish Watson Dysphagia Scale for adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dis. Esophagus 2022, 35, doab097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, I.; Moy, N.; Heckman, M.G.; Thomas, C.S.; Gonsalves, N.; Achem, S.R. Endoscopic assessment of the oesophageal features of eosinophilic oesophagitis: Validation of a novel classification and grading system. Gut 2013, 62, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.H.; Martin, L.J.; Alexander, E.S.; Boyd, J.T.; Sheridan, R.; He, H.; Pentiuk, S.; Putnam, P.E.; Abonia, J.P.; Mukkada, V.A.; et al. Newly developed and validated eosinophilic esophagitis histology scoring system and evidence that it outperforms peak eosinophil count for disease diagnosis and monitoring. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taft, T.H.; Kern, E.; Kwiatek, M.A.; Hirano, I.; Gonsalves, N.; Keefer, L. The adult eosinophilic oesophagitis quality of life questionnaire: A new measure of health-related quality of life. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stettler, C.; Allemann, S.; Wandel, S.; Kastrati, A.; Morice, M.C.; Schömig, A.; E Pfisterer, M.; Stone, G.W.; Leon, M.B.; Lezo, J.S.D.; et al. Drug eluting and bare metal stents in people with and without diabetes: Collaborative network meta-analysis. BMJ 2008, 337, a1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Kang, T. Node-Splitting Generalized Linear Mixed Models for Evaluation of Inconsistency in Network Meta-Analysis. Value Health J. Int. Soc. Pharmacoecono. Outcomes Res. 2016, 19, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, B.; Chaimani, A.; Li, T. Network meta-analysis: An introduction for clinicians. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2017, 12, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanti, G.; Ades, A.E. Ioannidis JPA Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: An overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.; Oxman, A.D.; Akl, E.A.; Kunz, R.; Vist, G.; Brozek, J.; Norris, S.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Glasziou, P.; DeBeer, H.; et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction—GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santesso, N.; Glenton, C.; Dahm, P.; Akl, E.A.; Alper, B.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Carrasco-Labra, A.; De Beer, H.; Hultcrantz, M. GRADE guidelines 26: Informative statements to communicate the findings of systematic reviews of interventions. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2020, 119, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, E.T.; Fitzgerald, J.F.; Molleston, J.P.; Croffie, J.M.; Pfefferkorn, M.D.; Corkins, M.R.; Lim, J.D.; Steiner, S.J.; Gupta, S.K. Comparison of oral prednisone and topical fluticasone in the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: A randomized trial in children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohil, R.; Newbury, R.; Fox, L.; Bastian, J.; Aceves, S. Oral viscous budesonide is effective in children with eosinophilic esophagitis in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, K.A.; Thomas, K.L.; Hilden, K.; Emerson, L.L.; Wills, J.C.; Fang, J.C. Comparison of esomeprazole to aerosolized, swallowed fluticasone for eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straumann, A.; Conus, S.; Degen, L.; Felder, S.; Kummer, M.; Engel, H.; Bussmann, C.; Beglinger, C.; Schoepfer, A.; Simon, H. Budesonide is effective in adolescent and adult patients with active eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.A.; Jung, K.W.; Arora, A.S.; Enders, F.; Katzka, D.A.; Kephardt, G.M.; Kita, H.; Kryzer, L.A.; Romero, Y.; Smyrk, T.C.; et al. Swallowed fluticasone improves histologic but not symptomatic response of adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 742–749.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, F.J.; Veerappan, G.R.; Dias, J.A.; Baker, T.P.; Maydonovitch, C.L.; Wong, R.K.H. Randomized controlled trial comparing aerosolized swallowed fluticasone to esomeprazole for esophageal eosinophilia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butz, B.K.; Wen, T.; Gleich, G.J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.; King, E.; Kramer, R.E.; Collins, M.H.; Stucke, E.; Mangeot, C.; et al. Efficacy, dose reduction, and resistance to high-dose fluticasone in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 324–333.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Vitanza, J.M.; Collins, M.H. Efficacy and safety of oral budesonide suspension in pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 66–76.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miehlke, S.; Hruz, P.; Vieth, M.; Bussmann, C.; Von Arnim, U.; Bajbouj, M.; Schlag, C.; Madisch, A.; Fibbe, C.; Wittenburg, H.; et al. A randomised, double-blind trial comparing budesonide formulations and dosages for short-term treatment of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Gut 2016, 65, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Katzka, D.A.; Collins, M.H.; Hamdani, M.; Gupta, S.K.; Hirano, I.; Kagalwalla, A.; Lewis, J.; Markowitz, J.; Nurko, S.; et al. Budesonide Oral Suspension Improves Symptomatic, Endoscopic, and Histologic Parameters Compared With Placebo in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 776–786.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Woosley, J.T.; Arrington, A.; McGee, S.J.; Covington, J.; Moist, S.E.; Gebhart, J.H.; Tylicki, A.E.; Shoyoye, S.O.; Martin, C.F.; et al. Efficacy of Budesonide vs Fluticasone for Initial Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 65–73.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Miehlke, S.; Schlag, C.; Vieth, M.; von Arnim, U.; Molina-Infante, J.; Hartmann, D.; Bredenoord, A.J.; de Los Rios, C.C.; Schubert, S.; et al. Efficacy of Budesonide Orodispersible Tablets as Induction Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis in a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 74–86.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Sheikh, A.; Speck, O.; Woodward, K.; Whitlow, A.B.; Hores, J.M.; Ivanovic, M.; Chau., A.; Woosley, J.T.; Madanick, R.D.; et al. Viscous topical is more effective than nebulized steroid therapy for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 321–324.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytor, J.; Larsson, H.; Bove, M.; Woodward, K.; Whitlow, A.B.; Hores, J.M.; Ivanovic, M.; Chau, A.; Woosley, J.T.; Madanick, R.D.; et al. Topically applied mometasone furoate improves dysphagia in adult eosinophilic esophagitis—Results from a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, I.; Collins, M.H.; Katzka, D.A.; Mukkada, V.A.; Falk, G.W.; Morey, R.; Desai, N.K.; Lan, L.; Williams, J.; Dellon, E.S. Budesonide Oral Suspension Improves Outcomes in Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Results from a Phase 3 Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 525–534.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Antunes, H.; Papadopoulou, A.; Auth, M.K.; Dutt, S.; Escher, J.C.; van Wijk, M.P.; Domínguez-Ortega, G.; Gutiérrez-Junquera, C.; Zevit, N.; et al. 960 Budesonide oral suspension is effective and safe as induction treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adolescents: Results from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled induction phase of a multicenter pediatric trial (PEDEOS-1). Gastroenterology 2024, 166, S-227–S-228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Lucendo, A.J.; Miehlke, S.; Vieth, M.; Schlag, C.; Biedermann, L.; Vaquero, C.S.; de Los Rios, C.C.; Schmoecker, C.; Madisch, A.; et al. Budesonide Orodispersible Tablets Maintain Remission in a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1672–1685.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, I.; Safroneeva, E.; Roumet, M.C.; Comer, G.M.; Eagle, G.; Schoepfer, A.; Falk, G.W. Randomised clinical trial: The safety and tolerability of fluticasone propionate orally disintegrating tablets versus placebo for eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Collins, M.H.; Katzka, D.A.; Mukkada, V.A.; Falk, G.W.; Morey, R.; Goodwin, B.; Eisner, J.D.; Lan, L.; Desai, N.K.; et al. Long-Term Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis with Budesonide Oral Suspension. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1488–1498.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Lucendo, A.J.; Schlag, C.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Falk, G.W.; Eagle, G.; Nezamis, J.; Comer, G.M.; Knoop, K.; Hirano, I. Fluticasone Propionate Orally Disintegrating Tablet (APT-1011) for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 2485–2494.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.H.; Dellon, E.S.; Katzka, D.A.; Hirano, I.; Williams, J.; Lan, L. Budesonide Oral Suspension Significantly Improves Eosinophilic Esophagitis Histology Scoring System Results: Analyses from a 12-Week, Phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, A.R.; Gupta, A.; Attar, B.M.; Ravi, V.; Koduru, P. Topical steroids in eosinophilic esophagitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J. Drug treatment strategies for eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2022, 23, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, I.; Chan, E.S.; Rank, M.A.; Sharaf, R.N.; Stollman, N.H.; Stukus, D.R.; Wang, K.; Greenhawt, M.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Chachu, K.A.; et al. AGA Institute and the Joint Task Force on Allergy-Immunology Practice Parameters Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, H.; Norder Grusell, E.; Tegtmeyer, B.; Ruth, M.; Bergquist, H.; Bove, M. Grade of eosinophilia versus symptoms in patients with dysphagia and esophageal eosinophilia. Dis. Esophagus 2016, 29, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Author, Year | Study Period | Country | Sites | Population | Study Type | N (Male) | Drug | Formulation | Daily Dose | Daily Intakes | Comparator | Treatment Duration | Co-Therapy Allowed * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Konikoff, 2006 [22] | January 2003 to August 2005 | USA | Single center | Children | Induction | 36 (26) | Fluticasone | Metered dose inhaler | 880 mcg | 2 | Placebo | 12 weeks | PPI |
| Schaefer, 2008 [48] | February 2000 to November 2004 | USA | Single center | Children and adolescents | Induction | 80 (59) | Fluticasone | Metered dose inhaler | 800 mcg for ages 1–10 1660 mcg for ages ≥ 11 years | 4 | Prednisone | 4 weeks | No |
| Dohil, 2010 [49] | February 2008 to July 2009 | USA | Single center | Children | Induction | 24 (20) | Budesonide | Oral viscous suspension + lansoprazole | 1 mg or 2 mg | 1 | Placebo + lansoprazole | 12 weeks | PPI |
| Peterson, 2010 [50] | January 2005 to October 2006 | USA | Single center | Adults | Induction | 30 (23) | Fluticasone | Metered dose inhaler | 880 mcg | 2 | Esomeprazole | 8 weeks | No |
| Straumann, 2010 [51] | May 2006 to April 2007 | Switzerland | Single center | Children and adults | Induction | 36 (31) | Budesonide | Metered dose inhaler | 2 mg | 2 | Placebo | 2 weeks | PPI |
| Straumann, 2011 [34] | June 2006 to May 2007 | Switzerland | Single center | Children and adults | Maintenance | 28 (24) | Budesonide | Metered dose inhaler | 0.5 mg | 2 | Placebo | 50 weeks | PPI |
| Alexander, 2012 [52] | October 2005 to December 2009 | USA | Single center | Adults | Induction | 42 (30) | Fluticasone | Metered dose inhaler | 1760 mcg | 2 | Placebo | 6 weeks | PPI |
| Dellon, 2012 [60] | March 2010 to May 2011 | USA | Single center | Children | Induction | 25 (15) | Budesonide | Oral viscous suspension | 2 mg | 2 | Budesonide metered dose inhaler | 8 weeks | NA |
| Moawad, 2013 [53] | April 2008 to October 2010 | USA | Single center | Adults | Induction | 42 (38) | Fluticasone | Metered dose inhaler | 880 mcg | 2 | Esomeprazole | 8 weeks | PPI |
| Butz, 2014 [54] | December 2006 | USA | Multicenter | Children and adults | Induction | 42 (35) | Fluticasone | Metered dose inhaler | 1760 mcg | 2 | Placebo | 12 weeks | PPI |
| Gupta, 2015 [55] | NA | USA | Multicenter | Children | Induction | 71 (57) | Budesonide | Oral viscous suspension | 0.35 to 0.5 mg | 1 | Placebo | 12 weeks | PPI |
| 1.4 to 2 mg | 1 | Placebo | |||||||||||
| 2.8 to 4 mg | 2 | Placebo | |||||||||||
| Miehlke, 2016 [56] | June 2011 to April 2013 | 3 European countries | Multicenter | Adults | Induction | 76 (63) | Budesonide | Orodispersible tablets | 2 mg | 2 | Placebo | 2 weeks | PPI |
| Orodispersible tables | 4 mg | 2 | |||||||||||
| Oral viscous | 4 mg | 2 | |||||||||||
| Dellon, 2017 [57] | July 2012 to October 2014 | USA | Multicenter | Children and adults | Induction | 93 (64) | Budesonide | Oral viscous suspension | 4 mg | 2 | Placebo | 12 weeks | PPI |
| Dellon, 2019 [58] | 2014 to 2018 | USA | Single-center | Adults | Induction | 111 (74) | Budesonide/ Fluticasone | Oral viscous suspension | 2 mg | 2 | Fluticasone | 8 weeks | PPI |
| Collins, 2019 [68] | NA | USA | Multicenter | Children and adolescents | Induction | 93 | Budesonide | Oral viscous suspension | 2 mg | 2 | Placebo | 24 weeks | PPI |
| Lucendo, 2019 [59] | November 2015 to October 2016 | Six European Countries | Multicenter | Adults | Induction | 88 (70) | Budesonide | Orodispersible tablets | 2 mg | 2 | Placebo | 6 weeks | PPI |
| Hirano, 2020 [65] | October 2011 to October 2012 | USA | Multicenter | Children and adults | Induction | 24 (15) | Fluticasone | Orodispersible tablets | 1.5 mg | 2 | Placebo | 8 weeks | PPI |
| 3 mg | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Straumann, 2020 [64] | 2016 to 2019 | Six European Countries | Multicenter | Adults | Maintenance | 204 (169) | Budesonide | Orodispersible tablet | 1 mg | 2 | Placebo | 48 weeks | PPI |
| 2 mg | |||||||||||||
| Tytor et al. 2021 [61] | April 2014 to August 2019 | Sweden | Multicenter | Adults | Induction | 36 (33) | Mometasone | Metered dose inhaler | 800 mcg | 4 | Placebo | 8 weeks | NA |
| Hirano, 2022 [63] | 2015 to 2019 | USA | Multicenter | Children and adults | Induction | 318 | Budesonide | Oral Viscous suspension | 4 mg | 2 | Placebo | 12 weeks | PPI |
| Dellon, 2022 [66] | May 2017 to August 2018 | USA, Canada, 4 European countries | Multicenter | Adults | Induction | 103 (70) | Fluticasone | Orodispersible tablets | 6 mg | 2 | Placebo | 14 weeks | PPI |
| 3 mg | 1 | ||||||||||||
| 3 mg | 2 | ||||||||||||
| 1.5 mg | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Dellon et al. 2022 [69] | 2016 to 2019 | USA | Multicenter | Children and adults | Maintenance | 48 (30) | Budesonide | Oral viscous suspension | 4 mg | 2 | Placebo | 36 weeks | PPI |
| Lucendo et al. 2024 [63] | 2019 to 2022 | 8 European countries and Turkey | Multicenter | Children and adolescents | Induction | 100 (76) | Budesonide | Oral viscous suspension | 0.5 mg | 1 | Placebo | 12 weeks | PPI |
| 1 mg | 2 | ||||||||||||
| 1 mg | 1 | ||||||||||||
| 2 mg | 2 |
| <15 to 20 Eosinophils per High-Power Field | |||||
| Rank Statistics | Probabilities | ||||
| Mean | Median | 95% CIs | Best | SUCRA | |
| Budesonide orodispersible tablets | 2.0 | 7.0 | 1.0–9.0 | 0.52 | 0.88 |
| Fluticasone orodispersible tablets | 3.0 | 6.0 | 1.0–8.0 | 0.13 | 0.75 |
| Oral prednisone | 4.2 | 3.0 | 2.0–6.0 | 0.16 | 0.60 |
| Esomeprazole | 3.6 | 4.0 | 2.0–5.0 | 0.14 | 0.67 |
| Budesonide inhalation devices | 4.9 | 4.0 | 1.0–5.0 | 0.05 | 0.51 |
| Budesonide viscous suspension | 5.2 | 6.0 | 2.0–7.0 | 0.01 | 0.48 |
| Fluticasone inhalation devices | 5.3 | 6.0 | 1.0–7.0 | 0.00 | 0.47 |
| Placebo | 8.1 | 9.0 | 1.0–9.0 | 0.00 | 0.11 |
| Lansoprazole | 8.7 | 8.0 | 1.0–8.0 | 0.00 | 0.04 |
| <5 to 6 Eosinophils per High-Power Field | |||||
| Rank Statistics | Probabilities | ||||
| Mean | Median | 95% CIs | Best | SUCRA | |
| Budesonide orodispersible tablets | 1.2 | 7.0 | 1.0–9.0 | 0.85 | 0.97 |
| Fluticasone orodispersible tablets | 3.0 | 6.0 | 1.0–7.0 | 0.06 | 0.75 |
| Oral prednisone | 4.1 | 4.0 | 2.0–5.0 | 0.06 | 0.61 |
| Esomeprazole | 4.1 | 4.0 | 2.0–5.0 | 0.04 | 0.61 |
| Fluticasone inhalation devices | 4.7 | 5.0 | 1.0–6.0 | 0.00 | 0.53 |
| Budesonide viscous suspension | 5.1 | 5.0 | 1.0–7.0 | 0.00 | 0.49 |
| Budesonide inhalation devices | 5.9 | 4.0 | 1.0–6.0 | 0.00 | 0.39 |
| Placebo | 8.1 | 8.0 | 1.0–9.0 | 0.00 | 0.11 |
| <1 Eosinophil per High-Power Field | |||||
| Rank Statistics | Probabilities | ||||
| Mean | Median | 95% CIs | Best | SUCRA | |
| Budesonide orodispersible tablets | 1.6 | 5.0 | 1.0–8.0 | 0.67 | 0.92 |
| Oral prednisone | 2.3 | 4.0 | 1.0–6.0 | 0.27 | 0.81 |
| Fluticasone orodispersible tablets | 3.1 | 4.0 | 1.0–7.0 | 0.04 | 0.69 |
| Fluticasone inhalation devices | 3.6 | 4.0 | 1.0–6.0 | 0.01 | 0.63 |
| Budesonide viscous suspension | 5.1 | 4.0 | 1.0–7.0 | 0.00 | 0.42 |
| Budesonide inhalation devices | 6.5 | 4.0 | 2.0–6.0 | 0.00 | 0.22 |
| Placebo | 6.9 | 7.5 | 1.0–8.0 | 0.00 | 0.16 |
| Lansoprazole | 6.9 | 5.0 | 1.0–7.0 | 0.00 | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucendo, A.J.; Arias, Á.; Álvarez-Bueno, C.; Martínez-Vizcaino, V.; Redondo-Cavero, I., on behalf of the EUREOS EoE Guidelines Committee. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Swallowed Topical Corticosteroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Network Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7823. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217823
Lucendo AJ, Arias Á, Álvarez-Bueno C, Martínez-Vizcaino V, Redondo-Cavero I on behalf of the EUREOS EoE Guidelines Committee. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Swallowed Topical Corticosteroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Network Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7823. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217823
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucendo, Alfredo J., Ángel Arias, Celia Álvarez-Bueno, Vicente Martínez-Vizcaino, and Iván Redondo-Cavero on behalf of the EUREOS EoE Guidelines Committee. 2025. "Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Swallowed Topical Corticosteroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Network Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7823. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217823
APA StyleLucendo, A. J., Arias, Á., Álvarez-Bueno, C., Martínez-Vizcaino, V., & Redondo-Cavero, I., on behalf of the EUREOS EoE Guidelines Committee. (2025). Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Swallowed Topical Corticosteroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Network Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7823. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217823









