Activated Complement System’s Impact in Antiphospholipid Syndrome Thrombosis: From Pathophysiology to Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
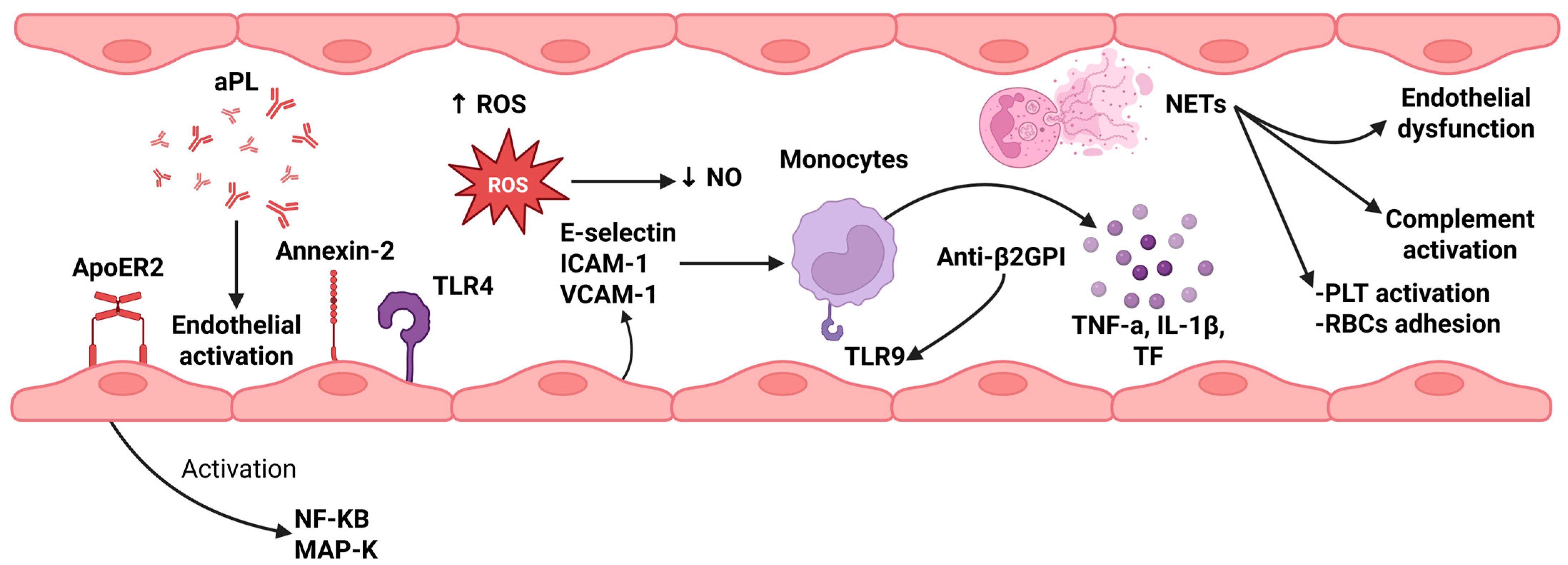
2. An Overview of APS Pathophysiology
2.1. Role of Endothelial Cell Activation
2.2. Role of Monocytes
2.3. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs)
2.4. Platelet Activation
2.5. Dysregulation of Coagulation and Fibrinolytic Systems
3. Complement System in APS
3.1. An Overview of Complement Biology
3.2. Complement System Activation in APS
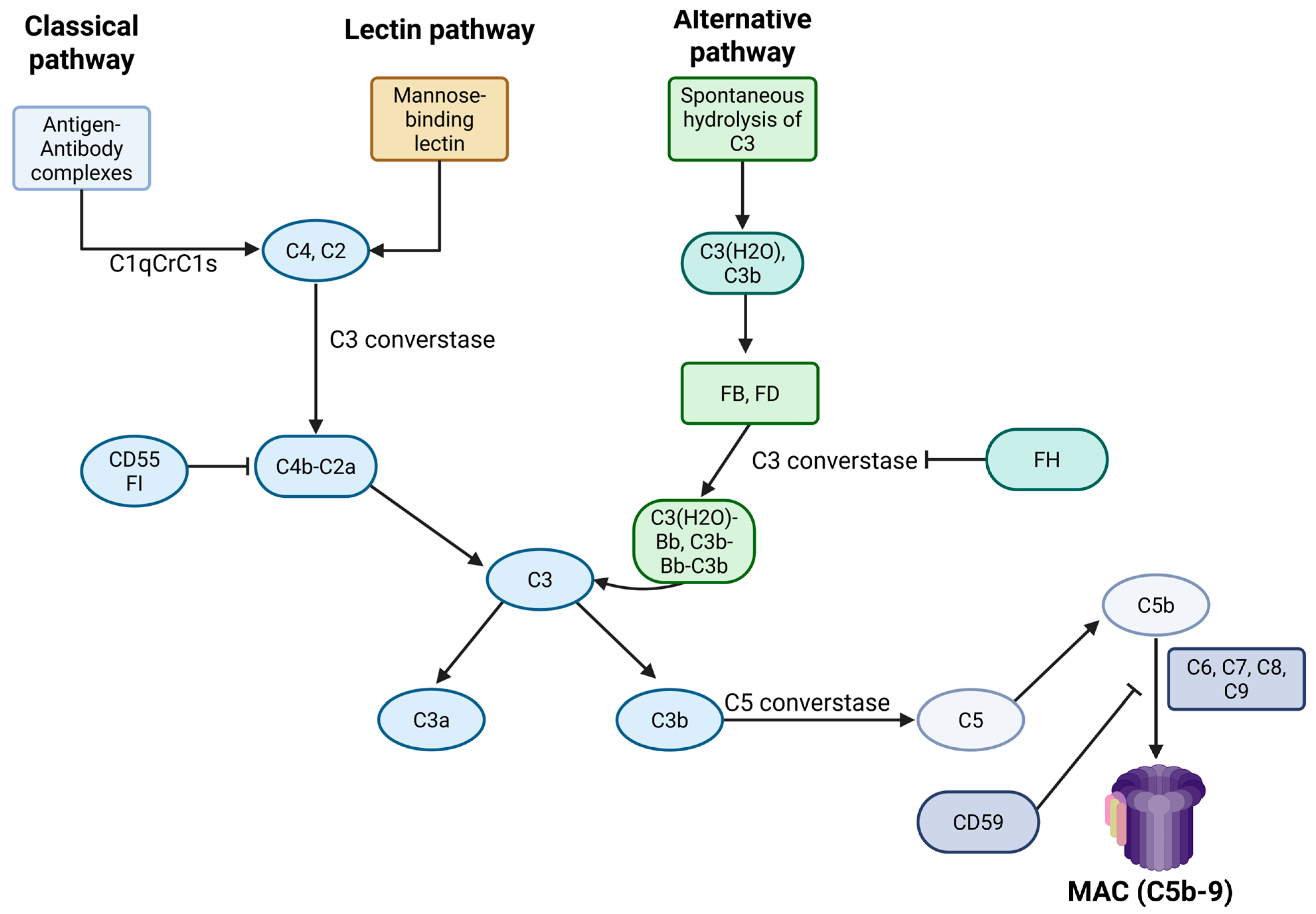
3.3. Underlying Mechanisms of Complement Dysregulation in APS
3.3.1. Activation Through the Classical Pathway
3.3.2. The Contribution of Platelets
3.3.3. The Significance of β2GPI
3.3.4. The Role of Factor H
3.3.5. The Impact of Mutations
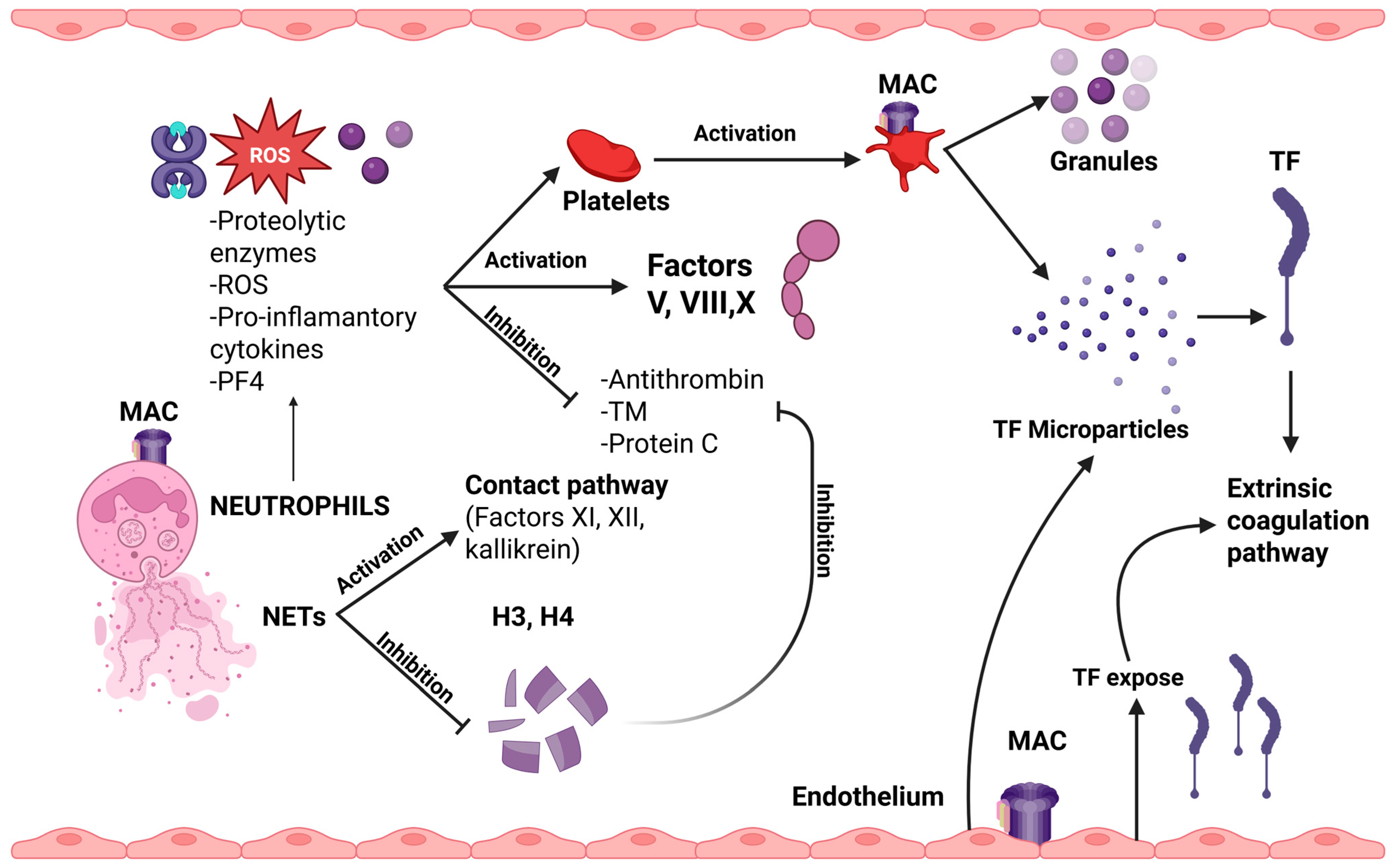
4. Complement’s Interplay with Thrombosis
- (a)
- modify cell membranes by inducing the exposure of negatively charged phospholipids, which are essential for the initiation of coagulation.
- (b)
- activate platelets and neutrophils.
- (c)
- induce the expression of TF by various cell types.
- (d)
- disrupt the fibrinolytic process.
5. APS Treatment Approach
5.1. Current Treatment
5.2. Emerging Therapies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, G.R. Thrombosis, Abortion, Cerebral Disease, and the Lupus Anticoagulant. Br. Med. J. 1983, 287, 1088–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Andreoli, L.; Limper, M.; Tincani, A.; Ward, M.M. Management of Thrombotic and Obstetric Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Systematic Literature Review Informing the EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Antiphospholipid Syndrome in Adults. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabit, J.Y.; Valenzuela-Almada, M.O.; Vallejo-Ramos, S.; Duarte-García, A. Epidemiology of Antiphospholipid Syndrome in the General Population. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2022, 23, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, S.; Amigo, M.-C.; Roccatello, D.; Khamashta, M. Diagnosing Antiphospholipid Syndrome: “extra-Criteria” Manifestations and Technical Advances. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devreese, K.M.J.; Zuily, S.; Meroni, P.L. Role of Antiphospholipid Antibodies in the Diagnosis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hasbani, G.; Viola, M.; Sciascia, S.; Taher, A.T.; Uthman, I. Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases Beyond Lupus: A Systematic Review of the Available Evidence. Rheumatol. Ther. 2021, 8, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorice, M.; Pittoni, V.; Griggi, T.; Losardo, A.; Leri, O.; Magno, M.S.; Misasi, R.; Valesini, G. Specificity of Anti-Phospholipid Antibodies in Infectious Mononucleosis: A Role for Anti-Cofactor Protein Antibodies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2001, 120, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asherson, R.A.; Cervera, R.; Merrill, J.T.; Erkan, D. Antiphospholipid Antibodies and the Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Clinical Significance and Treatment. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2008, 34, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriarcheas, V.; Tsamos, G.; Vasdeki, D.; Kotteas, E.; Kollias, A.; Nikas, D.; Kaiafa, G.; Dimakakos, E. Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Comprehensive Clinical Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Gao, W.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, C. Antiphospholipid Syndrome-Related Pulmonary Embolism: Clinical Characteristics and Early Recognition. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 872523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Cheng, G.-Y.; Denas, G.; Pengo, V. Arterial Thrombosis in Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS): Clinical Approach and Treatment. A Systematic Review. Blood Rev. 2021, 48, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelidis, P.; Kotsiou, N.; Kalmoukos, P.; Ntova, Z.; Papadopoulou, T.; Chissan, S.; Sarvani, A.; Kokoris, S.; Grouzi, E.; Doumas, M.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Acute Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Retrospective Monocenter Analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelidis, P.; Gavriilaki, E.; Kotsiou, N.; Ntova, Z.; Kalmoukos, P.; Papadopoulou, T.; Chissan, S.; Vakalopoulou, S. Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head in Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Case Series. Hematol. Rep. 2025, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asherson, R.A.; Cervera, R. Microvascular and Microangiopathic Antiphospholipid-Associated Syndromes (“MAPS”): Semantic or Antisemantic? Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 7, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniscalchi, C.; Basaglia, M.; Riva, M.; Meschi, M.; Meschi, T.; Castaldo, G.; Di Micco, P. Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Review. Immuno 2023, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, P.; Sciascia, S.; Tektonidou, M.G. Epidemiology of Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Macro- and Microvascular Manifestations. Rheumatology 2024, 63, SI24–SI36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Ding, Z.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Li, L.; Teng, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Su, Y.; et al. Risk Factors in Antiphospholipid Antibody-Associated Valvular Heart Disease: A 383-Patient Cohort Study. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 256, 109790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, G.; Song, X.; Fan, Y.; Li, C. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Prognosis of Central Nervous System Manifestations in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hasbani, G.; Saliba, A.N.; Uthman, I.; Taher, A.T. Hematological Manifestations of Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Going beyond Thrombosis. Blood Rev. 2023, 58, 101015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, R.; Giordano, G.; Romano, F.; Vaccarino, F.; Siragusa, S.; Lucchesi, A.; Napolitano, M. Immune Thrombocytopenia in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Is It Primary or Secondary? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthman, I.; Godeau, B.; Taher, A.; Khamashta, M. The Hematologic Manifestations of the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Blood Rev. 2008, 22, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsimi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.; Derksen, R.H.W.M.; De Groot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International Consensus Statement on an Update of the Classification Criteria for Definite Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Jang, S.; Park, C.-J.; Chi, H.-S. Clinical Application of Revised Laboratory Classification Criteria for Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Is the Follow-Up Interval of 12 Weeks Instead of 6 Weeks Significantly Useful? Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2641526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhaiya, M.; Zuily, S.; Naden, R.; Hendry, A.; Manneville, F.; Amigo, M.-C.; Amoura, Z.; Andrade, D.; Andreoli, L.; Artim-Esen, B.; et al. 2023 ACR/EULAR Antiphospholipid Syndrome Classification Criteria. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza, D.; Bou, N.; Puiggròs-Ferrer, A.; Veloza Morales, C.; Sirera Perello, H.; Ayza Farrerons, C.; Escarpenter Pitarch, O.; Pros, A.; Pérez-García, C.; Salman-Monte, T.; et al. AB0007 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF THE SYDNEY (2004) AND ACR/EULAR (2023) CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA FOR ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME: EMPHASIS ON RECENTLY INCLUDED CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS AS PART OF THE ACR/EULAR CRITERIA. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1228–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschi, E.; Borghi, M.O.; Tedesco, F.; Meroni, P.L. Antiphospholipid Syndrome Pathogenesis in 2023: An Update of New Mechanisms or Just a Reconsideration of the Old Ones? Rheumatology 2024, 63, SI4–SI13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygiel-Górniak, B.; Mazurkiewicz, Ł. Positive Antiphospholipid Antibodies: Observation or Treatment? J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2023, 56, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.S.; Kanthi, Y. Mechanisms of Immunothrombosis and Vasculopathy in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrottmaier, W.C.; Assinger, A. The Concept of Thromboinflammation. Hamostaseologie 2024, 44, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, M.; Rojas, M.; Abrahams, V.M.; Escudero, C.; Cadavid, Á.P. Mechanisms of Endothelial Dysfunction in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Association with Clinical Manifestations. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.S.; Branch, D.W.; Ortel, T.L. Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Advances in Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, and Management. BMJ 2023, 380, e069717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riitano, G.; Capozzi, A.; Recalchi, S.; Caissutti, D.; Longo, A.; Mattei, V.; Conti, F.; Misasi, R.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M.; et al. Anti-Β2-GPI Antibodies Induce Endothelial Cell Expression of Tissue Factor by LRP6 Signal Transduction Pathway Involving Lipid Rafts. Cells 2022, 11, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; You, L.; Lin, Y.; Wang, K.; Gou, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, S.; et al. The Role of Monocytes in Thrombotic Diseases: A Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1113827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štok, U.; Štucin, N.; Blokar, E.; Ambrožič, A.; Sodin-Šemrl, S.; Čučnik, S.; Žigon, P. Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome-Associated Increased Surface Expression of VLA4 Integrin on Human Monocytes. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z. Impact of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps on Thrombosis Formation: New Findings and Future Perspective. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 910908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnyak, T.; Nurbaeva, K. The Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi-Esfahani, I.; Mittal, P.; Isenberg, D.; Cohen, H.; Efthymiou, M. Platelets and Thrombotic Antiphospholipid Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Shi, H.; Chen, C.; Teng, J.; Dai, J.; Ouyang, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q.; Cheng, X.; Ye, J.; et al. Activation of Platelet MTORC2/Akt Pathway by Anti-Β2GP1 Antibody Promotes Thrombosis in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2023, 43, 1818–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, S.K.; Starke, R.D.; Lawrie, A.S.; Cohen, H.; Machin, S.J.; Mackie, I.J. The VWF/ADAMTS13 Axis in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome: ADAMTS13 Antibodies and ADAMTS13 Dysfunction. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Zha, C.; Liu, Y. Platelet-Derived Microparticles Stimulated by Anti-Β2GPI/Β2GPI Complexes Induce Pyroptosis of Endothelial Cells in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Platelets 2023, 34, 2156492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreola-Diaz, R.; Majluf-Cruz, A.; Sanchez-Torres, L.E.; Hernandez-Juarez, J. The Pathophysiology of the Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Perspective from the Blood Coagulation System. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2022, 28, 10760296221088576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.K.; Grossman, J.M.; Visvanathan, S.; Chukwuocha, R.U.; Woods, V.L.; Le, D.T.; Hahn, B.H.; Chen, P.P. Identification of Anti-Thrombin Antibodies in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome That Interfere with the Inactivation of Thrombin by Antithrombin. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 7192–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-H.; Chien, D.; Wu, M.; FitzGerald, J.; Grossman, J.M.; Hahn, B.H.; Hwang, K.-K.; Chen, P.P. Novel Autoantibodies against the Activated Coagulation Factor IX (FIXa) in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome That Interpose the FIXa Regulation by Antithrombin. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1674–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Braunstein, E.M.; Brodsky, R.A. Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Complement Activation, Complement Gene Mutations, and Therapeutic Implications. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, K.; Atsumi, T.; Bohgaki, M.; Amengual, O.; Kataoka, H.; Horita, T.; Yasuda, S.; Koike, T. Complement Activation in Patients with Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Oku, K.; Ogata, Y.; Ohmura, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Kitano, E.; Fujieda, Y.; Kato, M.; Bohgaki, T.; Amengual, O.; et al. Alternative Pathway Activation Due to Low Level of Complement Factor H in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Thromb. Res. 2018, 164, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Brodsky, R.A.; McCrae, K.R. Complement in the Pathophysiology of the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Brodsky, R.A. Complementopathies and Precision Medicine. J. Clin. Invest. 2020, 130, 2152–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruse, J.M.; Lewis, R.E. The Complement System. In Atlas of Immunology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Harboe, M.; Mollnes, T.E. The Alternative Complement Pathway Revisited. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkelberger, J.R.; Song, W.-C. Complement and Its Role in Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoris, S.; Polyviou, A.; Evangelidis, P.; Grouzi, E.; Valsami, S.; Tragiannidis, K.; Gialeraki, A.; Tsakiris, D.A.; Gavriilaki, E. Thrombosis in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH): From Pathogenesis to Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; de Latour, R.P.; Risitano, A.M. Advancing Therapeutic Complement Inhibition in Hematologic Diseases: PNH and Beyond. Blood 2022, 139, 3571–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangeli, S.S.; Girardi, G.; Vega-Ostertag, M.; Liu, X.; Espinola, R.G.; Salmon, J. Requirement of Activation of Complement C3 and C5 for Antiphospholipid Antibody-Mediated Thrombophilia. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2120–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischetti, F.; Durigutto, P.; Pellis, V.; Debeus, A.; Macor, P.; Bulla, R.; Bossi, F.; Ziller, F.; Sblattero, D.; Meroni, P.; et al. Thrombus Formation Induced by Antibodies to Beta2-Glycoprotein I Is Complement Dependent and Requires a Priming Factor. Blood 2005, 106, 2340–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera-Marín, A.; Romay-Penabad, Z.; Papalardo, E.; Reyes-Maldonado, E.; García-Latorre, E.; Vargas, G.; Shilagard, T.; Pierangeli, S. C6 Knock-out Mice Are Protected from Thrombophilia Mediated by Antiphospholipid Antibodies. Lupus 2012, 21, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.D.; Brey, R.L. Antiphospholipid Antibodies and Complement Activation in Patients with Cerebral Ischemia. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1992, 10, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Breen, K.A.; Seed, P.; Parmar, K.; Moore, G.W.; Stuart-Smith, S.E.; Hunt, B.J. Complement Activation in Patients with Isolated Antiphospholipid Antibodies or Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 107, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, P.L.; Macor, P.; Durigutto, P.; De Maso, L.; Gerosa, M.; Ferraresso, M.; Borghi, M.O.; Mollnes, T.E.; Tedesco, F. Complement Activation in Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Its Inhibition to Prevent Rethrombosis after Arterial Surgery. Blood 2016, 127, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonati, P.A.; Scavone, M.; Gerosa, M.; Borghi, M.O.; Pregnolato, F.; Curreli, D.; Podda, G.; Femia, E.A.; Barcellini, W.; Cattaneo, M.; et al. Blood Cell-Bound C4d as a Marker of Complement Activation in Patients with the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Braunstein, E.M.; Yuan, X.; Yu, J.; Alexander, A.; Chen, H.; Gavriilaki, E.; Alluri, R.; Streiff, M.B.; Petri, M.; et al. Complement Activity and Complement Regulatory Gene Mutations Are Associated with Thrombosis in APS and CAPS. Blood 2020, 135, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Yuan, X.; Ye, Z.; Ambinder, A.J.; Shanbhag, S.P.; Streiff, M.B.; Kickler, T.S.; Moliterno, A.R.; Sperati, C.J.; Brodsky, R.A. Modified Ham Test for Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Blood 2015, 125, 3637–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostal-Johnson, D.; Rote, N.S.; Branch, D.W. IgG1 and IgG2 Are the Predominant Subclasses of Antiphospholipid Antibody in Women with the Lupus Anticoagulant. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1990, 54, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerschke, E.I.B.; Yin, W.; Alpert, D.R.; Roubey, R.A.S.; Salmon, J.E.; Ghebrehiwet, B. Serum Complement Activation on Heterologous Platelets Is Associated with Arterial Thrombosis in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Antiphospholipid Antibodies. Lupus 2009, 18, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bećarević, M. Antibodies Against Complement Components: Relevance for the Antiphospholipid Syndrome—Biomarkers of the Disease and Biopharmaceuticals. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2017, 19, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, O.; Mohlin, C.; Nilsson, B.; Ekdahl, K.N. The Human Platelet as an Innate Immune Cell: Interactions Between Activated Platelets and the Complement System. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerschke, E.I.; Yin, W.; Ghebrehiwet, B. Complement Activation on Platelets: Implications for Vascular Inflammation and Thrombosis. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 2170–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gropp, K.; Weber, N.; Reuter, M.; Micklisch, S.; Kopka, I.; Hallström, T.; Skerka, C. Β2-Glycoprotein I, the Major Target in Antiphospholipid Syndrome, Is a Special Human Complement Regulator. Blood 2011, 118, 2774–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, N.; Acquasaliente, L.; Frasson, R.; Cristiani, A.; Moro, S.; Banzato, A.; Pengo, V.; Scaglione, G.L.; Arcovito, A.; De Cristofaro, R.; et al. Β2-Glycoprotein I Binds to Thrombin and Selectively Inhibits the Enzyme Procoagulant Functions. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserhalmi, M.; Papp, A.; Brandus, B.; Uzonyi, B.; Józsi, M. Regulation of Regulators: Role of the Complement Factor H-Related Proteins. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 45, 101341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferluga, J.; Kouser, L.; Murugaiah, V.; Sim, R.B.; Kishore, U. Potential Influences of Complement Factor H in Autoimmune Inflammatory and Thrombotic Disorders. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 84, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foltyn Zadura, A.; Memon, A.A.; Stojanovich, L.; Perricone, C.; Conti, F.; Valesini, G.; Bogdanovic, G.; Hillarp, A.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Sundquist, J.; et al. Factor H Autoantibodies in Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Thrombosis. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1786–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Navaz, S.; Tsodikov, A.; Kmetova, K.; Kluge, L.; Ambati, A.; Hoy, C.K.; Yalavarthi, S.; de Andrade, D.; Tektonidou, M.G.; et al. Anti-Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Antibodies in Antiphospholipid Antibody-Positive Patients: Results from the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Alliance for Clinical Trials and InternatiOnal Networking Clinical Database and Repository. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewski, M.M.; Nilsson, B.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Mollnes, T.E.; Lambris, J.D. Complement and Coagulation: Strangers or Partners in Crime? Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, E.M. Complement-Coagulation Connections. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2018, 29, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryzdial, E.L.G.; Leatherdale, A.; Conway, E.M. Coagulation and Complement: Key Innate Defense Participants in a Seamless Web. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 918775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, H.; Richards, A. Complement-Mediated Injury and Protection of Endothelium: Lessons from Atypical Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturelli, V.; Maranini, B.; Tohidi-Esfahani, I.; Isenberg, D.A.; Cohen, H.; Efthymiou, M. Can Complement Activation Be the Missing Link in Antiphospholipid Syndrome? Rheumatology 2024, 63, 3243–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Andreoli, L.; Limper, M.; Amoura, Z.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Dörner, T.; Ferrer-Oliveras, R.; Hambly, K.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Antiphospholipid Syndrome in Adults. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corban, M.T.; Duarte-Garcia, A.; McBane, R.D.; Matteson, E.L.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Role of Vascular Endothelial Cells and Implications for Risk Stratification and Targeted Therapeutics. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, V.; Hoxha, A.; Andreoli, L.; Tincani, A.; Silvestri, E.; Prisco, D.; Fierro, T.; Gresele, P.; Cafolla, A.; De Micheli, V.; et al. Trial of Rivaroxaban in AntiPhospholipid Syndrome (TRAPS): Two-Year Outcomes after the Study Closure. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woller, S.C.; Stevens, S.M.; Kaplan, D.; Wang, T.-F.; Branch, D.W.; Groat, D.; Wilson, E.L.; Armbruster, B.; Aston, V.T.; Lloyd, J.F.; et al. Apixaban Compared with Warfarin to Prevent Thrombosis in Thrombotic Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Randomized Trial. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.; Gafoor, R.; Sayar, Z.; Efthymiou, M.; Tohidi-Esfahani, I.; Appiah-Cubi, S.; Arachchillage, D.J.; Atkinson, D.; Bordea, E.; Cardoso, M.J.; et al. Rivaroxaban for Stroke Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndrome (RISAPS): Protocol for a Randomized Controlled, Phase IIb Proof-of-Principle Trial. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 8, 102468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelhelm, J.B.H.; Christensen, R.; Balbi, G.G.M.; Voss, A. Therapy with Direct Oral Anticoagulants for Secondary Prevention of Thromboembolic Events in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Trials. Lupus Sci. Med. 2023, 10, e001018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.-J.; Harjola, V.-P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism Developed in Collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortel, T.L.; Neumann, I.; Ageno, W.; Beyth, R.; Clark, N.P.; Cuker, A.; Hutten, B.A.; Jaff, M.R.; Manja, V.; Schulman, S.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism: Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4693–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchillage, D.J.; Platton, S.; Hickey, K.; Chu, J.; Pickering, M.; Sommerville, P.; MacCallum, P.; Breen, K. Guidelines on the Investigation and Management of Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 205, 855–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchillage, D.J.; Laffan, M.; Pericleous, C. Hydroxychloroquine as an Immunomodulatory and Antithrombotic Treatment in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayar, Z.; Moll, R.; Isenberg, D.; Cohen, H. Thrombotic Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Management. Thromb. Res. 2021, 198, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubben, A.; McCrae, K.R. Emerging Therapies in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2022, 36, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Pedrera, C.; Ruiz-Limon, P.; Aguirre, M.A.; Rodriguez-Ariza, A.; Cuadrado, M.J. Potential Use of Statins in the Treatment of Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2012, 14, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunton, N.E.; Casanegra, A.I.; Houghton, D.E. “No Shoes. No Shirt. No Thrombus.” Could Vitamin D Levels Change the Tune for Patients With Antiphospholipid Syndrome? Hematologist 2023, 20, 23110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.; Sayar, Z.; Efthymiou, M.; Gaspar, P.; Richards, T.; Isenberg, D. Management of Anticoagulant-Refractory Thrombotic Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e613–e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenti, S.; Guidelli, G.M.; Bellisai, F.; Galeazzi, M.; Fioravanti, A. Long-Term Treatment of Antiphospholipid Syndrome with Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Addition to Conventional Therapy. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2013, 31, 877–882. [Google Scholar]
- Erkan, D.; Vega, J.; Ramón, G.; Kozora, E.; Lockshin, M.D. A Pilot Open-Label Phase II Trial of Rituximab for Non-Criteria Manifestations of Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.; Tarantino, M.D.; Chaturvedi, S.; McCrae, K.R.; Roberts, J.C. Eculizumab for Refractory Thrombosis in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kello, N.; Khoury, L.E.; Marder, G.; Furie, R.; Zapantis, E.; Horowitz, D.L. Secondary Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Antiphospholipid Syndrome, the Role of Complement and Use of Eculizumab: Case Series and Review of Literature. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Benjume, B.; Rodríguez-Pintó, I.; Amigo, M.C.; Erkan, D.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Cervera, R.; Espinosa, G.; on behalf the CAPS Registry Project Group/European Forum on Antiphospholipid Antibodies. Eculizumab Use in Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome (CAPS): Descriptive Analysis from the “CAPS Registry”. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCT05671757, Daratumumab in Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome (DARE-APS). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05671757 (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Yun, Z.; Duan, L.; Liu, X.; Cai, Q.; Li, C. An Update on the Biologics for the Treatment of Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1145145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.A.; Estes, S.K.; Gandhi, A.A.; Yalavarthi, S.; Hoy, C.K.; Shi, H.; Zuo, Y.; Erkan, D.; Knight, J.S. Defibrotide Inhibits Antiphospholipid Antibody-Mediated Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation and Venous Thrombosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Evangelidis, P.; Mainou, M.; Venou, T.M.; Vlantos, V.T.; Vlachaki, E. Pegcetacoplan for the Treatment of Warm Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: A Case Report. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2025, 113–114, 102938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCT06723106, Phase 1b Long-Term Extension Trial of RAY121 in Immunological Diseases (RAINBOW-LTE Trial). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06723106 (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Anyfanti, P.; Evangelidis, P.; Kotsiou, N.; Papakonstantinou, A.; Eftychidis, I.; Sakellari, I.; Dimitroulas, T.; Gavriilaki, E. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Rheumatic Disorders: Where Are We Now? Cells 2025, 14, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelidis, P.; Gavriilaki, E.; Tsakiris, D.A. Thrombotic Complications after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Other Cellular Therapies. Thromb. Update 2024, 16, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodele, S.; Gavriilaki, E. Translating Biomarker Insights into Practice: A Path Forward in TA-TMA Management. Front Med. 2025, 12, 1550365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Criteria | Laboratory Criteria |
|---|---|
| 1. Venous thromboembolism | 1. Lupus anticoagulant positivity |
| 2. Arterial thrombosis | 2. aPL test positivity |
| 3. Microvascular manifestations | |
| 4. Obstetric complications | |
| 5. Manifestations from cardiac valves | |
| 6. Thrombocytopenia |
| Agent | Target | Pathophysiological Role |
|---|---|---|
| Adalimumab | TNFα antagonist | Reduces TF expression by monocytes |
| Rapamycin-Everolimus | mTOR pathway inhibitors | Prevent activation of monocytes and platelets |
| Dipyridamole | Antiplatelet agent | Reduces platelet hyperreactivity and oxidative stress |
| Ubiquinol | Antioxidant | Decreases reactive oxygen species |
| Anti-PSGL-1 mAb | Antibodies targeting P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 | Suppress neutrophil adhesion to endothelium |
| Defibrotide | Oligonucleotides | Decrease thrombus size, NETs formation, and endothelial activation |
| Eculizumab | C5 complement inhibitor | Blocks the terminal complement pathway |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tagara, S.; Valsami, S.; Gavriilaki, E.; Kyriakou, E.; Grouzi, E.; Evangelidis, P.; Karvouni, P.; Kaiafa, G.; Papadakis, I.; Poulis, A.; et al. Activated Complement System’s Impact in Antiphospholipid Syndrome Thrombosis: From Pathophysiology to Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186672
Tagara S, Valsami S, Gavriilaki E, Kyriakou E, Grouzi E, Evangelidis P, Karvouni P, Kaiafa G, Papadakis I, Poulis A, et al. Activated Complement System’s Impact in Antiphospholipid Syndrome Thrombosis: From Pathophysiology to Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186672
Chicago/Turabian StyleTagara, Sofia, Serena Valsami, Eleni Gavriilaki, Elias Kyriakou, Elisavet Grouzi, Paschalis Evangelidis, Paraskevi Karvouni, Georgia Kaiafa, Ioannis Papadakis, Aristarchos Poulis, and et al. 2025. "Activated Complement System’s Impact in Antiphospholipid Syndrome Thrombosis: From Pathophysiology to Treatment" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186672
APA StyleTagara, S., Valsami, S., Gavriilaki, E., Kyriakou, E., Grouzi, E., Evangelidis, P., Karvouni, P., Kaiafa, G., Papadakis, I., Poulis, A., Petrou, E., Politou, M., & Kokoris, S. (2025). Activated Complement System’s Impact in Antiphospholipid Syndrome Thrombosis: From Pathophysiology to Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6672. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186672







