Value of Post-/Pre-Procedural Aortic Regurgitation Ratio vs. Pre-Procedural Aortic Valve Calcium Score to Predict Moderate to Severe Paravalvular Leak Requiring Post-Dilation after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Patient Characteristics, Procedural Parameters, and Post-Procedural Outcomes
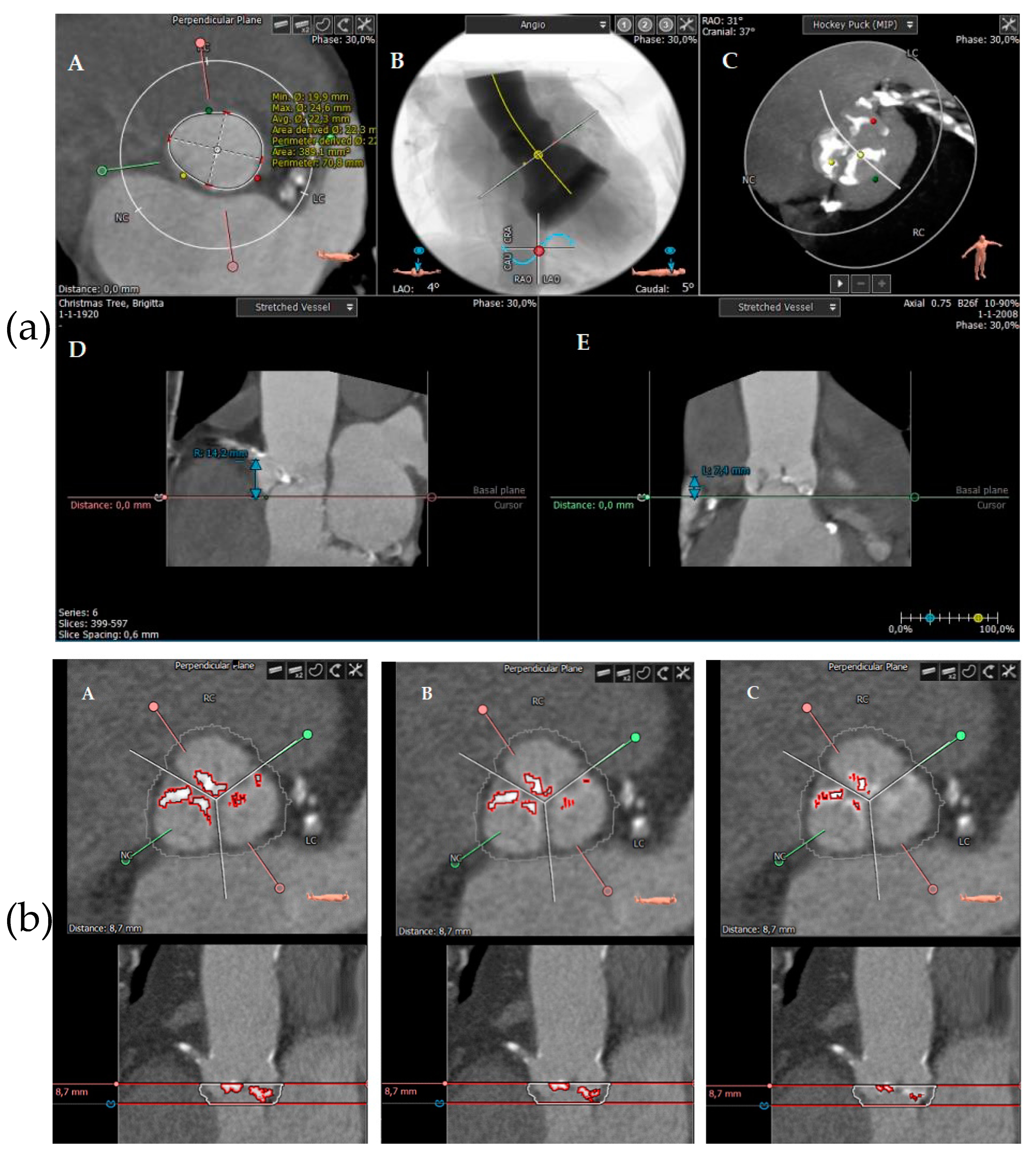
2.3. Calcification Measurements Using MSCT
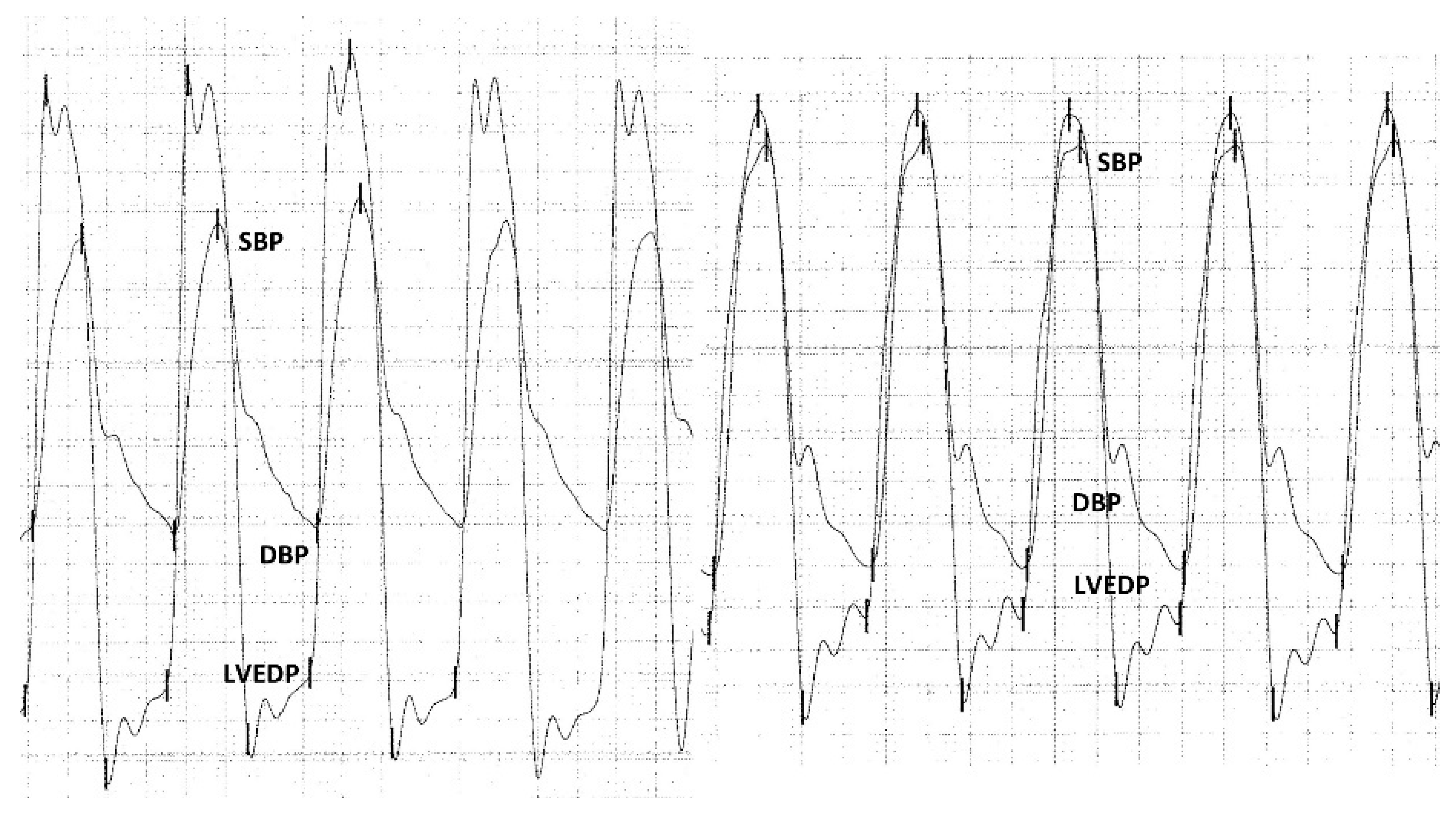
2.4. Hemodynamic Measurements
2.5. Study Endpoints
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Patient Characteristics, Procedural Parameters, and Post-Procedural Outcomes
3.3. Calcification Measurements Using MSCT
3.4. Hemodynamic Measurements
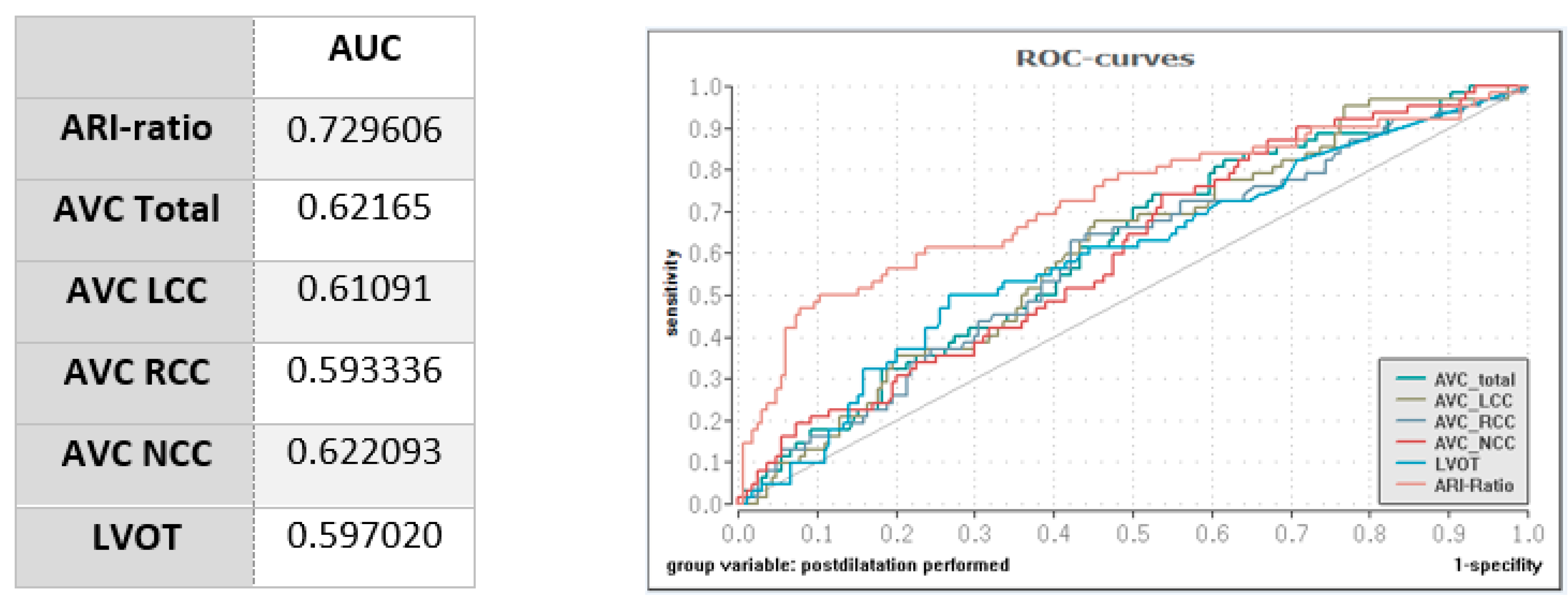
3.5. Impact of Calcification and Hemodynamic Measurements on PD
3.6. Residual PVL in Patients with High Calcification Undergoing Pre-Dilation
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lerakis, S.; Hayek, S.S.; Douglas, P.S. Paravalvular aortic leak after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: Current knowledge. Circulation 2013, 127, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athappan, G.; Patvardhan, E.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Svensson, L.G.; Lemos, P.A.; Fraccaro, C.; Tarantini, G.; Sinning, J.M.; Nickenig, G.; Capodanno, D.; et al. Incidence, predictors, and outcomes of aortic regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: Meta-analysis and systematic review of literature. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Wahab, M.; Zahn, R.; Horack, M.; Gerckens, U.; Schuler, G.; Sievert, H.; Eggebrecht, H.; Senges, J.; Richardt, G. Aortic regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Incidence and early outcome. Results from the German transcatheter aortic valve interventions registry. Heart 2011, 97, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nombela-Franco, L.; Rodés-Cabau, J.; Delarochellière, R.; Larose, E.; Doyle, D.; Villeneuve, J.; Bergeron, S.; Bernier, M.; Amat-Santos, I.J.; Mok, M.; et al. Predictive factors, efficacy, and safety of balloon post-dilation after transcatheter aortic valve implantation with a balloon-expandable valve. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 5, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Lal, S. Post-dilation in transcatheter aortic valve replacement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2017, 30, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.T.; Pibarot, P.; Webb, J.; Rodes-Cabau, J.; Herrmann, H.C.; Williams, M.; Makkar, R.; Szeto, W.Y.; Main, M.L.; Thourani, V.H.; et al. Outcomes with post-dilation following transcatheter aortic valve replacement: The PARTNER I trial (placement of aortic transcatheter valve). JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, C.; Rossi, A.; van Mieghem, N.; van der Boon, R.; Papadopoulou, S.-L.; van Domburg, R.; Moelker, A.; Mollet, N.; Krestin, G.; van Geuns, R.-J.; et al. Aortic annulus dimensions and leaflet calcification from contrast MSCT predict the need for balloon post-dilatation after TAVI with the Medtronic CoreValve prosthesis. EuroIntervention 2011, 7, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalique, O.K.; Hahn, R.T.; Gada, H.; Nazif, T.M.; Vahl, T.P.; George, I.; Kalesan, B.; Forster, M.; Williams, M.B.; Leon, M.B.; et al. Quantity and location of aortic valve complex calcification predicts severity and location of paravalvular regurgitation and frequency of post-dilation after balloon-expandable transcatheter aortic valve replacement. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sato, K.; Jobanputra, Y.; Betancor, J.; Halane, M.; George, R.; Banerjee, K.; Mohananey, D.; Menon, V.; Sammour, Y.M.; et al. Time-Integrated Aortic Regurgitation Index Helps Guide Balloon Postdilation During Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement and Predicts Survival. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vaan, J.; Verstraeten, L.; De Jaegere, P.; Schultz, C. The 3mensio ValvesTM multimodality workstation. EuroIntervention 2012, 7, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, N.; de Jaegere, P.; Schultz, C.; Becker, A.E.; Serruys, P.W.; Anderson, R.H. Anatomy of the aortic valvar complex and its implications for transcatheter implantation of the aortic valve. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2008, 1, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettinger, N.; Khalique, O.K.; Krepp, J.M.; Hamid, N.B.; Bae, D.J.; Pulerwitz, T.C.; Liao, M.; Hahn, R.T.; Vahl, T.P.; Nazif, T.M.; et al. Practical determination of aortic valve calcium volume score on contrast-enhanced computed tomography prior to transcatheter aortic valve replacement and impact on paravalvular regurgitation: Elucidating optimal threshold cutoffs. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2017, 11, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jilaihawi, H.; Makkar, R.R.; Kashif, M.; Okuyama, K.; Chakravarty, T.; Shiota, T.; Friede, G.; Nakamura, M.; Doctor, N.; Rafique, A.; et al. A revised methodology for aortic-valvar complex calcium quantification for transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 15, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinning, J.M.; Stundl, A.; Pingel, S.; Weber, M.; Sedaghat, A.; Hammerstingl, C.; Vasa-Nicotera, M.; Mellert, F.; Schiller, W.; Kovac, J.; et al. Pre-Procedural Hemodynamic Status Improves the Discriminatory Value of the Aortic Regurgitation Index in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 9, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Peiro, S.; Weiler, H.; Papadopoulos, N.; Zeiher, A.M.; Fichtlscherer, S.; Vasa-Nicotera, M. Post/preprocedural ratio of hemodynamically assessed aortic regurgitation index as a marker for the need for corrective measures during transcatheter valve replacement: A first confirmatory study in patients receiving a new generation transcatheter self-expandable prosthesis. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 93, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Généreux, P.; Piazza, N.; Alu, M.C.; Nazif, T.; Hahn, R.T.; Pibarot, P.; Bax, J.J.; Leipsic, J.A.; Blanke, P.; Blackstone, E.H.; et al. Valve Academic Research Consortium 3: Updated Endpoint Definitions for Aortic Valve Clinical Research. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 2717–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, S.; Delgado, V.; Hausleiter, J.; Schoenhagen, P.; Min, J.K.; Leipsic, J.A. SCCT expert consensus document on computed tomography imaging before transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI)/transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2012, 6, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawade, T.; Sheth, T.; Guzzetti, E.; Dweck, M.R.; Clavel, M.A. Why and How to Measure Aortic Valve Calcification in Patients With Aortic Stenosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1835–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leber, A.W.; Kasel, M.; Ischinger, T.; Ebersberger, U.H.; Antoni, D.; Schmidt, M.; Riess, G.; Renz, V.; Huber, A.; Helmberger, T.; et al. Aortic valve calcium score as a predictor for outcome after TAVI using the CoreValve revalving system. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 166, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiffert, M.; Fujita, B.; Avanesov, M.; Lunau, C.; Schön, G.; Conradi, L.; Prashovikj, E.; Scholtz, S.; Börgermann, J.; Scholtz, W.; et al. Device landing zone calcification and its impact on residual regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve implantation with different devices. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, P.; Figueiredo, B.; Almeida, C.; Almeida, J.; Bettencourt, N.; Sampaio, F.; Ferreira, N.; Gonçalves, H.; Braga, P.; Ribeiro, V.G. Aortic Valve Calcium Volume Predicts Paravalvular Regurgitation and the Need for Balloon Post-Dilatation after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2016, 29, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinning, J.M.; Hammerstingl, C.; Vasa-Nicotera, M.; Adenauer, V.; Lema Cachiguango, S.J.; Scheer, A.C.; Hausen, S.; Sedaghat, A.; Ghanem, A.; Mller, C.; et al. Aortic regurgitation index defines severity of peri-prosthetic regurgitation and predicts outcome in patients after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasa-Nicotera, M.; Sinning, J.M.; Chin, D.; Lim, T.K.; Spyt, T.; Jilaihawi, H.; Grube, E.; Werner, N.; Nickenig, G.; Kovac, J. Impact of paravalvular leakage on outcome in patients after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 5, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stundl, A.; Lucht, H.; Shamekhi, J.; Weber, M.; Sedaghat, A.; Mellert, F.; Grube, E.; Nickenig, G.; Werner, N.; Sinning, J.M. Early versus newer generation transcatheter heart valves for transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Echocardiographic and hemodynamic evaluation of an all-comers study cohort using the dimensionless aortic regurgitation index (AR-index). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wely, M.; van der Wulp, K.; Rooijakkers, M.; Vart, P.; Morshuis, W.; van Royen, N.; Gehlmann, H.; Verkroost, M.; Kievit, P.; van Garsse, L.; et al. Aortic Regurgitation Index Ratio Is a Strong Predictor of 1-Year Mortality After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Using Self-Expanding Devices. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 33, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoechlin, S.; Brennemann, T.; Allali, A.; Ruile, P.; Jander, N.; Allgeier, M.; Gick, M.; Richardt, G.; Neumann, F.J.; Abdel-Wahab, M. Hemodynamic classification of paravalvular leakage after transcatheter aortic valve implantation compared with angiographic or echocardiographic classification for prediction of 1-year mortality. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 91, E56–E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoechlin, S.; Hein, M.; Brennemann, T.; Eichenlaub, M.; Schulz, U.; Jander, N.; Neumann, F.-J. 5-Year outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Focus on paravalvular leakage assessed by echocardiography and hemodynamic parameters. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2022, 99, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabello, B.A.; Puskas, J.D. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement: The leak goes on. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 1033–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| All Patients (n = 237) | Without Post-Dilation (n = 172) | With Post-Dilation (n = 65) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 82 (78–85) | 81.5 (78–85) | 83 (79.5–85) | 0.17 |
| Female (%) | 102 (43%) | 75 (43.6%) | 27 (41.5%) | 0.774 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.8 (24.3–30.4) | 26.7 (24.5–30) | 27.3 (23.4–30.9) | 0.931 |
| NYHA I II III IV | (n = 236) 0 (0%) 45 (19.1%) 169 (71.6%) 22 (9.3%) | (n = 171) 0 (0%) 28 (16.4%) 126 (73.7%) 17 (9.9%) | 0 (0%) 17 (26.2%) 43 (66.2%) 5 (7.7%) | 0.109 |
| Euro Score II | 3.13 (2.16–6.03) | 3.53 (2.26–6.1) | 2.77 (2.02–5.55) | 0.109 |
| STS Score | 3.07 (2.26–4.68) | 3.07 (2.13–5.34) | 3.17 (2.41–4.24) | 0.935 |
| CAOD | 39 (16.5%) | 31 (18%) | 8 (12.3%) | 0.291 |
| PAOD | 33 (13.9%) | 23 (13.4%) | 10 (15.4%) | 0.69 |
| s/p heart surgery | 21 (8.9%) | 17 (9.9%) | 4 (6.2%) | 0.367 |
| COPD | 45 (19%) | 34 (19.8%) | 11 (16.9%) | 0.618 |
| Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus | 69 (29.1%) 22 (9.3%) | 51 (29.7%) 15 (8.7%) | 18 (27.7%) 7 (10.8%) | 0.767 0.628 |
| Hypertension | 210 (88.6%) | 151 (87.8%) | 59 (90.8%) | 0.52 |
| s/p myocardial infarction | 42 (17.7%) | 32 (18.6%) | 10 (15.4%) | 0.562 |
| s/p stroke | 29 (12.2%) | 22 (12.8%) | 7 (10.8%) | 0.672 |
| s/p TIA | 8 (3.4%) | 7 (4.1%) | 1 (1.5%) | 0.337 |
| s/p percutaneous coronary intervention | 100 (42.2%) | 74 (43.0%) | 26 (40.0%) | 0.674 |
| CAD none 1 Vessel CAD 2 Vessel CAD 3 Vessel CAD | 80 (33.8%) 61 (25.7%) 40 (16.9%) 56 (23.6%) | 55 (32%) 40 (23.3%) 32 (18.6%) 45 (26.2%) | 25 (38.5%) 21 (32.3%) 8 (12.3%) 11 (16.9%) | 0.079 |
| s/p pacemaker | 32 (13.5%) | 24 (14%) | 8 (12.3%) | 0.741 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 108 (45.6%) | 83 (48.3%) | 25 (38.5%) | 0.177 |
| LVEF (%) | 60 (50–60) (n = 234) | 60 (50–60) (n = 170) | 60 (50–65) (n = 64) | 0.369 |
| All Patients (n = 237) | Without Post-Dilation (n = 172) | With Post-Dilation (n = 65) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Procedural parameters | ||||
| Valve type Portico™ Symetis Acurate™ Sapien 3™ Evolut R™ | 72 (30.4%) 84 (35.4%) 54 (22.8%) 27 (11.4%) | 53 (30.8%) 48 (27.9%) 54 (31.4%) 17 (9.9%) | 19 (29.2%) 36 (55.4%) 0 (0%) 10 (15.4%) | <0.001 |
| Pre-dilation | 176 (74.3%) | 122 (70.9%) | 54 (83.1%) | 0.056 |
| Contrast dye use (mL) | 100 (70–140) | 90 (70–130) | 130 (100–155) | <0.001 |
| Procedure duration (min) | 60 (45–60) (n = 236) | 45 (45–60) (n = 171) | 60 (45–60) | 0.049 |
| Fluoroscopy time (min) | 14.0 (10–18.8) (n = 235) | 12.7 (9.45–18.5) (n = 171) | 16.5 (13.9–19.6) (n = 64) | <0.001 |
| Simultaneous coronary intervention | 5 (2.1%) (n = 236) | 4 (4.0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.168 |
| Post-procedural complications | ||||
| Myocardial infarction | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | ns |
| Stroke -Minor -Major | 3 (1.3%) 7 (3.0%) | 0 (0%) 5 (2.9%) | 3 (4.6%) 2 (3.1%) | 0.005 0.945 |
| Bleeding (major or life-threatening) | 12 (5.1%) | 9 (5.2%) | 3 (4.6%) | 0.847 |
| Pacemaker implantation | 33 (13.9%) | 26 (15.1%) | 7 (10.8%) | 0.388 |
| Major vascular complication | 12 (5.1%) | 8 (4.7%) | 4 (6.2%) | 0.638 |
| Cardiac tamponade | 4 (1.7%) | 1 (0.6%) | 3 (4.6%) | 0.032 |
| Short- and mid-term survival | ||||
| In-hospital mortality | 2 (0.8%) | 1 (0.6%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0.473 |
| 30-day mortality | 7 (3.0%) | 6 (3.5%) | 1 (1.5%) | 0.429 |
| One-year mortality | 42 (17.7%) | 26 (15.1%) | 16 (24.6%) | 0.088 |
| All Patients (n = 237) | Without Post-Dilation (n = 172) | With Post-Dilation (n = 65) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic MSCT parameters | ||||
| Annulus Perimeter derived (mm) | 25.49 ± 2.94 | 25.48 ± 2.88 | 25.51 ± 3.11 | 0.949 |
| STJ height (mm) | 23.29 ± 3.25 (n = 232) | 23.34 ± 3.24 (n = 169) | 23.15 ± 3.32 (n = 63) | 0.694 |
| STJ Perimeter (mm) | 91 ± 13.2 (n = 231 | 91.24 ± 9.77 n = 168 | 90.34 ± 10.18 n = 63 | 0.538 |
| LVOT Perimeter (mm) | 79.5 ± 9.8 (n = 226) | 79.8 ± 10.2 (n = 164 | 78.7 ± 8.8 (n = 62) | 0.451 |
| RCA height (mm) | 17.29 ± 3.16 (n = 236) | 17.29 ± 3.22 | 17.30 ± 3.04 (n = 64) | 0.971 |
| LCA height (mm) | 13.4 ± 3.11 (n = 234) | 13.35 ± 2.90 (n = 171) | 13.59 ± 3.65 (n = 63) | 0.573 |
| Calcification parameters | ||||
| Visual degree of calcification none Mild Moderate Severe | 4 (1.7%) 46 (19.4%) 99 (41.8%) 88 (37.1%) | 3 (1.7%) 36 (20.9%) 76 (44.2%) 57 (33.1%) | 1 (1.5%) 10 (15.4%) 23 (35.4%) 31 (47.7%) | 0.055 |
| Individ. AVC Total (mm3) | 390.5 (211.1–667.3) | 349.5 (179.4–640.4) | 461.2 (317.5–790.1) | 0.004 |
| Individ. AVC LCC (mm3) | 107.3 (49.6–210.2) | 93.95 (46.3–189.5) | 146.0 (64.6–248.5) | 0.008 |
| Individ. AVC RCC (mm3) | 89.9 (49.35–192.5) | 83.35 (43–165.8) | 128.2 (63.1–208.4) | 0.027 |
| Individ. AVC NCC (mm3) | 154.1 (83.1–298) | 139.4 (63.6–263.8) | 196.8 (124.1–339.8) | 0.004 |
| Individ. LVOT calcification (mm3) | 5.2 (0.1–42) (n = 226) | 4.35 (0–23.1) (n = 164) | 16.65(0.3–65.4) (n = 62) | 0.024 |
| Individual threshold (HUs) | 600 (550–685) | 600 (550–650) | 600 (550–700) | 0.066 |
| All Patients (n = 237) | Without Post-Dilation (n = 172) | With Post-Dilation (n = 65) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP pre (mmHg) | 141.74 ± 23.5 | 142.22 ± 23.85 | 140.48 ± 22.71 | 0.613 |
| DBP pre (mmHg) | 63 (57–72) | 63 (58–72) | 61 (55.5–70) | 0.207 |
| LVEDP pre (mmHg) | 21 (16–27) | 20.5 (16–26.8) | 21 (17–28) | 0.643 |
| ARI pre | 30.49 ± 9.65 | 30.69 ± 9.37 | 28.95 ± 10.4 | 0.601 |
| SBP post (mmHg) | 158.25 ± 24.08 | 159.59 ± 23.54 | 154.71 ± 25.28 | 0.164 |
| DBP post (mmHg) | 61 (54–69) | 63.5 (57–71.8) | 54 (50–59) | <0.001 |
| LVEDP post (mmHg) | 24 (19–30) | 24 (19–29) | 24 (19–33) | 0.280 |
| ARI post | 23.59 ± 8.3 | 25.26 ± 7.51 | 19.16 ± 8.73 | <0.001 |
| ARI ratio post/pre | 0.78 (0.61–0.96) | 0.82 (0.69–0.99) | 0.61 (0.49–0.8) | <0.001 |
| ARI ratio ≤ 0.6 | 55 (23.2%) | 23 (13.4%) | 32 (49.2%) | <0.001 |
| More than mild AR after valve deployment, before PD (angiographically) | 61 (25.7%) | 3 (1.7%) | 58 (89.2%) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uebelacker, R.; Martin, S.S.; Vasa-Nicotera, M.; Mas-Peiro, S. Value of Post-/Pre-Procedural Aortic Regurgitation Ratio vs. Pre-Procedural Aortic Valve Calcium Score to Predict Moderate to Severe Paravalvular Leak Requiring Post-Dilation after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7735. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247735
Uebelacker R, Martin SS, Vasa-Nicotera M, Mas-Peiro S. Value of Post-/Pre-Procedural Aortic Regurgitation Ratio vs. Pre-Procedural Aortic Valve Calcium Score to Predict Moderate to Severe Paravalvular Leak Requiring Post-Dilation after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(24):7735. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247735
Chicago/Turabian StyleUebelacker, Roman, Simon S. Martin, Mariuca Vasa-Nicotera, and Silvia Mas-Peiro. 2023. "Value of Post-/Pre-Procedural Aortic Regurgitation Ratio vs. Pre-Procedural Aortic Valve Calcium Score to Predict Moderate to Severe Paravalvular Leak Requiring Post-Dilation after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 24: 7735. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247735
APA StyleUebelacker, R., Martin, S. S., Vasa-Nicotera, M., & Mas-Peiro, S. (2023). Value of Post-/Pre-Procedural Aortic Regurgitation Ratio vs. Pre-Procedural Aortic Valve Calcium Score to Predict Moderate to Severe Paravalvular Leak Requiring Post-Dilation after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(24), 7735. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247735






