EEG Maturational Age Estimation: A Comparison of Visual and Automated Interpretation of the EEG in Preterm Infants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. EEG Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. EEG Data
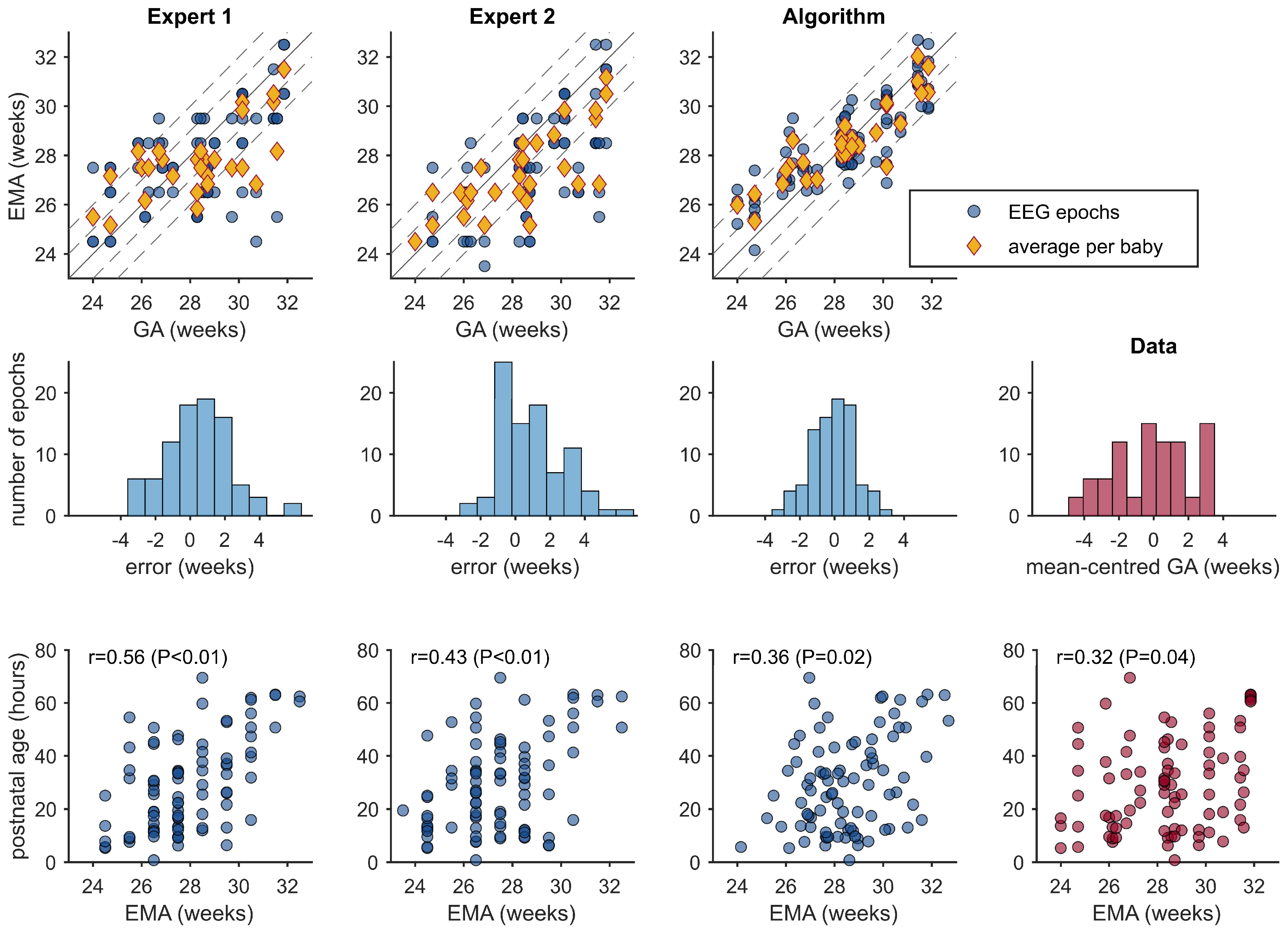
3.3. EMA Estimations
3.4. Mixed-Effects Models Postnatal Age
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EMA | EEG maturational age |
| PNA | Post-natal age |
| GA | Gestational age |
| NICU | Neonatal Intensive Care Unit |
| ICH-GCP | International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use of Good Clinical Practice |
| IVH | Intra-ventricular hemorrhage |
| PVL | Periventricular leukomalacia |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SDE | Standard deviation error |
| CRIB | Clinical risk for babies |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
References
- Hagen, C.M.; Hansen, T.W. Deaths in a neonatal intensive care unit: A 10-year perspective. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 5, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, T.; Hennessy, E.M.; Myles, J.; Johnson, S.J.; Draper, E.S.; Costeloe, K.L.; Marlow, N. Neurological and developmental outcome in extremely preterm children born in England in 1995 and 2006: The EPICure studies. BMJ 2012, 345, e7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyfus-Brisac, C. The electroencephalogram of the premature infant. Wld. Neurol. 1962, 3, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus-Brisac, C.; Flescher, J.; Plassart, E. L’électroencéphalogramme: Critère d’âge conceptionnel du nouveau-né à terme et prématuré. Biol. Neonat. 1962, 4, 154–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyfus-Brisac, C. The electroencephalogram of the premature infant and full-term newborn: Normal and abnormal development of waking and sleeping patterns. In Neurological and Electroencephalographic Correlative Studies in Infancy; Kelleway, P., Petersén, I., Eds.; Grune and Stratton: New York, NY, USA, 1964; pp. 186–207. [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus-Brisac, C. Ontogénèse du sommeil chez le premature humain: Etude polygraphique. In Regional Development of the Brain in Early Life; Minkowski, A., Ed.; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1967; pp. 437–457. [Google Scholar]
- Scher, M.S.; Steppe, D.A.; Dokianakis, S.G.; Guthrie, R.D. Maturation of phasic and continuity measures during sleep in preterm neonates. Pediatr. Res. 1994, 36, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, M.S.; Steppe, D.A.; Banks, D.L.; Guthrie, R.D.; Sclabassi, R.J. Maturational trends of EEG-sleep measures in the healthy preterm neonate. Pediatr. Neurol. 1995, 12, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selton, D.; Andre, M.; Hascoët, J.M. Normal EEG in very premature infants: Reference criteria. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 111, 2116–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchierini, M.F.; d’Allest, A.M.; Verpillat, P. EEG patterns in 10 extreme premature neonates with normal neurological outcome: Qualitative and quantitative data. Brain Dev. 2003, 25, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagioni, E.; Frisone, M.F.; Laroche, S.; Kapetanakis, B.A.; Ricci, D.; Adeyi-Obe, M.; Lewis, H.; Kennea, N.; Cioni, G.; Cowan, F.; et al. Maturation of cerebral electrical activity and development of cortical folding in young very preterm infants. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchierini, M.F.; André, M.; d’Allest, A.M. Normal EEG of premature infants born between 24 and 30 weeks gestational age: Terminology, definitions and maturation aspects. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2007, 37, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, M.; Lamblin, M.D.; d’Allest, A.M.; Curzi-Dascalova, L.; Moussalli-Salefranque, F.; SNguyenThe, T.; Vecchierini-Blineau, M.F.; Wallois, F.; Walls-Esquivel, E.; Plouin, P. Electroencephalography in premature and full-term infants. Developmental features and glossary. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2010, 40, 59–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemarkt, H.J.; Andriessen, P.; Peters, C.H.; Pasman, J.W.; Zimmermann, L.J.; BambangOetomo, S. Quantitative analysis of maturational changes in EEG background activity in very preterm infants with a normal neurodevelopment at 1 year of age. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlidis, E.; Lloyd, R.O.; Mathieson, S.; Boylan, G.B. A review of important electroencephalogram features for the assessment of brain maturation in premature infants. Acta Paediatr. 2017, 106, 1394–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Hayakawa, F.; Okumura, A. Neonatal EEG: A powerful tool in the assessment of brain damage in preterm infants. Brain Dev. 1999, 21, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, R.F.; Wang, X.; van Ooijen, I.M.; van der Velde, B.; Dudink, J.; Benders, M.J.N.L.; Tataranno, M.L. The relationship between early life EEG and brain MRI in preterm infants: A systematic review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2025, 170, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniczky, S.; Aurlien, H.; Brøgger, J.C.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A.; Martins-da-Silva, A.; Trinka, E.; Visser, G.; Rubboli, G.; Hjalgrim, H.; Stefan, H.; et al. Standardized computer-based organized reporting of EEG: SCORE. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1112–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniczky, S.; Aurlien, H.; Brøgger, J.C.; Hirsch, L.J.; Schomer, D.L.; Trinka, E.; Pressler, R.M.; Wennberg, R.; Visser, G.H.; Eisermann, M.; et al. Standardized computer-based organized reporting of EEG: SCORE—Secondversion. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 2334–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmu, K.; Stevenson, N.; Wikström, S.; Hellström-Westas, L.; Vanhatalo, S.; Palva, J.M. Optimization of an NLEO-based algorithm for automated detection of spontaneous activity transients in early preterm EEG. Physiol. Measur. 2010, 31, N85–N93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennekens, W.; Ruijs, L.S.; Lommen, C.M.L.; Niemarkt, H.J.; Pasman, J.W.; van Kranen-Mastenbroek, V.H.J.M.; Wijn, P.F.F.; van Pul, C.; Andriessen, P. Automatic burst detection for the EEG of the preterm infant. Physiol. Measur. 2011, 32, 1623–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolen, N.; Jansen, K.; Vervisch, J.; Matic, V.; DeVos, M.; Naulaers, G.; Van Huffel, S. Line length as a robust method to detect high-activity events: Automated burst detection in premature EEG recordings. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, N.J.; Oberdorfer, L.; Koolen, N.; O’Toole, J.M.; Werther, T.; Klebermass-Schrehof, K.; Vanhatalo, S. Functionalmaturation in preterm infants measured by serial recording of cortical activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, N.J.; Oberdorfer, L.; Tataranno, M.L.; Breakspear, M.; Colditz, P.B.; de Vries, L.S.; Benders, M.J.; Klebermass-Schrehof, K.; Vanhatalo, S.; Roberts, J.A. Automated cot-side tracking of functional brain age in preterm infants. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, N.J.; Tataranno, M.L.; Kaminska, A.; Pavlidis, E.; Clancy, R.R.; Griesmaier, E.; Roberts, J.A.; Klebermass-Schrehof, K.; Vanhatalo, S. Reliability and accuracy of EEG interpretation for estimating age in preterm infants. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, N.J.; Nordvik, T.; Espeland, C.N.; Giordano, V.; Moltu, S.J.; Larsson, P.G.; Klebermaß-Schrehof, K.; Stiris, T.; Vanhatalo, S. Inter-site generalizability of EEG based age prediction algorithms in the preterm infant. Physiol. Meas. 2023, 44, 07NT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, J.M.; Boylan, G.B.; Lloyd, R.O.; Goulding, R.M.; Vanhatalo, S.; Stevenson, N.J. Detecting bursts in the EEG of very and extremely premature infants using a multi-feature approach. Med. Eng. Phys. 2017, 45, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, J.M.; Boylan, G.B.; Vanhatalo, S.; Stevenson, N.J. Estimating functional brain maturity in very and extremely preterm neonates using automated analysis of the electroencephalogram. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, J.M.; Pavlidis, E.; Korotchikova, I.; Boylan, G.B.; Stevenson, N.J. Temporal evolution of quantitative EEG within 3 days of birth in early preterm infants. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Schielzeth, H. A general and simple method for obtaining R2 from generalized linear mixed-effects models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBihannic, A.; Beauvais, K.; Busnel, A.; deBarace, C.; Furby, A. Prognostic value of EEG in very premature newborns. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012, 97, F106–F109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | n = 29 |
|---|---|
| gestational age (weeks) | 28.4 (26.7, 30.1) |
| female | 21 (72.4%) |
| birth weight (g) | 980 (800, 1240) |
| Apgar score at 1 m | 8 (6, 8) |
| Apgar score at 5 m | 9 (8, 9) |
| pH | 7.21 (7.14, 7.28) |
| CRIB | 8 (7, 10) |
| cesarean delivery | 13 (44.8%) |
| Bayley scales III (26/29 newborns) | |
| cognitive | 95 (95, 104) |
| language | 103 (97, 111) |
| motor | 100 (97, 106) |
| Correlation | Bias (Days) | SDE (Days) | <1 Week (%) | <2 Weeks (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean GA in cohort | 0.0 (−3.24, 3.37) | 15.7 (13.8, 17.4) | 31.0 (21.8, 41.4) | 55.2 (44.8, 65.5) | |
| Expert 1 | 0.597 (0.416, 0.737) | 3.57 (0.83, 6.44) | 13.2 (10.9, 15.3) | 40.2 (29.9, 50.6) | 72.4 (62.1, 81.6) |
| Expert 2 | 0.659 (0.530, 0.757) | 7.03 (4.43, 9.61) | 12.4 (10.6, 14.0) | 46.0 (35.6, 56.3) | 72.4 (62.1, 81.6) |
| Algorithm | 0.833 (0.752, 0.890) | −0.79 (−2.75, 0.95) | 8.7 (7.3, 10.0) | 56.3 (44.8, 66.7) | 88.5 (81.6, 94.3) |
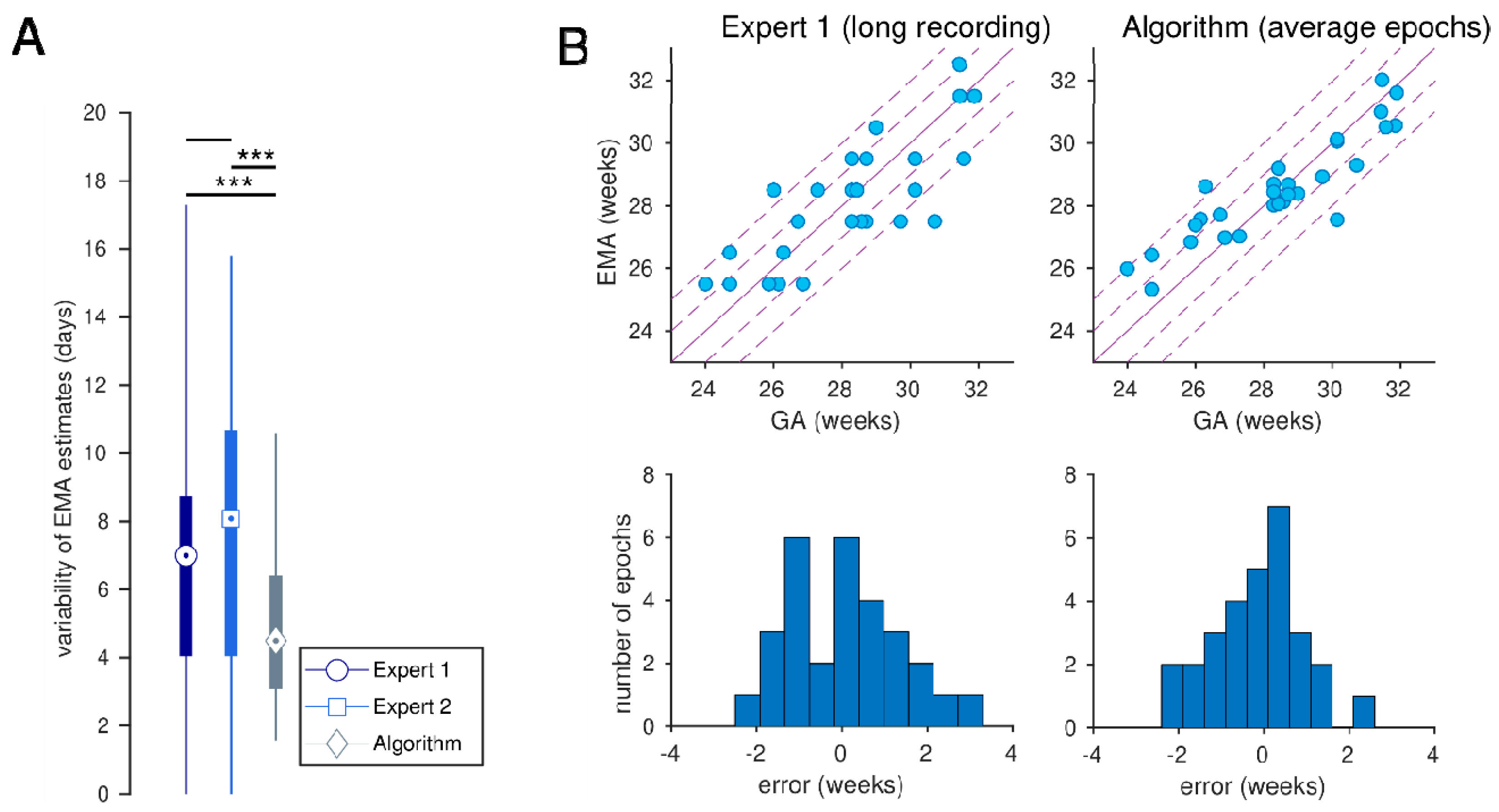
| Expert 1 (long recording) | 0.816 (0.671, 0.903) | 0.67 (−2.64, 3.91) | 9.2 (6.8, 11.3) | 51.7 (34.5, 69.0) | 86.2 (72.4, 96.6) |
| Algorithm | 0.896 | −0.79 | 7.6 | 69.0 | 93.1 |
| (average epochs) | (0.794, 0.957) | (−3.80, 1.88) | (5.4, 9.4) | (51.7, 86.2) | (82.8, 100.0) |
| Correlation | Bias (Days) | SDE (Days) | <1 Week (%) | <2 Weeks (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expert 1 | 0.704 | 3.57 | 11.3 | 44.8 | 75.9 |
| (0.438, 0.843) | (−0.35, 7.33) | (8.4, 13.5) | (27.6, 65.5) | (58.6, 89.7) | |
| Expert 2 | 0.762 | 7.03 | 10.3 | 55.2 | 82.8 |
| (0.574, 0.902) | (3.42, 10.60) | (6.9, 12.8) | (37.9, 72.4) | (69.0, 96.6) | |
| Algorithm | 0.896 | −0.79 | 7.6 | 69.0 | 93.1 |
| (0.799, 0.958) | (−3.56, 2.00) | (5.4, 9.4) | (51.7, 82.8) | (82.8, 100.0) |
| Correlation | Bias | SDE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| p a | p b | p c | |
| Expert 1 vs. Expert 2 | 0.416 (0.416) | 0.009 (0.009) | 0.584 (0.584) |
| Expert 1 vs. EMA | 0.006 (0.002) | 0.006 (0.003) | 0.175 (0.059) |
| Expert 2 vs. EMA | 0.049 (0.024) | <0.001 (<0.001) | 0.200 (0.399) |
| Expert 1 | Expert 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | |
| intercept (days) | 106.4 (77.7, 136.2) | <0.001 | 81.4 (45.1, 117.5) | <0.001 |
| PNA (days) | 6.57 (3.54 to 9.15) | <0.001 | 3.74 (0.47, 6.90) | 0.021 |
| GA (days) | 0.407 (0.251, 0.554) | <0.001 | 0.533 (0.349, 0.724) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavlidis, E.; O’Toole, J.M.; Pisani, F.; Boylan, G.B.; Stevenson, N.J. EEG Maturational Age Estimation: A Comparison of Visual and Automated Interpretation of the EEG in Preterm Infants. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103528
Pavlidis E, O’Toole JM, Pisani F, Boylan GB, Stevenson NJ. EEG Maturational Age Estimation: A Comparison of Visual and Automated Interpretation of the EEG in Preterm Infants. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103528
Chicago/Turabian StylePavlidis, Elena, John M. O’Toole, Francesco Pisani, Geraldine B. Boylan, and Nathan J. Stevenson. 2025. "EEG Maturational Age Estimation: A Comparison of Visual and Automated Interpretation of the EEG in Preterm Infants" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103528
APA StylePavlidis, E., O’Toole, J. M., Pisani, F., Boylan, G. B., & Stevenson, N. J. (2025). EEG Maturational Age Estimation: A Comparison of Visual and Automated Interpretation of the EEG in Preterm Infants. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103528






