Hematologic Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Clinical Features and Prognostic Implications in a Hematology-Referred Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Data Collection
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Statistical Analysis
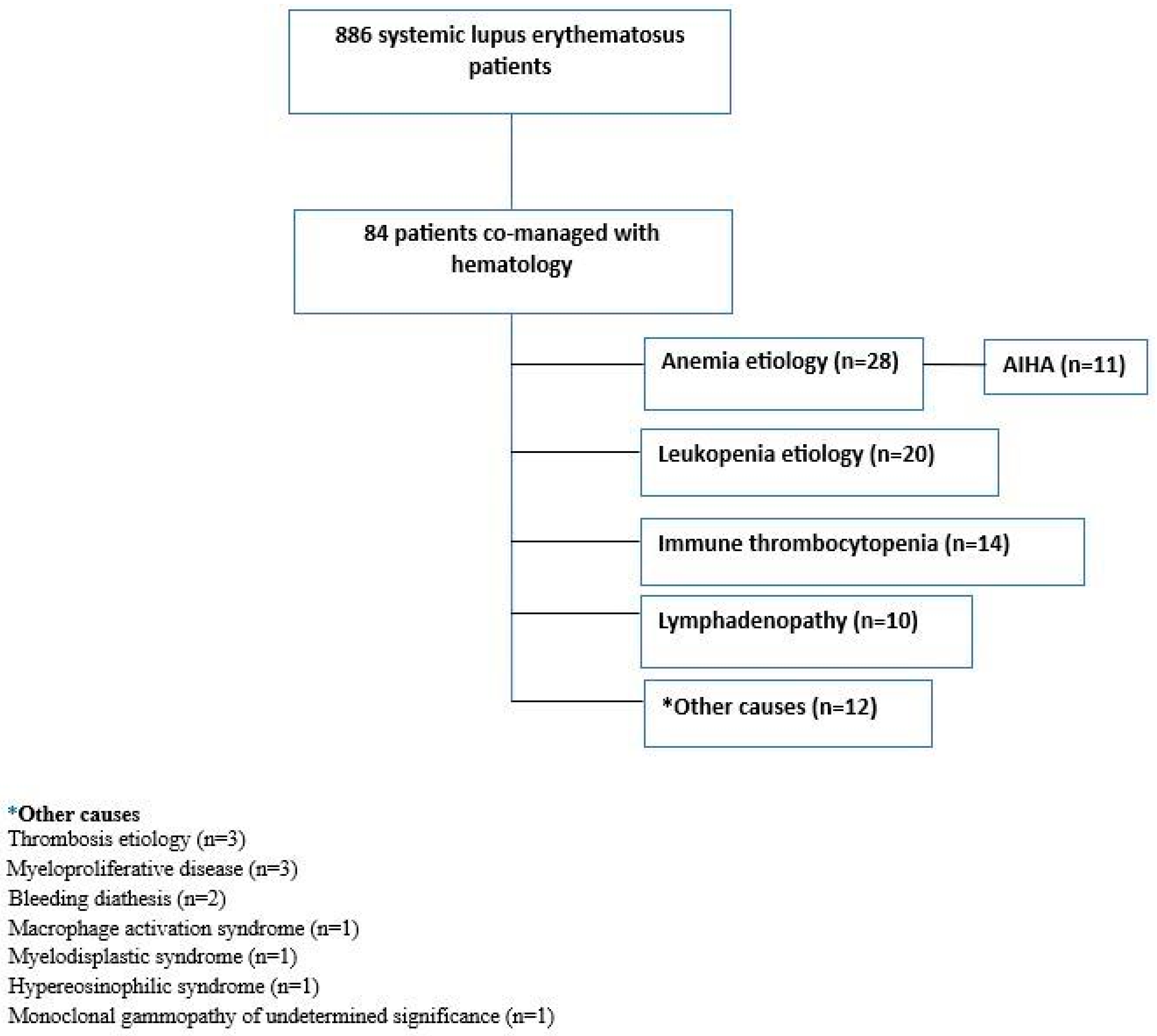
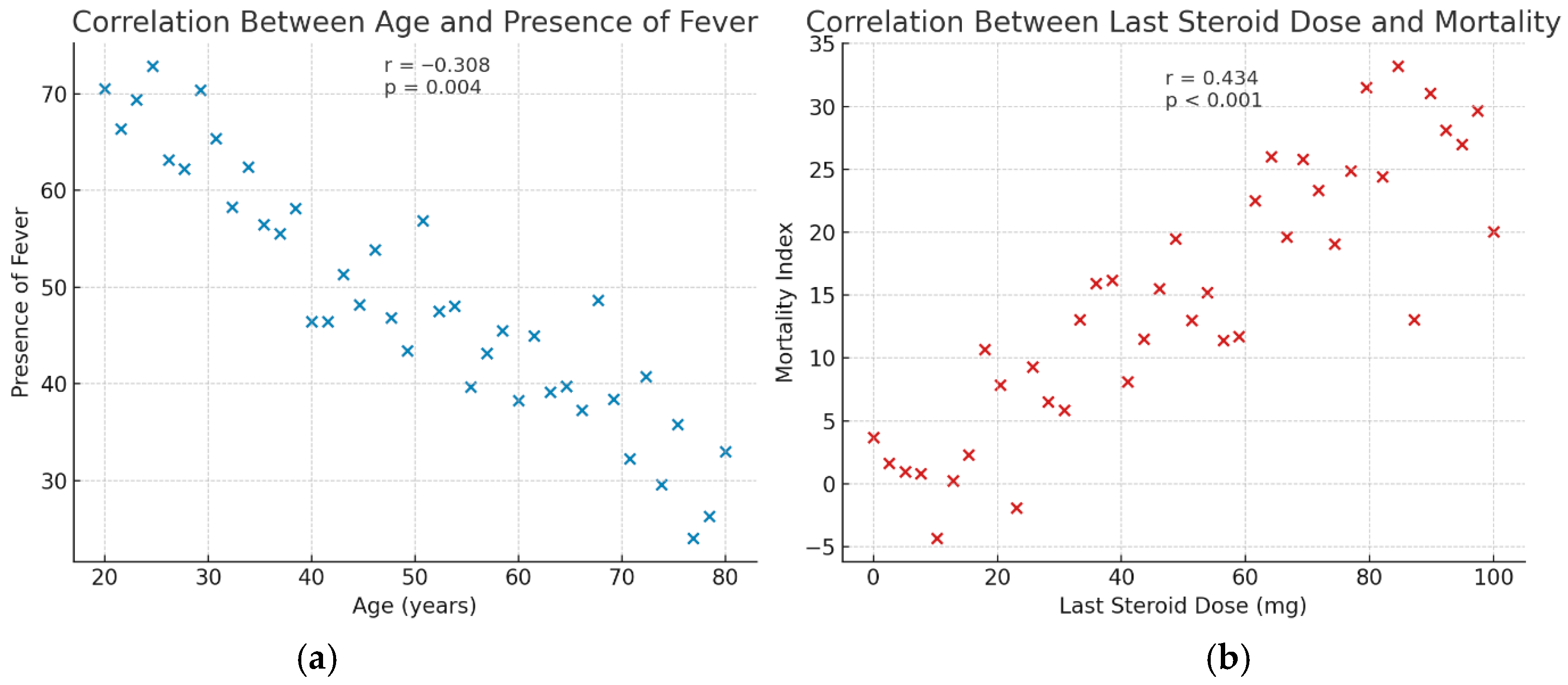
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Velo-García, A.; Castro, S.G.; Isenberg, D.A. The diagnosis and management of the haematologic manifestations of lupus. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 74, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, K.; Owlia, M.B.; El-Hemaidi, I.; Akhtari, M. Management of immune cytopenias in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus—Old and new. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, P.; Goldman, D.W.; Li, J.; Petri, M.; Krishna, N.; Cunnion, K. Classical complement activation on human erythrocytes in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus and a history of autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Lupus 2020, 29, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, L.; Tani, C.; Vagnani, S.; Signorini, V.; Mosca, M. (Eds.) Leukopenia, lymphopenia, and neutropenia in systemic lupus erythematosus: Prevalence and clinical impact—A systematic literature review. In Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, M.; Sjöwall, J.; Bendtsen, M.; Sjöwall, C. The prevalence of neutropenia and association with infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A Swedish single-center study conducted over 14 years. Rheumatol. Int. 2024, 44, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgarelis, M.; Kokori, S.I.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Kyriaki, D.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Anaemia in systemic lupus erythematosus: Aetiological profile and the role of erythropoietin. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chock, Y.P.; Moulinet, T.; Dufrost, V.; Erkan, D.; Wahl, D.; Zuily, S. Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombocytopenia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobha, V.; Rajasekhar, L.; Bhat, V.; Mathew, A.J.; Kavadichanda, C.; Rathi, M.; Gupta, R.; Selvam, S.; Aggarwal, A.; INSPIRE Investigators. Severe thrombocytopenia is associated with high mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus—Analysis from Indian SLE Inception cohort for Research (INSPIRE). Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 2279–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papachristodoulou, E.; Graef, E.; Magliulo, D.; Kyttaris, V. Prevalence and clinical significance of lymphadenopathy and its histological subtypes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A retrospective cohort study. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guariento, A.; Silva, M.F.C.; Tassetano, P.S.; Rocha, S.M.S.; Campos, L.; Valente, M.; Silva, C.A. Liver and spleen biometrics in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 2015, 55, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, M.; Orbai, A.M.; Alarcón, G.S.; Gordon, C.; Merrill, J.T.; Fortin, P.R.; Bruce, I.N.; Isenberg, D.; Wallace, D.J.; Nived, O.; et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez Gómez, L.; Uribe Uribe, O.; Osio Uribe, O.; Grisales Romero, H.; Cardiel, M.; Wojdyla, D.; Pons-Estel, B.; Grupo Latinoamericano de Estudio del Lupus (GLADEL); Catoggio, L.J.; Soriano, E.R.; et al. Childhood systemic lupus erythematosus in Latin America. The GLADEL experience in 230 children. Lupus 2008, 17, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Pires, T.; Caparrós-Ruiz, R.; Gaspar, P.; Isenberg, D.A. Prevalence and outcome of thrombocytopenia in systemic lupus erythematous: Single-centre cohort analysis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artım-Esen, B.; Çene, E.; Şahinkaya, Y.; Erdugan, M.; Oğuz, E.; Gül, A.; Öcal, L.; İnanç, M. Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia and thrombocytopaenia in a single-centre cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus from Turkey: Clinical associations and effect on disease damage and survival. Lupus 2019, 28, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Duan, X.; Xu, J.; Wu, L.; Wei, W.; Xiao, W.; Luo, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Risk prediction of new-onset thrombocytopenia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A multicenter prospective cohort study based on Chinese SLE treatment and research group (CSTAR) registry. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziakas, P.; Giannouli, S.; Zintzaras, E.; Tzioufas, A.; Voulgarelis, M. Lupus thrombocytopenia: Clinical implications and prognostic significance. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 1366–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Begum, S.; Isenberg, D. Prevalence, patterns of disease and outcome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus who develop severe haematological problems. Rheumatology 2003, 42, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, L.; Fei, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X. Management of severe refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: Real-world experience and literature review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 60, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.S.; Gamal, S.M.; Mokbel, A.; Alkamary, A.K.; Siam, I.; Soliman, A.; Elgengehy, F.T. Thrombocytopenia and disease outcomes in a cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. A post hoc analysis of the COMOSLE-EGYPT study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 27, e15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Alarcón, G.S.; Apte, M.; Andrade, R.M.; Vilá, L.M.; Reveille, J.D. Systemic lupus erythematosus in a multiethnic US cohort: XLIII. The significance of thrombocytopenia as a prognostic factor. Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 2007, 56, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannouli, S.; Voulgarelis, M.; Ziakas, P.D.; Tzioufas, A.G. Anaemia in systemic lupus erythematosus: From pathophysiology to clinical assessment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, M.; Hamadeh, F.; Aberle, T.; Glenn, S.; Kamen, D.; Kelly, J.; Reichlin, M.; Harley, J.; Sawalha, A. Haemolytic anaemia in a multi-ethnic cohort of lupus patients: A clinical and serological perspective. Lupus 2008, 17, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domiciano, D.S.; Shinjo, S.K. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia in systemic lupus erythematosus: Association with thrombocytopenia. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Naranjo, L.A.; Betancur, O.M.; Alarcón, G.S.; Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Jaramillo-Arroyave, D.; Wojdyla, D.; Pons-Estel, G.J.; Rondón-Herrera, F.; Vásquez-Duque, G.M.; Quintana-López, G.; et al. (Eds.) Features associated with hematologic abnormalities and their impact in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Data from a multiethnic Latin American cohort. In Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aleem, A.; Al Arfaj, A.S.; Khalil, N.; Alarfaj, H.; Carli, L.; Tani, C. Haematological abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2014, 39, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, S.H.; Park, H.S.; Ahn, S.M.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, C.K.; Yoo, B.; Hong, S. Clinical features of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with splenomegaly: Focussed on the cytopenias. Intern. Med. J. 2023, 53, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurien, B.; Newland, J.; Paczkowski, C.; Moore, K.; Scofield, R.H. Association of neutropenia in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with anti-Ro and binding of an immunologically cross-reactive neutrophil membrane antigen. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 120, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzayan, M.; Schmidt, R.; Witte, T. Prognostic parameters for flare in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 2000, 39, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, V.; Singh, A.; Aggarwal, A.; Naik, S.; Misra, R. Increased T-lymphocyte apoptosis in lupus correlates with disease activity and may be responsible for reduced T-cell frequency: A cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Lupus 2009, 18, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, C.M.; Castiblanque, A. Associations between biological markers and haematological manifestations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 575, 120383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durcan, L.; Petri, M. (Eds.) The clinical and serological associations of hypocomplementemia in a longitudinal sle cohort. In Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Akca, Ü.K.; Batu, E.D.; Kısaarslan, A.P.; Poyrazoğlu, H.; Ayaz, N.A.; Sözeri, B.; Sağ, E.; Atalay, E.; Demir, S.; Karadağ, Ş.G.; et al. Hematological involvement in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus: A multi-center study. Lupus 2021, 30, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.; Barr, S.G.; Magder, L.S.; Petri, M. A decrease in complement is associated with increased renal and hematologic activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Cladera, Y.; García-González, M.; Hernández-Díaz, M.; Gómez-Bernal, F.; Quevedo-Abeledo, J.C.; González-Rivero, A.F.; de Vera-González, A.; Gómez-Moreno, C.; González-Gay, M.Á.; Ferraz-Amaro, I. Relationship of Hematological Profiles with the Serum Complement System in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Baseline characteristics | |
| Gender (Female) | 78 (92.6) |
| Age, years * | 46 (36–62) |
| Age at diagnosis, years * | 39 (24–50) |
| Duration at diagnosis, years * | 9 (5–13) |
| Additional autoimmune disease | 35 (41.7) |
| Rheumatic disease in the family | 10 (11.9) |
| Clinical presentation | |
| Fever | 10 (11.9) |
| Hair loss | 27 (32.1) |
| Oral ulcer | 15 (17.9) |
| Photosensitivity | 48 (57.1) |
| Malar rash | 39 (46.4) |
| Subacute cutaneous lesions | 12 (14.3) |
| Arthritis | 35 (41.7) |
| Arthralgia | 67 (79.8) |
| Pleural effusion | 17 (20.2) |
| Pericardial effusion | 11 (13.1) |
| Dry mouth | 27 (32.1) |
| Dry eyes | 21 (25) |
| Raynaud | 27 (32.1) |
| Myalgia | 14 (16.7) |
| Neuropsychiatric involvement | 9 (10.7) |
| Lymphadenomegaly | 29 (34.5) |
| Splenomegaly | 16 (19) |
| Lupus nephritis | 7 (8.3) |
| Avascular necrosis | 4 (4.8) |
| Thrombosis | 18 (21.4) |
| Cutaneous vasculitis | 5 (6) |
| Laboratory tests | |
| Anti-Ro (SS-A) positivity | 23 (27.4) |
| Anti-La (SS-B) positivity | 7 (8.3) |
| Anti-Sm positivity | 12 (14.3) |
| Anti-nucleosome positivity | 19 (22.6) |
| Anti-RNP positivity | 15 (17.9) |
| Anti-dsDNA | 48 (57.1) |
| Low C3 | 46 (54.8) |
| Low C4 | 25 (29.8) |
| Lupus anticoagulant | 12 (14.3) |
| Anti-cardiolipin IgM | 17 (20.2) |
| Anti-cardiolipin IgG | 13 (15.5) |
| Anti-beta-2-Glycoprotein I IgM | 16 (19) |
| Anti-beta-2-Glycoprotein I IgG | 10 (11.9) |
| Therapeutic interventions | |
| Corticosteroid | 72 (85.7) |
| Azathioprine | 41 (48.8) |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | 19 (22.6) |
| Rituximab | 9 (10.7) |
| Cyclophosphamide | 15 (17.9) |
| Intravenous immunoglobulin | 5 (6) |
| Plasmapheresis | 2 (2.4) |
| Category | Association | OR (Odds Ratio) | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Splenomegaly | Serositis | 4.03 | 1.23–13.11 | 0.021 |
| Lupus anticoagulant | 8.81 | 1.70–45.57 | 0.009 | |
| Anti-β2GPI IgG | 5.42 | 1.23–23.81 | 0.025 | |
| Venous thrombosis | Anti-cardiolipin IgM | 5.30 | 1.51–18.58 | 0.009 |
| Anti-cardiolipin IgG | 8.00 | 2.01–31.82 | 0.003 | |
| Lupus anticoagulant | 6.88 | 1.68–28.24 | 0.007 | |
| Anti-β2GPI IgG | 9.33 | 2.01–43.41 | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuce Inel, T.; Uslu, S.; Demirci Yildirim, T.; Gulle, S.; Sen, G. Hematologic Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Clinical Features and Prognostic Implications in a Hematology-Referred Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7304. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207304
Yuce Inel T, Uslu S, Demirci Yildirim T, Gulle S, Sen G. Hematologic Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Clinical Features and Prognostic Implications in a Hematology-Referred Cohort. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7304. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207304
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuce Inel, Tuba, Sadettin Uslu, Tuba Demirci Yildirim, Semih Gulle, and Gercek Sen. 2025. "Hematologic Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Clinical Features and Prognostic Implications in a Hematology-Referred Cohort" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7304. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207304
APA StyleYuce Inel, T., Uslu, S., Demirci Yildirim, T., Gulle, S., & Sen, G. (2025). Hematologic Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Clinical Features and Prognostic Implications in a Hematology-Referred Cohort. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7304. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207304






