Long-Term Outcomes after Convergent Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
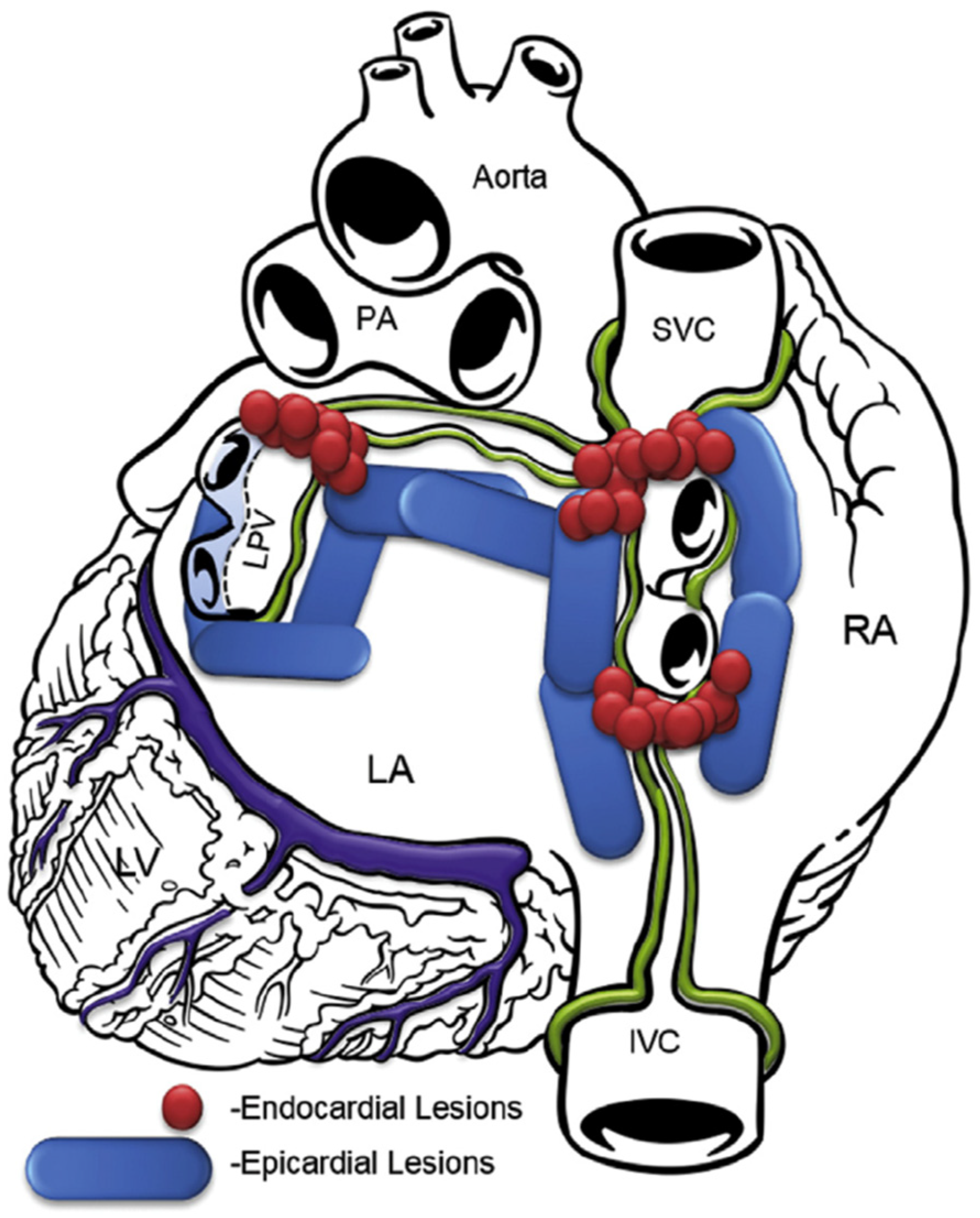
2.2. Convergent Procedure
2.3. Epicardial Ablation
2.4. Percutaneous Endocardial Ablation
2.5. Postoperative Management
2.6. Order of Procedures and Procedure Setting
2.7. Follow-Up Monitoring
2.7.1. One-Year Follow-Up
2.7.2. Long-Term Follow-Up
- Patients with history of persistent or long-standing persistent AF who had sinus rhythm at previous ambulatory visits were assessed with a 7-day Holter ECG monitor. AF burden was determined;
- A total of 8.4% (10/119) of patients with sinus rhythm on the 12-lead ECG recording at the last ambulatory visit refused the 7-day Holter ECG. For these patients, rhythm at long-term follow-up was assessed by clinical presentation and with a 12-lead ECG recording;
- Patients with an unclear history of recurrent AF and known to have had persistent or long-standing persistent AF were telephoned and invited to an ambulatory visit. They were assessed with a 7-day Holter monitor. AF burden was determined;
- Patients with history of persistent or long-standing persistent AF with known clinical history of recurrence of persistent AF during previous visits had a telephone call for demographic characteristics but were not evaluated with a 7-day Holter monitor;
- Patients with paroxysmal AF were evaluated with a 7-day Holter monitor.
2.8. Definition of Procedural Endpoint and Outcomes
2.9. Complications
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Enrolment and Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Outcomes
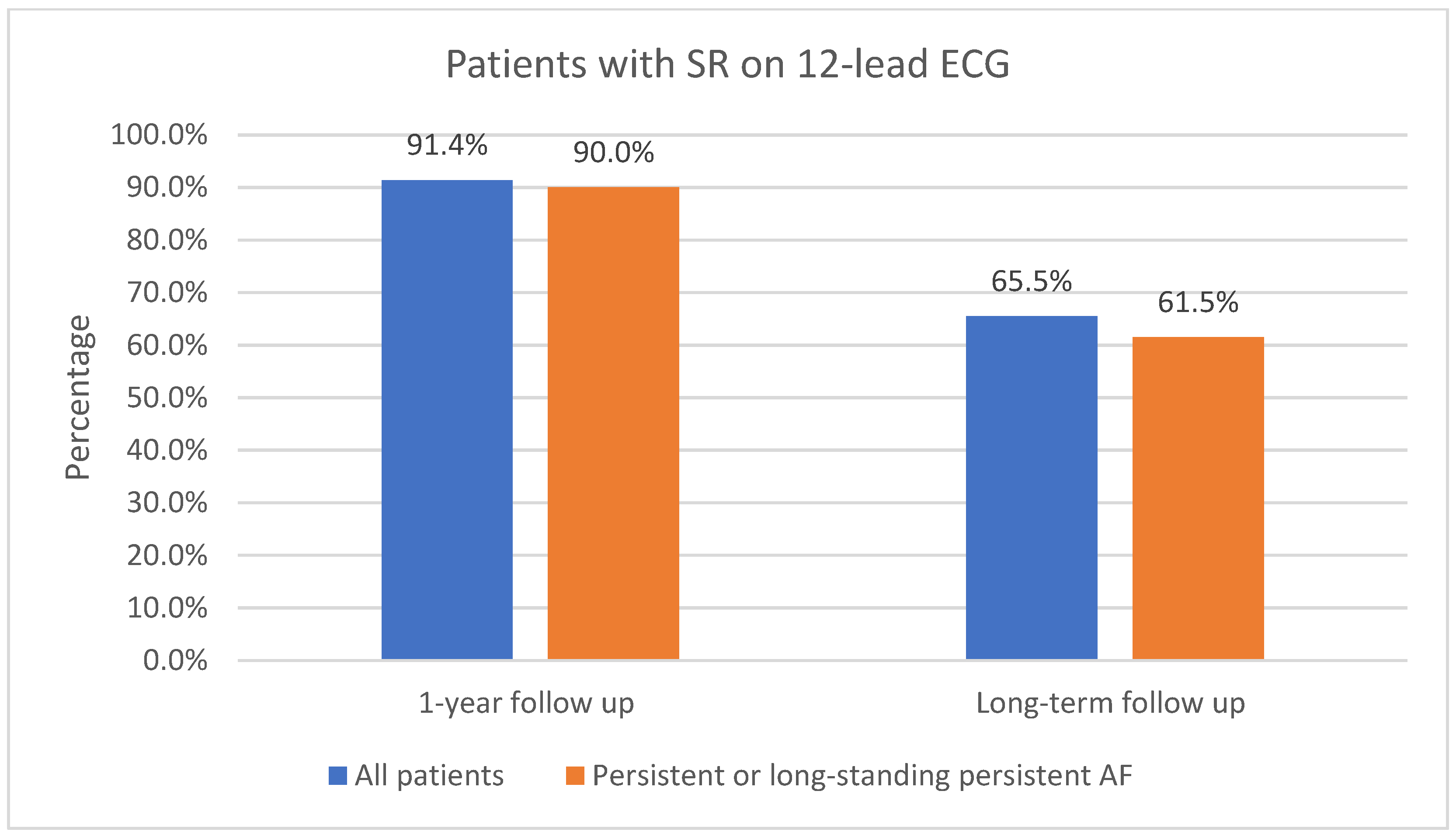
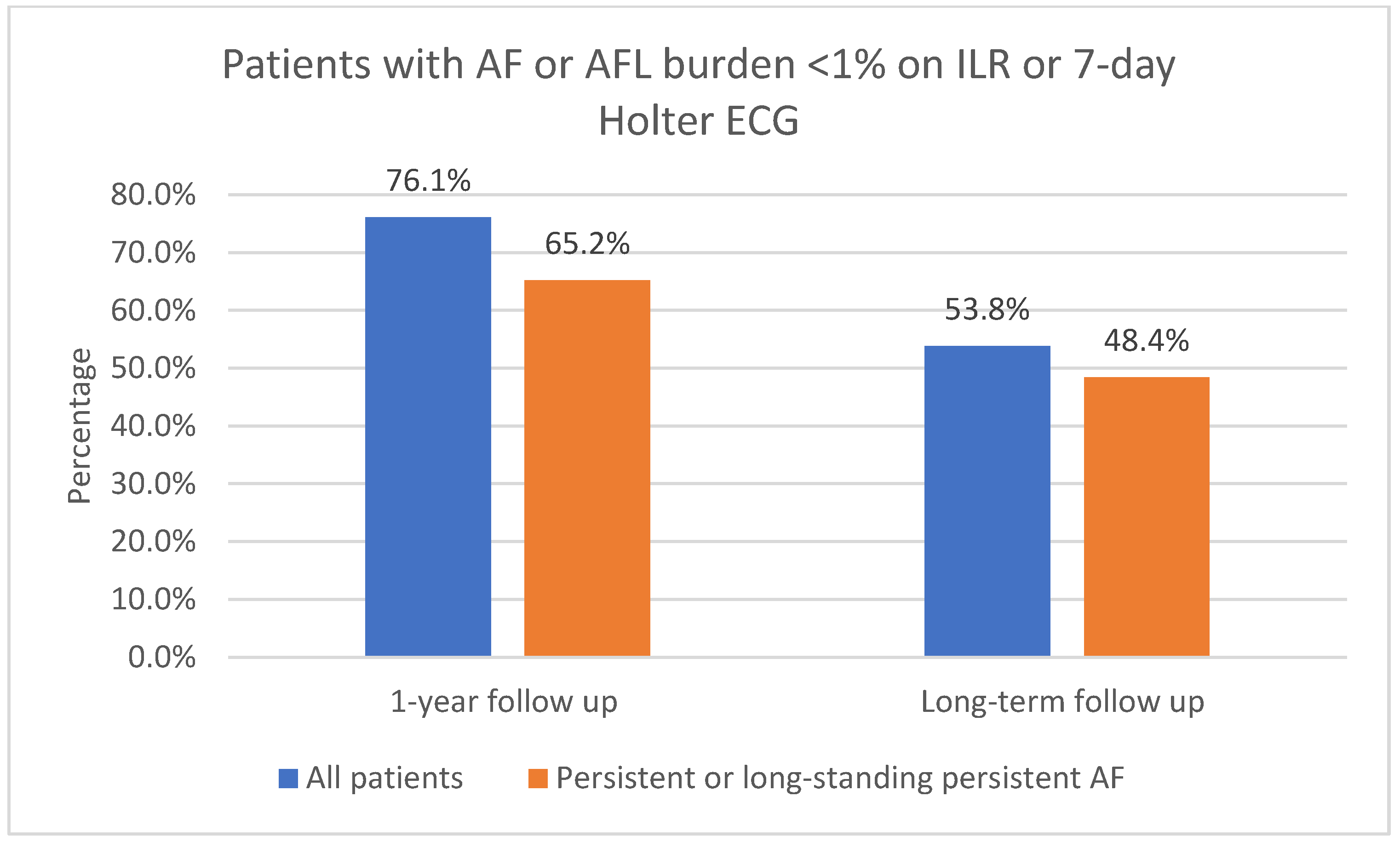
3.2.1. One-Year Follow-Up
3.2.2. Long-Term Follow-Up
3.3. Predictors of Recurrence
3.4. Complications
4. Discussion
4.1. Complications
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, F.; Kwan, G.F.; Benjamin, E.J. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morillo, C.A.; Banerjee, A.; Perel, P.; Wood, D.; Jouven, X. Atrial fibrillation: The current epidemic. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Chen, Y.; Lin, R.; Huang, W.; Zhou, H.; Lin, Y.; Xu, M. Burden of atrial fibrillation and its attributable risk factors from 1990 to 2019: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 997698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2019 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Staerk, L.; Sherer, J.A.; Ko, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Helm, R.H. Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Outcomes. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu, H.O.; Wang, W.; Otabil, E.M.; Saczynski, J.S.; Mehawej, J.; Mishra, A.; Tisminetzky, M.; Blanchard, G.; Gurwitz, J.H.; Goldberg, R.J.; et al. Perception of Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms: Impact on Quality of life and Treatment in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2022, 70, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochhäuser, S.; Joza, J.; Essebag, V.; Proietti, R.; Koehler, J.; Tsang, B.; Wulffhart, Z.; Pantano, A.; Khaykin, Y.; Ziegler, P.D.; et al. The Impact of Duration of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrences on Measures of Health-Related Quality of Life and Symptoms. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 39, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šinkovec, M.; Jan, M.; Antolič, B.; Klemen, L.; Pernat, A. Long-term outcomes after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Single centre experience. Zdravniski Vestnik. 2021, 90, 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, G.J.; Das, M.; Bonnett, L.J.; Panikker, S.; Wong, T.; Gupta, D. Efficacy of catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation a systematic review and meta-analysis of evidence from randomized and nonrandomized controlled trials. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskoboinik, A.; Moskovitch, J.T.; Harel, N.; Sanders, P.; Kistler, P.M.; Kalman, J.M. Revisiting pulmonary vein isolation alone for persistent atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLurgio, D.B.; Crossen, K.J.; Gill, J.; Blauth, C.; Oza, S.R.; Magnano, A.R.; Mostovych, M.A.; Halkos, M.E.; Tschopp, D.R.; Kerendi, F.; et al. Hybrid Convergent Procedure for the Treatment of Persistent and Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Results of CONVERGE Clinical Trial. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e009288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, W.R.; Meulendijks, E.R.; Limpens, J.; van den Berg, N.W.E.; Neefs, J.; Driessen, A.H.G.; Krul, S.P.; van Boven, W.J.P.; de Groot, J.R. Persistent atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of invasive strategies. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 278, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eranki, A.; Wilson-Smith, A.R.; Williams, M.L.; Flynn, C.D.; Manganas, C. Hybrid convergent ablation versus endocardial catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised control trials and propensity matched studies. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 17, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, M.; Žižek, D.; Geršak, Ž.M.; Geršak, B. Comparison of treatment outcomes between convergent procedure and catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation evaluated with implantable loop recorder monitoring. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eranki, A.; Wilson-Smith, A.; Flynn, C.; Williams, M.; Manganas, C. Mid term freedom from atrial fibrillation following hybrid ablation, a systematic review and meta analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2023, 18, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, L.; Mouram, S.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Sorgente, A.; Monaco, C.; Del Monte, A.; Gauthey, A.; Bisignani, A.; Kronenberger, R.; Paparella, G.; et al. Hybrid atrial fibrillation ablation: Long-term outcomes from a single-centre 10-year experience. Europace 2023, 25, euad114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geršak, B.; Jan, M. Long-Term Success for the Convergent Atrial Fibrillation Procedure: 4-Year Outcomes. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gersak, B.; Pernat, A.; Robic, B.; Sinkovec, M. Low Rate of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence Verified by Implantable Loop Recorder Monitoring Following a Convergent Epicardial and Endocardial Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2012, 23, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Calkins, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; Furie, K.L.; et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, e66–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLurgio, D.B.; Blauth, C.; Halkos, M.E.; Crossen, K.J.; Talton, D.; Oza, S.R.; Magnano, A.R.; Mostovych, M.A.; Billakanty, S.; Duff, S.; et al. Hybrid epicardial-endocardial ablation for long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: A subanalysis of the CONVERGE Trial. Heart Rhythm O2 2023, 4, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heijden, C.A.J.; Weberndörfer, V.; Vroomen, M.; Luermans, J.G.; Chaldoupi, S.M.; Bidar, E.; Vernooy, K.; Maessen, J.G.; Pison, L.; van Kuijk, S.M.; et al. Hybrid Ablation Versus Repeated Catheter Ablation in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varzaly, J.A.; Lau, D.H.; Chapman, D.; Edwards, J.; Worthington, M.; Sanders, P. Hybrid ablation for atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JTCVS Open 2021, 7, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilz, R.R.; Rillig, A.; Thum, A.M.; Arya, A.; Wohlmuth, P.; Metzner, A.; Mathew, S.; Yoshiga, Y.; Wissner, E.; Kuck, K.H.; et al. Catheter ablation of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: 5-year outcomes of the Hamburg Sequential Ablation Strategy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.N.; Shipp, N.J.; Brooks, A.G.; Kuklik, P.; Lau, D.H.; Lim, H.S.; Sullivan, T.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; Sanders, P. Long-term Outcomes of Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e004549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.; Macle, L.; Deyell, M.W.; Yao, R.; Hawkins, N.M.; Khairy, P.; Andrade, J.G. Influence of Monitoring Strategy on Assessment of Ablation Success and Postablation Atrial Fibrillation Burden Assessment: Implications for Practice and Clinical Trial Design. Circulation 2022, 145, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geršak, B.; Zembala, M.O.; Müller, D.; Folliguet, T.; Jan, M.; Kowalski, O.; Erler, S.; Bars, C.; Robic, B.; Filipiak, K.; et al. European experience of the convergent atrial fibrillation procedure: Multicenter outcomes in consecutive patients. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLurgio, D.B.; Gill, J.S.; Ahsan, S.; Kaba, R.A.; Plasseraud, K.M.; Halkos, M.E. Hybrid Convergent Procedure for the Treatment of Persistent and Long-standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2021, 10, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, Y.K.; Jeong, D.S. Updates in hybrid AF ablation: A hybrid approach to surgical epicardial ablation and cather endocardial ablation in persistent atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Arrhythmia 2022, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, J.; Merchant, F.M.; Patel, A.; Ndubisi, N.M.; Patel, A.M.; DeLurgio, D.B.; Lloyd, M.S.; El-Chami, M.F.; Leon, A.R.; Hoskins, M.H.; et al. Outcomes of convergent atrial fibrillation ablation with continuous rhythm monitoring. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wats, K.; Center, B.M.M.; Kiser, A.; Associates, P.S.C.C.S.; Makati, K.; Specialists, L.T.C.; Sood, N.; DeLurgio, D.; Hospital, A.E.S.J.; Greenberg, Y.; et al. The Convergent Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Procedure: Evolution of a Multidisciplinary Approach to Atrial Fibrillation Management. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2020, 9, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Plasseraud, K.M.; Makati, K.; Sood, N.; Killu, A.M.; Contractor, T.; Ahsan, S.; De Lurgio, D.B.; Shults, C.C.; Eldadah, Z.A.; et al. Hybrid Convergent ablation for atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Rhythm O2 2022, 3, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, J.; Qi, L.; Tang, Y. Efficacy and safety of the convergent atrial fibrillation procedure: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 28, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pison, L.; Gelsomino, S.; Lucà, F.; Parise, O.; Maessen, J.G.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; La Meir, M. Effectiveness and safety of simultaneous hybrid thoracoscopic and endocardial catheter ablation of lone atrial fibrillation. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 3, 38–44. [Google Scholar]

| Demographic Characteristics | Baseline at CP |
|---|---|
| Male, N (%) | 92 (77) |
| Age, years (SD) | 58.4 (8.0) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 (SD) | 29.6 (4.9) |
| AF duration, years (SD) | 4.9 (4.1) |
| AF type, N (%) | |
| Persistent | 7 (5.9) |
| Long-standing persistent | 84 (70.6) |
| Paroxysmal | 28 (23.5) |
| PLAX LA, cm (SD) | 4.5 (0.6) |
| LAVI, mL/m2 (SD) | 47 (13) |
| LVEF, % (SD) | 55 (11) |
| Type of CP, N | |
| CP—single setting | 108 (90.8) |
| CP—staged | 11 (9.2) |
| Chronic heart failure, N (%) | 17 (14.3) |
| Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, N (%) | 4 (3.4) |
| Arterial hypertension history, N (%) | 78 (65.5) |
| Vascular disease, N (%) | 8 (6.7) |
| Stroke/TIA/thromboembolic event, N (%) | 2 (1.7) |
| Diabetes mellitus type II, N (%) | 11 (9.2) |
| CHA2DS2VASc, N (%) | |
| CHA2DS2VASC 0 | 25 (21.0) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 1 | 46 (38.7) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 2 | 30 (25.2) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 3 | 10 (8.4) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 4 | 7 (5.9) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 5 | 1 (0.8) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 6 | 0 (0.0) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 7 | 0 (0.0) |
| Demographic Characteristics | At Long-Term Follow-Up |
|---|---|
| Chronic heart failure, N (%) | 44 (37.0) |
| Arterial hypertension history, N (%) | 90 (75.6) |
| Vascular disease, N (%) | 20 (16.8) |
| Stroke/TIA/thromboembolic event, N (%) | 2 (1.7) |
| Diabetes mellitus, N (%) | 16 (13.4) |
| CHA2DS2VASc, N (%) | |
| CHA2DS2VASC 0 | 10 (8.4) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 1 | 23 (19.3) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 2 | 26 (21.8) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 3 | 29 (24.4) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 4 | 17 (14.3) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 5 | 9 (7.6) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 6 | 4 (3.4) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 7 | 0 (0.0) |
| CHA2DS2VASC 8 | 1 (0.8) |
| Antiarrhythmic drugs | |
| Class Ic, N (%) | 4 (3.4) |
| Class III, N (%) | 13 (10.9) |
| Beta-blockers, N (%) | 59 (49.6) |
| Class IV, N (%) | 9 (7.6) |
| Complications | |
|---|---|
| Tamponade, N (%) | 3 (2.5) |
| Stroke, N (%) | 0 |
| Esophageal ulcer/perforation/fistula, N (%) | 0 |
| Bleeding, N (%) | 3 (2.5) |
| Infection, N (%) | 2 (1.68) |
| Vascular complication, N (%) | 1 (0.84) |
| Phrenic nerve palsy, N (%) | 1 (0.84) |
| Peripheral nerve compression, N (%) | 1 (0.84) |
| Acute worsening of previous heart disease, N (%) | 1 (0.84) |
| Pulmonary vein stenosis (clinical screening), N (%) | 0 |
| Overall, N (%) | 12 (10.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geršak, B.; Podlogar, V.; Prolič Kalinšek, T.; Jan, M. Long-Term Outcomes after Convergent Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185508
Geršak B, Podlogar V, Prolič Kalinšek T, Jan M. Long-Term Outcomes after Convergent Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(18):5508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185508
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeršak, Borut, Veronika Podlogar, Tine Prolič Kalinšek, and Matevž Jan. 2024. "Long-Term Outcomes after Convergent Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 18: 5508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185508
APA StyleGeršak, B., Podlogar, V., Prolič Kalinšek, T., & Jan, M. (2024). Long-Term Outcomes after Convergent Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(18), 5508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185508







