Early Risk Prediction for Biologic Therapy in Psoriasis Using Machine Learning Models Based on Routine Health Records
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Cohort Balancing and Data Partitioning
2.4. Biologic Medications
2.5. Predictor Variables
2.6. Model Development
2.6.1. Feature Engineering and Selection
2.6.2. Data Imputation and Scaling
2.6.3. Training and Validation Approach
2.6.4. Hyperparameter Tuning
2.6.5. Class Imbalance Handling
2.6.6. Model Performance Evaluation
2.6.7. Features Importance
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Use of Generative AI Tools
3. Results
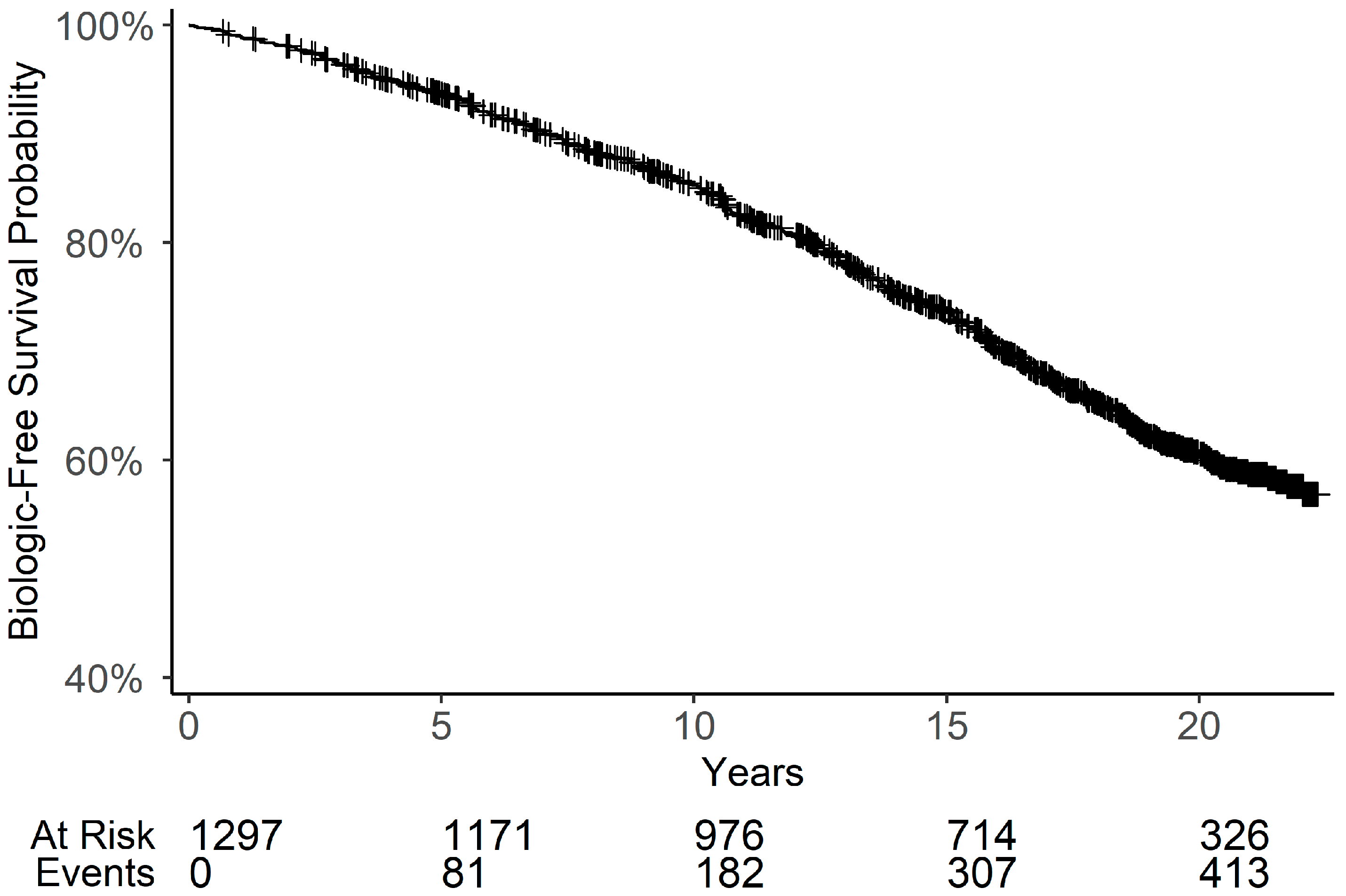
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Prediction of Biology Therapy Based on Data Recorded in the First 5 Years After Onset
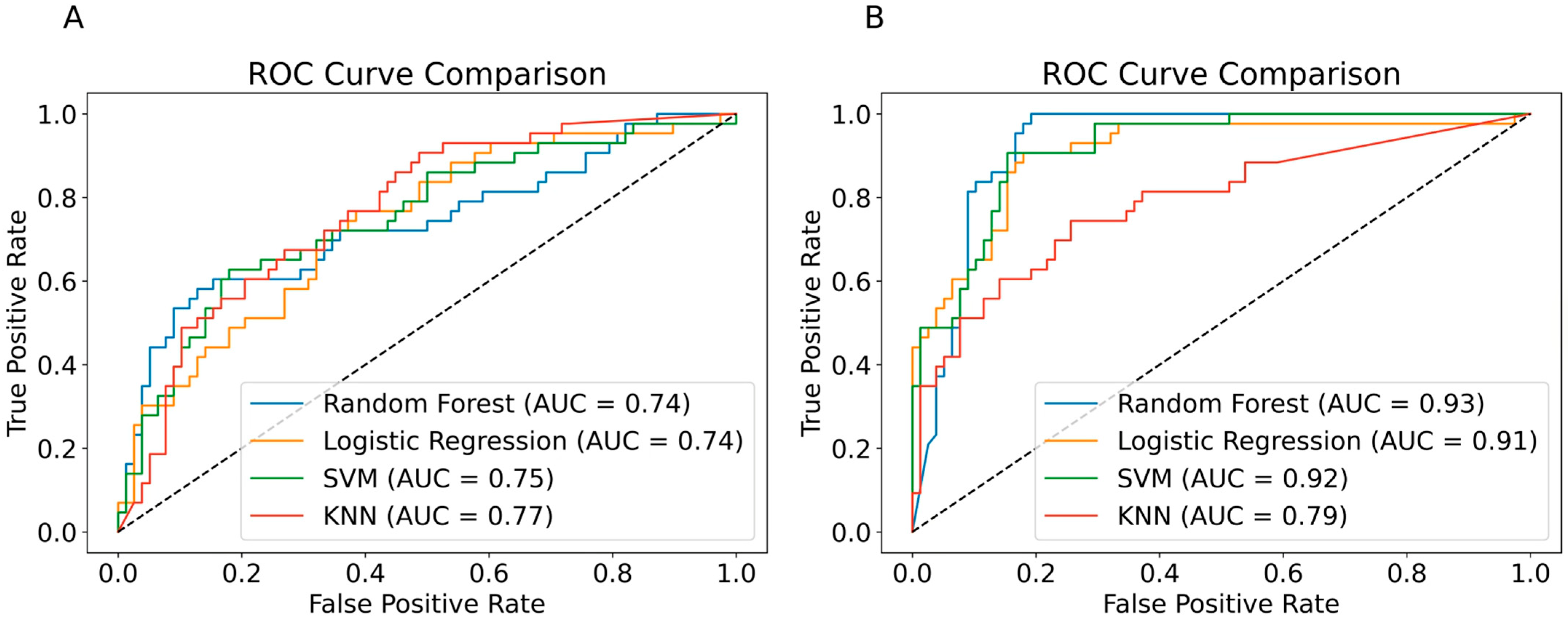
3.2.1. Model Performance Based on Laboratory Data Alone
3.2.2. Model Performance with Additional Clinical and Demographic Features
3.3. Prediction of Biologic Therapy Based on Data Recorded 5 Years Before the Index Date
3.3.1. Model Performance Based on Laboratory Data Alone
3.3.2. Model Performance with Additional Clinical and Demographic Features
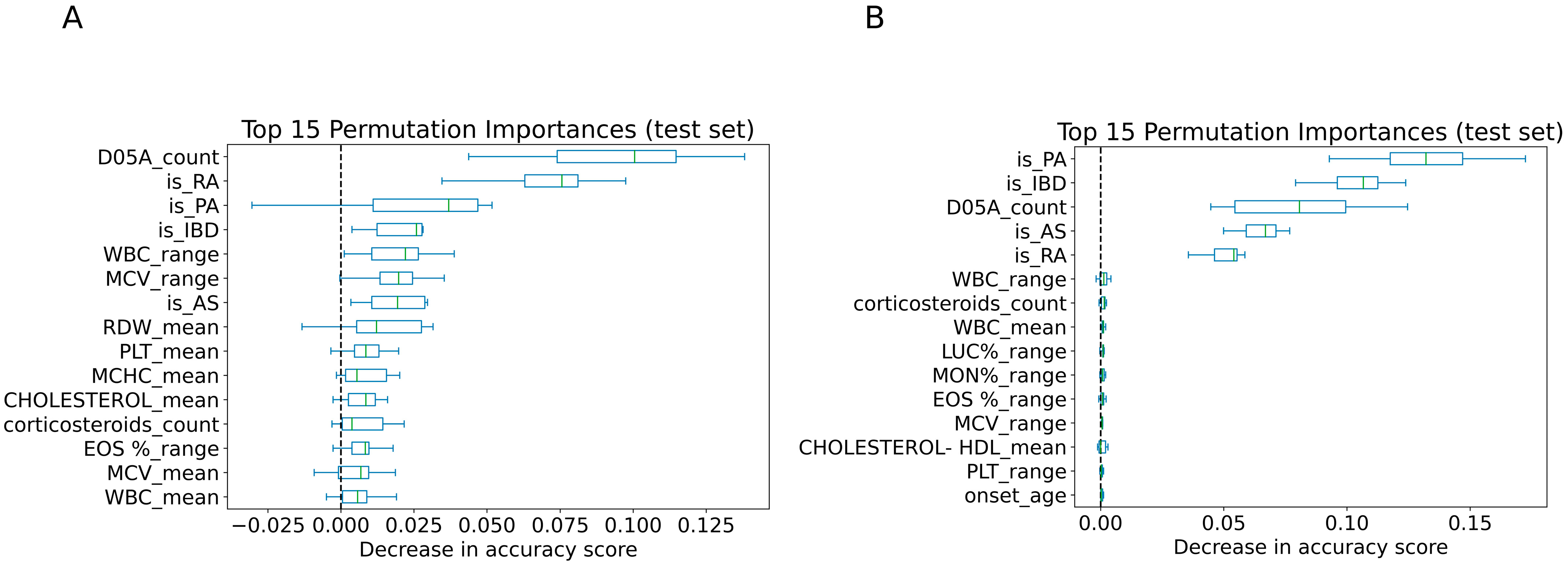
3.4. Features Importance Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IMID | Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disease |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| EHR | Electronic Health Records |
| CHS | Clalit Health Services |
| HMO | Health Maintenance Organization |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| RF | Random Forest |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under Curve |
| AS | Ankylosing Spondylitis |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| WBC | White Blood Cell |
| MPV | Mean Platelet Volume |
| MCHC | Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration |
| RDW | Red Cell Distribution Width |
| NEUT% | Neutrophil Percentage |
| MON% | Monocyte Percentage |
| LYMP.abs | Lymphocyte Absolute Count |
| EOS% | Eosinophil Percentage |
| PsA | Psoriatic Arthritis |
| HDL-C | High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| PASI | Psoriasis Area and Severity Index |
| BSA | Body Surface Area |
| DLQI | Dermatology Life Quality Index |
References
- Boehncke, W.-H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.-H.; Chi, C.-C.; Yeh, M.-L.; Wang, S.-H.; Tsai, Y.-S.; Hsu, M.-Y. Lifestyle Changes for Treating Psoriasis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD011972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolescu, A.C.; Ionescu, M.-A.; Constantin, M.M.; Ancuta, I.; Ionescu, S.; Niculet, E.; Tatu, A.L.; Zirpel, H.; Thaçi, D. Psoriasis Management Challenges Regarding Difficult-to-Treat Areas: Therapeutic Decision and Effectiveness. Life 2022, 12, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.-L.; Petersen, T.C.; Maul, J.-T.; Wu, J.J.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Bertelsen, T.; Ajgeiy, K.K.; Skov, L.; Thomsen, S.F.; Thyssen, J.P.; et al. Multivariable Predictive Models to Identify the Optimal Biologic Therapy for Treatment of Patients with Psoriasis at the Individual Level. JAMA Dermatol 2022, 158, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, S.; Du, A.X.; Surmanowicz, P.; Thomsen, S.F.; Greiner, R.; Gniadecki, R. Predicting the Long-term Outcomes of Biologics in Patients with Psoriasis Using Machine Learning. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 1305–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, A.X.; Ali, Z.; Ajgeiy, K.K.; Dalager, M.G.; Dam, T.N.; Egeberg, A.; Nissen, C.V.S.; Skov, L.; Thomsen, S.F.; Emam, S.; et al. Machine Learning Model for Predicting Outcomes of Biologic Therapy in Psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 88, 1364–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.I.; Park, S.J.; Chung, J.-W.; Kim, K.O.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, K.G.; Park, D.K.; Kim, Y.J. Development of Machine Learning Model to Predict the 5-Year Risk of Starting Biologic Agents in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): K-CDM Network Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöler, D.; Kostev, K.; Peters, M.; Zamfir, C.; Wolk, A.; Roderburg, C.; Loosen, S.H. Machine Learning Can Predict the Probability of Biologic Therapy in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. Predicting Psoriasis Using Routine Laboratory Tests with Random Forest. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Braanker, H.; Razawy, W.; Wervers, K.; Mus, A.-M.C.; Davelaar, N.; Kok, M.R.; Lubberts, E. Characterizing Memory T Helper Cells in Patients with Psoriasis, Subclinical, or Early Psoriatic Arthritis Using a Machine Learning Algorithm. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullen, E.P.; Al Naser, Y.A.; Maazi, M.; Grewal, R.S.; Abdel Hafeez, D.; Folino, T.R.; Vender, R.B. Predicting Psoriasis Severity Using Machine Learning: A Systematic Review. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2025, 50, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lv, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yao, M.; Wang, L.; Pan, G. Advancements in the Study of Biologic Agents in Comorbidities of Psoriasis: A Literature Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 3487–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, Y.S.; Schwartz, N.; Sagy, I.; Pavlovsky, L. Incidence of Psoriatic Arthritis Among Patients Receiving Biologic Treatments for Psoriasis: A Nested Case–Control Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, E.R.; Ogdie, A. Can Early Aggressive Treatment of Psoriasis Prevent Psoriatic Arthritis? A Debate at the GRAPPA Annual Meeting. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 50, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, A.; Mugheddu, C.; Sichi, L.; Anedda, J.; Frau, A.; Sorgia, J.; Li Volsi, L.; Paladino, M.T.; Congia, M.; Chessa, E.; et al. Treatment of Psoriasis with Different Classes of Biologics Reduces the Likelihood of Peripheral and Axial Psoriatic Arthritis Development. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loredo, M.; Braña, I.; Queiro, R. Does Pharmacological Intervention Prevent or Delay the Onset of Psoriatic Arthritis among Psoriasis Patients? Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2023, 23, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, S.; Reşorlu, H.; Işik, S.; Oymak, S.; Akbal, A.; Hız, M.M.; Öğretmen, Z. Association between Mean Platelet Volume and Disease Severity in Patients with Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2017, 34, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampa, M.; Mitran, M.I.; Mitran, C.I.; Matei, C.; Georgescu, S.R. Psoriasis: What Is New in Markers of Disease Severity? Med. Buenos Aires 2024, 60, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageen, S.; Shah, R.; Sharif, S.; Jamgochian, M.; Waqas, N.; Rao, B. Platelet Count, Mean Platelet Volume, and Red Cell Distribution Width as Markers for Psoriasis Severity. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2022, 21, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Savanelli, M.C.; Di Somma, C.; Napolitano, M.; Megna, M.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Vitamin D and Its Role in Psoriasis: An Overview of the Dermatologist and Nutritionist. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formisano, E.; Proietti, E.; Borgarelli, C.; Pisciotta, L. Psoriasis and Vitamin D: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambike, J.; Gosavi, A.; Pradhan, S.; Belgaumkar, V. Association of Serum Calcium Level and Serum Uric Acid Level in Psoriasis and Its Correlation with Severity of Psoriasis. Dermatol. Rev. 2024, 111, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.; Rathi, S. Correlation of Serum Calcium Levels with Severity of Psoriasis. Int. J. Res. Dermatol. 2018, 4, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, S.; Yoshikawa, K.; Fukuo, K.; Shiraishi, T.; Koh, E.; Imanaka, S.; Kitano, S.; Ogihara, T. Inverse Relation between Severity of Psoriasis and Serum 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D Level. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1990, 1, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, S.A.; Strümke, I.; Thambawita, V.; Hammou, M.; Riegler, M.A.; Halvorsen, P.; Parasa, S. On Evaluation Metrics for Medical Applications of Artificial Intelligence. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, V. A Correlative Study between Platelet Count, Mean Platelet Volume and Red Cell Distribution Width with the Disease Severity Index in Psoriasis Patients. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, EC13–EC16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunadevi, D.; Raghavan, V.; Nott, A. Comparative and Correlative Study of Hematologic Parameters and Selective Inflammatory Biomarkers in Psoriasis. Int. J. Nutr. Pharmacol. Neurol. Dis. 2022, 12, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, G.; İnan Yuksel, E.; Gökdeniz, O.; Karaman, K.; Canat, H.D. The Relationship of Hematological Parameters and C-Reactive Protein (CRP) With Disease Presence, Severity, and Response to Systemic Therapy in Patients with Psoriasis. Cureus 2023, 15, e43790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiucă, O.M.; Morariu, S.H.; Mariean, C.R.; Tiucă, R.A.; Nicolescu, A.C.; Cotoi, O.S. Impact of Blood-Count-Derived Inflammatory Markers in Psoriatic Disease Progression. Life 2024, 14, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, M.; Wolf, P.; Curcic, S.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; Weger, W.; Inzinger, M.; El-Gamal, D.; Wadsack, C.; Heinemann, A.; Marsche, G. Psoriasis Alters HDL Composition and Cholesterol Efflux Capacity. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, A.; Chabros, P.; Grywalska, E.; Kiciński, P.; Franciszkiewicz-Pietrzak, K.; Krasowska, D.; Kandzierski, G. Serum Lipid Metabolism in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis—An Update. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019, 15, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdinando, L.B.; Fukumoto, P.K.; Sanches, S.; Fabricio, L.H.Z.; Skare, T.L. Metabolic Syndrome and Psoriasis: A Study in 97 Patients. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2018, 64, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lax, T.; Stemmer, E.; Fallach, N.; Shrem, G.; Schreiber-Divon, M.; Ayalon, S.; Giat, E.; Mor, I.; Salmon-Divon, M. Exploring the Impact of Gender and Age of Onset on Psoriasis Treatment Management. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model | Laboratory Data | Laboratory and Additional Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Accuracy | |
| Random Forest | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.44 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.62 | 0.66 | 0.78 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.43 | 0.56 | 0.67 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.77 |
| SVM | 0.36 | 0.46 | 0.4 | 0.54 | 0.72 | 0.7 | 0.71 | 0.81 |
| KNN | 0.33 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.6 | 0.54 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.67 |
| Model | Laboratory Data | Laboratory and Additional Data | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Accuracy | |
| Random Forest | 0.53 | 0.65 | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.75 | 0.95 | 0.84 | 0.87 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.54 | 0.7 | 0.61 | 0.68 | 0.75 | 0.84 | 0.79 | 0.84 |
| SVM | 0.56 | 0.67 | 0.61 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.86 |
| KNN | 0.6 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.42 | 0.54 | 0.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lax, T.; Fallach, N.; Stemmer, E.; Shrem, G.; Salmon-Divon, M. Early Risk Prediction for Biologic Therapy in Psoriasis Using Machine Learning Models Based on Routine Health Records. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186421
Lax T, Fallach N, Stemmer E, Shrem G, Salmon-Divon M. Early Risk Prediction for Biologic Therapy in Psoriasis Using Machine Learning Models Based on Routine Health Records. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186421
Chicago/Turabian StyleLax, Tair, Noga Fallach, Edia Stemmer, Guy Shrem, and Mali Salmon-Divon. 2025. "Early Risk Prediction for Biologic Therapy in Psoriasis Using Machine Learning Models Based on Routine Health Records" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186421
APA StyleLax, T., Fallach, N., Stemmer, E., Shrem, G., & Salmon-Divon, M. (2025). Early Risk Prediction for Biologic Therapy in Psoriasis Using Machine Learning Models Based on Routine Health Records. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6421. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186421






