Relationship Between Simple Renal Cysts and Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Quality and Publication Bias Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
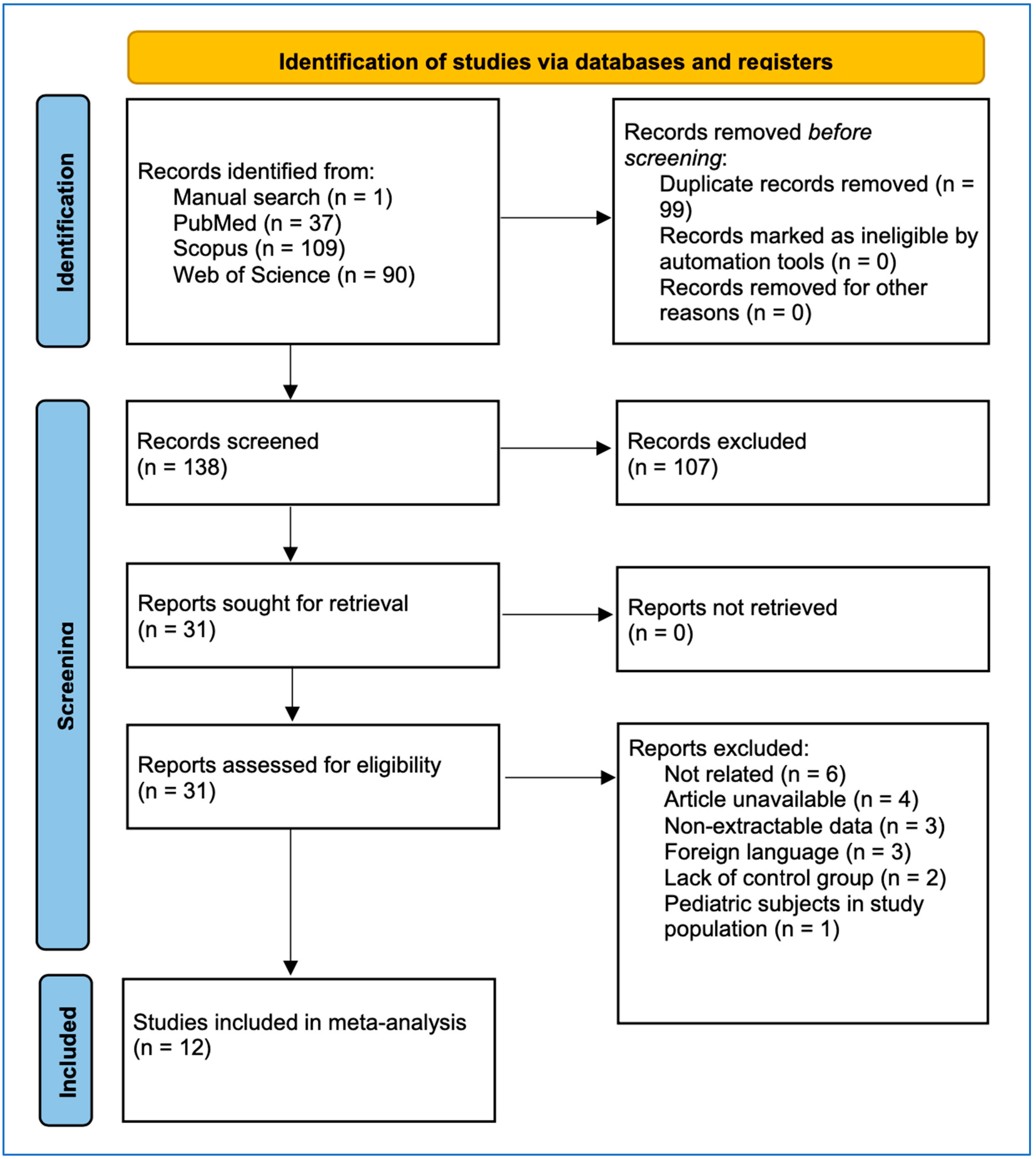
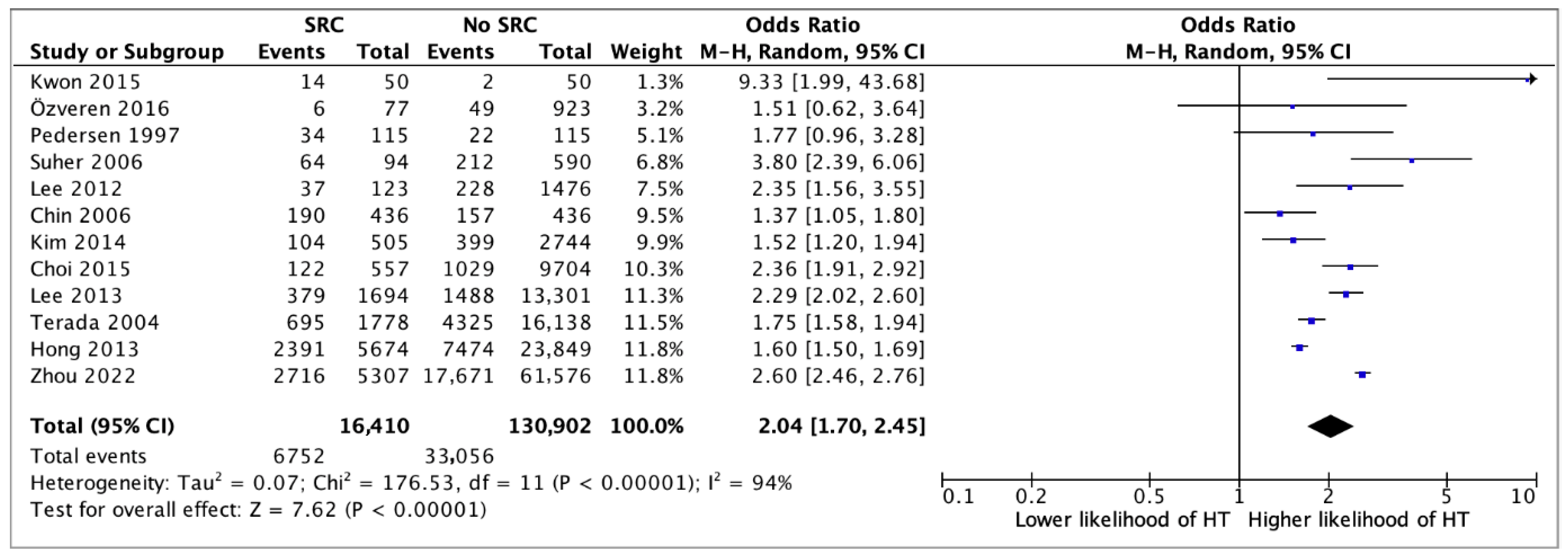
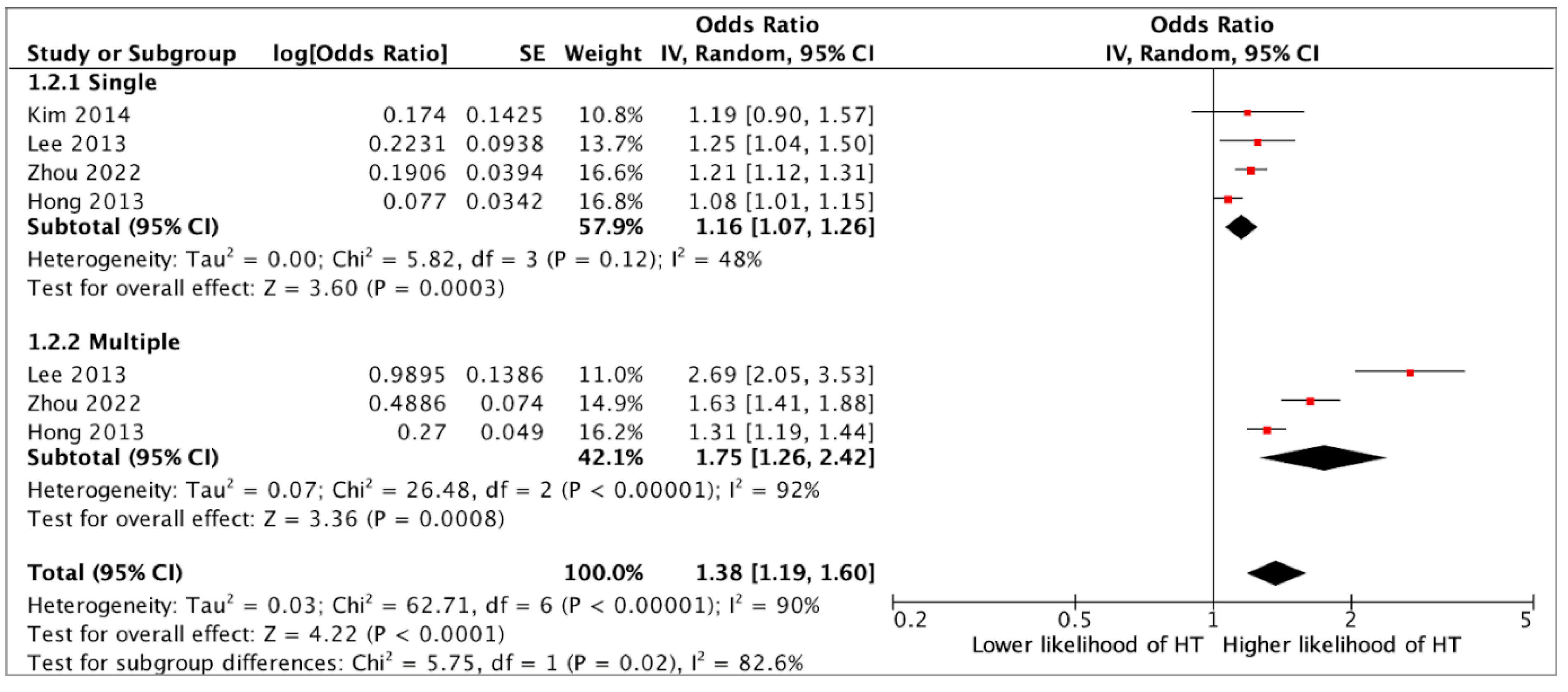
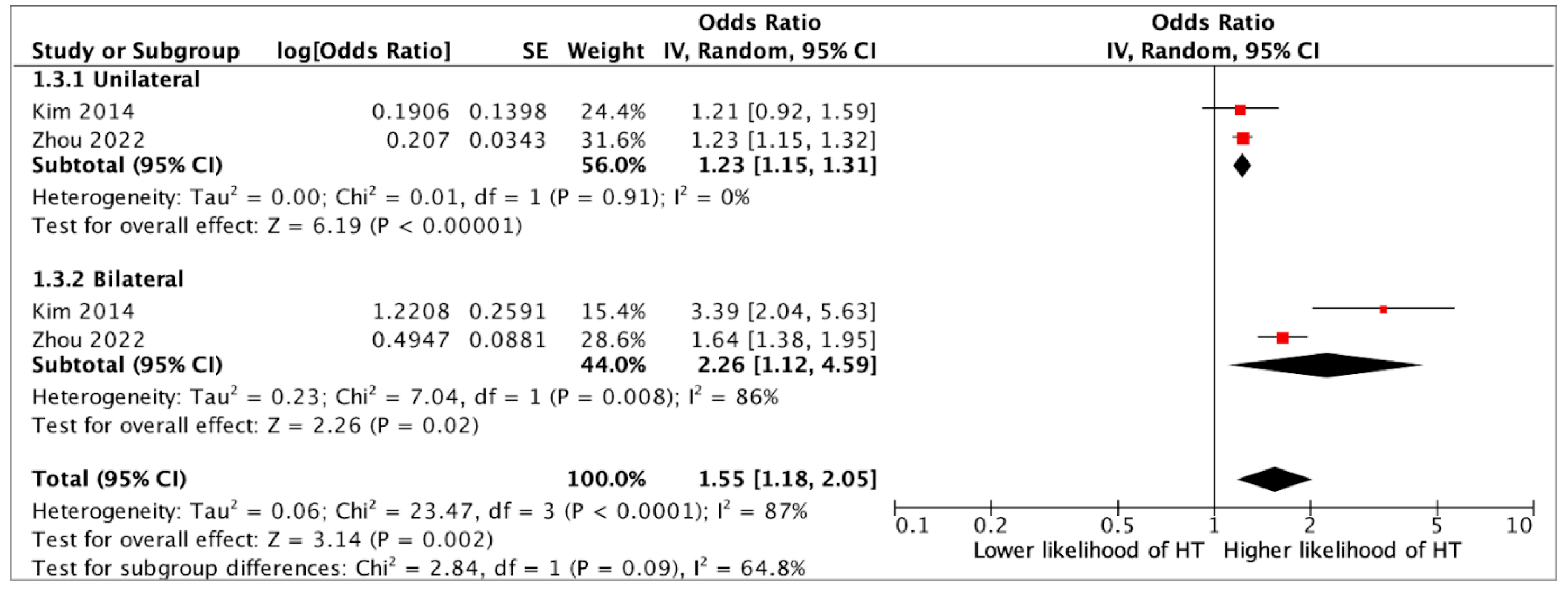
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrim, Z.I.; Murchison, J.T. The Prevalence of Simple Renal and Hepatic Cysts Detected by Spiral Computed Tomography. Clin. Radiol. 2003, 58, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-C.; Kuo, J.-Y.; Chan, W.-L.; Chen, K.-K.; Chang, L.S. Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Simple Renal Cyst. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. JCMA 2007, 70, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, K.; Leslie, S.W. Simple Renal Cyst. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ziganshin, B.A.; Theodoropoulos, P.; Salloum, M.N.; Zaza, K.J.; Tranquilli, M.; Mojibian, H.R.; Dahl, N.K.; Fang, H.; Rizzo, J.A.; Elefteriades, J.A. Simple Renal Cysts as Markers of Thoracic Aortic Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimpel, C.; Avni, E.F.; Breysem, L.; Burgmaier, K.; Caroli, A.; Cetiner, M.; Haffner, D.; Hartung, E.A.; Franke, D.; König, J.; et al. Imaging of Kidney Cysts and Cystic Kidney Diseases in Children: An International Working Group Consensus Statement. Radiology 2019, 290, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chewcharat, A.; Hamaya, R.; Thongprayoon, C.; Cato, L.D.; Mao, M.A.; Cheungpasitporn, W. The Association between Simple Renal Cyst and Aortic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Evid.-Based Med. 2020, 13, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Hu, H.-Y.; Chou, Y.-J.; Huang, N.; Chou, Y.-C.; Li, C.-P. High Blood Pressure and All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortalities in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Medicine 2015, 94, e2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Afshin, A.; Alexander, L.T.; Anderson, H.R.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Biryukov, S.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Cercy, K.; Charlson, F.J.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Comparative Risk Assessment of 79 Behavioural, Environmental and Occupational, and Metabolic Risks or Clusters of Risks, 1990–2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1659–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Hypertension Day—17 May 2025. Available online: https://eso-stroke.org/blog-world-hypertension-day-17-may-2025/ (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Pedersen, J.F.; Emamian, S.A.; Nielsen, M.B. Significant Association between Simple Renal Cysts and Arterial Blood Pressure. Br. J. Urol. 1997, 79, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, H.J.; Ro, H.; Lee, H.J.; Na, K.Y.; Chae, D.-W. The Clinical Significances of Simple Renal Cyst: Is It Related to Hypertension or Renal Dysfunction? Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jia, L.; Lu, B.; Bai, L.; Cui, W. Simple Renal Cyst as an Independent Risk Factor for Hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2022, 24, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lim, J.H.; Jeong, I.G.; Choe, J.; Kim, C.-S.; Hong, J.H. What Association Exists between Hypertension and Simple Renal Cyst in a Screened Population? J. Hum. Hypertens. 2013, 27, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-T.; Yang, Y.-C.; Wu, J.-S.; Chang, Y.-F.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lu, F.-H.; Chang, C.-J. Multiple and Large Simple Renal Cysts Are Associated with Prehypertension and Hypertension. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özveren, B.; Onganer, E.; Türkeri, L.N. Simple Renal Cysts: Prevalence, Associated Risk Factors and Follow-Up in a Health Screening Cohort. Urol. J. 2016, 13, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.D. Clinical characteristics and long-term observation of simple renal cysts in a healthy Korean population. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suher, M.; Koc, E.; Bayrak, G. Simple Renal Cyst Prevalence in Internal Medicine Department and Concomitant Diseases. Ren. Fail. 2006, 28, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, S.; Kim, S.R. Association between Simple Renal Cysts and Development of Hypertension in Healthy Middle-Aged Men. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.; Lim, B.; You, D.; Hong, B.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, C.; Jeong, I.G. Simple Renal Cyst and Renal Dysfunction: A Pilot Study Using Dimercaptosuccinic Acid Renal Scan. Nephrology 2016, 21, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Chung, T.-H.; Oh, M.-S.; Kwon, S.-G.; Bae, S.-J. Relationship of Simple Renal Cyst to Hypertension. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2014, 35, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Terada, N.; Arai, Y.; Kinukawa, N.; Yoshimura, K.; Terai, A. Risk Factors for Renal Cysts. BJU Int. 2004, 93, 1300–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Kim, C.-S. Natural 10-Year History of Simple Renal Cysts. Korean J. Urol. 2015, 56, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbay, M.; Copur, S.; Bakir, C.N.; Covic, A.; Ortiz, A.; Tuttle, K.R. Glomerular Hyperfiltration as a Therapeutic Target for CKD. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.-Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2024, 39, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floege, J.; Johnson, R.J.; Feehally, J. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher, T.F.; Wanner, C.; Siegenthaler, W.; Vetter, W. Simple Renal Cyst and Hypertension: Cause or Coincidence? Clin. Nephrol. 1986, 26, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Aloui, S.; Bouraoui, S.; Salem, R.; Toffahi, M.; Skhiri, H.; Frih, A.; Dhia, N.B.; Elmay, M. Remission of Arterial Hypertension after the Treatment of a Giant Renal Cyst. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2011, 22, 151–152. [Google Scholar]
- Pejcic, T.; Hadzi-Djokic, J.; Markovic, B.; Naumovic, R. Resolving Erythrocytosis and Hypertension after Open Surgical Extirpation of Giant Renal Cyst Measuring 30 Cm: Case Report. Ren. Fail. 2011, 33, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermüller, N.; Morente, N.; Kränzlin, B.; Gretz, N.; Witzgall, R. A Possible Role for Metalloproteinases in Renal Cyst Development. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2001, 280, F540–F550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.R.; Song, B.G.; Jang, S.Y.; Ko, S.M.; Choi, S.-H.; Sung, J.; Sung, K.; Choe, Y.H.; Oh, J.K.; et al. Presence of Simple Renal Cysts Is Associated with Increased Risk of Aortic Dissection: A Common Manifestation of Connective Tissue Degeneration? Heart 2011, 97, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taherkhani, S.; Sheibani, M.; Mohammadkhanizadeh, A.; Virag, J.A.I.; de Castro Braz, L.; Azizi, Y. Metalloproteinases (MMPs) in Hypertensive Disorders: Role, Function, Pharmacology, and Potential Strategies to Mitigate Pathophysiological Changes. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1559288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Hu, P.; Wang, J.; Yan, W.; He, Z.; Xu, T.; Yu, M.; Chen, S.; Ma, X.; Tan, X. Simple Renal Cysts Are Associated With 24-Month Prognosis of Patients With Type B Aortic Dissection and Hypertension. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, B.; Afsar, R.E.; Sen, S.T.; Kirkpantur, A.; Eyileten, T.; Yilmaz, M.I.; Caglar, K. Simple Renal Cysts and Circadian Blood Pressure: Are They Related to Each Other in Patients with Hypertension? Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2011, 43, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavone, C.; Salvatore, L.; Primavera, A.; Cuccurullo, F.; Verna, N.; Di Stefano, F.; Thomson, E.; Tenaglia, R.; Di Gioacchino, M. Simple Renal Cysts in Hypertensive Patients: Relation between Cyst Growing and Anti-Hypertensive Therapy. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2003, 16, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Simple Are ‘Simple Renal Cysts’?|Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/ndt/article-abstract/29/suppl_4/iv106/1908338?redirectedFrom=fulltext (accessed on 17 April 2025).

| Study | Country | Study Design | Level of Quality (NOS) | Mean Age (SD) | Definition for HT | Definition for SRC | Explicit Exclusion of Subjects with Polycystic Kidney Disease and/or Other Cystic Kidney Disease | SRC | No SRC | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pedersen 1997 [10] | Denmark | Retrospective cohort | High | 67.7 (31–91) | Diastolic BP ≥ 95 mm Hg | Cysts ≥ 10 mm, a round anechoic lesion that lay at least partly within the renal contour and showed distal echo enhancement | No | 115 | 115 | 230 |
| Chin 2006 [11] | South Korea | Retrospective cohort | High | 50.7 (m) and 50.9 (f) | NR | Anechoic lesion with homogeneity, water content, and sharp interface to renal parenchyma that did not have thickening, calcifications, or enhancement. | Yes | 436 | 436 | 872 |
| Zhou 2022 [12] | China | Retrospective cohort | High | 46.36 ± 13.35 | BP ≥ 140 and or/90 or controlled BP due to use of an antihypertensive drug | Cystic mass in or on the surface of the kidney, with no echo, a clear boundary, good internal sound transmission, enhanced posterior echo, a wall that is slender and hyperechoic, an inner wall that is smooth, and a spherical or ellipsoid morphology. | Yes | 5307 | 61,576 | 66,883 |
| Hong 2013 [13] | South Korea | Retrospective cohort | High | 56.03 ± 8.675 (SRC), 52.28 ± 7.933 (NSRC) | BP ≥ 130/85 or the use of antihypertensive drugs | Lack of internal echoes, and a smooth, sharply defined wall which was not suggestive of malignancy. | Yes | 5674 | 23,849 | 29,523 |
| Ting Lee 2013 [14] | Taiwan | Retrospective cohort | High | NR | BP ≥ 140/90 or documented history of HT | Echolucent, round or oval, thin-walled, smooth contours, well defined, sharply demarcated posterior wall, no calcifications, no doppler signals from within the cyst, and no sound wave amplification behind the cyst, which was not suggestive of a malignancy. | Yes | 1694 | 13,301 | 14,995 |
| Özveren 2016 [15] | Turkey | Retrospective cohort | High | 42.76 ± 10.89 | Systolic BP > 140, diastolic BP > 90, or use of antihypertensive drugs | Type 1 renal cyst according to the Bosniak classification. | No | 77 | 923 | 1000 |
| Choi 2016 [16] | South Korea | Retrospective cohort | Medium | 52.67 ± 0.31 (SRC) and 46.82 ± 0.09 (NSRC) | Systolic BP > 140/and or diastolic BP > 90, use of antihypertensive drugs | Absent internal echoes, smooth sharply defined walls, and posterior acoustic enhancement, indicating posterior through-transmission that was not suspicious for a renal malignancy. | Yes | 557 | 9704 | 10,261 |
| Suher 2006 [17] | Turkey | Retrospective cohort | Medium | 67.3 ± 12.1 years (SRC) | NR | Lack of internal echoes, thin wall, and distal enhancement. | Yes | 94 | 590 | 684 |
| Lee 2012 [18] | South Korea | Retrospective cohort | High | 42.3 ± 6.6 (SRC) and 42.2 ± 6.8 (NSRC) | Systolic BP > 140 and/or diastolic BP > 90, use of antihypertensive drugs | NR | Yes | 123 | 1476 | 1599 |
| Kwon 2016 [19] | South Korea | Prospective cohort | Medium | 59.1 (SRC) and 39.2 (NSRC) | Mean blood pressure ≥ 130/85 mmHg or antihypertensive drug use | Unilateral cysts ≥ 4 cm, water density, homogenous, hairline thin wall, no septa, no calcifications, and no enhancement. | No | 50 | 50 | 100 |
| Kim 2014 [20] | South Korea | Retrospective cohort | High | 54.0 ± 3.6 | Systolic BP > 140 or diastolic BP > 90 mmHg, or current use of antihypertensive medications | Internally anechoic, sharply defined, smooth-walled, and round or oval cyst. | No | 505 | 2744 | 3249 |
| Terada 2004 [21] | Japan | Retrospective cohort | Medium | 49.3 | Systolic BP > 140 or diastolic BP > 90 mmHg, or current use of antihypertensive medications | Lack of internal echoes and a smooth, sharply defined wall that was not suggestive of malignancy. | No | 1778 | 16,138 | 17,914 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kitlinski, M.; Kaushik, H.; Heleniak, Z.; Dębska-Ślizień, A. Relationship Between Simple Renal Cysts and Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165725
Kitlinski M, Kaushik H, Heleniak Z, Dębska-Ślizień A. Relationship Between Simple Renal Cysts and Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165725
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitlinski, Michael, Harshita Kaushik, Zbigniew Heleniak, and Alicja Dębska-Ślizień. 2025. "Relationship Between Simple Renal Cysts and Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165725
APA StyleKitlinski, M., Kaushik, H., Heleniak, Z., & Dębska-Ślizień, A. (2025). Relationship Between Simple Renal Cysts and Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5725. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165725








