Associations Between Pain Intensity and Inflammatory Profile in Women with Android and Gynoid Obesity Diagnosed with Chronic Pain: An Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Evaluation Parameters and Instruments
2.3.1. International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)
2.3.2. Visual Numeric Scale (VNS)
2.3.3. Body Composition Assessment
2.3.4. Blood Collection
2.3.5. Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
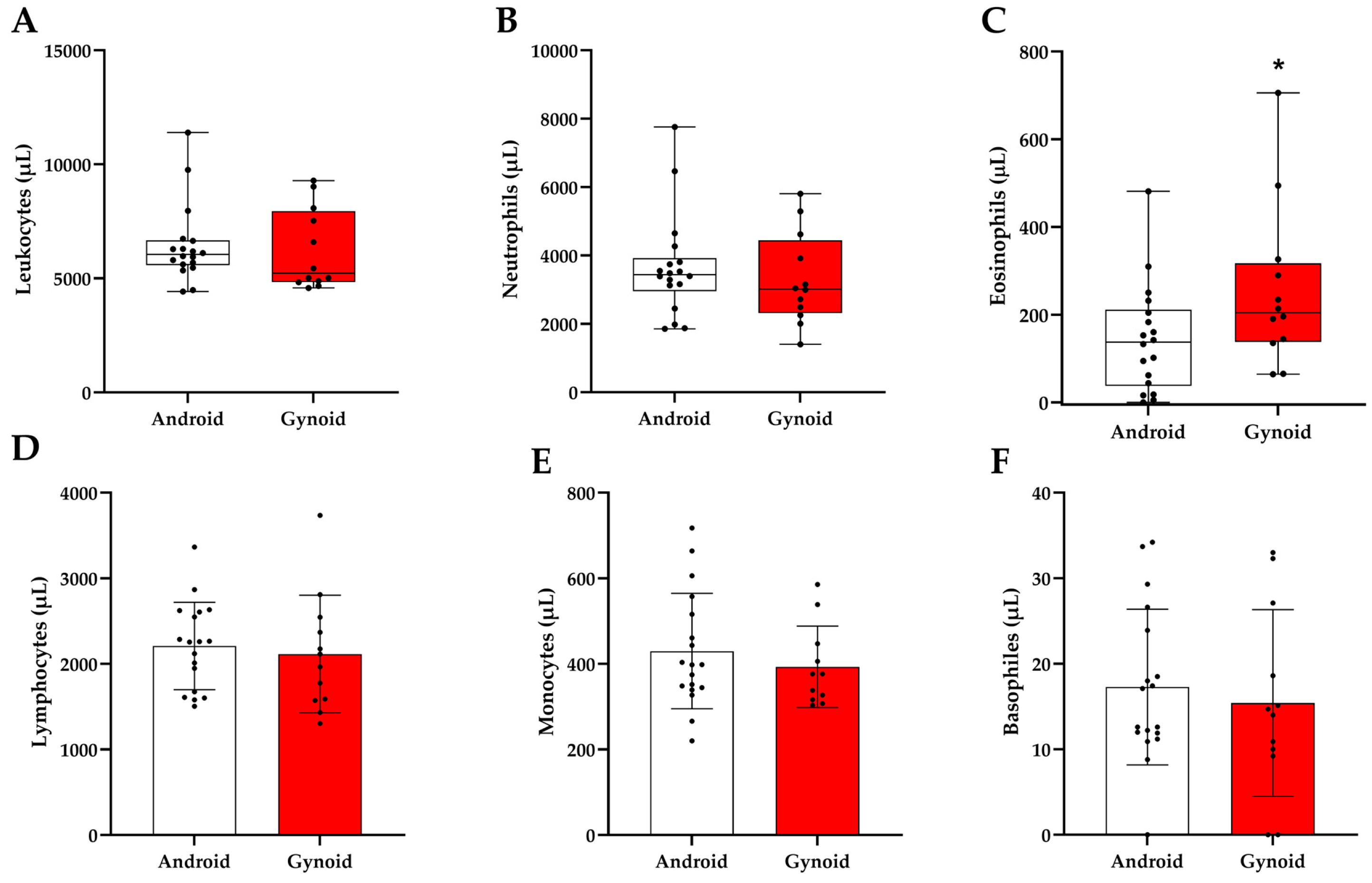
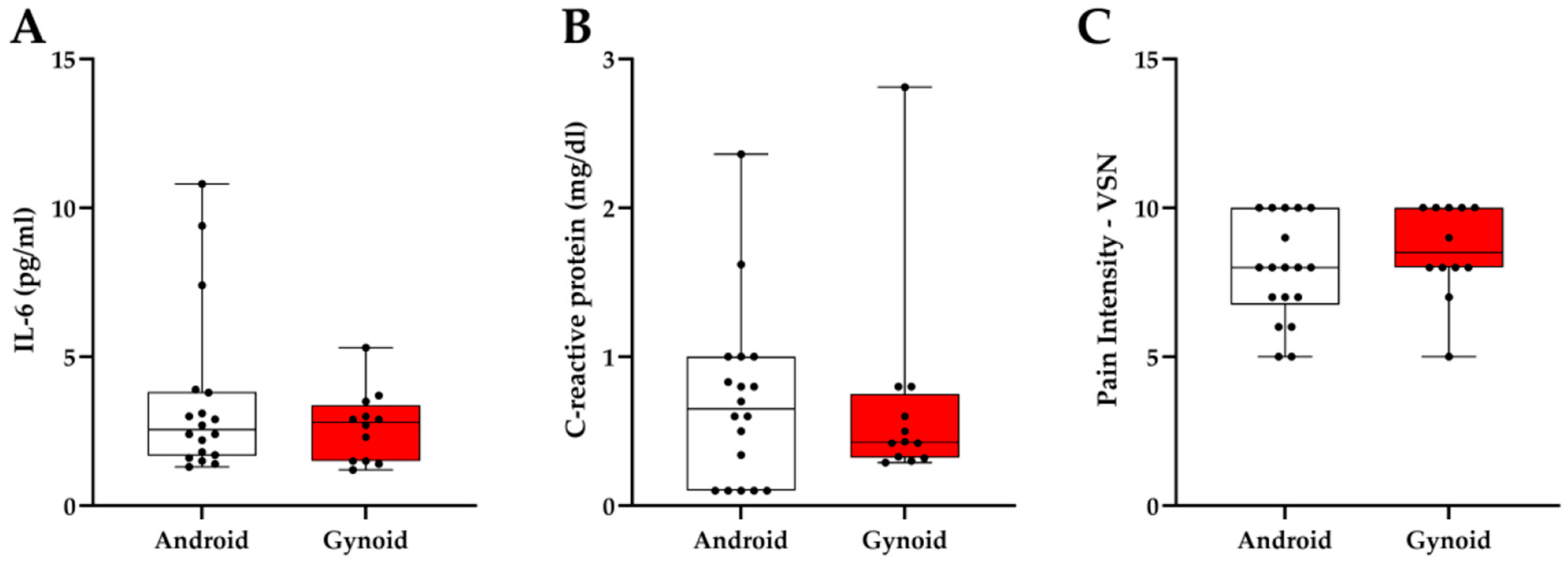
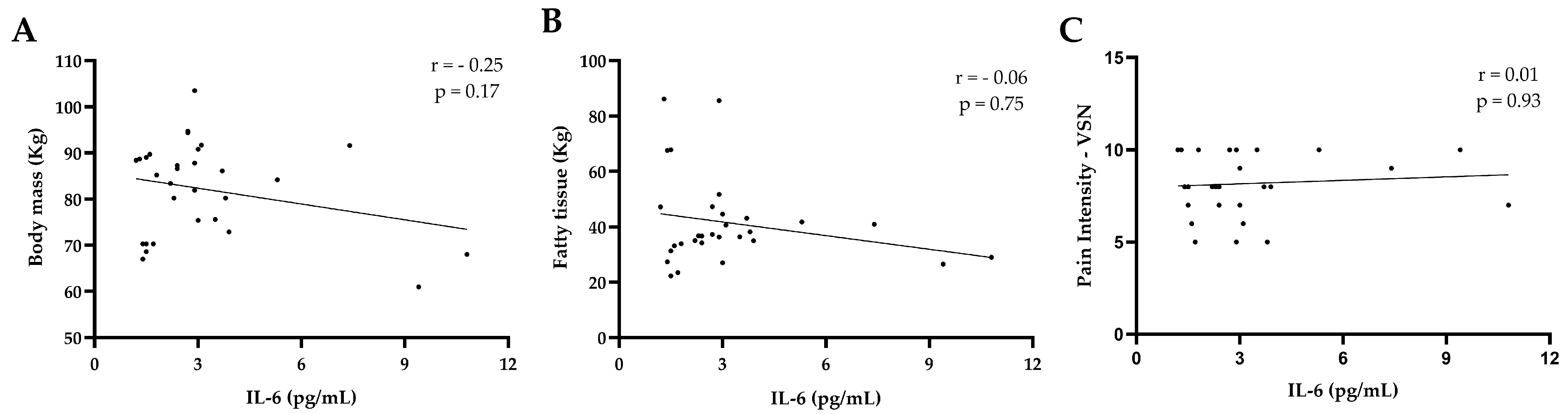
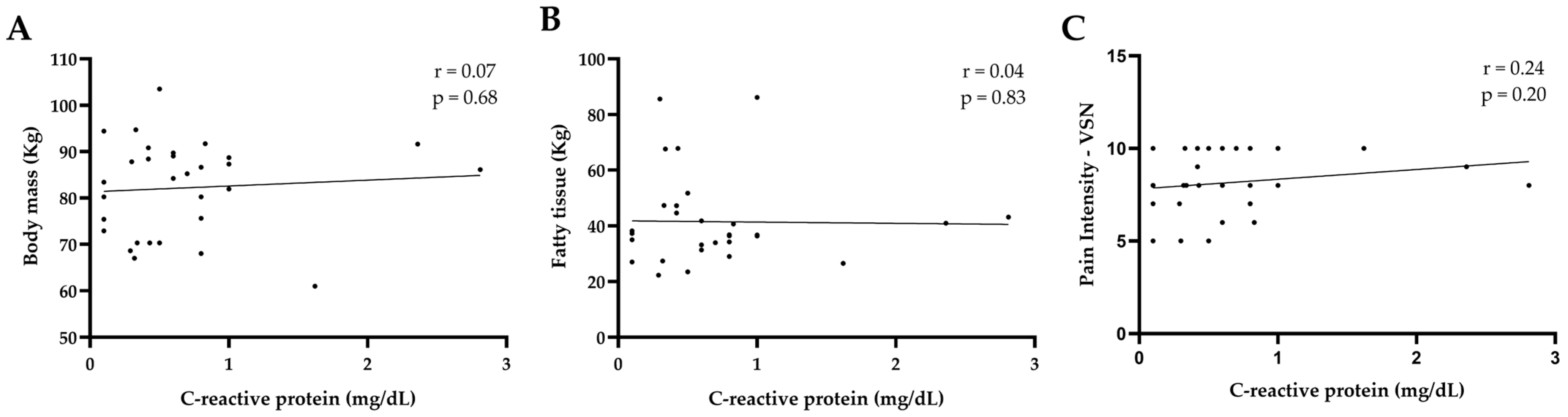
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths, Limitations, and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobs, E.J.; Jemal, A.; Gapstur, S.M.; Fedewa, S.A.; Shuval, K.; Siegel, R.L.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Sauer, A.G.; Torre, L.A.; Pearson-Stuttard, J.; et al. Global patterns in excess body weight and the associated cancer burden. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 88–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2014; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawley, J.; Meyerhoefer, C. The medical care costs of obesity: An instrumental variables approach. J. Health Econ. 2012, 31, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwick, R.K.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Horsley, V.; Plikus, M.V. Anatomical, physiological, and functional diversity of adipose tissue. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Yin, J.; Gan, L.; Xue, J. Two-sided roles of adipose tissue: Rethinking the obesity paradox in various human diseases from a new perspective. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishvanath, L.; Gupta, R.K. Contribution of adipogenesis to healthy adipose tissue expansion in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4022–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose tissue remodeling and obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wu, D.; Qiu, Y. Adipose tissue macrophage in obesity-associated metabolic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 977485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojta, I.; Chacińska, M.; Błachnio-Zabielska, A. Obesity, bioactive lipids, and adipose tissue inflammation in insulin resistance. Nutrients 2020, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Miele, C.; Raciti, G.A.; Zatterale, F.; Beguinot, F.; Naderi, J.; Desiderio, A. Chronic adipose tissue inflammation linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.; Bouwman, F.G.; van Baak, M.A.; Roumans, N.J.T.; Vink, R.G.; Mariman, E.C.M. Plasma levels of triglycerides and IL-6 are associated with weight regain and fat mass expansion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1920–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainous, A.G., 3rd; Sharma, P.; Jo, A. Systemic inflammation among adults with diagnosed and undiagnosed cardiometabolic conditions: A potential missed opportunity for cardiovascular disease prevention. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1327205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Narazaki, M.; Metwally, H.; Kishimoto, T. Historical overview of the interleukin-6 family cytokine. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandraki, K.; Piperi, C.; Kalofoutis, C.; Singh, J.; Alaveras, A.; Kalofoutis, A. Inflammatory process in type 2 diabetes: The role of cytokines. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1084, 89–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Akerström, T.C.; Nielsen, A.R.; Fischer, C.P. Role of myokines in exercise and metabolism. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K. Muscles and their myokines. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, M.; Gangestad, S.W. Rethinking IL-6 and CRP: Why they are more than inflammatory biomarkers, and why it matters. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 70, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, F.J.B.; Ferreira-Júnior, M.; Sales, M.M.; Cruz-Neto, L.M.; Fonseca, L.A.M.; Sumita, N.M.; Duarte, A.J.S. C-reactive protein: Clinical applications and proposals for a rational use. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2013, 59, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, D.R. Body mass index and musculoskeletal pain: Is there a connection? Chiropr. Man. Therap. 2013, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uceli, T.M. Impact of obesity on the immune system. In Manifesto Obesidade: Cuidar de Todas as Formas; Brazilian Association for the Study of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome (ABESO); Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabology (SBEM): São Paulo, Brazil, 2021; Available online: https://abeso.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Manifesto.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- Polli, A.; Coppieters, I.; Malfliet, A.; Deliens, T.; Clarys, P.; Yilmaz, S.T.; Nijs, J.; Elma, Ö. Chronic musculoskeletal pain and nutrition: Where are we and where are we heading? PM R 2020, 12, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, R.; Karppinen, J.; Leino-Arjas, P.; Solovieva, S.; Viikari-Juntura, E. The association between obesity and low back pain: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, D.W.; Tian, Q.B. Obesity as a risk factor for low back pain: A meta-analysis. Clin. Spine Surg. 2018, 31, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narouze, S.; Souzdalnitski, D. Obesity and chronic pain: Systematic review of prevalence and implications for pain practice. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2015, 40, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezelbash, F.; Shirazi-Adl, A.; Plamondon, A.; Arjmand, N.; Parnianpour, M. Obesity and obesity shape markedly influence spine biomechanics: A subject-specific risk assessment model. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearing, S.C.; Hennig, E.M.; Byrne, N.M.; Steele, J.R.; Hills, A.P. Musculoskeletal disorders associated with obesity: A biomechanical perspective. Obes. Rev. 2006, 7, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, W.J.; Sowers, M.; Hawthorne, V.M.; Weissfeld, L.A. Obesity as a risk factor for osteoarthritis of the hand and wrist: A prospective study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1994, 139, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotle, M.; Hagen, K.B.; Natvig, B.; Dahl, F.A.; Kvien, T.K. Obesity and osteoarthritis in knee, hip and/or hand: An epidemiological study in the general population with 10 years follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2008, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsudo, S.; Araújo, T.; Matsudo, V.; Andrade, D.; Andrade, E.; Oliveira, L.C. Questionário Internacional de Atividade Física (IPAQ): Estudo de validade e reprodutibilidade no Brasil. Rev. Bras. Ativ. Fís. Saúde 2012, 6, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Farrar, J.T.; Young, J.P., Jr.; LaMoreaux, L.; Werth, J.L.; Poole, M.R. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain 2001, 94, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjermstad, M.J.; Fayers, P.M.; Haugen, D.F.; Caraceni, A.; Hanks, G.W.; Loge, J.H.; Fainsinger, R.; Aass, N.; Kaasa, S. Studies comparing numerical rating scales, verbal rating scales, and visual analogue scales for assessment of pain intensity in adults: A systematic literature review. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2011, 41, 1073–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euasobhon, P.; Atisook, R.; Bumrungchatudom, K.; Zinboonyahgoon, N.; Saisavoey, N.; Jensen, M.P. Reliability and responsivity of pain intensity scales in individuals with chronic pain. Pain 2022, 163, e1184–e1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daentzer, D.; Hohls, T.; Noll, C. Has overweight any influence on the effectiveness of conservative treatment in patients with low back pain? Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzocchi, A.; Ponti, F.; Albisinni, U.; Battista, G.; Guglielmi, G. DXA: Technical aspects and application. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 1481–1492. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/european-journal-of-radiology (accessed on 11 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Meleger, A.L.; Froude, C.K.; Walker, J., 3rd. Nutrition and eating behavior in patients with chronic pain receiving long-term opioid therapy. PM R 2014, 6, 7–12.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisovskaya, A.; Chmelik, E.; Karnik, A. Exercise and chronic pain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1228, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verdú, E.; Homs, J.; Boadas-Vaello, P. Physiological changes and pathological pain associated with sedentary lifestyle-induced body systems fat accumulation and their modulation by physical exercise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, V.; de Courten, M.P.; Stojanovska, L.; Blatch, G.L.; Tangalakis, K.; de Courten, B. The complex immunological and inflammatory network of adipose tissue in obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, T.T. Does obesity cause chronic inflammation? The association between complete blood parameters with body mass index and fasting glucose. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locksley, R.M.; Liang, H.-E.; Chawla, A.; Wu, D.; Jouihan, H.A.; Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.R.; Bando, J.K.; Molofsky, A.B. Eosinophils sustain adipose alternatively activated macrophages associated with glucose homeostasis. Science 2011, 332, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Ham, M.; Kim, J.B. Crosstalk between adipocytes and immune cells in adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysregulation in obesity. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, M.M.; Clément, K.; Pinho, V.; Merabtene, F.; Costa, K.A.; Silveira, A.L.M.; Vieira, É.L.M.; Marcelin, G.; Lana, J.P.; de Oliveira, A.C.C.; et al. Eosinophils protect from metabolic alterations triggered by obesity. Metabolism 2023, 146, 155613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Metabolically healthy obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polley, E.C.; Parvizi, M.; Moore, N.; Kunz, H.E.; Hart, C.R.; Laurenti, M.; Gries, K.J.; Ryan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jensen, M.D.; et al. Adipose tissue macrophage populations and inflammation are associated with systemic inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 321, E105–E121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.M.; Pedersen, B.K. The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.S.; White, A.; Perry, R.J.; Camporez, J.-P.; Hidalgo, J.; Shulman, G.I.; Davis, R.J. Regulation of adipose tissue inflammation by interleukin 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2751–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.P.; Vase, L.; Hooten, W.M. Chronic pain: An update on burden, best practices, and new advances. Lancet 2021, 397, 2082–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graßmann, S.; Wirsching, J.; Eichelmann, F.; Aleksandrova, K. Association between peripheral adipokines and inflammation markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity 2017, 25, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murabito, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Massaro, J.M.; Pedley, A.; Kreger, B.E.; Rosenquist, K.J.; Fox, C.S.; Long, M.T.; Vasan, R.S. Fat quality and incident cardiovascular disease, all-cause mortality, and cancer mortality. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piening, B.D.; Zhou, W.; Contrepois, K.; Röst, H.; Urban, G.J.G.; Mishra, T.; Hanson, B.M.; Bautista, E.J.; Leopold, S.; Yeh, C.Y.; et al. Integrative personal omics profiles during periods of weight gain and loss. Cell Syst. 2018, 6, 157–170.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variables | Android | Gynoid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Min–Max | Mean ± SD | Min–Max | |
| Age (years) | 50.61 ± 9.41 | 30–63 | 50.67 ± 9.45 | 30–62 |
| Height (cm) | 157.88 ± 4.91 | 146.5–165.5 | 156.00 ± 4.59 | 148.5–159 |
| Total body mass (kg) | 81.53 ± 9.40 | 61–94.4 | 83.10 ± 10.67 | 75.6–103.5 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 33.19 ± 3.85 | 26.7–43.1 | 34.70 ± 4.62 | 34.7–41.7 |
| Fat mass (kg) | 38.44 ± 14.07 | 23.47–86.15 | 50.41 ± 18.42 | 36.39–85.56 |
| Fat percentage (%) | 42.79 ± 3.04 | 34.9–49.8 | 47.95 ± 0.05 | 47.2–51.7 |
| VSN (0–10) | 7.88 ± 1.66 | 5–10 | 8.58 ± 1.49 | 5–10 |
| IPAQ (min/week) | 165.83 ± 108.55 | 0–450 | 212.50 ± 153.80 | 0–540 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cota, C.C.; Miranda-Castro, S.; Souza-Gomes, A.F.; Leite, L.B.; Forte, P.; Monteiro, A.M.; Pereira, W.V.C.; de Moura, S.S.; Nunes-Silva, A. Associations Between Pain Intensity and Inflammatory Profile in Women with Android and Gynoid Obesity Diagnosed with Chronic Pain: An Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124170
Cota CC, Miranda-Castro S, Souza-Gomes AF, Leite LB, Forte P, Monteiro AM, Pereira WVC, de Moura SS, Nunes-Silva A. Associations Between Pain Intensity and Inflammatory Profile in Women with Android and Gynoid Obesity Diagnosed with Chronic Pain: An Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124170
Chicago/Turabian StyleCota, Cecília Cristina, Stefani Miranda-Castro, Antônio Felipe Souza-Gomes, Luciano Bernardes Leite, Pedro Forte, António M. Monteiro, William Valadares Campos Pereira, Samara Silva de Moura, and Albená Nunes-Silva. 2025. "Associations Between Pain Intensity and Inflammatory Profile in Women with Android and Gynoid Obesity Diagnosed with Chronic Pain: An Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124170
APA StyleCota, C. C., Miranda-Castro, S., Souza-Gomes, A. F., Leite, L. B., Forte, P., Monteiro, A. M., Pereira, W. V. C., de Moura, S. S., & Nunes-Silva, A. (2025). Associations Between Pain Intensity and Inflammatory Profile in Women with Android and Gynoid Obesity Diagnosed with Chronic Pain: An Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124170











