Historically Based Perspective on the Immunotherapy of Type 1 Diabetes: Where We Have Been, Where We Are, and Where We May Go
Abstract
1. Introduction
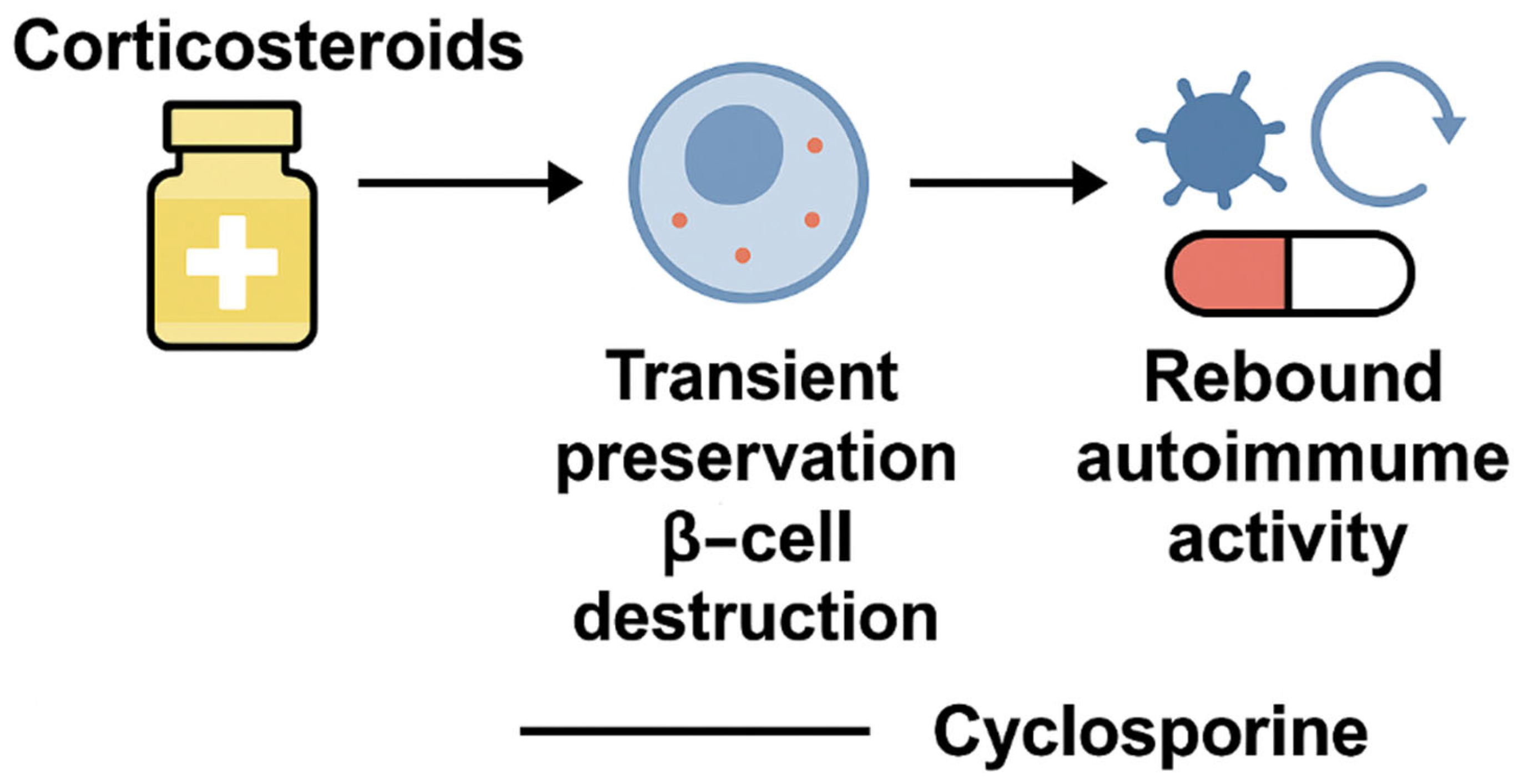
2. Early Immunosuppression in T1DM: From Corticosteroids to Cyclosporine
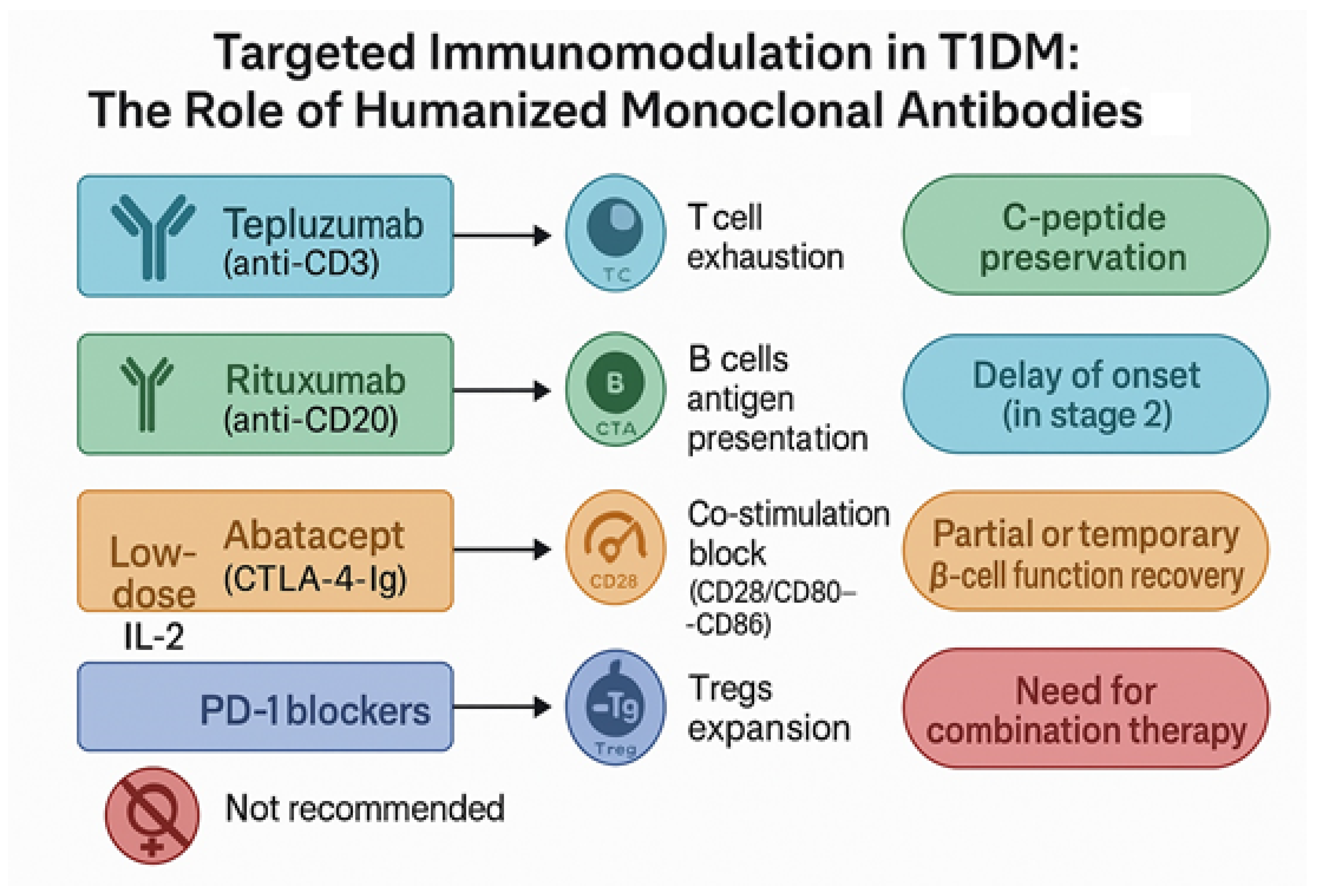
3. Humanized Monoclonal Antibodies in T1DM: Precision Immune Modulation
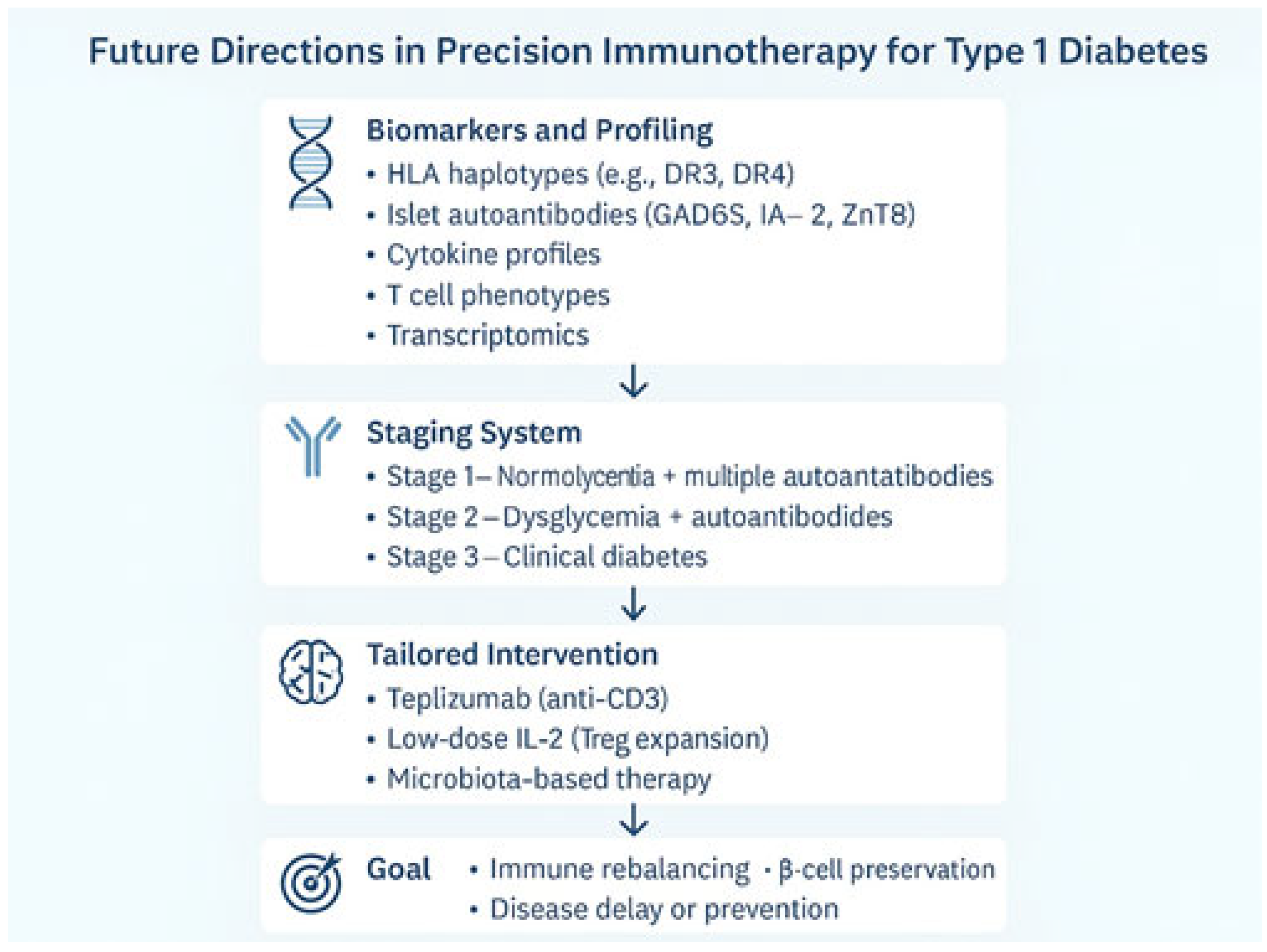
4. Future Perspectives: Toward Precision and Personalized Immunotherapy
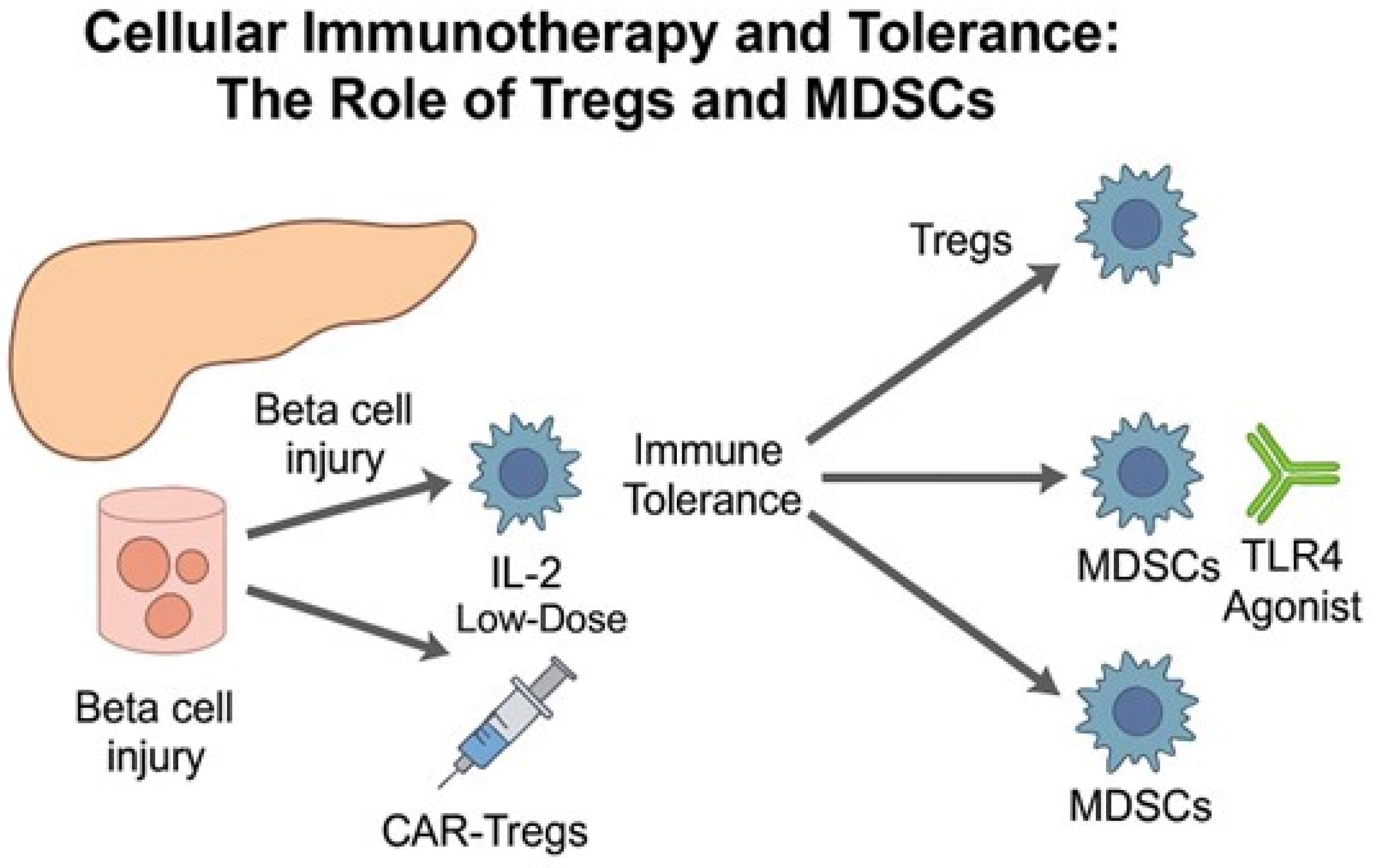
5. Cellular Immunotherapy in T1DM: The Pursuit of Durable Immune Tolerance
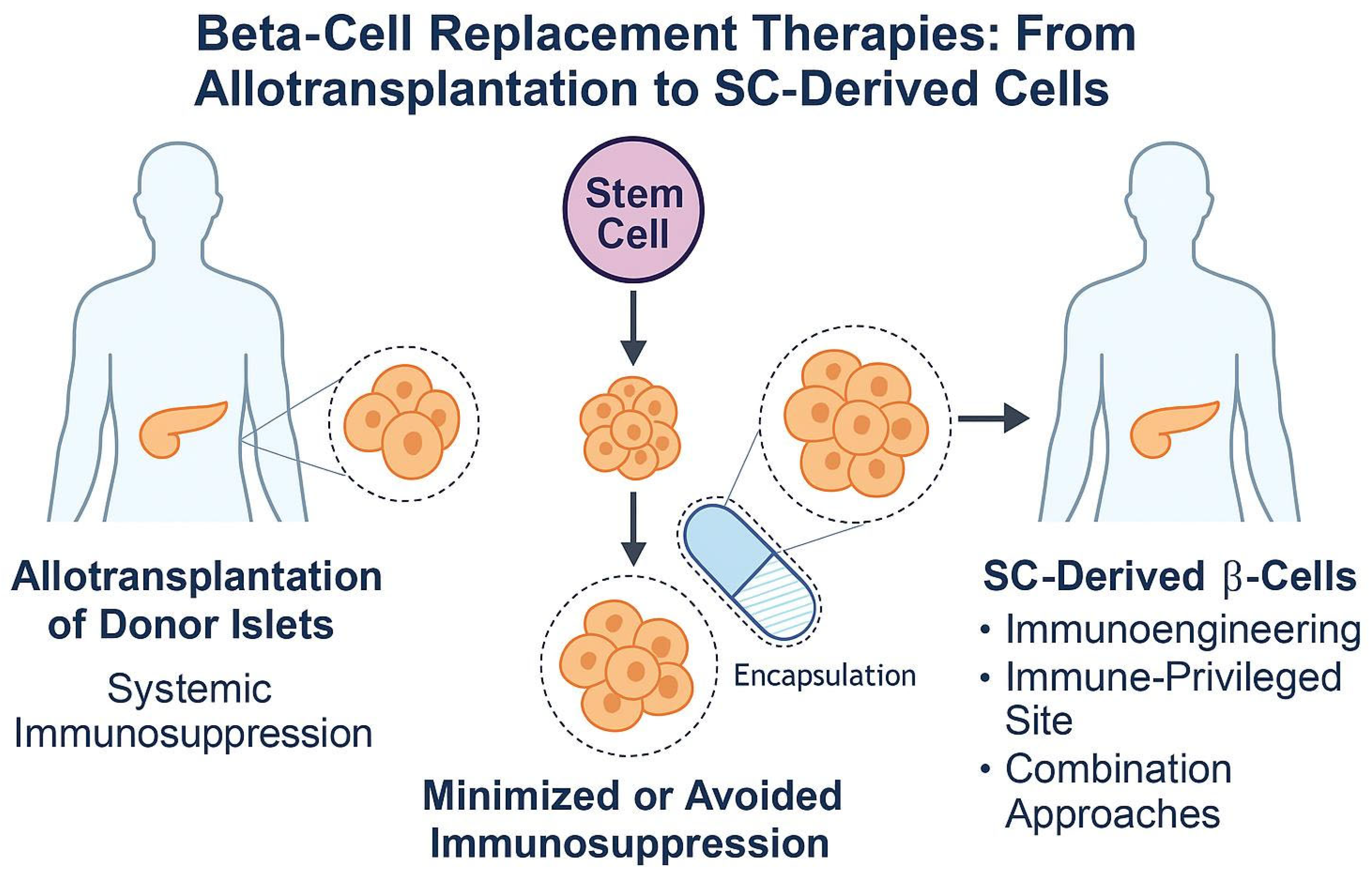
6. Beta-Cell Replacement in T1DM: From Islet Transplantation to Stem Cell-Derived Therapies
7. Clinical Translation of Cell-Based Therapies in T1DM
8. From Historical Lessons to Precision Immuno-Regeneration in T1DM
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Budd, M.A.; Monajemi, M.; Colpitts, S.J.; Crome, S.Q.; Verchere, C.B.; Levings, M.K. Interactions between islets and regulatory immune cells in health and type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 2378–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Conget, I.; Di Mauro, M.; Di Marco, R.; Mazzarino, M.; Bendtzen, K.; Messina, A.; Gomis, R. Serum concentrations of the interferon-γ-inducible chemokine IP-10/CXCL10 are augmented in both newly diagnosed type I diabetes mellitus patients and subjects at risk of developing the disease. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, F.; Conget, I.; Di Marco, R.; Speciale, A.M.; Morinigo, R.; Bendtzen, K.; Gomis, R. Serum levels of the interferon-γ-inducing cytokine interleukin-18 are increased in individuals at high risk of developing Type I diabetes. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, E.; Rosario, G.; Nicoletti, P.; Nicoletti, F. A Historical and Epistemological Review of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Gaglia, J.L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; Khunti, K.; et al. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S20–S42. [Google Scholar]
- Herold, K.C.; Bundy, B.N.; Long, S.A.; Bluestone, J.A.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Dufort, M.J.; Gitelman, S.E.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Krischer, J.P.; Linsley, P.S.; et al. An Anti-CD3 Antibody, Teplizumab, in Relatives at Risk for Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.R.; Khan, M.T. Teplizumab: A promising intervention for delaying type 1 diabetes progression. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1533748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambam, B.; Bratina, N.; Schatz, D. Immune Intervention in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, S141–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin, A.M.; Lombard-Vadnais, F.; Collin, R.; Aliesky, H.A.; McLachlan, S.M.; Lesage, S. The NOD Mouse Beyond Autoimmune Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 874769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.P.; Bruggeman, B.S.; Haller, M.J. Emerging Immunotherapies for Disease Modification of Type 1 Diabetes. Drugs 2025, 85, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.C.; Anand, V.; Achenbach, P.; Dunne, J.L.; Hagopian, W.; Hu, J.; Koski, E.; Lernmark, Å.; Lundgren, M.; Ng, K.; et al. Progression of type 1 diabetes from latency to symptomatic disease is predicted by distinct autoimmune trajectories. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insel, R.A.; Dunne, J.L.; Atkinson, M.A.; Chiang, J.L.; Dabelea, D.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Herold, K.C.; Krischer, J.P.; Lernmark, A.; et al. Staging presymptomatic type 1 diabetes: A scientific statement of jdrf, the endocrine society, and the American diabetes association. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1964–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, D.A.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Repaske, D.R.; Rich, S.S. Precision Medicine in Type 1 Diabetes. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2023, 103, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velikova, T.; Vasilev, G.V.; Linkwinstar, D.; Siliogka, E.; Kokudeva, M.; Miteva, D.; Vasilev, G.H.; Gulinac, M.; Atliev, K.; Shumnalieva, R. Regulatory T cell-based therapies for type 1 diabetes: A narrative review. Metab. Target Organ Damage 2025, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, W.; Liang, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Qiu, F.; Dai, Z. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) Treg: A promising approach to inducing immunological tolerance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 385915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, B.; Ma, G.; Yen, C.-Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, G.X.; Divino, C.M.; Casares, S.; Chen, S.-H.; Yang, W.-C.; Pan, P.-Y. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Prevent Type 1 Diabetes in Murine Models. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5828–5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łoskot, W.; Szwech, J.; Matczak, M.; Jasiński, K.; Broda, A.; Hoksa, K.; Jodłowski, K.; Dubniewicz, E.; Majewska, P.; Staszek, A. Artificial intelligence in type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Educ. Health Sport 2025, 79, 57913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, L.M.; Bratina, N.; Schatz, D. Immune Intervention and Replacement Therapies in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2025, 27, S200–S207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Goyal, A.; Sonthalia, S. Corticosteroid Adverse Effects. StatPearls 2023, 46, 434. [Google Scholar]
- Saboo, B.; Joshi, S.; Gupta, A.; Maheshwari, A.; Saboo, B.; Makkar, B.M.; Bantwal, G.; Kesavadev, J.; Sreenivasamurthy, L.; Tiwaskar, M.; et al. Responsible Use of Oral Corticosteroids in People with Comorbid Diabetes: An Expert Consensus. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2024, 72, 79–93. Available online: https://www.japi.org/article/japi-72-7-79 (accessed on 17 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Reyhanoglu, G.; Rehman, A. Somogyi Phenomenon. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Orlando, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pillay, S.; Pillay, A.; Kalhan, A. Efficacy of immunosuppression in preserving beta cell function and reducing insulin requirements in Type 1 diabetes mellitus: A comprehensive review. J. Endocrinol. Metab. Diabetes S. Afr. 2025, 30, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.; von Herrath, M. Immunotherapy for Type 1 Diabetes: Why Do Current Protocols Not Halt the Underlying Disease Process? Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warshauer, J.T.; Bluestone, J.A.; Anderson, M.S. New Frontiers in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, T.C.-E.R.C.T. Cyclosporin-Induced Remission of IDDM After Early Intervention: Association of 1 yr of Cyclosporin Treatment with Enhanced Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 1988, 37, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Stiller, C.R.; Dupré, J.; Gent, M.; Jenner, M.R.; Keown, P.A.; Laupacis, A.; Martell, R.; Rodger, N.W.; Graffenried, B.V.; Wolfe, B.M.J. Effects of cyclosporine immunosuppression in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus of recent onset. Science 1984, 223, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feutren, G.; Assan, R.; Karsenty, G.; Du Rostu, H.; Sirmai, J.; Papoz, L.; Vialettes, B.; Vexiau, P.; Rodier, M.; Lallemand, A.; et al. CYCLOSPORIN INCREASES THE RATE AND LENGTH OF REMISSIONS IN INSULIN-DEPENDENT DIABETES OF RECENT ONSET. Results of a Multicentre Double-blind Trial. Lancet 1986, 328, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.P.; Fleming, G.A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Herold, K.C.; Jansa, L.D.; Kolb, H.; Lachin, J.M.; Polonsky, K.S.; Pozzilli, P.; Skyler, J.S.; et al. C-Peptide Is the Appropriate Outcome Measure for Type 1 Diabetes Clinical Trials to Preserve β-Cell Function: Report of an ADA Workshop, 21–22 October 2001. Diabetes 2004, 53, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parving, H.H.; Tarnow, L.; Nielsen, F.S.; Rossing, P.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Østerby, R.; Nerup, J. Cyclosporine nephrotoxicity in type 1 diabetic patients. A 7-year follow-up study. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, G.A.; Sliem, H.A.; Ellethy, A.T.; Salama, M.E.-S. Role of immune system modulation in prevention of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, I.; Eldor, R.; Naparstek, Y. Immune modulation for prevention of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X.; Zhang, X. Leverage biomaterials to modulate immunity for type 1 diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 997287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, J.L.; Griffin, K.J.; Oram, R.A.; Speake, C.; Long, S.A.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Rich, S.S.; Monaco, G.S.F.; Evans-Molina, C.; DiMeglio, L.A.; et al. Disease-modifying therapies and features linked to treatment response in type 1 diabetes prevention: A systematic review. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodacki, M.; Silva, K.R.; Araujo, D.B.; Dantas, J.R.; Ramos, M.E.N.; Zajdenverg, L.; Baptista, L.S. Immunomodulatory agents and cell therapy for patients with type 1 diabetes. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 68, e240233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orban, T.; Bundy, B.; Becker, D.J.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Gitelman, S.E.; Goland, R.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Marks, J.B.; Monzavi, R.; et al. Co-stimulation modulation with abatacept in patients with recent-onset type 1 diabetes: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, F.; di Marcou, R.; Barcelliniu, W.; Magro, G.; Schorlemmeru, H.U.; Kurrleu, R.; Lunettau, M.; Grasso, S.; Zacconeu, P.; Meronif, P. Protection from experimental autoimmune diabetes in the non-obese diabetic mouse with soluble interleukin-1 receptor. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 1843–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drage, M.; Zaccone, P.; Phillips, J.M.; Nicoletti, F.; Dawson, J.; Bradley, J.A.; Cooke, A. Nondepleting anti-CD4 and soluble interleukin-1 receptor prevent autoimmune destruction of syngeneic islet grafts in diabetic NOD mice. Transplantation 2002, 74, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Di Marco, R.; Zaccone, P.; Magro, G.; Di Mauro, M.; Grasso, S.; Meroni, P.L. Endogenous interleukin-12 only plays a key pathogenetic role in non- obese diabetic mouse diabetes during the very early stages of the disease. Immunology 1999, 97, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccone, P.; Phillips, J.; Conget, I.; Cooke, A.; Nicoletti, F. IL-18 binding protein fusion construct delays the development of diabetes in adoptive transfer and cyclophosphamide-induced diabetes in NOD mouse. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Zaccone, P.; Di Marco, R.; Di Mauro, M.; Magro, G.; Grasso, S.; Mughini, L.; Meroni, P.; Garotta, G. The effects of a nonimmunogenic form of murine soluble interferon-γ receptor on the development of autoimmune diabetes in the NOD mouse. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 5567–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Zaccone, P.; Di Marco, R.; Lunetta, M.; Magro, G.; Grasso, S.; Meroni, P.; Garotta, G. Prevention of spontaneous autoimmune diabetes in diabetes-prone BB rats by prophylactic treatment with antirat interferon-γ antibody. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkovic, I.; Al-Abed, Y.; Miljkovic, D.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D.; Roth, J.; Bacher, M.; Lan, H.Y.; Nicoletti, F.; Stosic-Grujicic, S. Critical role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor activity in experimental autoimmune diabetes. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 2942–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stosic-Grujicic, S.; Stojanovic, I.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D.; Momcilovic, M.; Popadic, D.; Harhaji, L.; Miljkovic, D.; Metz, C.; Mangano, K.; Papaccio, G.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is necessary for progression of autoimmune diabetes mellitus. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 215, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamaullee, J.A.; Davis, J.; Merani, S.; Toso, C.; Elliott, J.F.; Thiesen, A.; Shapiro, A.M.J. Inhibition of Th17 cells regulates autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, A.; Bundy, B.; Becker, D.J.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Gitelman, S.E.; Goland, R.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Herold, K.C.; Marks, J.B.; Raskin, P.; et al. Interleukin-1 antagonism in type 1 diabetes of recent onset: Two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 2013, 381, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Herrath, M.; Peakman, M.; Roep, B. Progress in immune-based therapies for type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 172, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumpter, K.M.; Adhikari, S.; Grishman, E.K.; White, P.C. Preliminary studies related to anti-interleukin-1β therapy in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2011, 12, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablamunits, V.; Henegariu, O.; Hansen, J.B.; Opare-Addo, L.; Preston-Hurlburt, P.; Santamaria, P.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Herold, K.C. Synergistic reversal of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice with anti-CD3 and interleukin-1 blockade: Evidence of improved immune regulation. Diabetes 2012, 61, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study Details. Anti-Inflammatory Therapy with Anakinra in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes. ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00645840 (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Lee, L.F.; Xu, B.; Michie, S.A.; Beilhack, G.F.; Warganich, T.; Turley, S.; McDevitt, H.O. The role of TNF-α in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes in the nonobese diabetic mouse: Analysis of dendritic cell maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15995–16000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrandrea, L.; Yu, J.; Behrens, T.; Buchlis, J.; Albini, C.; Fourtner, S.; Quattrin, T. Etanercept treatment in children with new-onset type 1 diabetes: Pilot randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrin, T.; Haller, M.J.; Steck, A.K.; Felner, E.I.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Leu, J.H.; Zoka, R.; Hedrick, J.A.; Rigby, M.R.; et al. Golimumab and Beta-Cell Function in Youth with New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, C.J.; Kleijwegt, F.S.; Van Riel, P.L.C.M.; Roep, B.O. Development of type 1 diabetes in a patient treated with anti-TNF-α therapy for active rheumatoid arthritis. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1442–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.D.; Tisch, R.; Singer, S.M.; Cao, Z.A.; Liblau, R.S.; Schreiber, R.D.; McDevitt, H.O. Effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha on insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in NOD mice. I. The early development of autoimmunity and the diabetogenic process. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, M.R.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Rendell, M.S.; Felner, E.I.; Dostou, J.M.; Gitelman, S.E.; Patel, C.M.; Griffin, K.J.; Tsalikian, E.; Gottlieb, P.A.; et al. Targeting of memory T cells with alefacept in new-onset type 1 diabetes (T1DAL study): 12 month results of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Quinn, L.M.; Narendran, P. Long-term TNF-alpha therapy for preserving beta cell function in new onset type 1 diabetes: A case report. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatenoud, L.; Thervet, E.; Primo, J.; Bach, J.F. Anti-CD3 antibody induces long-term remission of overt autoimmunity in nonobese diabetic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, K.C.; Gitelman, S.E.; Ehlers, M.R.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Hagopian, W.; Boyle, K.D.; Keyes-Elstein, L.; Aggarwal, S.; Phippard, D.; et al. Teplizumab (Anti-CD3 mAb) treatment preserves C-peptide responses in patients with new-onset type 1 diabetes in a randomized controlled trial: Metabolic and immunologic features at baseline identify a subgroup of responders. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3766–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, E.K.; Bundy, B.N.; Stier, K.; Serti, E.; Lim, N.; Long, S.A.; Geyer, S.M.; Moran, A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Evans-Molina, C.; et al. Teplizumab improves and stabilizes beta cell function in antibody-positive high-risk individuals. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabc8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, M.R. Immune interventions to preserve â cell function in type 1 diabetes. J. Investig. Med. 2016, 64, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeun, R. Immunotherapies for prevention and treatment of type 1 diabetes. Immunotherapy 2025, 17, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatenoud, L.; Primo, J.; Bach, J.F. CD3 antibody-induced dominant self tolerance in overtly diabetic NOD mice. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 2947–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeester, S.; Keymeulen, B.; Kaufman, L.; Van Dalem, A.; Balti, E.V.; Van De Velde, U.; Goubert, P.; Verhaeghen, K.; Davidson, H.W.; Wenzlau, J.M.; et al. Preexisting insulin autoantibodies predict efficacy of otelixizumab in preserving residual b-Cell function in recent-onset type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Study Details. AbATE Follow-Up Study. ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02067923 (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Teplizumab approval for type 1 diabetes in the USA. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pescovitz, M.D.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Krause-Steinrauf, H.; Becker, D.J.; Gitelman, S.E.; Goland, R.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Marks, J.B.; McGee, P.F.; Moran, A.M.; et al. Rituximab, B-Lymphocyte Depletion, and Preservation of Beta-Cell Function. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tison, A.; Garaud, S.; Chiche, L.; Cornec, D.; Kostine, M. Immune-checkpoint inhibitor use in patients with cancer and pre-existing autoimmune diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Li, X.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J. PD-1 inhibitor-associated type 1 diabetes: A case report and systematic review. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 885001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, J.A.; Evangelou, M.; Cutler, A.J.; Pekalski, M.L.; Walker, N.M.; Stevens, H.E.; Porter, L.; Smyth, D.J.; Rainbow, D.B.; Ferreira, R.C.; et al. Regulatory T Cell Responses in Participants with Type 1 Diabetes after a Single Dose of Interleukin-2: A Non-Randomised, Open Label, Adaptive Dose-Finding Trial. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, K.C.; Delong, T.; Perdigoto, A.L.; Biru, N.; Brusko, T.M.; Walker, L.S.K. The immunology of type 1 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallone, R.; Roep, B.O. Biomarkers for immune intervention trials in type 1 diabetes. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 149, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossal, G.J.V.; Herold, K.C.; Goodnow, C.C. Autoimmune tolerance and Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1992, 35, S49–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fyvie, M.J.; Gillespie, K.M. The importance of biomarker development for monitoring type 1 diabetes progression rate and therapeutic responsiveness. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1158278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, M.J.; Hagopian, W.A.; Oram, R.; Steck, A.K.; Vehik, K.; Weedon, M.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Dabelea, D. The clinical consequences of heterogeneity within and between different diabetes types. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyler, J.S. Hope vs hype: Where are we in type 1 diabetes? Diabetologia 2018, 61, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, M.R.; Tallon, E.M.; Brown, M.E.; Posgai, A.L.; Clements, M.A.; Brusko, T.M. Leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning to accelerate discovery of disease-modifying therapies in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2024, 68, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrat, L.A.; Templeman, E.L.; Steck, A.K.; Parikh, H.M.; You, L.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Triolo, T.M.; Rich, S.S.; Krischer, J.; et al. Type 1 diabetes prediction in autoantibody-positive individuals: Performance, time and money matter. Diabetologia 2025, 68, 1709–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet Digital Health. Machine learning to predict type 1 diabetes in children. Lancet Digit. Health 2024, 6, e374. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes Association. Novel Artificial Intelligence Models Detect Type 1 Diabetes Risk Before Clinical Onset. Available online: https://diabetes.org/newsroom/press-releases/novel-artificial-intelligence-models-detect-type-1-diabetes-risk-clinical (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Bone, R.N.; Evans-Molina, C. Combination Immunotherapy for Type 1 Diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2017, 17, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, Z.; Yang, L.; Guo, K.; Zhou, Z. The impact of gut microbiome on immune and metabolic homeostasis in type 1 diabetes: Clinical insights for prevention and treatment strategies. J. Autoimmun. 2025, 151, 103371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek-Trzonkowska, N.; Wujtewicz, M.A.; Myśliwiec, M.; Witkowski, P.; Dobyszuk, A.; Møynarski, W.; Grabowska, M.; Balcerska, A.; Techmańska, I.; Myśliwska, J.; et al. Administration of CD4+CD25highCD127− Regulatory T Cells Preserves β-Cell Function in Type 1 Diabetes in Children. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1817–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartemann, A.; Bensimon, G.; Payan, C.A.; Jacqueminet, S.; Bourron, O.; Nicolas, N.; Fonfrede, M.; Rosenzwajg, M.; Bernard, C.; Klatzmann, D. Low-dose interleukin 2 in patients with type 1 diabetes: A phase 1/2 randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Hiam-Galvez, K.J.; Mowery, C.T.; Herold, K.C.; Gitelman, S.E.; Esensten, J.H.; Liu, W.; Lares, A.P.; Leinbach, A.S.; Lee, M.; et al. The effect of low-dose IL-2 and Treg adoptive cell therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e147474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, J.A.; Fung, V.; Wardell, C.M.; Alkhatib, M.H.; Chen, Y.; Swanson, L.A.; Dwyer, A.J.; Weno, M.E.; Silva, N.; Mitchell, J.S.; et al. Insulin B peptide-MHC class II-specific chimeric antigen receptor-Tregs prevent autoimmune diabetes. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatzmann, D.; Abbas, A.K. The promise of low-dose interleukin-2 therapy for autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetti, M.; Spreafico, R. Regulatory T-cell therapy in transplantation and severe autoimmunity. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 35, 479–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locker, K.C.S.; Kachapati, K.; Wu, Y.; Bednar, K.J.; Adams, D.; Patel, C.; Tsukamoto, H.; Heuer, L.S.; Aronow, B.J.; Herr, A.B.; et al. Endosomal Sequestration of TLR4 Antibody Induces Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Reverses Acute Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2022, 71, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veglia, F.; Sanseviero, E.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the era of increasing myeloid cell diversity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, R.A.; von Andrian, U.H. How Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells Induce Regulatory T Cells. Adv. Immunol. 2010, 108, 111–165. [Google Scholar]
- Parekkadan, B.; Milwid, J.M. Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 12, 87–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Huang, M.; Cui, D.; Xie, J. Myeloid-derived suppressor cell: A crucial player in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1021612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Bluestone, J.A. Regulatory T-Cell Therapy in Transplantation: Moving to the Clinic. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a015552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek-Trzonkowska, N.; Myśliwiec, M.; Dobyszuk, A.; Grabowska, M.; Derkowska, I.; Juścińska, J.; Owczuk, R.; Szadkowska, A.; Witkowski, P.; Młynarski, W.; et al. Therapy of type 1 diabetes with CD4+CD25highCD127-regulatory T cells prolongs survival of pancreatic islets—Results of one year follow-up. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 153, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhu, J. Regulatory T cell-based therapy in type 1 diabetes: Latest breakthroughs and evidence. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 140, 112724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayati, F.; Mohammadi, M.; Valadi, M.; Jamshidi, S.; Foma, A.M.; Sharif-Paghaleh, E. The Therapeutic Potential of Regulatory T Cells: Challenges and Opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 585819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.M.J.; Lakey, J.R.T.; Ryan, E.A.; Korbutt, G.S.; Toth, E.; Warnock, G.L.; Kneteman, N.M.; Rajotte, R.V. Islet Transplantation in Seven Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Using a Glucocorticoid-Free Immunosuppressive Regimen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hering, B.J.; Clarke, W.R.; Bridges, N.D.; Eggerman, T.L.; Alejandro, R.; Bellin, M.D.; Chaloner, K.; Czarniecki, C.W.; Goldstein, J.S.; Hunsicker, L.G.; et al. Phase 3 trial of transplantation of human islets in type 1 diabetes complicated by severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, F.B.; Rickels, M.R.; Alejandro, R.; Hering, B.J.; Wease, S.; Naziruddin, B.; Oberholzer, J.; Odorico, J.S.; Garfinkel, M.R.; Levy, M.; et al. Improvement in outcomes of clinical islet transplantation: 1999–2010. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliuca, F.W.; Millman, J.R.; Gürtler, M.; Segel, M.; Van Dervort, A.; Ryu, J.H.; Peterson, Q.P.; Greiner, D.; Melton, D.A. Generation of functional human pancreatic β cells in vitro. Cell 2014, 159, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzy, A.; Thompson, D.M.; Ward-Hartstonge, K.A.; Ivison, S.; Cook, L.; Garcia, R.V.; Loyal, J.; Kim, P.T.W.; Warnock, G.L.; Levings, M.K.; et al. Implanted pluripotent stem-cell-derived pancreatic endoderm cells secrete glucose-responsive C-peptide in patients with type 1 diabetes. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 2047–2061.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegas, A.J.; Veiseh, O.; Gürtler, M.; Millman, J.R.; Pagliuca, F.W.; Bader, A.R.; Doloff, J.C.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Olejnik, K.; et al. Long-term glycemic control using polymer-encapsulated human stem cell–derived beta cells in immune-competent mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millman, J.R.; Pagliuca, F.W. Autologous pluripotent stem cell-derived β-like cells for diabetes cellular therapy. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, F.L.; Buckle, I.; Forbes, J.M. Type 1 diabetes mellitus prevention: Present and future. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2025, 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, A.; Bruin, J.E.; Arora, P.; Rubin, A.; Batushansky, I.; Asadi, A.; O’Dwyer, S.; Quiskamp, N.; Mojibian, M.; Albrecht, T.; et al. Reversal of diabetes with insulin-producing cells derived in vitro from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.M.J.; Pokrywczynska, M.; Ricordi, C. Clinical pancreatic islet transplantation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Palui, R. Immunotherapy in type 1 diabetes: Novel pathway to the future ahead. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilleh, A.H.; Russ, H.A. Cell Replacement Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes Patients: Potential Mechanisms Leading to Stem-Cell-Derived Pancreatic β-Cell Loss upon Transplant. Cells 2023, 12, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miragaia, R.J.; Gomes, T.; Chomka, A.; Jardine, L.; Riedel, A.; Hegazy, A.N.; Whibley, N.; Tucci, A.; Chen, X.; Lindeman, I.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics of Regulatory T Cells Reveals Trajectories of Tissue Adaptation. Immunity 2019, 50, 493–504.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, A.L.; Safinia, N.; Medvec, A.; Laszkowska, M.; Wray, M.; Mintz, M.A.; Trotta, E.; Szot, G.L.; Liu, W.; Lares, A.; et al. Clinical grade manufacturing of human alloantigen-reactive regulatory T cells for use in transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 3010–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, T.C.; Young, H.Y.; Agulnick, A.D.; Babin, M.J.; Baetge, E.E.; Bang, A.G.; Bhoumik, A.; Cepa, I.; Cesario, R.M.; Haakmeester, C.; et al. A scalable system for production of functional pancreatic progenitors from human embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phase 1/2 Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of VX-880 in T1D Subjects—Health Research Authority. Available online: https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/application-summaries/research-summaries/phase-12-study-to-evaluate-the-safety-tolerability-and-efficacy-of-vx-880-in-t1d-subjects/ (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Vaithilingam, V.; Bal, S.; Tuch, B.E. Encapsulated Islet Transplantation: Where Do We Stand? Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2017, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sosinowski, T.; Cox, A.R.; Cepeda, J.R.; Sekhar, N.S.; Hartig, S.M.; Miao, D.; Yu, L.; Pietropaolo, M.; Davidson, H.W. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells targeting a pathogenic MHC class II:peptide complex modulate the progression of autoimmune diabetes. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 96, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals. Vertex Announces Program Updates for Type 1 Diabetes Portfolio. Available online: https://investors.vrtx.com/news-releases/news-release-details/vertex-announces-program-updates-type-1-diabetes-portfolio (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Bluestone, J.A.; Buckner, J.H.; Herold, K.C. Immunotherapy: Building a bridge to a cure for type 1 diabetes. Science 2021, 373, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, J.R.N.; Skyler, J.S. Challenges in Beta Cell Replacement for Type 1 Diabetes. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2024, 98, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, M.; Alejandro, R.; Ricordi, C.; Fabbri, A. The heterogeneity of type 1 diabetes: From immunopathology to immune intervention. Transl. Autoimmun. Autoimmune Dis. Differ. Organs 2022, 4, 83–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hollander, N.H.M.; de Roep, B.O. From Disease and Patient Heterogeneity to Precision Medicine in Type 1 Diabetes. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 932086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, N.; Wootton, G.E.; Bozward, A.G.; Oo, Y.H. Challenges and opportunities in achieving effective regulatory T cell therapy in autoimmune liver disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals. Vertex Presents Positive VX-880 Results from Ongoing Phase 1/2 Study in Type 1 Diabetes at the American Diabetes Association 83rd Scientific Sessions. Available online: https://investors.vrtx.com/news-releases/news-release-details/vertex-presents-positive-vx-880-results-ongoing-phase-12-study (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Gerace, D.; Zhou, Q.; Kenty, J.H.R.; Veres, A.; Sintov, E.; Wang, X.; Boulanger, K.R.; Li, H.; Melton, D.A. Engineering human stem cell-derived islets to evade immune rejection and promote localized immune tolerance. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Identifying New Biomarkers to Treat Type 1 Diabetes—RNA Genetherapy. Available online: https://www.rna-genetherapy.eu/identifying-new-biomarkers-to-treat-type-1-diabetes/ (accessed on 19 June 2025).
| Agent/Trial | Target | Clinical Setting | Outcome | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teplizumab (AbATE, Protégé, TN-10) | CD3 | New-onset and Stage 2 T1DM | Preserved C-peptide; delayed onset in high-risk relatives | Effect transient; stage-dependent; requires early intervention |
| Otelixizumab | CD3 | New-onset T1DM | Preserved β-cell function in early studies | Limited durability; dose-limiting side effects |
| Anakinra (IL-1Ra) | IL-1 receptor | New-onset T1DM | Reduced insulin needs early after diagnosis | Failed to show durable β-cell preservation in RCTs |
| Canakinumab | IL-1β | New-onset T1DM | No significant benefit on C-peptide at 9–12 months | Limited efficacy; no long-term effect |
| Etanercept/Golimumab | TNF-α | Pediatric Stage 3 T1DM (Phase II) | Signals of benefit in β-cell preservation | Risk of acceleration if mistimed; safety concerns |
| Rituximab (TrialNet) | CD20 | New-onset T1DM | Slowed early decline in C-peptide | Effects not durable; infection risk |
| Abatacept (CTLA-4 Ig) | CTLA-4 | New-onset T1DM (IMPACT trial) | Delayed β-cell decline | Modest effect; no prevention of clinical diabetes |
| PD-1 inhibitors | PD-1 | Experimental/early exploration | Limited use; theoretical potential | Safety risks; risk of precipitating autoimmunity |
| NCT | Therapy | Mechanism | Phase | Population | Primary Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01210664 | Expanded ex vivo Tregs | Immune tolerance via polyclonal Tregs | Phase 1 | Recent-onset T1DM | Safety, Treg persistence, C-peptide |
| NCT02772679 | Tregs + low-dose IL-2 (TILT) | Ex vivo and in vivo Treg expansion | Phase 1 | Recent-onset T1DM | Safety, immunologic response |
| NCT02691247 | Polyclonal Tregs (T-Rex) | Functional Treg increase in pediatric T1DM | Phase 2 | Pediatric recent-onset T1DM (n = 110) | Safety, β-cell function decline |
| NCT02265809 | ViaCyte PEC-Encap | SC-β encapsulated in device | Phase 1/2 | Long-standing T1DM | Safety, C-peptide production |
| NCT04786262 | Vertex VX-880 | SC-β cells infused via portal vein | Phase 1/2/3 | Adults with T1DM + hypoglycemia unawareness | Insulin independence, HbA1c, severe hypoglycemia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavalli, E.; Nicoletti, G.R.P.; Nicoletti, F. Historically Based Perspective on the Immunotherapy of Type 1 Diabetes: Where We Have Been, Where We Are, and Where We May Go. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5621. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165621
Cavalli E, Nicoletti GRP, Nicoletti F. Historically Based Perspective on the Immunotherapy of Type 1 Diabetes: Where We Have Been, Where We Are, and Where We May Go. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5621. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165621
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavalli, Eugenio, Giuseppe Rosario Pietro Nicoletti, and Ferdinando Nicoletti. 2025. "Historically Based Perspective on the Immunotherapy of Type 1 Diabetes: Where We Have Been, Where We Are, and Where We May Go" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5621. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165621
APA StyleCavalli, E., Nicoletti, G. R. P., & Nicoletti, F. (2025). Historically Based Perspective on the Immunotherapy of Type 1 Diabetes: Where We Have Been, Where We Are, and Where We May Go. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5621. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165621







