Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Hepatitis B Patients
Abstract
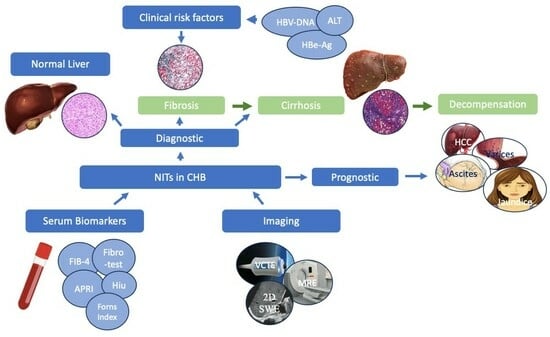
1. Introduction:
2. Serum Biomarkers:
2.1. AST-to-Platelet Ratio Index
2.2. FIB-4
2.3. FibroTest
2.4. Forns Index
2.5. Hui Score
2.6. Other Markers
2.7. Serum Markers and HBV Infection Phase
3. Imaging Tests:
3.1. Vibration Controlled Transient Elastography
3.1.1. Vibration Controlled Transient Elastography (VCTE) in Inactive CHB Infection
3.1.2. VCTE in Chronic Hepatitis B
3.2. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Elastography
3.3. Magnetic Resonance Elastography
3.4. Two-Dimensional (2D) Shear-Wave Elastography (SWE)
3.5. Combination of Non-Invasive Tests for Fibrosis Assessment
4. Longitudinal Assessment of Fibrosis Stage with Antiviral Therapy
5. Role of Serum Fibrosis Markers and Imaging Tests for Prognosis/Liver Outcomes
6. Summary
7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Progress Report on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 53. [Google Scholar]
- Ganem, D.; Prince, A.M. Hepatitis B virus infection--natural history and clinical consequences. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Huang, D.Q.; Nguyen, M.H. Global burden of hepatitis B virus: Current status, missed opportunities and a call for action. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheena, B.S.; Hiebert, L.; Han, H.; Ippolito, H.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, Z.; Abbastabar, H.; Abdoli, A.; Abubaker Ali, H.; Adane, M.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of hepatitis B, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 796–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Sarin, S.K.; Hissar, S.; Pande, C.; Sakhuja, P.; Sharma, B.C.; Chauhan, R.; Bose, S. Virologic and Histologic Features of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Asymptomatic Patients With Persistently Normal ALT. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marugán, R.B.; Garzóno, S.G. DNA-guided hepatitis B treatment, viral load is essential, but not sufficient. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Sebastiani, G. Limitations of non-invasive tests for assessment of liver fibrosis. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzigotti, A.; Tsochatzis, E.; Boursier, J.; Castera, L.; Cazzagon, N.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Petta, S.; Thiele, M. Reply to: Correspondence on “EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis—2021 update”. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver; Clinical Practice Guideline Panel. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis—2021 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 659–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-Y.; Kong, H.; Song, R.-X.; Zhai, Y.-H.; Wu, X.-F.; Ai, W.-S.; Liu, H.-B. The Effectiveness of Noninvasive Biomarkers to Predict Hepatitis B-Related Significant Fibrosis and Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Yang, J.; Yan, L. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis-4 index for detecting liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2015, 61, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; S Sulkowski, M.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, Y.; Gong, G. Evaluation of seven noninvasive models in staging liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y. The diagnostic value of the FIB-4 index for staging hepatitis B-related fibrosis: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneveld, M.J.; Brouwer, W.P.; Chan, H.L.; Piratvisuth, T.; Jia, J.D.; Zeuzem, S.; Liaw, Y.F.; Hansen, B.E.; Choi, H.; Wat, C.; et al. Optimisation of the use of APRI and FIB-4 to rule out cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Results from the SONIC-B study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thabut, D.; Imbert-Bismut, F.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Messous, D.; Muntenau, M.; Valla, D.C.; Moreau, R.; Poynard, T.; Lebrec, D. Relationship between the Fibrotest and portal hypertension in patients with liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynard, T.; Ngo, Y.; Munteanu, M.; Thabut, D.; Ratziu, V. Noninvasive Markers of Hepatic Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis B. Curr. Hepat. Rep. 2011, 10, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynard, T.; Morra, R.; Halfon, P.; Castera, L.; Ratziu, V.; Imbert-Bismut, F.; Naveau, S.; Thabut, D.; Lebrec, D.; Zoulim, F.; et al. Meta-analyses of FibroTest diagnostic value in chronic liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2007, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forns, X.; Ampurdanès, S.; Llovet, J.M.; Aponte, J.; Quintó, L.; Martínez-Bauer, E.; Bruguera, M.; Sánchez-Tapias, J.M.; Rodés, J. Identification of chronic hepatitis C patients without hepatic fibrosis by a simple predictive model: Identification of chronic hepatitis C patients without hepatic fibrosis by a simple predictive model. Hepatology 2002, 36, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar, F.; Sezer, S.; Ginis, Z.; Ozturk, G.; Albayrak, A.; Basar, O.; Ekiz, F.; Coban, S.; Yuksel, O.; Armutcu, F.; et al. APRI, the FIB-4 score, and Forn’s index have noninvasive diagnostic value for liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, A.Y.; Chan, H.L.; Wong, V.W.; Liew, C.T.; Chim, A.M.; Chan, F.K.; Sung, J.J. Identification of chronic hepatitis B patients without significant liver fibrosis by a simple noninvasive predictive model. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, V.; Sturm, N.; Faure, P.; Trocme, C.; Marlu, A.; Hilleret, M.N.; Morel, F.; Zarski, J.P. Prospective evaluation of FibroTest®, FibroMeter®, and HepaScore® for staging liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: Comparison with hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.D.; Lu, L.G.; Mao, Y.M.; Qiu, D.K.; Li, J.Q.; Wan, M.B.; Chen, C.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Cai, X.; Gao, C.F.; et al. Prediction of significant fibrosis in HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B by a noninvasive model. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Gao, C.F.; Zhou, K.; Zhao, Y.P.; Xu, M.Y.; Lu, L.G. Serum N-glycomic markers in combination with panels improves the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis B. Ann. Hepatol. 2012, 11, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, M.J.; Chen, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.M.; Zheng, G.S.; Hong, G.L. Diagnostic accuracy of mac-2-binding protein glycosylation isomer for diagnosing hepatitis B-related fibrosis: A meta-analysis. J. Dig. Dis. 2022, 23, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Kao, J.H. Development of hepatocellular carcinoma in treated and untreated patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.H.; Nguyen, S.T.; Phan, S.T.; Nguyen, K.M.; Nguyen, C.D. Evaluating M2BPGi as a Marker for Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 4407–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacob, D.G.; Rosca, A.; Ruta, S.M. Circulating microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for hepatitis B virus liver fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, N.; Huang, C.; Chen, M.; Cheng, Q.; Yu, K.; Chen, S.; Zhu, M.; Shi, G. Serum MicroRNA Levels as a Noninvasive Diagnostic Biomarker for the Early Diagnosis of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Liver Fibrosis. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.; Ahmad, N.; Mustafa, G.; Shrestha, A.; Alam, A.K.; Khan, M. Evaluation of normal or minimally elevated alanine transaminase, age and DNA level in predicting liver histological changes in chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-A.; Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Xia, J.; Wu, W.; Yin, S.; et al. Gamma-glutamyl Transpeptidase to Platelet Ratio Predicts Liver Injury in Hepatitis B e Antigen-negative Chronic Hepatitis B Patients With Normal Alanine Aminotransferase. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, M.; Beaugrand, M.; de Ledinghen, V.; Douvin, C.; Marcellin, P.; Poupon, R.; Sandrin, L.; Miette, V. Controlled attenuation parameter (CAP): A novel VCTE™ guided ultrasonic attenuation measurement for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis: Preliminary study and validation in a cohort of patients with chronic liver disease from various causes. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrin, L.; Fourquet, B.; Hasquenoph, J.M.; Yon, S.; Fournier, C.; Mal, F.; Christidis, C.; Ziol, M.; Poulet, B.; Kazemi, F.; et al. Transient elastography: A new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2003, 29, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castera, L.; Forns, X.; Alberti, A. Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis using transient elastography. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraquelli, M.; Rigamonti, C.; Casazza, G.; Conte, D.; Donato, M.F.; Ronchi, G.; Colombo, M. Reproducibility of transient elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease. Gut 2007, 56, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, F.; Coco, B.; Ciccorossi, P.; Colombatto, P.; Romagnoli, V.; Cherubini, B.; Bonino, F.; Brunetto, M.R. Liver stiffness in the hepatitis B virus carrier: A non-invasive marker of liver disease influenced by the pattern of transaminases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 6154–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimone, S.; Calvaruso, V.; Pleguezuelo, M.; Squadrito, G.; Amaddeo, G.; Jacobs, M.; Khanna, P.; Raimondo, G.; Dusheiko, G. An evaluation of transient elastography in the discrimination of HBeAg-negative disease from inactive hepatitis B carriers. J. Viral Hepat. 2009, 16, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristina, S.J.L.; Marta, C.M.; Mercedes, G.S.; Almudena, P.M.; Álvaro, H.M.; Luis, V.S.J.; Tesifón, P.C. Characterization and evaluation of liver fibrosis grade in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and normal transaminases. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2018, 24, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Margariti, A.; Papageorgiou, M.V.; Kranidioti, H.; Katoglou, A.; Kontos, G.; Adamidi, S.; Kafiri, G.; Deutsch, M.; et al. The usefulness of transient elastography in the assessment of patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.L.; Chan, H.L.; Yu, Z.; Chan, H.Y.; Tse, C.H.; Wong, V.W. Liver fibrosis progression is uncommon in patients with inactive chronic hepatitis B: A prospective cohort study with paired transient elastography examination. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 1842–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delle Monache, M.; Petrelli, A.; Rossi, A.; Cecere, R.; Mirisola, C.; Costanzo, G.; Francia, C.; Cerini, F.; Cavani, A.; Nosotti, L. Noninvasive Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis in a Sample of Putative Inactive HBV Carriers in Rome, Italy. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 3068690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 Hepatitis B Guidance. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 12, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.L.; Yu, X.P.; Li, J.L.; Lin, H.M.; Kang, N.L.; Jiang, J.J.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.R.; Zeng, D.W. Effect of liver inflammation on accuracy of FibroScan device in assessing liver fibrosis stage in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver; Asociacion Latinoamericana para el Estudio del Higado. EASL-ALEH Clinical Practice Guidelines: Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 237–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; An, M.; Wu, T.; Jiang, D.; Peng, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; the CHESS Study Group. Transient Elastography for Significant Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis in Chronic Hepatitis B: A Meta-Analysis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 3406789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Y.S.; Wang, Z.Z.; Yang, Z.R.; Sun, F.; Zhan, S.Y.; Liu, X.E.; Zhuang, H. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The diagnostic accuracy of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Su, Y.; Song, R.; Sheng, Y.; Ai, W.; Wu, X.; Liu, H. Performance of transient elastography assessing fibrosis of single hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of a diagnostic test. Hepatol. Int. 2015, 9, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chon, Y.E.; Choi, E.H.; Song, K.J.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, K.H.; Chon, C.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, S.U. Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, A.C.; Carvalho-Filho, R.J.; Stern, C.; Dipumpo, A.; Giuily, N.; Ripault, M.P.; Asselah, T.; Boyer, N.; Lada, O.; Castelnau, C.; et al. Direct comparison of diagnostic performance of transient elastography in patients with chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, H.H.; Vo, V.H.; Nguyen, C.D.; Phan, S.T.; Quach, P.T.; Nguyen, D.B. Diagnostic Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging in Evaluating Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection: A Cross-Sectional Study. Indian. J. Radiol. Imaging 2022, 32, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Qiu, L.; Liu, D.; Qian, L. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Elastography for non-invasive evaluation of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B and C patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Ultrason. 2017, 19, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.H.; Liao, C.H.; Liu, C.H.; Huang, K.W.; Tseng, T.C.; Yang, H.C.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S.; Kao, J.H. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse US Imaging: Liver Stiffness in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B with and without Antiviral Therapy. Radiology 2018, 288, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehman, R.L. Magnetic resonance elastography: From invention to standard of care. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 3028–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Talwalkar, J.A.; Yin, M.; Glaser, K.J.; Sanderson, S.O.; Ehman, R.L. Early detection of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by using MR elastography. Radiology 2011, 259, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, S.K.; Wang, G.; Lim, S.G.; Wee, A. Magnetic resonance elastography for the detection and staging of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennedige, T.P.; Wang, G.; Leung, F.P.; Alsaif, H.S.; Teo, L.L.; Lim, S.G.; Wee, A.; Venkatesh, S.K. Magnetic Resonance Elastography and Diffusion Weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Hepatic Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis B. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, S.; Motosugi, U.; Morisaka, H.; Sano, K.; Ichikawa, T.; Enomoto, N.; Matsuda, M.; Fujii, H.; Onishi, H. Validity and Reliability of Magnetic Resonance Elastography for Staging Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2015, 14, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procopet, B.; Berzigotti, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Turon, F.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; García-Pagán, J.C.; Bosch, J. Real-time shear-wave elastography: Applicability, reliability and accuracy for clinically significant portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, E.; de Lédinghen, V.; Cassinotto, C.; Chu, W.C.; Leung, V.Y.; Ferraioli, G.; Filice, C.; Castera, L.; Vilgrain, V.; Ronot, M.; et al. Assessment of biopsy-proven liver fibrosis by two-dimensional shear wave elastography: An individual patient data-based meta-analysis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zheng, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, T.; Zheng, R.; Lu, M. Comparison of 2-D Shear Wave Elastography and Transient Elastography for Assessing Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis B. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Lyu, G.; Chen, Y.; Lin, G.; Wang, H.; Qin, R.; Gu, J. Comparison of two-dimensional shear wave elastography, magnetic resonance elastography, and three serum markers for diagnosing fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A meta-analysis. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Jiang, H.Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Song, B. Two-dimensional shear wave elastography for significant liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 124, 108839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Li, G.; Yu, N.; Chang, X.; Arshad, T.; Liu, W.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wong, G.L.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, X.; et al. aMAP Score and Its Combination With Liver Stiffness Measurement Accurately Assess Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.R.; Berg, T.; Asselah, T.; Flisiak, R.; Fung, S.; Gordon, S.C.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lampertico, P.; Lau, D.; Bornstein, J.D.; et al. Evaluation of APRI and FIB-4 scoring systems for non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y. Dynamic Changes of the Aspartate Aminotransferase-to-Platelet Ratio and Transient Elastography in Predicting a Histologic Response in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B After Entecavir Treatment. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Lee, Y.B.; Ha, Y.; Chon, Y.E.; Kim, M.N.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H.; Rim, K.S.; Hwang, S.G. Changes in liver stiffness values assessed using transient elastography in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: A prospective observational study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.Q.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhao, H. Declining in liver stiffness cannot indicate fibrosis regression in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A 78-week prospective study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lédinghen, V.; Vergniol, J.; Barthe, C.; Foucher, J.; Chermak, F.; Le Bail, B.; Merrouche, W.; Bernard, P.H. Non-invasive tests for fibrosis and liver stiffness predict 5-year survival of patients chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.C.; Liu, C.J.; Su, T.H.; Yang, W.T.; Chen, C.L.; Yang, H.C.; Kuo, S.F.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S.; et al. Fibrosis-4 index predicts cirrhosis risk and liver-related mortality in 2075 patients with chronic HBV infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.H.; Lim, T.S.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; et al. Risk assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver-related events using ultrasonography and transient elastography in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 2021, 28, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.N.; Kim, S.U.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, K.H.; Chon, C.Y.; Ahn, S.H. Risk assessment of liver-related events using transient elastography in patients with chronic hepatitis B receiving entecavir. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Jung, K.S.; Choi, E.H.; Park, Y.N.; Han, K.H.; Chon, C.Y.; Park, J.Y. Prediction of liver-related events using fibroscan in chronic hepatitis B patients showing advanced liver fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, S.U.; Heo, J.Y.; Han, S.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Han, K.H. Subcirrhotic liver stiffness by FibroScan correlates with lower risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollerup, S.; Engsig, F.; Hallager, S.; Mocroft, A.; Roege, B.T.; Christensen, P.B.; Laursen, A.L.; Krarup, H.; Clausen, M.R.; Thielsen, P.; et al. Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis and Prognostic Accuracy of the PAGE-B HCC Risk Score in a Low Endemic Hepatitis B Virus Infected Population. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2022, 9, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.W.; Lim, T.S.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, S.U.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, B.K. Novel Liver Stiffness-Based Nomogram for Predicting Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Initiating Antiviral Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, L.; Jin, J.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zeng, J.; Guo, H.; Zheng, J.; Chen, S.; Zheng, R. Liver Stiffness Measured with Two-dimensional Shear-Wave Elastography Is Predictive of Liver-related Events in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Due to Hepatis B Viral Infection. Radiology 2020, 295, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, G.; Deng, X.; Zeng, J.; Jin, J.; Zeping, H.; Wu, M.; Zheng, R. APS (Age, Platelets, 2D Shear-Wave Elastography) Score Predicts Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B. Radiology 2021, 301, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgaris, T.; Papatheodoridi, M.; Lampertico, P.; Papatheodoridis, G.V. Clinical utility of hepatocellular carcinoma risk scores in chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biomarkers | Components | Formula | Benefits | Limitations | Cost | False Positivity | Thresholds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APRI | AST platelets | [(AST (IU/L)/(AST Upper Limit of Normal in IU/L)/(Platelets in 109/L)] × 100 | Simple biomarkers Accessible | Limited accuracy to for significant fibrosis | Low | Age, immune thrombocytopenia, | <0.5 (F0–1) and >1.5 (F2–4) <1 (F0–3) >2 (f4) |
| FIB-4 | Age AST Platelets ALT | [age (years) × AST (IU/L)]/[platelet count (109/L) × √ALT (IU/L)] | Simple biomarkers Accessible | Limited accuracy for advanced fibrosis | Low | Immune thrombocytopenia, age. | <1.45 (F0–2) and >3.25 (F3–4) |
| FibroTest | Alpha-2macroglobulin Apolipoprotein A1 Haptoglobin GGT Bilirubin | Patented | Accessible | Includes indirect biomarkers that can be influenced by other causes of inflammation | High | Haemolysis, Gilbert’s disease, cholestasis, immune thrombocytopenia, inflammation, age, exercise, non-fasting | >0.58 for advanced fibrosis >0.74 for cirrhosis No specific cut-offs for CHB |
| Forns Index | Age, GGT, cholesterol, and platelets | =7.811 − 3.131 × ln platelet + 0.781 × ln GGT + 3.647 × ln age − 0.014 × cholesterol | Simple biomarkers Accessible | Needs more validation | Low | Thrombocytopenia, inflammation, age, non-fasting | ≥4.05 to rule-in significant fibrosis |
| Hui Score | BMI, Bilirubin, Albumin and platelets | PP = exp (3.148 + 0.167 × BMI + 0.088 × bilirubin[μM] − 0.151 × albumin[g/l] − 0.019 × platelet [109/l])/(1 + exp(3.148 + 0.167 × BMI + 0.088 × bilirubin[μM] − 0.151 × albumin[g/l] − 0.019 × platelet[109/l])) | Simple biomarkers Accessible | Needs more validation | Low | Haemolysis, Gilbert’s disease, cholestasis, immune thrombocytopenia, inflammation, age, exercise, non-fasting | ≤0.15 to rule-out significant fibrosis |
| Author (Ref.) (Year) | Fibrosis, No of Studies, (No of Patients) | Prevalence | Optimal Cut Off (kPa) | Sensitivity | Specificity | Diagnostic Odd Ratio (CI) | AUROC (CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qi X et al. [46] (2018) | F2–4: 35 (n = 6202) | -- | 7.25 (5.2–10.3) | 0.78 (0.73–0.81) | 0.81 (0.77–0.84) | 14.44 (10.80–19.30) | 0.86 (0.83–0.89) |
| F4: 41 (n = 7205) | -- | 12.4 (range 9–18.2) | 0.84 (0.80–0.88) | 0.87 (0.84–0.90) | 36.63 (25.38–52.87) | 0.92 (0.90–0.94) | |
| Li Y et al. [47] (2016) | F ≥ 2: 27 (n = 4386) | -- | 7.2 (5.8–8.8) | 0.81 (0.76–0.85) | 0.82 (0.76–0.87) | -- | 0.88 (0.85–0.91) |
| F ≥ 3: 27 (n = 4386) | -- | 9.1 (7.0–13.5) | 0.819 (0.748–0.874) | 0.87(0.82–0.90) | --- | 0.91(0.88–0.93) | |
| F4: 27 (n = 4386) | -- | 12.2 (9.0–16.9) | 0.86(0.82–0.90) | 0.88(0.84–0.90) | -- | 0.93(0.91–0.95) | |
| Xu X et al. [48] (2015) | F2–4: 14 (n = 2318) | 51.8% (range 15–83%) | -- | Europe: 73% (69–77%) Asia: 73% (69–76%) | Europe: 66% (62–70%) Asia: 82% (79–85%) | 11.19 (6.63–18.89) | 0.823(SE = 0.02) |
| F4: 18 (n = 2996) | 17.6% (range 4–52%) | -- | Europe: 67% (57–76%) Asia: 81% (77–85%) | Europe: 92% (89–93%) Asia: 86% (85–88%) | 26.87 (17.88–40.38) | 0.91 (SE = 0.01) | |
| Chon Y E et al. [49] (2012) | F2:18 (2772) | -- | 7.9 (6.1–11.8) | 74.3% | 78.3% | -- | 0.86 (0.86–0.86) |
| F3:18 (2772) | -- | 8.8 (8.1–9.7) | 74.0% | 63.8% | -- | 0.89 (0.89–0.89) | |
| F4:18 (2772) | -- | 11.7 (7.3–17.5) | 84.6% | 81.5% | -- | 0.93(0.93–0.93) |
| Technical Limitations | Performance for Intermediate Fibrosis Stage | Cost and Availability | Confounding Factors and False Results | Failure | Cut-Off | Follow up of Dynamic Fibrosis Changes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transient elastography (VCTE) | Require training and experience, No B-mode image, unable to select liver region of interest | Overlapping LSM range | Not widely available particularly in the resource limited area | Acute hepatitis, inflammation, Non-fasting, intense exercise, hepatic venous congestion, inflammation, | Depending on the operator experience, Narrow intercostal space, ascites, body habitus | Significant Fibrosis: 7.25 kPa Cirrhosis 12.4 kPa in CHB infection | limited data |
| ARFI Elastography | Can be included in the standard B mode US equipment | No data | Required trained technician, Expensive, Narrow range of values | acute hepatitis, liver inflammation, transaminitis flares, obstructive cholestasis, hepatic congestion, and infiltrative liver diseases non-fasting, intense exercise, anatomical and physiological variation (Left vs Right lobe, breathing cycle) | Significant Fibrosis: 1.34 m/s Severe fibrosis: 1.55 m/s Cirrhosis: 1.8 m/s | No data | |
| 2D Shear wave elastography | Require dedicated US training | No data | Increasingly available | acute hepatitis, hepatic inflammation or infiltration, non-fasting, exercise, right heart failure, extrahepatic cholestasis, breathing cycle (end-expiration vs. end- inspiration) | Higher failure rates than serum tests: BMI, tissue depth > 2–3 cm below skin surface | No data | Limited data |
| MRE | Requires specializes radiologist and technician | No data | Highly expensive, Not available outside specialized imaging centers | Inflammation, cholestasis, hepatic venous congestion, postprandial state, and right heart failure | Higher failure than serum tests: waist circumference/BMI, claustrophobia, iron deposition, massive ascites, higher field strength (3 T vs. 1.5 T) | No data | No data |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bera, C.; Hamdan-Perez, N.; Patel, K. Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Hepatitis B Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13041046
Bera C, Hamdan-Perez N, Patel K. Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Hepatitis B Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(4):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13041046
Chicago/Turabian StyleBera, Chinmay, Nashla Hamdan-Perez, and Keyur Patel. 2024. "Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Hepatitis B Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 4: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13041046
APA StyleBera, C., Hamdan-Perez, N., & Patel, K. (2024). Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Hepatitis B Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(4), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13041046