The Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease in the U.S.: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
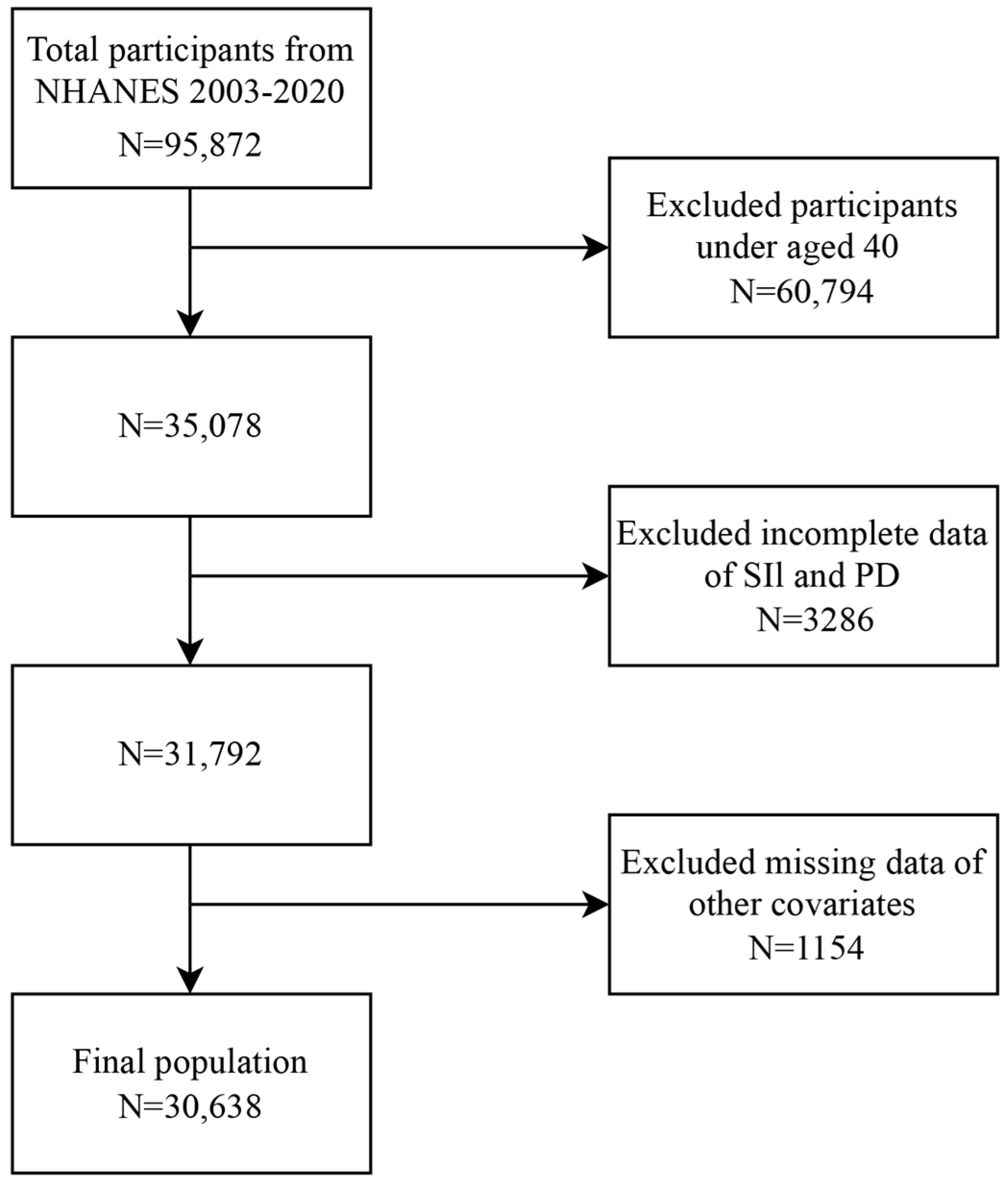
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Exposure and Outcome Definitions
2.3. Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Relationship Between the SII and PD
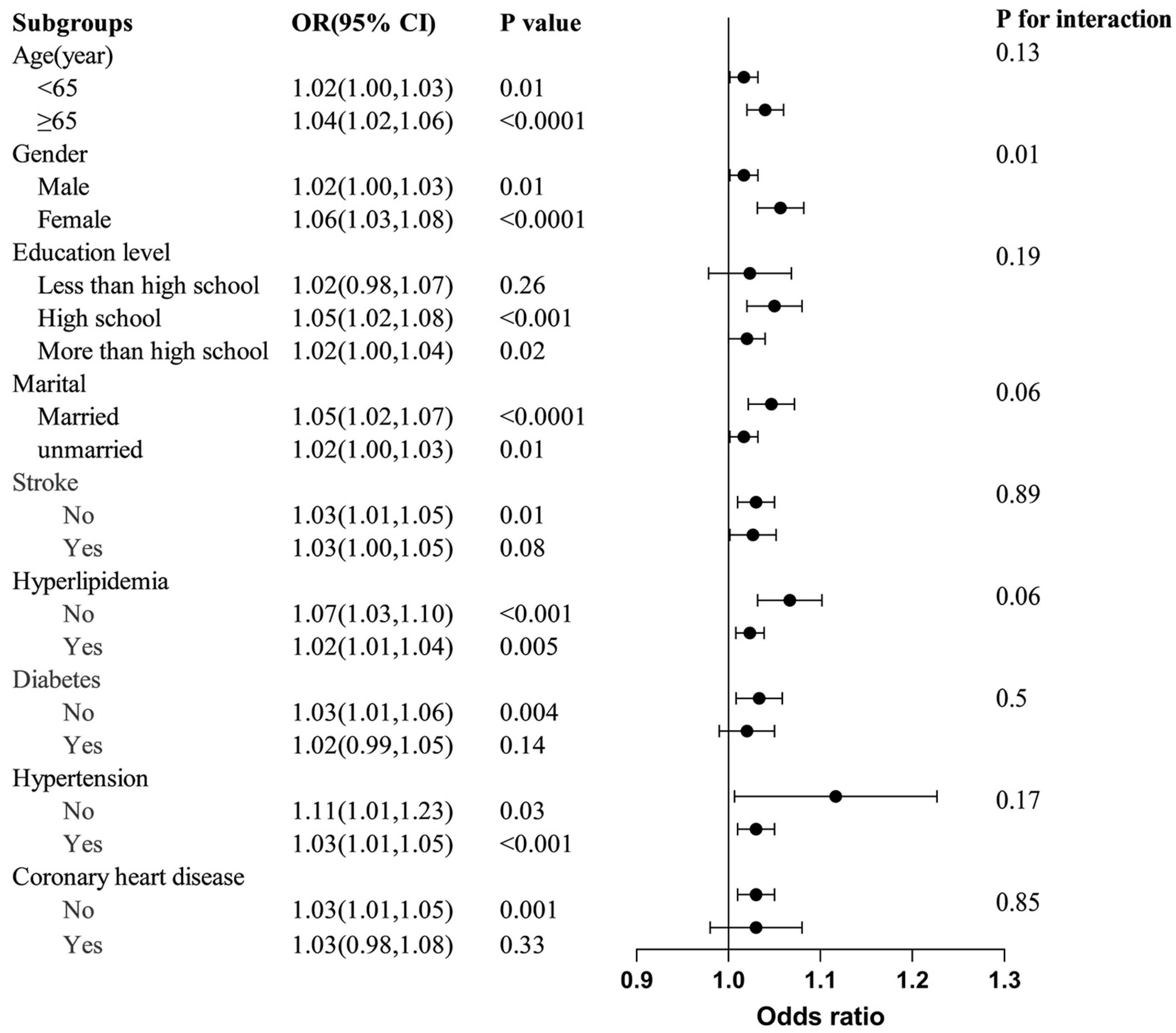
3.3. Subgroup Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, N.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Balbuena, L.; Ungvari, G.S.; Zang, Y.F.; Xiang, Y.T. Quality of life in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubo, E.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Gonzalez-Bernal, J.; Casas, E.; Arnaiz, S.; Miranda, J.; Gamez, P.; Santos-Garcia, D.; Coppadis Study, G. Effects of Motor Symptom Laterality on Clinical Manifestations and Quality of Life in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Parkinsons. Dis. 2020, 10, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.J.; West, A.B.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. Molecular pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 57–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamzadeh, F.N.; Surguchov, A. Parkinson’s Disease: Biomarkers, Treatment, and Risk Factors. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringsheim, T.; Jette, N.; Frolkis, A.; Steeves, T.D. The prevalence of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.C.; Chang, S.F.; Su, C.L.; Chen, T.H.; Yen, M.F.; Wu, H.M.; Chen, Z.Y.; Liou, H.H. Prevalence, incidence, and mortality of PD: A door-to-door survey in Ilan county, Taiwan. Neurology 2001, 57, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dommershuijsen, L.J.; Ruiter, R.; Erler, N.S.; Rizopoulos, D.; Ikram, M.A.; Ikram, M.K. Peripheral Immune Cell Numbers and C-Reactive Protein in Parkinson’s Disease: Results from a Population-Based Study. J. Parkinsons. Dis. 2022, 12, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Ou, R.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Shang, H. Serum inflammatory cytokines levels and the correlation analyses in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1104393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansey, M.G.; Wallings, R.L.; Houser, M.C.; Herrick, M.K.; Keating, C.E.; Joers, V. Inflammation and immune dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansey, M.G.; Goldberg, M.S. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: Its role in neuronal death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alster, P.; Otto-Slusarczyk, D.; Kutylowski, M.; Migda, B.; Wiercinska-Drapalo, A.; Jablonska, J.; Struga, M.; Madetko-Alster, N. The associations between common neuroimaging parameters of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy in magnetic resonance imaging and non-specific inflammatory factors—Pilot study. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1458713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Manda, G.; Bosca, L.; Cuadrado, A. Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2020, 9, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Weng, G.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, W.; Deng, B.; Luo, Y.; Tao, X.; Deng, M.; Guo, H.; Zhu, S.; et al. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio, and neutrophil-to-high-density-lipoprotein ratio are correlated with the severity of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1322228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirakoglu, O.F.; Yilmaz, A.S. Systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with increased carotid intima-media thickness in hypertensive patients. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2021, 43, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Delgado, L.; Labrador-Espinosa, M.A.; Macias-Garcia, D.; Jesus, S.; Benitez Zamora, B.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, P.; Adarmes-Gomez, A.D.; Reina Castillo, M.I.; Castro-Labrador, S.; Silva-Rodriguez, J.; et al. Peripheral Inflammation Is Associated with Dopaminergic Degeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, B.; Ren, W.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Jin, S.; Chang, Y. Association analysis of dopaminergic degeneration and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1377994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, X.; Ma, L.; Wang, M.; Du, J.; Chen, W.; Xi, X.; Li, B. Combined platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and blood-brain barrier biomarkers as indicators of disability in acute neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 45, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akil, E.; Bulut, A.; Kaplan, I.; Ozdemir, H.H.; Arslan, D.; Aluclu, M.U. The increase of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Xiao, J.; Cai, W.; Lu, X.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Song, G.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.; et al. Association of the systemic immune-inflammation index with anemia: A population-based study. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1391573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.H.; Huang, D.H.; Chen, Z.Y. Prognostic role of systemic immune-inflammation index in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75381–75388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, A.; Shobeiri, P.; Kulasinghe, A.; Rezaei, N. Novel Systemic Inflammation Markers to Predict COVID-19 Prognosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 741061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algul, F.E.; Kaplan, Y. Increased Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index as a Novel Indicator of Alzheimer’s Disease Severity. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2024, 13, 8919887241280880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiess, N.; Cataldi, R.; Okun, M.S.; Fothergill-Misbah, N.; Dorsey, E.R.; Bloem, B.R.; Barretto, M.; Bhidayasiri, R.; Brown, R.; Chishimba, L.; et al. Six Action Steps to Address Global Disparities in Parkinson Disease: A World Health Organization Priority. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Nie, K.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Serum Folate, Vitamin B12 Levels, and Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Correlate With Motor Performance in Parkinson’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 665075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Fan, Q.; Wu, S.; Wan, Y.; Lei, Y. Compared with the monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio (MHR) and the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein ratio (NHR) is more valuable for assessing the inflammatory process in Parkinson’s disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Bulut, M.; Kaya, M.C.; Demirpence, O.; Sevim, B.; Akil, E.; Varol, S. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and high mobility group box-1 levels in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, L.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, B.; Luo, W. The role of immune and inflammatory-related indicators in cognitive dysfunction and disease severity in patients with parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2024, 131, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.M.; Qiu, S.J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L. Prognostic Value of Preoperative Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in Patients with Cervical Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, W.; Ni, X.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Predicts Prognosis of Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Propensity Score-matched Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.H.; Zhai, E.T.; Yuan, Y.J.; Wu, K.M.; Xu, J.B.; Peng, J.J.; Chen, C.Q.; He, Y.L.; Cai, S.R. Systemic immune-inflammation index for predicting prognosis of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6261–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, B.; Gao, Y.; Wang, A.; Xu, Q.; Meng, X.; Xu, Y.; Song, B.; Wang, Y.; et al. Correlation of the systemic immune-inflammation index with short- and long-term prognosis after acute ischemic stroke. Aging 2022, 14, 6567–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shao, W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Sun, T.; Wang, B.; Hu, X. Association between systemic immune-inflammation index and metabolic syndrome and its components: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2016. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Wan, C.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, S. Association of systemic immune-inflammation index with insulin resistance and prediabetes: A cross-sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1377792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Li, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Han, X.; Tong, Y.; Tan, Y. Neutrophil/lymphocyte, platelet/lymphocyte, monocyte/lymphocyte ratios and systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with depression. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2023, 124, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Teng, Z.; Xu, J.; Qi, Q.; Guan, T.; Jiang, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, X.; Dong, Y.; Lv, P. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index is Associated with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden and Cognitive Impairment. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat 2023, 19, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, H.; Li, N. Systemic immune-inflammation Index is associated with chronic kidney disease in the U.S. population: Insights from NHANES 2007–2018. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1331610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, K.P.; Zhang, Q. The association between systemic immune-inflammation index and rheumatoid arthritis: Evidence from NHANES 1999–2018. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosu, A.R.; Biter, H.I. Association of systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) with presence of isolated coronary artery ectasia. Arch. Med. Sci. Atheroscler. Dis. 2021, 6, e152–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.C.; Pott Godoy, M.C.; Tarelli, R.; Chertoff, M.; Depino, A.M.; Pitossi, F.J. Progressive neurodegeneration and motor disabilities induced by chronic expression of IL-1beta in the substantia nigra. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 24, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pott Godoy, M.C.; Tarelli, R.; Ferrari, C.C.; Sarchi, M.I.; Pitossi, F.J. Central and systemic IL-1 exacerbates neurodegeneration and motor symptoms in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2008, 131, 1880–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.C.; Tarelli, R. Parkinson’s disease and systemic inflammation. Parkinsons. Dis. 2011, 2011, 436813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.T.; Kim, Y.J.; Ma, H.I.; Kim, Y.E. Evidence of Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease and Its Contribution to Synucleinopathy. J. Mov. Disord. 2022, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roodveldt, C.; Bernardino, L.; Oztop-Cakmak, O.; Dragic, M.; Fladmark, K.E.; Ertan, S.; Busra, A.; Pita, C.; Ciglar, L.; Garraux, G.; et al. The immune system in Parkinson’s disease: What we know so far. Brain 2024, 147, 3306–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, H.; Pacheco, R. T-cell-mediated regulation of neuroinflammation involved in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, H.; Contreras, F.; Pacheco, R. Regulation of the Neurodegenerative Process Associated to Parkinson’s Disease by CD4+ T-cells. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheoud, D.; Cannon, T.; Voisin, A.; Penttinen, A.M.; Ramet, L.; Fahmy, A.M.; Ducrot, C.; Laplante, A.; Bourque, M.J.; Zhu, L.; et al. Intestinal infection triggers Parkinson’s disease-like symptoms in Pink1−/− mice. Nature 2019, 571, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, M.; Shukla, R.; Dikshit, M.; Maheshwari, P.K.; Nag, D.; Srimal, R.C.; Seth, P.K.; Khanna, V.K. Altered platelet monoamine oxidase-B activity in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Total | Non-Parkinson | Parkinson | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | 30,638 | 30,222 | 416 | |
| Age (year), mean + SD | 58.34 ± 0.14 | 58.27 ± 0.14 | 63.02 ± 0.87 | <0.0001 |
| Gender, n (%) | 0.01 | |||
| Male | 15,014 (47.28) | 14,814 (47.40) | 200 (38.18) | |
| Female | 15,624 (52.72) | 15,408 (52.60) | 216 (61.82) | |
| Marital status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Married | 17,850 (63.96) | 17,640 (64.13) | 210 (51.96) | |
| Unmarried | 12,788 (36.04) | 12,582 (35.87) | 206 (48.04) | |
| Education level, n (%) | 0.65 | |||
| Less than high school | 4047 (6.45) | 4000 (6.45) | 47 (6.17) | |
| High school | 11,275 (34.45) | 11,117 (34.42) | 158 (36.86) | |
| More than high school | 15,316 (59.10) | 15,105 (59.13) | 211 (56.96) | |
| Race, n (%) | <0.0001 | |||
| White | 13,710 (72.62) | 13,439 (72.47) | 271 (83.49) | |
| Black | 6568 (9.82) | 6513 (9.87) | 55 (6.67) | |
| Other | 10,360 (17.56) | 10,270 (17.66) | 90 (9.85) | |
| Smoke, n (%) | 0.9 | |||
| No | 15,853 (51.79) | 15,658 (51.79) | 195 (51.41) | |
| Yes | 14,785 (48.21) | 14,564 (48.21) | 221 (48.59) | |
| Stroke, n (%) | <0.0001 | |||
| No | 28,756 (95.34) | 28,409 (95.48) | 347 (84.88) | |
| Yes | 1882 (4.66) | 1813 (4.52) | 69 (15.12) | |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 0.41 | |||
| No | 6279 (20.02) | 6208 (20.06) | 71 (17.43) | |
| Yes | 24,359 (79.98) | 24,014 (79.94) | 345 (82.57) | |
| Diabetes, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| No | 24,450 (84.69) | 24,158 (84.80) | 292 (76.59) | |
| Yes | 6188 (15.31) | 6064 (15.20) | 124 (23.41) | |
| Coronary heart disease | <0.001 | |||
| No | 28,661 (94.27) | 28,299 (94.35) | 362 (88.61) | |
| Yes | 1977 (5.73) | 1923 (5.65) | 54 (11.39) | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 0.004 | |||
| No | 1368 (4.31) | 1357 (4.34) | 11 (1.66) | |
| Yes | 29,270 (95.69) | 28,865 (95.66) | 405 (98.34) | |
| SII | 5.63 ± 0.04 | 5.61 ± 0.04 | 7.44 ± 0.65 | 0.005 |
| Red blood cell | 4.66 ± 0.01 | 4.66 ± 0.01 | 4.53 ± 0.04 | <0.001 |
| White blood cell | 7.19 ± 0.03 | 7.18 ± 0.03 | 7.58 ± 0.19 | 0.04 |
| Alanine aminotransferase IU/L | 24.66 ± 0.13 | 24.68 ± 0.13 | 22.92 ± 1.27 | 0.17 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase IU/L | 25.20 ± 0.12 | 25.20 ± 0.12 | 25.28 ± 1.19 | 0.95 |
| Globulin g/dL | 2.86 ± 0.01 | 2.86 ± 0.01 | 2.85 ± 0.03 | 0.74 |
| Creatinine mg/dL | 0.92 ± 0.00 | 0.92 ± 0.00 | 0.95 ± 0.02 | 0.07 |
| Uric acid μmol/L | 325.92 ± 0.76 | 325.97 ± 0.77 | 322.47 ± 5.40 | 0.52 |
| Sodium mmol/L | 139.51 ± 0.07 | 139.51 ± 0.07 | 139.50 ± 0.19 | 0.95 |
| Calcium total mg/dL | 9.40 ± 0.01 | 9.40 ± 0.01 | 9.35 ± 0.03 | 0.07 |
| Variables | OR (95% CI) | p Value |
| Age (years) | 1.03 (1.02, 1.05) | <0.0001 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | Ref. | Ref. |
| Female | 1.46 (1.09, 1.95) | 0.01 |
| Marital | ||
| Married | Ref. | Ref. |
| Unmarried | 1.65 (1.25, 2.19) | <0.001 |
| Education level | ||
| Less than high school | Ref. | Ref. |
| High school | 1.12 (0.74, 1.69) | 0.59 |
| More than high school | 1.01 (0.71, 1.42) | 0.97 |
| Race | ||
| White | Ref. | Ref. |
| Black | 0.59 (0.43, 0.80) | <0.001 |
| Other | 0.48 (0.36, 0.66) | <0.0001 |
| Stroke | ||
| No | Ref. | Ref. |
| Yes | 3.76 (2.61, 5.42) | <0.0001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | ||
| No | Ref. | Ref. |
| Yes | 1.19 (0.78, 1.80) | 0.41 |
| Diabetes | ||
| No | Ref. | Ref. |
| Yes | 1.70 (1.28, 2.27) | <0.001 |
| Coronary heart disease | ||
| No | Ref. | Ref. |
| Yes | 2.14 (1.44, 3.18) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | ||
| No | Ref. | Ref. |
| Yes | 2.70 (1.33, 5.46) | 0.01 |
| Smoke | ||
| No | Ref. | Ref. |
| Yes | 1.02 (0.80, 1.29) | 0.90 |
| SII | 1.07 (1.04, 1.10) | <0.0001 |
| Red blood cell | 0.58 (0.43, 0.78) | <0.001 |
| White blood cell | 1.01 (1.00, 1.02) | 0.01 |
| Alanine aminotransferase, IU/L | 0.99 (0.97, 1.01) | 0.31 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase, IU/L | 1.00 (0.99, 1.01) | 0.94 |
| Globulin g/dL | 0.95 (0.71, 1.29) | 0.75 |
| Creatinine mg/dL | 1.14 (1.04, 1.24) | 0.004 |
| Uric acid umol/L | 1.00 (1.00, 1.00) | 0.53 |
| Sodium mmol/L | 1.00 (0.95, 1.05) | 0.95 |
| Calcium total mg/dL | 0.69 (0.46, 1.04) | 0.08 |
| Crude Model * | Model 1 * | Model 2 * | Model 3 * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Character | 95% CI | p | 95% CI | p | 95% CI | p | 95% CI | p |
| Continuous | 1.07 (1.04, 1.10) | <0.0001 | 1.06 (1.03, 1.09) | <0.001 | 1.06 (1.02, 1.09) | <0.001 | 1.05 (1.02, 1.09) | <0.001 |
| SII quartiles | ||||||||
| Q1 | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | ||||
| Q2 | 1.32 (0.90, 1.96) | 0.1578 | 1.27 (0.86, 1.89) | 0.2258 | 1.27 (0.86, 1.87) | 0.2358 | 1.29 (0.87, 1.91) | 0.2008 |
| Q3 | 1.60 (1.18, 2.17) | 0.0029 | 1.43 (1.04, 1.95) | 0.0269 | 1.39 (1.02, 1.88) | 0.0360 | 1.39 (1.02, 1.91) | 0.0390 |
| p for trend | 0.0022 | 0.0239 | 0.0334 | 0.0377 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, F.; Ran, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. The Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease in the U.S.: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020403
Liu F, Ran Q, Zhang H, Chen J. The Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease in the U.S.: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(2):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020403
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Fujun, Qibo Ran, Huajin Zhang, and Jing Chen. 2025. "The Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease in the U.S.: A Cross-Sectional Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 2: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020403
APA StyleLiu, F., Ran, Q., Zhang, H., & Chen, J. (2025). The Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease in the U.S.: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(2), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020403





