Nogo-A and NfL Levels in CSF from Newly Diagnosed Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Patients Positive for Anti-HHV6-A IgG Autoantibody
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Statistical Analysis
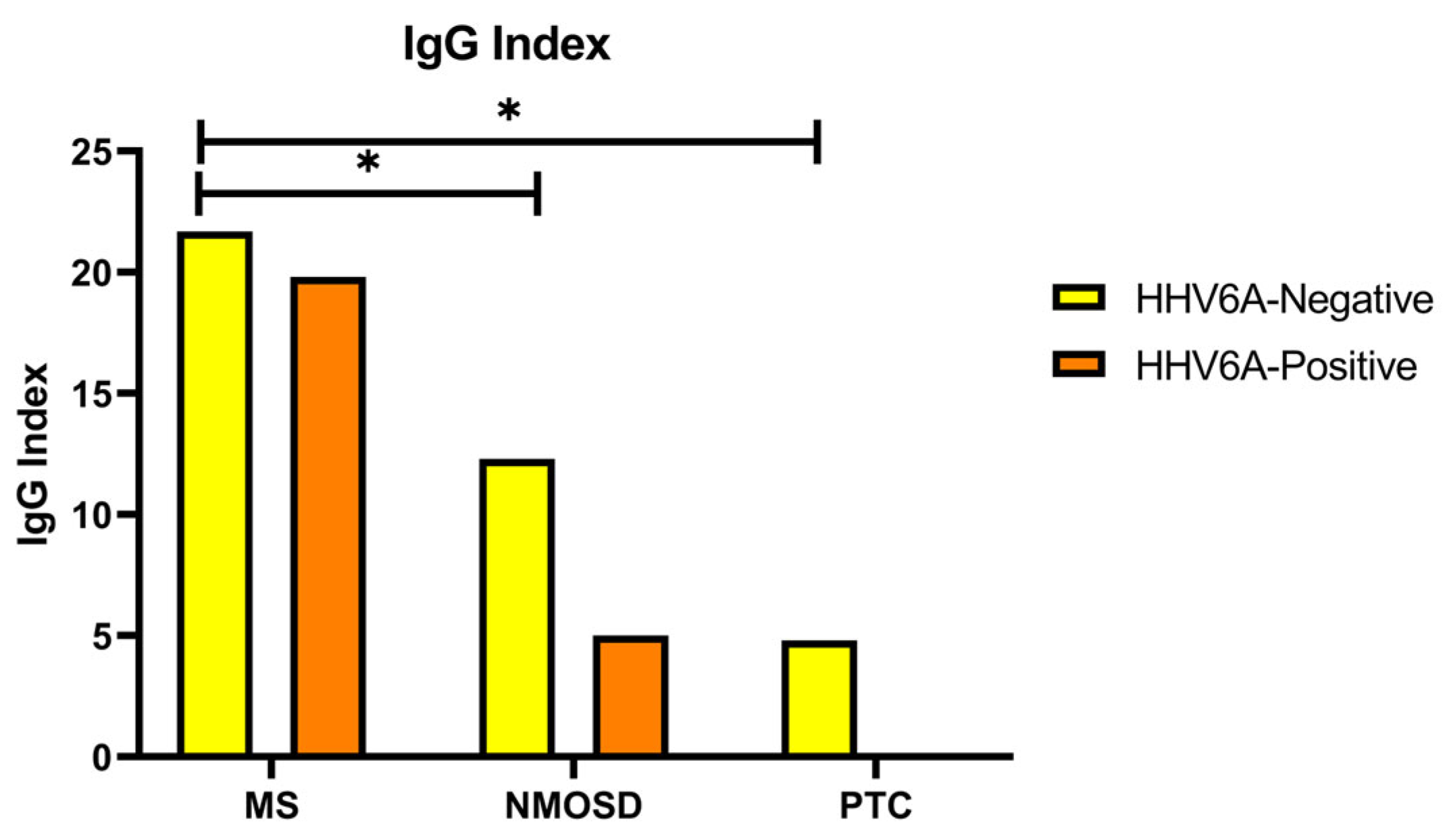
3. Results
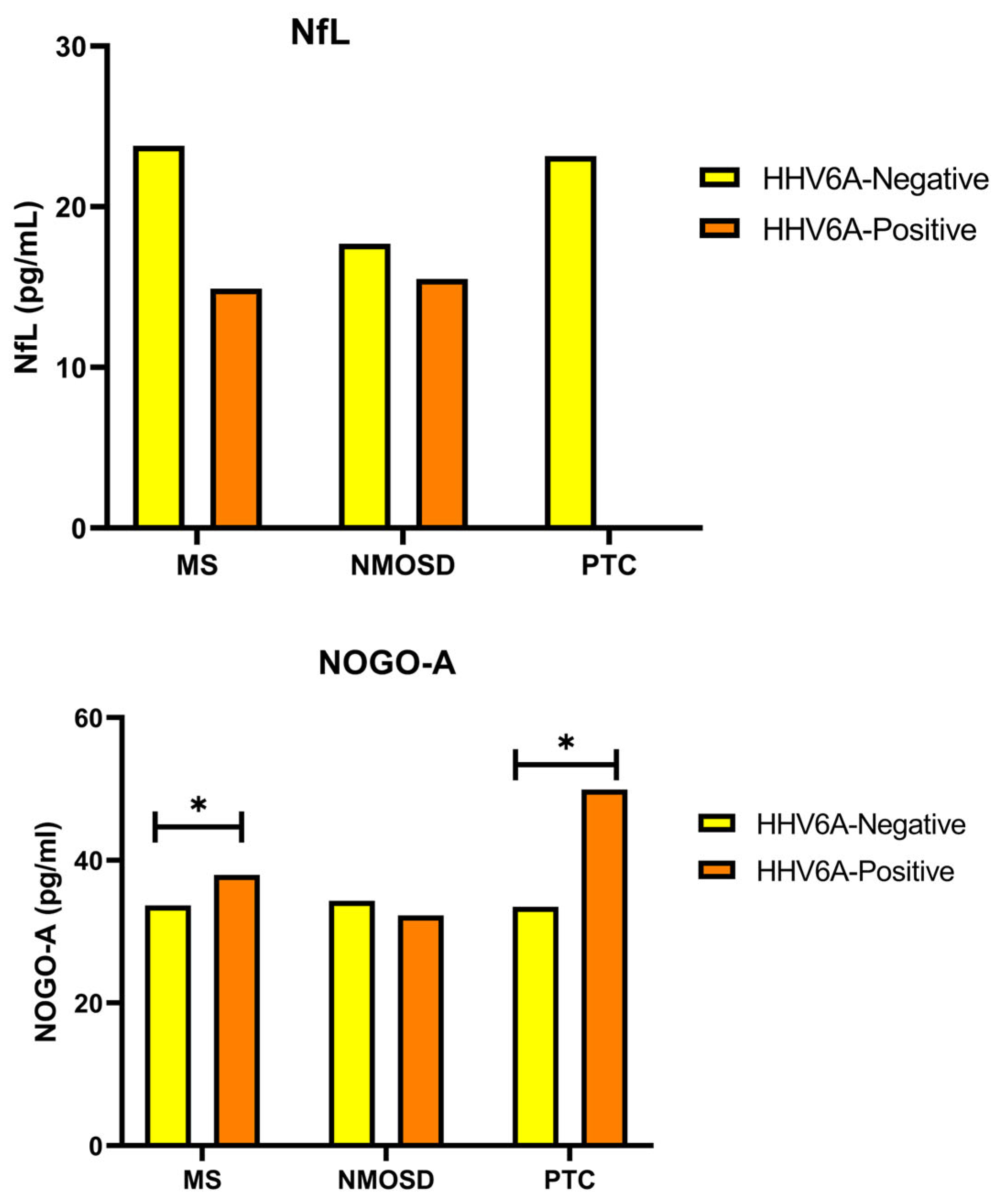
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kebir, H.; Ifergan, I.; Alvarez, J.I.; Bernard, M.; Poirier, J.; Arbour, N.; Prat, A. Preferential recruitment of interferon-γ-expressing T H 17 cells in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Goods, B.A.; Raddassi, K.; Nepom, G.T.; Kwok, W.W.; Love, J.C.; Hafler, D.A. Functional inflammatory profiles distinguish myelin-reactive T cells from patients with multiple sclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 287ra74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chunder, R.; Schropp, V.; Kuerten, S. B Cells in Multiple Sclerosis and virus-induced neuroinflammation. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 591894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Or, A.; Pender, M.P.; Khanna, R.; Steinman, L.; Hartung, H.-P.; Maniar, T.; Croze, E.; Aftab, B.T.; Giovannoni, G.; Joshi, M.A. Epstein–Barr Virus in multiple sclerosis: Theory and emerging immunotherapies. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, S.; Waters, P.; Bell, B.A.; Vincent, A.; Verkman, A.S.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Intra-cerebral injection of neuromyelitis optica immunoglobulin G and human complement produces neuromyelitis optica lesions in mice. Brain 2010, 133, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglhuber, K.; Berthele, A. Eculizumab in the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Immunotherapy 2020, 12, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, J.L.; Huda, S.; Whittam, D.H.; Matiello, M.; Morgan, B.P.; Jacob, A. Correction to: Role of complement and potential of complement inhibitors in myasthenia gravis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: A brief review. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lim, Y.-M.; Kim, G.; Lee, E.-J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, K.-K. Choroid plexus changes on magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 415, 116904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazis, P.W. Pseudotumor cerebri. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2004, 4, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, T.A. Pseudotumoral demyelinating lesions: Diagnostic approach and long-term outcome. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 32, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarlinton, R.E.; Martynova, E.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Khaiboullina, S.; Verma, S. Role of viruses in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Viruses 2020, 12, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, E.; Tanasescu, R.; Tarlinton, R.E.; Constantinescu, C.S.; Zhang, W.; Tench, C.; Gran, B.; Ruprecht, K. The association between human endogenous retroviruses and multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, T.; Rempe, T.; Leypoldt, F.; Riedel, C.; Jansen, O.; Berg, D.; Deuschl, G. The spectrum of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: A practical approach. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 566-e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caselli, E.; Boni, M.; Bracci, A.; Rotola, A.; Cermelli, C.; Castellazzi, M.; Cassai, E. Detection of antibodies directed against Human Herpesvirus 6 U94/REP in sera of patients affected by multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4131–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ablashi, D.; Agut, H.; Alvarez-Lafuente, R.; Clark, D.A.; Dewhurst, S.; DiLuca, D.; Flamand, L.; Frenkel, N.; Gallo, R.; Gompels, U.A.; et al. Classification of HHV-6A and HHV-6B as distinct viruses. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovitch, E.C.; Jacobson, S. Evidence linking HHV-6 with multiple sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 9, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Simpson-Yap, S.; Taylor, B.; Blizzard, L.; Lucas, R.; Ponsonby, A.-L.; Broadley, S.; van der Mei, I. Markers of Epstein-Barr virus and Human Herpesvirus-6 infection and multiple sclerosis clinical progression. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 59, 103561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, D.; Mishra, B.K.; Rout, S.; Lopez-Iranzo, F.J.; Lopez-Rodas, G.; Vallamkondu, J.; Kandimalla, R.; Casanova, B. Potential biomarkers associated with multiple sclerosis pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voumvourakis, K.I.; Fragkou, P.C.; Kitsos, D.K.; Foska, K.; Chondrogianni, M.; Tsiodras, S. Human herpesvirus 6 infection as a trigger of multiple sclerosis: An update of recent literature. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Salvadori, N.; Lisetti, V.; Eusebi, P.; Mancini, A.; Gentili, L.; Borrelli, A.; Portaccio, E.; Sarchielli, P.; Blennow, K.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain tracks cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leppert, D.; Kuhle, J. Blood neurofilament light chain at the doorstep of clinical application. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 6, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; Fan, P.; Ko, H.; Au, C.; Ng, A.; Au, L.; Wong, A.; Kermode, A.G.; Mok, V.; et al. High serum neurofilament levels among Chinese patients with aquaporin-4-IgG-seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 83, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disanto, G.; Barro, C.; Benkert, P.; Naegelin, Y.; Schädelin, S.; Giardiello, A.; Zecca, C.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Leppert, D.; et al. Serum neurofilament light: A biomarker of neuronal damage in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, B.; Portelius, E.; Cullen, N.C.; Sandelius, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Andreasson, U.; Höglund, K.; Irwin, D.; Grossman, M.; Weintraub, D.; et al. Association of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light protein levels with cognition in patients with dementia, motor neuron disease, and movement disorders. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridel, C.; van Wieringen, W.N.; Zetterberg, H.; Tijms, B.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; the NFL Group; Alvarez-Cermeño, J.C.; Andreasson, U.; Axelsson, M.; Bäckström, D.C.; et al. Diagnostic value of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light protein in neurology. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrinovic, M.M.; Duncan, C.S.; Bourikas, D.; Weinman, O.; Montani, L.; Schroeter, A.; Maerki, D.; Sommer, L.; Stoeckli, E.T.; Schwab, M.E. Neuronal Nogo-A regulates neurite fasciculation, branching and extension in the developing nervous system. Development 2010, 137, 2539–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmandke, A.; Schmandke, A.; Schwab, M.E. Nogo-A: Multiple roles in CNS development, maintenance, and disease. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickendesher, T.L.; Baldwin, K.T.; Mironova, Y.A.; Koriyama, Y.; Raiker, S.J.; Askew, K.L.; Wood, A.; Geoffroy, C.G.; Zheng, B.; Liepmann, C.D.; et al. NgR1 and NgR3 are receptors for chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ineichen, B.V.; Kapitza, S.; Bleul, C.; Good, N.; Plattner, P.S.; Seyedsadr, M.S.; Kaiser, J.; Schneider, M.P.; Zörner, B.; Martin, R.; et al. Nogo-A antibodies enhance axonal repair and remyelination in neuro-inflammatory and demyelinating pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, D.J.; Levy, M.; Kerr, D.; Wade, W.F. Neuromyelitis optica pathogenesis and aquaporin 4. J. Neuroınflamm. 2008, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka-Anstadt, J.L.; Mainou, B.A.; Sutherland, D.M.; Sekine, Y.; Strittmatter, S.M.; Dermody, T.S. The Nogo receptor NgR1 mediates infection by mammalian reovirus. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfinger, S.; Yamamoto, E.; Hirano, Y.; Zerbetto, F.; Narumi, T.; Yasuoka, K.; Yasui, M. Structural features of aquaporin 4 supporting the formation of arrays and junctions in biomembranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D.I.; Jacobson, D.M. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology 2002, 59, 1492–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, C.R.; Patel, N.R. A hybrid algorithm for fisher’s exact test in unordered rxc contingency tables. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 1986, 15, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, M.P.; Goldschmidt, C.H.; Rae-Grant, A.D. Diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis. JAMA 2021, 325, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıokka-Uzun, G.; Tüzün, E.; Ekizoğlu, E.; Ulusoy, C.; Yentür, S.; Kürtüncü, M.; Saruhan-Direskeneli, G.; Baykan, B. Oligoclonal bands and increased cytokine levels in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia 2015, 35, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıokka-Uzun, G.; Erdağ, E.; Baykan, B.; Tzartos, J.; Gezen-Ak, D.; Samancı, B.; Dursun, E.; Zisimopoulou, P.; Karagiorgou, K.; Stergiou, C.; et al. Glial and neuronal antibodies in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cai, M.-T.; Yang, F.; Zhou, J.-P.; Fang, W.; Shen, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Ding, M.-P. IgG index revisited: Diagnostic utility and prognostic value in multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyvani, H.; Zahednasab, H.; Aljanabi, H.A.A.; Asadi, M.; Mirzaei, R.; Esghaei, M.; Karampoor, S. The role of human herpesvirus-6 and inflammatory markers in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 346, 577313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, R.; Karampoor, S.; Zahednasab, H.; Keyvani, H.; Gheiasian, M.; Jalilian, F.A. Serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-2, -9, and vitamin D in patients with multiple sclerosis with or without herpesvirus-6 seropositivity. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 24, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotti, D.; Gentili, V.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Govoni, M.; Schiuma, G.; Beltrami, S.; Rizzo, S.; Baldi, E.; Caselli, E.; Pugliatti, M.; et al. Herpesvirus infections in KIR2DL2-positive multiple sclerosis patients: Mechanisms triggering autoimmunity. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundström, W.; Gustafsson, R. Human Herpesvirus 6A Is a Risk Factor for Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 10, 840753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, N.; Kharlamova, N.; Fogdell-Hahn, A. The role of herpesvirus 6A and 6B in multiple sclerosis and epilepsy. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 92, e12984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engdahl, E.; Gustafsson, R.; Huang, J.; Biström, M.; Lima Bomfim, I.; Stridh, P.; Khademi, M.; Brenner, N.; Butt, J.; Michel, A.; et al. Increased Serological Response Against Human Herpesvirus 6A Is Associated With Risk for Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 26, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, J.; Wohler, J.; Fenton, K.; Reich, D.; Jacobson, S. Oligoclonal bands in multiple sclerosis reactive against two herpesviruses and association with magnetic resonance imaging findings. Mult. Scler. J. 2014, 20, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, J.I.; Onoue, H.; Arima, K.; Yamamura, T. Nogo-A and Nogo receptor expression in demyelinating lesions of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thebault, S.; Reaume, M.; Marrie, R.A.; Marriott, J.J.; Furlan, R.; Laroni, A.; Booth, R.A.; Uccelli, A.; Freedman, M.S. High or increasing serum NfL is predictive of impending multiple sclerosis relapses. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 59, 103535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtazmanesh, S.; Shobeiri, P.; Saghazadeh, A.; Teunissen, C.E.; Burman, J.; Szalardy, L.; Klivenyi, P.; Bartos, A.; Fernandes, A.; Rezaei, N. Neuronal and glial CSF biomarkers in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 32, 573–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Petratos, S. Multiple sclerosis. Neuroscientist 2013, 19, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petratos, S.; Ozturk, E.; Azari, M.F.; Kenny, R.; Lee, J.Y.; Magee, K.A.; Harvey, A.R.; McDonald, C.; Taghian, K.; Moussa, L.; et al. Limiting multiple sclerosis related axonopathy by blocking Nogo receptor and CRMP-2 phosphorylation. Brain 2012, 135, 1794–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MS | NMOSD | PTC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HHV6A | Negative | Number of cases (n) | 14 | 7 | 14 |
| Percentage (%) | 73.7 | 87.5 | 93.3 | ||
| Positive | Number of cases (n) | 5 | 1 | 1 | |
| Percentage (%) | 26.3 | 12.5 | 6.7 | ||
| p | 0.367 f | ||||
| n | Median | Mean | STD | Min. | Max. | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NfL | MS | 19 | 102.00 | 110.16 | 25.08 | 76.00 | 169.00 | 0.373 k |
| NMOSD | 8 | 101.82 | 94.08 | 23.45 | 42.00 | 116.00 | ||
| PTC | 15 | 105.00 | 107.07 | 13.45 | 74.00 | 124.00 | ||
| Nogo-A | MS | 19 | 34.37 | 34.81 | 4.16 | 28.05 | 45.16 | 0.975 a |
| NMOSD | 8 | 34.50 | 34.60 | 7.50 | 23.84 | 43.84 | ||
| PTC | 15 | 34.06 | 34.35 | 6.79 | 24.11 | 49.90 |
| MS | Age of Disease Onset | Age | OCB | EDSS | HHV6A | Nogo-A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of disease onset | r | 1 | |||||
| p | |||||||
| Age | r | 0.874 ** | 1 | ||||
| p | 0.000 | ||||||
| OCB | r | 0.526 * | 0.480 * | 1 | |||
| p | 0.025 | 0.044 | |||||
| EDSS | r | 0.198 | 0.077 | 0.112 | 1 | ||
| p | 0.431 | 0.760 | 0.669 | ||||
| HHV6A | r | 0.108 | 0.016 | −0.263 | 0.483 * | 1 | |
| p | 0.659 | 0.948 | 0.291 | 0.042 | |||
| Nogo-A | r | 0.360 | 0.147 | 0.241 | 0.230 | 0.463 * | 1 |
| p | 0.130 | 0.549 | 0.335 | 0.358 | 0.046 | ||
| NMOSD | Age of Disease Onset | Age | OCB | EDSS | HHV6A | Nogo-A | |
| HHV6A | r | 0.884 ** | |||||
| p | 0.008 | ||||||
| PTC | Age of Disease Onset | Age | OCB | EDSS | HHV6A | Nogo-A | |
| The average age | r | 0.812 ** | |||||
| p | 0.000 | ||||||
| OCB | r | 0.902 * | |||||
| p | 0.014 | ||||||
| Nogo-A | r | 0.633 * | |||||
| p | 0.011 | ||||||
| NMOSD | IgG Index | NfL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age of disease onset | r | 0.144 | 0.764 * |
| p | 0.758 | 0.027 | |
| Age | r | 0.464 | 0.881 ** |
| p | 0.294 | 0.004 | |
| OCB | r | 0.116 | 0.694 |
| p | 0.805 | 0.083 | |
| EDSS | r | −0.771 * | −0.420 |
| p | 0.042 | 0.300 | |
| HHV6A | r | −0.612 | −0.082 |
| p | 0.144 | 0.846 | |
| NfL | r | 0.714 | 1.000 |
| p | 0.071 | ||
| Nogo-A | r | −0.286 | −0.095 |
| p | 0.535 | 0.823 | |
| PTC | IgG Index | NfL | |
| Nogo-A | r | 0.558 * | |
| p | 0.031 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karabörk, Ş.; Çelik, B.G.; Uluç, F.; Aydın Türkoğlu, Ş.; Yıldız, S. Nogo-A and NfL Levels in CSF from Newly Diagnosed Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Patients Positive for Anti-HHV6-A IgG Autoantibody. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5497. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155497
Karabörk Ş, Çelik BG, Uluç F, Aydın Türkoğlu Ş, Yıldız S. Nogo-A and NfL Levels in CSF from Newly Diagnosed Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Patients Positive for Anti-HHV6-A IgG Autoantibody. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5497. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155497
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarabörk, Şeyda, Bihter Gökçe Çelik, Firdevs Uluç, Şule Aydın Türkoğlu, and Serpil Yıldız. 2025. "Nogo-A and NfL Levels in CSF from Newly Diagnosed Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Patients Positive for Anti-HHV6-A IgG Autoantibody" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5497. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155497
APA StyleKarabörk, Ş., Çelik, B. G., Uluç, F., Aydın Türkoğlu, Ş., & Yıldız, S. (2025). Nogo-A and NfL Levels in CSF from Newly Diagnosed Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Patients Positive for Anti-HHV6-A IgG Autoantibody. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5497. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155497






