Targeted Endogenous Bioelectric Modulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Real-World Clinical Outcomes of the REAC BWO Neurodevelopment–Autism Protocol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of REAC Technology and BWO ND-A Protocol
2.2. Relation to Other REAC Neurobiological Modulation Protocols
2.3. Study Design and Setting
2.4. Participants
2.5. Intervention
2.6. Outcome Measures
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Outcomes by Age Group
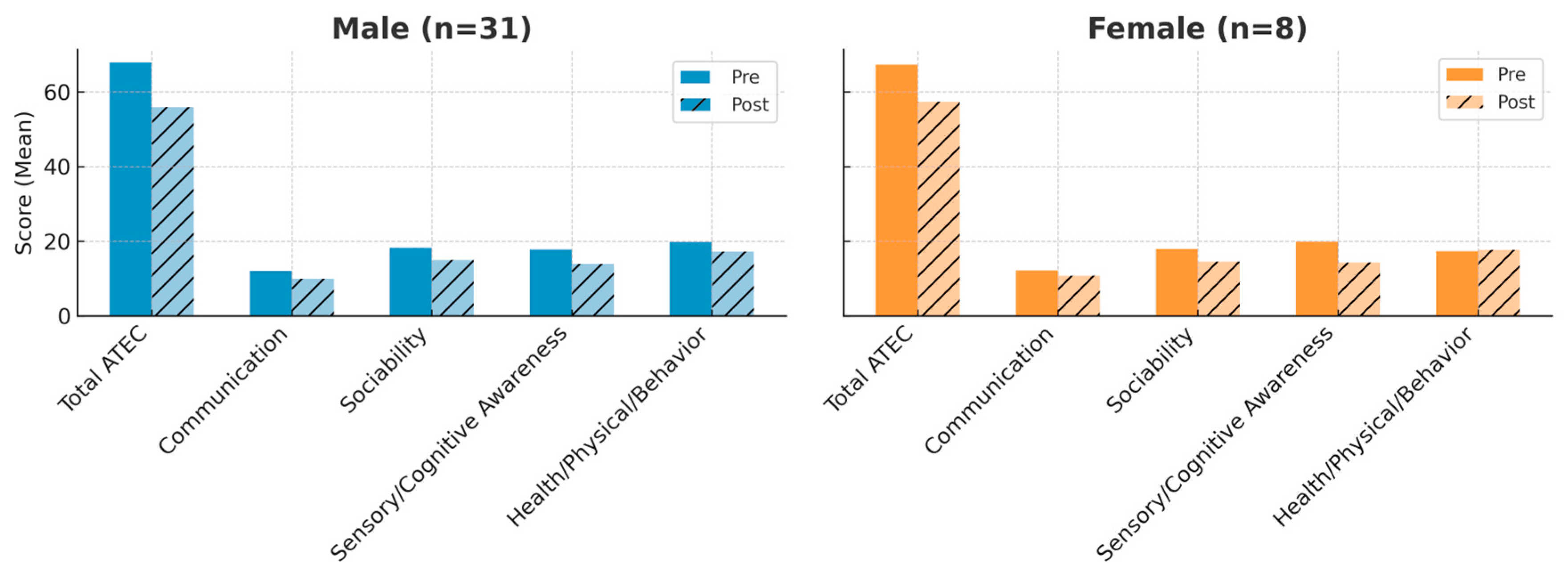
3.2. Outcomes by Sex
3.3. Clinical Observations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodges, H.; Fealko, C.; Soares, N. Autism spectrum disorder: Definition, epidemiology, causes, and clinical evaluation. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9, S55–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobrega, I.S.; Teles, E.S.A.L.; Yokota-Moreno, B.Y.; Sertie, A.L. The Importance of Large-Scale Genomic Studies to Unravel Genetic Risk Factors for Autism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talantseva, O.I.; Romanova, R.S.; Shurdova, E.M.; Dolgorukova, T.A.; Sologub, P.S.; Titova, O.S.; Kleeva, D.F.; Grigorenko, E.L. The global prevalence of autism spectrum disorder: A three-level meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1071181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dückert, S.; Gewohn, P.; König, H.; Schöttle, D.; Konnopka, A.; Rahlff, P.; Vogeley, K.; Schulz, H.; David, N.; Peth, J. Multidimensional Burden on Family Caregivers of Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Scoping Review. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.P.P.; Lau, B.W.M. Neurobiology of sensory processing in autism spectrum disorder. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 173, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, C.; Smith, E.S.; Lawson, R.P. A meta-analysis of cognitive flexibility in autism spectrum disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 157, 105511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restoy, D.; Oriol-Escude, M.; Alonzo-Castillo, T.; Magan-Maganto, M.; Canal-Bedia, R.; Diez-Villoria, E.; Gisbert-Gustemps, L.; Setien-Ramos, I.; Martinez-Ramirez, M.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A.; et al. Emotion regulation and emotion dysregulation in children and adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A meta-analysis of evaluation and intervention studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2024, 109, 102410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holanda, M.V.F.; Paiva, E.D.S.; de Souza, L.N.; Paiva, K.M.; Oliveira, R.F.; Tavares, E.A.F.; Morais, P.; de Andrade, A.M.; Knackfuss, M.I.; do Nascimento, E.G.C.; et al. Neurobiological basis of autism spectrum disorder: Mini review. Front. Psychol. 2025, 16, 1558081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monica, I.; Di Iorio, M.R.; Sica, A.; Rufino, F.; Sotira, C.; Pastore, L.; Lombardo, B. Autism Spectrum Disorder: Genetic Mechanisms and Inheritance Patterns. Genes 2025, 16, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuman, A.S.; van den Honert, R.N.; Huppert, T.J.; Wallace, G.L.; Martin, A. Aberrant Oscillatory Synchrony Is Biased Toward Specific Frequencies and Processing Domains in the Autistic Brain. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2017, 2, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Y.; Zhang, H.; Du, L.; Deng, Z. Abnormalities of brain dynamics based on large-scale cortical network modeling in autism spectrum disorder. Neural Netw. 2025, 189, 107561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximo, J.O.; Kana, R.K. Aberrant “deep connectivity” in autism: A cortico-subcortical functional connectivity magnetic resonance imaging study. Autism Res. 2019, 12, 384–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, X.H.; Han, Y. Aberrant dynamic and static functional connectivity of the striatum across specific low-frequency bands in patients with autism spectrum disorder. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2023, 336, 111749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez-Burraco, A.; Murphy, E. The Oscillopathic Nature of Language Deficits in Autism: From Genes to Language Evolution. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprunowicz, M.; Bogucka, J.; Szczerbinska, N.; Modzelewski, S.; Oracz, A.J.; Konarzewska, B.; Waszkiewicz, N. Neuroplasticity-Based Approaches to Sensory Processing Alterations in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, R.A.; Rippon, G.; Gooding-Williams, G.; Schoffelen, J.M.; Kessler, K. Dysregulated oscillatory connectivity in the visual system in autism spectrum disorder. Brain 2019, 142, 3294–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.M.; Wallace, M.T. Dysfunction of sensory oscillations in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, N.; Sarajlija, A. Neuroglial Dysregulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Pathogenetic Insights, Genetic Threads, and Therapeutic Horizons. Neuroglia 2025, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wang, H.; Ning, W.; Cui, M.; Wang, Q. New advances in the diagnosis and treatment of autism spectrum disorders. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishworiya, R.; Valica, T.; Hagerman, R.; Restrepo, B. An Update on Psychopharmacological Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Maioli, M.; Marins Martins, M.C.; de Castro, P.C.F.; de Oliveira Silva, N.A.P.; de Mattos, J.A.V.; Fontani, V.; Rinaldi, S. REAC Non-invasive Neurobiological Stimulation for Mitigating the Impact of Internalizing Disorders in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Adv. Neurodev. Disord. 2021, 5, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre Nogueira, J.A.; Souza Bulle Oliveira, A.; Pereira Motta, M.; Vieira de Souza Moscardi, A.A.; Manchim Favaro, V.; Munhoz Teixeira, C.; Orasmo Simcsik, A.; Patrizi, M.C.; Conde, M.S.; Rinaldi, A.; et al. Neurobiological modulation with REAC technology: Enhancing pain, depression, anxiety, stress, and quality of life in post-polio syndrome subjects. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, S.; Mura, M.; Castagna, A.; Fontani, V. Long-lasting changes in brain activation induced by a single REAC technology pulse in Wi-Fi bands. Randomized double-blind fMRI qualitative study. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, S.; Oliveira, A.S.; Modestto, V.; Rinaldi, A.; Fontani, V. Functional Brain Reorganization After Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyer (REAC) Brain Wave Optimization Gamma (BWO-G) Neuromodulation in Individuals With Chronic Stress Exposure: A Retrospective Case Series With Multimodal Evaluation. Cureus 2025, 17, e90951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippo, A.G.; Rinaldi, S.; Pellegata, G.; Caramenti, G.C.; Valente, M.; Fontani, V.; Biella, G.E. Electrophysiological effects of non-invasive Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyor (REAC) on thalamocortical neural activities and perturbed experimental conditions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, L.; Giuliani, A.; Sivilia, S.; Baldassarro, V.A.; Fernandez, M.; Lotti Margotti, M.; Giardino, L.; Fontani, V.; Rinaldi, S.; Calza, L. REAC technology modifies pathological neuroinflammation and motor behaviour in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaro, M.A.; Aloisi, A.; Nicolardi, G.; Lofrumento, D.D.; De Nuccio, F.; La Pesa, V.; Cianciulli, A.; Rinaldi, R.; Calvello, R.; Fontani, V.; et al. Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyer Technology Modulates Neuroinflammation in a Mouse Model of Neurodegeneration. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesto, V.; Rinaldi, A.; Fontani, V.; Rinaldi, S. Non-invasive Gamma Brain Wave Optimization (BWO-G) for Cognitive and Emotional Recovery in an Adolescent: A Case Study on Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyer (REAC) Neuro Psycho Physical Optimization (NPPO) BWO-G Treatment. Cureus 2024, 16, e72819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro Barcessat, A.R.; Nolli Bittencourt, M.; Goes Goncalves, R.; Goncalves de Oliveira Cruz, A.V.; Coelho Pereira, J.A.; Bechelli, F.A.; Rinaldi, A. REAC Neuromodulation Treatments in Depression, Anxiety and Stress. A Comparative Retrospective Study. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2020, 13, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves de Oliveira Cruz, A.V.; Goes Goncalves, R.; Nunes, L.; Douglas Quaresma de Oliveira, J.; Lima Monteiro, E.S.; Soares Eneias, I.; Guilherme Lima, T.C.; Duarte Ferreira, L.; Souza Neri, E.; da Cunha Pena, J.L.; et al. Neuro Postural Optimization Neuromodulation Treatment of Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyer Technology on Stress and Quality of Life in Institutionalized Children in a Capital City of the Brazilian Amazon. Cureus 2022, 14, e26550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira Motta, M.; Oliveira, A.S.B.; Andre Nogueira, J.A.; Vieira de Souza Moscardi, A.A.; Munhoz Teixeira, C.; Manchim Favaro, V.; Simcsik, A.O.; Conde, S.; Patrizi, M.C.; Rinaldi, C.; et al. Improving Strength and Fatigue Resistance in Post-Polio Syndrome Individuals with REAC Neurobiological Treatments. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, C.; Landre, C.B.; Volpe, M.I.; Goncalves, R.G.; Nunes, L.D.S.; Darienso, D.; Cruz, A.V.; Oliveira, J.D.; Rinaldi, S.; Fontani, V.; et al. Improving Functional Capacity and Quality of Life in Parkinson’s Disease Patients through REAC Neuromodulation Treatments for Mood and Behavioral Disorders. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Marins Martins, M.C.; De Almeida Martins Oliveira, A.C.; Rinaldi, S.; Fontani, V. Improving Functional Abilities in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Non-Invasive REAC Neuro Psycho Physical Optimization Treatments: A PEDI-CAT Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Martins, M.C.M.; Maioli, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Fontani, V. REAC Noninvasive Neurobiological Stimulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder for Alleviating Stress Impact. Adv. Neurodev. Disord. 2023, 7, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontani, V.; Cruciani, S.; Santaniello, S.; Rinaldi, S.; Maioli, M. Impact of REAC Regenerative Endogenous Bioelectrical Cell Reprogramming on MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikova, A.V.; Portnova, G.V.; Martynova, O.V. Brain oscillatory patterns of affective prosody perception in children with autism spectrum disorder. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2022, 96, 101993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrain-Valenzuela, J.; Zamorano, F.; Soto-Icaza, P.; Carrasco, X.; Herrera, C.; Daiber, F.; Aboitiz, F.; Billeke, P. Theta and Alpha Oscillation Impairments in Autistic Spectrum Disorder Reflect Working Memory Deficit. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Icaza, P.; Soto-Fernandez, P.; Kausel, L.; Marquez-Rodriguez, V.; Carvajal-Paredes, P.; Martinez-Molina, M.P.; Figueroa-Vargas, A.; Billeke, P. Oscillatory activity underlying cognitive performance in children and adolescents with autism: A systematic review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1320761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, K.; Seymour, R.A.; Rippon, G. Brain oscillations and connectivity in autism spectrum disorders (ASD): New approaches to methodology, measurement and modelling. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro Barcessat, A.R.; Nolli Bittencourt, M.; Duarte Ferreira, L.; de Souza Neri, E.; Coelho Pereira, J.A.; Bechelli, F.; Rinaldi, A. REAC Cervicobrachial Neuromodulation Treatment of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2020, 13, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontani, V.; Rinaldi, A.; Rinaldi, C.; Araldi, L.; Azzara, A.; Carta, A.M.; Casale, N.; Castagna, A.; Del Medico, M.; Di Stasio, M.; et al. Long-Lasting Efficacy of Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyer Neuromodulation Treatment on Functional Dysmetria, an Adaptive Motor Behavior. Cureus 2022, 14, e25768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.; Vyshedsky, D.; Martinez, S.; Kannel, B.; Braverman, J.; Edelson, S.M.; Vyshedskiy, A. Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC) Norms: A “Growth Chart” for ATEC Score Changes as a Function of Age. Children 2018, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, S.; Khokhlovich, E.; Martinez, S.; Kannel, B.; Edelson, S.M.; Vyshedskiy, A. Longitudinal Epidemiological Study of Autism Subgroups Using Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC) Score. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2020, 50, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netson, R.; Schmiedel Fucks, A.; Schmiedel Sanches Santos, A.; Poloni, L.E.P.; Nacano, N.N.; Fucks, E.; Radi, K.; Strong, W.E.; Carnaval, A.A.; Russo, M.; et al. A Comparison of Parent Reports, the Mental Synthesis Evaluation Checklist (MSEC) and the Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC), with the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS). Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Feinn, R. Using Effect Size—Or Why the P Value Is Not Enough. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posserud, M.B.; Skretting Solberg, B.; Engeland, A.; Haavik, J.; Klungsoyr, K. Male to female ratios in autism spectrum disorders by age, intellectual disability and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2021, 144, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, B.; Lloyd-Fox, S.; Begum-Ali, J.; Pirazzoli, L.; Goodwin, A.; Mason, L.; Pasco, G.; Charman, T.; Jones, E.J.H.; Johnson, M.H.; et al. Cortical responses to social stimuli in infants at elevated likelihood of ASD and/or ADHD: A prospective cross-condition fNIRS study. Cortex 2023, 169, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochaut, D.; Lehongre, K.; Saitovitch, A.; Devauchelle, A.D.; Olasagasti, I.; Chabane, N.; Zilbovicius, M.; Giraud, A.L. Atypical coordination of cortical oscillations in response to speech in autism. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, S.; Lugo-Marin, J.; Setien-Ramos, I.; Gisbert-Gustemps, L.; Arteaga-Henriquez, G.; Diez-Villoria, E.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A. Transcranial direct current stimulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 48, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, P.; Wang, Y. Assessing the impact of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on effective connectivity in autism spectrum disorder: An initial exploration using TMS-EEG analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.B.; Lin, H.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Hung, K.C.; Brunoni, A.R.; Chou, P.H.; Tseng, P.T.; Liang, C.S.; Tu, Y.K.; Lin, P.Y.; et al. A network meta-analysis of non-invasive brain stimulation interventions for autism spectrum disorder: Evidence from randomized controlled trials. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 164, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grefkes, C.; Fink, G.R. Recovery from stroke: Current concepts and future perspectives. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Areas, F.; Cordeiro, B.N.L.; Paiva, W.S. Neuromodulation in acute traumatic brain injury: A tool in the rehabilitation process that needs to be investigated. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2022, 140, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.M.Y.; Choi, C.X.T.; Tsoi, T.C.W.; Shea, C.K.S.; Yiu, K.W.K.; Han, Y.M.Y. Effects of multisession cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation with cognitive training on sociocognitive functioning and brain dynamics in autism: A double-blind, sham-controlled, randomized EEG study. Brain Stimul. 2023, 16, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | N (%)/Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Male | 31 (77.5%) |
| Female | 8 (22.5%) |
| Age (years) | 7.85 ± 2.90 (range 4–13) |
| Domain | Pre-Treatment Mean ± SD | Post-Treatment Mean ± SD | Mean Change ± SD | 95% CI Change | t (df = 38) | p-Value | Cohen’s dz (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
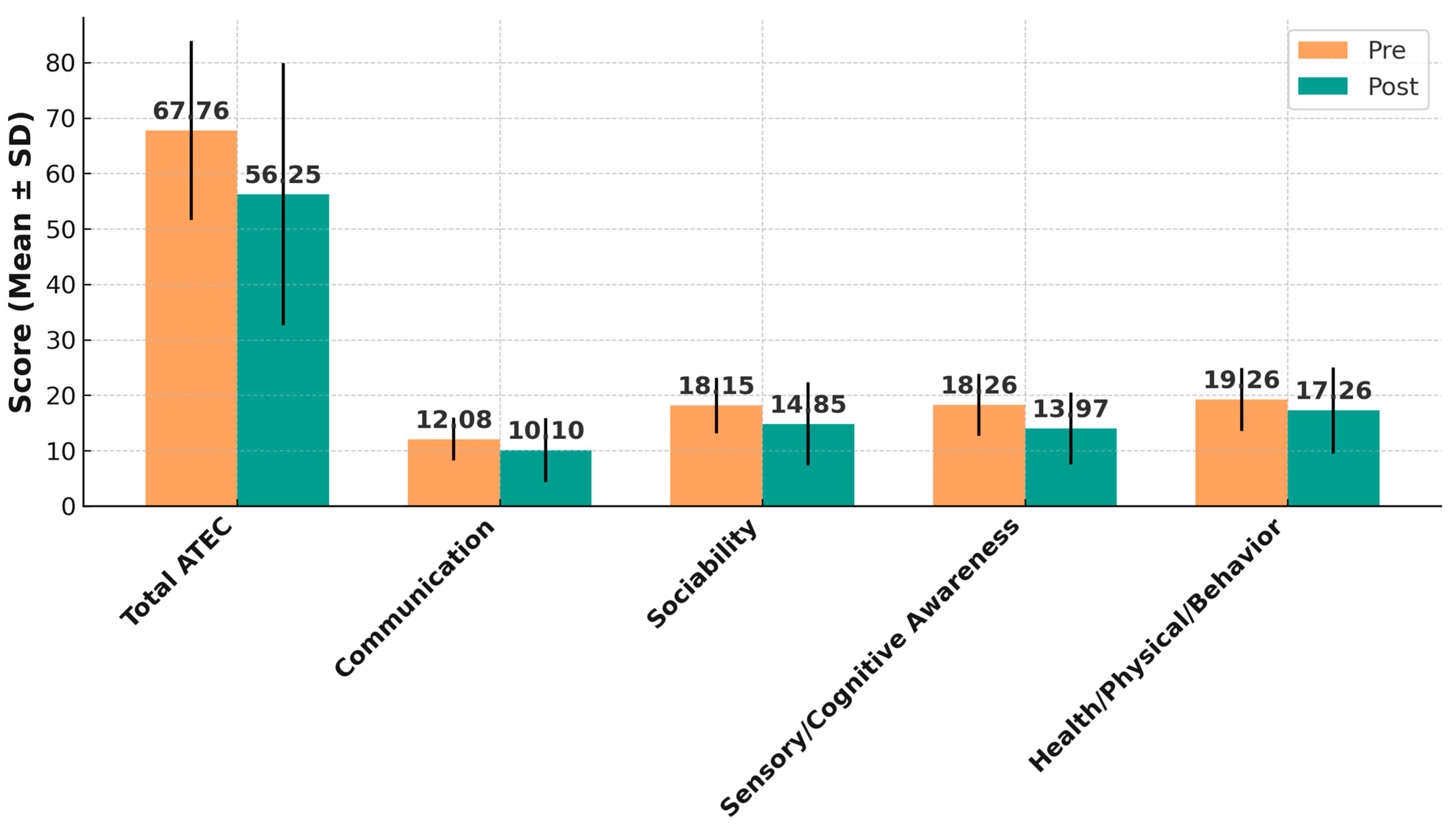
| Total ATEC | 67.76 ± 16.11 | 56.25 ± 23.66 | 11.51 ± 14.48 | 6.98 to 16.03 | 4.90 | <0.0001 | 0.78 (0.43–1.11) |
| Communication | 12.08 ± 3.86 | 10.10 ± 5.74 | 1.97 ± 5.10 | 0.33 to 3.60 | 2.40 | 0.021 | 0.38 (0.06–0.69) |
| Sociability | 18.15 ± 5.01 | 14.85 ± 7.51 | 3.31 ± 6.48 | 1.19 to 5.43 | 3.15 | 0.0032 | 0.50 (0.17–0.82) |
| Sensory/Cognitive Awareness | 18.26 ± 5.56 | 13.97 ± 6.48 | 4.28 ± 6.23 | 2.25 to 6.31 | 4.24 | 0.00014 | 0.68 (0.33–1.02) |
| Health/Physical/Behavior | 19.26 ± 5.70 | 17.26 ± 7.75 | 2.00 ± 5.71 | 0.14 to 3.86 | 2.17 | 0.036 | 0.35 (0.03–0.66) |
| Category | n | % | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinically significant improvement (≥8 points) | 23 | 59.0 | 42.1–74.4 |
| No clinically relevant change (<8 points) | 12 | 30.8 | 17.0–47.6 |
| Clinically significant worsening (≥8 points increase) | 4 | 10.3 | 3.3–25.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rinaldi, A.; Benetti Mota, H.A.; Rinaldi, S.; Fontani, V. Targeted Endogenous Bioelectric Modulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Real-World Clinical Outcomes of the REAC BWO Neurodevelopment–Autism Protocol. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7500. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217500
Rinaldi A, Benetti Mota HA, Rinaldi S, Fontani V. Targeted Endogenous Bioelectric Modulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Real-World Clinical Outcomes of the REAC BWO Neurodevelopment–Autism Protocol. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7500. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217500
Chicago/Turabian StyleRinaldi, Arianna, Hingrid Angélica Benetti Mota, Salvatore Rinaldi, and Vania Fontani. 2025. "Targeted Endogenous Bioelectric Modulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Real-World Clinical Outcomes of the REAC BWO Neurodevelopment–Autism Protocol" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7500. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217500
APA StyleRinaldi, A., Benetti Mota, H. A., Rinaldi, S., & Fontani, V. (2025). Targeted Endogenous Bioelectric Modulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Real-World Clinical Outcomes of the REAC BWO Neurodevelopment–Autism Protocol. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7500. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217500








