The Bimalleolar Method Shows the Most Reliable Results for Measuring Tibial Torsion in Rotational MRI
Abstract
1. Introduction
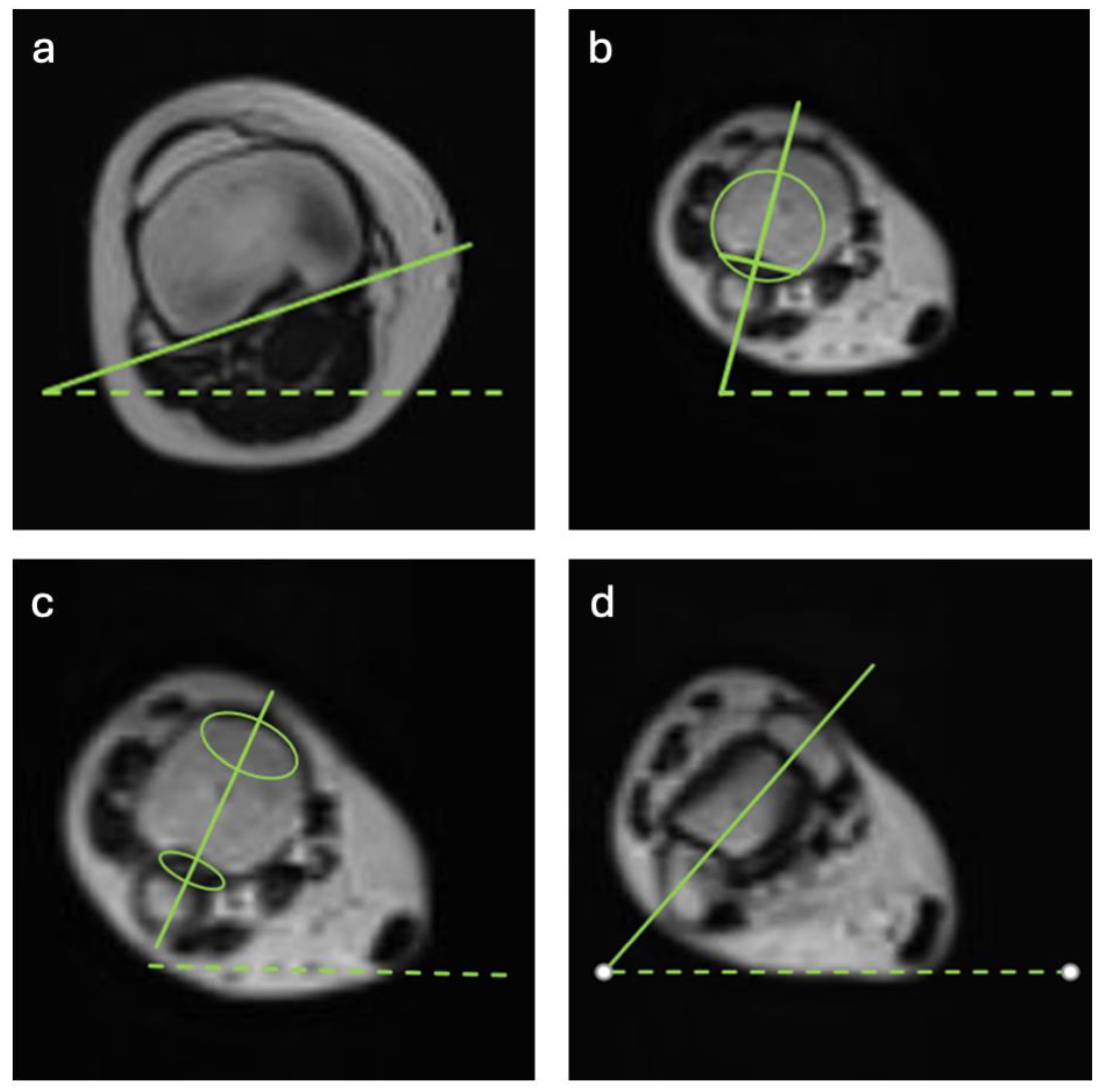
2. Methods
Statistical Analysis
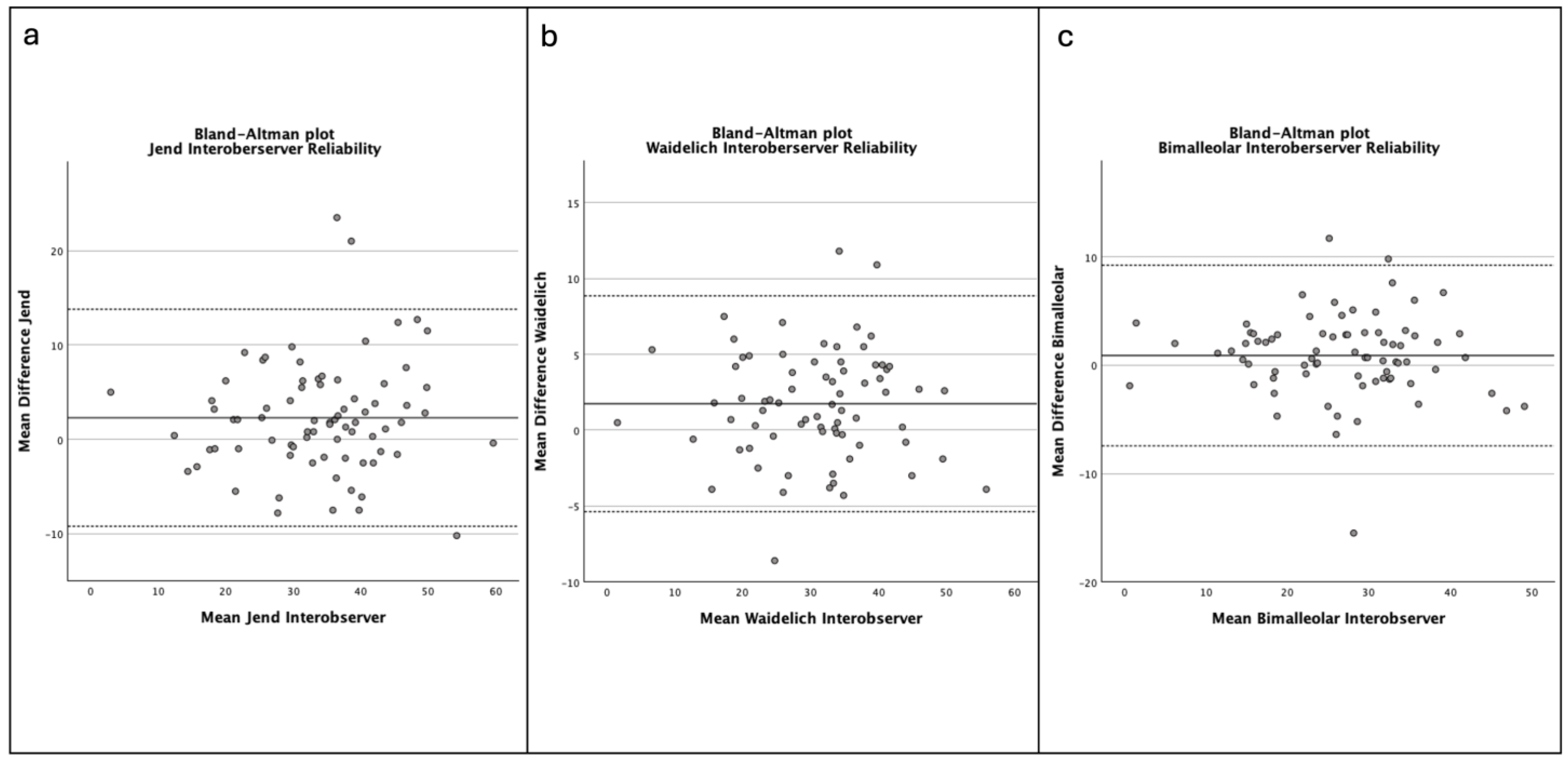
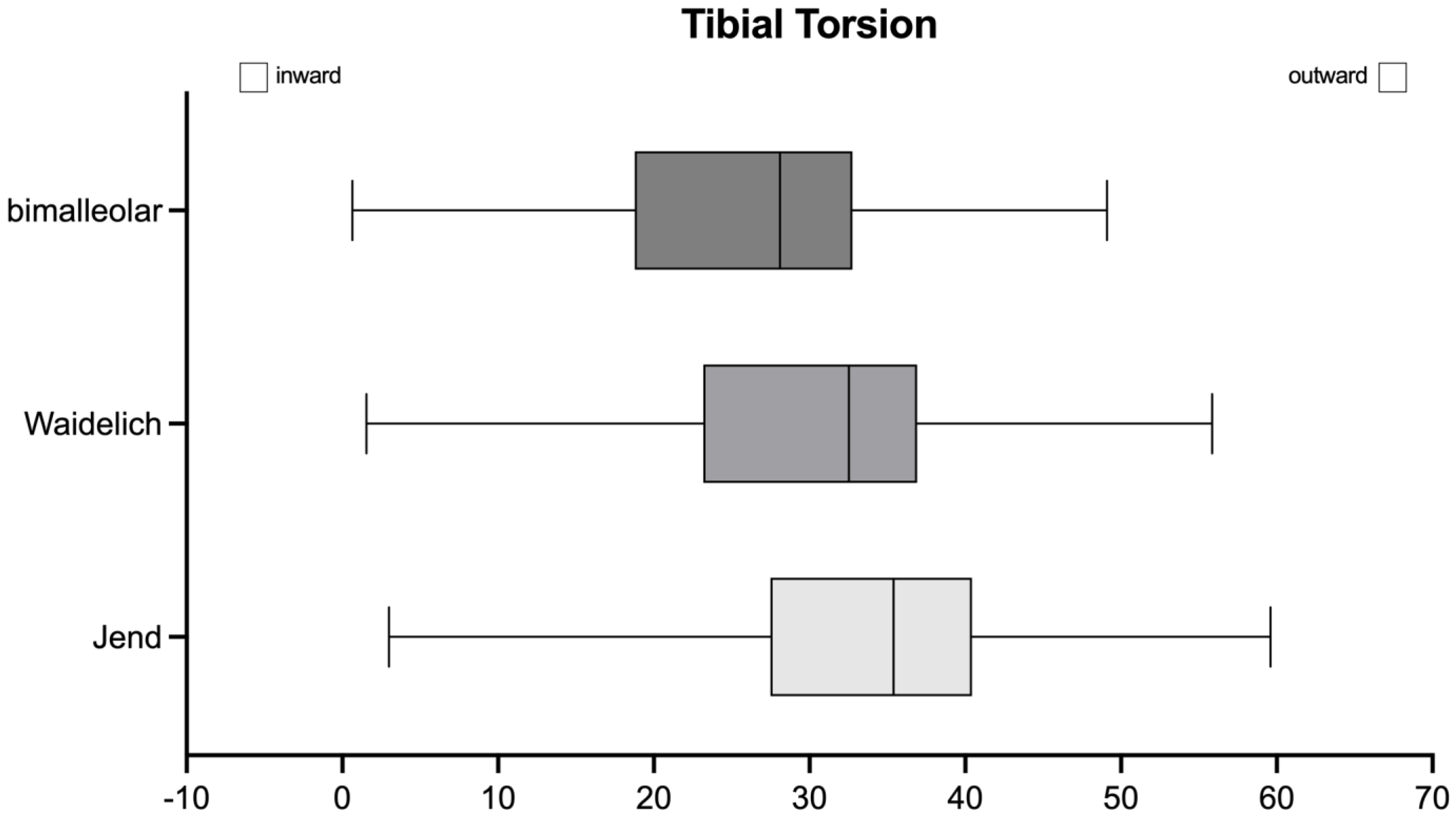
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| FPA | Foot Progression Angle |
| ICC | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| TT | Tibial Torsion |
References
- Fabry, G.; Cheng, L.X.; Molenaers, G. Normal and abnormal torsional development in children. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994, 302, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Tarrazo, X.; Escalona-Marfil, C.; Pla-Campas, G.; Coda, A. Validity and reliability of ultrasonographic assessment of femoral and tibial torsion in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2024, 183, 3159–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhoff, F.B.; Funke, V.; Muench, L.N.; Sauter, A.; Englmaier, M.; Woertler, K.; Imhoff, A.B.; Feucht, M.J. The complexity of bony malalignment in patellofemoral disorders: Femoral and tibial torsion, trochlear dysplasia, TT-TG distance, and frontal mechanical axis correlate with each other. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2020, 28, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akcali, O.; Tiner, M.; Ozaksoy, D. Effects of lower extremity rotation on prognosis of flexible flatfoot in children. Foot Ankle Int. 2000, 21, 772–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, C.F.; Weinberg, D.S.; Liu, R.W. Internal tibial torsion is related to syndesmosis injury in a large osteological collection. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 26, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, K.I.; Boldt, K.R.; Sogbein, O.A.; Steiner, N.J.; Moatshe, G.; Arendt, E.; Getgood, A. Femoral internal torsion greater than twenty-five degrees and/or external tibial torsion greater than thirty degrees as measured by computed tomography are threshold values for axial alignment correction in patellofemoral instability. J. ISAKOS 2024, 9, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, P.; Schmoelz, W.; Schoettle, P.; Zwierzina, M.; Heinrichs, C.; Attal, R. Increased internal femoral torsion can be regarded as a risk factor for patellar instability—A biomechanical study. Clin. Biomech. 2017, 47, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albersheim, M.; Noonan, B.; Chau, M.; Cooper, T.; Tompkins, M. Rotational Osteotomy for Femoral Version/Tibial Torsion. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2022, 15, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, C.M. The influence of altered lower-extremity kinematics on patellofemoral joint dysfunction: A theoretical perspective. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2003, 33, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulos, L.; Swanson, S.C.; Stoddard, G.J.; Barber-Westin, S. Surgical correction of limb malalignment for instability of the patella: A comparison of 2 techniques. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.S. The association between tibial torsion and knee joint pathology. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994, 302, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.; Lakin, G. The effect of tibial torsion on the dynamic function of the soleus during gait. Gait Posture 2003, 17, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selber, P.; Filho, E.R.; Dallalana, R.; Pirpiris, M.; Nattrass, G.R.; Graham, H.K. Supramalleolar derotation osteotomy of the tibia, with T plate fixation. Technique and results in patients with neuromuscular disease. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2004, 86, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krengel, W.F.; Staheli, L.T., 3rd. Tibial rotational osteotomy for idiopathic torsion. A comparison of the proximal and distal osteotomy levels. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 283, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Chung, C.Y.; Park, M.S.; Choi, I.H.; Cho, T.J. Tibial torsion in cerebral palsy: Validity and reliability of measurement. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 2098–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodgin, D.A.; De Swart, R.J.; Stefko, R.M.; Wenger, D.R.; Ko, J.Y. Distal tibial/fibular derotation osteotomy for correction of tibial torsion: Review of technique and results in 63 cases. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1998, 18, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, P.; Attal, R.; Kammerer, M.; Thauerer, M.; Hamberger, L.; Mayr, R.; Schmoelz, W. Significant differences in femoral torsion values depending on the CT measurement technique. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2016, 136, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemier, M.; Glard, Y.; Pomero, V.; Viehweger, E.; Jouve, J.L.; Bollini, G. Rotational profile of the lower limb in 1319 healthy children. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawi, H.; Kaireit, T.F.; Krettek, C.; Liodakis, E. Clinical assessment of tibial torsion differences. Do we always need a computed tomography? Eur. J. Trauma. Emerg. Surg. 2022, 48, 3229–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, F.; Rivera, F.; Zorzan, A.; Ali, S.M. Bilateral double osteotomy in severe torsional malalignment syndrome: 16 years follow-up. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2014, 15, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhove, F.; Noppe, N.; Fragomen, A.T.; Hoekstra, H.; Vanderschueren, G.; Metsemakers, W.J. Standardization of torsional CT measurements of the lower limbs with threshold values for corrective osteotomy. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2019, 139, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, K.; Naor, N.; Merlob, P.; Wielunsky, E. Rotational deformities of the tibia and foot in preterm infants. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1990, 10, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botser, I.B.; Ozoude, G.C.; Martin, D.E.; Siddiqi, A.J.; Kuppuswami, S.; Domb, B.G. Femoral anteversion in the hip: Comparison of measurement by computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and physical examination. Arthroscopy 2012, 28, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liodakis, E.; Doxastaki, I.; Chu, K.; Krettek, C.; Gaulke, R.; Citak, M.; Kenawey, M. Reliability of the assessment of lower limb torsion using computed tomography: Analysis of five different techniques. Skelet. Radiol. 2012, 41, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, L.; Histing, T.; Springer, F.; Keller, G. MRI-based torsion measurement of the lower limb is a reliable and valid alternative for CT measurement: A prospective study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2023, 31, 4903–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jend, H.H.; Heller, M.; Schontag, H.; Schoettle, H. A computer tomographic method for the determination of tibial torsion (author’s transl). Rofo 1980, 133, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waidelich, H.A.; Strecker, W.; Schneider, E. Computed tomographic torsion-angle and length measurement of the lower extremity. The methods, normal values and radiation load. Rofo 1992, 157, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.F.; Ma, K.L.; Shan, H.; Liu, T.F.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wan, Y.; Jun, Z.; Wang, H.Q. CT Scans and Cancer Risks: A Systematic Review and Dose-response Meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, G.; Gotz, S.; Kraus, M.S.; Grunwald, L.; Springer, F.; Afat, S. Radiation Dose Reduction in CT Torsion Measurement of the Lower Limb: Introduction of a New Ultra-Low Dose Protocol. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlic, P.W.; Runer, A.; Seeber, C.; Thoni, M.; Seitlinger, G.; Liebensteiner, M.C. Segmental torsion assessment is a reliable method for in-depth analysis of femoral alignment in Computer Tomography. Int. Orthop. 2018, 42, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesham, K.; Carry, P.M.; Freese, K.; Kestel, L.; Stewart, J.R.; Delavan, J.A.; Novais, E.N. Measurement of Femoral Version by MRI is as Reliable and Reproducible as CT in Children and Adolescents With Hip Disorders. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2017, 37, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosskopf, A.B.; Buck, F.M.; Pfirrmann, C.W.; Ramseier, L.E. Femoral and tibial torsion measurements in children and adolescents: Comparison of MRI and 3D models based on low-dose biplanar radiographs. Skelet. Radiol. 2017, 46, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisch, D.; Dreher, T. Torsion and torsional development of the lower extremities. Orthopade 2019, 48, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrisevic, E.; Westberry, D.E.; Pugh, L.I.; Bagley, A.M.; Tanner, S.; Davids, J.R. Correction of Tibial Torsion in Children With Cerebral Palsy by Isolated Distal Tibia Rotation Osteotomy: A Short-term, In Vivo Anatomic Study. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2016, 36, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattey, T.; Hyndman, J. Rotational osteotomies of the leg: Tibia alone versus both tibia and fibula. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1994, 14, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmar, A.J.; Stinner, D.J.; Pennings, J.; Mitchell, P.M. Prevalence of Individual Differences in Tibial Torsion: A CT-Based Study. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 30, e199–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, M.J.; Wylie, J.D.; Bodine, B.G.; Kapron, A.L.; Maak, T.G.; Mei-Dan, O.; Aoki, S.K. Accuracy and Reliability of Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Compared With True Anatomic Femoral Version. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2017, 37, e265–e270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, A.R.; Freitas, J.M.; Bomar, J.D.; Dwek, J.; Hosalkar, H.S. CT and MRI lower extremity torsional profile studies: Measurement reproducibility. J. Child. Orthop. 2012, 6, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaran, S.H.; Ercin, E.; Bayrak, A.; Cumen, H.; Bilgili, M.G.; Inci, E.; Avkan, M.C. The measurement of tibial torsion by magnetic resonance imaging in children: The comparison of three different methods. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2015, 25, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.B.; Draper, C.E.; Fredericson, M.; Powers, C.M. Femur rotation and patellofemoral joint kinematics: A weight-bearing magnetic resonance imaging analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2010, 40, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaiman, R.H.; Shih, Y.; Bakker, C.; Arendt, E.A.; Tompkins, M.A. Tibial derotational osteotomy for idiopathic tibial torsion: A systematic review of surgical indications based on clinical presentation and measurement technique. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2024, 32, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmaranzer, F.; Lerch, T.D.; Siebenrock, K.A.; Tannast, M.; Steppacher, S.D. Differences in Femoral Torsion Among Various Measurement Methods Increase in Hips With Excessive Femoral Torsion. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2019, 477, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, C.W.; Park, K.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Seo, I.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Yoon, S.H. Minimally Invasive Derotational Osteotomy of Long Bones: Smartphone Application Used to Improve the Accuracy of Correction. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.; Suzuki, A.; Reitz, C.; Saxena, A.; Kuo, J.; Tetsworth, K. Measurement of rotational deformity: Using a smartphone application is more accurate than conventional methods. ANZ J. Surg. 2013, 83, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Interobserver Reliability | Intraobserver Reliability | |
|---|---|---|
| ICC (95% CI) | ICC (95% CI) | |
| Jend | 0.933 (0.903–0.955) | 0.903 (0.848–0.938) |
| Waidelich | 0.966 (0.950–0.977) | 0.942 (0.909–0.963 |
| bimalleolar | 0.966 (0.950–0.977) | 0.947 (0.916–0.966) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vertesich, K.; Chiari, C.; Zalaudek, M.; Hebenstreit, K.; Schneider, E.; Windhager, R.; Willegger, M. The Bimalleolar Method Shows the Most Reliable Results for Measuring Tibial Torsion in Rotational MRI. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134523
Vertesich K, Chiari C, Zalaudek M, Hebenstreit K, Schneider E, Windhager R, Willegger M. The Bimalleolar Method Shows the Most Reliable Results for Measuring Tibial Torsion in Rotational MRI. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134523
Chicago/Turabian StyleVertesich, Klemens, Catharina Chiari, Martin Zalaudek, Karin Hebenstreit, Eleonora Schneider, Reinhard Windhager, and Madeleine Willegger. 2025. "The Bimalleolar Method Shows the Most Reliable Results for Measuring Tibial Torsion in Rotational MRI" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134523
APA StyleVertesich, K., Chiari, C., Zalaudek, M., Hebenstreit, K., Schneider, E., Windhager, R., & Willegger, M. (2025). The Bimalleolar Method Shows the Most Reliable Results for Measuring Tibial Torsion in Rotational MRI. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134523








