Differential Modulation of the Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Circuits of Retinal Ganglion Cells via Asiatic Acid in a Chronic Glaucoma Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Animals
2.3. Rat Model of Ocular Hypertension
2.4. Fluorogold Retrograde Labeled RGCs and Whole-Mount Retinas
2.5. Preparation of Retinal Slice and Recordings of Electrophysiological
2.6. Drug Administration
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
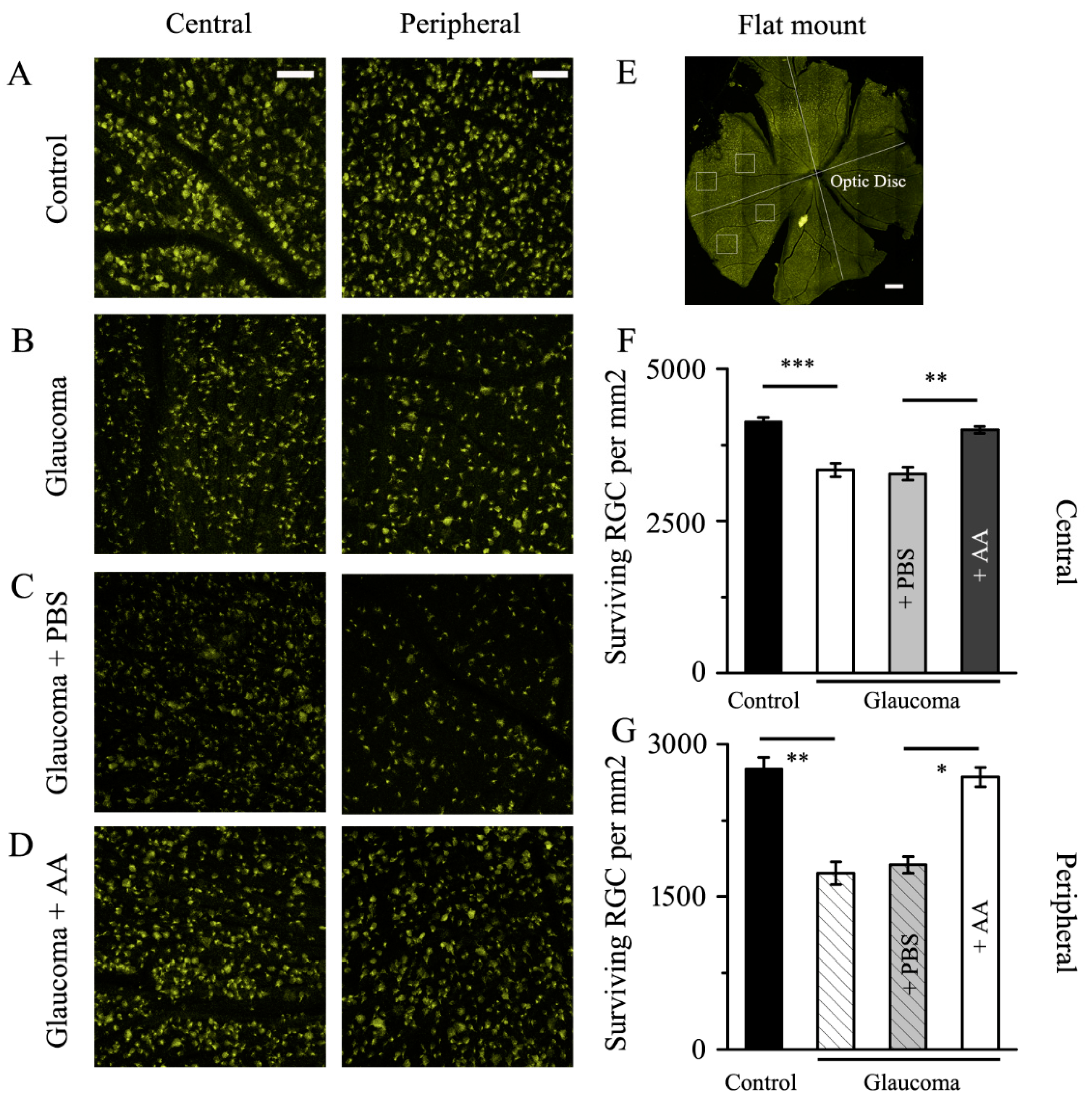
3.1. AA Reduced the RGCs Loss Induced by Chronic Glaucoma
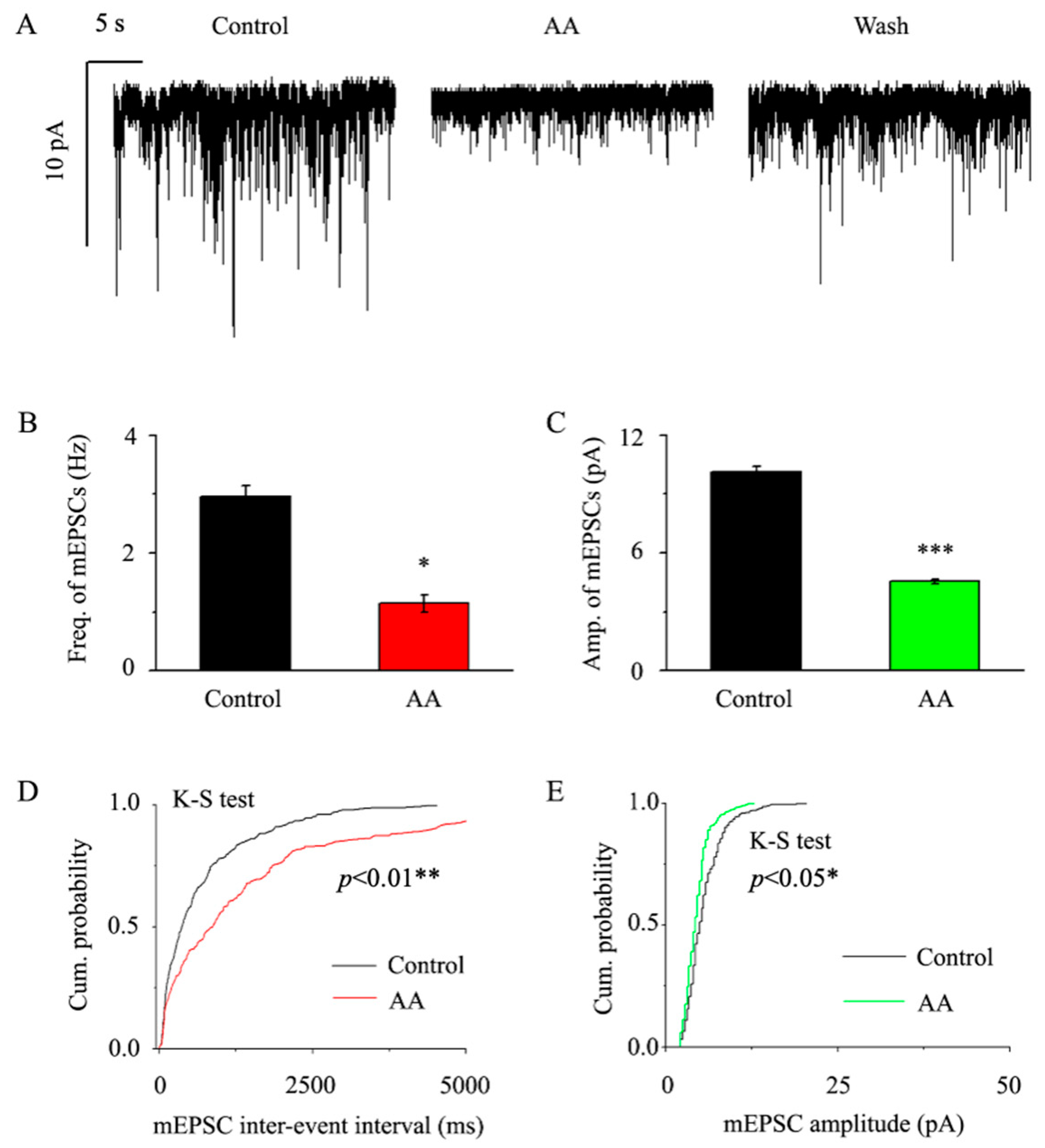
3.2. AA Decreased the Frequency and Amplitude of mEPSCs in Glaucomatous RGCs
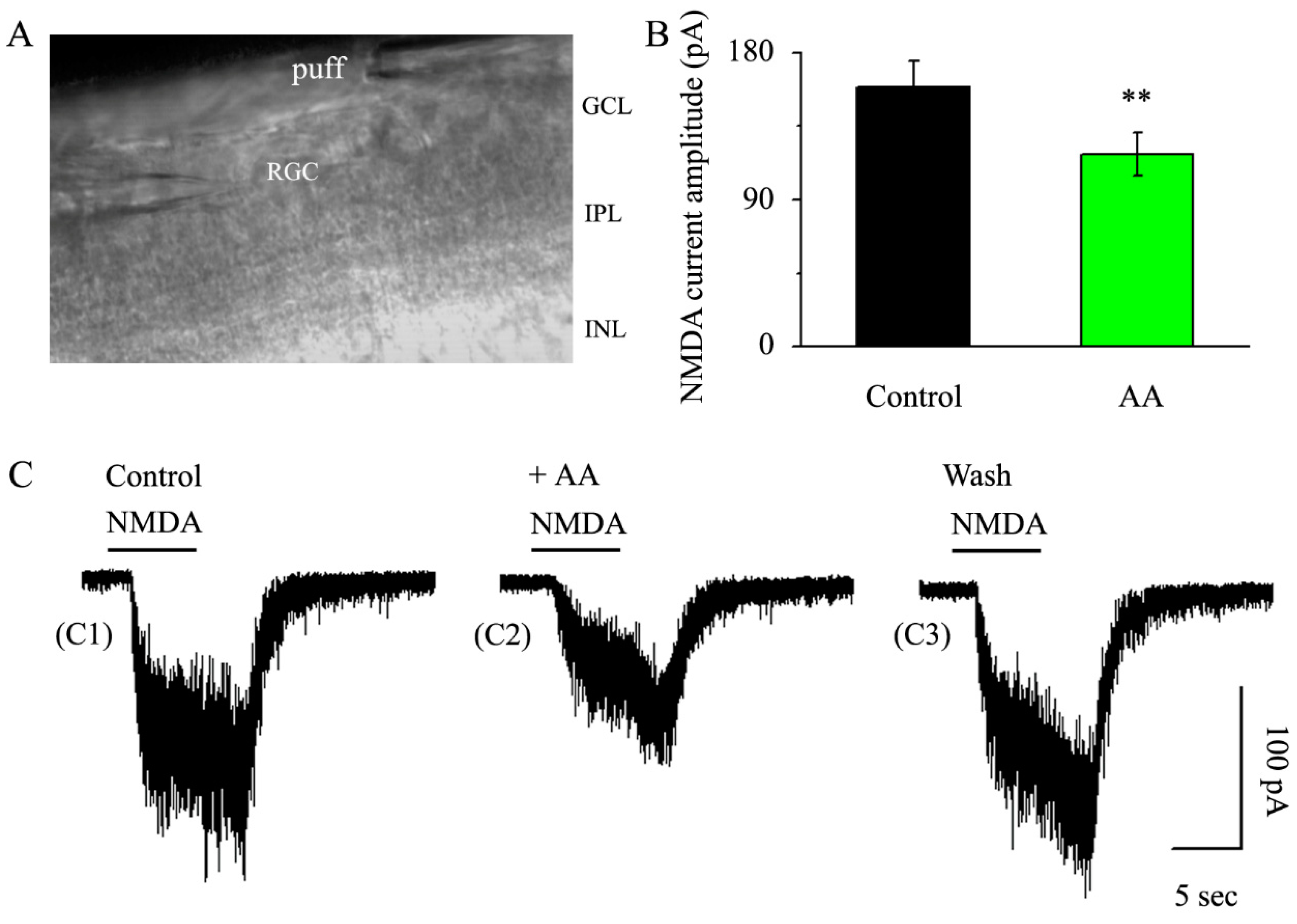
3.3. AA Reduced the Synaptic NMDA-Induced Current Amplitude
3.4. AA Enhanced the Frequency and Amplitude of GABAergic mIPSCs in Glaucomatous RGCs
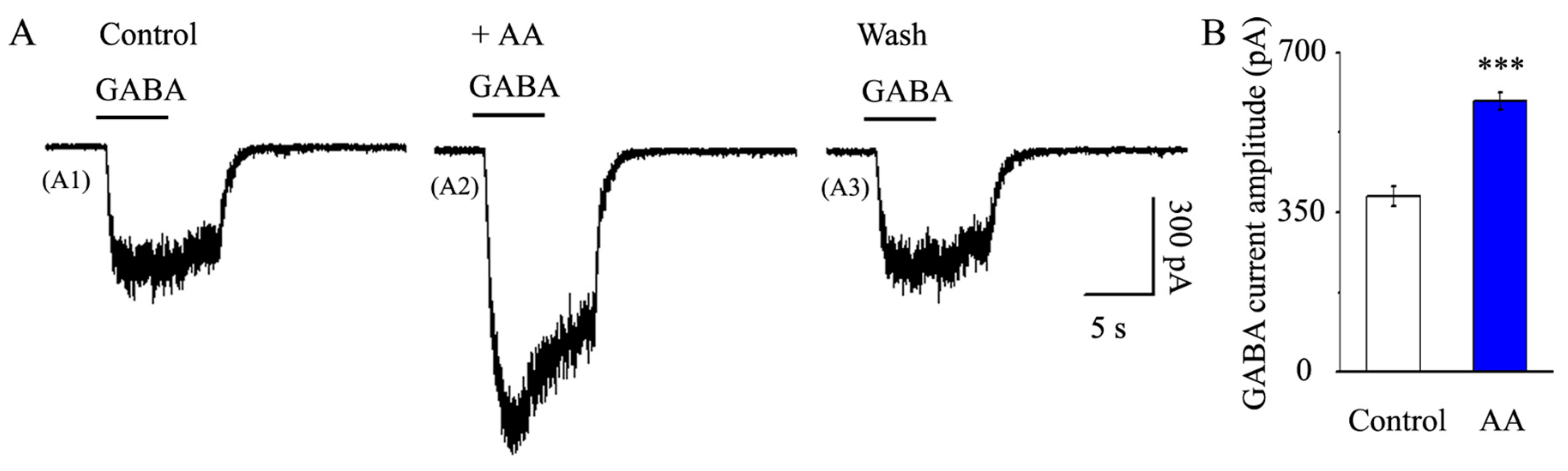
3.5. AA Enhanced the Synaptic GABA-Induced Current Amplitude
3.6. AA Reduced the Spontaneous Action Potential Frequency in RGCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allison, K.; Patel, D.; Alabi, O. Epidemiology of glaucoma: The past, present, and predictions for the future. Cureus 2020, 12, e11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountouras, J.; Zavos, C.; Deretzi, G.; Polyzos, S.A.; Gavalas, E.; Tsiaousi, E.; Giartza-Taxidou, E.; Chatzopoulos, D.; Michael, S.; Tsarouchas, G. Neuroprotection in glaucoma: Is there a future role of Helicobacter pylori eradication? Exp. Eye Res. 2011, 92, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.L.; Li, X.; Yip, H.K.; Shao, Z.; Wu, W.; Mi, S.; So, K.F. Combined effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and LINGO-1 fusion protein on long-term survival of retinal ganglion cells in chronic glaucoma. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Shim, M.S.; Choi, S.H.; Choi, S.; Ellisman, M.H.; Weinreb, R.N.; Perkins, G.A.; Ju, W.K. Inhibition of oxidative stress by coenzyme Q10 increases mitochondrial mass and improves bioenergetic function in optic nerve head astrocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yohannan, J.; Boland, M.V.; Ramulu, P. The association between intraocular pressure and visual field worsening in treated glaucoma patients. J. Glaucoma 2021, 30, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfill, M.; Mangas, S.; Cusido, R.M.; Osuna, L.; Pinol, M.T.; Palazon, J. Identification of triterpenoid compounds of Centella asiatica by thin-layer chromatography and mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, R.G.; Senut, M.C.; Zemke, D.; Min, J.; Frenkel, M.B.; Greenberg, E.J.; Yu, S.W.; Ahn, N.; Goudreau, J.; Kassab, M.; et al. Asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene from Centella asiatica, is neuroprotective in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.F.; Xiong, Y.Y.; Liu, J.K.; Qian, J.J.; Zhu, L.; Gao, J. Asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene in Centella asiatica, attenuates glutamate-induced cognitive deficits in mice and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Ding, H.; Xu, M.; Gao, J. Protective effects of Asiatic acid on rotenone- or H2O2-induced injury in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Dou, Y.; Xia, B.; Rong, W.; Rimbach, G.; Lou, Y. Asiatic acid protects primary neurons against C2-ceramide-induced apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 679, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Kim, S.R.; Sung, S.H.; Lim, D.; Kim, H.; Choi, H.; Park, H.K.; Je, S.; Ki, Y.C. Asiatic acid derivatives protect cultured cortical neurons from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 2000, 108, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wanasuntronwong, A.; Tantisira, M.H.; Tantisira, B.; Watanabe, H. Anxiolytic effects of standardized extract of Centella asiatica (ECa 233) after chronic immobilization stress in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebib, M.; Johnston, G.A. GABA-activated ligand gated ion channels: Medicinal chemistry and molecular biology. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 1427–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somogyi, P.; Tamas, G.; Lujan, R.; Buhl, E.H. Salient features of synaptic organisation in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res. Rev. 1998, 26, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, K.; Ng, I.; Tallapragada, V.J.; Varadi, L.; Hibbs, D.E.; Hanrahan, J.; Groundwater, P.W. An investigation of the differential effects of ursane triterpenoids from Centella asiatica, and their semisynthetic analogues, on GABAA receptors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 88, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Sun, X. Activation of 5-HT1A receptors promotes retinal ganglion cell function by inhibiting the cAMP-PKA pathway to modulate presynaptic GABA release in chronic glaucoma. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 1484–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittag, T.W.; Danias, J.; Pohorenec, G.; Yuan, H.M.; Burakgazi, E.; Chalmers-Redman, R.; Podos, S.M.; Tatton, W.G. Retinal damage after 3 to 4 months of elevated intraocular pressure in a rat glaucoma model. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 3451–3459. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X. Neuroprotective effect of upregulated sonic Hedgehog in retinal ganglion cells following chronic ocular hypertension. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 2986–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Miao, Y.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, Z. Elevation of p-NR2A(S1232) by Cdk5/p35 contributes to retinal ganglion cell apoptosis in a rat experimental glaucoma model. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 43, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inatani, M.; Tanihara, H.; Katsuta, H.; Honjo, M.; Kido, N.; Honda, Y. Transforming growth factor-beta 2 levels in aqueous humor of glaucomatous eyes. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2001, 239, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xu, J.; Sarunic, M.V.; Saragovi, U.H.; Zhuo, Y. Validation of glaucoma-like features in the rat episcleral vein cauterization model. Chin. Med. J. 2014, 127, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Cui, P.; Miao, Y.; Gao, F.; Li, X.Y.; Qian, W.J.; Jiang, S.X.; Wu, N.; Sun, X.H.; Wang, Z. Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors regulates the excitability of rat retinal ganglion cells by suppressing Kir and I h. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 222, 813–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, G.; Yang, B.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist promotes retinal ganglion cell function via modulating GABAergic presynaptic activity in a chronic glaucomatous model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasieh, M.; Zhou, Y.; Kelly, M.E.; Casanova, C.; Di Polo, A. Structural and functional neuroprotection in glaucoma: Role of galantamine-mediated activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Gao, F.; Hu, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Xu, P.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Asiatic acid prevents retinal ganglion cell apoptosis in a rat model of glaucoma. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, B.; Tomarev, S. Evaluating retinal ganglion cell loss and dysfunction. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 151, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, C.J.; Choe, T.E.; Lusardi, T.A.; Burgoyne, C.F.; Wang, L.; Fortune, B. Imaging axonal transport in the rat visual pathway. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 364–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Sanz, M.; Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Ortin-Martinez, A.; Nadal-Nicolas, F.M.; Jimenez-Lopez, M.; Salinas-Navarro, M.; Alarcon-Martinez, L.; Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Aviles-Trigueros, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M.; et al. Retinal neurodegeneration in experimental glaucoma. Prog. Brain Res. 2015, 220, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Downs, J.C.; Roberts, M.D.; Burgoyne, C.F. Mechanical environment of the optic nerve head in glaucoma. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2008, 85, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munemasa, Y.; Kitaoka, Y. Autophagy in axonal degeneration in glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 47, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.N.; Abdullah, J.; Habsah, M.; Ghani, R.I.; Rammes, G. Inhibitory effect of Asiatic acid on acetylcholinesterase, excitatory post synaptic potential and locomotor activity. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saint, D.A.; Thomas, T.; Gage, P.W. GABAB agonists modulate a transient potassium current in cultured mammalian hippocampal neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 1990, 118, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binti Mohd Yusuf Yeo, N.A.; Muthuraju, S.; Wong, J.H.; Mohammed, F.R.; Senik, M.H.; Zhang, J.; Yusof, S.R.; Jaafar, H.; Adenan, M.L.; Mohamad, H.; et al. Hippocampal amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid GluA1 (AMPA GluA1) receptor subunit involves in learning and memory improvement following treatment with Centella asiatica extract in adolescent rats. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e01093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Niu, C.; Hong, J.; Zhou, X. Differential Modulation of the Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Circuits of Retinal Ganglion Cells via Asiatic Acid in a Chronic Glaucoma Rat Model. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031056
Zhang Y, Hu C, Niu C, Hong J, Zhou X. Differential Modulation of the Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Circuits of Retinal Ganglion Cells via Asiatic Acid in a Chronic Glaucoma Rat Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031056
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yinglei, Chunyan Hu, Cong Niu, Jiaxu Hong, and Xujiao Zhou. 2023. "Differential Modulation of the Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Circuits of Retinal Ganglion Cells via Asiatic Acid in a Chronic Glaucoma Rat Model" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031056
APA StyleZhang, Y., Hu, C., Niu, C., Hong, J., & Zhou, X. (2023). Differential Modulation of the Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Circuits of Retinal Ganglion Cells via Asiatic Acid in a Chronic Glaucoma Rat Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031056




