Mentalizing, Loneliness and Pain-Related Depressive Symptoms Are Associated with Pain Severity in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: Results of a Cross-Sectional Secondary Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Procedures
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Mentalization Questionnaire (MZQ)
2.2.2. Pain Related Depressive Symptoms
2.2.3. UCLA Loneliness Scale
2.2.4. Pain Severity
2.2.5. Clinical Data
2.3. Statistical Procedures
3. Results
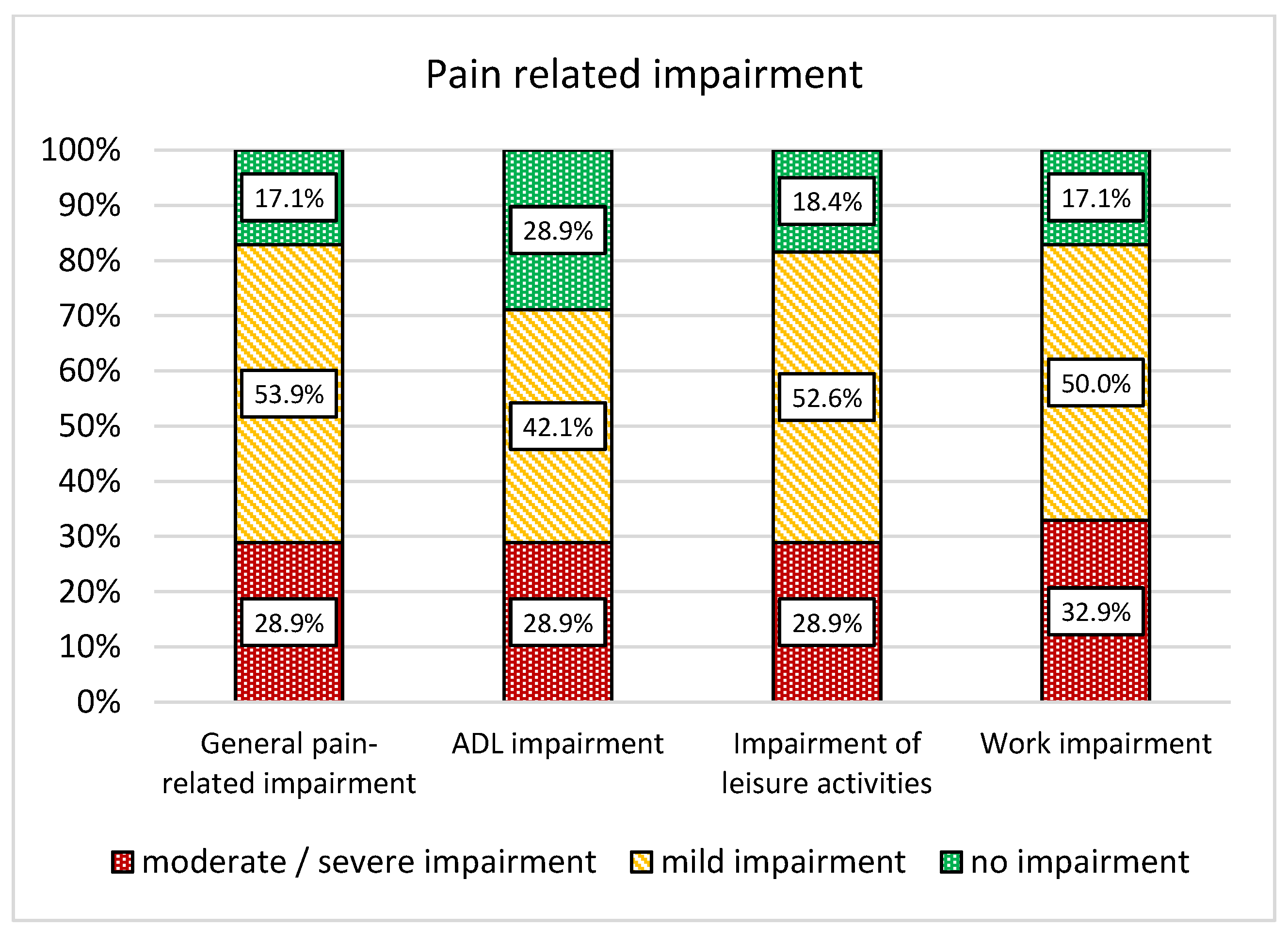
3.1. Baseline Association of Loneliness, Pain-Related Depressive Symptoms, Pain Severity and Mentalizing
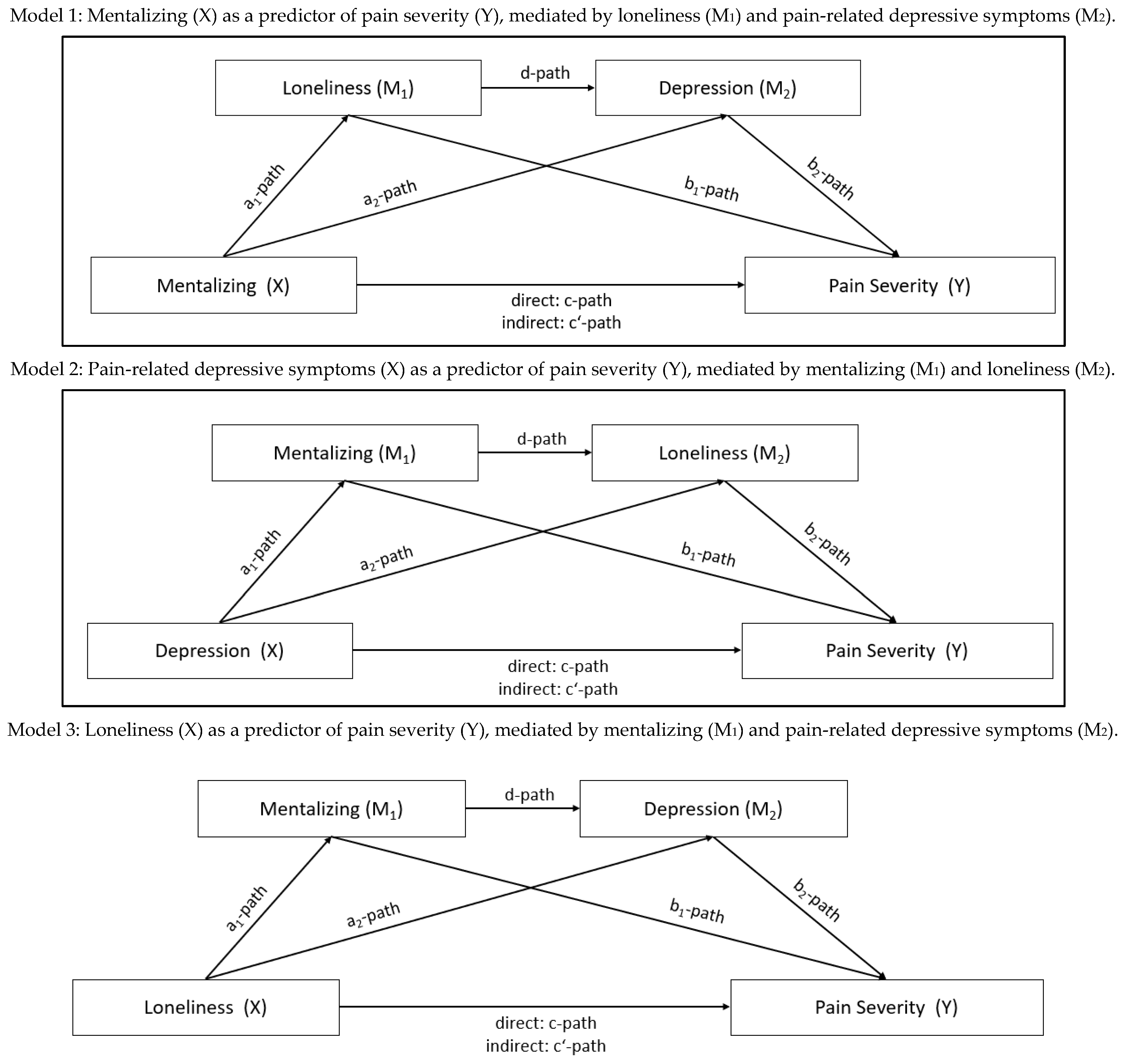
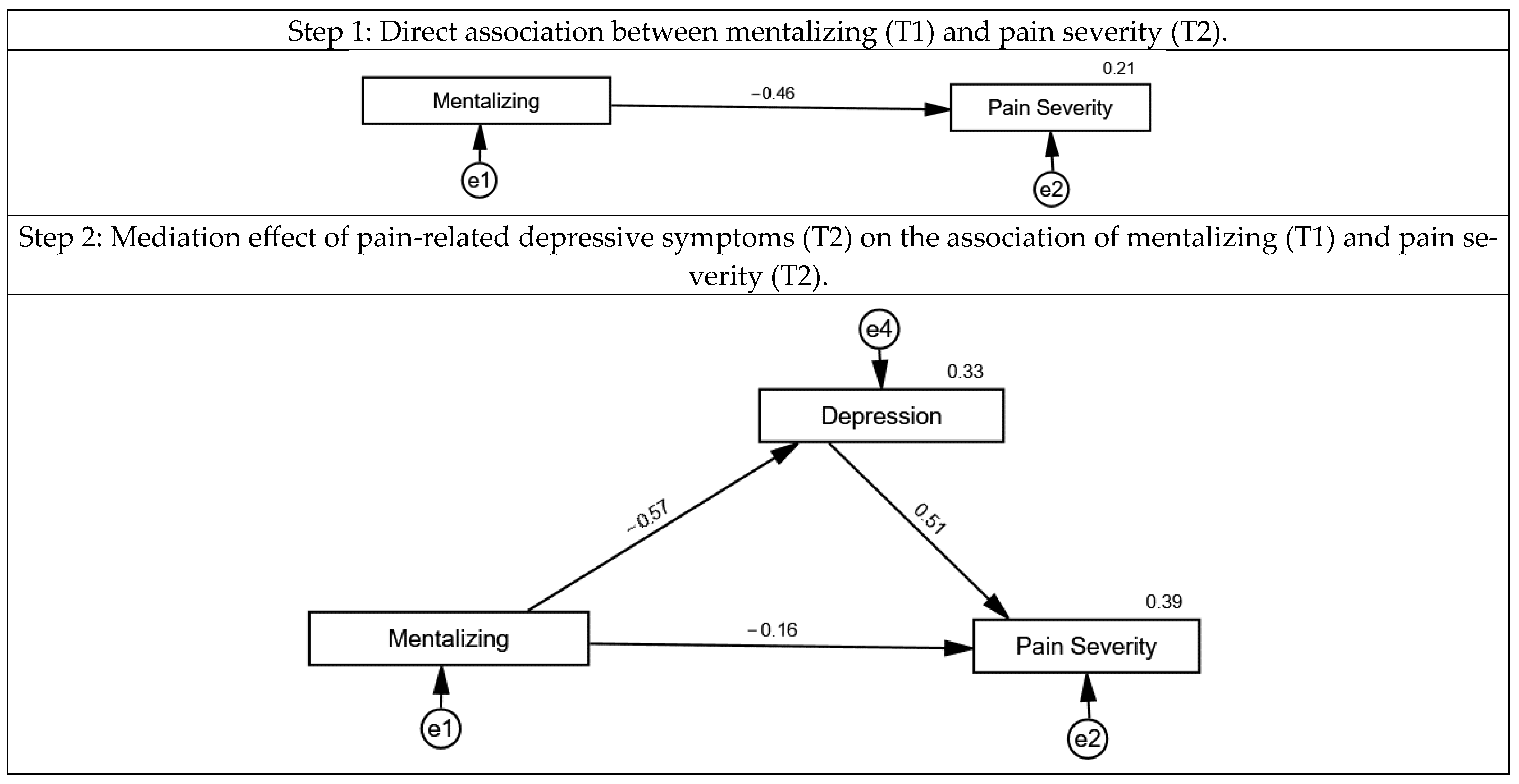
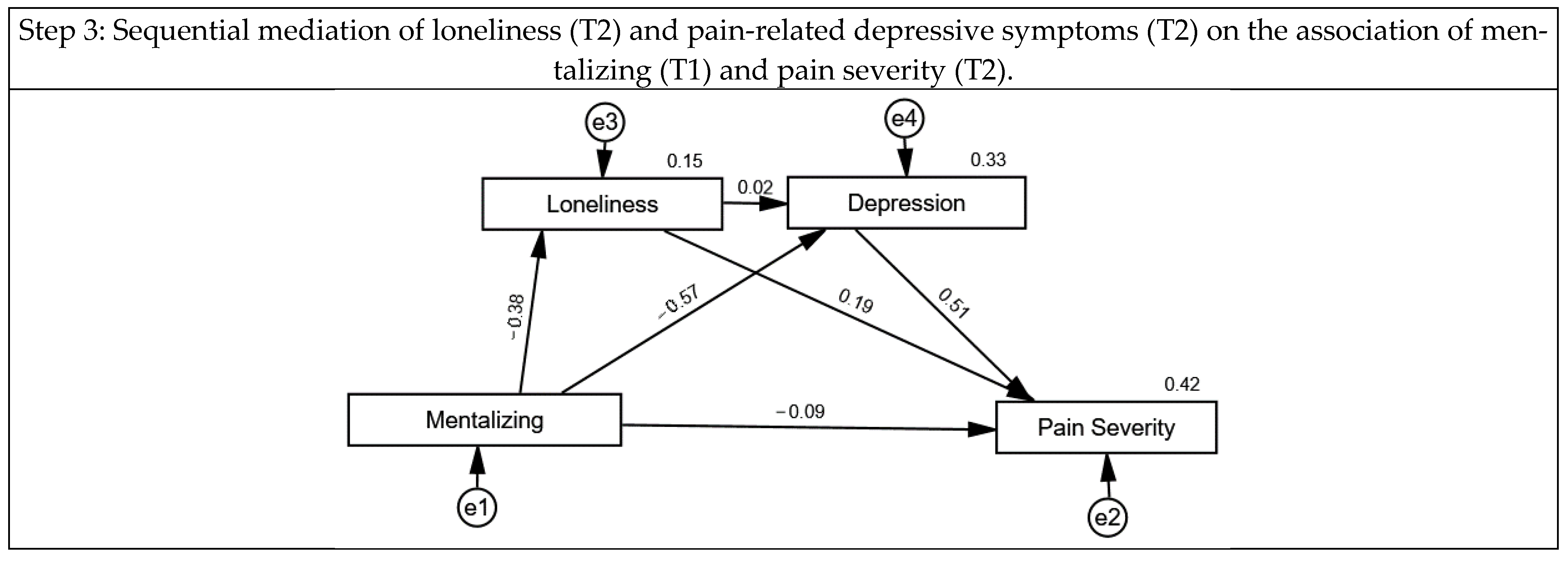
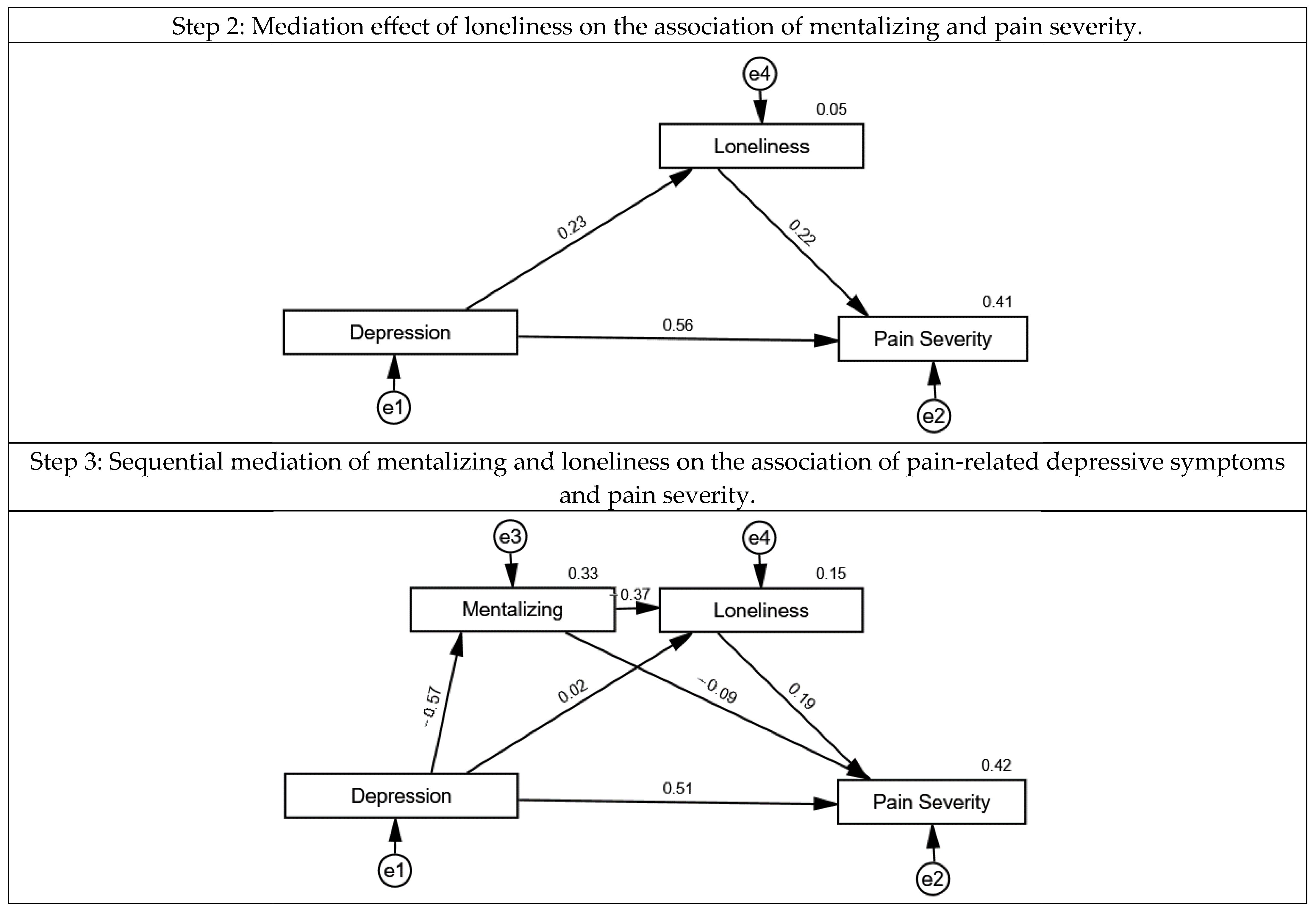
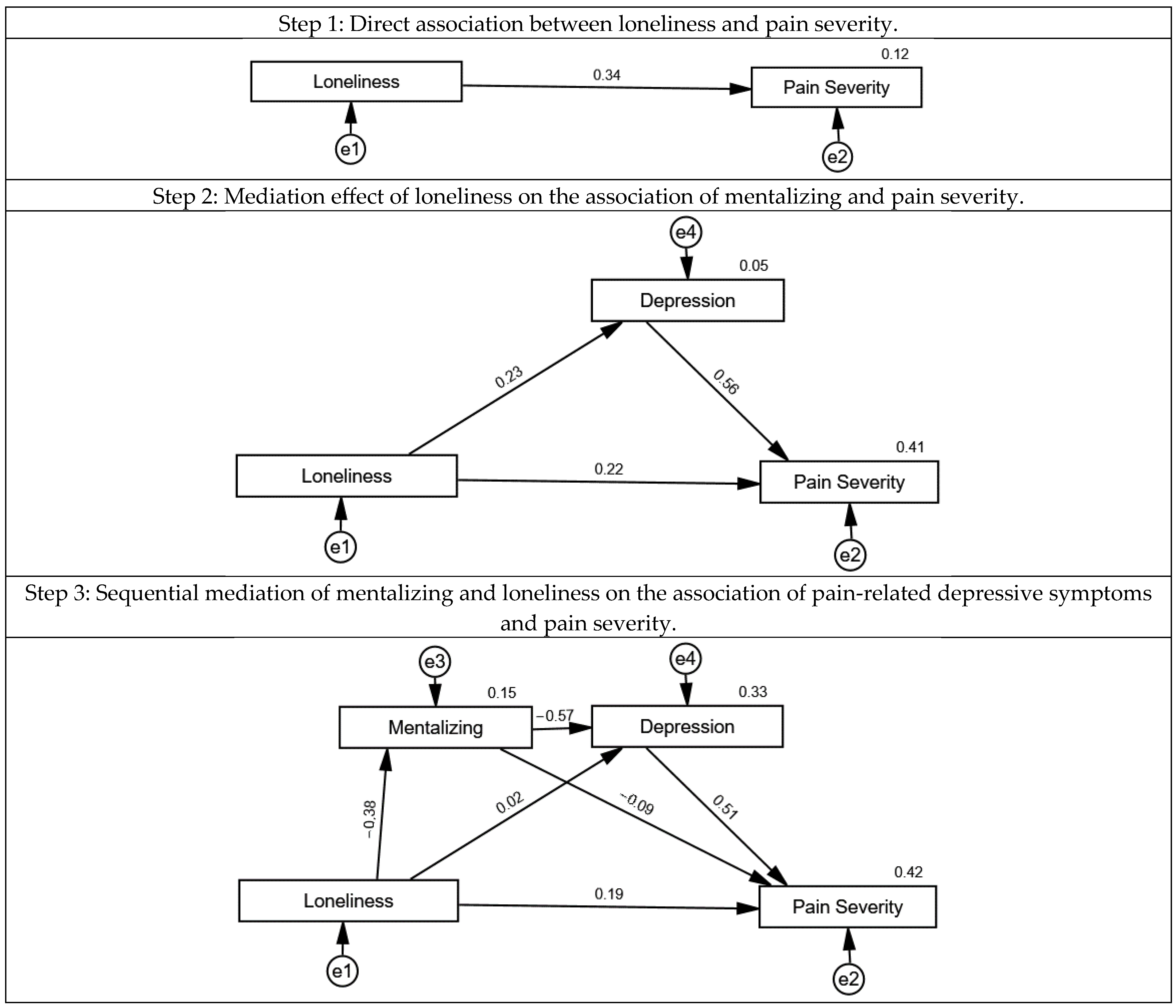
3.2. The Association of Mentalizing, Loneliness, Pain-Related Depressive Symptoms and Pain Severity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zis, P.; Daskalaki, A.; Bountouni, I.; Sykioti, P.; Varrassi, G.; Paladini, A. Depression and chronic pain in the elderly: Links and management challenges. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, M.; Smith, E.; Hoy, D.; Carmona, L.; Wolfe, F.; Vos, T.; Williams, B.; Gabriel, S.; Lassere, M.; Johns, N.; et al. The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: Estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelin, E.; Callahan, L.F. The economic cost and social and psychological impact of musculoskeletal conditions. National Arthritis Data Work Groups. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallerand, I.A.; Patten, S.B.; Barnabe, C. Depression and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.R.; Cahalan, C.; Mensing, G.; Smith, M.; Haythornthwaite, J.A. Pain, catastrophizing, and depression in the rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IsHak, W.W.; Wen, R.Y.; Naghdechi, L.; Vanle, B.; Dang, J.; Knosp, M.; Dascal, J.; Marcia, L.; Gohar, Y.; Eskander, L.; et al. Pain and Depression: A Systematic Review. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2018, 26, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.J.; Van Drunen, S.; Egorova-Brumley, N. Neural correlates of co-occurring pain and depression: An activation-likelihood estimation (ALE) meta-analysis and systematic review. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaremka, L.M.; Fagundes, C.P.; Glaser, R.; Bennett, J.M.; Malarkey, W.B.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Loneliness predicts pain, depression, and fatigue: Understanding the role of immune dysregulation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaremka, L.M.; Andridge, R.R.; Fagundes, C.P.; Alfano, C.M.; Povoski, S.P.; Lipari, A.M.; Agnese, D.M.; Arnold, M.W.; Farrar, W.B.; Yee, L.D.; et al. Pain, depression, and fatigue: Loneliness as a longitudinal risk factor. Health Psychol. Off. J. Div. Health Psychol. Am. Psychol. Assoc. 2014, 33, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, V.D.; Kumar, N.; Galecki, A.T.; Kabeto, M.; Clauw, D.J.; Williams, D.A.; Hassett, A.; Silveira, M.J. Bad company: Loneliness longitudinally predicts the symptom cluster of pain, fatigue, and depression in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2022, 70, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Colebaugh, C.A.; Meints, S.M.; Flowers, K.M.; Edwards, R.R.; Schreiber, K.L. Loneliness and Pain Catastrophizing Among Individuals with Chronic Pain: The Mediating Role of Depression. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 2939–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, S.; Schiller, J.; Gross, E.B. Felt Understanding and Misunderstanding Affect the Perception of Pain, Slant, and Distance. Soc. Psychol. Personal. Sci. 2012, 4, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Hawkley, L.C.; Thisted, R.A. Perceived social isolation makes me sad: 5-year cross-lagged analyses of loneliness and depressive symptomatology in the Chicago Health, Aging, and Social Relations Study. Psychol. Aging 2010, 25, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkley, L.C.; Preacher, K.J.; Cacioppo, J.T. Loneliness impairs daytime functioning but not sleep duration. Health Psychol. Off. J. Div. Health Psychol. Am. Psychol. Assoc. 2010, 29, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.F.; Gilbody, S.; Atkin, K.; van der Feltz-Cornelis, C. The associations between loneliness, social exclusion and pain in the general population: A N = 502,528 cross-sectional UK Biobank study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 130, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberger, N.I. The pain of social disconnection: Examining the shared neural underpinnings of physical and social pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberger, N.I.; Lieberman, M.D.; Williams, K.D. Does rejection hurt? An FMRI study of social exclusion. Science 2003, 302, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourriyahi, H.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Saghazadeh, A.; Rezaei, N. Loneliness: An Immunometabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Cacioppo, S.; Capitanio, J.P.; Cole, S.W. The neuroendocrinology of social isolation. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2015, 66, 733–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, M.J.; Robinson, R.L.; Katon, W.; Kroenke, K. Depression and Pain Comorbidity: A Literature Review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 2433–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Cacioppo, S. The growing problem of loneliness. Lancet 2018, 391, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulincer, M.; Shaver, P.R. An Attachment Perspective on Loneliness. In The Handbook of Solitude; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Innamorati, M.; Imperatori, C.; Harnic, D.; Erbuto, D.; Patitucci, E.; Janiri, L.; Lamis, D.A.; Pompili, M.; Tamburello, S.; Fabbricatore, M. Emotion Regulation and Mentalization in People at Risk for Food Addiction. Behav. Med. 2017, 43, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubner, S.; Fonagy, P.; Bateman, A. Mentalisierungsbasierte Theraoie; Hogrefe: Göttingen, Germany, 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, A.; Fonagy, P. Handbook of Mentalizing in Mental Health Practice; American Psychiatric Publishing Inc.: Arlington, TX, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Probst, T.; Dehoust, M.; Brütt, A.L.; Schulz, H.; Pieh, C.; Andreas, S. Mentalization and Self-Efficacy as Mediators between Psychological Symptom Severity and Disabilities in Activities and Participation in Psychotherapy Patients. Psychopathology 2018, 51, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.; Fonagy, P. The development of an attachment-based treatment program for borderline personality disorder. Bull. Menn. Clin. 2003, 67, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, A.; Fonagy, P. Effectiveness of partial hospitalization in the treatment of borderline personality disorder: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, A.; Fonagy, P. 8-year follow-up of patients treated for borderline personality disorder: Mentalization-based treatment versus treatment as usual. Am. J. Psychiatry 2008, 165, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Kern, M.; Fonagy, P.; Kapusta, N.D.; Luyten, P.; Boss, S.; Naderer, A.; Blüml, V.; Leithner, K. Mentalizing in female inpatients with major depressive disorder. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2013, 201, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Kern, M.; Tmej, A. Mentalization and Depression: Theoretical Concepts, Treatment Approaches and Empirical Studies—An Overview. Z. Psychosom. Med. Psychother. 2019, 65, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Kern, M.; Tmej, A.; Naderer, A.; Zimmermann, J.; Nolte, T. Failure to resolve loss and compromised mentalizing in female inpatients with major depressive disorder. Attach. Hum. Dev. 2022, 24, 503–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubner, S.; Kessler, H.; Buchheim, A.; Kächele, H.; Staun, L. The role of mentalization in the psychoanalytic treatment of chronic depression. Psychiatry 2011, 74, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Fonagy, P.; Feigenbaum, J.; Montague, P.R.; Nolte, T. Multidirectional Pathways between Attachment, Mentalizing, and Posttraumatic Stress Symptomatology in the Context of Childhood Trauma. Psychopathology 2020, 53, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner-Skacel, J.; Riedl, D.; Kampling, H.; Lampe, A. Mentalization and dissociation after adverse childhood experiences. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cate, R.; Khademi, M.; Judd, P.; Miller, H. Deficits in mentalization: A risk factor for future development of eating disorders among pre-adolescent girls. Adv. Eat. Disord. 2013, 1, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.; Hellier, J.; Barrett, B.; Barzdaitiene, D.; Bateman, A.; Bogaardt, A.; Clare, A.; Somers, N.; O’Callaghan, A.; Goldsmith, K.; et al. The NOURISHED randomised controlled trial comparing mentalisation-based treatment for eating disorders (MBT-ED) with specialist supportive clinical management (SSCM-ED) for patients with eating disorders and symptoms of borderline personality disorder. Trials 2016, 17, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, D.; Rothmund, M.; Grote, V.; Fischer, M.J.; Kampling, H.; Kruse, J.; Nolte, T.; Labek, K.; Lampe, A. Mentalizing and epistemic trust as critical success factors in psychosomatic rehabilitation-Results of a single center longitudinal observational study. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1150422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, J.; Riedl, D.; Schirmer, M. Improved social functioning and role functioning in rheumatic patients using a non-verbal communication tool: Results from a randomized, double-blind, controlled pilot-study. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1142350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausberg, M.C.; Schulz, H.; Piegler, T.; Happach, C.G.; Klopper, M.; Brutt, A.L.; Sammet, I.; Andreas, S. Is a self-rated instrument appropriate to assess mentalization in patients with mental disorders? Development and first validation of the mentalization questionnaire (MZQ). Psychother. Res. J. Soc. Psychother. Res. 2012, 22, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, D.; Kampling, H.; Nolte, T.; Lampe, A.; Beutel, M.E.; Brähler, E.; Kruse, J. Measuring Impairments of Mentalization with the 15-Item Mentalization Questionnaire (MZQ) and Introducing the MZQ-6 Short Scale: Reliability, Validity and Norm Values Based on a Representative Sample of the German Population. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissner, E. Verarbeitung chronischer Schmerzen—Skalen zur Erfassung der Schmerzbewältigung und der schmerzbedingten psychischen Beeinträchtigung. = Coping with chronic pain—Assessment of coping strategies and distress. Z. Klin. Psychol. 1999, 28, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.; Peplau, L.A.; Ferguson, M.L. Developing a measure of loneliness. J. Pers. Assess. 1978, 42, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, N.; Bortz, J. Psychometrische Einsamkeitsforschung: Deutsche Neukonstruktion der UCLA Loneliness Scale. [Psychometric research on loneliness: A new German version of the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) Loneliness Scale.]. Diagnostica 1993, 39, 224–239. [Google Scholar]
- German Pain Association. German Pain Questionnaire. Available online: https://www.schmerzgesellschaft.de/schmerzfragebogen (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Boonstra, A.M.; Stewart, R.E.; Köke, A.J.; Oosterwijk, R.F.; Swaan, J.L.; Schreurs, K.M.; Schiphorst Preuper, H.R. Cut-Off Points for Mild, Moderate, and Severe Pain on the Numeric Rating Scale for Pain in Patients with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: Variability and Influence of Sex and Catastrophizing. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.-t.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokka, T.; Kautiainen, H.; Pincus, T.; Verstappen, S.M.M.; Aggarwal, A.; Alten, R.; Andersone, D.; Badsha, H.; Baecklund, E.; Belmonte, M.; et al. Work disability remains a major problem in rheumatoid arthritis in the 2000s: Data from 32 countries in the QUEST-RA Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenbach, B.P.; Koelkebeck, K.; Knoch, D. Mentalising and depression: A mini-review on behavior, neural substrates, and treatment options. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, B.A.; Sutherland, S.; Garber, J. Theory of mind performance in depression: A meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 303, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, E.; Berk, M. Theory of mind in major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 191, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, V. Negative interpretation of social cue in depression: Evidence from reading mind from eyes test. Neurol. Psychiatry Brain Res. 2018, 27, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, F.; Hermans, D.; Williams, J.M. Negative bias in the perception of others’ facial emotional expressions in major depression: The role of depressive rumination. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2006, 194, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, K.; Schulz, S.M.; Witthöft, M. Emotional Reactivity, Emotion Regulation, and Regulatory Choice in Somatic Symptom Disorder. Psychosom. Med. 2022, 84, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leithner-Dziubas, K.; Fischer-Kern, M. Psychische Struktur und Mentalisierung als Forschungsansatz bei chronischen Schmerz-Patienten. PDP-Psychodyn. Psychother. 2011, 10, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Kampling, H.; Kruse, J.; Lampe, A.; Nolte, T.; Hettich, N.; Brähler, E.; Sachser, C.; Fegert, J.M.; Gingelmaier, S.; Fonagy, P.; et al. Epistemic trust and personality functioning mediate the association between adverse childhood experiences and posttraumatic stress disorder and complex posttraumatic stress disorder in adulthood. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 919191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdemann, J.; Rabung, S.; Andreas, S. Systematic Review on Mentalization as Key Factor in Psychotherapy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballespí, S.; Vives, J.; Alonso, N.; Sharp, C.; Ramírez, M.S.; Fonagy, P.; Barrantes-Vidal, N. To know or not to know? Mentalization as protection from somatic complaints. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, M.A.; Cohen, J.L.; Borszcz, G.S.; Cano, A.; Radcliffe, A.M.; Porter, L.S.; Schubiner, H.; Keefe, F.J. Pain and emotion: A biopsychosocial review of recent research. J. Clin. Psychol. 2011, 67, 942–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okruszek, Ł.; Jarkiewicz, M.; Piejka, A.; Chrustowicz, M.; Krawczyk, M.; Schudy, A.; Harvey, P.D.; Penn, D.L.; Ludwig, K.; Green, M.F.; et al. Loneliness is associated with mentalizing and emotion recognition abilities in schizophrenia, but only in a cluster of patients with social cognitive deficits. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2024, 30, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, L.A.; Pfeifer, A.C.; Volkert, J.; Schiltenwolf, M.; Taubner, S. “Den Schmerz mentalisieren”—Implementierung eines mentalisierungsbasierten Manuals für die therapeutische Begleitung von Schmerzpatient:innen. Der. Schmerz. 2023, 38, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, P.L.; Rau, K.M.; Yu, T.W.; Huang, T.L.; Sun, J.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Lin, C.C. Patient-clinician relationship seems to affect adherence to analgesic use in cancer patients: A cross sectional study in a Taiwanese population. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2017, 29, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, J.N.; Anand, P.; Haggerty, G.; Kestenbaum, M.; Rosenblum, G.C. The physician-patient working alliance and patient psychological attachment, adherence, outcome expectations, and satisfaction in a sample of rheumatology patients. Behav. Med. 2015, 41, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorflinger, L.; Kerns, R.D.; Auerbach, S.M. Providers’ roles in enhancing patients’ adherence to pain self management. Transl. Behav. Med. 2013, 3, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, M.; Correia, H.; Ditchburn, G.; Drummond, P.D. Defining pain-validation: The importance of validation in reducing the stresses of chronic pain. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 884335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.; Pilat, C. Effects of meditation on pain intensity, physical function, quality of life and depression in adults with low back pain—A systematic review with meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2023, 72, 102924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandel, M.G.; Lin, C.; Hennel, D.; Khazen, O.; Pilitsis, J.G.; Ben-Haim, S. Mindfulness Meditation in the Treatment of Chronic Pain. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 33, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreisoerner, A.; Junker, N.M.; van Dick, R. The Relationship Among the Components of Self-compassion: A Pilot Study Using a Compassionate Writing Intervention to Enhance Self-kindness, Common Humanity, and Mindfulness. J. Happiness Stud. 2021, 22, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, D.; Schüssler, G. The Influence of Doctor-Patient Communication on Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Z. Psychosom. Med. Psychother. 2017, 63, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| n | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 15 | 19.7% |
| Female | 61 | 80.3% |
| Age (M = 45.6; SD = 12.5) | ||
| <40 | 14 | 18.4% |
| 40–60 | 49 | 64.5% |
| >60 | 13 | 17.1% |
| Smoker | ||
| No | 49 | 64.5% |
| Yes | 16 | 21.1% |
| Ex-Smoker | 11 | 14.5% |
| BMI | ||
| Underweight (BMI ≤ 18.5) | 1 | 1.3% |
| Average weight (BMI 18.5–25) | 29 | 38.2% |
| Obese (BMI > 25) | 39 | 51.3% |
| Missing | 7 | 9.2% |
| Diagnosis | ||
| Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) | 25 | 32.9% |
| Axial spondylarthritis (axSpA) | 24 | 31.6% |
| Peripheral spondylarthritis (pSpA)/ Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) | 16 | 21.1% |
| Vasculitis/collagenosis | 9 | 11.8% |
| Others | 2 | 2.6% |
| Loneliness | Depression | ADL Impairment | Leisure Time Impairment | Working Impairment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | (p) | r | (p) | r | (p) | r | (p) | r | (p) | |
| Mentalizing | −0.38 | (<0.001) | −0.57 | (<0.001) | −0.39 | (<0.001) | −0.43 | (<0.001) | −0.44 | (<0.001) |
| Loneliness | -- | -- | 0.23 | (0.044) | 0.29 | (0.013) | 0.34 | (0.003) | 0.33 | (0.003) |
| Depression | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.51 | (<0.001) | 0.54 | (<0.001) | 0.62 | (<0.001) |
| ADL impairment | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.68 | (<0.001) | 0.84 | (<0.001) |
| Leisure time impairment | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.80 | (<0.001) |
| Working impairment | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riedl, D.; Karnik, J.; Lampe, A.; Kirchhoff, C.; Labek, K.; Schirmer, M. Mentalizing, Loneliness and Pain-Related Depressive Symptoms Are Associated with Pain Severity in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: Results of a Cross-Sectional Secondary Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3624. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113624
Riedl D, Karnik J, Lampe A, Kirchhoff C, Labek K, Schirmer M. Mentalizing, Loneliness and Pain-Related Depressive Symptoms Are Associated with Pain Severity in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: Results of a Cross-Sectional Secondary Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3624. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113624
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiedl, David, Julia Karnik, Astrid Lampe, Christina Kirchhoff, Karin Labek, and Michael Schirmer. 2025. "Mentalizing, Loneliness and Pain-Related Depressive Symptoms Are Associated with Pain Severity in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: Results of a Cross-Sectional Secondary Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3624. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113624
APA StyleRiedl, D., Karnik, J., Lampe, A., Kirchhoff, C., Labek, K., & Schirmer, M. (2025). Mentalizing, Loneliness and Pain-Related Depressive Symptoms Are Associated with Pain Severity in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: Results of a Cross-Sectional Secondary Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3624. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113624








