Body Temperature, Metabolic, and Circulatory Changes After 8 Days of Water-Only Fasting in Healthy Middle-Aged Men
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Participants
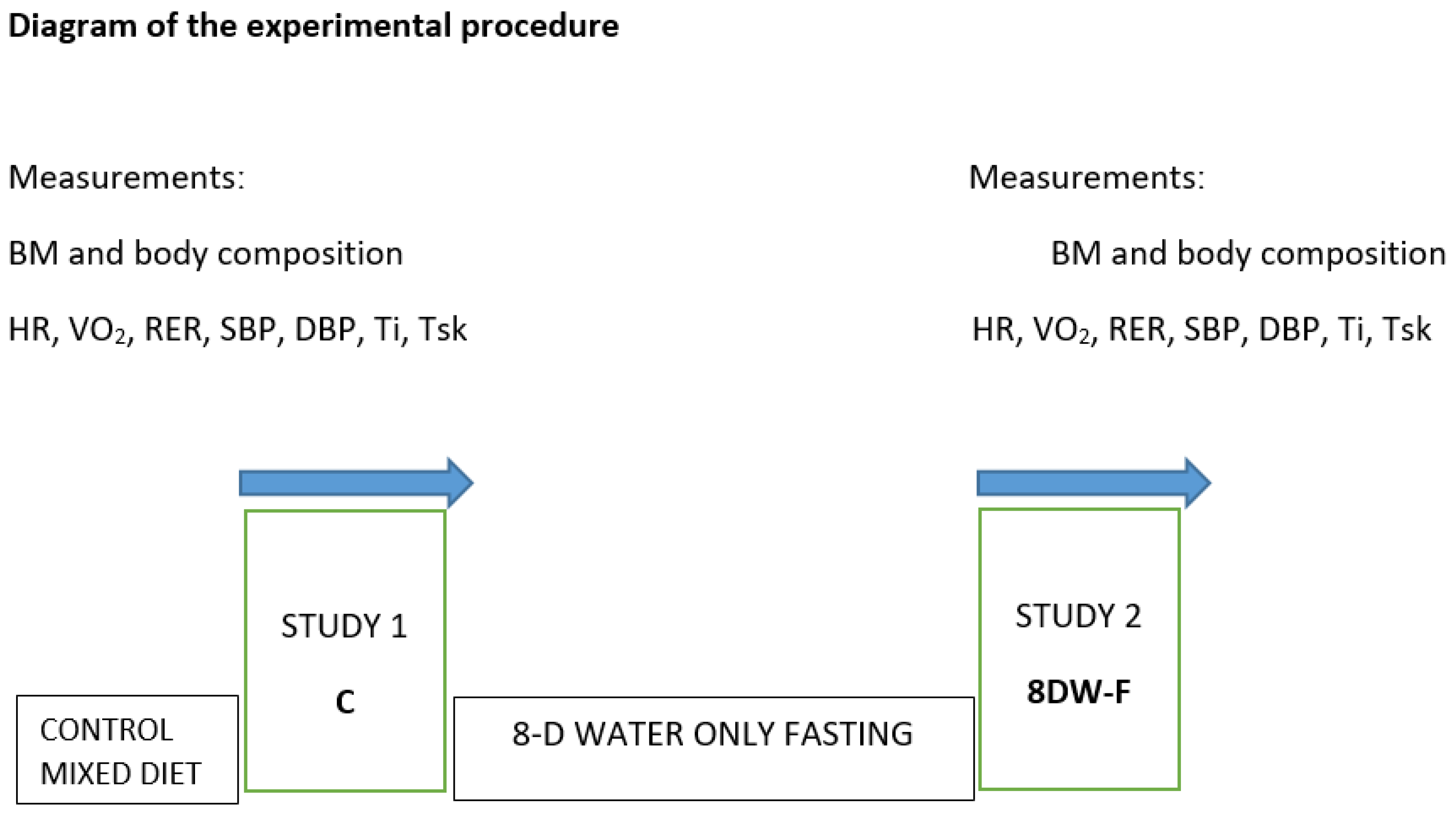
2.3. Experimental Designs
2.4. Measurements
2.4.1. Body Mass and Composition Measurement
2.4.2. Circulatory Assessments
2.4.3. Resting Metabolic Rate
2.4.4. Body Temperature Measurement
2.5. Calculations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of 8DW-F on Somatic Variables
3.2. Changes in the Circulatory, Metabolic, and Thermal Status Under the Influence of 8DW-F
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vinales, K.L.; Begaye, B.; Thearle, M.S.; Krakoff, J.; Piaggi, P. Core body temperature, energy expenditure, and epinephrine during fasting, eucaloric feeding, and overfeeding in healthy adult men: Evidence for a ceiling effect for human thermogenic response to diet. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2019, 94, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullmer, S.; Benson-Davies, S.; Earthman, C.P.; Frankenfield, D.C.; Gradwell, E.; Lee, P.S.; Piemonte, T.; Trabulsi, J. Evidence analysis library review of best practices for performing indirect calorimetry in healthy and non-critically ill individuals. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1417–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, G.P.; Journeay, W.S. Human thermoregulation: Separating thermal and nonthermal effects on heat loss. Front. Biosci. 2010, 15, 259–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Smith, B.; Dahle, J.; Kennedy, S.; Fearnbach, N.; Thomas, D.M.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Müller, M.J. Resting Energy Expenditure: From Cellular to Whole-Body Level, a Mechanistic Historical Perspective. Obesity 2021, 29, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, F.G. Factors Affecting Basal Metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 1915, 20, 263–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.R.; Seymour, R.S. Allometric scaling of mammalian metabolism. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.A.S.; Notley, S.R. Morphological and Physiological Considerations for the Modelling of Human Heat Loss. In Theory and Applications of Heat Transfer in Humans; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 463–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikke, B.A.; Johnson, T.E. Lower body temperature as a potential mechanism of life extension in homeotherms. Exp. Gerontol. 2004, 39, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Thomas, D.M. Dynamics of starvation in humans. J. Math. Biol. 2007, 54, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, P.S.; Bergouignan, A.; Cornier, M.A.; Jackman, M.R. Biology’s response to dieting: The impetus for weight regain. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R581–R600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenacci, V.A.; Pan, Z.; Ostendorf, D.; Brannon, S.; Gozansky, W.S.; Mattson, M.P.; Martin, B.; MacLean, P.S.; Melanson, E.L.; Donahoo, W.T. A randomized pilot study comparing zero-calorie alternate-day fasting to daily caloric restriction in adults with obesity. Obesity 2016, 24, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L. Adaptive thermogenesis in humans. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, S47–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokora, I.; Grucza, R.; Kaciuba-Uściłko, H. Influence of a low-carbohydrate diet on thermoregulatory responses to prolonged exercise in men. J. Therm. Biol. 1999, 24, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, J.L.; Deitrick, R.W.; Hillman, A.R. Exercising in the Fasted State Reduced 24-Hour Energy Intake in Active Male Adults. J. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 2016, 1984198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severinsen, T.; Munch, I.C. Body core temperature during food restriction in rats. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1999, 165, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnell, J.S.; Saul, B.C.; Goldhamer, A.C.; Myers, T.R. Is fasting safe? A chart review of adverse events during medically supervised, water-only fasting. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Most, J.; Redman, L.M. Impact of calorie restriction on energy metabolism in humans. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 133, 110875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Tang, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Fu, X. Fasting: From Physiology to Pathology. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2204487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, H.; Sui, X.; Guo, Y.; Xin, B.; Guo, Z. Effects of 10-Day Complete Fasting on Physiological Homeostasis, Nutrition and Health Markers in Male Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, J.E.; Caudwell, P.; Gibbons, C.; Hopkins, M.; Naslund, E.; King, N.; Finlayson, G. Role of resting metabolic rate and energy expenditure in hunger and appetite control: A new formulation. Dis. Model. Mech. 2012, 5, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, M.; Gibbons, C.; Blundell, J. Fat-free mass and resting metabolic rate are determinants of energy intake: Implications for a theory of appetite control. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2022, 378, 20220213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, R.J.; Hopkins, M.; Finlayson, G.S.; Duarte, C.; Gibbons, C.; Blundell, J.E. Potential effects of fat mass and fat-free mass on energy intake in different states of energy balance. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, M.; Finlayson, G.; Duarte, C.; Whybrow, S.; Ritz, P.; Horgan, G.W.; Blundell, J.E.; Stubbs, R.J. Modelling the associations between fat-free mass, resting metabolic rate and energy intake in the context of total energy balance. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu-Vieira, G.; Xiao, C.; Gavrilova, O.; Reitman, M.L. Integration of body temperature into the analysis of energy expenditure in the mouse. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohal, R.S.; Weindruch, R. Oxidative stress, caloric restriction, and aging. Science 1996, 273, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikke, B.A.; Yerg, J.E.; Battaglia, M.E.; Nagy, T.R.; Allison, D.B.; Johnson, T.E. Strain variation in the response of body temperature to dietary restriction. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2003, 124, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, L. Core temperature: A forgotten variable in energy expenditure and obesity? Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, S.D.; Moehl, K.; Donahoo, W.T.; Marosi, K.; Lee, S.A.; Mainous, A.G.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Mattson, M.P. Flipping the Metabolic Switch: Understanding and Applying the Health Benefits of Fasting. Obesity 2018, 26, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhamer, A.; Lisle, D.; Parpia, B.; Anderson, S.V.; Campbell, T.C. Medically supervised water-only fasting in the treatment of hypertension. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2001, 24, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatamra, K.; Daniel, P.M.; Lam, D.K.C. The Effects of Fasting on Core Temperature, Blood Glucose and Body and Organ Weights in Rats. Q. J. Exp. Physiol. 1984, 69, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.J. Thermal physiology of laboratory mice: Defining thermoneutrality. J. Therm. Biol. 2012, 37, 654–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, K.; Tokizawa, K.; Marui, S.; Uchida, Y. Circadian Body Temperature Rhythm and the Interaction with Energy State. In Homeostasis—An Integrated Vision; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arens, E.; Zhang, H. The skin’s role in human thermoregulation and comfort. In Thermal and Moisture Transport in Fibrous Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 560–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, D.S.; Pandolf, K.B.; Shapiro, Y.; Heled, Y.; Shani, Y.; Matthew, W.T.; Gonzales, R.R. An environmental stress index (ESI) as a substitute for the wet bulb globe temperature (WBGT). J. Therm. Biol. 2001, 26, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, Y. Measurement of thermal balance in man. Bioeng. Therm. Physiol. Comf. 1981, 1, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Du Bois, D.; Du Bois, E.F. A formula to estimate the approximate surface area if height and weight be known. Arch. Intern. Med. 1916, 17, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A. The application of the theory of heat flow to the study of energy metabolism. J. Nutr. 1934, 7, 497–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolwijk, J.A.J.; Hardy, J.D. Temperature regulation in man—A theoretical study. Pflüg. Arch. 1966, 291, 129–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: A practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, R.; Anderson, V. A comprehensive tissue properties database provided for the thermal assessment of a human at rest. Biophys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 5, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Nakamura, K. Central regulation of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and energy homeostasis dependent on food availability. Pflug. Arch. 2018, 470, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulloo, A.G.; Jacquet, J.; Montani, J.P.; Schutz, Y. Adaptive thermogenesis in human body weight regulation: More of a concept than a measurable entity? Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulloo, A.G.; Schutz, Y. Adaptive Thermogenesis in Resistance to Obesity Therapies: Issues in Quantifying Thrifty Energy Expenditure Phenotypes in Humans. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.D. Predicting metabolic adaptation, body weight change, and energy intake in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E449–E466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letkiewicz, S.; Pilis, K.; Ślęzak, A.; Pilis, A.; Pilis, W.; Żychowska, M.; Langfort, J. Eight days of water-only fasting promotes favorable changes in the functioning of the urogenital system of middle-aged healthy men. Nutrients 2021, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulloo, A.G. Physiology of weight regain: Lessons from the classic Minnesota Starvation Experiment on human body composition regulation. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.; Albu, J.; He, Q.; Heshka, S.; Boxt, L.; Krasnow, N.; Elia, M. Small organs with a high metabolic rate explain lower resting energy expenditure in African American than in white adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. Starvation Ketosis and the Kidney. Am. J. Nephrol. 2021, 52, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulloo, A.G.; Jacquet, J. Adaptive reduction in basal metabolic rate in response to food deprivation in humans: A role for feedback signals from fat stores. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heshka, S.; Yang, M.U.; Wang, J.; Burt, P.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X. Weight loss and change in resting metabolic rate. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 52, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachakonda, V.P.; DeLany, J.P.; Kershaw, E.E.; Behari, J. Impact of hepatic steatosis on resting metabolic rate and metabolic adaptation in response to intentional weight loss. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said Camilleri, J.; Farrugia, L.; Curto, S.; Rodrigues, D.B.; Farina, L.; Caruana Dingli, G.; Bonello, J.; Farhat, I.; Sammut, C.V. Review of Thermal and Physiological Properties of Human Breast. Tissue Sens. 2022, 22, 3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahon, K.J.; Boon, M.R.; Doornink, F.; Jazet, I.M.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Abreu-Vieira, G. Lower critical temperature and cold-induced thermogenesis of lean and overweight humans are inversely related to body mass and basal metabolic rate. J. Therm. Biol. 2017, 69, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.A.; Machado-Moreira, C.A.; van den Heuvel, A.M.; Caldwell, J.N. Hands, and feet: Physiological insulators, radiators and evaporators. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 2037–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | C (n = 13) X ± SD | 8DW-F (n = 13) X ± SD | Δ [8DW-F—C] | Cohen’s d | Δ [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 51.36 ± 13.0 | ---------- | ---------- | -------- | -------- |
| BH [cm] | 178.57 ± 4.45 | ---------- | ---------- | -------- | -------- |
| BM [kg] | 79.62 ± 10.69 | 74.20 ± 10.77 ** | −5.42 ± 1.32 | 0.52 | −6.9 ± 1.7 |
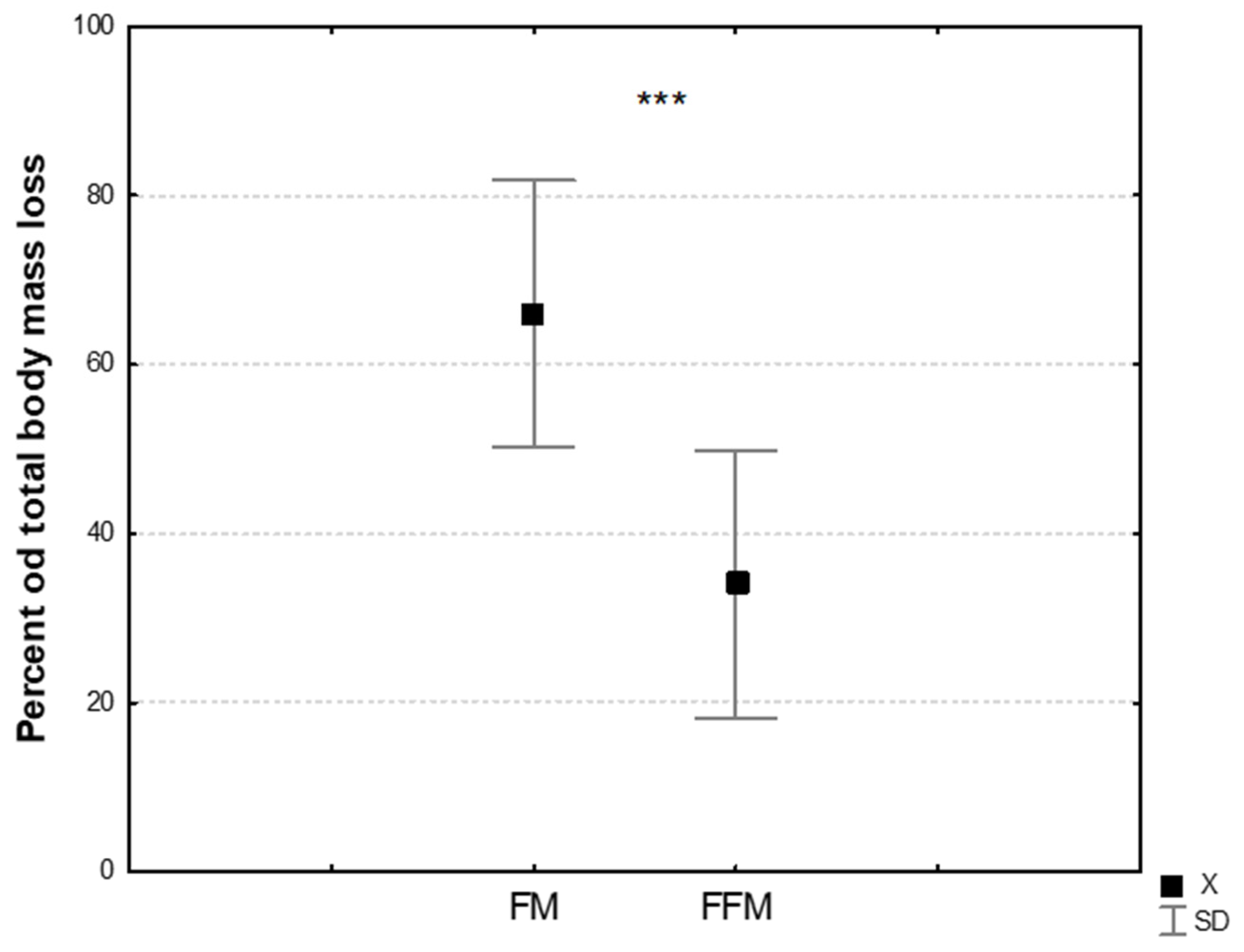
| FM [kg] | 15.55 ± 5.66 | 13.62 ± 5.59 ** | −1.98 ± 0.63 | 0.36 | −11.2 ± 5.1 |
| FFM [kg] | 64.2 ± 5.65 | 60.44 ± 5.99 ** | −3.76 ± 1.29 | 0.67 | −5.9 ± 2.1 |
| TBW [kg] | 47.8 ± 4.13 | 44.34 ± 4.22 ** | −2.67 ± 0.91 | 0.66 | −5.7 ± 1.8 |
| BSA [m2] | 1.98 ± 0.14 | 1.91 ± 0.15 ** | −0.069 ± 0.02 | 0.48 | −3.5 ± 0.9 |
| BSA/BM [m2/kg] | 0.025 ± 0.002 | 0.026 ± 0.002 ** | 0.0009 ± 0.0003 | 0.59 | +3.7 ± 0.9 |
| Variable | C (n = 13) X ± SD | 8DW-F (n = 13) X ± SD | Δ [8DW-F—C] | Cohen’s d | Δ [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VO2 [L/min] | 0.39 ± 0.10 | 0.32 ± 0.12 * | −0.07 ± 0.10 | 0.60 | −16.3 ± 23.2 |
| VO2 [mL/kg/min] | 4.91 ± 1.13 | 4.32 ± 1.27 | −0.58 ± 1.29 | 0.50 | −10.2 ± 24.2 |
| RER | 0.79 ± 0.07 | 0.83 ± 0.07 | 0.04 ± 0.09 | 0.55 | 5.9 ± 5.2 |
| BMR [kcal] | 1706.5 ± 123.9 | 1648.7 ± 116.9 *** | −75.42 ± 18.6 | 0.48 | −4.4 ± 1.1 |
| RMR [W/kg] | 1.64 ± 1.55 | 1.45 ± 1.56 | −0.19 ± 1.67 | 0.51 | −9.9 ± 23.4 |
| RMR [W/m2] | 65.92 ± 16.43 | 54.25 ± 19.52 * | −10.0 ± 16.3 | 0.64 | −14.6 ± 22.9 |
| Ti [°C] | 36.44 ± 0.52 | 36.38 ± 0.59 | −0.05 ± 0.74 | 0.46 | −0.13 ± 2.04 |
| MTB [°C] | 34.69 ± 1.75 | 34.79 ± 1.86 | 0.13 ± 0.57 | 0.17 | 0.37 ± 1.61 |
| MTsk [°C] | 30.57 ± 0.65 | 31.35 ± 0.60 | 0.68 ± 1.07 | 0.78 | 2.3 ± 3.54 |
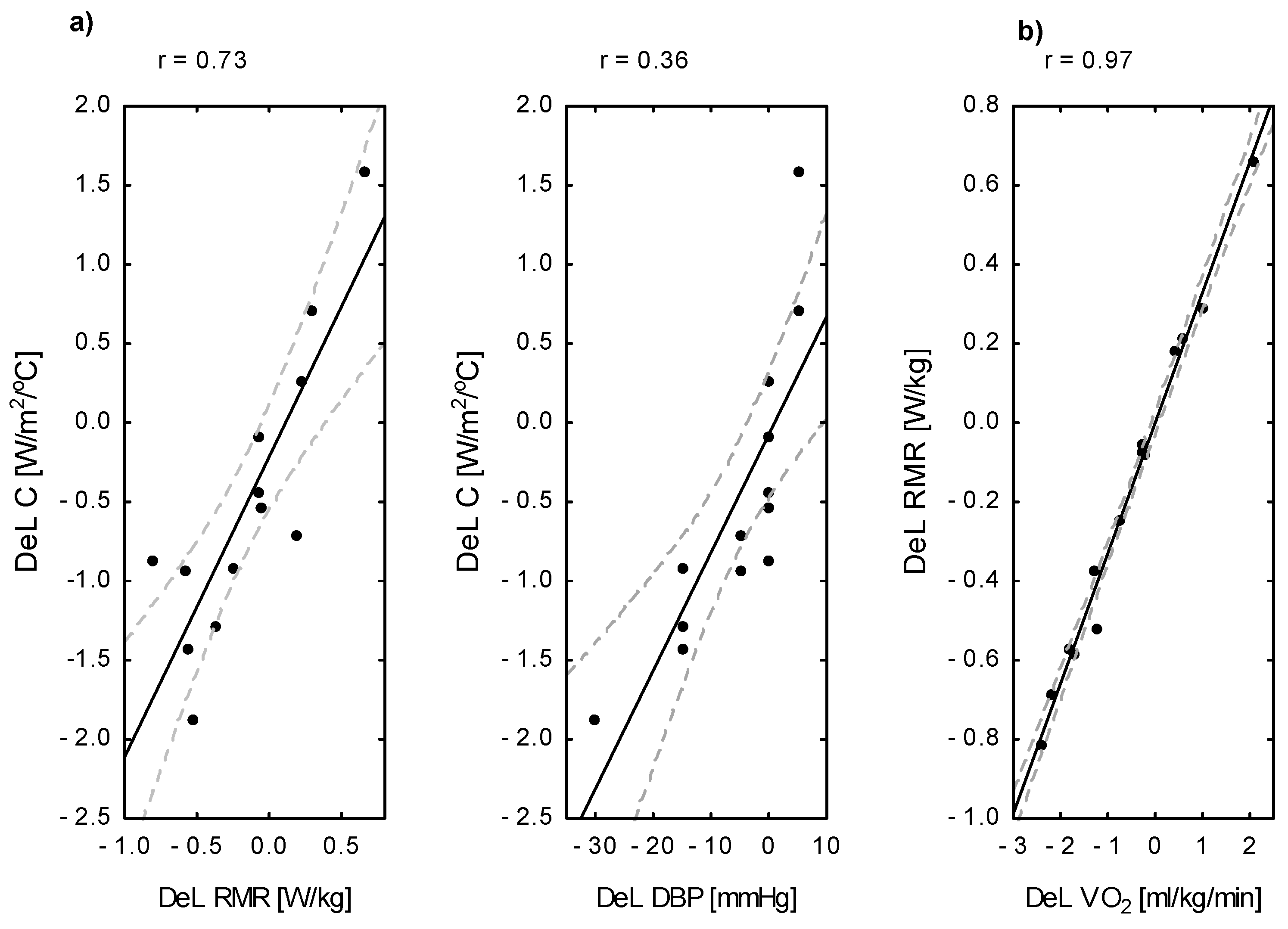
| C [W/m2/°C] | 3.99 ± 1.08 | 3.53 ± 1.32 | −0.47 ± 0.92 | 0.46 | −12.5 ± 27.2 |
| g [°C] | 5.82 ± 0.84 | 4.89 ± 1.0 | −0.93 ± 1.51 | 0.54 | −13.2 ± 26.5 |
| SBP [mmHg] | 126.42 ± 12.92 | 112.14 ± 11.38 *** | −14.28 ± 9.77 | 1.22 | −11.01 ± 6.8 |
| DBP [mmHg] | 82.5 ± 10.14 | 75 ± 11.09 | −7.5 ± 14.10 | 0.73 | −8.06 ± 11.2 |
| MAP [mmHg] | 95.67 ± 10.28 | 86.14 ± 9.97 ** | −9.53 ± 10.91 | 0.98 | −9. 9 ± 10.1 |
| Components | Variables | Δ Ti [%] | Δ MTB [%] | Δ C [%] | Δ g [%] | Δ BMR [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Δ Ti [%] R2 | — | — | — | 0.58 *** | — |
| Δ MTsk [%] R2 | — | — | — | 0.73 *** | — | |
| Metabolic | Δ VO2 [%] R2 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Δ RMR [%] R2 | — | — | 0.92 *** | — | — | |
| Δ BMR [%] R2 | — | 0.41 * | — | — | — | |
| Somatic | Δ BM [%] R2 | — | 0.44 ** | — | — | 0.89 *** |
| Δ FAT [%] R2 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| Δ FFM [%] R2 | — | — | — | — | 0.88 *** | |
| Δ TBW [%] R2 | — | 0.19 | — | — | — | |
| Δ BSA/BM [%] R2 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| Circulatory | Δ SBP [%] R2 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Δ DBP [%] R2 | — | — | 0.56 ** | — | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pokora, I.; Wyderka, P.; Pilis, W.; Pilis, K. Body Temperature, Metabolic, and Circulatory Changes After 8 Days of Water-Only Fasting in Healthy Middle-Aged Men. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5735. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165735
Pokora I, Wyderka P, Pilis W, Pilis K. Body Temperature, Metabolic, and Circulatory Changes After 8 Days of Water-Only Fasting in Healthy Middle-Aged Men. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5735. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165735
Chicago/Turabian StylePokora, Ilona, Piotr Wyderka, Wiesław Pilis, and Karol Pilis. 2025. "Body Temperature, Metabolic, and Circulatory Changes After 8 Days of Water-Only Fasting in Healthy Middle-Aged Men" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5735. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165735
APA StylePokora, I., Wyderka, P., Pilis, W., & Pilis, K. (2025). Body Temperature, Metabolic, and Circulatory Changes After 8 Days of Water-Only Fasting in Healthy Middle-Aged Men. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5735. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165735







