The Brain Fatigue Syndrome—Symptoms, Probable Definition, and Pathophysiological Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Symptoms of BFS
- -
- Impaired attention and ability to concentrate over time.
- -
- After overexertion, a long recovery time that is not proportional to the level of exertion.
- -
- Daily variation in the fatigue symptoms where the fatigue is often better in the morning and worse in the afternoons and evenings. Often it varies from one day to the next.
- -
- Problems with memory.
- -
- Slowness of thinking.
- -
- Reduced ability to start activities.
- -
- Mood swings and tearfulness.
- -
- Irritability.
- -
- Sensitivity to stress.
- -
- Sensitivity to light and noise.
- -
- Sleep problems.
- -
- Headache after overexertion.
3. Who May Suffer from BFS?
4. Self-Diagnostic Instrument for Brain Fatigue and BFS
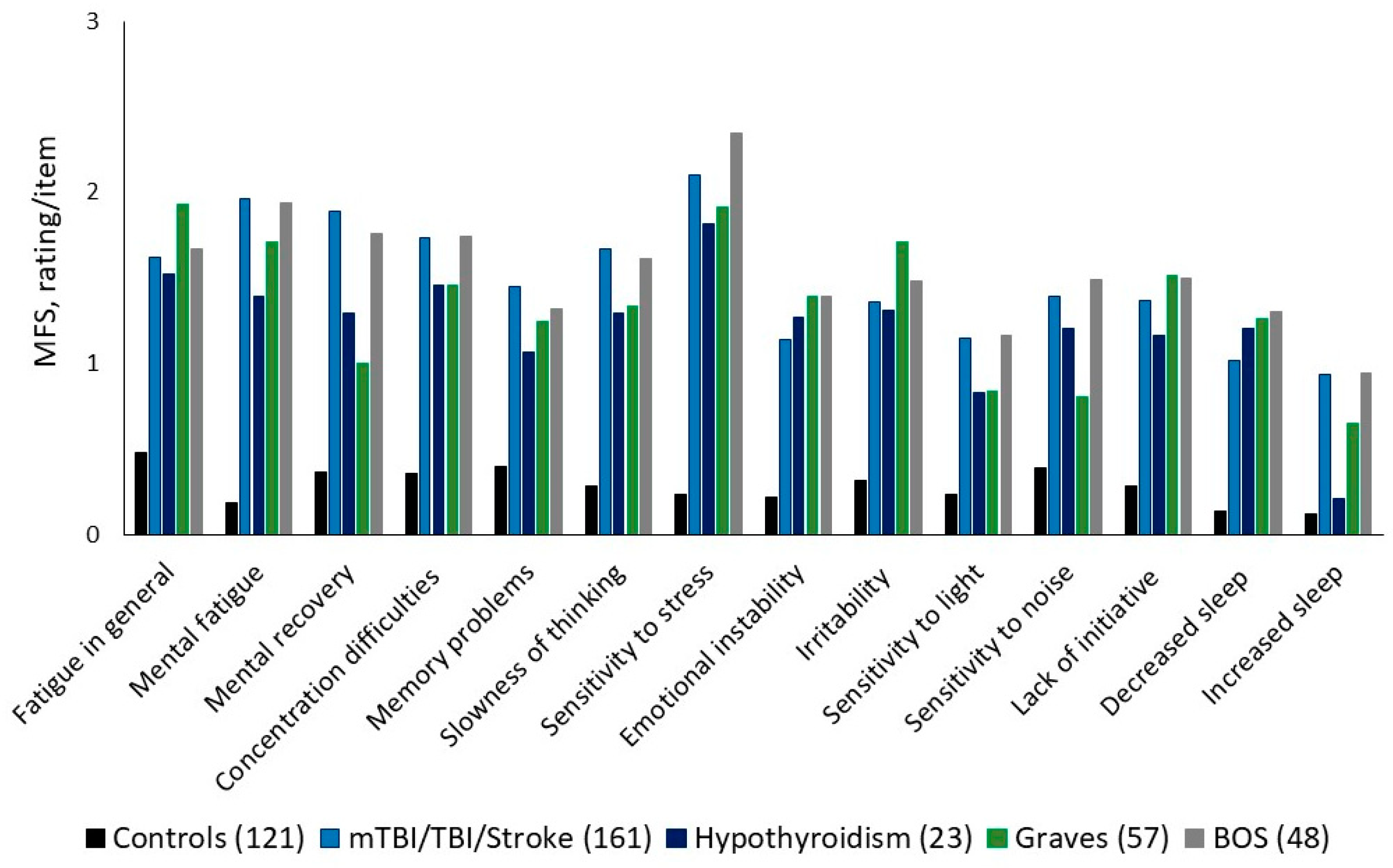
5. Aspects of Different Symptoms Within BFS
5.1. Emotionality
5.2. Cognitive and Sensory Functions
5.3. Neurotransmitters in Relation to BFS
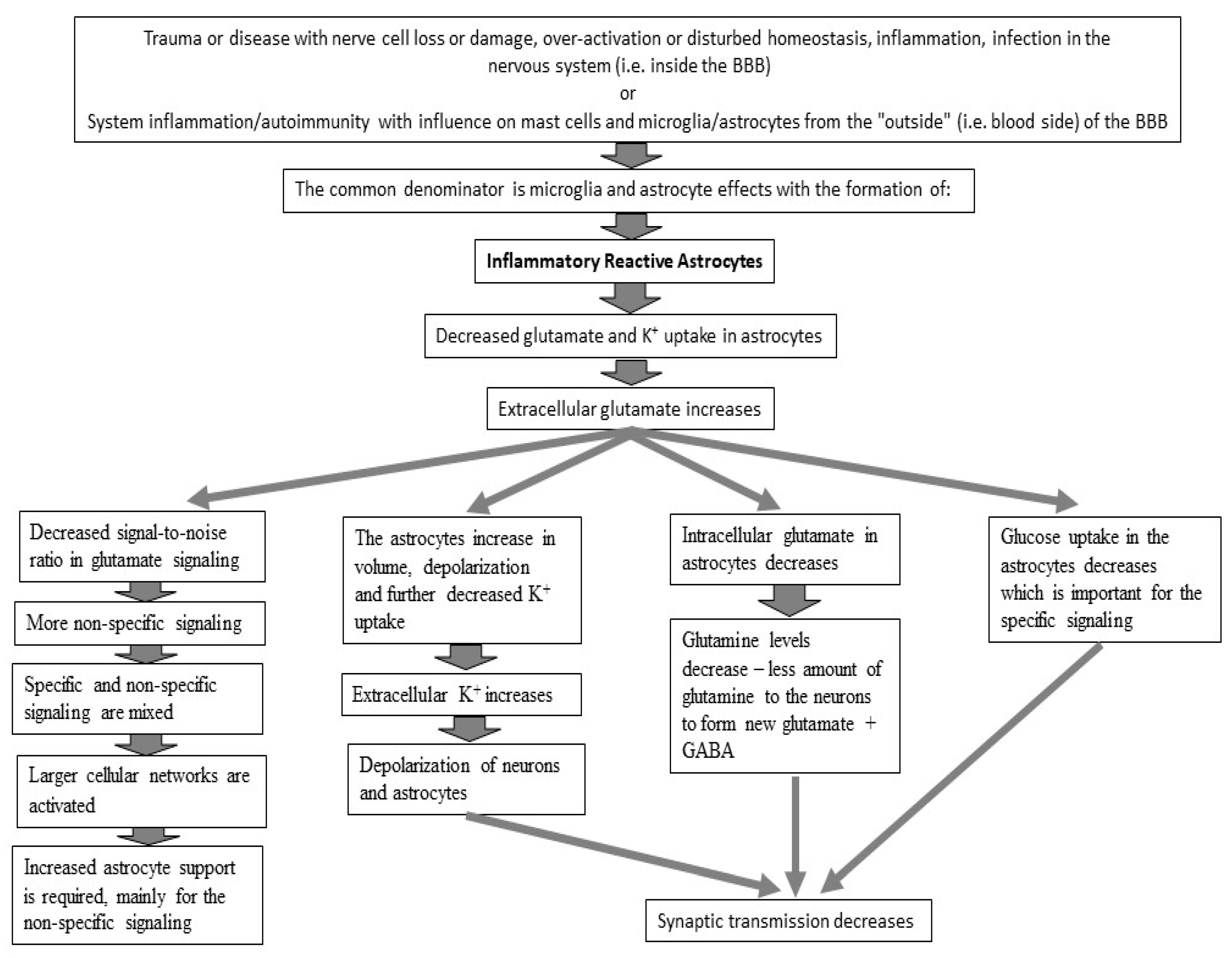
6. Probable Pathophysiology of BFS at the Cellular Level
6.1. Glutamate Transmission
6.2. Energy to the Brain
6.3. Reduced Glutamate Uptake
7. BFS and Its Relation to Glutamate Signaling
- Problems with motivation and initiating an activity might relate to dopamine [43].
- Emotional symptoms such as tearfulness and irritability might be related to serotonin and dopamine [47].
Long-Lasting BFS
8. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
8.1. The Brain Fatigue Syndrome (BFS) Proposal
8.2. Limitations
8.3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindqvist, G.; Malmgren, H. Organic Mental Disorders as Hypothetical Pathogenetic Processes. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1993, 88, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, N.S.; Crawford, S.; Wenden, F.J.; Moss, N.E.G.; Wade, D.T. The Rivermead Post Concussion Symptoms Questionnaire: A measure of symptoms commonly experienced after head injury and its reliability. J. Neurol. 1995, 242, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohnen, N.; Twijnstra, A.; Jolles, J. Post-traumatic and emotional symptoms in different subgroups of patients with mild head injury. Brain Inj. 1992, 6, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, A.; St George, B.; Fenton, M.; Firkins, L. Top 10 research priorities relating to life after stroke--consensus from stroke survivors, caregivers, and health professionals. Int. J. Stroke 2014, 9, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glader, E.L.; Stegmayr, B.; Asplund, K. Poststroke fatigue. A 2-year follow-up study of stroke patients in Sweden. Stroke 2002, 33, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Port, I.G.; Kwakkel, G.; Schepers, V.P.; Heinemans, C.T.; Lindeman, E. Is fatigue an independent factor associated with activities of daily living, instrumental activities of daily living and health-related quality of life in chronic stroke? Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2007, 23, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, J.B.; Ashman, T.; Gordon, W.; Ginsberg, A.; Engmann, C.; Egan, M.; Spielman, L.; Dijkers, M.; Flanagan, S. Fatigue After Traumatic Brain Injury and Its Impact on Participation and Quality of Life. J. Head Trauma. Rehabil. 2008, 23, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, G.; Gruen, R.L.; Kaye, A.H. Traumatic brain injury and long-term quality of life: Findings from an Australian study. J. Neurotrauma 2009, 26, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B. Screening Method for Assessment of Work Ability for Patients Suffering From Mental Fatigue. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 869377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, G.; Christensen, D.; Kirkevold, M.; Johnsen, S.P. Post-stroke fatigue and return to work: A 2-year follow-up. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2011, 125, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, S.; Rönnbäck, L.; Johansson, B. Long-term mental fatigue after traumatic brain injury and impact on capacity for workemployment status. J. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 49, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, J.J.; Bird, M.-L.; Godecke, E.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Laurin, C.; Olaoye, O.A.; Solomon, J.; Teasell, R.; Watkins, C.L.; Walker, M.F. Moving Stroke Rehabilitation Research Evidence into Clinical Practice: Consensus-Based Core Recommendations From the Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Roundtable. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair. 2019, 33, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Behan, P.O. Fatigue in neurological disorders. Lancet 2004, 363, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönnbäck, L.; Johansson, B. Long-Lasting Pathological Mental Fatigue After Brain Injury–A Dysfunction in Glutamate Neurotransmission? Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 791984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.J.; Tomé, A.R.; Cunha, R.A. ATP as a multi-target danger signal in the brain. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K. Microglial activation by purines and pyrimidines. Glia 2002, 40, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluger, B.M.; Krupp, L.B.; Enoka, R.M. Fatigue and fatigability in neurologic illnesses. Neurology 2013, 80, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergqvist, L.; Öhrvall, A.-M.; Rönnbäck, L.; Johansson, B.; Himmelmann, K.; Peny-Dahlstrand, M. Evidence of Construct Validity for the Modified Mental Fatigue Scale When Used in Persons with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2019, 23, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrenfort, J.; Wilterdink, A.; van der Veen, E. Long-term residual complaints and psychosocial sequelae after remission of hyperthyroidism. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2000, 25, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B.; Holmberg, M.; Skau, S.; Malmgren, H.; Nyström, H.F. The relationship between mental fatigue, depression, and cognition in Graves’ disease. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2023, 12, e230040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B.; Rönnbäck, L. Evaluation of the Mental Fatigue Scale and its relation to Cognitive and Emotional Functioning after Traumatic Brain Injury or Stroke. Int. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 2, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, B.; Starmark, A.; Berglund, P.; Rödholm, M.; Rönnbäck, L. Mental trötthet—Subjektivt problem som kan skattas. Läkartidningen 2010, 107, 2964–2967. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, B.; Wentzel, A.-P.; Andréll, P.; Mannheimer, C.; Rönnbäck, L. Methylphenidate reduces mental fatigue and improves processing speed in persons suffered a traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2015, 29, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.; Berglund, P.; Rönnbäck, L. Mental fatigue and impaired information processing after mild and moderate traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2009, 23, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.; Starmark, A.; Berglund, P.; Rödholm, M.; Rönnbäck, L. A self-assessment questionnaire for mental fatigue and related symptoms after neurological disorders and injuries. Brain Inj. 2009, 24, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skau, S.; Bunketorp-Käll, L.; Kuhn, H.G.; Johansson, B. Mental Fatigue and Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS)—Based Assessment of Cognitive Performance After Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Barugh, A.; Macleod, M.; Mead, G. Psychological Associations of Poststroke Fatigue A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2014, 45, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, F.; Bogousslavsky, J. Fatigue after Stroke: A Major but Neglected Issue. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2001, 12, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsford, J.; Schönberger, M.; Rajaratnam, S.M. A Model of Fatigue Following Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Head Trauma. Rehabil. 2015, 30, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi-Kwon, S.; Han, S.W.; Kwon, S.U.; Kang, D.W.; Choi, J.M.; Kim, J.S. Fluoxetine Treatment in Poststroke Depression, Emotional Incontinence, and Anger Proneness A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2007, 23, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juengst, S.; Skidmore, E.; Arenth, P.M.; Niyonkuru, C.; Raina, K.D. Unique Contribution of Fatigue to Disability in Community-Dwelling Adults With Traumatic Brain Injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 94, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromwell, H.C.; Mears, R.P.; Wan, L.; Boutros, N.N. Sensory Gating: A Translational Effort from Basic to Clinical Science. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2008, 39, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, A.; van Zwieten, G.; Kotz, S.A.; Temel, Y.; Almasabi, F.; Schultz, B.G.; Schwartze, M.; Janssen, M.L. Sensory gating functions of the auditory thalamus: Adaptation and modulations through noise-exposure and high-frequency stimulation in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2023, 450, 114498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLuca, J. Information processing speed: How fast, how slow, and how come? In Information Processing Speed in Clinical Populations; DeLuca, J., Kalmar, J.H., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen, A.K.; Spliid, P.E.; Andersen, H.; Jakobsen, J. Fatigue and processing speed are related in multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziino, C.; Ponsford, J. Vigilance and fatigue following traumatic brain injury. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2006, 12, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.M. Glutamate: The Master Neurotransmitter and Its Implications in Chronic Stress and Mood Disorders. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 722323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niciu, M.J.; Kelmendi, B.; Sanacora, G. Overview of glutamatergic neurotransmission in the nervous system. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 100, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholey, E.; Apps, M.A. Fatigue: Tough days at work change your prefrontal metabolites. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, R876–R879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Edden, R.A.E.; Gao, F.; Li, H.; Gong, T.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Zhao, B. Reduced GABA levels correlate with cognitive impairment in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, S.; Hare, B.D.; Duman, R.S. Prefrontal cortex GABAergic deficits and circuit dysfunction in the pathophysiology and treatment of chronic stress and depression. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2017, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammett, S.T.; Cook, E.; Hassan, O.; Hughes, C.-A.; Rooslien, H.; Tizkar, R.; Larsson, J. GABA, noise and gain in human visual cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 736, 135294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebowitz, J.J.; Khoshbouei, H. Heterogeneity of dopamine release sites in health and degeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, T.; Nieder, A. Dopamine and Cognitive Control in Prefrontal Cortex. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnsten, A.F. Catecholamine Influences on Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortical Networks. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, e89–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, E.L.; Gupta, K.; Climer, J.R.; Monaghan, C.K.; Hasselmo, M.E. Cholinergic modulation of cognitive processing: Insights drawn from computational models. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Stackman, R.W., Jr. The role of serotonin 5-HT2A receptors in memory and cognition. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, J.L.; Ngwenya, L.B.; McCullumsmith, R.E. Neurotransmitter changes after traumatic brain injury: An update for new treatment strategies. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 24, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. On the potential role of glutamate transport in mental fatigue. J. Neuroinflamm. 2004, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudkoff, M.; Nissim, I.; Daikhin, Y.; Lin, Z.-P.; Nelson, D.; Pleasure, D.; Erecinska, M. Brain Glutamate Metabolism: Neuronal-Astroglial Relationships. Dev. Neurosci. 1993, 15, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the healthy brain. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 799–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magistretti, P.J.; Allaman, I. A cellular perspective on brain energy metabolism and fuctional imaging. Neuron Rev. 2015, 86, 883–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mink, J.W.; Blumenschine, R.J.; Adams, D.B. Ratio of central nervous system to body metabolism in vertebrates: Its constancy and functional basis. Am. J. Physiol. 1981, 421, R203–R210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.J.; Jolivet, R.; Attwell, D. Synaptic Energy Use and Supply. Neuron 2012, 75, 762–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergenthaler, P.; Lindauer, U.; Dienel, G.A.; Meisel, A. Sugar for the brain: The role of glucose in physiological and pathological brain function. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, K.R.; Wilson, C.M.; Brabazon, F.; von Leden, R.; Jurgens, J.S.; Oakes, T.R.; Selwyn, R.G. FDG-PET imaging in mild traumatic brain injury: A critical review. Front. Neuroenerg. 2014, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.H.; Brown, R.G.; Comella, C.; Garber, C.E.; Krupp, L.B.; Lou, J.S.; Marsh, L.; Nail, L.; Shulman, L.; Taylor, C.B. Fatigue in Parkinsons’s disease: A review. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Yuan, Y.; Tong, Q.; Jiang, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, K. Brain metabolic correlates of fatigue in Parkinson’s disease: A PET study. Int. J. Neurosci. 2018, 128, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.S.; Aminian, K.; Li, C.; Lang, A.E.; Houle, S.; Strafella, A.P. Fatigue in Parkinson’s disease: The contribution of cerebral metabolic changes. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelcke, U.; Kappos, L.; Lechner-Scott, J.; Brunnschweiler, H.; Huber, S.; Ammann, W.; Plohmann, A.; Dellas, S.; Maguire, R.P.; Missimer, J.; et al. Reduced Glucose Metabolism in the Frontal Cortex and Basal Ganglia of Multiple Sclerosis Patients With Fatigue: A 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Study. Neurology 1997, 48, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berginström, N.; Nordström, P.; Ekman, U.; Eriksson, J.; Andersson, M.; Nyberg, L.; Nordström, A. Using Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Detect Chronic Fatigue in Patients With Previous Traumatic Brain Injury: Changes Linked to Altered Striato-Thalamic-Cortical Functioning. J. Head Trauma. Rehabil. 2018, 33, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, G.R.; Dobryakova, E.; DeLuca, J.; Chiaravalloti, N.; Essad, K.; Genova, H. Cognitive fatigue in individuals with traumatic brain injury is associated with caudate activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, L.E.; Möller, M.C.; Julin, P.; Bartfai, A.; Hashim, F.; Li, T.-Q. Post mTBI fatigue is associated with abnormal brain functional connectivity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, A.D.; Wylie, G.R.; Genova, H.M.; Hillary, F.G.; DeLuca, J. The neural correlates of cognitive fatigue in traumatic brain injury using functional MRI. Brain Inj. 2009, 23, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Astrocytes: Role and Functions in Brain Pathologies. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienel, G.A. Brain Glucose Metabolism: Integration of Energetics With Function. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 1, 949–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.W. Excitotoxic cell death. J. Neurobiol. 1992, 23, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syková, E. Extrasynaptic volume transmission and diffusion parameters of the extracellular space. Neuroscience 2004, 129, 861–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, E.; Muyderman, H.; Leonova, J.; Allansson, L.; Sinclair, J.; Blomstrand, F.; Thorlin, T.; Nilsson, M.; Rönnbäck, L. Astroglia and glutamate in physiology and pathology: Aspects on glutamate transport, glutamate-induced cell swelling and gap-junction communication. Neurochem. Int. 2000, 37, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeks, J.P.; Mennerick, S. Selective Effects of Potassium Elevations on Glutamate Signaling and Action Potential Conduction in Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, R.I.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Roza, E.; Vladâcenco, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Neurotransmitters—Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnsten, A.F.; Dudley, A.G. Methylphenidate improves prefrontal cortical cognitive function through α2 adrenoceptor and dopamine D1 receptor actions: Relevance to therapeutic effects in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Behav. Brain Funct. 2005, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmo, M.E. The role of acetylcholine in learning and memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2006, 16, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.; Gavelin, H.M.; Boraxbekk, C.-J.; Eskilsson, T.; Josefsson, M.; Järvholm, L.S.; Neely, A.S. Subjective cognitive complaints in patients with stress-related exhaustion disorder: A cross sectional study. BMC Psychol. 2021, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patching, S.G. Glucose Transporters at the Blood-Brain Barrier: Function, Regulation and Gateways for Drug Delivery. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 1046–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, C.R.; Noe-Letschnig, M.; Handschuh, P.; Noe, C.A.; Lanzenberger, R. Dysfunction of the Blood-Brain Barrier—A Key Step in Neurodegeneration and Dementia. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traina, G. Mast Cells in Gut and Brain and Their Potential Role as an Emerging Therapeutic Target for Neural Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara, R.C.; Jaramillo-Riveri, S.; Luarte, A.; Moënne-Loccoz, C.; Fuentes, R.; Couve, A.; Maldonado, P.E. The Energy Homeostasis Principle: Neuronal Energy Regulation Drives Local Network Dynamics Generating Behavior. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raichle, M.E. The restless brain: How intrinsic activity organizes brain function. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, M.A.; Dohi, K.; Banks, W.A. Neuroinflammation: A Common Pathway in CNS Diseases as Mediated at the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neuroimmunomodulation 2012, 19, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervellati, C.; Trentini, A.; Pecorelli, A.; Valacchi, G. Inflammation in Neurological Disorders: The Thin Boundary Between Brain and Periphery. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 33, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galea, I. The blood–brain barrier in systemic infection and inflammation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2489–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponsford, J.; Lee, N.K.; Wong, D.; McKay, A.; Haines, K.; Downing, M.; Alway, Y.; Furtado, C.; O’Donnell, M.L. Factors Associated With Response to Adapted Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Anxiety and Depression Following Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Head Trauma. Rehabil. 2020, 35, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johansson, B.; Rönnbäck, L. The Brain Fatigue Syndrome—Symptoms, Probable Definition, and Pathophysiological Mechanisms. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103271
Johansson B, Rönnbäck L. The Brain Fatigue Syndrome—Symptoms, Probable Definition, and Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103271
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohansson, Birgitta, and Lars Rönnbäck. 2025. "The Brain Fatigue Syndrome—Symptoms, Probable Definition, and Pathophysiological Mechanisms" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103271
APA StyleJohansson, B., & Rönnbäck, L. (2025). The Brain Fatigue Syndrome—Symptoms, Probable Definition, and Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103271







