Renal Fat Accumulation Assessed by MRI or CT and Its Association with Clinical and Metabolic Disorders: A Systematic Imaging Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
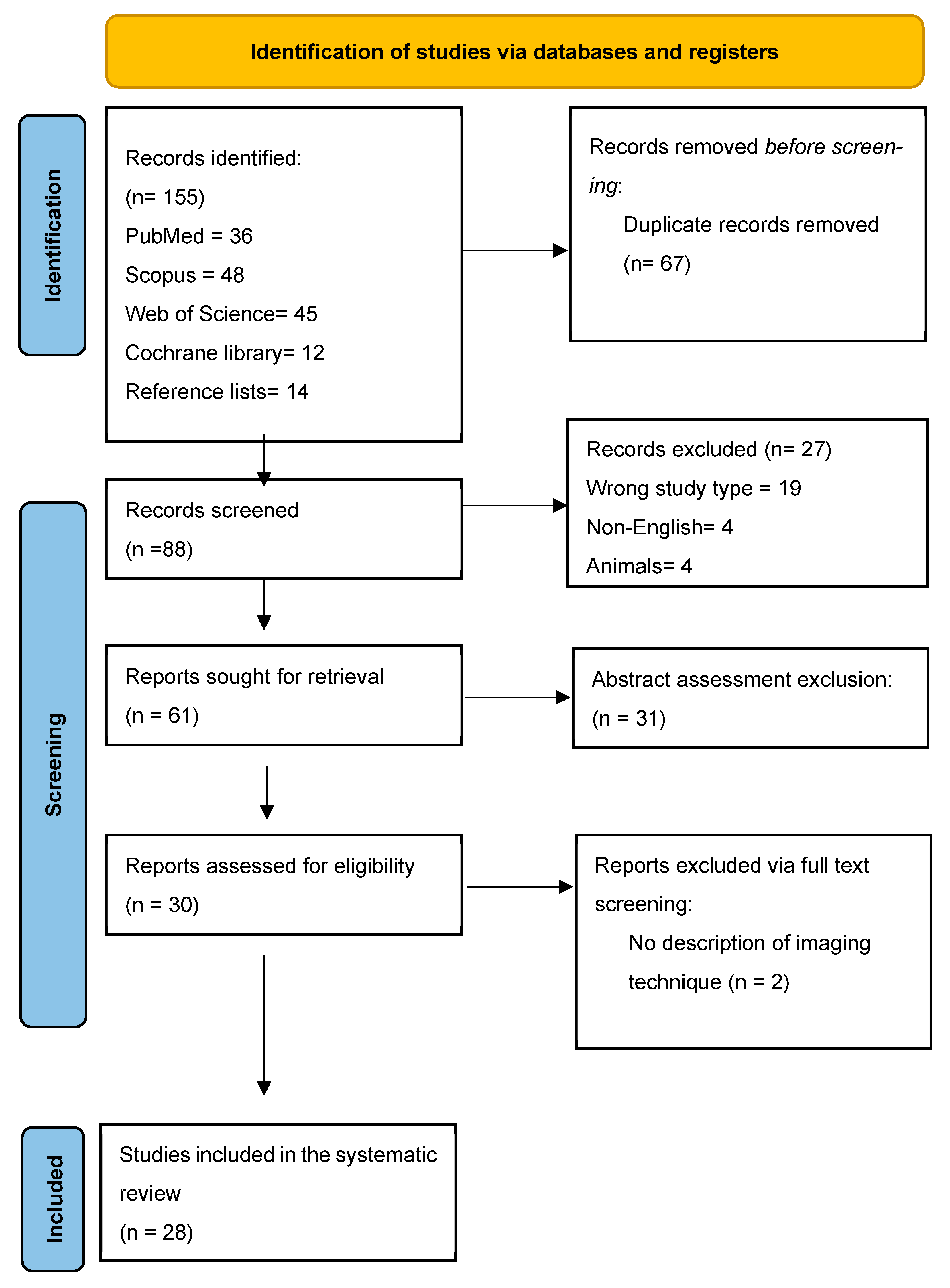
3.1. Search Results and Study Selection
3.2. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
3.3. Overview of Included Studies
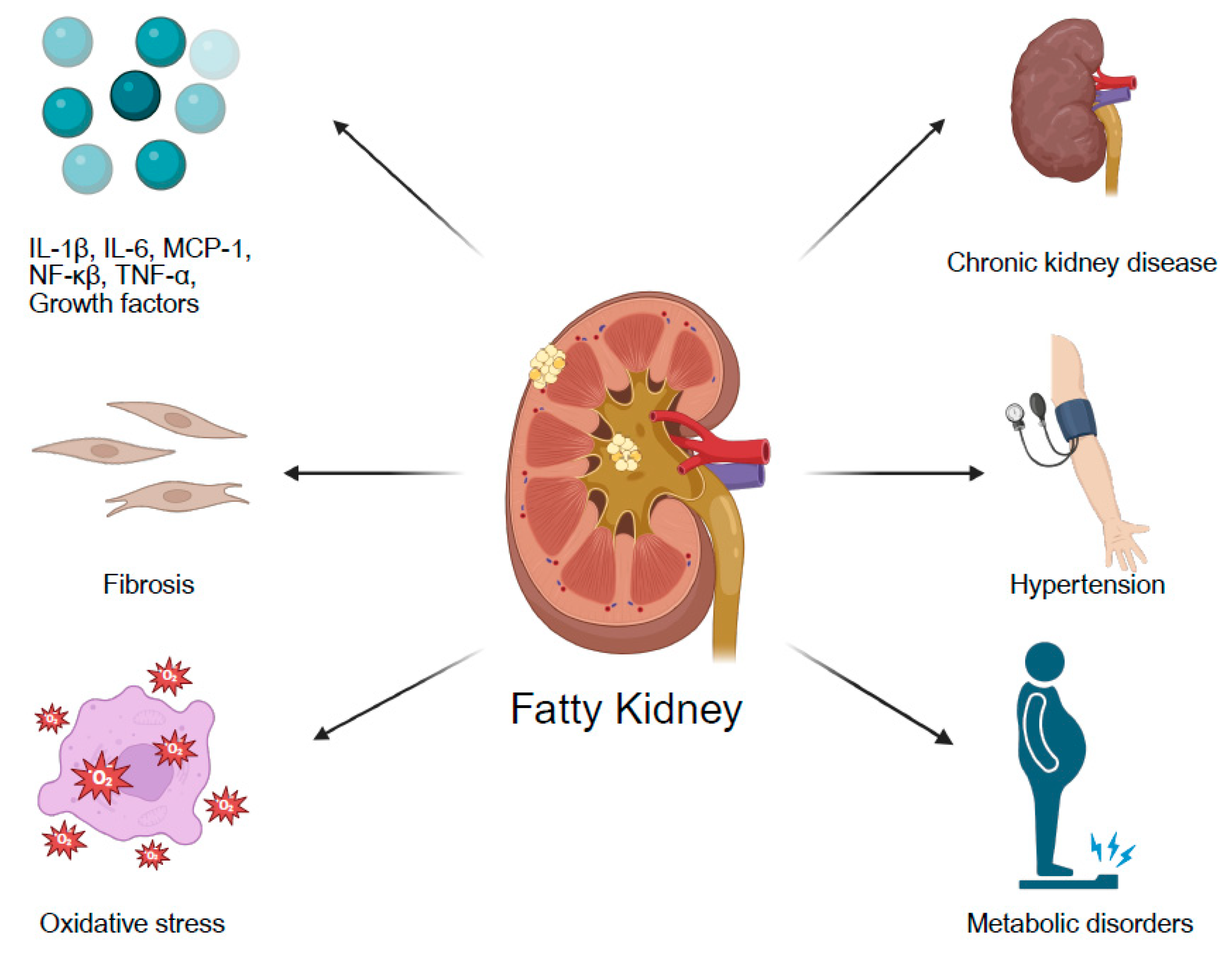
4. Association of Fatty Kidney with Specific Comorbidities
4.1. Diabetes Mellitus
4.2. Obesity
4.3. Chronic Kidney Disease
4.4. Hypertension
4.5. The Association Between Fatty Liver and Fatty Kidney
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giardini, E.; Moore, D.; Sadlier, D.; Godson, C.; Brennan, E. The dual role of lipids in chronic kidney disease: Pathogenic culprits and therapeutic allies. Atherosclerosis 2024, 398, 118615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobulescu, I.A. Renal lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2010, 19, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mende, C.W.; Einhorn, D. Fatty Kidney Disease: A New Renal And Endocrine Clinical Entity? Describing the Role of the Kidney in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Type 2 Diabetes. Endocr. Pract. 2019, 25, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphael, H.; Klang, E.; Konen, E.; Inbar, Y.; Leibowitz, A.; Frenkel-Nir, Y.; Apter, S.; Grossman, E. Obesity Is Associated with Fatty Liver and Fat Changes in the Kidneys in Humans as Assessed by MRI. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Hernando, D.; Harris, D.T.; Hinshaw, L.A.; Li, K.; Ananthakrishnan, L.; Bashir, M.R.; Duan, X.; Ghasabeh, M.A.; Kamel, I.R.; et al. Multisite multivendor validation of a quantitative MRI and CT compatible fat phantom. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 4375–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, D.; Sharma, S.D.; Aliyari Ghasabeh, M.; Alvis, B.D.; Arora, S.S.; Hamilton, G.; Pan, L.; Shaffer, J.M.; Sofue, K.; Szeverenyi, N.M.; et al. Multisite, multivendor validation of the ac-curacy and reproducibility of proton-density fat-fraction quantification at 1.5T and 3T using a fat-water phantom. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Peltzer, K.; von Krüchten, R.; Lorbeer, R.; Rospleszcz, S.; Schulz, H.; Peters, A.; Bamberg, F.; Schlett, C.L.; Mujaj, B. Adipose tissue is associated with kidney function parameters. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbay, M.; Copur, S.; Demiray, A.; Sag, A.A.; Covic, A.; Ortiz, A.; Tuttle, K.R. Fatty kidney: A possible future for chronic kidney disease research. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuno, R.; Kaneko, K.; Nakamura, T.; Kojima, D.; Mizutani, Y.; Azegami, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yamada, Y.; Jinzaki, M.; Kinouchi, K.; et al. Association Between Renal Sinus Fat and Cardiometabolic and Renin-Angiotensin System Parameters in Primary Aldosteronism. J. Endocr. Soc. 2023, 8, bvad154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoo, T.; Clark, H.R.; Pedrosa, I.; Yuan, Q.; Dimitrov, I.; Zhang, Y.; Lingvay, I.; Beg, M.S.; Bobulescu, I.A. Quantification of renal steatosis in type II diabetes mellitus using dixon-based MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 44, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhulail, A.A.; Servati, M.; Ooms, N.; Akin, O.; Dincer, A.; Thomas, M.A.; Dydak, U.; Emir, U.E. In Vivo Renal Lipid Quantification by Accelerated Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging at 3T: Feasibility and Reliability Study. Metabolites 2022, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Min, Z.; Wei, G.; Lei, H.; Feifei, Z.; Yunfei, Z. Volumetric evaluation of renal sinus adipose tissue on computed tomography images in bilateral nephrolithiasis patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Nagatani, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Ikeda, M.; Miyazawa, I.; Morino, K.; Ohkubo, T.; Maegawa, H.; Nitta, N.; Sakai, H.; et al. Renal sinus fat volume on computed tomography in middle-aged patients at risk for cardiovascular disease and its association with coronary artery calcification. Atherosclerosis 2016, 246, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idilman, I.S.; Tuzun, A.; Savas, B.; Elhan, A.H.; Celik, A.; Idilman, R.; Karcaaltincaba, M. Quantification of liver, pancreas, kidney, and vertebral body MRI-PDFF in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Abdom. Imaging 2015, 40, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, H.; Aydin, H.; Karaibrahimoglu, A.; Afsar, B. Evaluation of the parenchymal distribution of renal steatosis in chronic kidney disease using chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 33, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chughtai, H.L.; Morgan, T.M.; Rocco, M.; Stacey, B.; Brinkley, T.E.; Ding, J.; Nicklas, B.; Hamilton, C.; Hundley, W.G. Renal sinus fat and poor blood pressure control in middle-aged and elderly individuals at risk for cardiovascular events. Hypertension 2010, 56, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.A.; Fowler, L.A.; Goss, A.M.; Gower, B.A. Associations of renal sinus fat with blood pressure and ectopic fat in a diverse cohort of adults. Int. J. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Risk Prev. 2023, 16, 200165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, E.; Sarı, F.B. Is Fat Deposition of Renal Sinus a Concomitant Finding to Fatty Liver Disease? The First Study Regarding the Relationship Between Kidney and Liver Fat Content with Non-Contrast Computed Tomography. Spartan Med. Res. J. 2022, 7, 32411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.C.; Hwang, S.J.; Porter, S.A.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Fox, C.S. Fatty kidney, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease: The Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension 2011, 58, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjela, M.; Askeland, A.; Frøkjær, J.B.; Mellergaard, M.; Handberg, A. MRI-based quantification of renal fat in obese individuals using different image analysis approaches. Abdom. Imaging 2022, 47, 3546–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, M.; Sun, H.; Shi, B. Correlation between circulating advanced glycation end products and thioredox-in-interacting protein levels and renal fat content in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krievina, G.; Tretjakovs, P.; Skuja, I.; Silina, V.; Keisa, L.; Krievina, D.; Bahs, G. Ectopic Adipose Tissue Storage in the Left and the Right Renal Sinus is Asymmetric and Associated with Serum Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Levels Increase. eBioMedicine 2016, 13, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Cho, N.-J.; Kim, H.; Nam, B.; Jeon, J.S.; Noh, H.; Han, D.C.; Kim, S.H.; Kwon, S.H. Abdominal periaortic and renal sinus fat attenuation indices measured on computed tomography are associated with metabolic syndrome. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Dekkers, I.A.; Tao, Q.; Paiman, E.H.; Bizino, M.B.; Jazet, I.M.; Lamb, H.J. MR Assessed Changes of Renal Sinus Fat in Response to Glucose Regulation in West European and South Asian Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 60, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, E.; Dadson, P.; Saukko, E.; Honka, M.-J.; Koskensalo, K.; Seppälä, K.; Pekkarinen, L.; Moriconi, D.; Helmiö, M.; Salminen, P.; et al. Renal Sinus Fat Is Expanded in Patients with Obesity and/or Hypertension and Reduced by Bariatric Surgery Associated with Hypertension Remission. Metabolites 2022, 12, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notohamiprodjo, M.; Goepfert, M.; Will, S.; Lorbeer, R.; Schick, F.; Rathmann, W.; Martirosian, P.; Peters, A.; Müller-Peltzer, K.; Helck, A.; et al. Renal and renal sinus fat volumes as quantified by magnetic resonance imaging in subjects with prediabetes, diabetes, and normal glucose tolerance. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0216635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordulj, I.; Tandara, M.; Jerković, K.; Šarić, F.; Beneš, M.; Lovrić Kojundžić, S.; Marinović Guić, M.; Budimir Mršić, D. Does the Lo-cation of Fat Accumulation Affect the Degree of Aortic and Renal Arterial Calcification? Biomedicines 2024, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xie, L.; Chen, X.; Mao, L.; Qin, Y.; Lan, R.; Yang, S.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Ye, H.; et al. Renal fat fraction is significantly associated with the risk of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 995028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijens, P.E.; Edens, M.A.; Bakker, S.J.; Stolk, R.P. MRI-determined fat content of human liver, pancreas and kidney. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurny, M.; Jiang, Y.; Sowah, S.A.; Nonnenmacher, T.; Schübel, R.; Kirsten, R.; Johnson, T.; von Stackelberg, O.; Ulrich, C.M.; Kaaks, R.; et al. Changes in Kidney Fat upon Dietary-Induced Weight Loss. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Xie, L.; Liu, L.; Shen, Y.; Yang, P.; Wu, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Mao, Y. Renal fat deposition measured on dixon-based MRI is significantly associated with early kidney damage in obesity. Abdom. Imaging 2024, 49, 3476–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Feng, Y.; Lu, C.-Q.; Ju, S. Renal fat fraction and diffusion tensor imaging in patients with early-stage diabetic nephropathy. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3326–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. MRI Assessment of Renal Lipid Deposition and Abnormal Oxygen Metabolism of Type 2 diabetes Mellitus Based on mDixon-Quant. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 58, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, A.B.; Vehbi, S.; Copur, S.; Gurses, B.; Siriopol, D.; Karakaya, B.A.D.; Hasbal, N.B.; Tekin, B.; Akyıldız, M.; van Raalte, D.H.; et al. Kidney and liver fat accumulation: From imaging to clinical consequences. J. Nephrol. 2024, 37, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelicha, H.; Schwarzfuchs, D.; Shelef, I.; Gepner, Y.; Tsaban, G.; Tene, L.; Meir, A.Y.; Bilitzky, A.; Komy, O.; Cohen, N.; et al. Changes of renal sinus fat and renal parenchymal fat during an 18-month randomized weight loss trial. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-H.; Chen, L.-H.; An, Q.; Pi, P.; Dong, Y.-F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, N.; Fang, X.; Pu, R.-W.; Song, Q.-W.; et al. Quantification of the renal sinus fat and exploration of its relationship with ectopic fat deposition in normal subjects using MRI fat fraction mapping. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1187781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, A.; Shapira, E.; Khasbab, R.; Sharabi, Y.; Grossman, E.; Leibowitz, A. High-Fructose Diet Increases Renal ChREBPβ Expression, Leading to Intrarenal Fat Accumulation in a Rat Model with Metabolic Syndrome. Biology 2022, 11, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year of Publication | Modality | Study Type | Patients, n | Age (Years) | Female Sex (%) | BMI, kg/m2, Median | Comorbidities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hüseyin Aydın, 2023 [15] | MRI | Retrospective | 88 | Control 55.4 CKD 59.3 | 46.7% | N/A | CKD, Diabetes |
| Huali Tang, 2024 [31] | MRI | Prospective | 103 | Control 27 Obese 50.5 | Control 41% Obese 77%, | Control 21.6 Obese 30.1 | Obesity |
| Manuela Spurny, 2022 [30] | MRI | RCT | 137 | N/A | N/A | ~31 | Obesity, Fatty liver |
| Takeshi Yokoo, 2016 [10] | MRI | Retrospective | 69 | 58 | 34.8% | 30.6 | Diabetes, Fatty liver |
| Mimoza Gjela, 2022 [20] | MRI | Retrospective Observational Case-control | 42 | Lean 44.4 Obese 46.5 | Lean 57.1% Obese 67.8% | Lean 24 Obese 35.5 | Obesity |
| Yan Shen, 2022 [28] | MRI | Cross-sectional Observational | 189 | 57 | 34% | 25.3 | CKD, Diabetes |
| Meredith C. Foster, 2011 [19] | CT | Cross-sectional | 2923 | 54 | 51 | Non-fatty kidney 26.6 Fatty kidney 30.3 | N/A |
| Yulin Hua, 2024 [21] | MRI | Retrospective | 118 | 54 | 29.7% | 24.9 | Diabetes |
| Paul E Sijens, 2010 [29] | MRI, MRS | Prospective Observational | 36 | 39 | 33.3% | 27.5 | Obesity, Fatty liver |
| Yuan-Cheng Wang, 2018 [32] | MRI | Prospective Observational | 95 | Control 61 Diabetic normoalbuminuric 57 Diabetic microalbuminuric 59 | 43.2% | Control 22.6 Diabetic normoalbuminuric 25.3 Diabetic microalbuminuric 25.2 | Diabetes, CKD |
| Hadar Raphael, 2024 [4] | MRI | Retrospective | 399 | 51 | 52.4% | 24.6 | Obesity, Fatty liver |
| Abdullah B. Yıldız, 2024 [34] | MRI | Retrospective Cross-sectional | 51 | 34 | 51 | 26.4 | Fatty liver |
| Chun Yang, 2023 [33] | MRI | Prospective | 60 | N/A | 45 | N/A | Diabetes, CKD |
| Ahmad A. Alhulail, 2022 [11] | MRS | Prospective | 5 | 31 | 20% | 25 | N/A |
| Emrah Doğan, 2022 [18] | CT | Retrospective | 92 | 30.2 | 20.7% | N/A | Fatty liver |
| Emilia Moritz, 2022 [25] | MRI | Prospective | 120 | Control 46 Obese 45 | Control 78.3% Obese 91.9% | Control 23.4 Obese 41.5 | Obesity, Hypertension |
| Gita Krievina, 2016 [22] | CT | Cross-sectional Observational | 280 | 38.3 | 50% | 27.9 | N/A |
| Haroon L Chughtai, 2010 [16] | MRI | Cross-sectional Observational | 205 | 69 | 49% | 30 | Hypertension |
| Ling Lin, 2023 [24] | MRI | Retrospective | 93 | 56.9 | 50.5% | 30.8 | Diabetes |
| Ivan Ordulj, 2024 [27] | CT | Retrospective | 302 | 49.5 | 28.2% | N/A | Fatty liver |
| Peng Lin, 2020 [12] | CT | Retrospective | 232 | 47 | 50% | Control 20.8 Nephrolithiasis 22.4 | Nephrolithiasis |
| Catharine A. Couch, 2022 [17] | MRI | Prospective Cross-sectional | 116 | 29.2 | 52.6% | 27.4 | Fatty liver |
| Eun Ji Lee, 2021 [23] | CT | Retrospective | 239 | 41.2 | 65.3% | By groups | Obesity |
| Mike Notohamiprodjo, 2020 [26] | MRI | Cross-sectional Observational | 366 | 56.2 | 43.2 | 28.1 | Diabetes, Fatty liver |
| Hila Zelicha, 2018 [35] | MRI | Observational | 278 | 47.8 | 11% | 31 | Obesity |
| Yoko Murakami, 2015 [13] | CT | Retrospective | 189 | 66.7 | 28% | CAC ≤ 10 25.1 CAC > 10 24 | Coronary artery disease |
| Ilkay S. Idilman, 2015 [14] | MRI | Retrospective | 41 | 47 | 51.2% | 29.9 | Fatty liver |
| Qin-He Zhang, 2023 [36] | MRI | Retrospective | 126 | 56 | 63.5% | 23.6 | Fatty liver |
| Author, Year of Publication | Study Population | Measured Area | Result- Renal Fat | Patients with Fatty Kidney, (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Disease | All | ||||
| Hüseyin Aydın, 2023 [15] | CKD, Diabetes | Parenchyma | Cortex 5.7% FF Medulla 4.5% FF | CKD with diabetes: cortex 8.1% FF, medulla 6.9% FF CKD without diabetes: cortex 6.6% FF, medulla 5.8% FF CKD: cortex 7.2% FF, medulla 6.3% FF | N/A | N/A |
| Huali Tang, 2024 [31] | Obesity | Parenchyma, Sinus | 1.38% FF, 8.42 cm3 | 2.01% FF, 17.41 cm3 | N/A | N/A |
| Manuela Spurny, 2022 [30] | Obesity, Weight loss quartiles | Parenchyma, Sinus | N/A | Cortex: Q1 3.6% FF, Q2 3.2% FF, Q3 2.9% FF, Q4 3.4% FF [avg 3.3% FF] Sinus: 55.3% FF, 49.2% FF, 49.1% FF, 49.4% FF [avg 50.8% FF] | N/A | N/A |
| Takeshi Yokoo, 2016 [10] | Diabetes | Parenchyma | 0.79% FF | 2.18% FF | 1.33% FF | N/A |
| Mimoza Gjela, 2022 [20] | Obesity | Parenchyma | method 1 1.8% FF, method 2 2% FF, method 3 0.4% FF, method 4 1.4% FF | 2.3% FF, 2.4% FF, 0.5% FF, 1.6% FF | N/A | N/A |
| Yan Shen, 2022 [28] | Diabetes with or without CKD | Parenchyma | Right kidney: 1.87% FF Left kidney: 2.23% FF | Right kidney: 2.17% FF Left kidney: 2.49% FF | N/A | N/A |
| Meredith C. Foster, 2011 [19] | N/A | Sinus | 0.31 cm2 | N/A | N/A | 30.1% |
| Yulin Hua, 2024 [21] | Diabetes | Parenchyma | N/A | 4.89% FF | N/A | N/A |
| Paul E Sijens, 2010 [29] | Obesity | Parenchyma | 0.64% FF | 1.35% FF | 0.7% FF | N/A |
| Yuan-Cheng Wang, 2018 [32] | Diabetes with normoalbuminuria or microalbuminuria | Parenchyma | 4.3% FF | Normoalbuminuria 4.7% FF Microalbuminuria 5.6% FF | N/A | N/A |
| Hadar Raphael, 2024 [4] | Obesity | Parenchyma | N/A | N/A | N/A | 18.6% |
| Abdullah B. Yıldız, 2024 [34] | Parenchyma | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Chun Yang, 2023 [33] | Diabetes with or without Diabetic Nephropathy | Parenchyma | 1.11% FF | Diabetes 1.52% FF Diabetic nephropathy 1.99% FF | N/A | N/A |
| Ahmad A. Alhulail, 2022 [11] | Parenchyma | 1.48% FF | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Emrah Doğan, 2022 [18] | Fatty liver | Sinus | 9.3 mm | 12.5 mm | N/A | N/A |
| Emilia Moritz, 2022 [25] | Obesity | Sinus | 1.8 cm2 | 2.3 cm2 (avg two kidneys) | N/A | N/A |
| Gita Krievina, 2016 [22] | Sinus | Right kidney 1.07 cm3 Left kidney 2.5 cm3 | N/A | N/A | 28.9% | |
| Haroon L Chughtai, 2010 [16] | Sinus | 4.2 cm3 | N/A | N/A | 28.9% | |
| Ling Lin, 2023 [24] | Diabetes | Sinus | N/A | N/A | Left kidney West European 18.2 cm3 Left kidney South Asian 12.3 cm3 | N/A |
| Ivan Ordulj, 2024 [27] | Sinus | N/A | N/A | Right kidney: 2.56 cm2 Left kidney: 2.83 cm2 | N/A | |
| Peng Lin, 2020 [12] | Nephrolithiasis | Sinus | Right kidney 3.34 cm3 Left kidney 4.56 cm3 | Right kidney 4.14 cm3 Left kidney 5.47 cm3 | N/A | N/A |
| Catharine A. Couch, 2022 [17] | Sinus | 1.05 cm3 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Eun Ji Lee, 2021 [23] | Obesity, Metabolic syndrome | Sinus | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Mike Notohamiprodjo, 2020 [26] | Prediabetes, Diabetes | Sinus | 22.2 mL | Prediabetes 32 mL Diabetes 34.5 mL | 26.2 mL | N/A |
| Hila Zelicha, 2018 [35] | Obesity | Parenchyma, Sinus | N/A | N/A | Parenchyma 7.9% FF Sinus 2.7 cm2 | N/A |
| Yoko Murakami, 2015 [13] | Coronary artery disease with CAC score > 10 | Sinus | 5.60 cm3 | 7.48 cm3 | 7.05 cm3 | N/A |
| Ilkay S. Idilman, 2015 [14] | NAFLD | Parenchyma, Sinus | N/A | N/A | Cortex 1.7% FF Sinus 51% FF | N/A |
| Qin-He Zhang, 2023 [36] | Men vs. Women | Sinus | Men: Right kidney 28.3% FF, 26.8 cm3 Left kidney 31.2% FF, 31.6 cm3 | Women: Right kidney 23.8% FF, 21.4 cm3 Left kidney 27.9% FF, 26 cm3 | Right kidney 25.4% FF, 23.4 cm3 Left kidney 29% FF, 28 cm3 | N/A |
| First Author | Comorbidities | Measured Area | Result- Renal Fat | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Diabetes | With Comorbidity | All | |||
| Hüseyin Aydın [15] | CKD | Cortex | 5.7% FF | 8.1% FF | N/A | |
| Medulla | 4.5% FF | 6.9% FF | N/A | |||
| Takeshi Yokoo [10] | N/A | Parenchyma | 0.79% FF | 2.18% FF | N/A | 1.33% FF |
| Yan Shen [28] | CKD | Right parenchyma | N/A | 1.87% FF | 2.17% FF | N/A |
| Left Parenchyma | N/A | 2.23% FF | 2.49% FF | N/A | ||
| Yulin Hua [21] | N/A | Parenchyma | N/A | 4.89% FF | N/A | N/A |
| Yuan-Cheng Wang [32] | Normoalbuminuria | Parenchyma | N/A | 4.3% FF | 4.7% FF | N/A |
| Microalbuminuria | Parenchyma | N/A | 4.3% FF | 5.6% FF | N/A | |
| Chun Yang [33] | Diabetic Nephropathy | Parenchyma | 1.11% FF | 1.52% FF | 1.99% FF | N/A |
| Ling Lin [24] | N/A, (West European) | Left sinus | N/A | 18.2 cm3 | N/A | N/A |
| N/A (South Asian) | Left sinus | N/A | 12.3 cm3 | N/A | N/A | |
| Mike Notohamiprodjo [26] | Prediabetes | Sinus | 22.2 mL | 34.5 mL | 32 mL | 26.2 mL |
| First Author | Comorbidities | Measured Area | Result- Renal Fat | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Obese | With Comorbidity | All | |||
| Huali Tang [31] | N/A | Parenchyma | 1.38% FF | 2.01% FF | N/A | N/A |
| Sinus | 8.42 cm3 | 17.41 cm3 | N/A | N/A | ||
| Manuela Spurny [30] | Weight loss quartiles | Cortex | N/A | Q1 3.6% FF, Q2 3.2% FF, Q3 2.9% FF, Q4 3.4% FF, Avg 3.3% FF | N/A | N/A |
| Sinus | N/A | 55.3% FF, 49.2% FF, 49.1% FF, 49.4% FF, Avg 50.8% FF | N/A | |||
| Mimoza Gjela [20] | N/A | Parenchyma | method 1 1.8% FF, method 2 2% FF, method 3 0.4% FF, method 4 1.4% FF | 2.3% FF, 2.4% FF, 0.5% FF, 1.6% FF | N/A | N/A |
| Paul E Sijens [29] | N/A | Parenchyma | 0.64% FF | 1.35% FF | N/A | 0.7% FF |
| Hadar Raphael [4] | N/A | Parenchyma | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Emilia Moritz [25] | N/A | Average of two kidneys Sinus | 1.8 cm2 | 2.3 cm2 | N/A | N/A |
| Eun Ji Lee [23] | N/A | Sinus | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Hila Zelicha [35] | N/A | Parenchyma | N/A | N/A | N/A | 7.9% FF |
| Sinus | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2.7 cm2 | ||
| Author | Comorbidities | Measured Area | Result- Renal Fat | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | CKD | With Comorbidity | All | |||
| Hüseyin Aydın [15] | Diabetes | Cortex | 5.7% FF | 7.2% FF without diabetes: 6.6% FF | 8.1% FF | N/A |
| Medulla | 4.5% FF | 6.3% FF without diabetes: 5.8% FF | 6.9% FF | N/A | ||
| Yan Shen [28] | Diabetes | Right parenchyma | N/A | N/A | 2.17% FF | N/A |
| Left Parenchyma | N/A | N/A | 2.49% FF | N/A | ||
| Yuan-Cheng Wang [32] | Diabetes | Parenchyma | N/A | N/A | 5.6% FF | N/A |
| Chun Yang [33] | Diabetes | Parenchyma | 1.11% FF | N/A | 1.99% FF | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raphael, H.; Klang, E.; Konen, E.; Leibowitz, A.; Frenkel-Nir, Y.; Apter, S.; Grossman, E. Renal Fat Accumulation Assessed by MRI or CT and Its Association with Clinical and Metabolic Disorders: A Systematic Imaging Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4305. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124305
Raphael H, Klang E, Konen E, Leibowitz A, Frenkel-Nir Y, Apter S, Grossman E. Renal Fat Accumulation Assessed by MRI or CT and Its Association with Clinical and Metabolic Disorders: A Systematic Imaging Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4305. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124305
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaphael, Hadar, Eyal Klang, Eli Konen, Avshalom Leibowitz, Yael Frenkel-Nir, Sara Apter, and Ehud Grossman. 2025. "Renal Fat Accumulation Assessed by MRI or CT and Its Association with Clinical and Metabolic Disorders: A Systematic Imaging Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4305. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124305
APA StyleRaphael, H., Klang, E., Konen, E., Leibowitz, A., Frenkel-Nir, Y., Apter, S., & Grossman, E. (2025). Renal Fat Accumulation Assessed by MRI or CT and Its Association with Clinical and Metabolic Disorders: A Systematic Imaging Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4305. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124305








