Sub-Symptom Threshold Balance Training Facilitates Post-Concussion Syndrome Symptom Resolution Beyond Balance Dysfunction
Abstract
1. Introduction
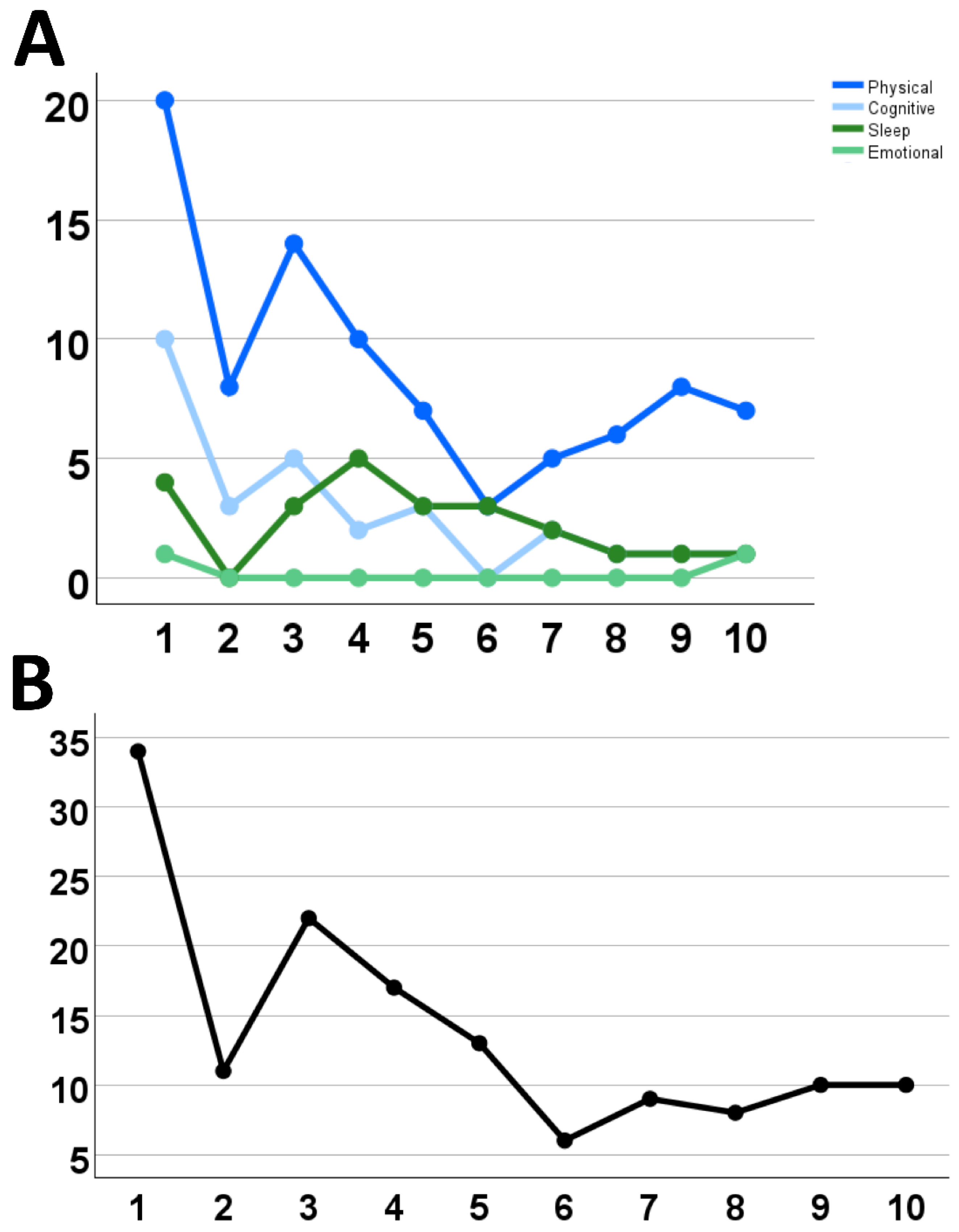
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PPCS | Persistent Post-Concussion Syndrome |
| HAE | Head Acceleration Event |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| AP | Anterior–Posterior |
| ML | Medial-Lateral |
| PCSC | Post-Concussion Symptom Scale |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| BPPV | Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo |
| VOR | Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex |
| BESS | Balance Error Scoring System |
| SOT | Sensory Organization Test |
| AMTI | Advanced Mechanical Technology, Inc. |
| NCAA | National Collegiate Athletic Association |
References
- Logsdon, A.F.; Lucke-Wold, B.P.; Turner, R.C.; Huber, J.D.; Rosen, C.L.; Simpkins, J.W. Role of Microvascular Disruption in Brain Damage from Traumatic Brain Injury. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mckee, A.C.; Daneshvar, D.H. The Neuropathology of Traumatic Brain Injury. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 127, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianoli, G.J. Post-Concussive Dizziness: A Review and Clinical Approach to the Patient. Front. Neurol. 2022, 12, 718318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePadilla, L.; Miller, G.F.; Jones, S.E.; Peterson, A.B.; Breiding, M.J. Self-Reported Concussions from Playing a Sport or Being Physically Active among High School Students—United States, 2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.; Lovell, M.R.; Iverson, G.L.; Ide, T.; Maroon, J. Examining Concussion Rates and Return to Play in High School Football Players Wearing Newer Helmet Technology: A Three-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Neurosurgery 2006, 58, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinder, S.; Cnossen, M.C.; Real, R.G.L.; Covic, A.; Gorbunova, A.; Voormolen, D.C.; Master, C.L.; Haagsma, J.A.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; von Steinbuechel, N. A Multidimensional Approach to Post-Concussion Symptoms in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strebel, S.; Lam, A.M.; Matta, B.F.; Newell, D.W. Impaired Cerebral Autoregulation after Mild Brain Injury. Surg. Neurol. 1997, 47, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.M.; Hsiang, J.N.; Poon, W.S. Monitoring of Autoregulation Using Laser Doppler Flowmetry in Patients with Head Injury. J. Neurosurg. 1997, 86, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetjen, N.M.; Pichelmann, M.A.; Atkinson, J.L.D. Second Impact Syndrome: Concussion and Second Injury Brain Complications. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2010, 211, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltus, J. Rehabilitation Strategies Addressing Neurocognitive and Balance Deficits Following a Concussion in a Female Snowboard Athlete: A Case Report. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2014, 9, 232–241. [Google Scholar]
- Guskiewicz, K.M.; Riemann, B.L.; Perrin, D.H.; Nashner, L.M. Alternative Approaches to the Assessment of Mild Head Injury in Athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1997, 29, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Herdman, S.J. Vestibular Rehabilitation. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, D.R.; Lynall, R.C.; Buckley, T.A.; Herman, D.C. Neuromuscular Control Deficits and the Risk of Subsequent Injury after a Concussion: A Scoping Review. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 1097–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivry, R.B.; Baldo, J.V. Is the Cerebellum Involved in Learning and Cognition? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1992, 2, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisilevski, V.; Podoshin, L.; Ben-David, J.; Soustiel, J.F.; Teszler, C.B.; Hafner, H.; Chistyakov, A. Results of Otovestibular Tests in Mild Head Injuries. Int. Tinnitus J. 2001, 7, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kleffelgaard, I.; Roe, C.; Soberg, H.L.; Bergland, A. Associations among Self-Reported Balance Problems, Post-Concussion Symptoms and Performance-Based Tests: A Longitudinal Follow-up Study. Disabil. Rehabil. 2012, 34, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleffelgaard, I.; Soberg, H.L.; Bruusgaard, K.A.; Tamber, A.L.; Langhammer, B. Vestibular Rehabilitation after Traumatic Brain Injury: Case Series. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lu, L.; Shang, S.; Hu, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yin, X. Disrupted Functional Network Connectivity Predicts Cognitive Impairment after Acute Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, M.R.; Collins, M.W.; Iverson, G.L.; Field, M.; Maroon, J.C.; Cantu, R.; Podell, K.; Powell, J.W.; Belza, M.; Fu, F.H. Recovery from Mild Concussion in High School Athletes. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 98, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.; Patton, D.; Rooks, T. On-Field Deployment and Validation for Wearable Devices. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 50, 1372–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskell, F.; Chiarelli, P.; Isles, R. Dizziness after Traumatic Brain Injury: Overview and Measurement in the Clinical Setting. Brain Inj. 2006, 20, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, F.; Maurette, P.; Salmi, L.R.; Dartigues, J.-F.; Vecsey, J.; Destaillats, J.-M.; Erny, P. Prevalence of Impairments 5 Years after a Head Injury, and Their Relationship with Disabilities and Outcome. Brain Inj. 1996, 10, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrea, M.; Prichep, L.; Powell, M.R.; Chabot, R.; Barr, W.B. Acute Effects and Recovery after Sport-Related Concussion: A Neurocognitive and Quantitative Brain Electrical Activity Study. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2010, 25, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, D.A.; Meldrum, D.; Lennon, O. Can Vestibular Rehabilitation Exercises Help Patients with Concussion? A Systematic Review of Efficacy, Prescription and Progression Patterns. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, A. Vestibular Dysfunction and Concussion. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 158, pp. 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.N.; Herget, L.; Zafonte, R.D.; Lamm, A.G.; Wong, B.M.; Leddy, J.J. Rehabilitation of Sport-Related Concussion. Clin. Sports Med. 2021, 40, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, E.S.; Straumann, D. Why and When to Refer Patients for Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials: A Critical Review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1539–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrington, L.; Fino, P.C.; Swanson, C.W.; Murchison, C.F.; Chesnutt, J.; King, L.A. Longitudinal Assessment of Balance and Gait after Concussion and Return to Play in Collegiate Athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2019, 54, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemann, B.L.; Guskiewicz, K.M. Effects of Mild Head Injury on Postural Stability as Measured through Clinical Balance Testing. J. Athl. Train. 2000, 35, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Riva, E.; Freire, T.; Bassi, M. The Flow Experience in Clinical Settings: Applications in Psychotherapy and Mental Health Rehabilitation. In Flow Experience: Empirical Research and Applications; Harmat, L., Ørsted Andersen, F., Ullén, F., Wright, J., Sadlo, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, G.; Castelnuovo, G.; Mantovani, F. Transformation of Flow in Rehabilitation: The Role of Advanced Communication Technologies. Behav. Res. Methods 2006, 38, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, A.-K.; Röder, B.; Zech, A.; Nagel, V.; Hollander, K.; Braumann, K.-M.; Hötting, K. Balance Training Improves Memory and Spatial Cognition in Healthy Adults. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.; Soule, E.; Fiester, P.; Natter, P.; Tavanaiepour, D.; Rahmathulla, G.; Rao, D. Brainstem Diffuse Axonal Injury and Consciousness. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2019, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawle, G. Visual Vertigo. Lancet 1996, 347, 986–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valovich McLeod, T.C.; Hale, T.D. Vestibular and Balance Issues Following Sport-Related Concussion. Brain Inj. 2015, 29, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Duan, L.; Ou, Y.; Ling, Q.; Cao, L.; Qian, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, X. The Cerebellum and Cognitive Neural Networks. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1197459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, R. Altered Cerebellar White Matter Integrity in Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in the Acute Stage. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, G.; McColl, R.; Barnard, H.; Ringe, W.K.; Fleckenstein, J.; Cullum, C.M. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Cerebellar-Prefrontal and Cerebellar-Parietal Functional Connectivity. NeuroImage 2005, 28, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovici, A.; Itzhaki, N.; Shapsa, H.; Yvgeny, J.; Lerer; Shechtman, M.; Mesika, D.; Raizman, R.; Tsarfaty, G.; Zibly, Z.; et al. Compensatory Cerebellar Activation during Fluid Intelligence Processing Following Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 28377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontos, A.P.; Collins, M.W.; Holland, C.L.; Reeves, V.L.; Edelman, K.; Benso, S.; Schneider, W.; Okonkwo, D. Preliminary Evidence for Improvement in Symptoms, Cognitive, Vestibular, and Oculomotor Outcomes Following Targeted Intervention with Chronic mTBI Patients. Mil. Med. 2018, 183, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMarshall, S.J.; Stevens, L.M.; Ragg, N.P.; Barnes, L.; Foster, J.; Canetti, E.F.D. Virtual Reality-Based Interventions for the Rehabilitation of Vestibular and Balance Impairments Post-Concussion: A Scoping Review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasic, D.; Morgan, L.; Panezai, A.; Syrmos, N.; Ligarotti, G.K.I.; Zaed, I.; Chibbaro, S.; Khan, T.; Prisco, L.; Ganau, M. A Scoping Review on the Challenges, Improvement Programs, and Relevant Output Metrics for Neurotrauma Services in Major Trauma Centers. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2022, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Napora, Z.; McLaughlin, M.; Vurraro, A.; Kelly, J.; Griffith, O. Sub-Symptom Threshold Balance Training Facilitates Post-Concussion Syndrome Symptom Resolution Beyond Balance Dysfunction. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207229
Napora Z, McLaughlin M, Vurraro A, Kelly J, Griffith O. Sub-Symptom Threshold Balance Training Facilitates Post-Concussion Syndrome Symptom Resolution Beyond Balance Dysfunction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207229
Chicago/Turabian StyleNapora, Zach, Madeline McLaughlin, Abby Vurraro, Jon Kelly, and Owen Griffith. 2025. "Sub-Symptom Threshold Balance Training Facilitates Post-Concussion Syndrome Symptom Resolution Beyond Balance Dysfunction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207229
APA StyleNapora, Z., McLaughlin, M., Vurraro, A., Kelly, J., & Griffith, O. (2025). Sub-Symptom Threshold Balance Training Facilitates Post-Concussion Syndrome Symptom Resolution Beyond Balance Dysfunction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207229






