Age-Related Variation of Pulpal Oxygen Saturation in Healthy Primary and Permanent Teeth in Children: A Clinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
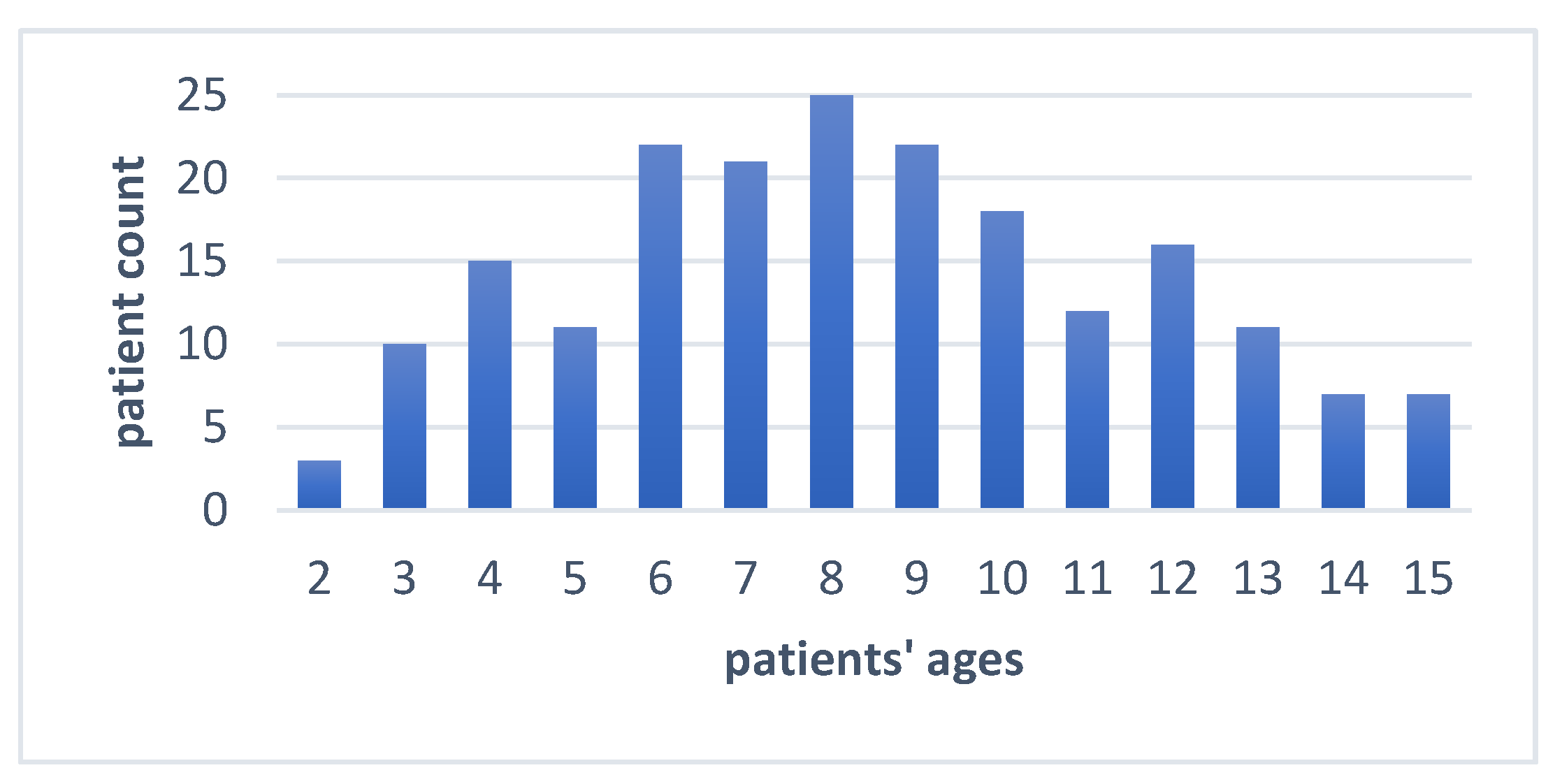
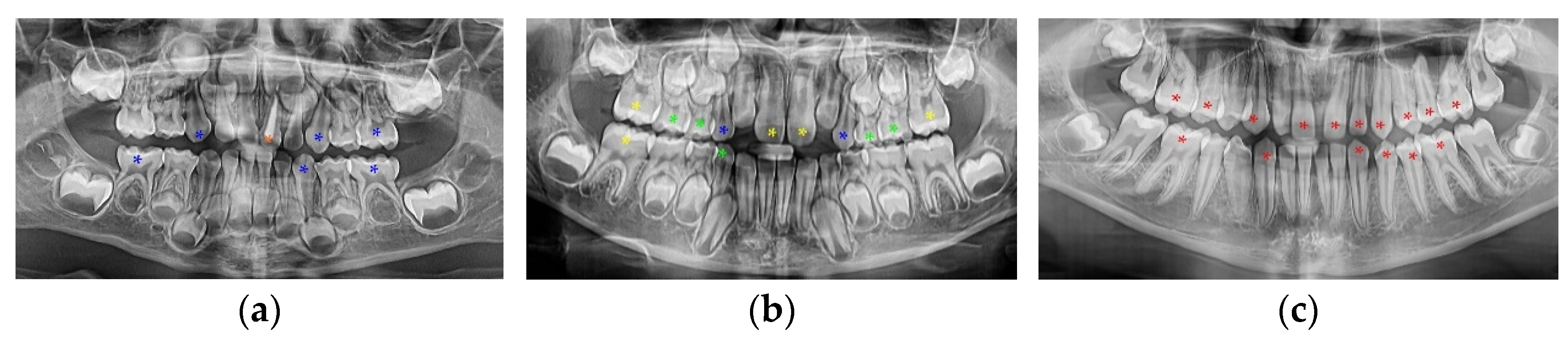
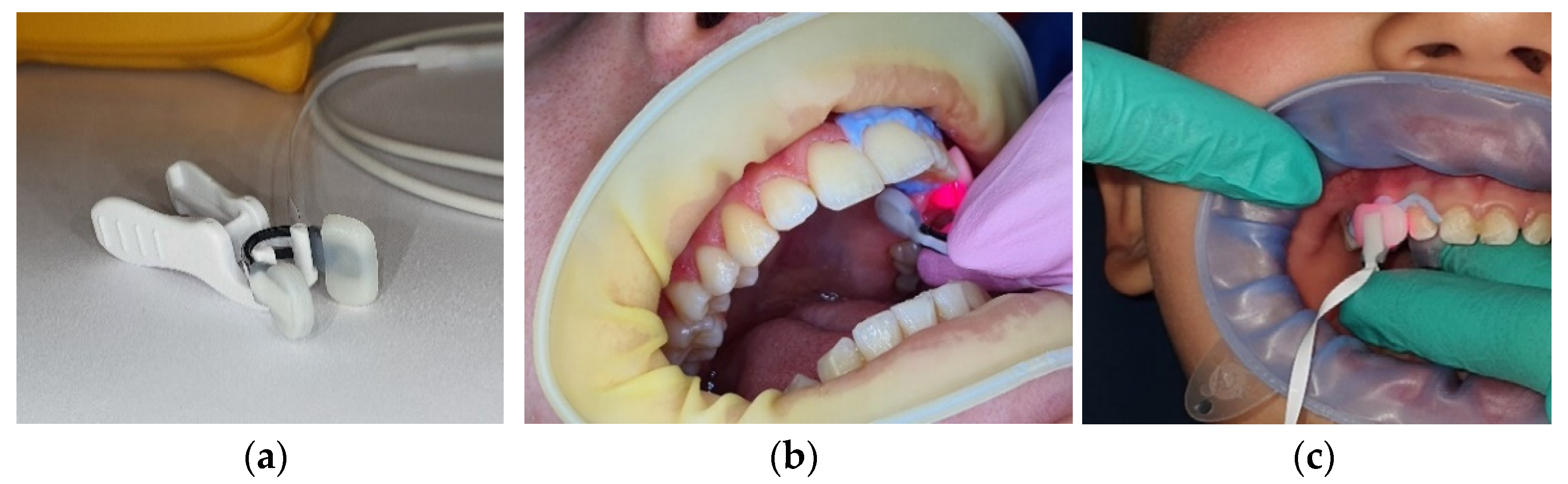
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gopikrishna, V.; Tinagupta, K.; Kandaswamy, D. Evaluation of Efficacy of a New Custom-Made Pulse Oximeter Dental Probe in Comparison With the Electrical and Thermal Tests for Assessing Pulp Vitality. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almudever-Garcia, A.; Forner, L.; Sanz, J.L.; Llena, C.; Rodríguez-Lozano, F.J.; Guerrero-Gironés, J.; Melo, M. Pulse Oximetry as a Diagnostic Tool to Determine Pulp Vitality: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, P.; Miguens, S.A.Q.; Solda, C.; Sganzerla, J.T.; Reichert, L.A.; Estrela, C.; Barletta, F.B. Reference Values for Pulp Oxygen Saturation as a Diagnostic Tool in Endodontics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2020, 45, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadique, M.; Ravi, S.V.; Thomas, K.; Dhanapal, P.; Simon, E.P.; Shaheen, M. Evaluation of a Pulse Oximeter to Assess Pulp Vitality. J. Int. Oral Heal. 2014, 6, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bargrizan, M.; Ashari, M.A.; Ahmadi, M.; Ramezani, J. The Use of Pulse Oximetry in Evaluation of Pulp Vitality in Immature Permanent Teeth. Dent. Traumatol. 2016, 32, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.D.; Maria, R. Pulse Oximetry: A New Tool in Pulpal Vitality Testing. People’s J. Sci. Res. 2013, 6, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Grabliauskienė, Ž.; Zamaliauskienė, R.; Lodienė, G. Pulp Vitality Testing with a Developed Universal Pulse Oximeter Probe Holder. Medicina 2021, 57, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, K.; Palanivelu, A.; Sandhya, R. Diagnostic Accuracy of Dental Pulse Oximeter with Customized Sensor Holder, Thermal Test and Electric Pulp Test for the Evaluation of Pulp Vitality: An in Vivo Study. Braz. Dent. Sci. 2020, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.S.; Mishra, S.; Banda, N.R.; Vaswani, S. In Vivo Evaluation of Customized Pulse Oximeter and Sensitivity Pulp Tests for Assessment of Pulp Vitality. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2019, 43, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, S.; Thomas, A.; Singh, N. A Comparative Study of Pulse Oximetry with the Conventional Pulp Testing Methods to Assess Vitality in Immature and Mature Permanent Maxillary Incisors. J. Heal. Res. 2014, 1, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, P.F.; Flores, M.T.; O’Connell, A.C.; Abbott, P.V.; Tsilingaridis, G.; Fouad, A.F.; Cohenca, N.; Lauridsen, E.; Bourguignon, C.; Hicks, L.; et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology Guidelines for the Management of Traumatic Dental Injuries: 3. Injuries in the Primary Dentition. Dent. Traumatol. 2020, 36, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, J.A.; Seale, N.S.; Vargas, K.; Marghalani, A.A.; Al Shamali, S.; Graham, L. Primary Tooth Vital Pulp Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pediatr. Dent. 2017, 39, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAPD. Pulp Therapy for Primary and Immature Permanent Teeth. In The Reference Manual of Pediatric Dentistry; AAPD: Chicago, IL, USA, 2021; p. 399. [Google Scholar]
- Igna, A.; Igna, C.; Miron, M.I.; Schuszler, L.; Dascălu, R.; Moldovan, M.; Voicu, A.A.; Todea, C.D.; Boariu, M.; Mârțu, M.A.; et al. Assessment of Pulpal Status in Primary Teeth Following Direct Pulp Capping in an Experimental Canine Model. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briseño-Marroquín, B.; López-Murillo, H.; Kuchen, R.; Casasa-Araujo, A.; Wolf, T.G. Pulp Sensitivity Changes during Orthodontic Treatment at Different Time Periods: A Prospective Study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 3207–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helena, D.; Henriques, N.; Alves, A.M.H.; Pottmaier, L.F.; Da Fonseca, L.; Garcia, R.; Bortoluzzi, E.A.; Teixeira, C.S. Evaluation of the Pulp Oxygen Saturation Reading after Tooth Bleaching: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Dent. 2022, 1598145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fátima Carvalho, S.S.; Thomaz, E.B.A.F.; Costa, C.P.S. Healthy Dental Pulp Oxygen Saturation Rates in Subjects with Homozygous Sickle Cell Anemia: A Cross-Sectional Study Nested in a Cohort. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1997–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, S.H.H.; Setzer, F.C.; Gondim-Junior, E.; Fregnani, E.R.; Moraes, C.J.P.; Pessoa, O.F.; Gavini, G.; Caldeira, C.L. Late Effects of Head and Neck Radiotherapy on Pulp Vitality Assessed by Pulse Oximetry. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, K.; Teja, K.V.; Jose, J. Assessment of Actual Pulp Status Using Pulp Sensibility Tests and Pulp Vascularity Tests: A Systematic Review. Endodontology 2022, 34, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Sharma, D.S.; Bhusari, C. Assessing Inflammatory Status of Pulp in Irreversible Pulpitis Cases with Pulse Oximeter and Dental Hemogram. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2019, 43, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calil, E.; Caldeira, C.L.; Gavini, G.; Lemos, E.M. Determination of Pulp Vitality in Vivo with Pulse Oximetry. Int. Endod. J. 2008, 41, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosturkov, D.; Uzunov, T. Pulse Oximetry and Electric Pulp Test in Intact Teeth and Teeth with Hyperaemia Pulpae. Acta Med. Bulg. 2017, 44, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kakanur, M.; Prasad, G.; Arun, R.; Chakrapani, N.; Raju, S. Evaluation of Pulp Vitality in Primary Teeth Using Invasive and Noninvasive Techniques. RGUHS J. Dent. Sci. 2012, 4, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Pozzobon, M.H.; de Sousa Vieira, R.; Alves, A.M.H.; Reyes-Carmona, J.; Teixeira, C.S.; de Souza, B.D.M.; Felippe, W.T. Assessment of Pulp Blood Flow in Primary and Permanent Teeth Using Pulse Oximetry. Dent. Traumatol. 2011, 27, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Madan, M.; Shahi, P.; Sood, P.; Shahi, N. Comparative Study of Pulp Vitality in Primary and Young Permanent Molars in Human Children with Pulse Oximeter and Electric Pulp Tester. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2015, 8, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayilmaz, H.; Kirzioǧlu, Z. Evaluation of Pulpal Blood Flow Changes in Primary Molars with Physiological Root Resorption by Laser Doppler Flowmetry and Pulse Oximetry. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2011, 36, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, J.; Day, P.; Duggal, M.; Morgan, C.; Rodd, H. Pulpal Status of Human Primary Teeth with Physiological Root Resorption. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2009, 19, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, H.; Ikawa, M.; Mayanagi, H. Age-Related Changes of Pulpal Blood Flow in Primary Teeth Measured by Laser Doppler Blood Flowmetry. Pediatr. Dent. J. 2007, 17, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Waterhouse, P.; Whitworth, J.; Camp, J.; Fuks, A. Pediatric Endodontics. In Cohen’s Pathways of the Pulp; Hargreaves, K.M., Cohen, S., Berman, L.H., Eds.; Mosby Elsevier: St. Loius, MI, USA, 2011; pp. 809–818. [Google Scholar]
- Molaasadolah, F.; Zargar, N.; Bargrizan, M.; Akbari, F.; Khozestani, P.K.; Sabour, S.; Bakhshi, M. Comparison of Pulse Oximeter, Cold Test, and Electric Pulp Test for Assessment of Pulp Vitality in Permanent Immature Teeth. Folia Med. 2022, 64, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, T.; Lima, R.; Luize, S.; Kelly, T.; Silva, L.; Jo, E.; Lima, T.F.R.; dos Santos, S.L.; da Silva Fidalgo, T.K.; Silva, E.J.N.L. Vitality Tests for Pulp Diagnosis of Traumatized Teeth: A Systematic Review. J. Endod. 2021, 45, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, C.L.; Barletta, F.B.; Ilha, M.C.; Abrão, C.V.; Gavini, G. Pulse Oximetry: A Useful Test for Evaluating Pulp Vitality in Traumatized Teeth. Dent. Traumatol. 2016, 32, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainkar, A.; Kim, S.G. Diagnostic Accuracy of 5 Dental Pulp Tests: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, J.P.F.; Barletta, F.B.; Giovanella, L.B.; Grazziotin-Soares, R.; Tovo, M.F.; Felippe, W.T.; Estrela, C. Oxygen Saturation in Dental Pulp of Permanent Teeth: Difference between Children/Adolescents and Adults. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrela, C.R.A.C.; Serpa, G.C.; Alencar, A.H.G.; Bruno, K.F.; Barletta, F.B.; Felippe, W.T.; Estrela, C.R.A.C.; Souza, J.B. Oxygen Saturation in the Dental Pulp of Maxillary Premolars in Different Age Groups—Part 1. Braz. Dent. J. 2017, 28, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Siddheswaran, V.; Adyanthaya, R. Pulse Oximetry: A Diagnostic Instrument in Pulpal Vitality Testing—An in Vivo Study. World J. Dent. 2011, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, C.; Oliveira, K.S.A.; Alencar, A.H.G.; Barletta, F.B.; Estrela, C.R.A.; Felippe, W.T. Oxygen Saturation in the Dental Pulp of Maxillaryandmandibularmolars-Part 2. Braz. Dent. J. 2017, 28, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusha, B.; Madhusudhana, K.; Chinni, S.K.; Paramesh, Y. Assessment of Pulp Oxygen Saturation Levels by Pulse Oximetry for Pulpal Diseases -a Diagnostic Study. J. Clin. Diagnostic Res. 2017, 11, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, K.; Ajitha, P.; Sandhya, R.; Subbaiyan, H.; Jose, J. Efficiency of New Custom-Made Pulse Oximeter Sensor Holder in Assessment of Actual Pulp Status. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 3333–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallom, M.; Prentice, D.; Sona, C.; Arroyo, C.; Mazuski, J. Comparison of Nasal and Forehead Oximetry Accuracy and Pressure Injury in Critically Ill Patients. Hear. Lung 2018, 47, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastmalchi, N.; Jafarzadeh, H.; Moradi, S. Comparison of the Efficacy of a Custom-Made Pulse Oximeter Probe with Digital Electric Pulp Tester, Cold Spray, and Rubber Cup for Assessing Pulp Vitality. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A.; de Alencar, A.H.G.; Sestari, L.E.; Barbosa, H.A.; de Siqueira, P.C.; Decurcio, D.A.; Barletta, F.B.; Estrela, C. Interference of Coronal Enamel and Dentin Thickness and Ambient Light on Pulse Oximetry Interpretation. Braz. Oral Res. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosturkov, D.; Uzunov, T.U.P. Influence of the Gingival Tissues on the Measured Saturation Level of the Dental Pulp Blood Flow. Bulg. J. Chem. Educ. 2018, 27, 454–459. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, D.H.N.; Alves, A.M.H.; Kuntze, M.M.; Garcia, L.; Garcia, L.D.F.R.; Bortoluzzi, E.A.; Teixeira, C.D.S. Effect of Dental Tissue Thickness on the Measurement of Oxygen Saturation by Two Different Pulse Oximeters. Braz. Dent. J. 2022, 33, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banthitkhunanon, P.; Chintakanan, S.; Wanachantararak, S.; Vongsavan, N.; Matthews, B. Effects of Enamel and Dentine Thickness on Laser Doppler Blood-Flow Signals Recorded from the Underlying Pulp Cavity in Human Teeth in Vitro. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop-Ciutrila, I.S.; Ghinea, R.; Colosi, H.A.; Dudea, D. Dentin Translucency and Color Evaluation in Human Incisors, Canines, and Molars. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

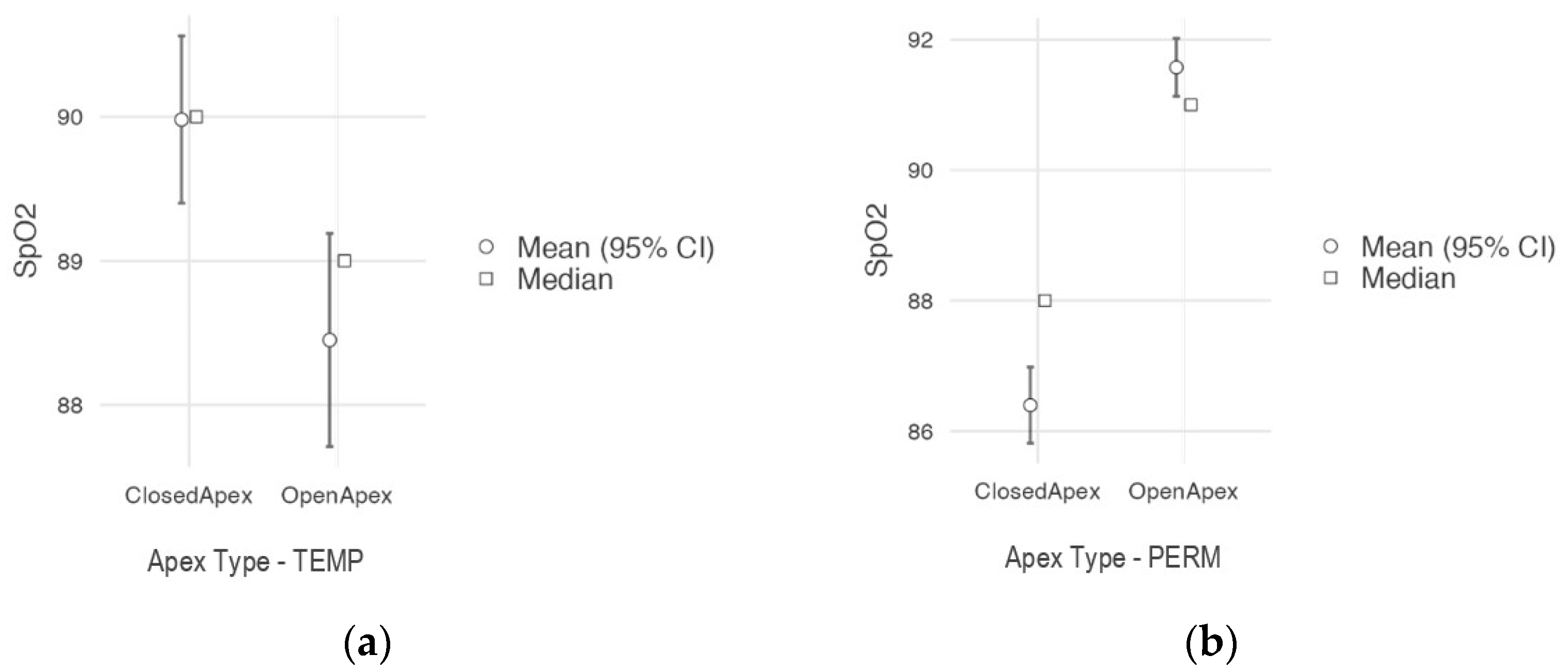
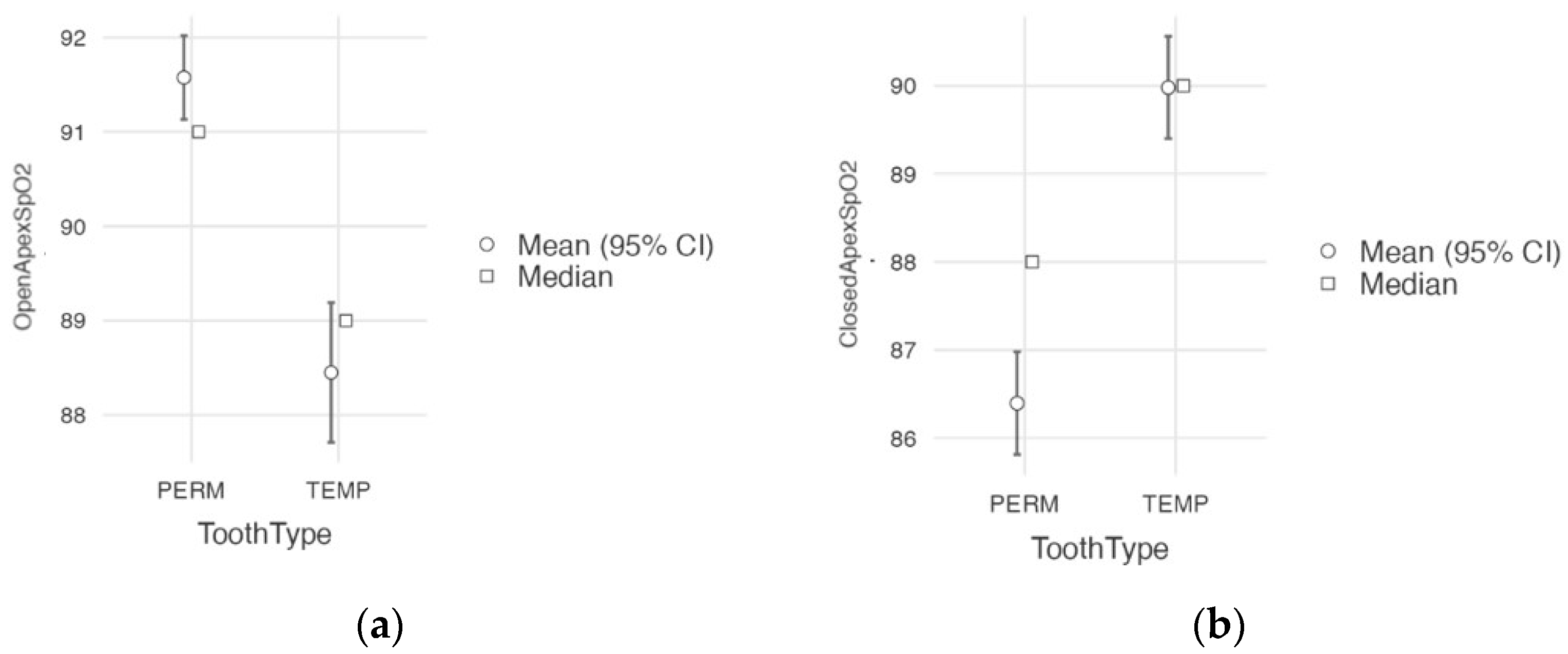
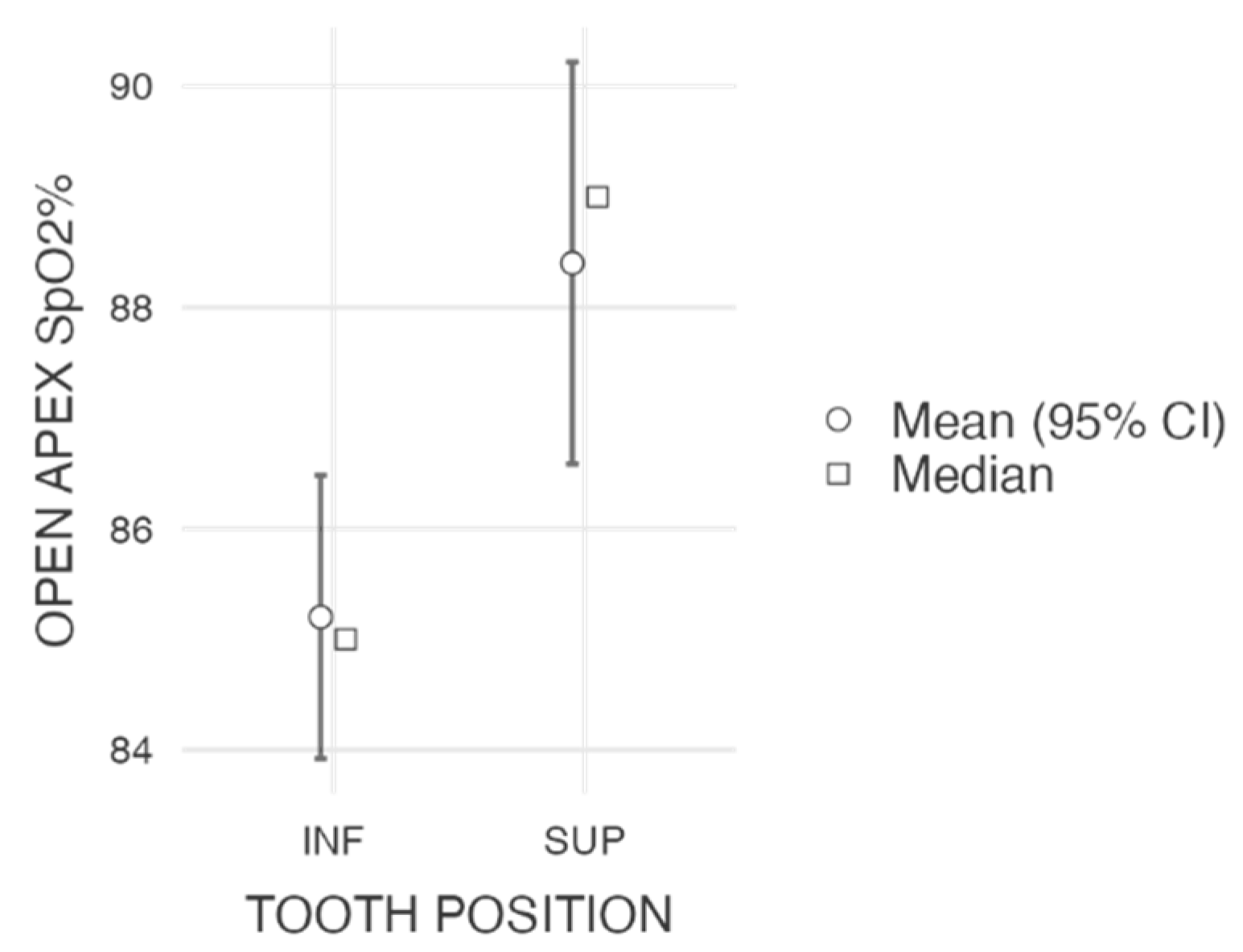
| Apex Type | Tooth Type 1 | N | Mean SpO2 (%) | Median SpO2 (%) | SD | Min. SpO2 (%) | Max. SpO2 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open apex | TEMP | I | 50 | 86.6 | 87.0 | 7.5 | 72 | 97 |
| C | 50 | 86.8 | 87.0 | 4.3 | 80 | 97 | ||
| M1 | 50 | 88.8 | 88.5 | 3.8 | 82 | 97 | ||
| M2 | 50 | 91.6 | 91.0 | 4.2 | 72 | 97 | ||
| PERM | I | 50 | 92.3 | 92.0 | 2.5 | 88 | 97 | |
| C | 50 | 88.0 | 87.0 | 1.5 | 87 | 91 | ||
| PM | 50 | 93.3 | 94.0 | 2.7 | 89 | 97 | ||
| M | 50 | 92.7 | 93.0 | 2.9 | 72 | 97 | ||
| Closed apex | TEMP | I | 50 | 91.8 | 91.0 | 1.7 | 89 | 95 |
| C | 50 | 87.7 | 88.0 | 4.1 | 78 | 97 | ||
| M1 | 50 | 89.2 | 90.0 | 4.8 | 76 | 98 | ||
| M2 | 50 | 91.2 | 91.0 | 4.2 | 72 | 97 | ||
| PERM | I | 50 | 87.1 | 88.0 | 3.3 | 78 | 93 | |
| C | 50 | 83.0 | 82.0 | 4.0 | 77 | 90 | ||
| PM | 50 | 89.3 | 90.0 | 2.7 | 81 | 93 | ||
| M | 50 | 86.1 | 87.0 | 4.2 | 78 | 94 | ||
| Apex Type | Tooth type 1–Pairwise Comparisons | p |
|---|---|---|
| Open | I–C | 0.995 |
| I–M | 0.092 | |
| C–M | <0.001 | |
| M1–M2 | 0.986 | |
| Closed | I–C | <0.001 |
| I–M | 0.121 | |
| C–M | <0.001 | |
| M1–M2 | 0.516 |
| Apex Type | Tooth Type 1–Pairwise Comparisons | p |
|---|---|---|
| Open | I–C | <0.001 |
| I–PM | 0 .005 | |
| I–M | 0.955 | |
| C–PM | <0.001 | |
| C–M | <0.001 | |
| PM–M | 0.002 | |
| Closed | I–C | <0.001 |
| I–PM | 0.910 | |
| I–M | 0.895 | |
| C–PM | <0.001 | |
| C–M | <0.001 | |
| PM–M | 0.999 |
| Apex Type | Tooth Type 1 and Position 2–Pairwise Comparisons | p |
|---|---|---|
| Open | C sup.–C inf. | 0.010 |
| M1 sup.–M1 inf. | 0.106 | |
| M2 sup.–M2 inf. | 0.984 | |
| Closed | C sup.–C inf. | 0.155 |
| M1 sup.–M1 inf. | 0.066 | |
| M2 sup.–M2 inf. | 0.096 |
| Apex Type | Tooth Type1 and Position 2–Pairwise Comparisons | p |
|---|---|---|
| Open | C sup.–C inf. | 0.937 |
| PM sup.–PM inf. | 0.550 | |
| M sup.–M inf. | 0.550 | |
| Closed | C sup.–C inf. | 0.206 |
| PM sup.–PM inf. | 0.698 | |
| M sup.–M inf. | 0.513 |
| Apex Type | Tooth Type 1 | Tooth Position 2 | N | Mean SpO2% | Median SpO2% | SD | Min. SpO2% | Max. SpO2% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open apex | TEMP | C | sup. | 25 | 88.4 | 89.0 | 4.64 | 80 | 97 |
| C | inf. | 25 | 85.2 | 85.0 | 3.27 | 80 | 92 | ||
| M | sup. | 25 | 89.8 | 90.0 | 3.82 | 83 | 97 | ||
| M | inf. | 25 | 90.5 | 90.0 | 3.77 | 82 | 97 | ||
| PERM | C | sup. | 25 | 87.8 | 89.0 | 2.58 | 82 | 92 | |
| C | inf. | 25 | 88.0 | 87.0 | 1.54 | 87 | 91 | ||
| PM | sup. | 25 | 93.0 | 94.0 | 2.88 | 89 | 97 | ||
| PM | inf. | 25 | 93.5 | 94.0 | 2.47 | 89 | 97 | ||
| M | sup. | 25 | 93.0 | 93.0 | 2.89 | 87 | 97 | ||
| M | inf. | 25 | 92.4 | 91 | 2.93 | 87 | 97 | ||
| Clpsed apex | TEMP | C | sup. | 25 | 86.9 | 86.0 | 3.43 | 81 | 94 |
| C | inf. | 25 | 88.6 | 88.0 | 4.62 | 78 | 97 | ||
| M | sup. | 25 | 90.1 | 90.0 | 5.15 | 76 | 98 | ||
| M | inf. | 25 | 90.3 | 90.0 | 4.03 | 72 | 96 | ||
| PERM | C | sup. | 25 | 84.4 | 85.0 | 4.09 | 75 | 90 | |
| C | inf. | 25 | 83.0 | 82.0 | 4.05 | 77 | 90 | ||
| PM | sup. | 25 | 89.2 | 89.0 | 2.66 | 81 | 93 | ||
| PM | inf. | 25 | 89.3 | 90.0 | 2.78 | 81 | 93 | ||
| M | sup. | 25 | 85.7 | 87.0 | 4.84 | 78 | 94 | ||
| M | inf. | 25 | 86.6 | 87.0 | 3.44 | 80 | 92 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Igna, A.; Rusu, D.; Ogodescu, E.; Dinu, Ș.; Boariu, M.; Voicu, A.; Stratul, Ș.-I. Age-Related Variation of Pulpal Oxygen Saturation in Healthy Primary and Permanent Teeth in Children: A Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010170
Igna A, Rusu D, Ogodescu E, Dinu Ș, Boariu M, Voicu A, Stratul Ș-I. Age-Related Variation of Pulpal Oxygen Saturation in Healthy Primary and Permanent Teeth in Children: A Clinical Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010170
Chicago/Turabian StyleIgna, Andreea, Darian Rusu, Emilia Ogodescu, Ștefania Dinu, Marius Boariu, Adrian Voicu, and Ștefan-Ioan Stratul. 2023. "Age-Related Variation of Pulpal Oxygen Saturation in Healthy Primary and Permanent Teeth in Children: A Clinical Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010170
APA StyleIgna, A., Rusu, D., Ogodescu, E., Dinu, Ș., Boariu, M., Voicu, A., & Stratul, Ș.-I. (2023). Age-Related Variation of Pulpal Oxygen Saturation in Healthy Primary and Permanent Teeth in Children: A Clinical Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010170








