Interventional Management of Acute Pancreatitis and Its Complications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatigraphy in Acute Pancreatitis
2.2. Interventional Radiology-Guided Percutaneous Drainage of Early Pancreatic Fluid Collections
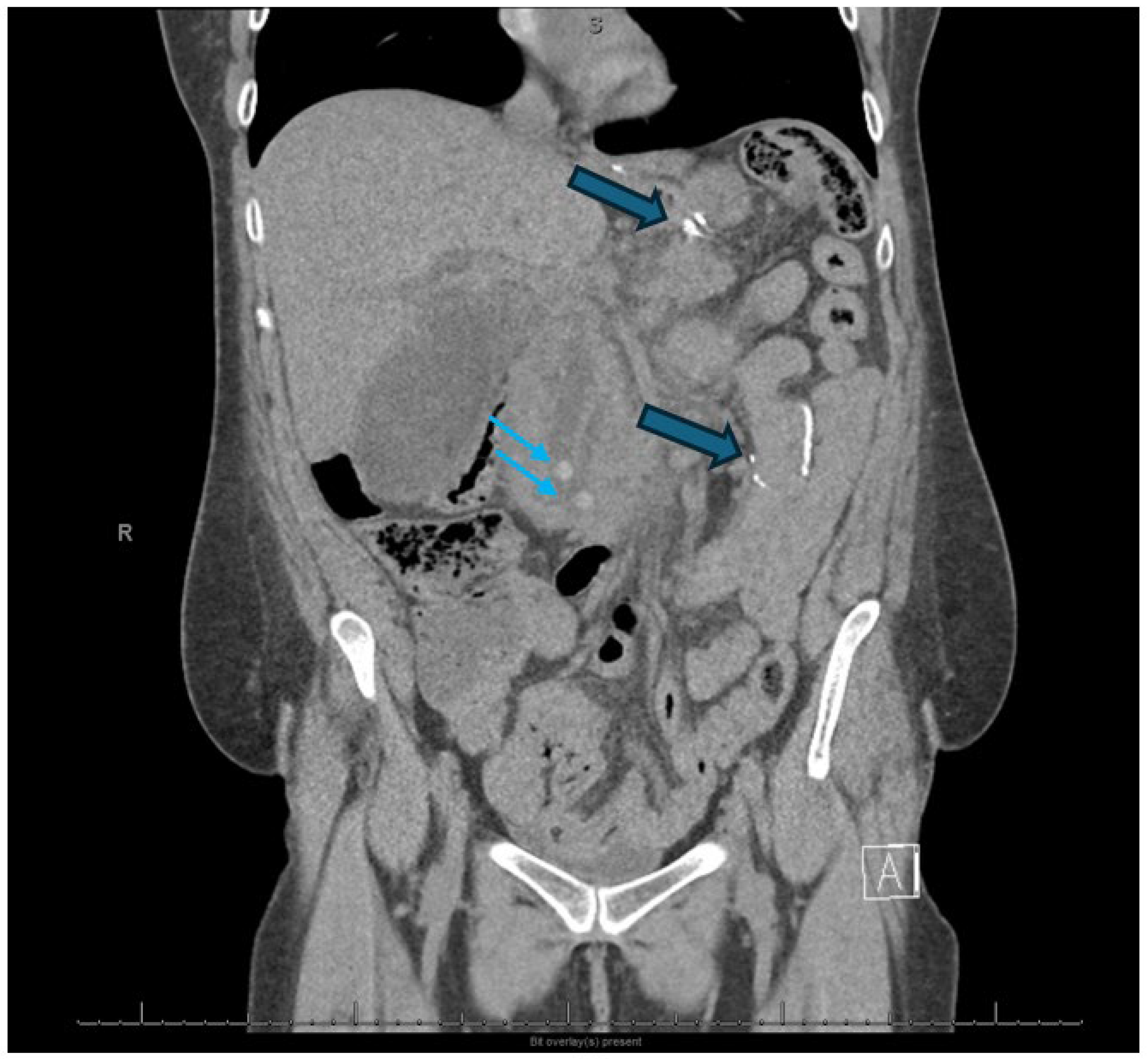
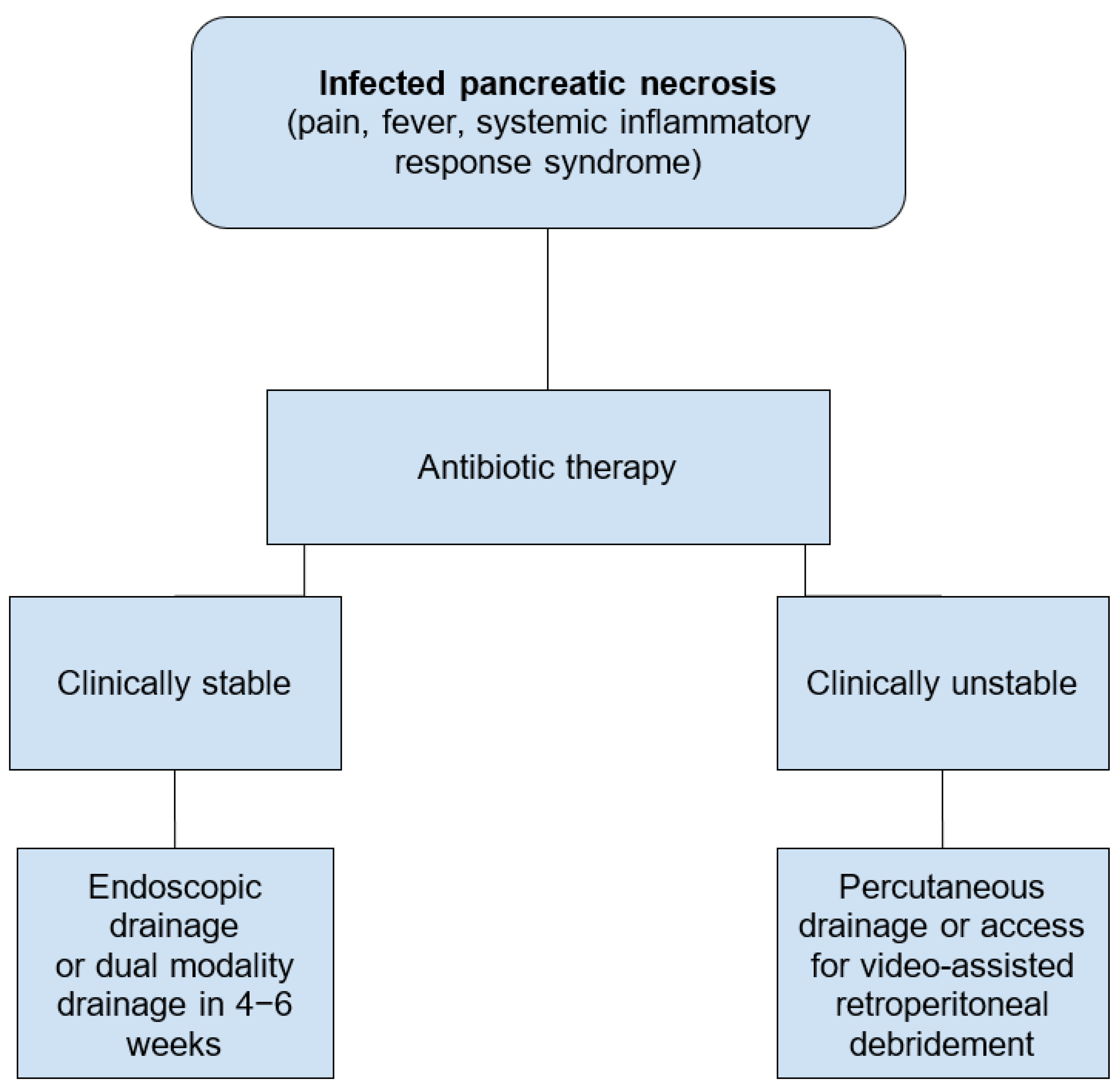
2.3. Infected Pancreatic Necrosis
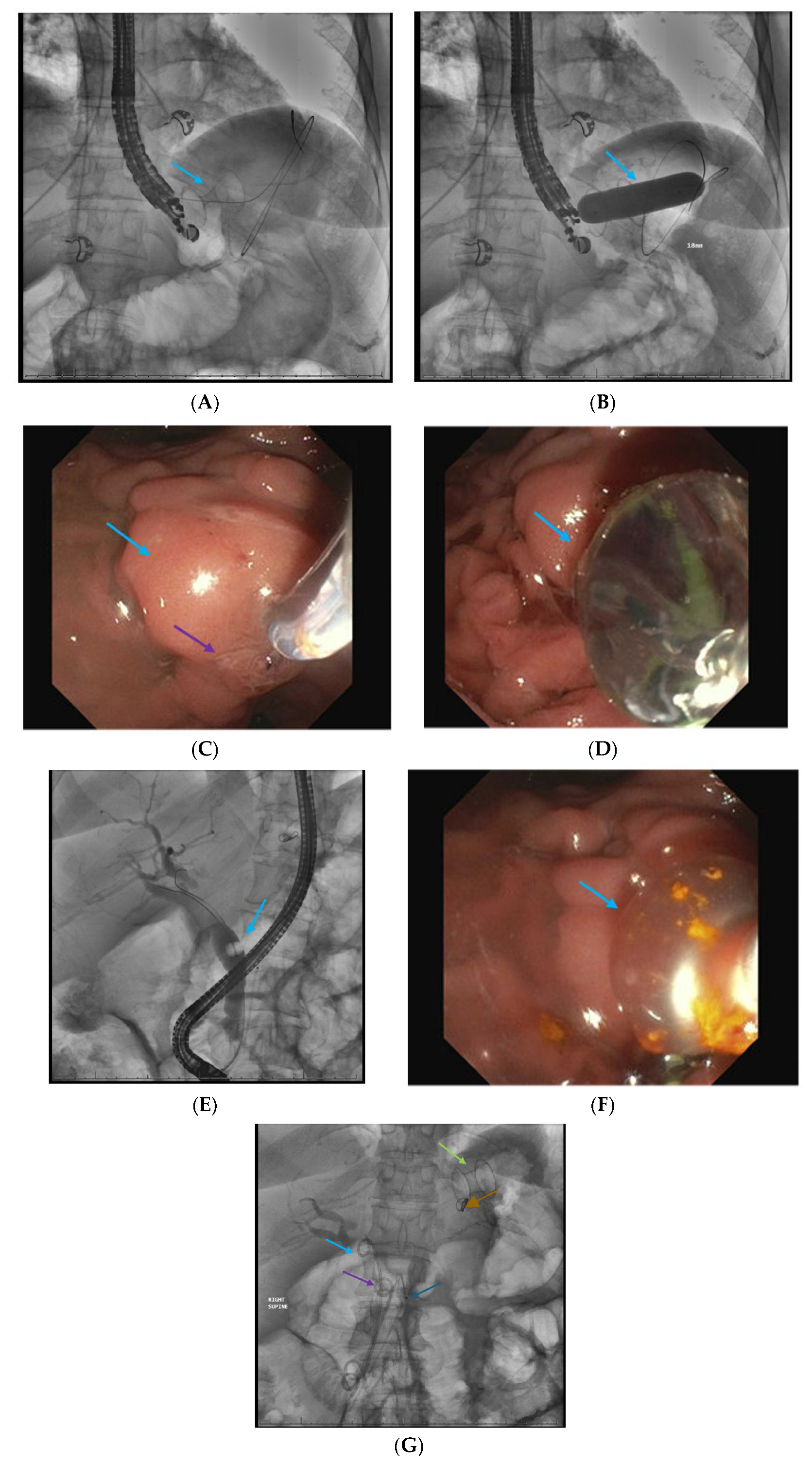
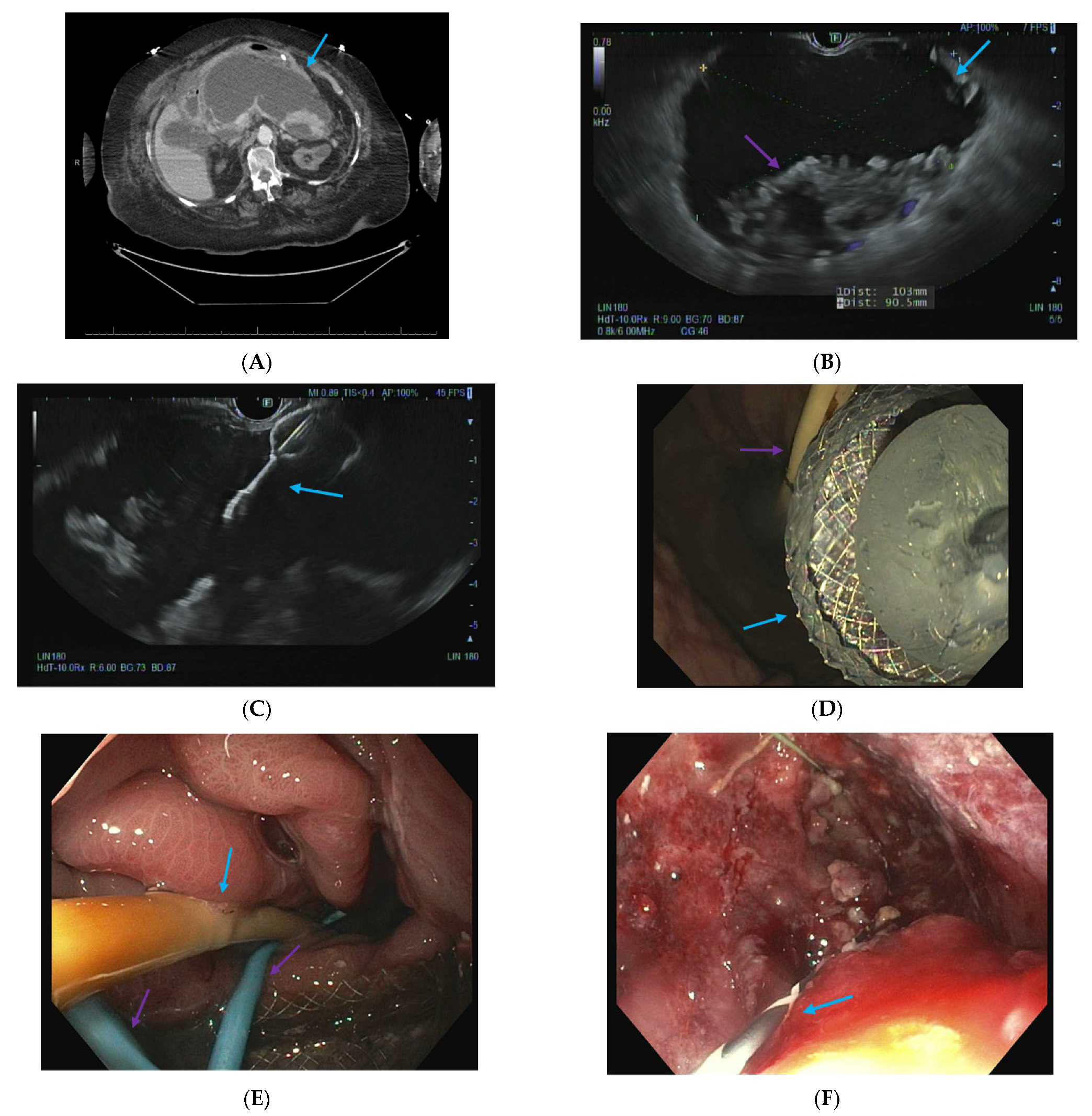
2.4. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Techniques for Walled-Off Pancreatic Necrosis (WON)
2.5. Direct Endoscopic Necrosectomy
2.6. Dual Modality Drainage
2.7. Interventional Radiology-Guided Embolization of Pseudoaneurysms
2.8. Pancreatic Fistula Treatment
2.9. Approach to Disconnected Pancreatic Duct Syndrome (DPDS) After Severe Pancreatitis
2.10. Acute on Chronic Pancreatitis—Fibrotic PD Strictures or Calculi
2.11. Outcomes in Quality of Life and Cost Effectiveness
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tenner, S.; Baillie, J.; DeWitt, J.; Vege, S.S.; American College of Gastroenterology. American College of Gastroenterology Guideline: Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1400–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammann, R.W. The natural history of alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. Intern. Med. 2001, 40, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghdassi, A.A.; Weiss, F.U.; Mayerle, J.; Lerch, M.M.; Simon, P. Genetic susceptibility factors for alcohol-induced chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2015, 15, S23–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coté, G.A.; Xu, H.; Easler, J.J.; Imler, T.D.; Teal, E.; Sherman, S.; Korc, M. Informative Patterns of Health-Care Utilization Prior to the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 186, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Petrov, M.S.; Shanbhag, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Phillips, A.R.; Windsor, J.A. Organ failure and infection of pancreatic necrosis as determinants of mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, R.A.; Halloran, C.; Guo, Q.; Umapathy, C.; Jalaly, N.Y.; Jain, S.; Cowzer, D.; Robles, E.P.C.; Quesada-Vázquez, N.; Szentesi, A.; et al. Early infection is an independent risk factor for increased mortality in patients with culture-confirmed infected pancreatic necrosis. Pancreatology 2022, 22, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Carr-Locke, D.L.; London, N.J.; Bailey, I.A.; James, D.; Fossard, D.P. Controlled trial of urgent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic sphincterotomy versus conservative treatment for acute pancreatitis due to gallstones. Lancet 1988, 2, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissman, S.; Sharma, S.; Ehrlich, D.; Aziz, M.; Bangolo, A.; Gade, A.; Thompson-Edwards, A.; Singla, K.; Venkatesh, H.K.; Kim, M.H.; et al. The role and timing of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in acute biliary pancreatitis without cholangitis: A nationwide analysis. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Sci. 2023, 30, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenner, S.; Vege, S.S.; Sheth, S.G.; Sauer, B.; Yang, A.; Conwell, D.L.; Yadlapati, R.H.; Gardner, T.B. American College of Gastroenterology Guidelines: Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Menno Stavron, J.; Ardiles, V.; Fratantoni, M.E.; Uad, P.; Sanchez Clariá, R.; de Santibañes, M.; Pekolj, J.; Mazza, O. Laparoscopic one-step approach for the management of acute biliary pancreatitis: 10 years experience in a high volume center. Laparosc. Surg. 2021, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, C.; Lewin, J.; Waters, P.; Weber, L.; Cavallucci, D.; Bryant, R.; O’Rourke, N. Long Term Outcomes of Trans-Cystic Bile Duct Exploration. HPB 2021, 23, S89–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.K.N.; DeCicco, J.; Semanate, R.C.; Kara, A.M.; Tran, A.H.; Kim, H.K.; Abraham, A.; Lee, M.; Haurin, S.; Prasad, R.; et al. Lessons learned from implementing laparoscopic common bile duct exploration at a safety net hospital. Surgery 2025, 179, 108887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, L.S.; Friis-Andersen, H.; Zinther, N.B.; Öztoprak, M.; Gotschalck, K.A. Feasibility and outcome of transcystic laparoscopic common bile duct exploration as first-line treatment for common bile duct stones: A retrospective cross-sectional study. Surg. Endosc. 2025, 39, 2256–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balthazar, E.J.; Freeny, P.C.; van Sonnenberg, E. Imaging and intervention in acute pancreatitis. Radiology 1994, 193, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortele, K.J.; Wiesner, W.; Intriere, L.; Shankar, S.; Zou, K.H.; Kalantari, B.N.; Perez, A.; Vansonnenberg, E.; Ros, P.R.; Banks, P.A.; et al. A Modified CT Severity Index for Evaluating Acute Pancreatitis: Improved Correlation with Patient Outcome. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2004, 183, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Gupta, S.; Chawla, A.; Agarwal, Y.; Thukral, B. Comparative study of Balthazar Computed Tomography Severity Index and Modified Computed Tomography Severity Index in predicting the outcome of acute pancreatitis. Apollo Med. 2014, 11, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kulkarni, A.; Babu, R.; Shenvi, S.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, G.; Kang, M.; Gorsi, U.; Rana, S.S. Complications of Percutaneous Drainage in Step-Up Approach for Management of Pancreatic Necrosis: Experience of 10 Years from a Tertiary Care Center. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudin, G.; Chassang, M.; Gelsi, E.; Novellas, S.; Bernardin, G.; Hébuterne, X.; Chevallier, P. CT-Guided Percutaneous Catheter Drainage of Acute Infectious Necrotizing Pancreatitis: Assessment of Effectiveness and Safety. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Freeman, M.L.; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Practice Guidelines in Acute Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2379–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, T.H.; DiMaio, C.J.; Wang, A.Y.; Morgan, K.A. American Gastroenterological Association Clinical Practice Update: Management of Pancreatic Necrosis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 67–75.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatman, T.K.; Zyromski, N.J. Surgical Step-Up Approach in Management of Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2025, 54, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, W.; Werner, J.; Müller, C.A.; Uhl, W.; Büchler, M.W. Surgical management of severe pancreatitis including sterile necrosis. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surg. 2002, 9, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenvi, S.; Gupta, R.; Kang, M.; Khullar, M.; Rana, S.S.; Singh, R.; Bhasin, D.K. Timing of surgical intervention in patients of infected necrotizing pancreatitis not responding to percutaneous catheter drainage. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Santvoort, H.C.; Besselink, M.G.; Bakker, O.J.; Hofker, H.S.; Boermeester, M.A.; Dejong, C.H.; van Goor, H.; Schaapherder, A.F.; van Eijck, C.H.; Bollen, T.L.; et al. A step-up approach or open necrosectomy for necrotizing pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, J.; Dhar, J.; Muktesh, G.; Gupta, P.; Kumar, M.P.; Das, A.; Agarwala, R.; Bellam, B.L.; Chauhan, R.; Kumar, K.H.; et al. Endoscopic drainage versus percutaneous drainage for the management of infected walled-off necrosis: A comparative analysis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 16, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Candio, G.; Guadagni, S.; Furbetta, N.; Gianardi, D.; Palmeri, M.; Di Franco, G.; Bianchini, M.; Gambaccini, D.; Marciano, E.; Cervelli, R.; et al. A “tailored” interventional and surgical management for moderate to critical acute pancreatitis in late phase: A cohort study. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2022, 407, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahim, M.; Werge, M.P.; Hadi, A.; Lahchich, M.; Nagras, Z.G.; Lauritsen, M.L.; Schmidt, P.N.; Hansen, E.F.; Novovic, S.; Karstensen, J.G. Clinical outcomes following endoscopic or video-assisted retroperitoneal management of acute pancreatitis with large (>15 cm) walled-off pancreatic necrosis: Retrospective, single tertiary center cohort study. Dig. Endosc. 2022, 34, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroud, S.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Storm, A.C.; Law, R.J.; Vargas, E.J.; Levy, M.J.; Mahmoud, T.; Bazerbachi, F.; Bofill-Garcia, A.; Ghazi, R.; et al. A Protocolized Management of Walled-Off Necrosis (WON) Reduces Time to WON Resolution and Improves Outcomes. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 2543–2550.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollemans, R.A.; Timmerhuis, H.C.; Besselink, M.G.; Bouwense, S.A.W.; Bruno, M.; van Duijvendijk, P.; van Geenen, E.-J.; Hadithi, M.; Hofker, S.; E Van-Hooft, J.; et al. Long-term follow-up study of necrotising pancreatitis: Interventions, complications and quality of life. Gut 2024, 73, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.Y.; Lakhtakia, S.; Thakkar, S.; Buxbaum, J.L.; Waxman, I.; Sutton, B.; Memon, S.F.; Singh, S.; Basha, J.; Singh, A.; et al. Upfront endoscopic necrosectomy or step-up endoscopic approach for infected necrotising pancreatitis (DESTIN): A single-blinded, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahyadi, O.; Dhir, V.; Leeds, J.; de-Madaria, E.; Tehami, N. The DESTIN trial: To step up or not? Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avudiappan, M.; Bhargava, V.; Kulkarni, A.; Kang, M.; Rana, S.S.; Gupta, R. Evaluating the role of the Minimal Incision Retroperitoneal Necrosectomy (MIRN) in the management of infected pancreatic necrosis: Experience from a tertiary care center. Surg. Open Sci. 2023, 15, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rana, S.S.; Sharma, R.; Kishore, K.; Dhalaria, L.; Gupta, R. Safety and Efficacy of Early (<4 Weeks of Illness) Endoscopic Transmural Drainage of Post-acute Pancreatic Necrosis Predominantly Located in the Body of the Pancreas. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 25, 2328–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaleh, M.; Sundaram, V.; Condron, S.L.; De La Rue, S.A.; Hall, J.D.; Tokar, J.; Friel, C.M.; Foley, E.F.; Adams, R.B.; Yeaton, P. Temporary placement of covered self-expandable metallic stents in patients with biliary leak: Midterm evaluation of a pilot study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007, 66, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzatti, G.; Rimbas, M.; Impagnatiello, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Costamagna, G.; Larghi, A. Endorotor-Based Endoscopic Necrosectomy as a Rescue or Primary Treatment of Complicated Walled-off Pancreatic Necrosis. A Case Series. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2020, 29, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, M.; Bachmann, J.; Schlag, C.; Huegle, U.; Rahman, I.; Wedi, E.; Walter, B.; Möschler, O.; Sturm, L.; Meining, A. Over-the-scope-grasper: A new tool for pancreatic necrosectomy and beyond—First multicenter experience. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2022, 14, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bomman, S.; Sanders, D.; Coy, D.; La Selva, D.; Pham, Q.; Zehr, T.; Law, J.; Larsen, M.; Irani, S.; Kozarek, R.A.; et al. Safety and clinical outcomes of early dual modality drainage (< 28 days) compared to later drainage of pancreatic necrotic fluid collections: A propensity score-matched study. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomman, S.; Canakis, A.; Masood, M.; Klair, J.S.; Alvarez, R.; Muthusamy, A.; Chandra, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Gavini, H.; Krishnamoorthi, R. Early versus late drainage of pancreatic necrotic fluid collections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Gastroenterol. 2025, 38, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abdallah, M.; Vantanasiri, K.; Young, S.; Azeem, N.; Amateau, S.K.; Mallery, S.; Freeman, M.L.; Trikudanathan, G. Visceral artery pseudoaneurysms in necrotizing pancreatitis: Risk of early bleeding with lumen-apposing metal stents. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Tong, H.; Chen, L.X.; Wu, M.J.; Liu, T.Q.; Mao, X.X.; Xie, J.; Yang, F.; Zhou, D.; Quan, X.; et al. Prevalence, treatment efficacy, and risk factors of vascular complications in acute pancreatitis: A case-control study. J. Dig. Dis. 2024, 25, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhusudhan, K.S.; Gopi, S.; Singh, A.N.; Agarwal, L.; Gunjan, D.; Srivastava, D.N.; Garg, P.K. Immediate and Long-Term Outcomes of Percutaneous Radiological Interventions for Hemorrhagic Complications in Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 32, 1591–1600.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielli, D.; Taglialatela, F.; Mantini, C.; Giammarino, A.; Modestino, F.; Cotroneo, A.R. Endovascular Treatment of Visceral Artery Pseudoaneurysms in Patients with Chronic Pancreatitis: Our Single-Center Experience. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 45, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talwar, A.; Knight, G.; Al Asadi, A.; Entezari, P.; Chen, R.; Resnick, S.; Komanduri, S.; Gabr, A.; Thornburg, B.; Salem, R.; et al. Post-embolization outcomes of splenic artery pseudoaneurysms: A single-center experience. Clin. Imaging 2021, 80, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagielski, M.; Piątkowski, J.; Jackowski, M. Endoscopic treatment of pancreaticopleural fistulas. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 939137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kayyal, L.; Al-Khafaji, M.Q.M.; Al-Khafaji, M.Q.; Mehta, A.; Kayyal, R.; Al-Khafaji, Y.Q.; Akilimali, A.; Al Hasani, A. Management of pancreaticopleural fistulas secondary to pancreatitis: A systematic review. Int. J. Surg. 2025, 111, 5572–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozarek, R.A.; Traverso, L.W. Pancreatic fistulas: Etiology, consequences, and treatment. Gastroenterologist 1996, 4, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Rana, S.S. Disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome: Updated review on clinical implications and management. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, M.; Saito, T.; Hamada, T.; Omoto, S.; Shiomi, H.; Iwashita, T.; Masuda, A.; Matsubara, S.; Maruta, A.; Iwata, K.; et al. Disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome: Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges and future directions. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 18, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutlas, N.; Bentley, B.; Dorrell, R.; Ferris, T.; Pawa, R. Clinical outcomes of long-term transmural drainage with double pigtail stents in disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chong, E.; Ratnayake, C.B.; Saikia, S.; Nayar, M.; Oppong, K.; French, J.J.; Windsor, J.A.; Pandanaboyana, S. Endoscopic transmural drainage is associated with improved outcomes in disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee; Sheth, S.G.; Machicado, J.D.; Chalhoub, J.M.; Forsmark, C.; Zyromski, N.; Thosani, N.C.; Thiruvengadam, N.R.; Ruan, W.; Pawa, S.; et al. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guideline on the role of endoscopy in the management of chronic pancreatitis: Summary and recommendations. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2024, 100, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jearth, V.; Giri, S.; Sundaram, S. Approach to management of pancreatic strictures: The gastroenterologist’s perspective. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, D.S.; Law, R.J.; Yang, D.; Elmunzer, B.J. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Endoscopic Approach to Recurrent Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.Y.; Arnoletti, J.P.; Holt, B.A.; Sutton, B.; Hasan, M.K.; Navaneethan, U.; Feranec, N.; Wilcox, C.M.; Tharian, B.; Hawes, R.H.; et al. An Endoscopic Transluminal Approach, Compared with Minimally Invasive Surgery, Reduces Complications and Costs for Patients with Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1027–1040.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, Z.; Xu, J.; Verma, A.; Ebrahimian, S.; Cho, N.Y.; Benharash, P.; Burruss, S. National trends and clinical outcomes of interventional approaches following admission for infected necrotizing pancreatitis in the United States. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023, 94, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, U.; Abbasi, A.F.; Tarar, Z.I.; Chaudhary, A.J.; Kamal, F. Understanding the role of frailty in local and systemic complications and healthcare resource utilization in acute pancreatitis: Findings from a national cohort. Pancreatology 2024, 24, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, J.A.; Hsu, J.; Bawazeer, M.; Marshall, J.; Friedrich, J.O.; Nathens, A.; Coburn, N.; May, G.R.; Pearsall, E.; McLeod, R.S. Clinical practice guideline: Management of acute pancreatitis. Can. J. Surg. 2016, 59, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]


| Biliary pancreatitis |
|
| Severe acute pancreatitis |
|
| Biliary pancreatitis with cholecystitis and a poor surgical candidate |
|
| Acute pancreatic fluid collections |
|
| Enteral nutrition |
|
| Acute symptomatic pancreatic fluid collections |
|
| Necrotic fluid collections |
|
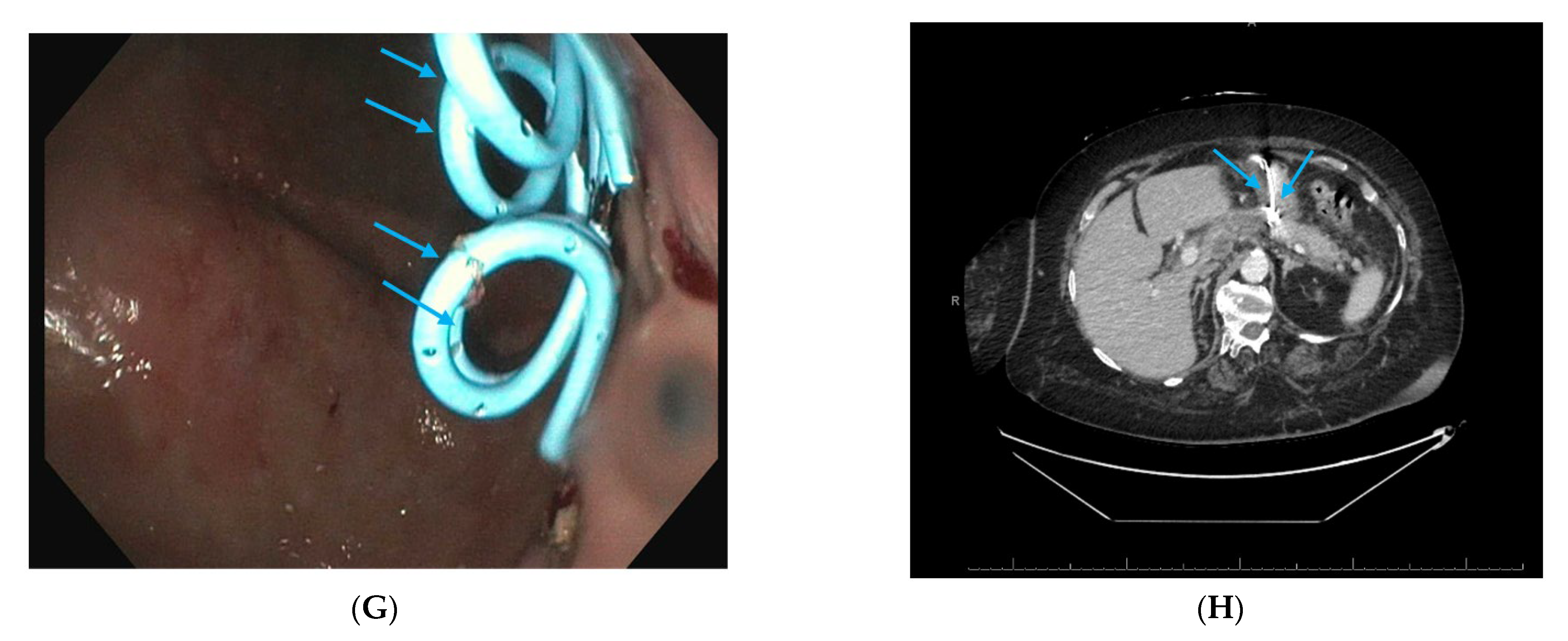
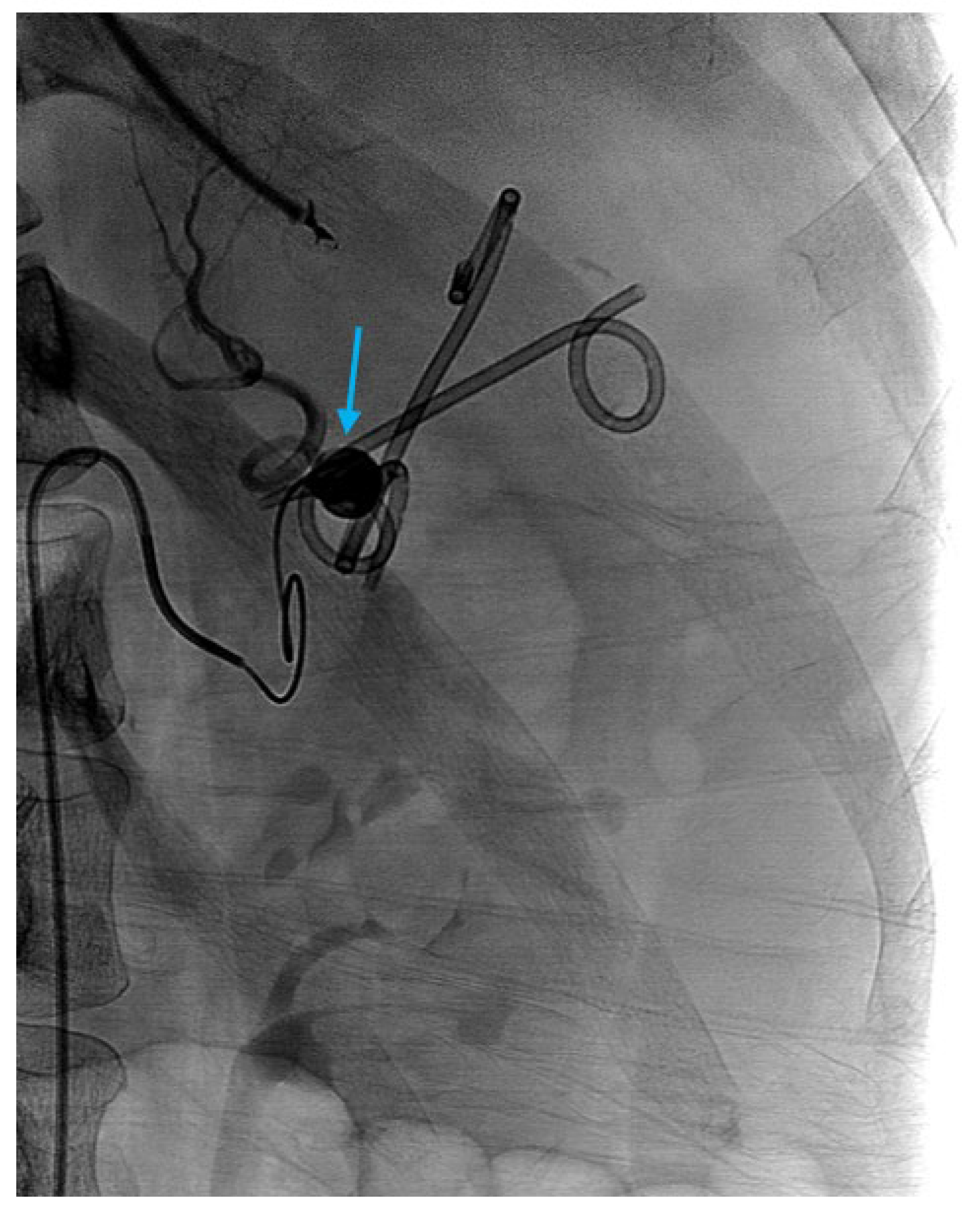
| Pseudoaneurysm |
|
| Obstructive jaundice and a failed endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography |
|
| Pancreatitis with acute cholecystitis and a poor surgical candidate |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Walled-off necrosis |
|
| Pancreatic pseudocyst |
|
| Disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome |
|
| Pancreatitis with acute cholecystitis and a poor surgical candidate |
|
| Gastric outlet obstruction |
|
| Altered anatomy |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masood, M.; Vedamurthy, A.; Krishnamoorthi, R.; Irani, S.; Fotoohi, M.; Kozarek, R. Interventional Management of Acute Pancreatitis and Its Complications. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6683. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186683
Masood M, Vedamurthy A, Krishnamoorthi R, Irani S, Fotoohi M, Kozarek R. Interventional Management of Acute Pancreatitis and Its Complications. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6683. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186683
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasood, Muaaz, Amar Vedamurthy, Rajesh Krishnamoorthi, Shayan Irani, Mehran Fotoohi, and Richard Kozarek. 2025. "Interventional Management of Acute Pancreatitis and Its Complications" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6683. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186683
APA StyleMasood, M., Vedamurthy, A., Krishnamoorthi, R., Irani, S., Fotoohi, M., & Kozarek, R. (2025). Interventional Management of Acute Pancreatitis and Its Complications. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6683. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186683






