Abstract
Background/Objective: Bullous Pemphigoid (BP) is a well-recognized autoimmune subepidermal blistering disease. However, its occurrence following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is extremely rare. The objective of this study is to systematically review the available data on BP following an allogeneic HSCT with focus on treatment options. Methods: A systematic review of studies evaluating BP following allogeneic HSCT, incorporating a highly treatment-resistant case from our graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) dermatology clinic, of a 47-year-old patient, notable as the only reported instance of BP following HSCT in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) that transformed into diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and GvHD due to HSCT. The review yielded 15 publications that met the eligibility criteria. Including our case, a total of 16 cases were analyzed. Results: Nearly all patients (14/16) in this review had chronic GvHD due to their HSCT. Twelve patients were males, and six were of Japanese origin. The mean age for BP diagnosis was 38 years (a range of 5–67). On average, BP developed one year post-HSCT. The most common treatment for BP in these patients was prednisolone, with the majority experiencing complete resolution of symptoms. Conclusions: BP following HSCT is an exceptionally rare condition with an unclear underlying mechanism.
1. Introduction
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is the most common autoimmune subepidermal blistering disease. It typically presents in older adults as a chronic, relapsing–remitting, generalized pruritic bullous eruption and is potentially associated with significant morbidity. In the early pre-bullous stages, urticarial plaques may be present. The diagnosis is based on the presence of a characteristic clinical and histological feature and is supported by immune-serological assays, particularly direct and indirect immunofluorescence microscopy (DIF, IIF), as well as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), for anti-BP180/BP230 autoantibodies [1].
BP is associated with tissue-bound and circulating autoantibodies directed against BP antigen 180 (BP180, BPAG2, or type XVII collagen) and BP antigen 230 (BP230 or BPAG1e), components of the hemidesmosomes which are essential for dermal–epidermal adhesion. CD4+ T cells, with a mixed Th1/Th2 cytokine profile, proliferate in response to BP180 peptides, while B cells produce antibodies against BP180 and BP230. Macrophages facilitate blister formation by recruiting neutrophils and promoting proinflammatory crosstalk [2].
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) involves the administration of healthy hematopoietic stem cells to patients with various hematopoietic malignancies. Several types of HSCT are used clinically, with transplanted cells sourced from various origins. In allogeneic HSCT, donors may be HLA-matched relatives, haploidentical family members, or unrelated individuals matched for the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) [3]. HSCT may be complicated by graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) which arises when donor T lymphocytes recognize the recipient tissues as foreign because of histocompatibility differences and initiate an immune response [4].
Previous studies demonstrated an important role of the B-cell immune response in chronic GvHD. Donor B cells function as antigen-presenting cells, promoting the survival and proliferation of pathogenic CD4+ T cells, which are essential for the development of chronic GvHD [5]. Furthermore, chronic GvHD B cells produce circulating antibodies against exposed basement membrane components, such as collagen VII, BP230, BP180, and laminin γ1 in response to GvHD keratinocyte damage and reduced self-tolerance [6]. The dysregulated CD4+ T cells and circulating autoantibodies may contribute to BP formation in patients with GvHD. Some researchers have speculated that HLA types or micro-chimerism may also play a role in autoimmune blistering dermatosis [7].
Reports on BP following solid organ transplantation or HSCT are scarce [8], and the pathogenesis remains unclear. We systematically reviewed the literature on the prevalence, characteristics, and management of BP following HSCT. In addition, we describe a novel case from our dermatology clinic of BP following HSCT in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) that transformed to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review
The systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and was prospectively registered in the PROSPERO database (Registration No. CRD420251021202). A PRISMA flow diagram summarizing the study selection process is provided in the Supplementary Material (Figure S1).
2.2. Search Strategy
A comprehensive database search was performed independently using PubMed, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, and the ongoing trials registry of the US National Institutes of Health (www.clinicaltrials.gov). The following search criteria were used: (“Bullous Pemphigoid” OR “Pemphigoid”) AND (“Bone Marrow Transplantation” OR “Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation”) AND (“Graft versus Host Disease” OR GvHD), in [MeSH terms] OR [All fields]. Reference lists from the included studies were manually scanned to identify any additional results.
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility criteria were defined as follows: (i) relevance—case reports of any design describing patients with BP following HSCT and (ii) participants—patients of all ages and sex with a clinical diagnosis of BP following HSCT.
Included were studies of any design that described at least one case of BP following HSCT from which relevant data were extracted. Studies of any language were eligible for inclusion, and non-English reports were translated by the authors when relevant. No restrictions were applied regarding patient age; both adult and pediatric cases were included, provided they met the diagnostic criteria for BP following HSCT.
2.4. Data Extraction and Quality
Two reviewers (SGL and AA) independently screened the titles and abstracts of all retrieved articles and subsequently examined the full texts of those considered potentially eligible. Data extraction onto an electronic form was executed by one reviewer (SGL) and validated by the other (AA). The extracted data included the first author’s name, the year of publication, the number of patients, patient age, sex and characteristics, the duration of cutaneous symptoms, the time from HSCT to cutaneous symptoms onset, diagnostic workup, and treatment.
Given that the included studies were primarily case reports or small case series, formal risk of bias tools (e.g., ROBINS-I or GRADE) were not applicable. However, we assessed each report’s diagnostic rigor by confirming the presence of clinical, histological, and immunological findings consistent with BP and by considering the completeness of the reported data.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Continuous variables were expressed as prevalence and percentages.
3. Index Case
In February 2022, a 47-year-old male with no significant family history presented to a tertiary dermatology clinic with a 2-month history of an extensive, painful, pruritic rash involving the scalp, face, torso, and limbs.
His medical history was remarkable for CLL diagnosed in December 2016 and treated with ibrutinib. In June 2019, the disease transformed into DLBCL and was treated with the R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) regimen. Three months later, the patient received an allogeneic bone marrow transplant from his sister (100% HLA match). GvHD developed in June 2020, initially involving the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea) and liver (elevated bilirubin). Additional symptoms, including recurrent conjunctivitis, sinusitis, dysphagia, and hoarseness, along with oral findings of restricted mouth opening, bilateral buccal reticular white lacing, vesicles, erosions, and sloughing, supported the diagnosis of mucosal GvHD involving the ocular, oral, nasal, and laryngeal sites. No cutaneous involvement was observed at that time.
In January 2022, 1.5 years after transplantation, when he was stable and afebrile, the patient experienced the sudden onset of a new, widespread rash on the scalp, face, torso, and limbs. It consisted of tense bullae filled with clear or hemorrhagic fluid along with erosions imposed on erythematous plaques or normal-appearing skin (Figure 1).
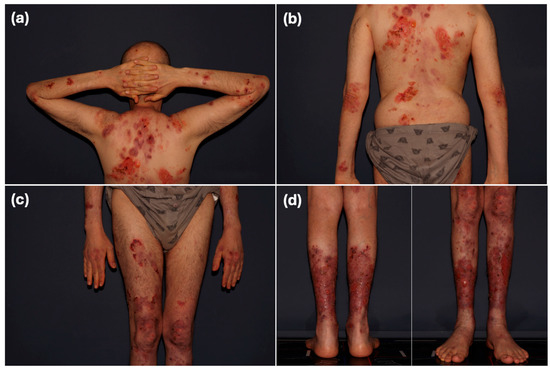
Figure 1.
Physical exam of the index case as he first presented to our clinic. (a,b) Extensive erythematous erosive plaques involving most of the back surface and upper limbs. (c,d) Extensive erythematous erosive plaques involving the lower limbs. Lesions measured approximately 5–10 cm in diameter. Note: Scale bars are not included in this figure.
The patient did not receive any vaccines in the months preceding the onset of the bullous eruption. No temporal or causal association was identified between the patient’s medications and the rash.
No significant laboratory abnormalities were noted. A punch biopsy from the edge of an erosion on the shin showed subepidermal separation with a dermal infiltrate composed of eosinophils, lymphocytes, and neutrophils. The DIF of uninvolved perilesional skin showed linear deposits of IgG and C3 along the dermo-epidermal junction. IIF and ELISA were negative. The BIOCHIP mosaic-based IIF test was negative for the collagen VII antigen but showed dermal deposition of IgG on a salt-split substrate. Based on the correlation of the clinical, pathological, and immunofluorescence findings, a diagnosis of BP was made.
The patient was initially treated with standard therapeutic regimens for BP and/or GvHD. Twice daily total body application of an ultrapotent topical steroid (clobetasol propionate) for BP failed to improve symptoms. Many subsequent treatments were attempted over the years, all of which were discontinued for various reasons: Systemic prednisone [a maximal dose of 40 mg/day (equivalent to 0.8 mg/kg/day)] led to glaucoma and eventually vision loss in the left eye. Minocycline/doxycycline proved ineffective and raised concerns of exacerbating GvHD-related esophagitis. Dapsone led to worsening anemia. Intravenous immunoglobulin (2 g/kg/day) caused significant hemolysis. Methotrexate (5 mg/wk) dramatically increased liver enzyme levels.
GvHD-approved treatments were also associated with serious side effects or proved ineffective. Ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor (5 mg twice daily), led to multiple hospitalizations for systemic infections, including near-lethal pneumonia, and belumosudil, a rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase 2 (ROCK-2) pathway inhibitor (200 mg/day), caused severe hypophosphatemia. Extracorporeal photopheresis did not lead to the desired improvement.
By March 2024, nearly 2 years after his initial presentation, the patient’s severe cutaneous condition worsened, resulting in another hospitalization. Given the failure of the many previous treatments, we opted for severe refractory BP therapies. The patient received two doses of rituximab at 375 mg/m2 and underwent five rounds of plasma exchange once a week. Additionally, prompted by emerging evidence from the Autoimmune Disease Early Intervention and Prevention Trial (ADEPT) of the effectiveness of dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13, for moderate–severe BP (20% vs. 4% for placebo, p = 0.114) [9], we administered a loading dose of subcutaneous dupilumab at 600 mg.
Concurrent weekly plasma exchange with dupilumab at a dose of 300 mg every 2 weeks was ineffective. It was only in August 2024, when under this regimen, rituximab at a dose of 375 mg/m2 once a week (3 doses) was readministered with prednisone 40 mg/day, that the re-epithelialization of the existing erosions occurred, and no new lesions developed (Figure 2). Disease control has been maintained as of the time of writing this article.
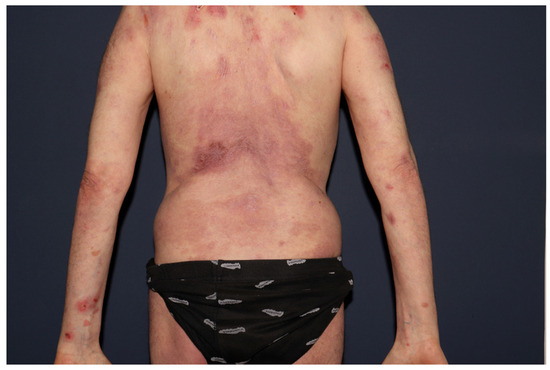
Figure 2.
Near-complete re-epithelialization of the extensive cutaneous erosions on the index patient’s back, six weeks after initiating rituximab, dupilumab, and prednisone (August 2024).
Although the patient underwent standard HLA typing as part of the transplantation protocol, no specific testing was performed to identify HLA alleles previously associated with bullous pemphigoid, such as HLA-DQB1*03:01 [10]. Therefore, it remains unclear whether genetic predisposition contributed to the development of BP in this case.
This is the only reported case of post-HSCT GvHD in a patient with CLL transforming to DLBCL who was diagnosed with severe and recalcitrant new-onset BP. The patient was refractory to multiple standard and advanced treatment modalities administered for the dual morbidity of BP and GvHD. This required a personalized treatment approach that combined several therapies to achieve disease control. This unique case prompted the present in-depth literature review and highlighted the need for a comprehensive systematic review on these combined morbidities.
4. Results
The literature search yielded 15 cases, all extracted from case reports or case series dating back to 1986 [6,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. The data were collected and aggregated along with the data from the present case (no. 16). Table 1 summarizes their main characteristics.

Table 1.
Main characteristics of 16 patients with GvHD/BP after HSCT.
There were 12 male and 4 female patients with a mean age of 38 years (range 5–67) at BP diagnosis. Six patients were of Japanese origin. The most common initial hematological disease was acute lymphocytic lymphoma or acute myeloid lymphoma, with four patients each. Fourteen patients presented with GvHD following HSCT; in two cases, GvHD was not mentioned [21,22]. The average time from HSCT to the onset of BP was one year.
4.1. Diagnosis
Table 2 summarizes the diagnostic evaluation for BP. A typical clinical presentation of BP was recorded in 13 of the 15 reported patients and in the index patient (no. 16). Further diagnostic workup was available for 13/16 patients. All but one had histological findings characteristic of BP. One patient had histological features of both BP and GvHD (dyskeratotic keratinocytes). All cases but one had a positive DIF test that confirmed BP. The one patient without a DIF test had a positive IIF test but did not undergo salt-split testing. Among the remaining patients, nine had positive IIF–salt-split tests, with antibody localization observed on the epidermal (n = 5), dermal (n = 2), or both sides (n = 2). ELISA or immunoblotting results were positive in 10 patients and negative in 2.

Table 2.
Diagnostic evaluation of included cases.
4.2. Treatment
Table 3 summarizes the systemic treatments administered for BP. Twelve of the sixteen patients (75%) achieved complete remission (CR), of whom four responded within one month of treatment initiation; seven (58%) achieved CR with prednisolone alone. Two patients (12.5%), including the index case, had refractory disease, and two patients (12.5%) died, one from sepsis and the other from disease progression.

Table 3.
Systemic treatment received for BP by all included cases.
5. Discussion
This systematic review raises the awareness of the rare comorbidity of BP and GvHD. Of the 15 reported patients, 13 had chronic GvHD. BP developed in all of them 3 to 30 months after HSCT. These data suggest a potential causal link between GvHD and BP in the post-transplant setting [25,26]. We also added a complex case from our dermatology clinic of a patient with CLL that transformed to DLBCL prior to the development of HSCT-related GvHD, followed 2 years later by BP that was refractory to all standard treatments.
Chronic GvHD is characterized by multi-organ fibrosis and autoantibody production [24,27]. It typically manifests with skin lesions resembling lichen planus or scleroderma [28]. Although GvHD, mostly in the acute setting, can cause subepidermal blisters through basal cell degeneration [4], its association with BP is exceedingly rare [6,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. The pathophysiology underlying the association between HSCT, GvHD, and BP is complex and not fully understood. The current hypothesis suggests that the GvHD-induced basal epidermal damage may expose basement membrane zone (BMZ) proteins, potentially trigger antigen presentation and autoantibody production [6,18]. CD4+ T cells recognize these antigens via major histocompatibility complex-II (MHC-II) on antigen-presenting cells or keratinocytes [29]. In response, they release cytokines that recruit CD8+ cytotoxic T cells [30,31], further exposing BMZ antigens and promoting BP development. This immunological cascade may resemble the phenomenon of epitope spreading, as described in other autoimmune bullous diseases such as BP associated with psoriasis [32]. In this model, initial immune responses to exposed autoantigens may gradually expand to include additional, secondary targets, further amplifying the disease process. Such a mechanism could potentially explain the sequential development of GvHD followed by BP in our and other reported cases. Additionally, GvHD and its treatments (prednisolone and cyclosporine) may disrupt immune homeostasis, altering the Th1/Th2 balance and regulatory T-cell function and fostering autoimmunity [18]. In chronic GvHD, B-cell dysregulation, including heightened B-cell receptor signaling and survival, may further drive the production of autoantibodies against BMZ proteins, such as BP180 and BP230 [26,33,34,35,36]. This immune imbalance is characterized not only by Th1/Th17 skewing but also by enhanced Th2 cytokine expression, which plays a well-established role in BP pathogenesis [37]. Specifically, IL-4 and IL-13 are central to this process: they promote class-switching of B cells toward the IgG4 and IgE isotypes and enhance eosinophilic infiltration [38], both hallmark features of BP [39]. In the GVHD milieu, elevated Th2 cytokines may act synergistically with tissue damage to amplify the autoimmune cascade [40]. Although dupilumab monotherapy did not yield clinical improvement, disease control was ultimately achieved when it was combined with rituximab and plasma exchange. This observation supports a contributory role for Th2 cytokines (IL-4/IL-13) in the pathogenesis of post-HSCT BP, although they likely represent only one component of broader, multifactorial immune dysregulation.
Moreover, chronic GvHD has been linked to profound B-cell dysregulation, including increased autoreactive B-cell survival and antibody production—a key feature in BP development. This dysregulation includes the expansion of autoreactive B-cell clones capable of bypassing central and peripheral tolerance [33]. These clones produce pathogenic autoantibodies against hemidesmosomal components, particularly BP180 and BP230, which are central to BP pathogenesis [1].
The diagnosis of BP in the reported patients with GvHD was well founded due to the distinct histological and immunopathological features of each condition. Chronic GvHD is characterized histologically by hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, acanthosis, apoptotic or necrotic keratinocytes, and sub-epidermal splitting. The mainly lymphocytic infiltrate, in any pattern (dermal, epidermal, or both), sometimes extends to the subcutaneous tissue. DIF is positive in up to 86% of patients, exhibiting variable IgM and IgG deposition in a granular and/or linear pattern within the epidermis, BMZ, or upper dermis [41,42,43]. In contrast, BP has a distinct and uniform DIF pattern, with linear IgG ± C3 deposition along the BMZ [1].
Of the 13/16 patients with diagnostic data, all but 1 [6] had a positive DIF test that confirmed BP. This same patient [6] also had a positive IIF test but did not undergo salt-split testing. Among the remaining patients, nine had positive IIF–salt-split tests, with antibody localization observed on the epidermal (n = 5 [13,14,15,19,20]), dermal (n = 2 [24] and the index case), or both sides (n = 2 [18,23]). ELISA or immunoblotting results were positive in 10 patients and negative in 2 ([19] and the index case).
The index case represents a diagnostically unique instance of BP following HSCT. While a bullous form of chronic GvHD (histopathological necrotic keratinocytes) has been described [28,44], the histological findings in this case corresponded with BP. The DIF results were compatible with BP, but IIF and ELISA were negative. In addition, BIOCHIP IIF was negative for collagen VII but positive for dermal deposition of IgG on a salt-split substrate. Although these findings may not fully align with BP criteria [1], IIF negativity occurs in up to 30% of BP cases [45], and the absence of BP-specific antibodies after HSCT has been previously reported [19]. Ultimately, the diagnosis of BP was supported by the characteristic clinical presentation, the absence of dyskeratotic keratinocytes, and positive DIF.
Treatment approaches for BP in this context mirror those for idiopathic BP. Systemic corticosteroids are the cornerstone of treatment, often combined with steroid-sparing immunosuppressants [1]. In our review, 75% of patients achieved full remission, with 58% responding to corticosteroids alone. Our case represents the most treatment-refractory post-HSCT BP reported to date, necessitating more aggressive interventions. For refractory idiopathic BP, several advanced therapies have been explored [46]. Plasmapheresis rapidly removes circulating autoantibodies but can lead to rebound after cessation. Rituximab, a monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody, targets B lymphocytes to reduce autoantibody production and may promote long-term remission. Dupilumab, an anti-IL-4 receptor-α monoclonal antibody and IL-4 and IL-13 blocker, downregulates Th2 responses implicated in BP pathogenesis [46].
Despite its promise, dupilumab alone did not achieve adequate disease control in our case. As such, emerging therapies such as IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors, may offer alternative avenues for treatment [46]. These agents modulate distinct immunologic pathways implicated in both BP and chronic GVHD and merit further exploration, particularly in refractory cases.
Our multi-pronged approach combining these therapies led to clinical improvement and disease control and may represent a potential treatment strategy for managing refractory BP, both post-HSCT and idiopathic.
Notably, JAK inhibitors such as ruxolitinib have demonstrated efficacy in chronic GvHD, although their role in treating BP remains unclear [47]. In our case, ruxolitinib was attempted but discontinued due to serious infections, emphasizing the delicate balance required in managing overlapping GvHD and BP pathologies.
Importantly, BP is not the only autoimmune bullous disease reported to follow HSCT. Cases of pemphigus foliaceus [48], epidermolysis bullosa acquisita [6,49,50], mucous membrane pemphigoid [51,52,53,54,55,56,57], and linear IgA dermatosis [58] have been documented. Large-scale studies, such as those by Kasperkiewicz et al. [8], indicated an increased but still low overall risk of autoimmune bullous disease post-transplantation. The study by Hofmann et al. [6] further elucidated the immunological landscape, demonstrating a higher frequency of circulating anti-BMZ antibodies, particularly those targeting BP180, in patients with GvHD.
The consistent association of BP with chronic GvHD, as well as its average onset of one year after transplantation, suggests an increased susceptibility in these patients. Interestingly, the mean age of patients in this review (38 years) is substantially lower than the typical age of idiopathic BP, which usually affects elderly individuals. This age discrepancy suggests that BP following HSCT may arise through distinct pathophysiological mechanisms, possibly involving extrinsic post-transplant immune dysregulation rather than intrinsic age-related factors. While BP following HSCT shares clinical and immunopathological features with classic BP, its distinct age distribution and strong association with chronic GvHD may suggest a unique transplant-associated subtype.
Compared to classic BP, which predominantly affects individuals over the age of 70 [1], is associated with HLA-DQB1*03:01 [10], and has a strong IgG4 autoantibody profile [59], post-HSCT BP appears in significantly younger patients (a mean age of 38 in our cohort), with variable or negative serological profiles and unclear HLA associations. These differences suggest distinct immunological drivers, supporting the hypothesis of a “transplant-associated subtype” of BP. However, further studies are needed to validate this classification.
As previously noted, our case represents the most resistant form of BP reported to date, underscoring the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in managing complex presentations.
Looking ahead, several avenues for future research emerge. Identifying predictive biomarkers for BP risk in HSCT recipients would make early intervention possible. Comprehensive immunophenotyping before and after HSCT, during GvHD, and at BP onset could provide crucial insights into the immunopathological cascade. Given the rarity of post-HSCT BP, multi-center collaborations and registries will be vital for accumulating sufficient data to guide evidence-based management.
Limitations
This review is limited by the small number of reported cases and potential publication bias inherent in case report studies. Furthermore, heterogeneity in diagnostic criteria, treatment reporting, and visual documentation, such as the absence of calibrated scale bars in published images, limits the generalizability and reproducibility of the findings. The retrospective nature and the lack of control groups in included studies further restrict conclusions regarding causality or standardized treatment approaches.
6. Conclusions
The study of post-HSCT BP offers valuable insights into the complex interplay among transplantation, GvHD, and autoimmunity. Furthermore, our successful management of a refractory case underscores the importance of an innovative, multidisciplinary approach. As our understanding deepens, we may uncover new therapeutic targets and strategies benefiting not only patients with post-HSCT BP patients but also those with other autoimmune bullous diseases. Given the possible predisposition of patients with GVHD for BP, future research should focus on developing predictive biomarkers and conducting immunophenotyping to better understand the immunopathological mechanisms. The rarity of these cases highlights the need for multi-center collaborations to gather sufficient data for evidence-based management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm14124068/s1. Figure S1: PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for new systematic reviews which included searches of databases and registers only.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.; methodology, A.A.; validation, A.A.; investigation, A.A. and S.G.L.; resources, A.A., M.Y. and P.R.; data curation, A.A., S.G.L. and M.F.; writing—original draft preparation, S.G.L.; writing—review and editing, A.A., M.O.-S., L.P. and D.M.; visualization, A.A., S.G.L. and M.O.-S.; supervision, A.A., L.P. and D.M.; project administration, A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the subject involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author due to medical confidentiality and patient privacy regulations.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Sapir Glazer Levavi, Moshe Yeshurun, Pia Raanani, Mor Frisch, Meital Oren-Shabtai, Daniel Mimouni, and Anna Aronovich declare no conflicts of interest. Author Lev Pavlovsky has served as an investigator for Abbvie, Coherus, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Janssen Biotech, Eli Lilly, and Bristol Myers Squibb and as an advisor, consultant, and/or invited lecturer for Abbvie, Janssen Biotech, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Pfizer Inc., Dexcel Pharma, Eli Lilly, Bristol Myers Squibb, Neopharm, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BMZ | Basement membrane zone |
| BP | Bullous pemphigoid |
| CLL | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| IIF | Indirect immunofluorescence |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| CR | Complete resolution |
| DIF | Direct immunofluorescence |
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GvHD | Graft-versus-host disease |
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigens |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| IIF | Indirect immunofluorescence |
References
- Borradori, L.; Van Beek, N.; Feliciani, C.; Tedbirt, B.; Antiga, E.; Bergman, R.; Böckle, B.C.; Caproni, M.; Caux, F.; Chandran, N.S.; et al. Updated S2 K Guidelines for the Management of Bullous Pemphigoid Initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X. Immune Cells in Pemphigus Vulgaris and Bullous Pemphigoid: From Pathogenic Roles to Targeting Therapies. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 123, 110694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copelan, E.A. Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, J.L.; Levine, J.E.; Reddy, P.; Holler, E. Graft-versus-Host Disease. Lancet 2009, 373, 1550–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.S.; Kim, H.T.; Nikiforow, S.; Heubeck, A.T.; Ho, V.T.; Koreth, J.; Alyea, E.P.; Armand, P.; Blazar, B.R.; Soiffer, R.J.; et al. Antibodies Targeting Surface Membrane Antigens in Patients with Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. Blood 2017, 130, 2889–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, S.; Kopp, G.; Gall, C.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Bertz, H. Basement Membrane Antibodies in Sera of Haematopoietic Cell Recipients Are Associated with Graft-versus-host Disease. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, F.; Fania, L.; Sinagra, J.L.M.; Salemme, A.; Di Zenzo, G. Bullous Pemphigoid: Trigger and Predisposing Factors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperkiewicz, M.; Kupiec-Weglinski, J.W.; Ngo, B.T.; Kridin, K.; Ludwig, R.J. Risk of de Novo Bullous Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Following Transplantation: A Global Wide-scale Cohort Study. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, e231–e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, D.F.; Joly, P.; Werth, V.P.; Ujiie, H.; Worm, M.; Mangold, A.R.; Avetisova, E.; Maloney, J.; Laws, E.; Mortensen, E.; et al. Study Design of a Phase 2/3 Randomized Controlled Trial of Dupilumab in Adults with Bullous Pemphigoid: LIBERTY-BP ADEPT. Adv. Ther. 2024, 41, 2991–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, G. Genetic Predisposition to Bullous Pemphigoid. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 100, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M.; Mori, T.; Shiobara, S.; Harada, M.; Yoshida, T.; Matsuda, T.; Hattori, K.; Mizoguchi, H.; Sullivan, K.M.; Witherspoon, R.P. DEVELOPMENT OF BULLOUS PEMPHIGOLD AFTER ALLOGENEIC BONE MARROW TRANSPLANTATION Report of a Case. Transplantation 1986, 42, 320–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacour, J.P.; Adrien, A.; Gratecos, N.; Pesce, A.; Dujardin, P.; Ortonne, J.P. Bullous pemphigoid following graft-versus-host reaction after bone marrow allograft. Presse Med. 1988, 17, 1367–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Delbaldo, C.; Rieckhoff-Cantoni, L.; Helg, C.; Saurat, J.H. Bullous Pemphigoid Associated with Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease after Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1992, 10, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, A. Tense Blisters After Bone Marrow Transplantation. Arch. Dermatol. 1999, 135, 81-c–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabolcs, P.; Reese, M.; Yancey, K.; Hall, R.; Kurtzberg, J. Combination Treatment of Bullous Pemphigoid with Anti-CD20 and Anti-CD25 Antibodies in a Patient with Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002, 30, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nagai, H.; Shirakata, Y.; Midorikawa, K.; Murakami, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Komai, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Narumi, H.; Fujita, S. A Case of Bullous Pemphigoid Associated with Graft Versus Host Disease. Nishinihon J. Dermatol. 2004, 66, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasuji, A.; Matsushita, Y.; Oishi, N.; Kaji, T.; Takata, M. Bullous Pemphigoid after Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation. Rinsho Derma 2004, 46, 1823–1826. [Google Scholar]
- Izumi, R.; Fujimoto, M.; Yazawa, N.; Nakashima, H.; Asashima, N.; Watanabe, R.; Kuwano, Y.; Kurokawa, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Tamaki, K. Bullous Pemphigoid Positive for Anti-BP180 and Anti-Laminin 5 Antibodies in a Patient with Graft-vs-Host Disease. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 56, S94–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, K.; Demitsu, T.; Kakurai, M.; Narita, T.; Nakai, K.; Kubota, Y.; Ishii, N.; Hashimoto, T. Detection of Apoptotic Keratinocytes in a Case of Bullous Pemphigoid Developed after Graft-versus-Host Disease. Acta Derm. Venerol. 2014, 94, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Koike, K.; Kobayashi, C.; Iijima, S.; Hashimoto, T.; Tsuchida, M. Bullous Pemphigoid after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Pediatr. Int. 2015, 57, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, R.; Bourrat, E.; Derache, A.-F.; Rivet, J.; Bagot, M.; Dalle, J.-H.; Bouaziz, J.-D. Image Gallery: Juvenile Cutaneous Chronic Graft-versus-host Disease Presenting as Bullous Pemphigoid. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamazian, S.; Simpson, C.L. Autoimmune Bullous Disease in Skin of Color: A Case Series. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, H.; Kageji, R.; Hida, Y.; Goto, T.; Ishii, N.; Hashimoto, T. Case of Pemphigoid with Antibodies to BP180 C-terminal Domain and A3 Subunit of Laminin-332 Associated with Chronic Graft-versus-host Disease. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, e447–e448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, Y.; Kageji, R.; Bekku, H.; Ishii, N. Anti-Laminin 332 Antibodies in Graft-versus-Host Disease-Associated Bullous Pemphigoid after Allogeneic Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation. Dermatol. Online J. 2023, 29, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Zhang, Z. Adaptive and Innate Immune Pathogenesis of Bullous Pemphigoid: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1144429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiser, R.; Sarantopoulos, S.; Blazar, B.R. B-Cell Targeting in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. Blood 2018, 131, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, A.; Alsuliman, A.; Basar, R.; Sobieski, C.; Kondo, K.; Alousi, A.M.; Szydlo, R.; Muftuoglu, M.; Shaim, H.; Apperley, J.F.; et al. Evidence for B Cell Exhaustion in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymes, S.R.; Turner, M.L.; Champlin, R.E.; Couriel, D.R. Cutaneous Manifestations of Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006, 12, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vičić, M.; Hlača, N.; Kaštelan, M.; Brajac, I.; Sotošek, V.; Prpić Massari, L. Comprehensive Insight into Lichen Planus Immunopathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Howati, A.; Thornhill, M.H.; Colley, H.E.; Murdoch, C. Immune Mechanisms in Oral Lichen Planus. Oral. Dis. 2023, 29, 1400–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinner, J.; Cunha, T.; Mayer, J.U.; Hörster, S.; Kind, P.; Didona, D.; Keber, C.; Hertl, M.; Worzfeld, T.; Juratli, H.A. Skin-Infiltrating T Cells Display Distinct Inflammatory Signatures in Lichen Planus, Bullous Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1203776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maronese, C.A.; Cassano, N.; Genovese, G.; Foti, C.; Vena, G.A.; Marzano, A.V. The Intriguing Links between Psoriasis and Bullous Pemphigoid. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManigle, W.; Youssef, A.; Sarantopoulos, S. B Cells in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. Hum. Immunol. 2019, 80, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimabukuro-Vornhagen, A.; Hallek, M.J.; Storb, R.F.; von Bergwelt-Baildon, M.S. The Role of B Cells in the Pathogenesis of Graft-versus-Host Disease. Blood 2009, 114, 4919–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Shao, S.; Xue, K.; Yuan, X.; Qiao, P.; Zhang, J.; Cao, T.; Luo, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, W.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Contribute to Immune Dysregulation in Bullous Pemphigoid via Inducing B-Cell Differentiation and Antibody Production. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkani, N.; Joly, P.; Golinski, M.-L.; Colliou, N.; Lim, A.; Larbi, A.; Riou, G.; Caillot, F.; Bernard, P.; Bedane, C.; et al. B-Cell Depletion Induces a Shift in Self Antigen Specific B-Cell Repertoire and Cytokine Pattern in Patients with Bullous Pemphigoid. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giomi, B.; Caproni, M.; Calzolari, A.; Bianchi, B.; Fabbri, P. Th1, Th2 and Th3 Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Bullous Pemphigoid. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2002, 30, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Floc’h, A.; Allinne, J.; Nagashima, K.; Scott, G.; Birchard, D.; Asrat, S.; Bai, Y.; Lim, W.K.; Martin, J.; Huang, T.; et al. Dual Blockade of IL-4 and IL-13 with Dupilumab, an IL-4Rα Antibody, Is Required to Broadly Inhibit Type 2 Inflammation. Allergy 2020, 75, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Kong, L.; Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Gao, Y. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab for Severe Bullous Pemphigoid: A Prospective Cohort Study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 125, 111157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mohammadpour, H.; Cao, X. Targeting Cytokines in GVHD Therapy. J. Immunol. Res. Ther. 2017, 2, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Girolomoni, G.; Pincelli, C.; Zambruno, G.; Andreani, M.; Giardini, C.; Lucarelli, G.; Giannetti, A. Immunohistochemistry of Cutaneous Graft-versus-Host Disease after Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation. J. Dermatol. 1991, 18, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, M.S.; Storb, R.; Jones, E.; Weiden, P.L.; Shulman, H.; Witherspoon, R.; Atkinson, K.; Thomas, E.D. Deposition of IgM and Complement at the Dermoepidermal Junction in Acute and Chronic Cutaneous Graft-vs-Host Disease in Man. J. Immunol. 1978, 120, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurat, J.H.; Bonnetblanc, J.M.; Gluckman, E.; Didierjean, L.; Bussell, A.; Puissant, A. Skin Antibodies in Bone Marrow Transplanted Patients. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1976, 1, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pozo, J.; García-Silva, J.; Yebra-Pimentel, M.T. Chronic graft-versus-host disease presenting as bullous lesions. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2008, 99, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghohestani, R.; Kanitakis, J.; Nicolas, J.F.; Cozzani, E.; Claudy, A. Comparative Sensitivity of Indirect Immunofluorescence to Immunoblot Assay for the Detection of Circulating Antibodies to Bullous Pemphigoid Antigens 1 and 2. Br. J. Dermatol. 1996, 135, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakioulaki, M.; Eyerich, K.; Patsatsi, A. Advancements in Bullous Pemphigoid Treatment: A Comprehensive Pipeline Update. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2024, 25, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, L.; Lu, J.; Shi, Y. Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Autoimmune Bullous Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1220887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, A.L.; Hatami, A.; Kokta, V.; Dalle, J.H.; Champagne, M.A.; Duval, M. Successful Anti-CD20 Antibody Treatment of Pemphigus Foliaceus after Unrelated Cord Blood Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005, 35, 427–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Gmür, J.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita, a Rare Late Complication of Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation? Bone Marrow Transplant. 1992, 9, 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Leverkus, M.; Schmidt, E.; Lazarova, Z.; Bröcker, E.-B.; Yancey, K.B.; Zillikens, D. Antiepiligrin Cicatricial Pemphigoid: An. Underdiagnosed Entity Within the Spectrum of Scarring Autoimmune Subepidermal Bullous Diseases? Arch. Dermatol. 1999, 135, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisa, Y.; Mori, T.; Nakazato, T.; Yamazaki, R.; Yamagami, J.; Amagai, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Okamoto, S. Cicatricial Pemphigoid of the Oropharynx after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Relapsed Follicular Lymphoma. Int. J. Hematol. 2005, 82, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahara, M.; Tsuji, G.; Ishii, N.; Dainichi, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Kohno, K.; Kamezaki, K.; Nagafuji, K.; Takeuchi, S.; Moroi, Y.; et al. Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid with Antibodies to the Beta(3) Subunit of Laminin 332 in a Patient with Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia and Graft-versus-Host Disease. Dermatology 2009, 219, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Lim, Z.Y.; Benton, E.; du Vivier, A.; Bhogal, B.; Mufti, G.J.; Pagliuca, A. Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid Following Reduced Intensity Conditioning Allogeneic Haematopoietic SCT for Biphenotypic Leukaemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010, 45, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masunaga, K.; Toyoda, M.; Kokuba, H.; Takahara, M.; Ohyama, B.; Hashimoto, T.; Furue, M. Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid with Antibodies to the Β3 Subunit of Laminin 332. J. Dermatol. 2011, 38, 1082–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, R.; Fujimoto, N.; Kito, K.; Uchiyama, K.; Koga, H.; Hodohara, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Fujiyama, Y.; Tanaka, T. Refractory Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid Which Developed after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation and Was Successfully Treated with Rituximab. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2013, 23, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, N.; Ibusuki, A.; Higashi, Y.; Ishii, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Yoshimitsu, M.; Kanekura, T. Anti-Laminin-332-Type Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid in a Patient with Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma and Graft-versus-Host Disease. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, e300–e301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, S.B.; Vasu, S.; Kaffenberger, B.H. Epitope Spread in Chronic Mucosal GVHD: Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid Resolution with Rituximab. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, 240–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultewolter, T.; Goos, M.; Dissemond, J. Linear IgA Dermatosis in an Immunosuppressed Patient after Allogenic Bone Marrow Transplantation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2004, 18, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainichi, T.; Chow, Z.; Kabashima, K. IgG4, Complement, and the Mechanisms of Blister Formation in Pemphigus and Bullous Pemphigoid. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).