Classification Model for Epileptic Seizure Using Simple Postictal Laboratory Indices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
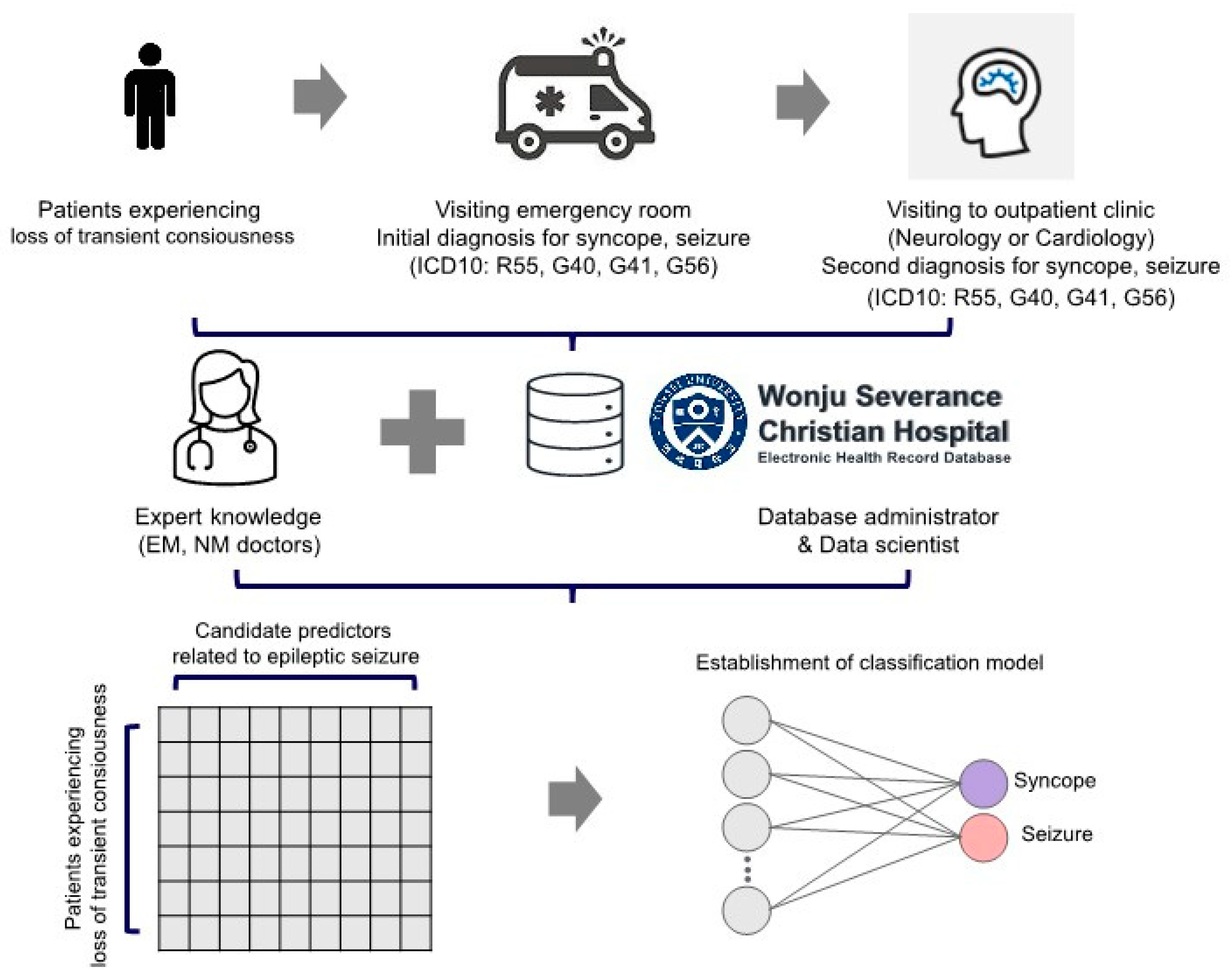
2.1. Participants
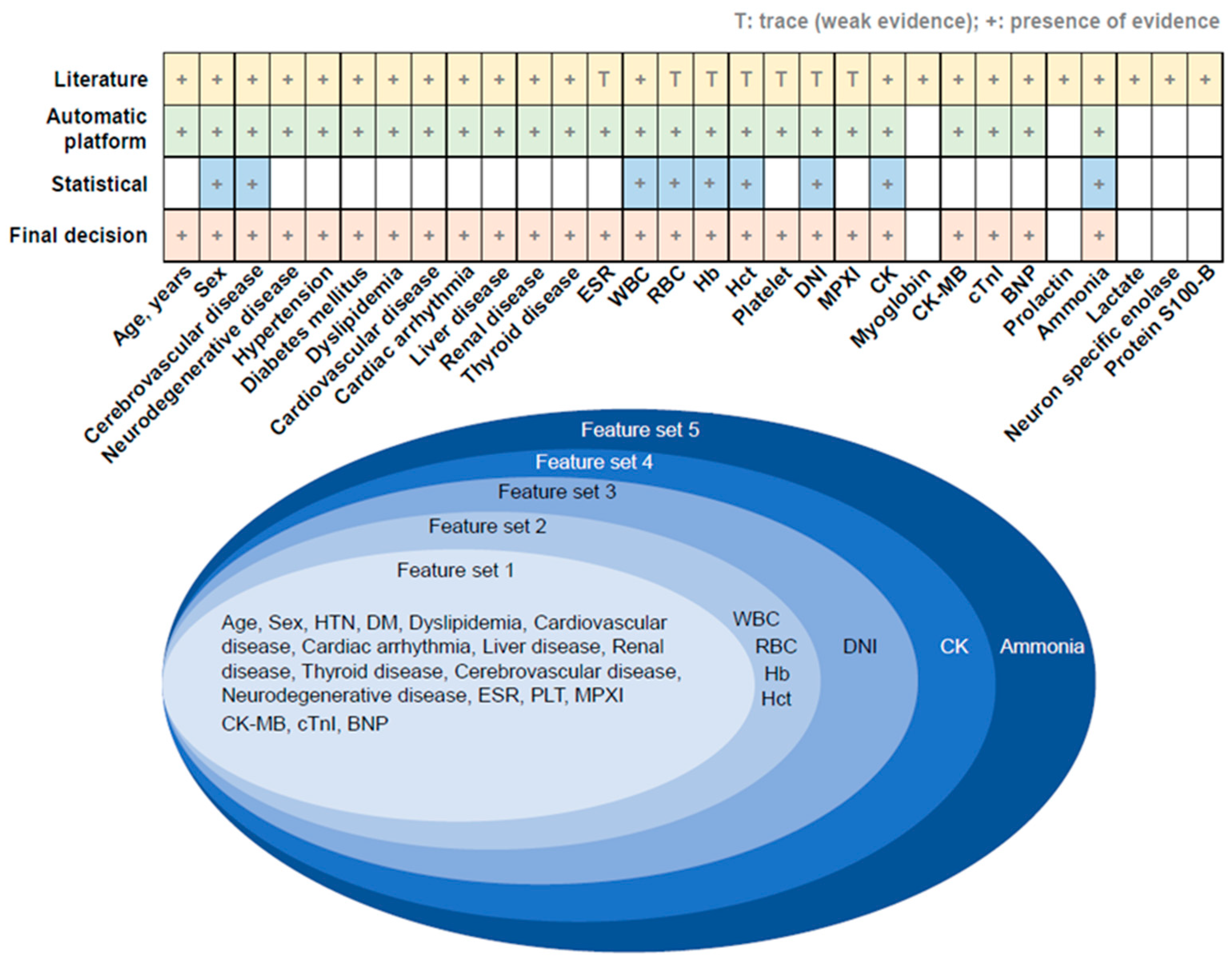
2.2. Determination of Outcome and Predictor Variables Related to Epileptic Seizure
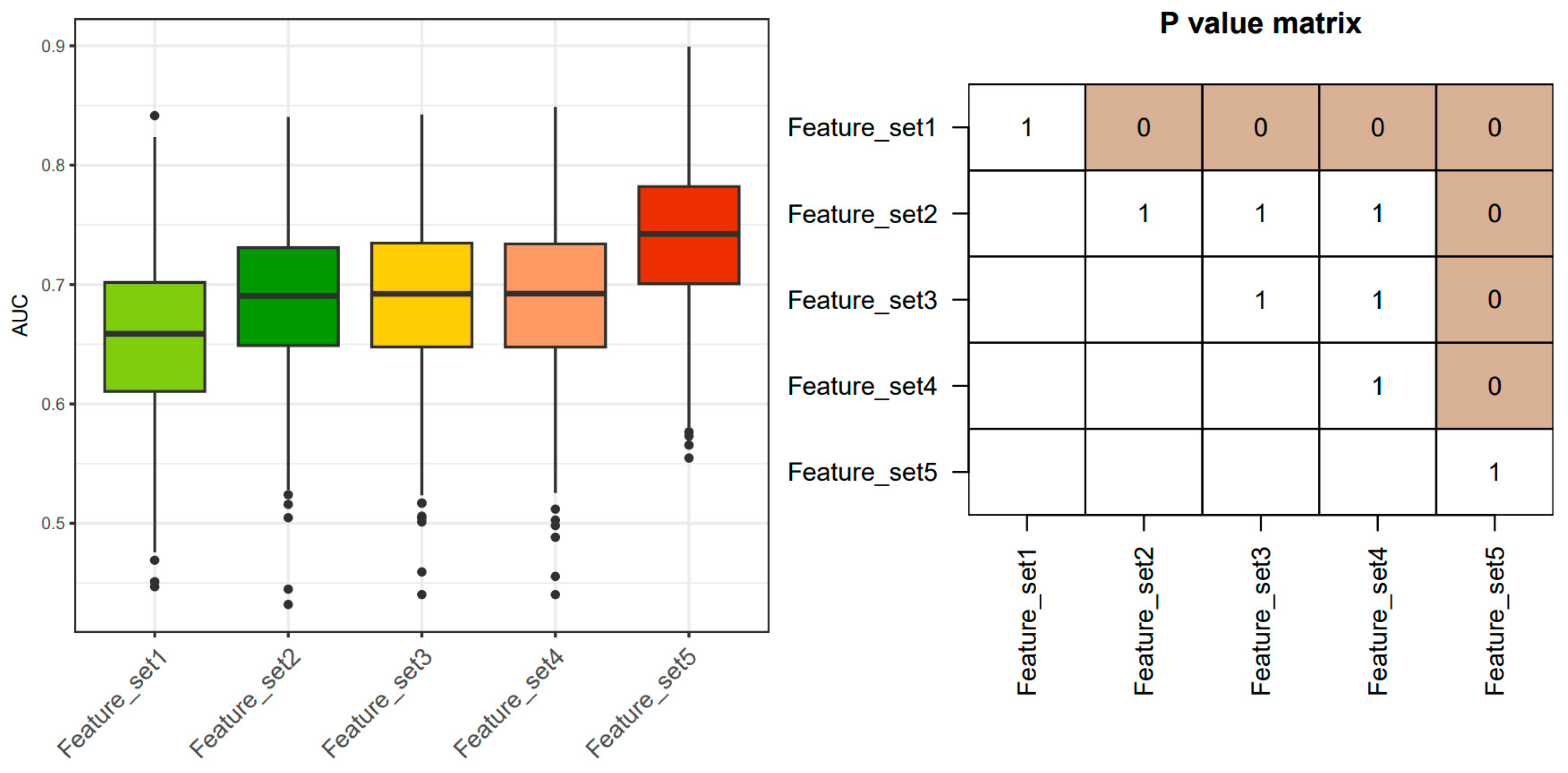
2.3. Cross-Validation to Compare Predictive Performance
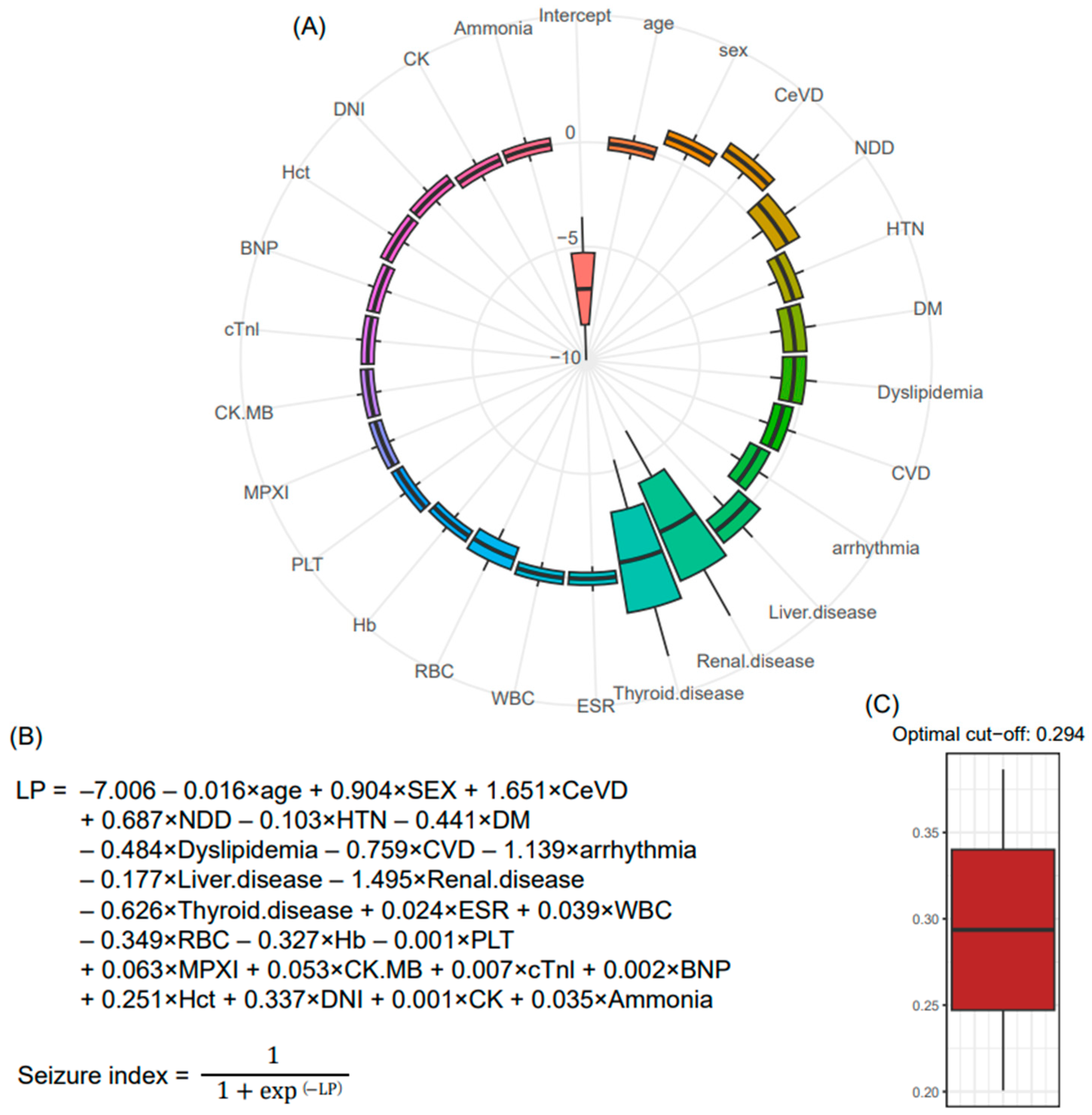
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McKeon, A.; Vaughan, C.; Delanty, N. Seizure versus syncope. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi-Pooya, A.A.; Nikseresht, A.; Yaghoubi, E. Vasovagal syncope treated as epilepsy for 16 years. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 36, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.T.; Ziegler, D.K.; Lai, C.W.; Bayer, W. Convulsive syncope in blood donors. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 11, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoumi, B.; Mozafari, S.; Golshani, K.; Heydari, F.; Nasr-Esfahani, M. Differential diagnosis of seizure and syncope by the means of biochemical markers in emergency department patients. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2022, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nass, R.D.; Meiling, S.; Andrié, R.P.; Elger, C.E.; Surges, R. Laboratory markers of cardiac and metabolic complications after generalized tonic-clonic seizures. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petramfar, P.; Yaghoobi, E.; Nemati, R.; Asadi-Pooya, A.A. Serum creatine phosphokinase is helpful in distinguishing generalized tonic-clonic seizures from psychogenic nonepileptic seizures and vasovagal syncope. Epilepsy Behav. 2009, 15, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.T.; Rego, R.; Rocha, H.; Sá, F.; Farinha, R.; Oliveira, A.; Barata, P.; Alves, D.; Pereira, J.; Rocha-Gonçalves, F.; et al. cTnI, BNP and CRP profiling after seizures in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy. Seizure 2020, 80, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.I. Plasma brain-type natriuretic Peptide level following seizure and syncope: Pilot study. J. Epilepsy Res. 2014, 4, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Ko, W.; Kim, H.I.; Kim, W.J. Differential diagnostic value of transient increase of plasma ammonia level in seizure and syncope. J. Korean Neurol. Assoc. 2012, 30, 279–283. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, B.; Tang, J. Changes of biochemical biomarkers in the serum of children with convulsion status epilepticus: A prospective study. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Chadda, R.K.; Rusia, U.; Jain, N. Effect of electroconvulsive therapy on hematological parameters. Psychiatry Res. 2001, 104, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.K.; Shein, N.; Fuerst, D.; Yangala, R.; Shah, J.; Watson, C. Peripheral WBC count and serum prolactin level in various seizure types and nonepileptic events. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 1472–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkis, R.A.; Jehi, L.; Silveira, D.; Janigro, D.; Najm, I. Patients with generalised epilepsy have a higher white blood cell count than patients with focal epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2012, 14, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon-kyung, J.; Hyun-Ho, S. A study on the relationship between CBC and EEG for epilepsy patients. Korean J. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 47, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.Y.; Yoo, G.; Lee, T.; Uh, Y.; Kim, J. Identification of the robust predictor for sepsis based on clustering analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoo, G.; Lee, T.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, D.M.; Kim, J. Classification model for diabetic foot, necrotizing fasciitis, and osteomyelitis. Biology 2022, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Gwon, C.; Seo, D.M.; Cho, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Uh, Y. A deep neural network for estimating low-density lipoprotein cholesterol from electronic health records: Real-time routine clinical application. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e29331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nass, R.D.; Sassen, R.; Elger, C.E.; Surges, R. The role of postictal laboratory blood analyses in the diagnosis and prognosis of seizures. Seizure 2017, 47, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goksu, E.; Oktay, C.; Kilicaslan, I.; Kartal, M. Seizure or syncope: The diagnostic value of serum creatine kinase and myoglobin levels. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2009, 16, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtkamp, M.; Othman, J.; Buchheim, K.; Meierkord, H. Diagnosis of psychogenic nonepileptic status epilepticus in the emergency setting. Neurology 2006, 66, 1727–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigo, F.; Igwe, S.C.; Erro, R.; Bongiovanni, L.G.; Marangi, A.; Nardone, R.; Tinazzi, M.; Trinka, E. Postictal serum creatine kinase for the differential diagnosis of epileptic seizures and psychogenic non-epileptic seizures: A systematic review. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagawa, Y.; Nishi, K.; Sakamoto, T. Hyperammonemia is associated with generalized convulsion. Intern. Med. 2008, 47, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albadareen, R.; Gronseth, G.; Landazuri, P.; He, J.; Hammond, N.; Uysal, U. Postictal ammonia as a biomarker for electrographic convulsive seizures: A prospective study. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Wang, T.L.; Su, C.F.; Wang, R.F. Transient hyperammonemia in seizures: A prospective study. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.L.; Hollander, J.E.; Pines, J.M.; Mullins, P.M.; Chang, A.M. Electrocardiogram and cardiac testing among patients in the emergency department with seizure versus syncope. Clin. Exp. Emerg. Med. 2019, 6, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Köller, M.; Cepok, S.; Todorova-Rudolph, A.; Nowak, M.; Nockher, W.A.; Lorenz, R.; Tackenberg, B.; Oertel, W.H.; Rosenow, F.; et al. NK and CD4+ T cell changes in blood after seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 211, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Bauer, S.; Nowak, M.; Norwood, B.; Tackenberg, B.; Rosenow, F.; Knake, S.; Oertel, W.H.; Hamer, H.M. Cytokines and epilepsy. Seizure 2011, 20, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peneva, P.; Nikolova, S.; Bocheva, Y. Delta neutrophil index: In search of an early indicator of sepsis. Folia Med. 2021, 63, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Jeong, R.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.; Yu, W.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, H.J. The usefulness of serum biomarker C-reactive protein, delta neutrophil index, lactic acid and ammonia for differential diagnosis in patients with drowsy mentality in emergency department. J. Korean Soc. Emerg. Med. 2022, 33, 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Güneş, M.; Büyükgöl, H. Relationship between generalized epileptic seizure and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, platelet/lymphocyte ratio, and neutrophil mediated inflammation. Int. J. Neurosci. 2020, 130, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkavuk, G.; Koc, G.; Leventoglu, A. Is the differential diagnosis of epilepsy and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures possible by assessing the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio? Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 116, 107736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Örnek, Z.; Kardeş, H.; Pİşkİn, İ.E.; Çalik, M. Comparison of hemogram parameters in febrile seizures types. Düzce Tıp Fak. Derg. 2020, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarian, R.; Asghari, N.; Darban, M.; Ghorbani, R. Cardiac troponin levels following complicated and uncomplicated epileptic seizures. Arch. Med. Res. 2011, 42, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alehan, F.; Erol, I.; Cemil, T.; Bayraktar, N.; Ogüs, E.; Tokel, K. Elevated CK-MB mass and plasma brain-type natriuretic peptide concentrations following convulsive seizures in children and adolescents: Possible evidence of subtle cardiac dysfunction. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matz, O.; Zdebik, C.; Zechbauer, S.; Bündgens, L.; Litmathe, J.; Willmes, K.; Schulz, J.B.; Dafotakis, M. Lactate as a diagnostic marker in transient loss of consciousness. Seizure 2016, 40, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, M.R. Serum prolactin in epilepsy and hysteria. Br. Med. J. 1978, 2, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Beckett, M.W. Value of serum prolactin in the management of syncope. Emerg. Med. J. 2004, 21, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijdicks, E.F.; Hijdra, A.; Young, G.B.; Bassetti, C.L.; Wiebe, S.; Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Practice parameter: Prediction of outcome in comatose survivors after cardiopulmonary resuscitation (an evidence-based review): Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2006, 67, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Choi, Y.C.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, W.J. Serum neuron-specific enolase level as a biomarker in differential diagnosis of seizure and syncope. J. Neurol. 2010, 257, 1708–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, T.; Eom, M.; Cho, H.S.; Ku, J. Quantitative ultrasound for non-invasive evaluation of subclinical rejection in renal transplantation. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Syncope (n = 170) | Seizure (n = 90) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 59.5 ± 1.54 | 55.4 ± 1.76 | 0.105 |
| Male | 79 (46.5) | 54 (60) | 0.052 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 23 (13.5) | 31 (34.4) | <0.001 |
| Neurodegenerative disease | 10 (5.9) | 6 (6.7) | 1 |
| Hypertension | 43 (25.3) | 21 (23.3) | 0.843 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 26 (15.3) | 10 (11.1) | 0.459 |
| Dyslipidemia | 30 (17.6) | 8 (8.9) | 0.086 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 30 (17.6) | 12 (13.3) | 0.47 |
| Cardiac arrhythmia | 24 (14.1) | 8 (8.9) | 0.307 |
| Liver disease | 10 (5.9) | 10 (11.1) | 0.207 |
| Renal disease | 14 (8.2) | 3 (3.3) | 0.209 |
| Thyroid disease | 10 (5.9) | 3 (3.3) | 0.55 |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (mm/h) | 9 ± 0.8 | 10.6 ± 1.21 | 0.255 |
| White blood cell counts (×103/μL) | 7.6 ± 0.23 | 9.9 ± 0.48 | <0.001 |
| Red blood cell counts, (×106/μL) | 4.4 ± 0.04 | 4.5 ± 0.07 | 0.029 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.4 ± 0.15 | 14 ± 0.19 | 0.013 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 40 ± 0.4 | 42.4 ± 0.62 | 0.002 |
| Platelet counts (×103/μL) | 230.3 ± 5.22 | 235.6 ± 10.49 | 0.647 |
| Delta neutrophil index (%) | 0.3 ± 0.06 | 0.7 ± 0.18 | 0.017 |
| Myeloperoxidase index | 0.9 ± 0.32 | 1.1 ± 0.47 | 0.8 |
| Creatinine kinase (IU/L) | 132 ± 12.75 | 336.1 ± 79.45 | 0.013 |
| Creatinine kinase-myoglobin binding (ng/mL) | 1.6 ± 0.13 | 4.6 ± 1.7 | 0.084 |
| Cardiac troponin I (ng/mL) | 20.2 ± 13.59 | 63 ± 34.58 | 0.252 |
| Brain-type natriuretic peptide (pg/mL) | 63 ± 9.66 | 95.7 ± 20.85 | 0.158 |
| Ammonia (µg/dL) | 29.2 ± 1.45 | 93.9 ± 12.79 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, S.J.; Lee, T.; Moon, H.E.; Park, E.S.; Lee, S.H.; Roh, Y.I.; Seo, D.M.; Kim, W.-J.; Hwang, H. Classification Model for Epileptic Seizure Using Simple Postictal Laboratory Indices. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124031
Jin SJ, Lee T, Moon HE, Park ES, Lee SH, Roh YI, Seo DM, Kim W-J, Hwang H. Classification Model for Epileptic Seizure Using Simple Postictal Laboratory Indices. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124031
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Sun Jin, Taesic Lee, Hyun Eui Moon, Eun Seok Park, Sue Hyun Lee, Young Il Roh, Dong Min Seo, Won-Joo Kim, and Heewon Hwang. 2023. "Classification Model for Epileptic Seizure Using Simple Postictal Laboratory Indices" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124031
APA StyleJin, S. J., Lee, T., Moon, H. E., Park, E. S., Lee, S. H., Roh, Y. I., Seo, D. M., Kim, W.-J., & Hwang, H. (2023). Classification Model for Epileptic Seizure Using Simple Postictal Laboratory Indices. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124031






