Double-Puncture Arthrocentesis in Arthrogenous TMJ Disorders: Bioviscosupplementation vs. Viscosupplementation a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Outcome Evaluation
2.3. Randomization
2.4. Treatment Protocol
2.4.1. Double-Puncture TMJ Arthrocentesis Under Local Anesthesia
2.4.2. Hyaluronic Acid and Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation
2.4.3. Hyaluronic Acid and Platelet-Rich Plasma Administration
2.5. Statistical Analysis
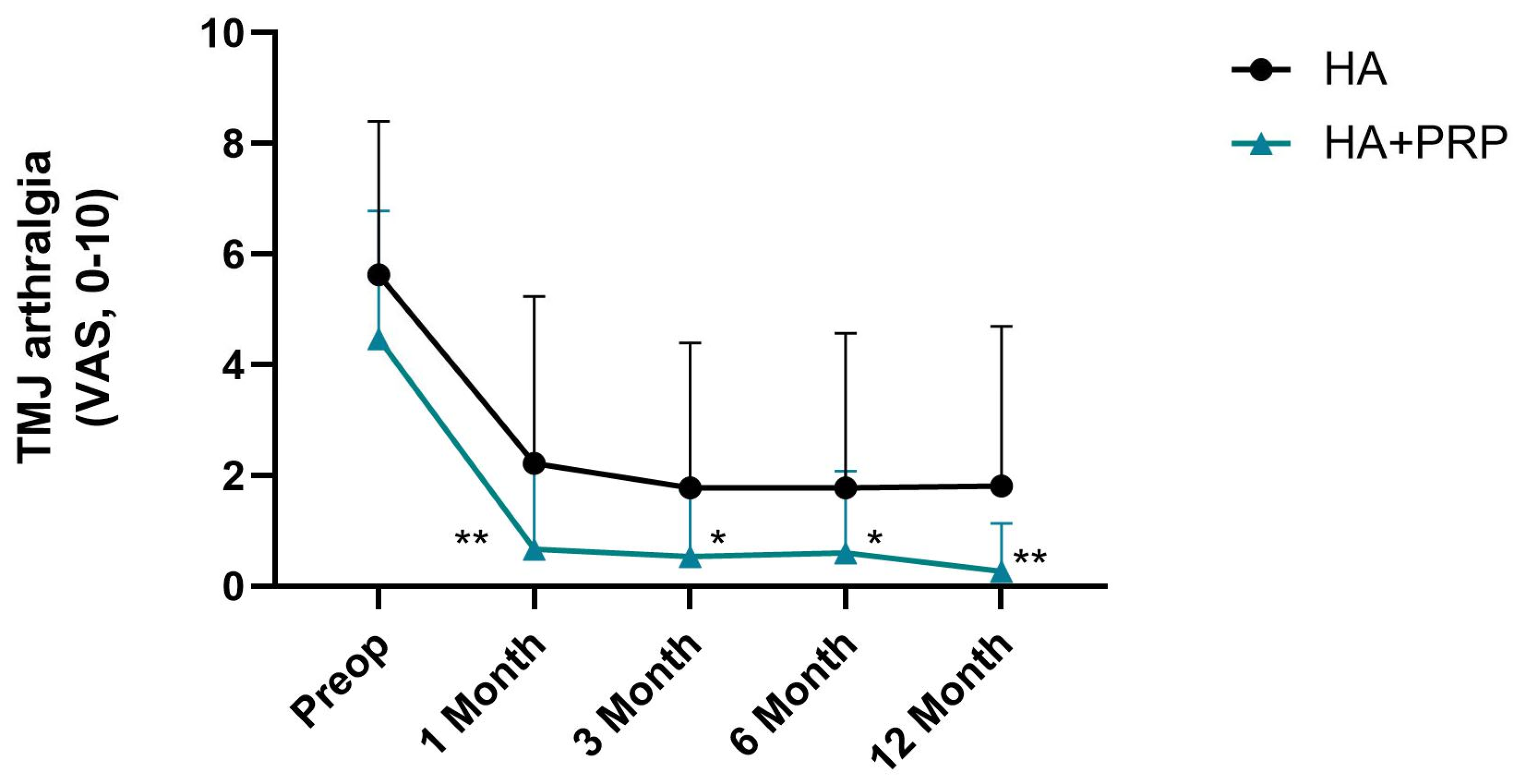
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Temporomandibular Disorders: Priorities for Research and Care; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; p. 426. [Google Scholar]
- Zieliński, G.; Pająk-Zielińska, B.; Ginszt, M. A Meta-Analysis of the Global Prevalence of Temporomandibular Disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Schiffman, E.L. Temporomandibular Joint Disorders and Orofacial Pain. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 60, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikora, M.; Sielski, M.; Chęciński, M.; Nowak, Z.; Czerwińska-Niezabitowska, B.; Chlubek, D. Repeated Intra-Articular Administration of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Temporomandibular Disorders: A Clinical Case Series. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ângelo, D.F.; Sanz, D.; Cardoso, H.J. Effectiveness of double-puncture temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis with viscosupplementation in different categories of severity—A prospective study. J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 2023, 51, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlawar, A.N.; Mundada, B.P. Enhancing Pain Relief in Temporomandibular Joint Arthrocentesis: Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid Synergy. Cureus 2023, 15, e45646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagori, S.A.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Rangarajan, H.; Kulkarni, V.; Roychoudhury, A. Does intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma/platelet-rich fibrin improve outcomes after temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 62, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelemen, K.; König, J.; Váncsa, S.; Szabó, B.; Hegyi, P.; Gerber, G.; Schmidt, P.; Hermann, P. Efficacy of different intraarticular injection materials in the arthrocentesis of arthrogenic temporomandibular disorders: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2025, 69, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.C.; Lall, R.; Srivastava, A.; Sinha, A. Hyaluronic Acid: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Trajectory. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Tominaga, K.; Takano, H.; Ariyoshi, W.; Habu, M.; Fukuda, J.; Maeda, H. A decrease in the molecular weight of hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid from patients with temporomandibular disorders. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2004, 33, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, T.M. Hyaluronan and synovial joint: Function, distribution and healing. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2013, 6, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, Y.T.; Altıntas, N.Y.; Korkmaz, F.M.; Candırlı, C.; Coskun, U.; Durmuslar, M.C. Is Hyaluronic Acid Injection Effective for the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Disc Displacement With Reduction? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Czerwińska-Niezabitowska, B.; Chęciński, M.A.; Sielski, M.; Chlubek, D. Short-Term Effects of Intra-Articular Hyaluronic Acid Administration in Patients with Temporomandibular Joint Disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiato, M.C.; da Silva, E.V.; de Medeiros, R.A.; Túrcio, K.H.; Dos Santos, D.M. Are intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid effective for the treatment of temporomandibular disorders? A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldez, M.A.; Camones, V.R.; Ramos, G.E.; Padilla, M.; Enciso, R. Effectiveness of Intra-Articular Injections of Sodium Hyaluronate or Corticosteroids for Intracapsular Temporomandibular Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2018, 32, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, V.; Ciric, M.; Jovanovic, V.; Stojanovic, P. Platelet Rich Plasma: A short overview of certain bioactive components. Open Med. 2016, 11, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Chen, L.; Chu, J.; Wu, H. Platelet Rich Plasma in the Repair of Articular Cartilage Injury: A Narrative Review. Cartilage 2022, 13, 19476035221118419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihut, M.; Gala, A. The Application of Intra-Articulr Injections for Management of the Consequences of Disc Displacement without Reduction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xu, P.; Huang, G.; Liu, L. Clinical therapy of hyaluronic acid combined with platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadpour, N.; Shooshtari, Z.; Kazemian, M.; Gholami, M.; Vatanparast, N.; Samieirad, S. Combined Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid can Reduce Pain in Patients Undergoing Arthrocentesis for Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 1474–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harba, A.N.; Harfoush, M. Evaluation of the participation of hyaluronic acid with platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of temporomandibular joint disorders. Dent. Med. Probl. 2021, 58, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sielski, M.; Chęcińska, K.; Turosz, N.; Chęciński, M.; Sikora, M. Single intra-articular administration of injectable platelet-rich fibrin (I-PRF) in alleviating temporomandibular joint pain: A pilot clinical trial. Dent. Med. Probl. 2025, 62, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitroulis, G. A new surgical classification for temporomandibular joint disorders. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 42, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, E.; Ohrbach, R.; Truelove, E.; Look, J.; Anderson, G.; Goulet, J.-P.; List, T.; Svensson, P.; Gonzalez, Y.; Lobbezoo, F.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders (DC/TMD) for Clinical and Research Applications. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2014, 28, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derwich, M.; Mitus-Kenig, M.; Pawlowska, E. Mechanisms of Action and Efficacy of Hyaluronic Acid, Corticosteroids and Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A. Arthrocentesis of Temporomandibular Joint- Bridging the Gap Between Non-Surgical and Surgical Treatment. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 9, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichera, G.; Polizzi, A.; Scapellato, S.; Palazzo, G.; Indelicato, F. Craniomandibular Disorders in Pregnant Women: An Epidemiological Survey. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, E.L.; Ohrbach, R.; Truelove, E.L.; Tai, F.; Anderson, G.C.; Pan, W.; Gonzalez, Y.M.; John, M.T.; Sommers, E.; List, T.; et al. The Research Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders. V: Methods used to establish and validate revised Axis I diagnostic algorithms. J. Orofac. Pain 2010, 24, 63–78. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, G.Z.; Manuguerra, M.; Chow, R. How to analyze the Visual Analogue Scale: Myths, truths and clinical relevance. Scand. J. Pain 2016, 13, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, L.; Westesson, P.L. Discectomy as an effective treatment for painful temporomandibular joint internal derangement: A 5-year clinical and radiographic follow-up. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 59, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ângelo, D.F.; Lopes, C.S.; Sanz, D.; Faria-Teixeira, M.C.; Marques, R.; Maffia, F.; Cardoso, H.J. Temporomandibular Joint Minimally Invasive Procedures in the Pediatric Population: A Prospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, T.; Singh, R.K.; Mohammad, S.; Pal, U.S.; Mahdi, A.A.; Kumar, M. Efficacy of arthrocentesis versus arthrocentesis with sodium hyaluronic acid in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: A comparison. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 8, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomello, M.; Mortellaro, C.; Viganoni, C.; Crimella, A.; Fossati, J.; Lauritano, D. PRGF® endoret injections for temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis treatment: A one-year follow-up. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giacomello, M.; Giacomello, A.; Mortellaro, C.; Gallesio, G.; Mozzati, M. Temporomandibular joint disorders treated with articular injection: The effectiveness of plasma rich in growth factors-Endoret. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2015, 26, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrella, R.J. Hyaluronic acid for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: Long-term outcomes from a naturalistic primary care experience. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 84, 278–283, quiz 284, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, G.; Gawda, P. Defining Effect Size Standards in Temporomandibular Joint and Masticatory Muscle Research. Med. Sci. Monit. 2025, 31, e948365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Feinn, R. Using Effect Size-or Why the P Value Is Not Enough. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, A.F.; Hameed, H.; Hassaneen, A.M.; Hyder, A. Synergistic effect of platelet rich plasma with hyaluronic acid injection following arthrocentesis to reduce pain and improve function in TMJ osteoarthritis. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmotti, A.; Bruzzone, M.; Bonasia, D.E.; Castoldi, F.; Rossi, R.; Piras, L.; Maiello, A.; Realmuto, C.; Peretti, G.M. One-step osteochondral repair with cartilage fragments in a composite scaffold. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2012, 20, 2590–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E. Plasma rich in growth factors: Preliminary results of use in the preparation of future sites for implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1999, 14, 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Everts, P.A.; Knape, J.T.; Weibrich, G.; Schönberger, J.P.; Hoffmann, J.; Overdevest, E.P.; Box, H.A.; van Zundert, A. Platelet-rich plasma and platelet gel: A review. J. Extra-Corpor. Technol. 2006, 38, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, M.R.; Thomas, R.; Shah, R.; Gowda, I.; Gowda, T.M. Comparison of the angiogenic efficacy of conventional leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin versus low-speed advanced platelet-rich fibrin: An in vitro chorioallantoic membrane assay study. Dent. Med. Probl. 2024, 61, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nordenflycht, D.; Tesch, R.S. Advantages of ultrasound guidance for TMJ arthrocentesis and intra-articular injection: A narrative review. Dent. Med. Probl. 2022, 59, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolba, Y.M.; Omar, S.S.; Nagui, D.A.; Nawwar, M.A. Effect of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid in treatment of osteoarthritic temporomandibular joints of rats. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2020, 110, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, M.; Ortega-Mata, D.; Tamez-Mata, Y.; Olivo, C.A.A.; Vilchez-Cavazos, F. Comparison of the clinical effectiveness of activated and non-activated platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader-Ruiz, J.; Beitia, M.; Delgado, D.; Sánchez, P.; Porras, B.; Gimeno, I.; González, S.; Benito-Lopez, F.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Sánchez, M. Current Challenges in the Development of Platelet-Rich Plasma-Based Therapies. BioMed Res. Int. 2024, 2024, 6444120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitzan, D.W.; Price, A. The use of arthrocentesis for the treatment of osteoarthritic temporomandibular joints. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 59, 1154–1159, discussion 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diraçoğlu, D.; Saral, I.B.; Keklik, B.; Kurt, H.; Emekli, U.; Ozçakar, L.; Karan, A.; Aksoy, C. Arthrocentesis versus nonsurgical methods in the treatment of temporomandibular disc displacement without reduction. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2009, 108, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Moraissi, E.A.; Wolford, L.M.; Ellis, E., 3rd; Neff, A. The hierarchy of different treatments for arthrogenous temporomandibular disorders: A network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 2020, 48, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chęciński, M.; Chęcińska, K.; Turosz, N.; Brzozowska, A.; Chlubek, D.; Sikora, M. Current Clinical Research Directions on Temporomandibular Joint Intra-Articular Injections: A Mapping Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cömert Kiliç, S.; Güngörmüş, M. Is arthrocentesis plus platelet-rich plasma superior to arthrocentesis plus hyaluronic acid for the treatment of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: A randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, A.F.; Ali, H.E.; Elmasry, M.; Khallaf, M.G. Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection as an Effective Treatment for Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 1706–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosgor, H. Is arthrocentesis plus hyaluronic acid superior to arthrocentesis alone in the treatment of disc displacement without reduction in patients with bruxism? J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 2020, 48, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Successful | No pain or only mild pain level (0–2 on a 0–10 VAS) and MMO ≥ 35 mm |
| Acceptable | No pain or only mild pain level (VAS ≤ 2 on a 0–10 scale) and MMO ≥ 30 mm and < 35 mm |
| Failure | Pain constant or moderate (3–10 on a 0–10 VAS) and/or MMO ≤ 30 mm |
| Total (n = 46) (83 Joints) | HA (n = 23) (38 Joints) | HA+PRP (n = 23) (45 Joints) | p, Cramér’s V or Cohen’s r [95% CI] r or V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic data | ||||
| Age M ± SD | 45.83 ± 20.62 | 46.87 ± 23.12 | 44.78 ± 18.25 | 0.84, 0.03 [−0.26, 0.32] |
| Sex (F) | 33 (71.74%) | 15 (65.22%) | 18 (78.26%) | 0.51, 0.15 [−0.15, 0.42] |
| Diagnosis | ||||
| Osteoarthrosis | 83 (100.00%) | 38 (100.00%) | 45 (100.00%) | 1.00, 0.00 [0.00, 0.00] |
| Arthralgia | 40 (48.19%) | 19 (50.00%) | 21 (46.67%) | 0.83, 0.01 [−0.21, 0.22] |
| DDwR | 32 (38.55%) | 15 (39.47%) | 17 (37.78%) | 0.99, 0.01 [−0.21, 0.22] |
| DDwoR | 29 (34.94%) | 16 (42.11%) | 13 (28.89%) | 0.25, 0.12 [−0.09, 0.33] |
| Osteophytes | 5 (6.02%) | 2 (5.26%) | 3 (6.67%) | 0.99, 0.05 [−0.17, 0.26] |
| Disc Perforation | 3 (3.61%) | 2 (5.26%) | 1 (2.22%) | 0.51, 0.08 [−0.14, 0.29] |
| Condylar Resorption | 3 (3.61%) | 2 (5.26%) | 1 (2.22%) | 0.51, 0.08 [−0.14, 0.29] |
| Success Rate | Need for Reintervention | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success: Acceptable N (%) | Failure N (%) | p, Cramér’s V | N (%) | p, Cramér’s V | |
| HA | 15 (65.22%) | 8 (34.78%) | 0.047, 0.32 | 8 (34.78%) | 0.047, 0.32 |
| HA+PRP | 22 (95.65%) | 1 (4.35%) | [0.24–0.33] | 1 (4.35%) | [0.24–0.33] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ângelo, D.F.; Cardoso, H.J.; Sanz, D.; Maffia, F.; Sarkis, M.; Mota, B.; Salvado, F. Double-Puncture Arthrocentesis in Arthrogenous TMJ Disorders: Bioviscosupplementation vs. Viscosupplementation a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113750
Ângelo DF, Cardoso HJ, Sanz D, Maffia F, Sarkis M, Mota B, Salvado F. Double-Puncture Arthrocentesis in Arthrogenous TMJ Disorders: Bioviscosupplementation vs. Viscosupplementation a Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113750
Chicago/Turabian StyleÂngelo, David Faustino, Henrique José Cardoso, David Sanz, Francesco Maffia, Marcella Sarkis, Beatriz Mota, and Francisco Salvado. 2025. "Double-Puncture Arthrocentesis in Arthrogenous TMJ Disorders: Bioviscosupplementation vs. Viscosupplementation a Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113750
APA StyleÂngelo, D. F., Cardoso, H. J., Sanz, D., Maffia, F., Sarkis, M., Mota, B., & Salvado, F. (2025). Double-Puncture Arthrocentesis in Arthrogenous TMJ Disorders: Bioviscosupplementation vs. Viscosupplementation a Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3750. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113750








