Comparing Non-Invasive Spectrophotometry to Hematology Analysis for Hemoglobin Measurements in Sickle Cell Disease Patients
Abstract
Highlights
- The SpHb concentration was found to be higher than the lab Hb concentrations, with a positive correlation.
- SpHb measurement sensitivity and precision were lower than expected.
- Non-invasive SpHb measurement can play a role in excluding anemia in outpatient clinics.
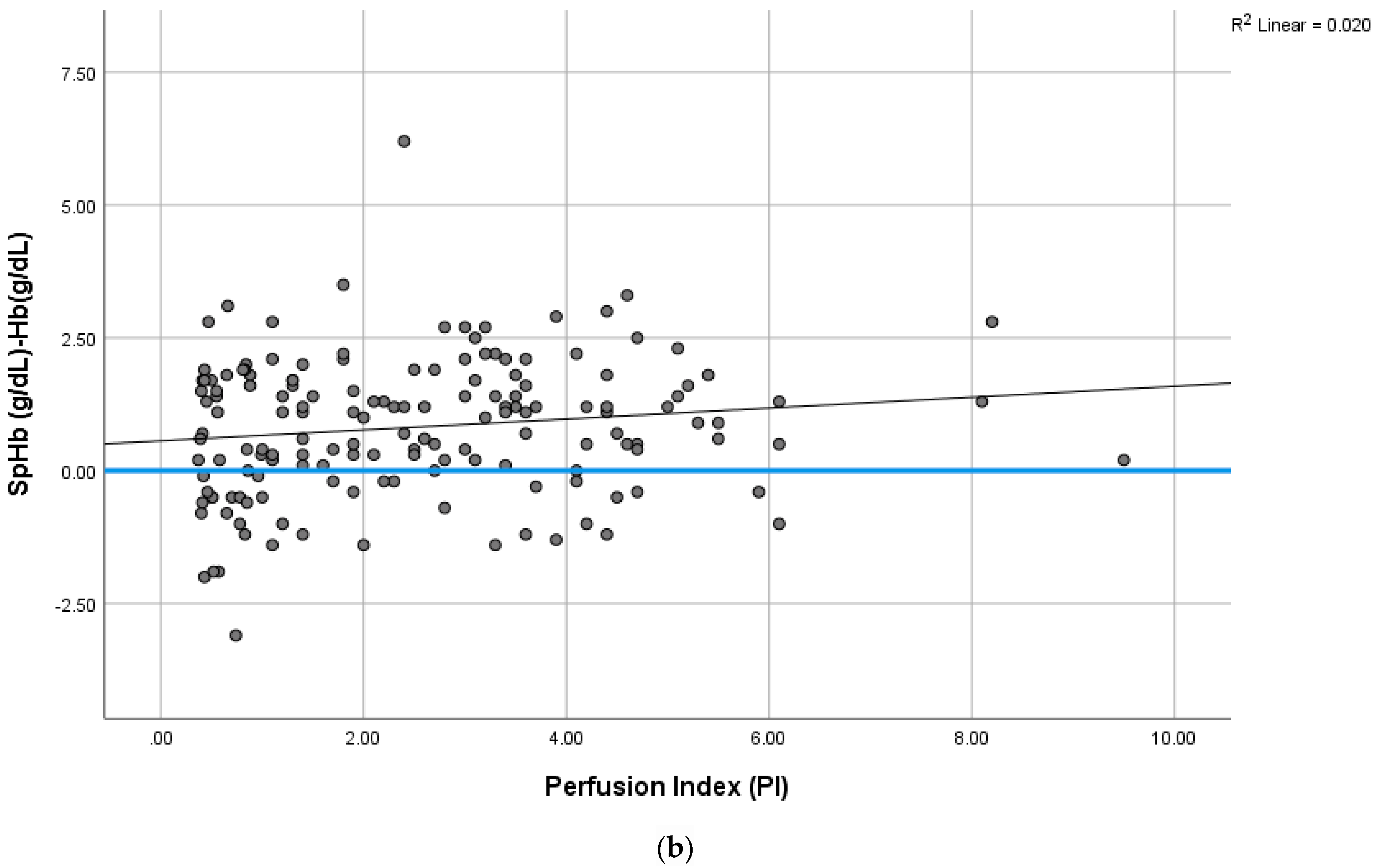
- The PI values among the SCD patients were lower than the patients with a normal hemoglobin structure.
- SpHb measurement requires technological improvements to overcome the low PI observed in SCD patients.
Abstract
1. Introduction
Aim of this Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. SpHb, Pleth Variability Index (PVI, %), and Perfusion Index (PI)
2.3. Laboratory Hemoglobin Measurement
2.4. Measurement Time and Site
2.5. Statistical Analysis
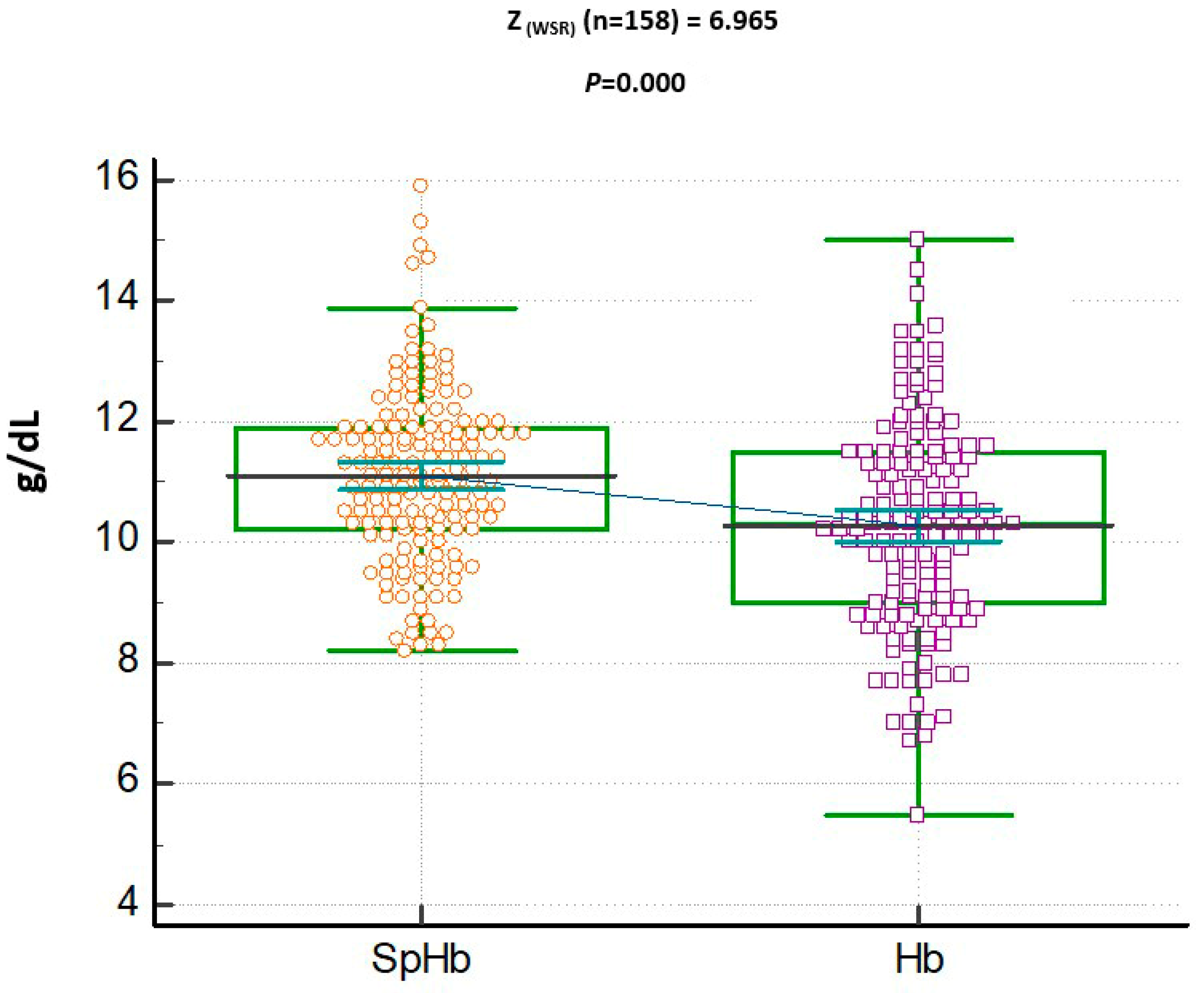
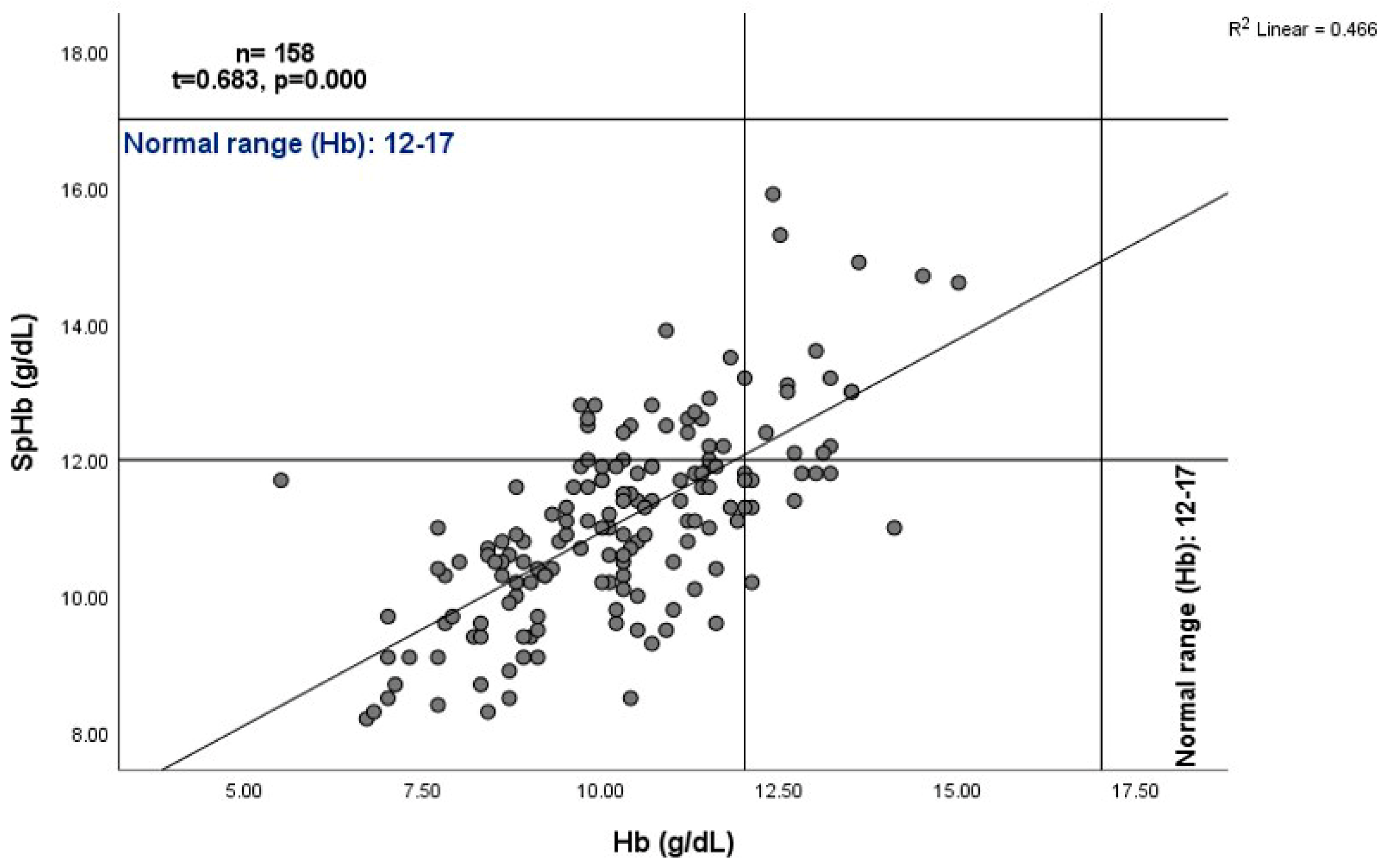
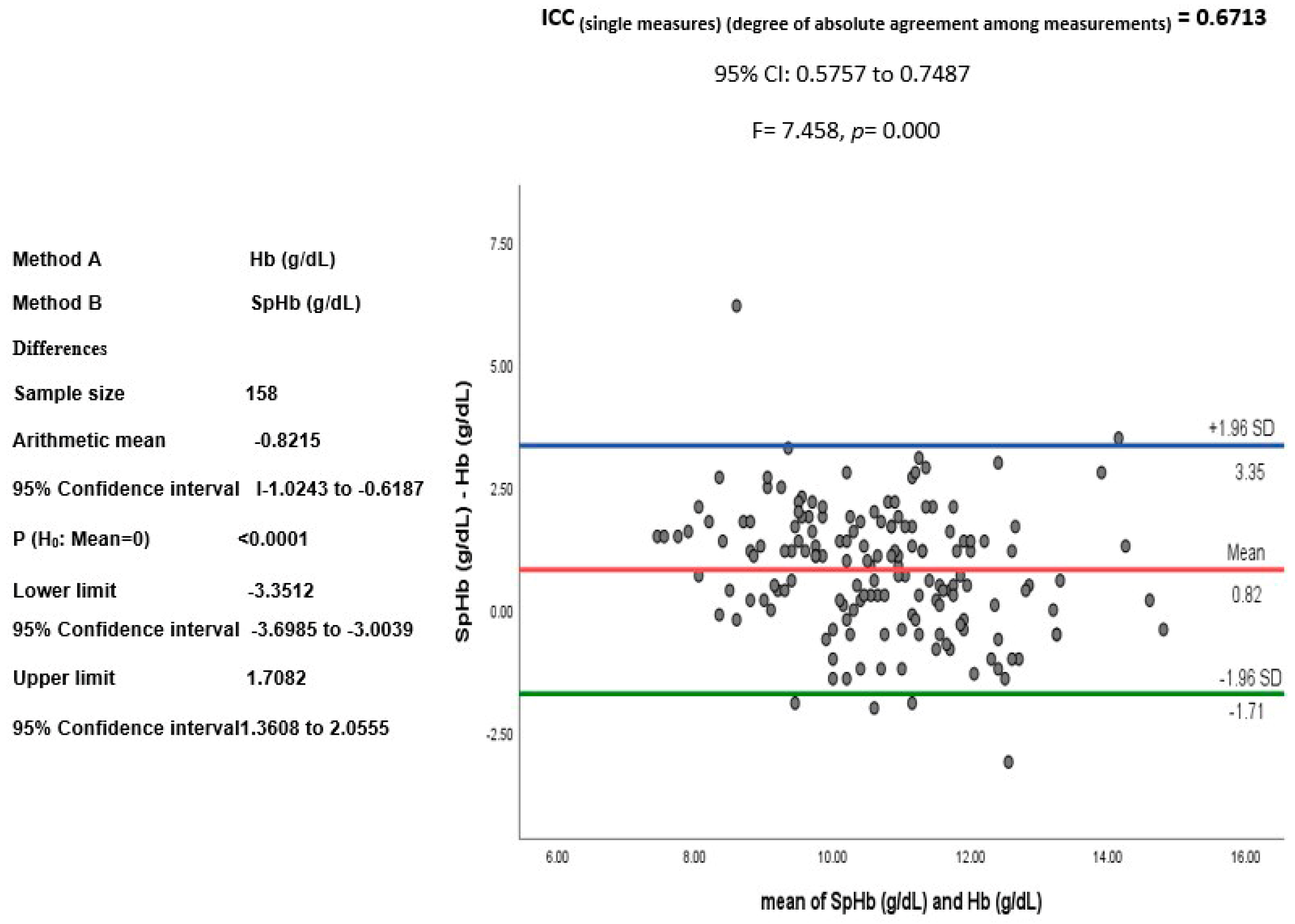
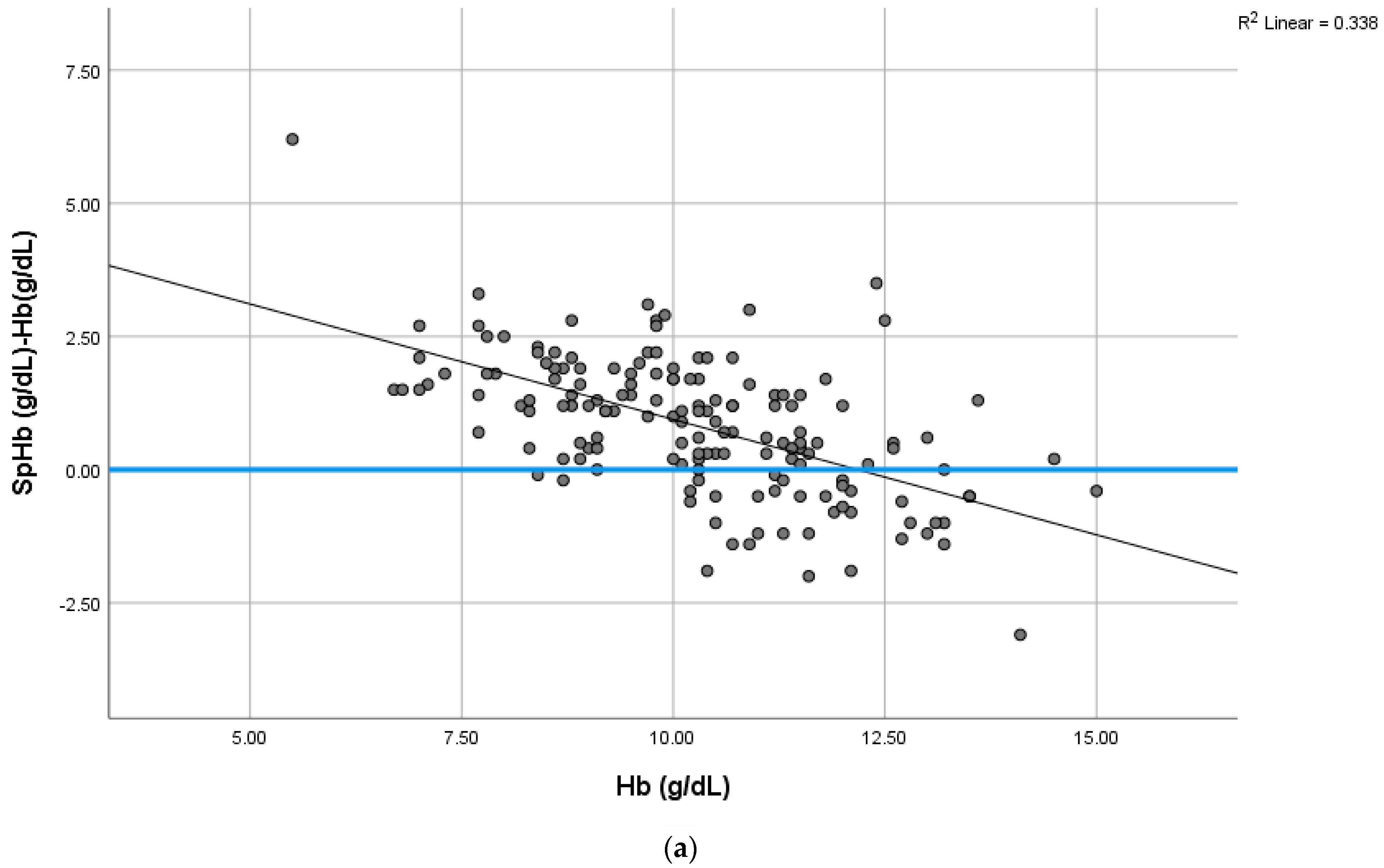
3. Results
SpHb and Hb Relationship
4. Discussion
4.1. Failure to Measure SpHb
4.2. SpHb-Hb Relationship Variations
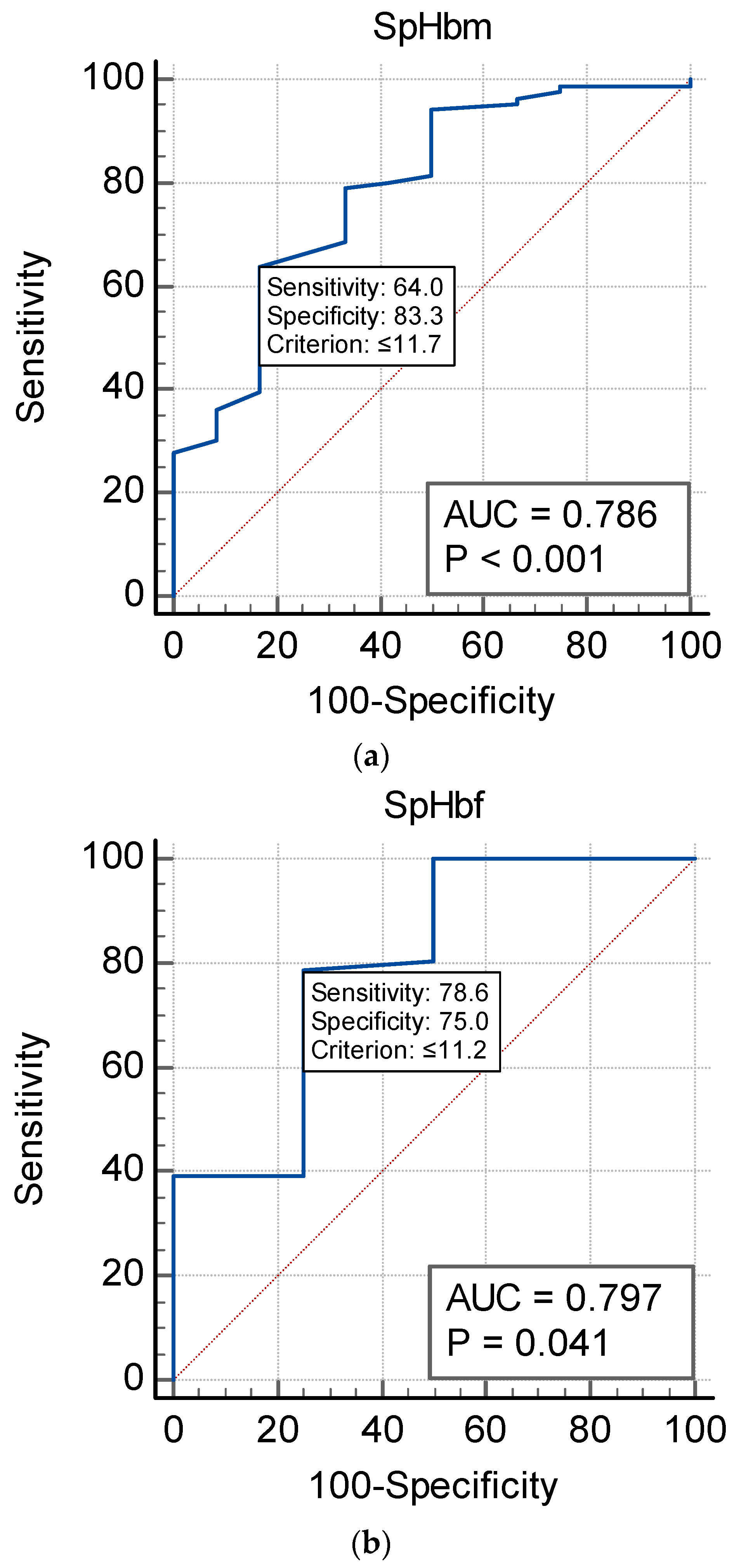
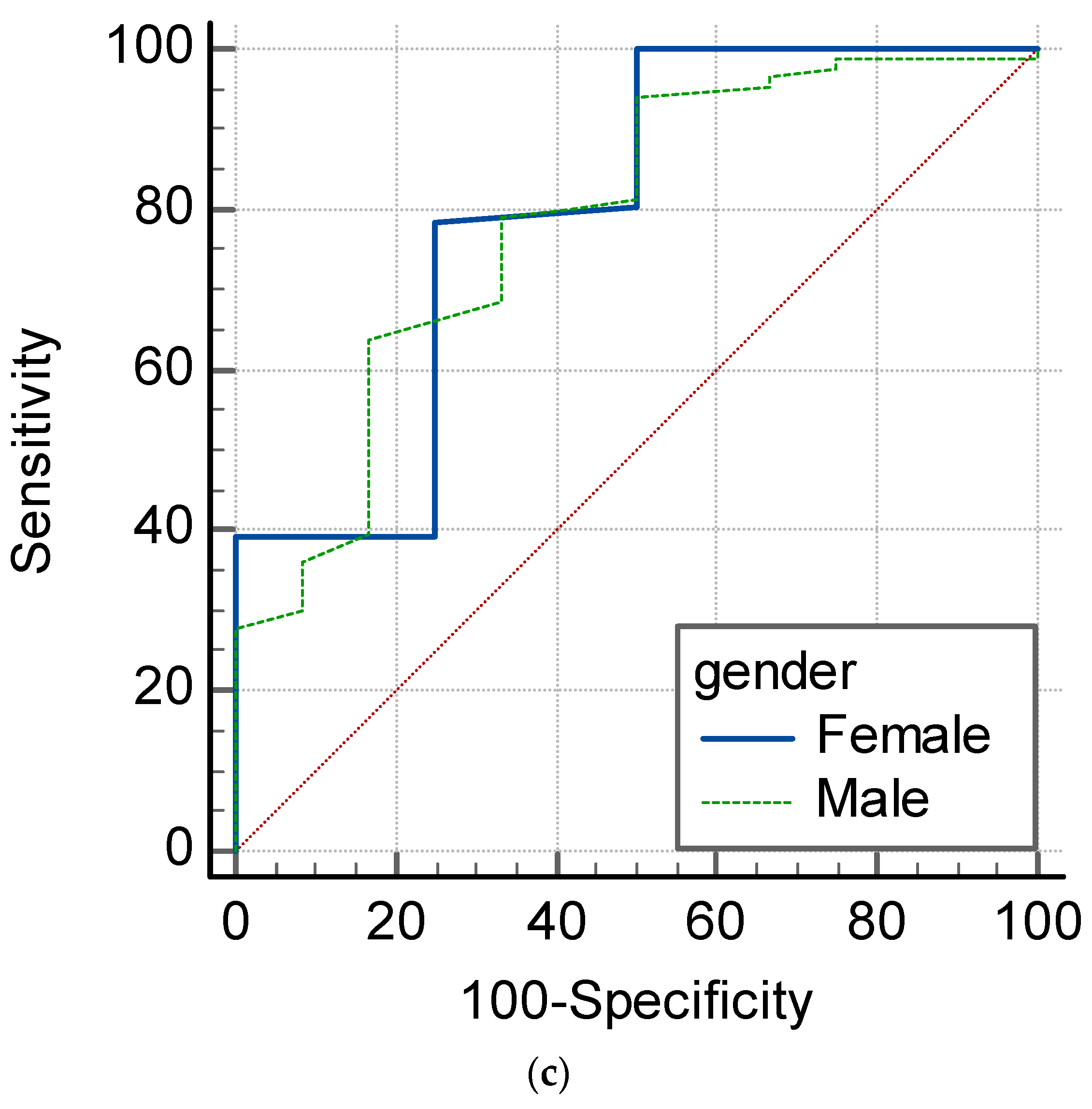
4.3. SpHb as an Anemia Screening Monitor
4.4. The Effect of a Low PI on SpHb
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alabdulaali, M.K. Sickle cell disease patients in eastern province of Saudi Arabia suffer less severe acute chest syndrome than patients with African haplotypes. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2007, 2, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastaniah, W. Epidemiology of Sickle Cell Disease in Saudi Arabia. Ann. Saudi Med. 2011, 31, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, P.L.; Fasipe, T.A.; Wun, T. Sickle Cell Disease: A Review. JAMA 2022, 328, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, M.H. Pathophysiology of sickle cell disease. Baillieres Clin. Haematol. 1998, 11, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumayr, L.D.; Hoppe, C.C.; Brown, C. Sickle cell disease: Current treatment and emerging therapies. Am. J. Manag. Care 2019, 25 (Suppl. 18), S335–S343. [Google Scholar]
- Hiscock, R.; Kumar, D.; Simmons, S.W. Systematic review and meta-analysis of method comparison studies of Masimo pulse co-oximeters (Radical-7™ or Pronto-7™) and HemoCue® absorption spectrometers (B-Hemoglobin or 201+) with laboratory haemoglobin estimation. Anaesth. Intensiv. Care 2015, 43, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, K.; Okazaki, K.; Uesugi, M.; Matsusima, T.; Hataya, H. Evaluation of the accuracy of a non-invasive hemoglobin-monitoring device in schoolchildren. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2022, 63, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Khalid, S.G.; Alib, U.; Hameeda, K. A blueprint design of optical-based wristband for non-invasive and continuous health status monitoring of sickle cell disease patients. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2023, 21, 133–144. Available online: https://www.scielo.org.mx/pdf/jart/v21n1/2448-6736-jart-21-01-133.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Timm, U.; Leen, G.; Lewis, E.; McGrath, D.; Kraitl, J.; Ewald, H. Non-invasive optical real-time measurement of total hemoglobin content. Procedia Eng. 2010, 5, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khalafallah, A.A.; Chilvers, C.R.; Thomas, M.; Chilvers, C.M.; Sexton, M.; Vialle, M.; Robertson, I.K. Usefulness of noninvasive spectrophotometric hemoglobin estimation for detecting low hemoglobin levels when compared with a standard laboratory assay for preoperative assessment. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honnef, G.; Auinger, D.; Eichinger, M.; Eichlseder, M.; Metnitz, P.G.H.; Rief, M.; Zajic, P.; Zoidl, P.; Bornemann-Cimenti, H. Evaluation of the usefulness of non-invasive serum hemoglobin measurement in a perioperative setting in a prospective observational study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenmeier, E.; Paumen, Y.; Mildenberger, P.; Smetiprach, J.; Pirlich, N.; Griemert, E.V.; Kriege, M.; Engelhard, K. Non-invasive hemoglobin measurement as an index test to detect pre-operative anemia in elective surgery patients—A prospective study. Anaesthesia 2021, 76, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-T. Current Use of Noninvasive Hemoglobin Monitoring in Anesthesia. Curr. Anesth. Rep. 2014, 4, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barker, S.J.; Badal, J.J. The measurement of dyshemoglobins and total hemoglobin by pulse oximetry. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2008, 21, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.masimo.co.jp/pdf/clinical/hemoglobin/szmuk-evaluation-of-noninvasive-and-continuous-hemoglobin-monitoring-in-children-with-sickle-cell-disease-oct-2011.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Al-Khabori, M.K.; Al-Hashim, A.; Jabeen, Z.; Farsi, K.A.; Al-Huneini, M.; Al-Riyami, A.Z.; Al-Kemyani, N.; Daar, S. Validation of a Non-Invasive Hemoglobin Estimation in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease, American Society of Hematology. 2012. Available online: https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/120/21/4770/85207/Validation-of-a-Non-Invasive-Hemoglobin-Estimation (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- El-Hazmi, M.A. Heterogeneity and variation of clinical and haematological expression of haemoglobin S in Saudi Arabs. Acta Haematol. 1992, 88, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappellini, M.D.; Motta, I. Anemia in Clinical Practice-Definition and Classification: Does Hemoglobin Change With Aging? Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwabari, M.; Alhamad, F.; Alsahaf, F.; Al Amer, F.; Alniniya, F.; Alherz, I.; Omer, N.; Bushehab, A.; Yassen, K. Can Non-Invasive Spectrophotometric Hemoglobin Replace Laboratory Hemoglobin Concentrations for Preoperative Anemia Screening? A Diagnostic Test Accuracy Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masimo Corporation. 2015. Available online: http://www.masimo.com/ (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Whitehead, R.D., Jr.; Mei, Z.; Mapango, C.; Jefferds, M.E.D. Methods and analyzers for hemoglobin measurement in clinical laboratories and field settings. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1450, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwood, P.C.; Jacobs, A. Haemoglobin estimation: A comparison of different techniques. Br. Med. J. 1966, 1, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, R.; Dubey, A.; Sonker, A. Techniques used for the screening of hemoglobin levels in blood donors: Current insights and future directions. J. Blood Med. 2017, 8, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.sysmex-europe.com/products/products-detail/xn-1000.html (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- Gomaa, D.; Rodriquez, D.; Petro, M.; Blakeman, T.C.; Branson, R.D. Impact of Oxygenation Status on the Noninvasive Measurement of Hemoglobin. Mil. Med. 2017, 182, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows; Version 21.0.; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics, 4th ed.; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, M. The use of ranks to avoid the assumption of normality implicit in the analysis of variance. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1937, 32, 675–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 1938, 30, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, G.G. Intraclass correlation coefficient. In Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences; Kotz, S., Johnson, N.L., Read, C.B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Mantha, S.; Roizen, M.F.; Fleisher, L.A.; Thisted, R.; Foss, J. Comparing methods of clinical measurement: Reporting standards for bland and altman analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 90, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchetti, D.V. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol. Assess. 1994, 6, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.F.; Raines, K.; Jameel, F.; Sidi, M.; Oliveira-Streiff, S.; Nwajei, P.; McGlamry, K.; Ou, J.; Oladele, A.; Suchdev, P.S. Non-invasive hemoglobin measurement devices require refinement to match diagnostic performance with their high level of usability and acceptability. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czempik, P.F.; Pluta, M.P.; Krzych, Ł.J. Hemoglobin Determination Using Pulse Co-Oximetry and Reduced-Volume Blood Gas Analysis in the Critically Ill: A Prospective Cohort Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasca, D.; Dahyot-Fizelier, C.; Catherine, K.; Levrat, Q.; Debaene, B.; Mimoz, O. Accuracy of a continuous noninvasive hemoglobin monitor in intensive care unit patients. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornedo-González, K.D.; Jacob, A.K.; Burt, J.M.; Higgins, A.A.; Engel, E.M.; Hanson, A.C.; Belch, L.; Kor, D.J.; Warner, M.A. Non-invasive hemoglobin estimation for preoperative anemia screening. Transfusion 2023, 63, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www2.pedsanesthesia.org/meetings/2010winter/syllabus/pdfs/abstracts/casereports/CR88.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Gayat, E.; Aulagnier, J.; Matthieu, E.; Boisson, M.; Fischler, M. Noninvasive measurement of hemoglobin: Assessment of two different point-of-care technologies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macknet, M.R.; Allard, M.; Applegate, R.L., 2nd; Rook, J. The accuracy of noninvasive and continuous total hemoglobin measurement by pulse CO-Oximetry in human subjects undergoing hemodilution. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 111, 1424–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, J.J.; Kalmar, A.F.; Struys, M.M.; Porte, R.J.; Wietasch, J.K.; Scheeren, T.W.; Hendriks, H.G. Accuracy of non-invasive measurement of haemoglobin concentration by pulse co-oximetry during steady-state and dynamic conditions in liver surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.D.; Ward, T.A.; Shiboski, S.C.; Cohen, N.H. A comparison of three methods of hemoglobin monitoring in patients undergoing spine surgery. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 112, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bıcılıoğlu, Y.; Bal, A.; Yenigürbüz, F.D.; Ergonul, E.; Geter, S.; Kazanasmaz, H.; Bal, U. Noninvasive Hemoglobin Measurement Reduce Invasive Procedures in Thalassemia Patients. Hemoglobin 2022, 46, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, U.; Wolf, M.; Choi, J.H.; Levi, M.; Choudhury, D.; Hull, S.; Coussirat, D.; Paunescu, L.; Safonova, L.P.; Michalos, A.; et al. Localized irregularities in hemoglobin flow and oxygenation in calf muscle in patients with peripheral vascular disease detected with near-infrared spectrophotometry. J. Vasc. Surg. 2003, 37, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalacheva, P.; Kato, R.M.; Shah, P.; Veluswamy, S.; Denton, C.C.; Sunwoo, J.; Thuptimdang, W.; Wood, J.C.; Detterich, J.A.; Coates, T.D.; et al. Sickle Cell Disease Subjects Have a Distinct Abnormal Autonomic Phenotype Characterized by Peripheral Vasoconstriction With Blunted Cardiac Response to Head-Up Tilt. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharawy, M.A.; Moghazy, K.M. Peripheral Arterial Lesions in Patient with Sickle Cell Disease. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2007, 34, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miller, R.D.; Ward, T.A.; McCulloch, C.E.; Cohen, N.H. Does a digital regional nerve block improve the accuracy of noninvasive hemoglobin monitoring? J. Anesth. 2012, 26, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.G.; Lee, O.H.; Park, Y.H.; Shin, H.Y.; Kang, H.; Baek, C.W.; Jung, Y.H.; Woo, Y.C. The changes of non-invasive hemoglobin and perfusion index of Pulse CO-Oximetry during induction of general anesthesia. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2015, 68, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, A.; Awada, W.; Abdelhamid, B.; Omar, H.; Abd El Dayem, O.; Hasanin, A.; Rady, A. Accuracy and trending of non-invasive hemoglobin measurement during different volume and perfusion statuses. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2018, 32, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Median | Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SpHb (g/dL) | 11 | 11.10 | 1.44 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 10.3 | 10.28 | 1.73 |
| PVI (%) | 15 | 16.74 | 7.70 |
| PI | 2.25 | 2.53 | 1.80 |
| Oxygen saturation (%) | 98 | 98.81 | 1.15 |
| Hb A (%) | 0.00 | 1.21 | 5.65 |
| Hb A2 (%) | 3.10 | 4.61 | 15.85 |
| Hb S (%) | 79.25 | 78.16 | 9.80 |
| Hb F (%) | 16.20 | 16.77 | 7.63 |
| Hemoglobin Type | Medications | n | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | No | 43 | Mean | 1.76 | 0.462 |
| Median | 0 | ||||
| Std. Deviation | 5.47 | ||||
| Yes | 111 | Mean | 1.01 | ||
| Median | 0 | ||||
| Std. Deviation | 5.75 | ||||
| A2 | No | 43 | Mean | 3.21 | 0.497 |
| Median | 3.00 | ||||
| Std. Deviation | 1.06 | ||||
| Yes | 114 | Mean | 5.20 | ||
| Median | 3.20 | ||||
| Std. Deviation | 18.89 | ||||
| S | No | 43 | Mean | 76.28 | 0.145 |
| Median | 77.60 | ||||
| Std. Deviation | 13.51 | ||||
| Yes | 114 | Mean | 78.74 | ||
| Median | 79.30 | ||||
| Std. Deviation | 8.07 | ||||
| F | No | 43 | Mean | 17.27 | 0.612 |
| Median | 17.10 | ||||
| Std. Deviation | 9.17 | ||||
| Yes | 114 | Mean | 16.66 | ||
| Median | 16.30 | ||||
| Std. Deviation | 7.10 | ||||
| Hb (g/dL) | SpHb | Sens | Spec | NPV | PPV | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHO (F) Hb < 12 | 11.4 | 57.1 | 75 | 22.2 | 85.7 | 0.60 |
| WHO (M) Hb < 13 | 11.7 | 64.4 | 90.9 | 10.5 | 95.6 | 0.83 |
| CBC (F + M) Hb < 12 | 11.2 | 78.6 | 75 | 21.1 | 91.9 | 0.80 |
| CBC (F + M) Hb < 13 | 11.7 | 64 | 83.3 | 7.9 | 93.5 | 0.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yassen, K.; Omer, N.; Alsahaf, F.; Al Amer, F.; Alhamad, F.; Alherz, I.; Bushehab, A.; Alniniya, F.; Alwabari, M. Comparing Non-Invasive Spectrophotometry to Hematology Analysis for Hemoglobin Measurements in Sickle Cell Disease Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7517. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247517
Yassen K, Omer N, Alsahaf F, Al Amer F, Alhamad F, Alherz I, Bushehab A, Alniniya F, Alwabari M. Comparing Non-Invasive Spectrophotometry to Hematology Analysis for Hemoglobin Measurements in Sickle Cell Disease Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(24):7517. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247517
Chicago/Turabian StyleYassen, Khaled, Nawal Omer, Fatimah Alsahaf, Fatima Al Amer, Fatimah Alhamad, Imran Alherz, Abdulaziz Bushehab, Fatma Alniniya, and Maryam Alwabari. 2023. "Comparing Non-Invasive Spectrophotometry to Hematology Analysis for Hemoglobin Measurements in Sickle Cell Disease Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 24: 7517. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247517
APA StyleYassen, K., Omer, N., Alsahaf, F., Al Amer, F., Alhamad, F., Alherz, I., Bushehab, A., Alniniya, F., & Alwabari, M. (2023). Comparing Non-Invasive Spectrophotometry to Hematology Analysis for Hemoglobin Measurements in Sickle Cell Disease Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(24), 7517. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247517







