Pregnant and Postpartum Women Requiring Intensive Care Treatment for COVID-19—First Data from the CRONOS-Registry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
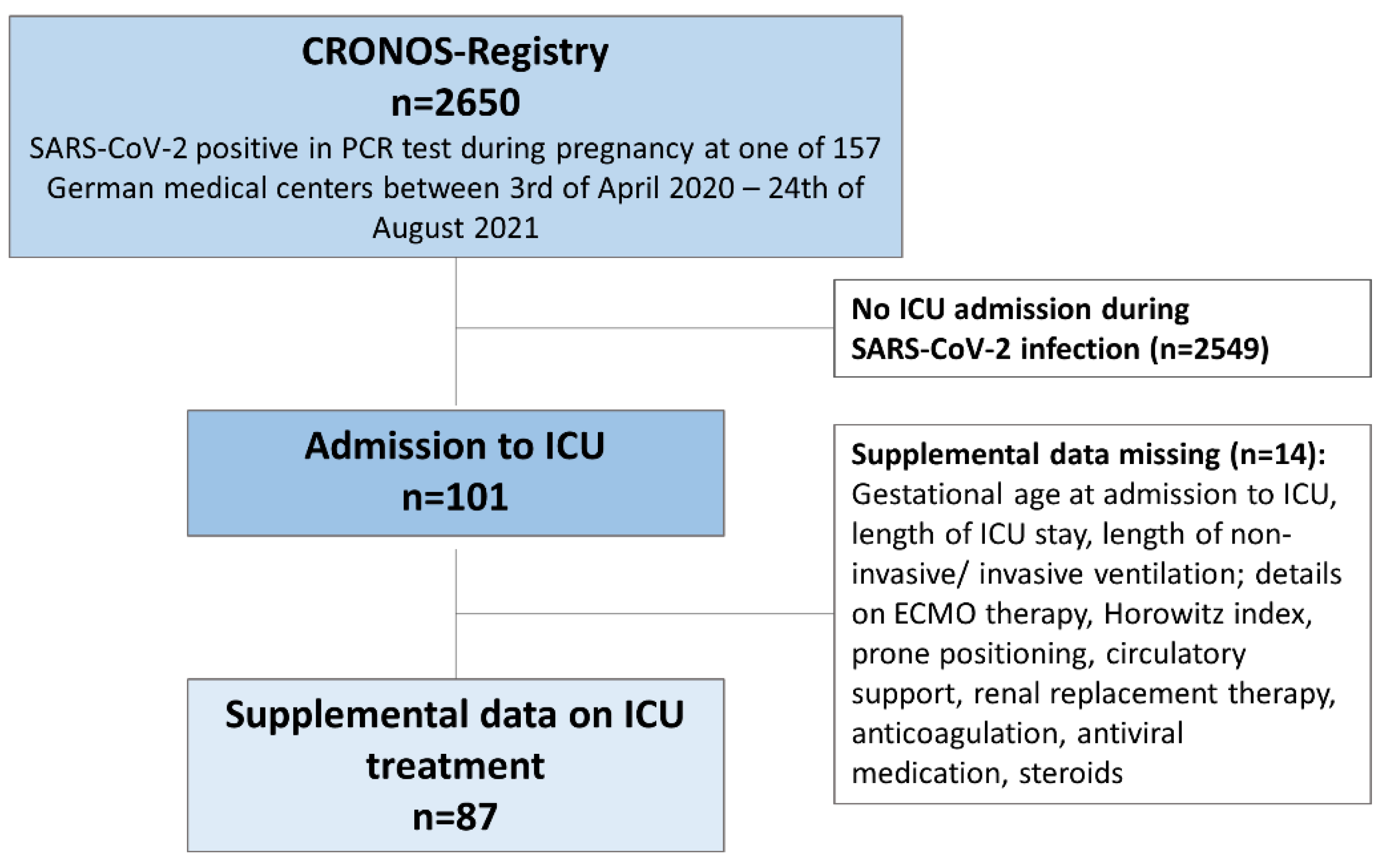
2.1. CRONOS-Registry
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Additional Data Collection for ICU Population
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
3.2. Maternal Characteristics
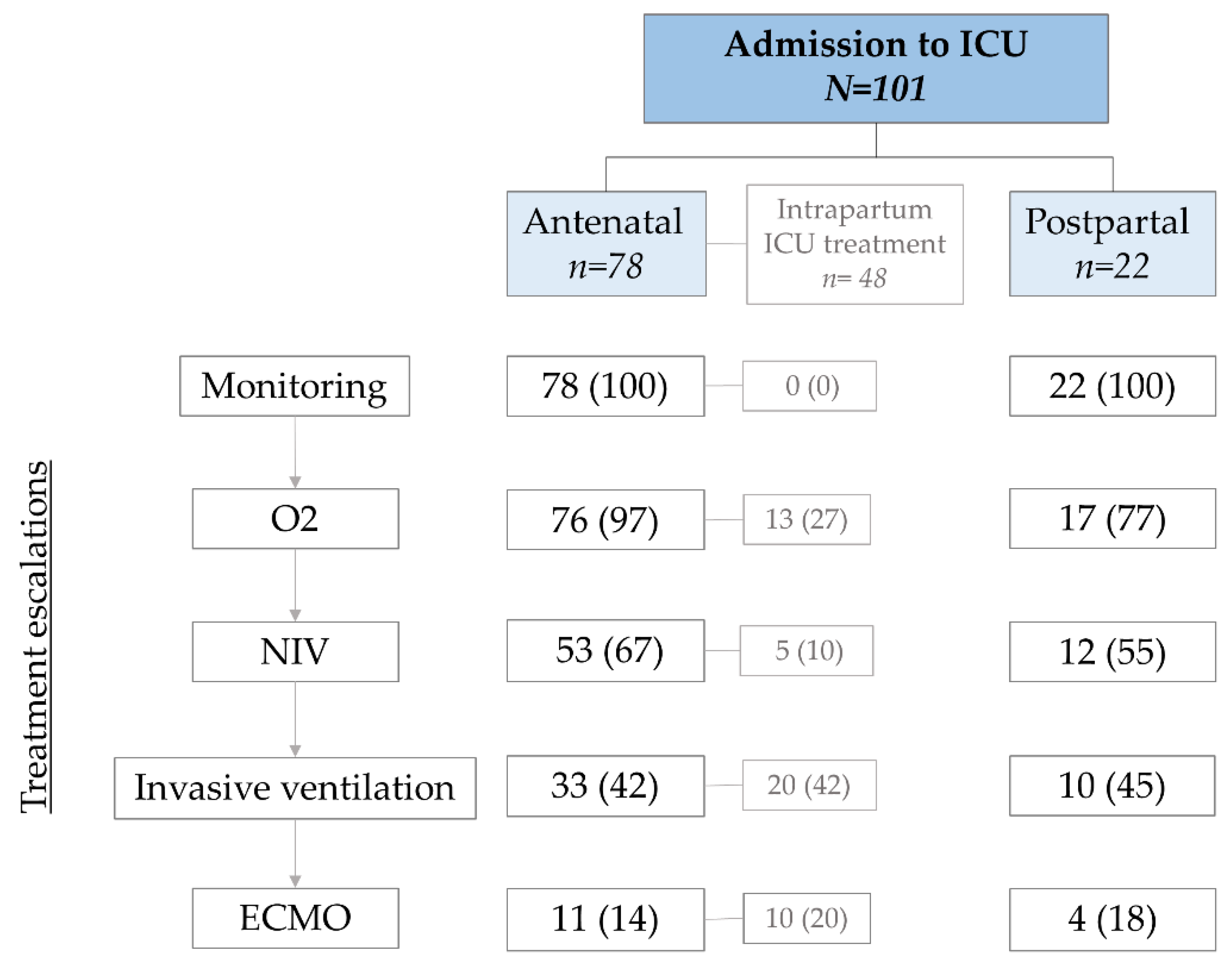
3.3. ICU Treatment—Stage of Pregnancy
3.4. ICU Treatment—Respiratory Treatment
3.5. Obstetric Outcome
3.6. Neonatal Outcome
3.7. Follow-Up of Mother–Infant Dyads
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- RKI-Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2-COVID-19: Fallzahlen in Deutschland und Weltweit. Available online: https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/InfAZ/N/Neuartiges_Coronavirus/Fallzahlen.html (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Intensivbetten: Die Kapazitäten Schwinden. Available online: https://www.aerzteblatt.de/archiv/216577/Intensivbetten-Die-Kapazitaeten-schwinden (accessed on 17 April 2021).
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.-L.; Zhao, S.-J.; Kwak-Kim, J.; Mor, G.; Liao, A.-H. Why are pregnant women susceptible to COVID-19? An immunological viewpoint. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2020, 139, 103122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behzad, S.; Aghaghazvini, L.; Radmard, A.R.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19: Radiologic and clinical overview. Clin. Imaging 2020, 66, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wastnedge, E.A.N.; Reynolds, R.M.; Van Boeckel, S.R.; Stock, S.J.; Denison, F.C.; Maybin, J.A.; Critchley, H.O.D. Pregnancy and COVID-19. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoMauro, A.; Aliverti, A. Respiratory physiology of pregnancy. Breathe 2015, 11, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Mascio, D.; Khalil, A.; Saccone, G.; Rizzo, G.; Buca, D.; Liberati, M.; Vecchiet, J.; Nappi, L.; Scambia, G.; Berghella, V.; et al. Outcome of coronavirus spectrum infections (SARS, MERS, COVID-19) during pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2020, 2, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecks, U.; Kuschel, B.; Mense, L.; Oppelt, P.; Rüdiger, M. Pregnancy and SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Germany—The CRONOS Registry. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Online 2020, 117, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castor—Top-Rated eClinical Data Management Platform. Available online: https://www.castoredc.com/ (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Marshall, J.C.; Murthy, S.; Diaz, J.; Adhikari, N.K.; Angus, D.C.; Arabi, Y.M.; Baillie, K.; Bauer, M.; Berry, S.; Blackwood, B.; et al. A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e192–e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allotey, J.; Stallings, E.; Bonet, M.; Yap, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Kew, T.; Debenham, L.; Llavall, A.C.; Dixit, A.; Zhou, D.; et al. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: Living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 370, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makvandi, S.; Mahdavian, M.; Kazemi-Nia, G.; Vahedian-Azimi, A.; Guest, P.C.; Karimi, L.; Sahebkar, A. The 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1321, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, R.; Alrahmani, L.; Monzer, N.; Debiane, L.G.; Berbari, E.; Fares, J.; Fitzpatrick, F.; Murad, M.H. Clinical Presentation and Outcomes of Pregnant Women With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 72, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafeey, F.; Magdi, R.; Hindi, N.; Elshebiny, M.; Farrag, N.; Mahdy, S.; Sabbour, M.; Gebril, S.; Nasser, M.; Kamel, M.; et al. A systematic scoping review of COVID-19 during pregnancy and childbirth. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2020, 150, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaigham, M.; Andersson, O. Maternal and perinatal outcomes with COVID-19: A systematic review of 108 pregnancies. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zambrano, L.D.; Ellington, S.; Strid, P.; Galang, R.R.; Oduyebo, T.; Tong, V.T.; Woodworth, K.R.; Nahabedian, J.F.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Gilboa, S.M.; et al. Update: Characteristics of Symptomatic Women of Reproductive Age with Laboratory-Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Pregnancy Status—United States, January 22–October 3, 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jering, K.S.; Claggett, B.L.; Cunningham, J.W.; Rosenthal, N.; Vardeny, O.; Greene, M.F.; Solomon, S.D. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Hospitalized Women Giving Birth with and without COVID-19. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 181, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullins, E.; Hudak, M.L.; Banerjee, J.; Getzlaff, T.; Townson, J.; Barnette, K.; Playle, R.; Perry, A.; Bourne, T.; Lees, C.C.; et al. Pregnancy and neonatal outcomes of COVID-19: Coreporting of common outcomes from PAN-COVID and AAP SONPM registries. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 57, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easter, S.R.; Gupta, S.; Brenner, S.K.; Leaf, D.E. Outcomes of Critically Ill Pregnant Women with COVID-19 in the United States. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tug, N.; Yassa, M.; Köle, E.; Sakin, Ö.; Köle, M.Ç.; Karateke, A.; Yiyit, N.; Yavuz, E.; Birol, P.; Budak, D.; et al. Pregnancy worsens the morbidity of COVID-19 and this effect becomes more prominent as pregnancy advances. Turk. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 17, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soheili, M.; Moradi, G.; Baradaran, H.R.; Soheili, M.; Mokhtari, M.M.; Moradi, Y. Clinical manifestation and maternal complications and neonatal outcomes in pregnant women with COVID-19: A comprehensive evidence synthesis and meta-analysis. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| N = 101 | |
|---|---|
| Maternal age at SARS-CoV-2 infection (years) | 33 (30–36) |
| <20 years | 2 (2) |
| 20–34 years | 69 (68) |
| ≥35 years | 30 (30) |
| Multiple pregnancy | 4 (4) |
| Gestational age | 33 (28–35) |
| Trimester enrolled | |
| 1st trimester | 1 (1) |
| 2nd trimester | 26 (26) |
| 3rd trimester | 74 (73) |
| Ethnic origin | |
| Middle East | 34 (34) |
| Northern Europe | 30 (30) |
| Africa (others) | 11 (11) |
| Eastern Europe | 9 (9) |
| South East Asia | 8 (8) |
| Southern Europe | 2 (2) |
| Northern Africa | 1 (1) |
| Open/Unknown | 6 (6) |
| Australia, New Zealand | 0 (0) |
| North America | 0 (0) |
| Baseline data | |
| Body height (cm) | 164 (160–166) |
| Body weight before pregnancy (kg) | 77 (65–80) |
| Body weight at inclusion (kg) | 85 (72–98) |
| BMI before pregnancy (kg/m2) | 31.2 (26.3–33.0) |
| Underweight (<18.5) | 1 (1) |
| Normal weight (18.5–25.0) | 18 (18) |
| Overweight (25.0–30.0) | 27 (27) |
| Obese (>30.0) | 26 (26) |
| Unknown | 29 (29) |
| BMI at inclusion (kg/mg2) | 32 (28.6–34.2) |
| History of smoking before pregnancy | 1 (1) |
| Smoking during pregnancy | 1 (1) |
| Passive smoking | 5 (5) |
| Medical History | N = 101 |
|---|---|
| Pre-existing illnesses a | |
| None | 54 (53) |
| Mild | 27 (27) |
| Moderate | 13 (13) |
| Severe | 2 (2) |
| Pre-existing conditions | |
| Hypertension | 3 (3) |
| Diabetes | |
| Diabetes mellitus Type I | 1 (1) |
| Diabetes mellitus Type II | 3 (3) |
| Gestational Diabetes | 16 (16) |
| Thyroid Disease | |
| Hypothyroidism | 5 (5) |
| Asthma | 4 (4) |
| Hepatitis B | 3 (3) |
| Others | 5 (5) |
| Concomitant Medication | |
| None | 63 (62) |
| Antibiotics | 6 (6) |
| Acetylsalicylic Acid | 3 (3) |
| Other NSAIDs | 2 (2) |
| Immunosuppressive Drugs | 1 (1) |
| Antihypertensive Drugs | 5 (5) |
| Asthma Medication | 1 (1) |
| Antidiabetic Drugs | 10 (10) |
| Heparin derivative | 11 (11) |
| Important Others | 3 (3) |
| COVID-19 | |
| Symptoms b | n = 99 (98) |
| Number of symptoms per patient | 6 (±3) |
| Cough | 79 (78) |
| Dyspnea | 84 (83) |
| Malaise | 77 (76) |
| Fever | 70 (69) |
| Fatigue | 57 (56) |
| Clinical examination—diagnostic Imaging | |
| Imaging | n = 45 (45) |
| Ultrasound examination of the lungs | 5 (11) |
| Thoracic X-ray | 31 (69) |
| Thoracic CAT-Scan | 14 (31) |
| Thoracic MRI | 2 (4) |
| Radiological Findings typical for COVID-19 | 41 (91) |
| Treatment for COVID-19 | All N = 101 a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monitoring n = 6 | O2 n = 30 | NIV n = 22 | ITN n = 28 | ECMO n = 15 | ||
| General Information | ||||||
| Maternal age (years), mean (±SD) | 30 (29–34) | 33 (30–36) | 34 (31–35) | 34 (30–38) | 34 (30–37) | 34 (30–36) |
| Booking BMI (kg/m2) | 31 (29–35) | 29 (24–34) | 27 (23–31) | 29 (25–32) | 29 (26–30) | 31 (26–33) |
| Gestational age at diagnosis (weeks), median (IQR) | 36 (35–36) | 35 (31–37) | 29 (25–33) | 33 (28–35) | 31 (27–36) | 33 (28–35) |
| Gestational age at childbirth (weeks) b, median (IQR) | 37 (36–40) | 38 (36–39) | 39 (37–41) | 33 (29–36) | 33 (31–36) | 36 (33–39) |
| Time between diagnosis and childbirth (weeks) c, median (IQR) | 0 (0–2) | 1 (0–5) | 8 (4–14) b | 0 (0–2) | 1 (0–2) | 3 (0–4) |
| Length of ICU stay (days), median (IQR) | 1 (1–2) | 4 (2–5) | 7 (5–9) | 20 (11–28) | 38 (16–71) | 9 (4–19) |
| Duration of treatment (days), median (IQR) | - | - | 4 (3–6) | 10 (3–16) | 25 (12–41) | - |
| Horowitz Index (mmHg), median (IQR) | - | - | 180 (136–233) | 85 (68–176) | 60 (50–67) | 120 (67–184) |
| Prone position a | - | - | 4 (18) | 13 (57) | 9 (60) | 26 (30) |
| Circulatory support a | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (18) | 16 (70) | 13 (87) | 33 (41) |
| Renal Replacement Therapy a | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (9) | 3 (20) | 5 (6) |
| Thromboembolic event | 1 (17) | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 3 (13) | 6 (40) | 11 (13) |
| Anticoagulation a | ||||||
| Prophylactic | 1 (17) | 13 (62) | 14 (64) | 12 (52) | 6 (40) | 46 (53) |
| Therapeutic | 0 (0) | 7 (33) | 3 (14) | 7 (30) | 3 (20) | 20 (23) |
| Antiviral medication a | 0 (0) | 2 (10) | 3 (14) | 5 (22) | 5 (33) | 15 (17) |
| Steroids a | 0 (0) | 8 (38) | 14 (64) | 17 (74) | 7 (47) | 46 (53) |
| Treatment for COVID-19 | All N = 101 a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monitoring n = 6 | O2 n = 30 | NIV n = 22 | ITN n = 28 | ECMO n = 15 | ||
| Maternal outcome | ||||||
| Recovery | 5 (83) | 20 (67) | 16 (73) | 19 (68) | 6 (40) | 66 (65) |
| Death | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 3 (20) | 5 (5) |
| Unknown/open | 1 (17) | 10 (33) | 6 (27) | 8 (35) | 7 (47) | 32 (32) |
| Neonatal outcome | ||||||
| Preterm labour b | 3 (50) | 8 (33) | 3 (18) | 23 (79) | 11 (73) | 48 (48) |
| Livebirth | 5 (83) | 22 (73) | 15 (68) | 23 (82) | 11 (73) | 77 (76) |
| Stillbirth | 1 (17) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (7) | 3 (20) | 6 (6) |
| Unknown/open | 0 (0) | 8 (27) | 7 (32) | 3 (11) | 1 (7) | 19 (19) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sitter, M.; Pecks, U.; Rüdiger, M.; Friedrich, S.; Fill Malfertheiner, S.; Hein, A.; Königbauer, J.T.; Becke-Jakob, K.; Zöllkau, J.; Ramsauer, B.; et al. Pregnant and Postpartum Women Requiring Intensive Care Treatment for COVID-19—First Data from the CRONOS-Registry. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030701
Sitter M, Pecks U, Rüdiger M, Friedrich S, Fill Malfertheiner S, Hein A, Königbauer JT, Becke-Jakob K, Zöllkau J, Ramsauer B, et al. Pregnant and Postpartum Women Requiring Intensive Care Treatment for COVID-19—First Data from the CRONOS-Registry. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(3):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030701
Chicago/Turabian StyleSitter, Magdalena, Ulrich Pecks, Mario Rüdiger, Sabine Friedrich, Sara Fill Malfertheiner, Alexander Hein, Josefine T. Königbauer, Karin Becke-Jakob, Janine Zöllkau, Babett Ramsauer, and et al. 2022. "Pregnant and Postpartum Women Requiring Intensive Care Treatment for COVID-19—First Data from the CRONOS-Registry" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 3: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030701
APA StyleSitter, M., Pecks, U., Rüdiger, M., Friedrich, S., Fill Malfertheiner, S., Hein, A., Königbauer, J. T., Becke-Jakob, K., Zöllkau, J., Ramsauer, B., Rathberger, K., Pontones, C. A., Kraft, K., Meybohm, P., Härtel, C., Kranke, P., & CRONOS Network. (2022). Pregnant and Postpartum Women Requiring Intensive Care Treatment for COVID-19—First Data from the CRONOS-Registry. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(3), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030701






