Abstract
Background: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) was implicated in the progression of atherosclerosis and is associated with elevated stroke risk. However, there is limited evidence regarding the MCP-1 role as an early biomarker for predicting the severity and outcomes of acute ischemic stroke (AIS). This prospective pilot case–control study aims to offer preliminary evidence into whether MCP-1 levels are elevated in AIS, whether they vary across different stroke subtypes, and their potential utility as a biomarker for assessing stroke severity and predicting outcomes. Methods: MCP-1 levels were quantified using ELISA in patients with AIS or transients ischemic attack (TIA) and healthy participants. Stroke severity was assessed with the NIHSS score and functional outcome with the mRS scale. Results: A total of 32 patients with AIS or TIA were compared to 13 healthy controls. MCP-1 levels were found to be 77% higher in stroke patients compared to healthy controls (p < 0.001). No significant differences in MCP-1 levels were observed between patients with AIS and those with TIA, nor among different stroke subtypes. A positive correlation was observed between MCP-1 levels and NIHSS changes from admission to discharge (b = 0.376, p < 0.05) and mRS scale at 6-month follow-up (b = 0.507, p < 0.05). Conclusions: This prospective pilot study provides preliminary evidence that MCP-1 levels are significantly elevated in AIS and are associated with NIHSS change during hospitalization and unfavorable outcome at 6-month follow-up. These findings indicate the potential of MCP-1 as an early biomarker for assessing disease severity and predicting outcomes in AIS.
1. Introduction
Stroke ranks as the third leading cause of death worldwide, with over 7 million deaths attributed to it [1], and it is the leading cause of long-term disability, placing a growing burden on global health systems [2,3]. Inflammatory mechanisms play a significant role in the pathophysiology of stroke. Cytokines and growth factors are key regulators of the inflammatory response and have been implicated in both the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis and vascular disease, including coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, and stroke. Consequently, they may represent potential targets for the prevention and therapy of cardiovascular diseases [4].
A recent genome-wide association study conducted on Finnish healthy individuals uncovered several common genetic variants that affect the circulating levels of 41 cytokines and growth factors [5]. Their associations with stroke subtypes were evaluated in the MEGASTROKE genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects [6]. A Mendelian randomization study has demonstrated that, among chemokines, a genetic predisposition to elevated circulating levels of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) is associated with an increased risk of stroke, particularly large-artery atherosclerotic stroke and cardioembolic stroke [7].
MCP-1, also known as chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 (CCL2), is a chemokine that plays a critical role in attracting monocytes to sites of inflammation and it is primarily produced by inflammatory and endothelial cells [8]. MCP-1 is significantly involved in the initiation, development, and progression of atherosclerosis by facilitating the recruitment of monocytes into the forming atheromatous plaques [9,10]. In animal studies, the levels of MCP-1 and its receptor on monocytes, C-C chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2), correlate closely with the severity of atherosclerosis and the degree of macrophage accumulation within the plaques [11].
A meta-analysis of six population-based cohort studies, which included 17,000 individuals without a history of stroke and followed them over 16 years, revealed that higher baseline levels of MCP-1 were linked to an increased risk of stroke, even after adjustment for traditional vascular risk factors. Combined with genetic and experimental data, these findings strengthen the evidence supporting MCP-1 as a causal risk factor for stroke, as well as a potential target for therapeutic intervention [12].
However, there are very limited data to prove that MCP-1 levels are elevated in acute phase of an ischemic stroke and that can be used as an early predictor to distinguish stroke subtype and subjective etiology or to estimate the severity and the disease outcome. This pilot preliminary study aims to assess whether MCP-1 levels are elevated during the acute phase of ischemic stroke and vary across stroke subtypes. Results support the design of a larger study aiming to examine in depth the role of MCP-1 for the prediction of early and long-term outcomes in patients after an ischemic stroke.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
This is a case–control study conducted between January 2022 and July 2022. Patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) or transient ischemic attack (TIA) admitted to the Stroke Unit of AHEPA University Hospital in Thessaloniki, Greece, within 12 h of symptom onset or the last known well time were recruited along with healthy control subjects. Stroke pathophysiology was classified according to the TOAST criteria [13].
Inclusion criteria were as follows: age > 18 years old, AIS or TIA. Exclusion criteria were: intracranial hemorrhage, malignancy, central nervous or any other acute infection, and severe renal or hepatic disease.
Plasma levels of MCP-1 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA; Quantikine® ELISA Human CCL2/MCP-1; R&D SYSTEMS, Minneapolis, MN, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The reference interval of this assay is 31.3–2000 pg/mL, while the reference range of apparently healthy individuals is up to 436 pg/mL [14]. MCP-1 levels were compared between patients and healthy controls, and correlations between MCP-1 levels and comorbidities, as well as baseline laboratory values, were examined.
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) was used for assessment of stroke severity [15,16] and modified Rankin Score (mRS) [17] was used for assessment of functional outcome. We also performed two additional analyses focusing on cardioembolic strokes vs. non-cardioembolic and on lacunar vs. non-lacunar strokes.
The outcomes of the study were as follows: NIHSS score at admission and discharge, mRS score at admission, discharge and at 6-month follow-up, NIHSS change from admission to discharge (δ-NIHSS), mRS change from prior to admission, from admission to discharge and from admission to 6-month follow-up, as well as in-hospital mortality and 12-month follow-up mortality.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Quantitative data were summarized using mean values for parameters that are normally distributed and median values for parameters that are not normally distributed, while categorical data were described using frequency (count) and relative frequency (percentage). Comparisons between quantitative variables were performed using the independent t-test for normally distributed variables and the Kruskal–Wallis and Mann–Whitney tests for non-normally distributed data. Correlations between quantitative variables were analyzed using the Spearman correlation coefficient and linear regression analysis was conducted to estimate the regression coefficients. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) version 23.
2.3. Ethical Review Board
The ethical review board of Aristotle University of Thessaloniki revised and approved the study protocol (No. 09/2022). All the study participants were treated according to the Helsinki declaration of Biomedical ethics and written informed consent was obtained from the patients or their caregivers.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
This study included 32 patients with AIS or TIA, with a median age of 80 years, of whom 13 were women (40.6%). Additionally, we recruited 13 healthy controls with a median age of 73 years (61.5% women). Patients with AIS were categorized into the following subtypes: nine large artery atherosclerotic, eight cardioembolic, four lacunar, and one of undetermined etiology. Table 1 summarizes the baseline characteristics of the recruited patients.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients with acute ischemic stroke or TIA at admission.
The median duration of hospitalization was 7 days. The median NIHSS at admission and at discharge was four and three, respectively. The median mRS before the AIS or TIA, at admission, at discharge, and at 6-month follow-up was two, four, four, and four respectively. Seventeen deaths were recorded at the 12-month follow-up, with eight deaths occurring during the in-hospital period. Among the causes of death, four were attributed to neurological deterioration, four to acute cardiovascular event, and nine to infections. Seven deaths (21.8%) were linked to confirmed (five cases) or suspected (two cases) SARS-CoV-2 infections.
3.2. MCP-1 Levels at Admission and Correlation with Baseline Characteristics
At admission, the median MCP-1 levels were 381 pg/mL in patients compared to 251 pg/mL in healthy controls (p < 0.001). There was no difference in MCP-1 levels between patients with stroke and TIA (394 vs. 346 pg/mL, p = 0.309). Also, there was no difference in MCP-1 levels among different stroke types (Figure 1). More specifically, there was no difference in MCP-1 levels between cardioembolic and non-cardioembolic strokes (390 vs. 394 pg/mL, p = 0.707), but MCP-1 levels were higher in lacunar strokes compared to non-lacunar strokes, although this difference did not reach statistical significance (483 vs. 377 pg/mL, p = 0.061).
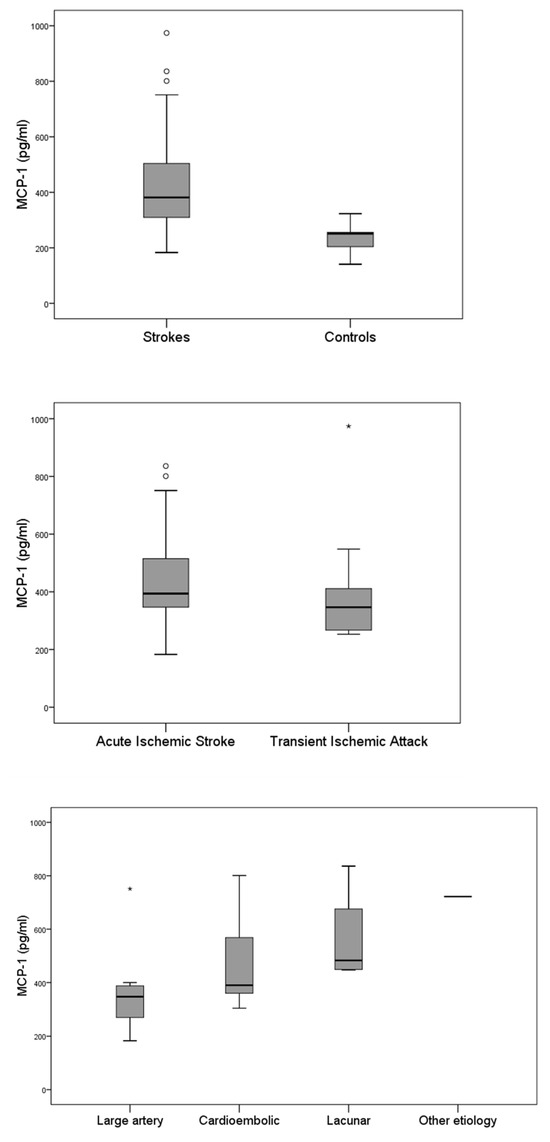
Figure 1.
ΜCP-1 levels in the patient and healthy control groups (upper panel), acute ischemic strokes and TIA (middle panel), and according to the TOAST classification (lower panel). In the box plot, circles (○) represent mild outliers (1.5–3 × IQR beyond the quartiles), while asterisks (*) indicate extreme outliers (>3 × IQR).
Νo correlation was observed between MCP-1 levels at admission and age, sex, the main comorbidities (arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, atrial fibrillation, dyslipidaemia, peripheral arterial disease, coronary disease, stroke history), the main laboratory values (plasma glucose, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, HBA1c), and arterial blood pressure at baseline (Table 2).

Table 2.
Correlation of MCP-1 levels with baseline characteristics.
3.3. Correlation of MCP-1 Levels and Outcomes
A positive correlation was observed between the levels of MCP-1 and the difference in the NIHSS from admission to discharge from the hospital (δ-ΝIHSS) (p = 0.048) (Table 3 and Figure 2).

Table 3.
Correlation of MCP-1 levels with outcomes.
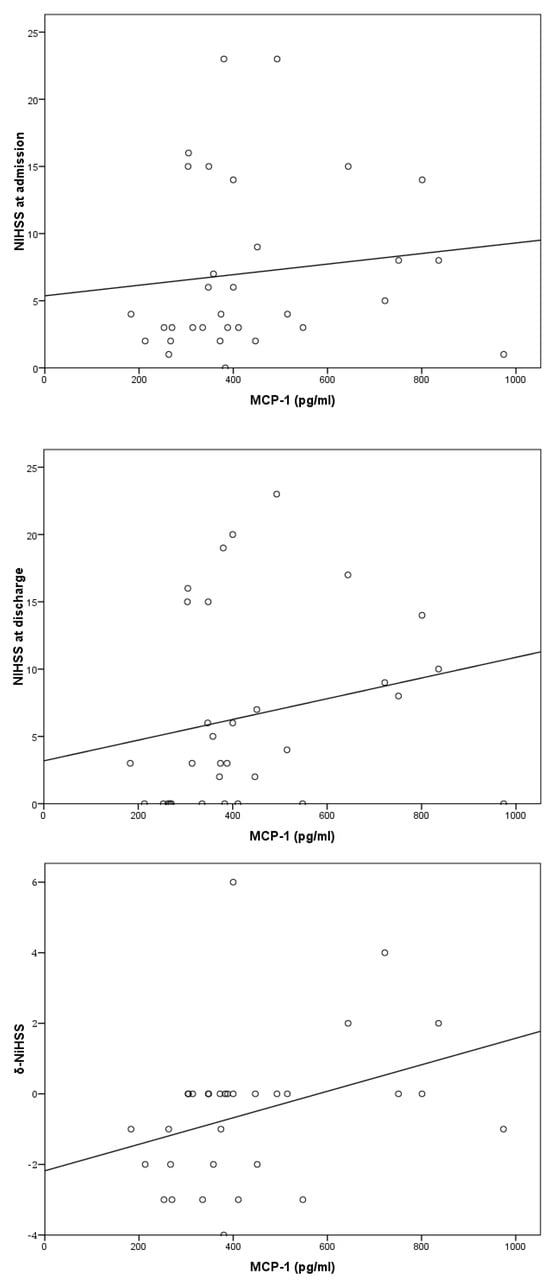
Figure 2.
Correlation of MCP-1 to NIHSS at admission (upper panel), discharge (middle panel), and δ-NIHSS (lower panel).
There was also a positive correlation between the levels of MCP-1 and the mRS score at 6-month follow-up (p = 0.03). However, there was no statistically significant association between MCP-1 levels and NIHSS or mRS score at admission and at discharge, nor with in-hospital mortality or death at 12 months (Table 3).
4. Discussion
In this prospective pilot study, we found that MCP-1 levels were higher in patients with AIS compared to healthy individuals. However, no significant differences in MCP-1 levels were identified between AIS and TIA or among different AIS subtypes classified by the TOAST criteria. A positive correlation was found between MCP-1 levels and the change in NIHSS scores from admission to discharge, as well as between MCP-1 levels and mRS score at 6-month follow-up. However, no significant correlations were observed between MCP-1 levels and NIHSS and mRS scores at admission and discharge, in-hospital mortality, or mortality at the 12-month follow-up.
The results of the present study demonstrate that the levels of the chemokine MCP-1 are elevated in the acute phase of ischemia compared to random samples from healthy controls. Our findings are consistent with evidence from various ischemia models, suggesting that elevated MCP-1 levels represent an immune response to ischemic injury and the coordinated recruitment of lymphocytes and monocytes to the site of damage shortly after the onset of ischemia [18].
Ischemic stroke is accompanied by an imbalance between the injured central nervous system and the immune system, resulting in a secondary condition of immunosuppression [19]. The ischemic core is characterized by the recruitment of neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages from the systemic circulation to the injured brain tissue [20]. As the blood–brain barrier loses its integrity, monocytes/macrophages, along with T-cells and NK cells, penetrate through the vascular endothelium to reach the damaged neural tissue. The initial purpose of this recruitment is to restore the immune response at site of local ischemia. However, it simultaneously increases the extent of local inflammation, contributing to extensive local brain damage and worse outcome in the ischemic stroke [19].
For this entire process, the damaged tissue expresses chemokine receptors on the surface of endothelial cells that interact with adhesion molecules on the surface of immune cells. Among chemokines, monocyte chemotactic protein-1 is primarily produced by inflammatory cells and endothelial cells and plays a critical role in attraction and recruitment of monocytes to sites of local brain inflammation [8]. However, activated monocytes can reduce the production of certain cytokines, leading to a decrease in MCP-1 secretion and, consequently, a reduction in the recruitment of additional monocytes to the site of inflammation [20,21]. Some authors suggest that the migration of monocytes out of the peripheral circulation decreases after the initial wave of mobilization, a decline that appears to be more pronounced in patients with TIA [21].
In our study, no difference was observed in the MCP-1 protein levels between patients with AIS and those with TIA, but this could be attributed to our limited sample size. According to the existing literature, monocytes accumulate in the injured tissue between days 3 and 6 post injury and infiltrate the damaged tissues within 72 h after the onset of the injury [20,22]. Therefore, during this period, a downregulation of MCP-1 could potentially occur, leading to lower MCP-1 plasma levels. It might be beneficial to design future studies with a larger sample size for each group, stroke vs. TIA, and reassess MCP-1 levels at different time points after the acute phase to prove this statement.
In our study, no significant difference was observed in MCP-1 levels when comparing among ischemic stroke subtypes. Given the distinct pathophysiological mechanisms, prognosis, and clinical features between cardioembolic and non-cardioembolic strokes [23,24], as well as lacunar and non-lacunar strokes [25], we examined these subgroups separately. However, no significant difference in MCP-1 levels was found. It is worth noting, though, that MCP-1 levels were higher in lacunar strokes compared to non-lacunar strokes, approaching statistical significance, although previous studies have suggested a correlation between elevated MCP-1 levels and an increased risk of large-artery atherosclerotic and cardioembolic strokes [7]. We hypothesize that, during the acute phase of cerebral ischemia, elevated MCP-1 levels are primarily reflective of the inflammatory response itself rather than being specific to the stroke etiology. Consequently, we may not expect differences in MCP-1 levels across different stroke subtypes. However, prospective cohort studies or meta-analyses of population-based follow-up studies may provide further knowledge whether MCP-1 levels are associated with specific ischemic stroke subtypes.
The levels of inflammatory markers and mediators in the blood following an acute ischemic stroke may vary and are associated with stroke outcomes [26]. It seems reasonable to hypothesize that an increase in MCP-1 levels would correlate with an advanced immune response and consequently greater neuronal damage. In our study, while we did not observe a difference in clinical severity during the acute phase of ischemic stroke in relation to MCP-1 levels, we did observe differences in clinical deterioration during the progression of ischemic stroke in the first days of hospitalization. That observation may indicate that immune response is ongoing during first days of stroke progression. Furthermore, elevated levels of MCP-1 during the acute phase of ischemic stroke have been associated with unfavorable outcomes at the 6-month follow-up. This finding underscores the potential utility of MCP-1 as an early biomarker for predicting long-term clinical outcomes as well.
No significant correlation was identified between the levels of MCP-1 and in-hospital or 12-month mortality. The reported mortality rate was higher than the mortality rate described typically in most acute stroke registries [27], but only one-quarter of the deaths were attributed to neurological deterioration. This was most probably attributed to the fact that the study was performed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
A recent study highlighted MCP-1 as a potential biomarker for identifying patients who could benefit from early antithrombotic therapy after an ischemic stroke [28]. However, other potential drugs targeting the immune response could also be applicable during the acute phase. Animal studies indicate that monocytes present at the site of ischemic injury play a role in promoting angiogenesis within the area of occlusion [21,29,30]. Considering that MCP-1 plays a crucial role in the migration and attachment of monocytes to brain injury sites, it may also contribute to angiogenesis. Therefore, targeting MCP-1 to modulate the immune response during the acute phase of ischemic stroke presents a promising therapeutic strategy. Such an approach could not only reduce neuronal damage by limiting excessive inflammation, but also promote therapeutic angiogenesis, thereby facilitating the recovery and repair of the damaged brain tissue.
Despite the insights provided by this prospective study, several limitations should be acknowledged when interpreting the results. First, the sample sizes of the stroke, TIA, and healthy cohorts, as well as the stroke subtypes, were relatively small, which limited the ability to match these cohorts for age, sex, and co-morbidities. Nevertheless, as this was a pilot study designed to explore the role of immunological biomarkers, such as MCP-1, in the pathophysiology of AIS and TIA, and to identify potential associations between MCP-1 levels and stroke outcomes, these limitations highlight the need for further prospective studies and randomized controlled trials with larger, more homogeneous cohorts. Such studies are essential to validate and extend these findings, ultimately facilitating the establishment of reliable, causal relationships. Additionally, MCP-1 levels were assessed only at a single time point during the acute phase of ischemic stroke. Repeated measurements at multiple time intervals can provide a more thorough understanding of the biomarker’s role in disease progression, especially across various stroke subtypes and TIA, offering a clearer picture of its dynamic changes over time.
In conclusion, this prospective pilot study provides evidence supporting the hypothesis that MCP-1 levels are elevated during the acute phase of ischemic stroke and these findings strengthen the need for further investigation through multicenter studies to evaluate the potential utility of MCP-1 as a biomarker in AIS. MCP-1 could serve as an early biological marker for assessing disease severity and predicting disease progression. Monitoring plasma MCP-1 levels may become an essential component of the management protocol for patients during the acute phase of ischemic stroke. Given the distinct pathophysiology underlying each stroke subtype, further investigation into the role of immunological biomarkers such as MCP-1 across different stroke subtypes is critical, as they may emerge as potential therapeutic targets. Further research into MCP-1 may be proven useful in developing therapeutic agents aiming at immune modulation. Considering the established pathways of the immune response in ischemic stroke, targeting the inhibition of the pro-inflammatory immune response could serve as a therapeutic approach to prevent secondary damage while maintaining the anti-inflammatory response and its immunoprotective effects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.K.; methodology, E.Z., I.C.M., D.L., A.T., G.N., G.K. and C.S.; formal analysis, E.Z.; investigation, E.Z.; data curation, E.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, E.Z.; writing—review and editing, E.Z., A.T., G.N. and G.K.; visualization, G.K.; supervision, G.K.; project administration, G.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Part of this research was funded by Hellenic College of Nephrology and Hypertension through a scholarship.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics and Research Deontology Committee of Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (protocol code: No.09/2022 and date of approval: 11 October 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are not available due to privacy and ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
We express our sincere gratitude to the Hellenic College of Nephrology and Hypertension for their unwavering support in advancing research through a scholarship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| δ-NIHSS | NIHSS change from admission to discharge |
| Adm | Admission |
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| AIS | Acute ischemic stroke |
| CCL2 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 |
| CCR2 | C-C chemokine receptor type 2 |
| CN | Coronary disease |
| DaysHosp | Days of hospital stay |
| Diff | Difference |
| Dis | Discharge |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| HDL-cholesterol | High-density lipoprotein–cholesterol |
| LDL-cholesterol | Low-density lipoprotein–cholesterol |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 |
| mRS | Modified Rankin score |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| PVD | Peripheral vascular disease |
| Pre | Prior to admission |
| SPSS | Statistical package for the social sciences |
| TIA | Transient ischemic attack |
| TOAST | Trial of Org 10,172 in acute stroke treatment |
References
- GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global Burden of 288 Causes of Death and Life Expectancy Decomposition in 204 Countries and Territories and 811 Subnational Locations, 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2100–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global Incidence, Prevalence, Years Lived with Disability (YLDs), Disability-Adjusted Life-Years (DALYs), and Healthy Life Expectancy (HALE) for 371 Diseases and Injuries in 204 Countries and Territories and 811 Subnational Locations, 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2133–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderer, S. Stroke Deaths and Burden Increased Around the World From 1990 to 2021. JAMA 2024, 332, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Hansson, G.K. Leducq Transatlantic Network on Atherothrombosis Inflammation in Atherosclerosis: From Pathophysiology to Practice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahola-Olli, A.V.; Würtz, P.; Havulinna, A.S.; Aalto, K.; Pitkänen, N.; Lehtimäki, T.; Kähönen, M.; Lyytikäinen, L.-P.; Raitoharju, E.; Seppälä, I.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies 27 Loci Influencing Concentrations of Circulating Cytokines and Growth Factors. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 100, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Chauhan, G.; Traylor, M.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Okada, Y.; Mishra, A.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.; Giese, A.-K.; van der Laan, S.W.; Gretarsdottir, S.; et al. Multiancestry Genome-Wide Association Study of 520,000 Subjects Identifies 32 Loci Associated with Stroke and Stroke Subtypes. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakis, M.K.; Gill, D.; Rannikmäe, K.; Traylor, M.; Anderson, C.D.; Lee, J.-M.; Kamatani, Y.; Hopewell, J.C.; Worrall, B.B.; Bernhagen, J.; et al. Genetically Determined Levels of Circulating Cytokines and Risk of Stroke. Circulation 2019, 139, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, G.; Kelley, J.; Yerra, L.; Smith, J.K.; Chi, D.S. Human Endothelium as a Source of Multifunctional Cytokines: Molecular Regulation and Possible Role in Human Disease. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1999, 19, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Kakkar, V.; Lu, X. Impact of MCP-1 in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 4580–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, R.; Khera, A.; McGuire, D.K.; Murphy, S.A.; de Meo Neto, J.P.; Morrow, D.A.; de Lemos, J.A. Association among Plasma Levels of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1, Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Subclinical Atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiki, M.; Kawashima, S.; Yamashita, T.; Ozaki, M.; Hirase, T.; Ishida, T.; Inoue, N.; Hirata, K.; Matsukawa, A.; Morishita, R.; et al. Local Overexpression of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 at Vessel Wall Induces Infiltration of Macrophages and Formation of Atherosclerotic Lesion: Synergism with Hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakis, M.K.; Malik, R.; Björkbacka, H.; Pana, T.A.; Demissie, S.; Ayers, C.; Elhadad, M.A.; Fornage, M.; Beiser, A.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; et al. Circulating Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 and Risk of Stroke: Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Studies Involving 17 180 Individuals. Circ. Res. 2019, 125, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E. Classification of Subtype of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Definitions for Use in a Multicenter Clinical Trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FineTest® Human MCP-1 (Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1) ELISA Kit. Available online: https://www.fn-test.com/product/eh0222/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Brott, T.; Adams, H.P.; Olinger, C.P.; Marler, J.R.; Barsan, W.G.; Biller, J.; Spilker, J.; Holleran, R.; Eberle, R.; Hertzberg, V. Measurements of Acute Cerebral Infarction: A Clinical Examination Scale. Stroke 1989, 20, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P.; Davis, P.H.; Leira, E.C.; Chang, K.C.; Bendixen, B.H.; Clarke, W.R.; Woolson, R.F.; Hansen, M.D. Baseline NIH Stroke Scale Score Strongly Predicts Outcome after Stroke: A Report of the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST). Neurology 1999, 53, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Swieten, J.C.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Visser, M.C.; Schouten, H.J.; van Gijn, J. Interobserver Agreement for the Assessment of Handicap in Stroke Patients. Stroke 1988, 19, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagami, S.; Tamura, M.; Hayashi, M.; Endo, N.; Tanabe, H.; Katsuura, Y.; Komoriya, K. Differential Production of MCP-1 and Cytokine-Induced Neutrophil Chemoattractant in the Ischemic Brain after Transient Focal Ischemia in Rats. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 65, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, C.; Schwab, J.M.; Prass, K.; Meisel, A.; Dirnagl, U. Central Nervous System Injury-Induced Immune Deficiency Syndrome. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hallenbeck, J.M.; Ruetzler, C.; Bol, D.; Thomas, K.; Berman, N.E.J.; Vogel, S.N. Overexpression of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 in the Brain Exacerbates Ischemic Brain Injury and Is Associated with Recruitment of Inflammatory Cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2003, 23, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifačić, D.; Toplak, A.; Benjak, I.; Tokmadžić, V.S.; Lekić, A.; Kučić, N. Monocytes and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 (MCP-1) as Early Predictors of Disease Outcome in Patients with Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2016, 128, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J. Peripheral Immune Cells in the Pathology of Traumatic Brain Injury? Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2011, 17, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pius, P.; Li, C.; Theertham, A.; Khanna, S.; Bhat, A. Differentiation of Cardioembolic and Non-Cardioembolic Stroke Subtypes Based on Clinical and Echocardiographic Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Heart Lung Circ. 2024, 33, S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.G.; Pearce, L.A.; Miller, V.T.; Anderson, D.C.; Rothrock, J.F.; Albers, G.W.; Nasco, E. Cardioembolic vs. Noncardioembolic Strokes in Atrial Fibrillation: Frequency and Effect of Antithrombotic Agents in the Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Studies. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2000, 10, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboix, A.; Massons, J.; García-Eroles, L.; Targa, C.; Comes, E.; Parra, O. Clinical Predictors of Lacunar Syndrome Not Due to Lacunar Infarction. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthmann, H.; Tryc, A.B.; Goldbecker, A.; Ma, Y.T.; Tountopoulou, A.; Hahn, A.; Dengler, R.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Weissenborn, K. The Temporal Profile of Inflammatory Markers and Mediators in Blood after Acute Ischemic Stroke Differs Depending on Stroke Outcome. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2010, 30, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, P.; Odier, C.; Rutgers, M.; Reichhart, M.; Maeder, P.; Meuli, R.; Wintermark, M.; Maghraoui, A.; Faouzi, M.; Croquelois, A.; et al. The Acute STroke Registry and Analysis of Lausanne (ASTRAL): Design and Baseline Analysis of an Ischemic Stroke Registry Including Acute Multimodal Imaging. Stroke 2010, 41, 2491–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthmann, H.; Dengler, R.; Schumacher, H.; Schwartz, A.; Eisert, W.G.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Weissenborn, K. Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 as a Potential Biomarker for Early Anti-Thrombotic Therapy after Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8670–8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capoccia, B.J.; Gregory, A.D.; Link, D.C. Recruitment of the Inflammatory Subset of Monocytes to Sites of Ischemia Induces Angiogenesis in a Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1-Dependent Fashion. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhan, S.E.; Kirchgessner, A.; Hofer, M. Inflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Therapeutic Approaches. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).