Using an Interpretable Amino Acid-Based Machine Learning Method to Enhance the Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Size and Participants
2.2. Blood Collection and Metabolite Analysis
2.3. Classification Algorithm
2.4. Cross-Validation Framework
2.5. Performance Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Logistic Regression Model Classification Performance
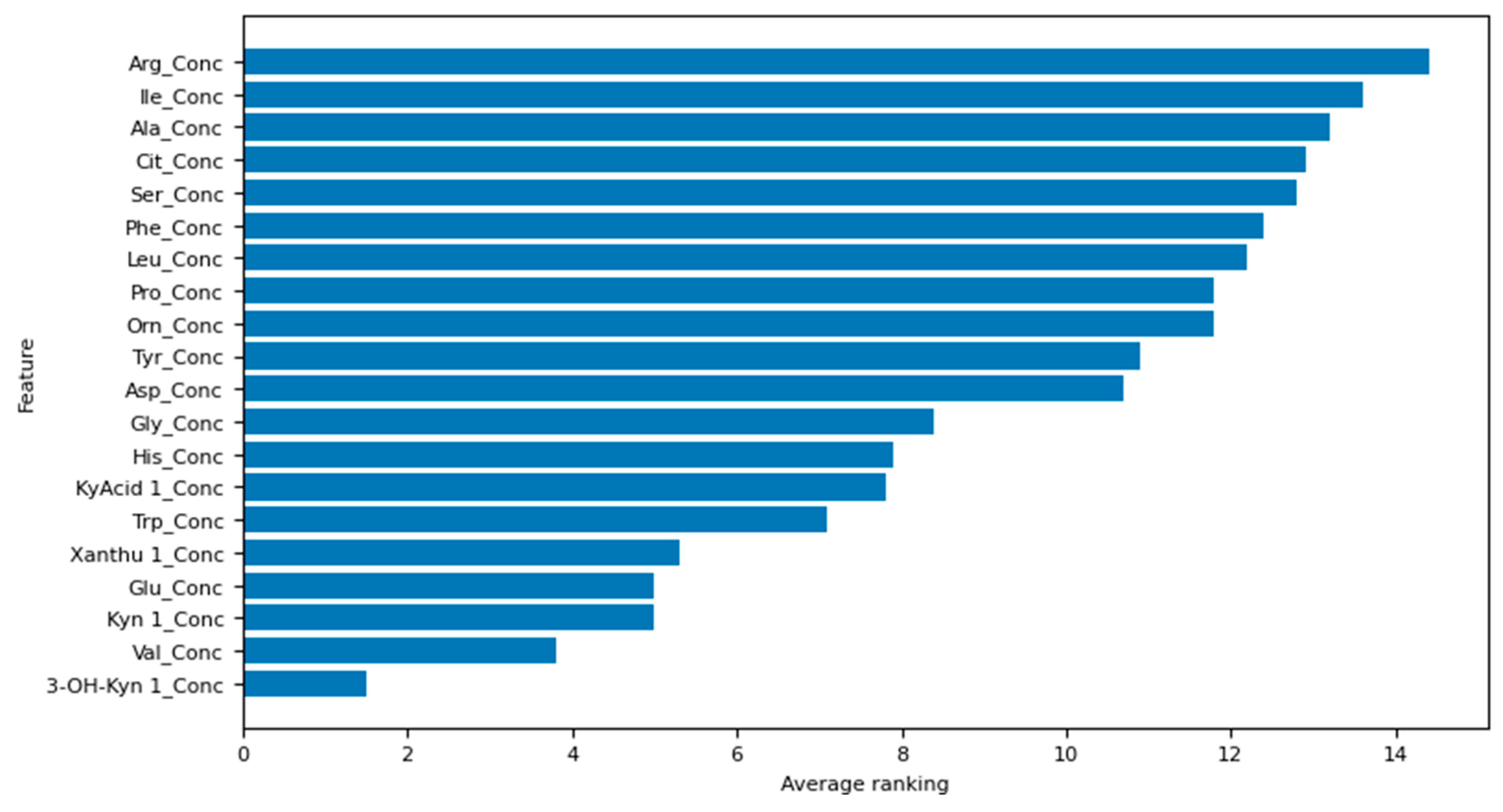
3.3. Logistic Regression Model-Selected Features
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates. 2017. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254610/WHO-MSD-MER-2017.2-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Costa, L.N.F.G.; Carneiro, B.A.; Alves, G.S.; Silva, D.H.L.; Guimaraes, D.F.; Souza, L.S.; Bandeira, I.D.; Beanes, G.; Scippa, A.M.; Quarantini, L.C. Metabolomics of Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies. Cureus 2022, 14, e23009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormel, J.; Hartman, C.A.; Snieder, H. The genetics of depression: Successful genome-wide association studies introduce new challenges. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandal, M.J.; Leppa, V.; Won, H.; Parikshak, N.N.; Geschwind, D.H. The road to precision psychiatry: Translating genetics into disease mechanisms. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, A.; Tolosi, L.; Sander, O.; Lengauer, T. Permutation importance: A corrected feature importance measure. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulaal, M.J.; Casson, A.J.; Gaydecki, P. Critical Analysis of Cross-Validation Methods and Their Impact on Neural Networks Performance Inflation in Electroencephalography Analysis. IEEE Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2021, 44, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabalas, A.; Gowen, E.; Poliakoff, E.; Casson, A.J. Machine learning algorithm validation with a limited sample size. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morilak, D.A.; Frazer, A. Antidepressants and brain monoaminergic systems: A dimensional approach to understanding their behavioural effects in depression and anxiety disorders. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004, 7, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, T.A.; Nguyen, J.C.; Polglaze, K.E.; Bertrand, P.P. Influence of Tryptophan and Serotonin on Mood and Cognition with a Possible Role of the Gut-Brain Axis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranyi, A.; Amouzadeh-Ghadikolai, O.; von Lewinski, D.; Rothenhausler, H.B.; Theokas, S.; Robier, C.; Mangge, H.; Reicht, G.; Hlade, P.; Meinitzer, A. Branched-Chain Amino Acids as New Biomarkers of Major Depression—A Novel Neurobiology of Mood Disorder. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setoyama, D.; Kato, T.A.; Hashimoto, R.; Kunugi, H.; Hattori, K.; Hayakawa, K.; Sato-Kasai, M.; Shimokawa, N.; Kaneko, S.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Plasma Metabolites Predict Severity of Depression and Suicidal Ideation in Psychiatric Patients—A Multicenter Pilot Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, S. The potential biomarker panels for identification of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) patients with and without early life stress (ELS) by metabonomic analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.I.; Lin, G.; Chiang, M.H.; Chiu, C.Y. Metabolomics-based discrimination of patients with remitted depression from healthy controls using (1)H-NMR spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moaddel, R.; Shardell, M.; Khadeer, M.; Lovett, J.; Kadriu, B.; Ravichandran, S.; Morris, P.J.; Yuan, P.; Thomas, C.J.; Gould, T.D.; et al. Plasma metabolomic profiling of a ketamine and placebo crossover trial of major depressive disorder and healthy control subjects. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 3017–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciocan, D.; Cassard, A.M.; Becquemont, L.; Verstuyft, C.; Voican, C.S.; El Asmar, K.; Colle, R.; David, D.; Trabado, S.; Feve, B.; et al. Blood microbiota and metabolomic signature of major depression before and after antidepressant treatment: A prospective case-control study. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2021, 46, E358–E368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ray, B.; Neavin, D.R.; Zhang, J.; Athreya, A.P.; Biernacka, J.M.; Bobo, W.V.; Hall-Flavin, D.K.; Skime, M.K.; Zhu, H.; et al. Beta-defensin 1, aryl hydrocarbon receptor and plasma kynurenine in major depressive disorder: Metabolomics-informed genomics. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Kim, Y.K. Ketamine in Major Depressive Disorder: Mechanisms and Future Perspectives. Psychiatry Investig. 2020, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Fang, L.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J.; Cheng, K.; Zhou, C.; Zhan, Y.; Melgiri, N.D.; et al. The Extrinsic Coagulation Pathway: A Biomarker for Suicidal Behavior in Major Depressive Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, A.; Zhou, X.; Del Giovane, C.; Hetrick, S.E.; Qin, B.; Whittington, C.; Coghill, D.; Zhang, Y.; Hazell, P.; Leucht, S.; et al. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of antidepressants for major depressive disorder in children and adolescents: A network meta-analysis. Lancet 2016, 388, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Lin, C.H.; Lane, H.Y. Precision Psychiatry Applications with Pharmacogenomics: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzdok, D.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Machine Learning for Precision Psychiatry: Opportunities and Challenges. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davatzikos, C. Machine learning in neuroimaging: Progress and challenges. NeuroImage 2019, 197, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, L.; Jia, J.; Tang, S.; Xu, P.; Xie, P.; Gao, H. Predictive diagnosis of major depression using NMR-based metabolomics and least-squares support vector machine. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 464, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, B.S.; Williams, L.M.; Steiner, J.; Leboyer, M.; Carvalho, A.F.; Berk, M. The new field of ‘precision psychiatry’. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissler, E.H.; Naumann, T.; Andersson, T.; Ranganath, R.; Elemento, O.; Luo, Y.; Freitag, D.F.; Benoit, J.; Hughes, M.C.; Khan, F.; et al. The role of machine learning in clinical research: Transforming the future of evidence generation. Trials 2021, 22, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panch, T.; Szolovits, P.; Atun, R. Artificial intelligence, machine learning and health systems. J. Glob. Health 2018, 8, 020303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friederich, P.; Krenn, M.; Tamblyn, I.; Aspuru-Guzik, A. Scientific intuition inspired by machine learning-generated hypotheses. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2, 025027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, Q.; Herbinger, J.; Stachl, C.; Bischl, B.; Casalicchio, G. Grouped feature importance and combined features effect plot. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2022, 36, 1401–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.X.; Xia, J.J.; Deng, F.L.; Liang, W.W.; Wu, J.; Yin, B.M.; Dong, M.X.; Chen, J.J.; Ye, F.; Wang, H.Y.; et al. Diagnosis of major depressive disorder based on changes in multiple plasma neurotransmitters: A targeted metabolomics study. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiglic, G.; Kocbek, P.; Fijacko, N.; Zitnik, M.; Verbert, K.; Cilar, L. Interpretability of machine learning-based prediction models in healthcare. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 10, e1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Li, S.; Ong, M.E.H.; Xie, F.; Chakraborty, B.; Ting, D.S.W.; Liu, N. A novel interpretable machine learning system to generate clinical risk scores: An application for predicting early mortality or unplanned readmission in a retrospective cohort study. PLoS Digit. Health 2022, 1, e0000062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyeong, S.; Shin, J. Two-stage credit scoring using Bayesian approach. J. Big Data 2022, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevade, S.K.; Keerthi, S.S. A simple and efficient algorithm for gene selection using sparse logistic regression. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Bahadori, M.T.; Kulas, J.A.; Schuetz, A.; Stewart, W.F.; Sun, J. RETAIN: An interpretable predictive model for healthcare using reverse time attention mechanism. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 3512–3520. [Google Scholar]
- Sheu, Y.H. Illuminating the Black Box: Interpreting Deep Neural Network Models for Psychiatric Research. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 551299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.B.; Fang, L.; Hu, Z.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, J.J.; Li, F.F.; Lu, J.; Mu, J.; Xie, P. Potential clinical utility of plasma amino acid profiling in the detection of major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 200, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.L.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Borah, S.; Gogoi, P.; Gohain, P.; Boro, C.; Muchahari, M.K. Machine Learning for Detection of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Smart Intell. Comput. Appl. 2022, 2, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, F.; Zameer, A.; Muneeb, M. Predictions for COVID-19 with deep learning models of LSTM, GRU and Bi-LSTM. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, H.; Bieda, A.; Michalak, J.; Schneider, S.; Margraf, J. Education and mental health: Do psychosocial resources matter? SSM Popul. Health 2019, 7, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalar, B.; Blatnik, A.; Maver, A.; Klemenc-Ketiš, Z.; Peterlin, B. Family History as an Important Factor for Stratifying Participants in Genetic Studies of Major Depression. Balk. J. Med. Genet. 2018, 21, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorp, J.G.; Gerring, Z.F.; Colodro-Conde, L.; Byrne, E.M.; Medland, S.E.; Middeldorp, C.M.; Derks, E.M. The association between trauma exposure, polygenic risk and individual depression symptoms. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 321, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-F.; Zhou, Y.-N.; Liu, Y.-H.; Hao, Y.-Z.; Zhang, J.-H.; Liu, T.-Q.; Ma, Y.-J. Social support and depressive symptoms: Exploring stigma and self-efficacy in a moderated mediation model. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; Xie, P.; Xu, G. Discovery and validation of plasma biomarkers for major depressive disorder classification based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Ali, S.; Karmoker, J.R.; Kadir, M.F.; Ahmed, M.U.; Nahar, Z.; Islam, S.M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Hasnat, A.; Islam, M.S. Evaluation of serum amino acids and non-enzymatic antioxidants in drug-naive first-episode major depressive disorder. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, N.; Shinoda, K.; Sato, H.; Sasaki, K.; Suzuki, M.; Yamaki, K.; Fujimori, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Osei-Hyiaman, D.; Ohashi, Y. Plasma metabolome analysis of patients with major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 72, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.K.; Husain, S.F.; Wee, H.N.; Ching, J.; Kovalik, J.P.; Cheng, M.S.; Schwarz, H.; Tang, T.B.; Ho, C.S. Integration of the Cortical Haemodynamic Response Measured by Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Amino Acid Analysis to Aid in the Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Koga, N.; Hattori, K.; Matsuo, J.; Ota, M.; Hori, H.; Sasayama, D.; Teraishi, T.; Ishida, I.; Yoshida, F.; et al. Plasma amino acid profile in major depressive disorder: Analyses in two independent case-control sample sets. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 96, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzdok, D.; Altman, N.; Krzywinski, M. Statistics versus machine learning. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, C.; Martin, R.K.; Pareek, A.; Groll, A.; Seil, R.; Tischer, T. Machine learning and conventional statistics: Making sense of the differences. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2022, 30, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yieh, L.; Yang, T.; Drinkenburg, W.; Peeters, P.; Steckler, T.; Narayan, V.A.; Wittenberg, G.; Ye, J. Metabolomic biosignature differentiates melancholic depressive patients from healthy controls. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Saito, H.; Katsuki, H. 3-Hydroxykynurenine, an endogenous oxidative stress generator, causes neuronal cell death with apoptotic features and region selectivity. J. Neurochem. 1998, 70, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ding, L.; Zhang, H.; Mellor, D.; Wu, H.; Zhao, D.; Wu, C.; Lin, Z.; Yuan, J.; Peng, D. The Metabolic Factor Kynurenic Acid of Kynurenine Pathway Predicts Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoes, M.J.; Sijben, N. The clinical significance of disordered renal excretion of xanthurenic acid in depressive patients. Psychopharmacology 1981, 75, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanke, M.; VanDongen, A. Activation Mechanisms of the NMDA Receptor. In Biology of the NMDA Receptor; VanDongen, A., Ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer, J.W.; Farber, N.B.; Olney, J.W. NMDA receptor function, memory, and brain aging. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2000, 2, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bot, M.; Milaneschi, Y.; Al-Shehri, T.; Amin, N.; Garmaeva, S.; Onderwater, G.L.J.; Pool, R.; Thesing, C.S.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Vogelzangs, N.; et al. Metabolomics Profile in Depression: A Pooled Analysis of 230 Metabolic Markers in 5283 Cases with Depression and 10,145 Controls. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koochakpoor, G.; Salari-Moghaddam, A.; Keshteli, A.H.; Afshar, H.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Adibi, P. Dietary intake of branched-chain amino acids in relation to depression, anxiety and psychological distress. Nutr. J. 2021, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.J.; McTavish, S.F.; Park, S.B.; Cowen, P.J. Effect of valine on 5-HT-mediated prolactin release in healthy volunteers, and on mood in remitted depressed patients. Br. J. Psychiatry 1995, 167, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.K. Primer on binary logistic regression. Fam. Med. Community Health 2021, 9 (Suppl. S1), e001290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| MDD (n = 70) | HC (n = 70) | p Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 28.3 (SD 7.2) | 28.2 (SD 7.3) | 0.926 |
| Sex | 1.000 | ||
| Male | 16 (22.9%) | 16 (22.9%) | |
| Female | 54 (77.1%) | 54 (77.1%) | |
| Ethnicity | 1.000 | ||
| Chinese | 45 (64.3%) | 45 (64.3%) | |
| Malay | 15 (21.4%) | 15 (21.4%) | |
| Indian | 9 (12.9%) | 9 (12.9%) | |
| Eurasian | 1 (1.4%) | 1 (1.4%) | |
| Education (years) | 14.5 (SD 1.8) | 15.6 (SD 1.2) | <0.001 |
| Perceived social support | |||
| Poor | 17 (24.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | <0.001 |
| Average | 44 (62.9%) | 18 (25.7%) | |
| Good | 9 (12.9%) | 52 (74.3%) | |
| HAM-D 17 score | 19.8 (SD 5.4) | 1.9 (SD 2.5) | <0.001 |
| Mild (8–16) | 21 (30.0%) | 4 (5.7%) | |
| Moderate (17–23) | 30 (42.9%) | 0 | |
| Severe (≥24) | 19 (27.1%) | 0 | |
| Family psychiatric history | 30 (42.9%) | 17 (24.3%) | 0.032 |
| History of trauma | 35 (50%) | 14 (20.0%) | <0.001 |
| Past admission to a psychiatric ward | 16 (22.9%) | ||
| Past suicide attempt | 32 (45.7%) | ||
| Pharmacotherapy | 60 (85.7%) |
| Validation Set Performance | Test Set Performance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Logistic Regression Model | AUC | AUC | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Number of Features Selected |
| With feature selection and with hyperparameter optimisation | 0.74 ± 0.03 | 0.76 ± 0.16 | 68.6 ± 15.7 | 71.2 ± 18.7 | 65.7 ± 21.4 | 14.6 ± 1.56 |
| No feature selection and with hyperparameter optimisation | 0.73 ± 0.03 | 0.72 ± 0.17 | 67.9 ± 14.0 | 70.6 ± 17.3 | 65.7 ± 19.4 | 21.0 ± 0.00 |
| No feature selection and no hyperparameter optimisation | 0.71 ± 0.04 | 0.73 ± 0.17 | 65.0 ± 14.8 | 66.6 ± 20.1 | 60.0 ± 20.0 | 21.0 ± 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, C.S.H.; Tan, T.W.K.; Khoe, H.C.H.; Chan, Y.L.; Tay, G.W.N.; Tang, T.B. Using an Interpretable Amino Acid-Based Machine Learning Method to Enhance the Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051222
Ho CSH, Tan TWK, Khoe HCH, Chan YL, Tay GWN, Tang TB. Using an Interpretable Amino Acid-Based Machine Learning Method to Enhance the Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(5):1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051222
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Cyrus Su Hui, Trevor Wei Kiat Tan, Howard Cai Hao Khoe, Yee Ling Chan, Gabrielle Wann Nii Tay, and Tong Boon Tang. 2024. "Using an Interpretable Amino Acid-Based Machine Learning Method to Enhance the Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 5: 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051222
APA StyleHo, C. S. H., Tan, T. W. K., Khoe, H. C. H., Chan, Y. L., Tay, G. W. N., & Tang, T. B. (2024). Using an Interpretable Amino Acid-Based Machine Learning Method to Enhance the Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(5), 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051222








