Effect of Dietary Modifications on Blood Pressure and Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters in a Woman with Hypotension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Subject
2.2. The Diet Applied
2.3. Physical Activity
2.4. Blood Pressure Measurements
2.5. Anthropometric Measurements
2.6. Biochemical Measurements
2.7. Statistical Elaboration of the Results
3. Results
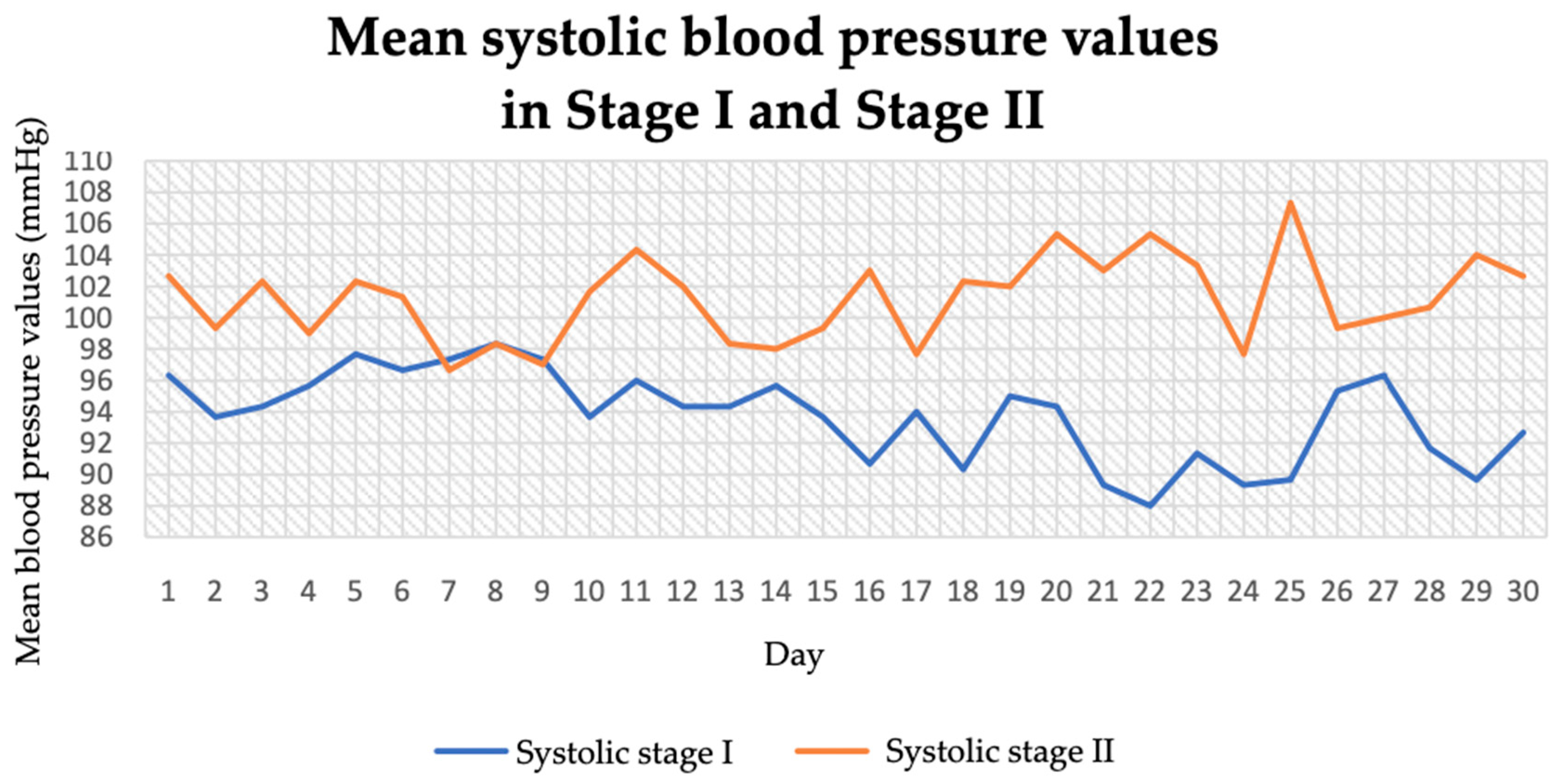
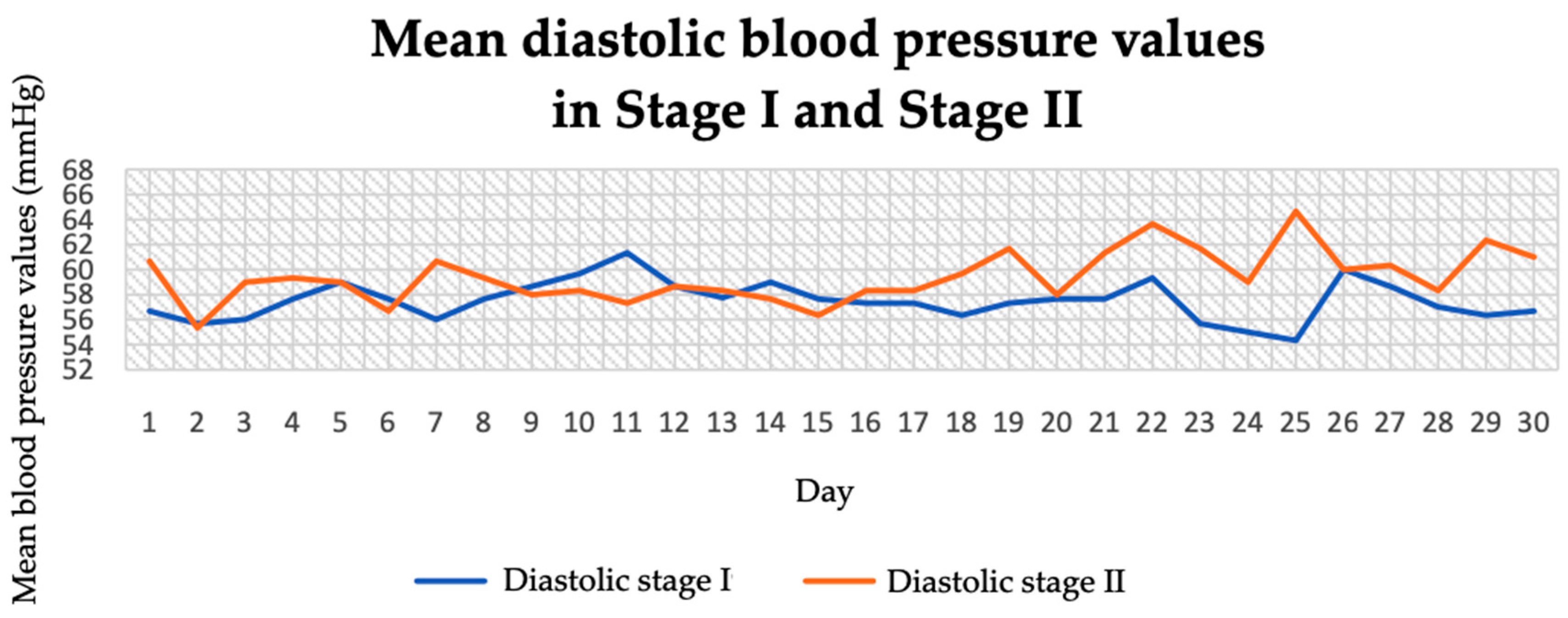
3.1. Blood Pressure and Pulse (Before and During the Intervention)
3.2. Anthropometric Parameters
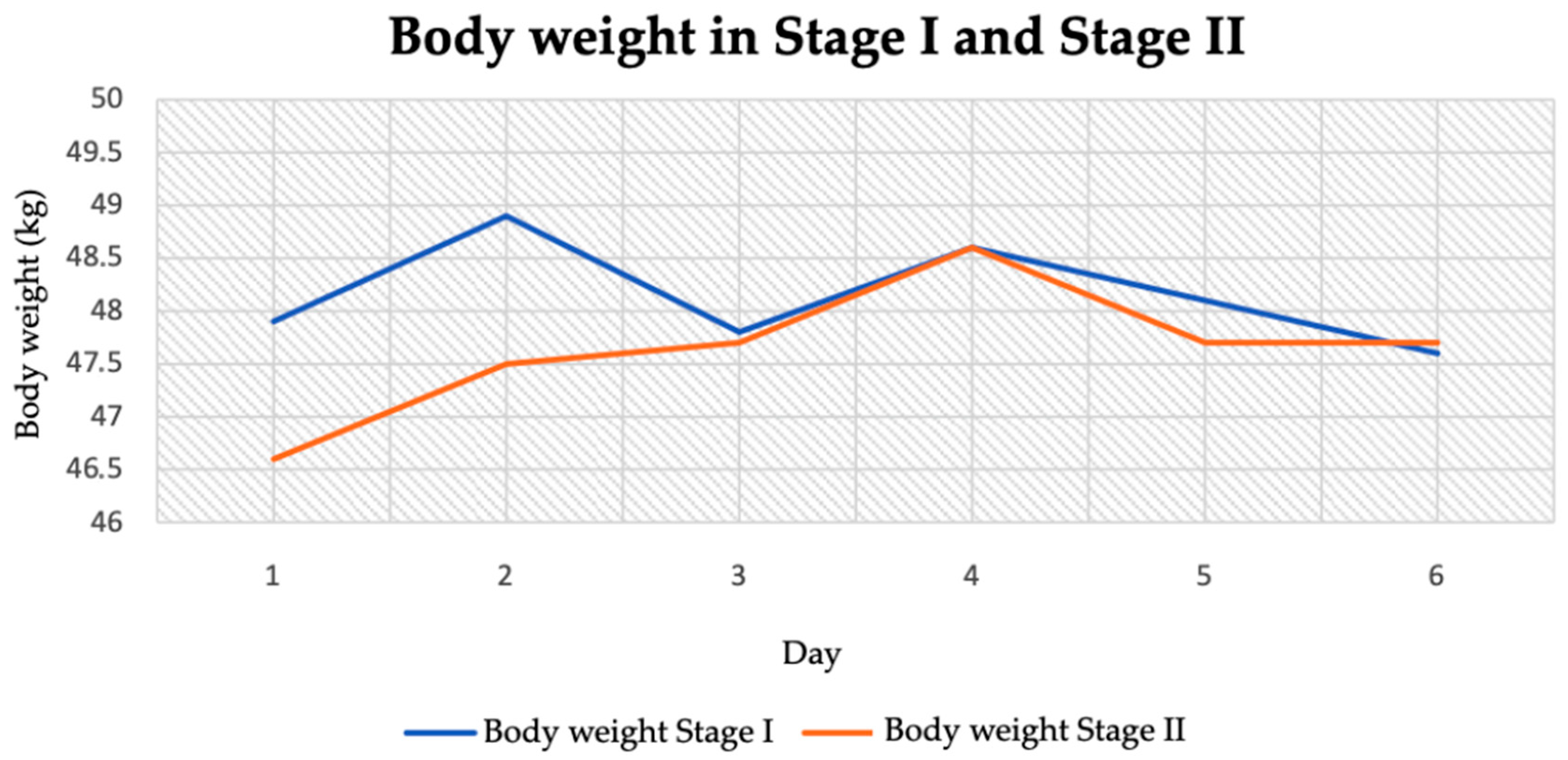
3.2.1. Body Weight
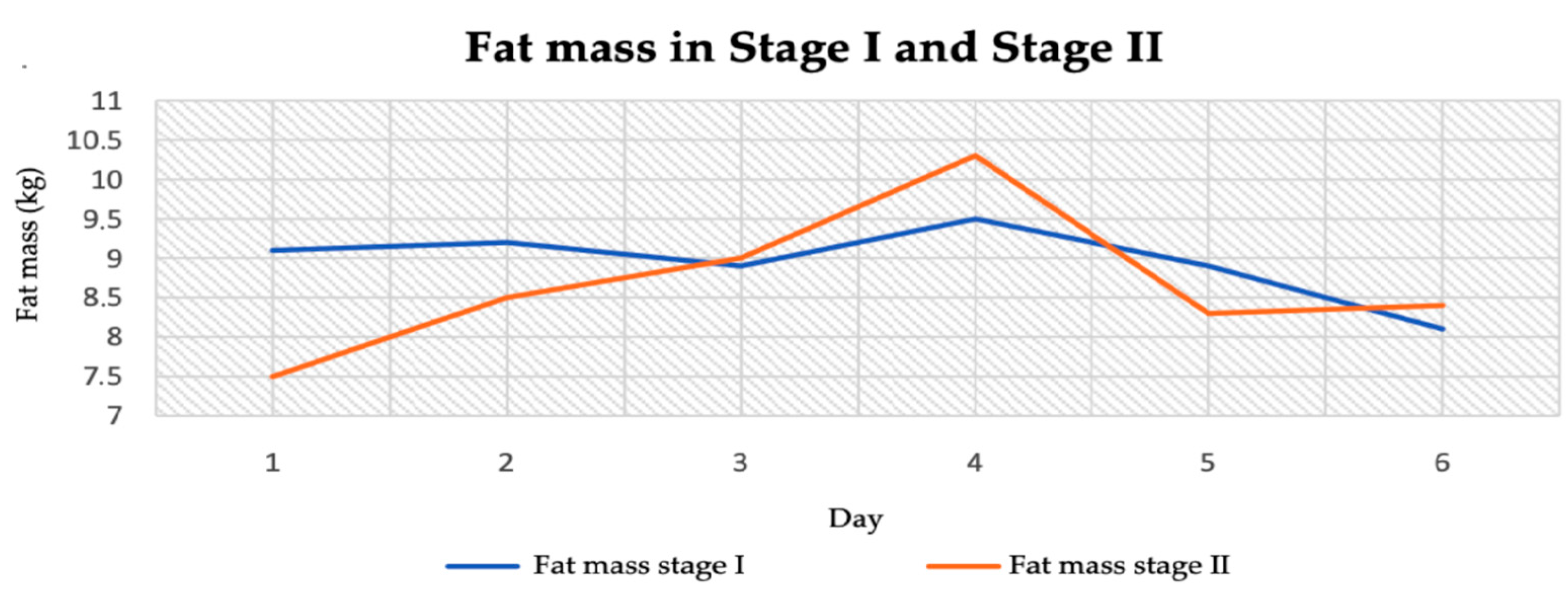
3.2.2. Body Fat Mass
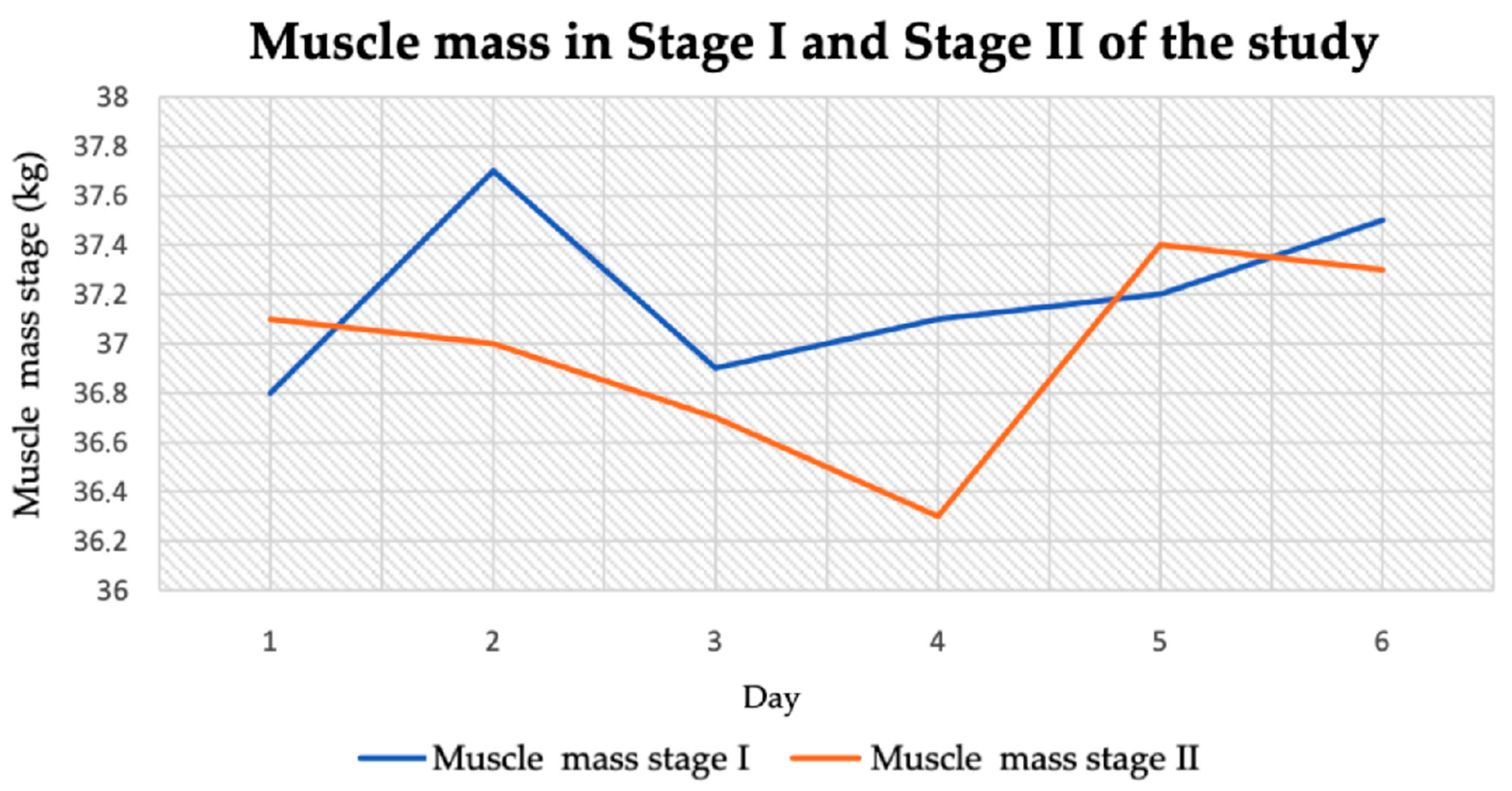
3.2.3. Muscle Tissue Mass
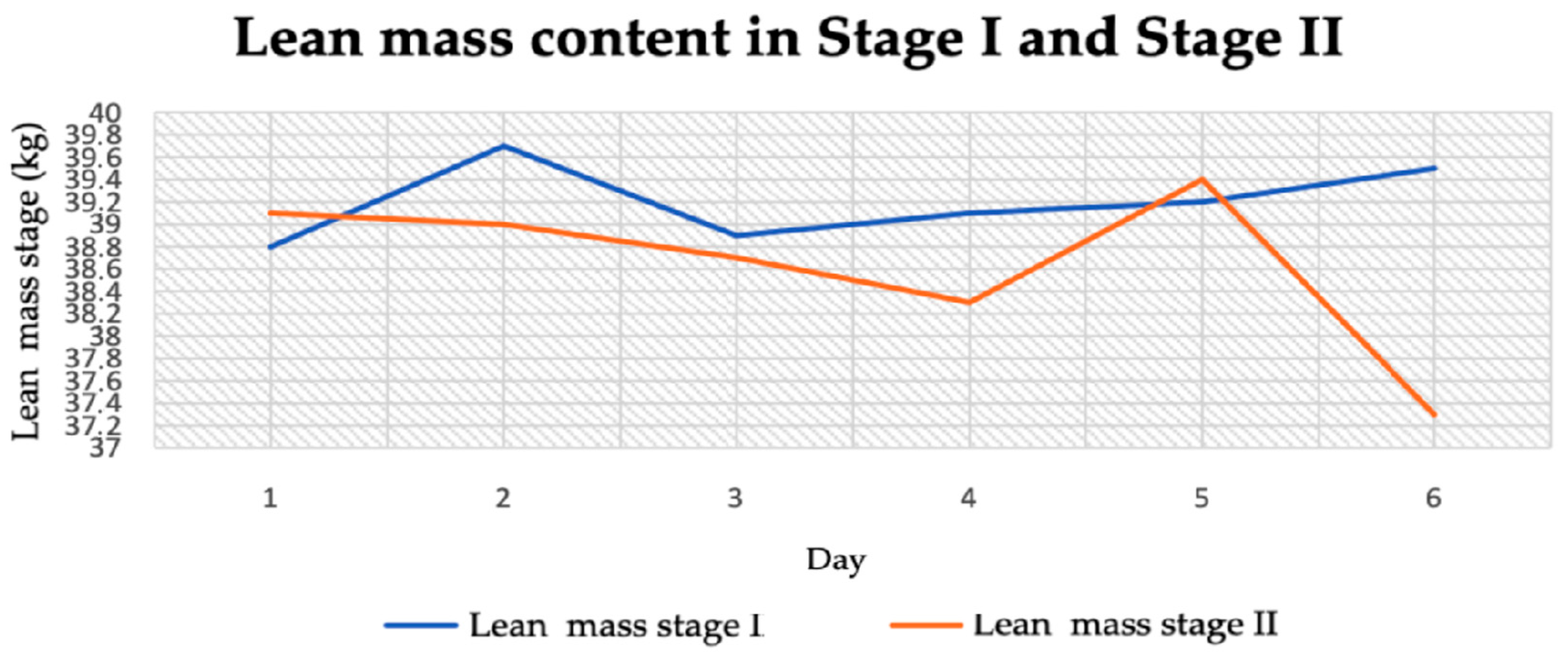
3.2.4. Lean Body Mass
3.2.5. Body Water Content
3.3. Biochemical Parameters
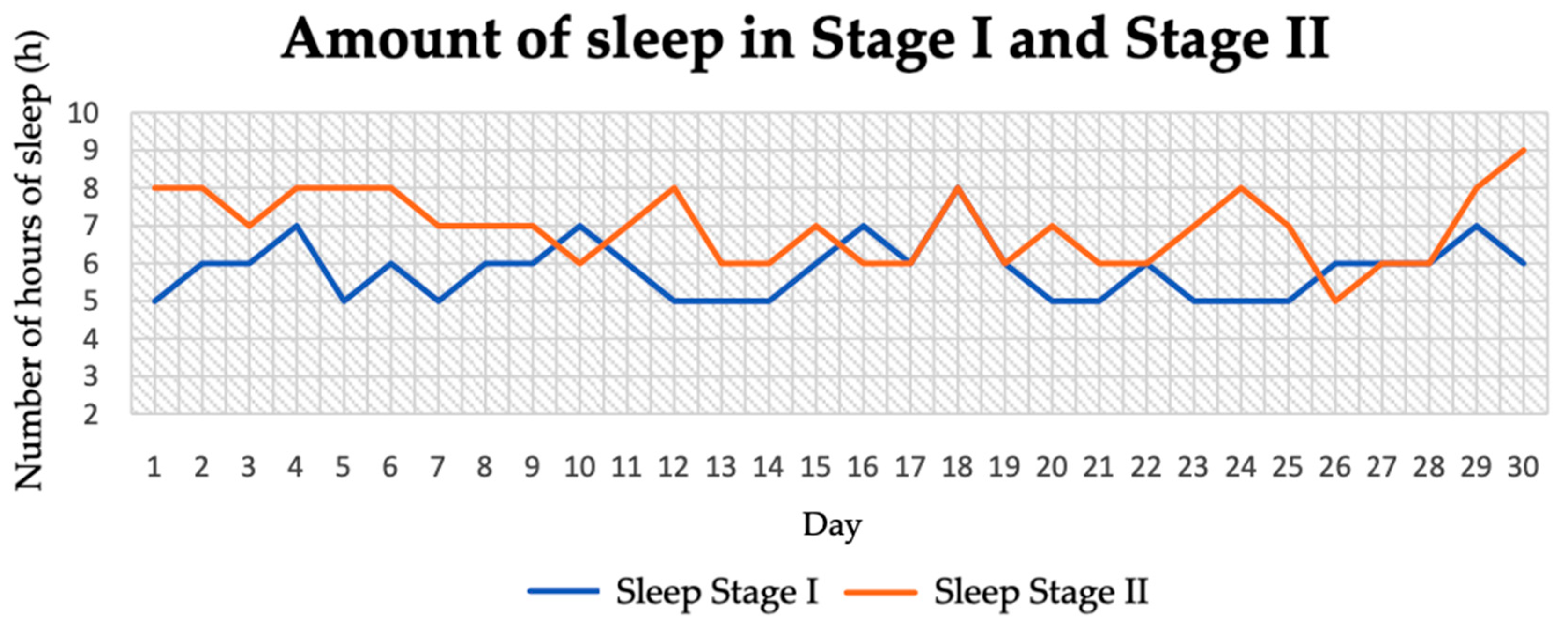
3.4. Length of Sleep
3.5. Quality of Life
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nolan, P.; McEvoy, J.W. Salt restriction for treatment of hypertension—Current state and future directions. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2024, 39, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.J.; Parikh, N.; Ahmed, S.; Ruzicka, M.; Hiremath, S. Blood Pressure Control Should Focus on More Potassium: Controversies in Hypertension. Hypertension 2024, 81, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurvita, S.; Rizkapriliza, W. Coffee and blood pressure. Coffee Sci. 2024, 19, e192193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales Barbosa, S.; Martin Sousa, L.C.; de Oliveira Silva, D.F.; Bastos Pimentel, J.; Cavalcanti Mauricio de Sena Evangelista, K.; de Oliveira Lyra, C.; Gomes Dantas Lopes, M.M.; Vieira Cunha Lima, S.C. A Systematic Review on Processed/Ultra-Processed Foods and Arterial Hypertension in Adults and Older People. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nestel, P.J.; Mori, T.A. Diet to Stop Hypertension: Should Fats be Included? Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2024, 26, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strilchuk, L.; Cincione, R.I.; Fogacci, F.; Cicero, A.F.G. Dietary interventions in blood pressure lowering: Current evidence in 2020. Kardiol Pol. 2020, 78, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lari, A.; Sohouli, M.H.; Fatahi, S.; Cerqueira, H.S.; Santos, H.O.; Pourrajab, B.; Rezaei, M.; Saneie, S.; Rahideh, S.T. The effects of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet on metabolic risk factors in patients with chronic disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 2766–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Hashmi, M.F.; Bhattacharya, P.T. Hypotension. Updated 2023 February 19. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499961/ (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Bhalke, R.D.; Giri, M.A.; Anil, R.Y.; Balasaheb, N.M.; Nanasaheb, P.A.; Pande, V.V. Hypotension: A comprehensive review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2021, 10, 1945–1947. [Google Scholar]
- Mayo Clinic. Low Blood pressure (Hypotension). Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/low-blood-pressure/symptoms-causes/syc-20355465 (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Kreutz, R.; Brunström, M.; Burnier, M.; Grassi, G.; Januszewicz, A.; Muiesan, M.L.; Tsioufis, K.; de Pinho, R.M.; Albini, F.L.; Boivin, J.M.; et al. 2024 European Society of Hypertension clinical practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 126, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Hypertension. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Chen, R.J.; Sharma, S.; Bhattacharya, P.T. Hypotension. Updated 2025 May 3. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK499961/ (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- WHO. Sodium Reduction. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salt-reduction (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Filippini, T.; Malavolti, M.; Whelton, P.K.; Vinceti, M. Sodium Intake and Risk of Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-analysis of Observational Cohort Studies. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2022, 24, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Chen, L.; Xiong, H.; Ma, Y.; Pombo-Rodrigues, S.; MacGregor, G.A.; He, F.J. Blood Pressure-Lowering Medications, Sodium Reduction, and Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2024, 81, e149–e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esselink, A.C.; Bril, L.M.; Langenhuijsen, R.W.; Bilos, A.; Riksen, N.P.; Rongen, G.A. Effect of two dosages of sodium chloride intake on the blood pressure response to caffeinated coffee in humans in vivo. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, J.T.; Sutterfield, S.L.; Post, H.K.; Lovoy, G.M.; Banister, H.R.; Turpin, V.G.; Colburn, T.D.; Hammond, S.S.; Copp, S.W.; Ade, C.J. Impact of high sodium intake on blood pressure and functional sympatholysis during rhythmic handgrip exercise. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duus, C.L.; Nielsen, S.F.; Hornstrup, B.G.; Mose, F.H.; Bech, J.N. Self-Performed Dietary Sodium Reduction and Blood Pressure in Patients with Essential Hypertension: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e034632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mehta, V. Addictive salt may not be solely responsible for causing hypertension: A sweet and fatty hypothesis. Hipertens. Riesgo Vasc. 2018, 35, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikilidou, M.I.; Lasaridis, A.N.; Sarafidis, P.A.; Tziolas, I.M.; Zebekakis, P.E.; Dombros, N.V.; Giannoulis, E. Blood Pressure and Serum Potassium Levels in Hypertensive Patients Receiving or Not Receiving Antihypertensive Treatment. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2007, 29, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barche, B.; Dzudie, A.; Moor, V.; Azabji, M.; Stanis, F.; Messaline, F.; Peter, E.; Mouliom, S.; Felicite, K.; Halle, M.; et al. Prevalence and associated factors of hypokalemia in hypertension: The perspective in a low to middle-income setting. J. Xiangya Med. 2020, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesas, A.E.; Leon-Muñoz, L.M.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F.; Lopez-Garcia, E. The effect of coffee on blood pressure and cardiovascular disease in hypertensive individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, J.E. Critical review of dietary caffeine and blood pressure: A relationship that should be taken more seriously. Psychosom. Med. 2004, 66, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevano, F.Q.; Vela-Bernal, S.; Facchetti, R.; Cuspidi, C.; Mancia, G.; Grassi, G. Habitual coffee consumption and office, home, and ambulatory blood pressure: Results of a 10-year prospective study. J. Hypertens. 2024, 42, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighatdoost, F.; Hajihashemi, P.; de Sousa Romeiro, A.M.; Mohammadifard, N.; Sarrafzadegan, N.; de Oliveira, C.; Silveira, E.A. Coffee Consumption and Risk of Hypertension in Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tajima, Y. Coffee-induced Hypokalaemia. Clin. Med. Insights Case Rep. 2010, 3, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Han, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, J.H.; Hwang, J.H. Caffeine-induced hypokalemia: A case report. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, T.; Morita, S.; Saito, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Inokuchi, S. Serum potassium level as a biomarker for acute caffeine poisoning. Acute Med. Surg. 2020, 7, e568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Madhavulu, B.; Mohan, P.R.; Raju, D.S. Acute effect of excess waterintake on blood pressure in healthy individuals. Asian Pac. J. Health Sci. 2014, 1, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jormeus, A.; Karlsson, S.; Dahlgren, C.; Lindström, T.; Nystrom, F.H. Doubling of water intake increases daytime blood pressure and reduces vertigo in healthy subjects. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2010, 32, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisamatsu, T.; Kogure, M.; Tabara, Y.; Hozawa, A.; Sakima, A.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Yoshita, K.; Hayabuchi, H.; Node, K.; Takemi, Y.; et al. Practical use and target value of urine sodium-to-potassium ratio in assessment of hypertension risk for Japanese: Consensus Statement by the Japanese Society of Hypertension Working Group on Urine Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 3288–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, B.W.; Bartholomew, C.L.; Summerhays, C.; Deru, L.; Compton, S.; Tucker, L.A.; LeCheminant, J.D.; Hicks, J. The Impact of Step Recommendations on Body Composition and Physical Activity Patterns in College Freshman Women: A Randomized Trial. J. Obes. 2019, 2019, 4036825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thomson, J.L.; Landry, A.S.; Zoellner, J.M.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Webster, M.; Connell, C.; Yadrick, K. Several steps/day indicators predict changes in anthropometric outcomes: HUB City Steps. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, E.; Torres-Costoso, A.; Martínez-García, I.; de Arenas-Arroyo, S.N.; Medrano-Echeverría, M.; Lucerón-Lucas-Torres, M.; Sequí-Domínguez, I.; Álvarez-Bueno, C.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V. Influence of Steps per Day on health-Related Quality of Life in Cchoolchildren: The Mediator Role of Cardiorespiratory Fitness; PREPRINT (Version 1). 2023; Research Square. Available online: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3219966/v1 (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Polak, P.; Polaszek, M.; Stencel, K.; Berner, A.; Pękała, M.; Olszewska, A.; Stelmaszak, K.; Bogowska, M.; Matyja, K.; Marczyk, K. One step closer—The impact of daily step count on health and how many steps should be taken per day. J. Educ. Health Sport 2023, 21, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuenyongchaiwat, K. Effects of 10,000 steps a day on physical and mental health in overweight participants in a community setting: A preliminary study. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2016, 20, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kimura, N.; Aso, Y.; Yabuuchi, K.; Matsubara, E. Association between objectively measured walking steps and sleep in community-dwelling older adults: A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Takács, J.; Török, L. The relationship between daily physical activity, subjective sleep quality, and mood in sedentary Hungarian adults: A longitudinal within-subjects study. Dev. Health Sci. DHS 2019, 2, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Menu, Stage I | Menu, Stage II | Student’s t-Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average and Standard Deviation | Average and Standard Deviation | t | p | |
| Energy (kcal) | 1455.04 ± 120.20 | 1834.92 ± 98.62 | −13.16 | 0.01 |
| Protein (g) | 75.61 ± 11.84 | 97.04 ± 13.18 | −6.51 | 0.01 |
| Fat (g) | 47.7 ± 6.51 | 63.74 ± 7.82 | −8.49 | 0.01 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 170.5 ± 21.2 | 204.13 ± 26.87 | −5.29 | 0.01 |
| Sodium (mg) | 1601.09 ± 535.56 | 4400.02 ± 728.55 | −16.67 | 0.01 |
| Potassium (mg) | 2936.06 ± 639.79 | 4358.58 ± 887.02 | −7.00 | 0.01 |
| Calcium (mg) | 676.84 ± 296.07 | 879.52 ± 277.11 | −2.69 | 0.01 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 1516.25 ± 2211.3 | 1538.85 ± 205.25 | −0.05 | 0.96 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 308.73 ± 81.84 | 488.73 ± 104.81 | −7.29 | 0.01 |
| Iron (mg) | 10.73 ± 2.56 | 16.79 ± 3.55 | −7.46 | 0.01 |
| Zinc (mg) | 7.45 ± 1.99 | 10.97 ± 2.52 | −5.90 | 0.01 |
| Folate (µg) | 348.86 ± 107.1 | 533.54 ± 139.62 | −5.65 | 0.01 |
| Vitamin B12 (µg) | 2.47 ± 1.1 | 4.21 ± 2.5 | −3.42 | 0.01 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 175.74 ± 84.06 | 263.81 ± 137.38 | −2.94 | 0.01 |
| Vitamin D (µg) | 2.44 ± 2.74 | 5.18 ± 4.74 | −2.69 | 0.01 |
| Saturated fatty acids (g) | 11.79 ± 3.7 | 14.83 ± 3.55 | 3.20 | 0.01 |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids (g) | 18.59 ± 4.37 | 26.91 ± 5.3 | −6.52 | 0.01 |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids (g) | 9.66 ± 3.1 | 12.82 ± 3.70 | −3.52 | 0.01 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 226.05 ± 155.81 | 345.48 ± 134.05 | −3.13 | 0.01 |
| Water (g) | 2349.3 ± 226.65 | 3923.26 ± 508.02 | −15.24 | 0.01 |
| Salt (g) | 2.42 ± 1.16 | 9.16 ± 1.83 | −16.74 | 0.01 |
| Glucose (g) | 10.43 ± 5.45 | 13.79 ± 6.11 | −2.21 | 0.04 |
| Fibre (g) | 24.15 ± 6.61 | 32.18 ± 5.50 | −5.03 | 0.01 |
| Menu, Stage I | Menu, Stage II | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day I | Day II | Day III | Day I | Day II | Day III | |
| Breakfast | Whole eggs, 120 g Rapeseed oil, 5 g Tomato, 100 g Spelt bread, 50 g Ketchup, 5 g | Graham roll, 53 g Plant-based butter, 2 g Turkey ham, 22 g Semi-fat salami cheese, 5 g Cherry tomatoes, 20 g Green tea, 250 mL | Green tea, 500 mL Eggs, 56 g WPC protein powder, 15 g Wheat flour, 45 g Banana, 120 g Peanut butter, 10 g | Graham bread, 60 g Plant-based butter, 5 g Edam cheese, 15 g Tomato, 50 g Salt, 2 g Green tea, 900 mL Black coffee, no sugar, 250 mL | Green tea, 250 mL Black coffee, no sugar, 250 mL Spelt bread, 60 g Peanut butter, 15 g Banana, 120 g Salt, 2 g | Oatmeal flakes, 50 g Banana, 120 g Chicken eggs, 56 g Natural bee honey, 12 g Dark chocolate, 12 g Baking powder, 3 g Salt, 2 g Green tea, 250 mL Black coffee, no sugar, 250 mL |
| Brunch | Banana, 120 g Vanilla Skyr yogurt, 150 g Water, 500 mL | Wholegrain roll, 65 g Plant-based butter, 3 g Turkey ham, 22 g Semi-fat salami cheese, 5 g Tomato, 22 g Red bell pepper, 6 g Apple, 200 g | Millet flakes, 50 g Eggs, 112 g Banana, 75 g Water, 1000 mL | Mineral water, 2000 mL Banana, 120 g Cocoa, 10 g Milk 2%, 250 mL | Mineral water, 2250 mL Oats, 30 g Oat bran, 14 g Cottage cheese, 50 g Milk 2%, 80 mL Eggs, 112 g Raspberries, 50 g Banana, 50 g | Rice waffles with muesli, 30 g Raspberries, 60 g Blueberries (American), 50 g Milk 1.5% fat, 125 mL Whey protein concentrate (WPC), 30 g |
| Lunch | Chicken breast cutlet, 133 g Boiled potatoes, 120 g Pickled cucumbers, 80 g Grated carrot salad, 102 g | Boiled potatoes, 120 g Turkey breast cutlet, 133 g Warm beets, 213 g Water, 500 mL | Chicken breast fillet, 100 g Potatoes, 200 g Cucumber, 150 g Sour cream 10%, 70 g | Wheat flour, 55 g Eggs, 56 g Baking powder, 3 g Milk 2%, 50 mL Rapeseed oil, 5 g 100% jam, 30 g Peanut butter, 15 g Salt, 2 g | Chicken breast, 150 g White rice, 60 g Stir-fry vegetables, 200 g Salt, 3 g | Barley groats (pearl barley), 60 g Fresh salmon, 100 g Pickled cucumber, 60 g Tabasco sauce, 10 g Salt, 3 g |
| Afternoon Tea | Apple, 200 g Unsalted cashew nuts, 15 g Apple juice, 375 mL | Light cottage cheese, 150 g Graham roll, 65 g Blueberries, 50 g Cinnamon, 3 g | Pineapple, 150 g | Natural yogurt, 250 g Kiwi, 150 g Walnuts, 15 g Corn flakes, 40 g | Raisins, 30 g Dark chocolate, 18 g Pistachios, 9 g Pomelo, 150 g Salted chips, 15 g Salt, 2 g | Chicken eggs, 112 g Cocktail tomatoes, 80 g Graham roll, 65 g Arugula, 20 g Milk 1.5% fat, 10 g Plant-based butter, 5 g Pepper, 1 g Salt, 2 g |
| Dinner | Natural cottage cheese, 200 g Tomato, 120 g Chives, 5 g Black pepper, 1 g White salt, 1 g Water, 500 mL | Wholegrain tortilla, 61 g Cream cheese, 10 g, Delicatessen chicken ham, 15 g, Salad mix, 80 g, Mozzarella cheese, 7 g, Water, 300 ml | Ciabatta, 50 g Red pesto, 20 g Parma ham, 15 g Arugula, 10 g Sun-dried tomatoes, 14 g | Boiled potatoes, 150 g Fresh cod, 200 g Sauerkraut salad, 178 g Salt, 2 g Natural rice cakes, 20 g Hummus, 20 g Radish, 60 g | Spinach, 25 g Orange, 100 g Water, 125 mL Banana, 80 g | Red bell pepper, 80 g Cucumber, 120 g Radish sprouts, 20 g Feta cheese, 60 g Rapeseed oil, 5 g Apple cider vinegar, 5 g Pepper, 1 g Oregano, 1 g Basil, 1 g |
| Stage I | Stage II | Student’s t-Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average and Standard Deviation | Average and Standard Deviation | t | p | |
| Systolic blood pressure, morning (mmHg) | 94.57 ± 3.59 | 100.23 ± 5.42 | −4.69 | 0.01 |
| Systolic blood pressure, afternoon (mmHg) | 94.57 ± 3.72 | 104.07 ± 4.19 | −9.13 | 0.01 |
| Systolic blood pressure, evening (mmHg) | 92.13 ± 4.01 | 99.33 ± 4.89 | −6.13 | 0.01 |
| Systolic blood pressure, whole day (mmHg) | 93.76 ± 3.86 | 101.21 ± 4.81 | −11.41 | 0.01 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, morning (mmHg) (g) | 57.67 ± 2.08 | 59.27 ± 3.99 | −1.91 | 0.01 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, afternoon (mmHg) | 58.13 ± 1.93 | 60.63 ± 3.14 | −3.65 | 0.01 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, evening (mmHg) | 56.73 ± 6.81 | 58.4 ± 7.26 | −0.90 | 0.01 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, whole day (mmHg) | 57.51 ± 2.99 | 59.43 ± 4.68 | −3.26 | 0.01 |
| Pulse, morning (bpm) | 76.1 ± 5.37 | 76.87 ± 10.05 | −0.36 | 0.81 |
| Pulse, afternoon (bpm) | 76.4 ± 7.65 | 75.7 ± 6.68 | 0.37 | 0.77 |
| Pulse, evening (bpm) | 73.57 ± 6.21 | 75.03 ± 7.11 | −0.84 | 0.79 |
| Pulse, whole day (bpm) | 75.36 ± 6.6 | 75.87 ± 8.23 | −0.46 | 0.86 |
| Steps | 4589.83 ± 852.38 | 8695.5 ± 1655.46 | −11.87 | 0.01 |
| Sleep (h) | 5.83 ± 0.78 | 6.97 ± 0.95 | −4.98 | 0.01 |
| Stage I | Stage II | Student’s t-Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average and Standard Deviation | Average and Standard Deviation | t | p | |
| Body mass (kg) | 48.15 ± 0.46 | 47.63 ± 0.58 | 1.56 | 0.15 |
| Fat mass (kg) | 8.95 ± 0.43 | 8.67 ± 0.85 | 0.66 | 0.52 |
| Muscle mass (kg) | 37.2 ± 0.32 | 36.97 ± 0.37 | 1.07 | 0.31 |
| Lean body mass (kg) | 39.2 ± 0.32 | 38.63 ± 0.69 | 1.68 | 0.12 |
| Water content (kg) | 28.37 ± 0.46 | 28.4 ± 0.59 | −0.10 | 0.92 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.12 ± 0.18 | 17.95 ± 0.24 | 1.26 | 0.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antosik, K.; Dyńka, D.; Ziętara, K. Effect of Dietary Modifications on Blood Pressure and Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters in a Woman with Hypotension. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134415
Antosik K, Dyńka D, Ziętara K. Effect of Dietary Modifications on Blood Pressure and Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters in a Woman with Hypotension. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134415
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntosik, Katarzyna, Damian Dyńka, and Kinga Ziętara. 2025. "Effect of Dietary Modifications on Blood Pressure and Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters in a Woman with Hypotension" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134415
APA StyleAntosik, K., Dyńka, D., & Ziętara, K. (2025). Effect of Dietary Modifications on Blood Pressure and Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters in a Woman with Hypotension. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134415






