Association of Body Mass Index with Long-Term All-Cause Mortality in Patients Who Had Undergone a Vertebroplasty for a Vertebral Compression Fracture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
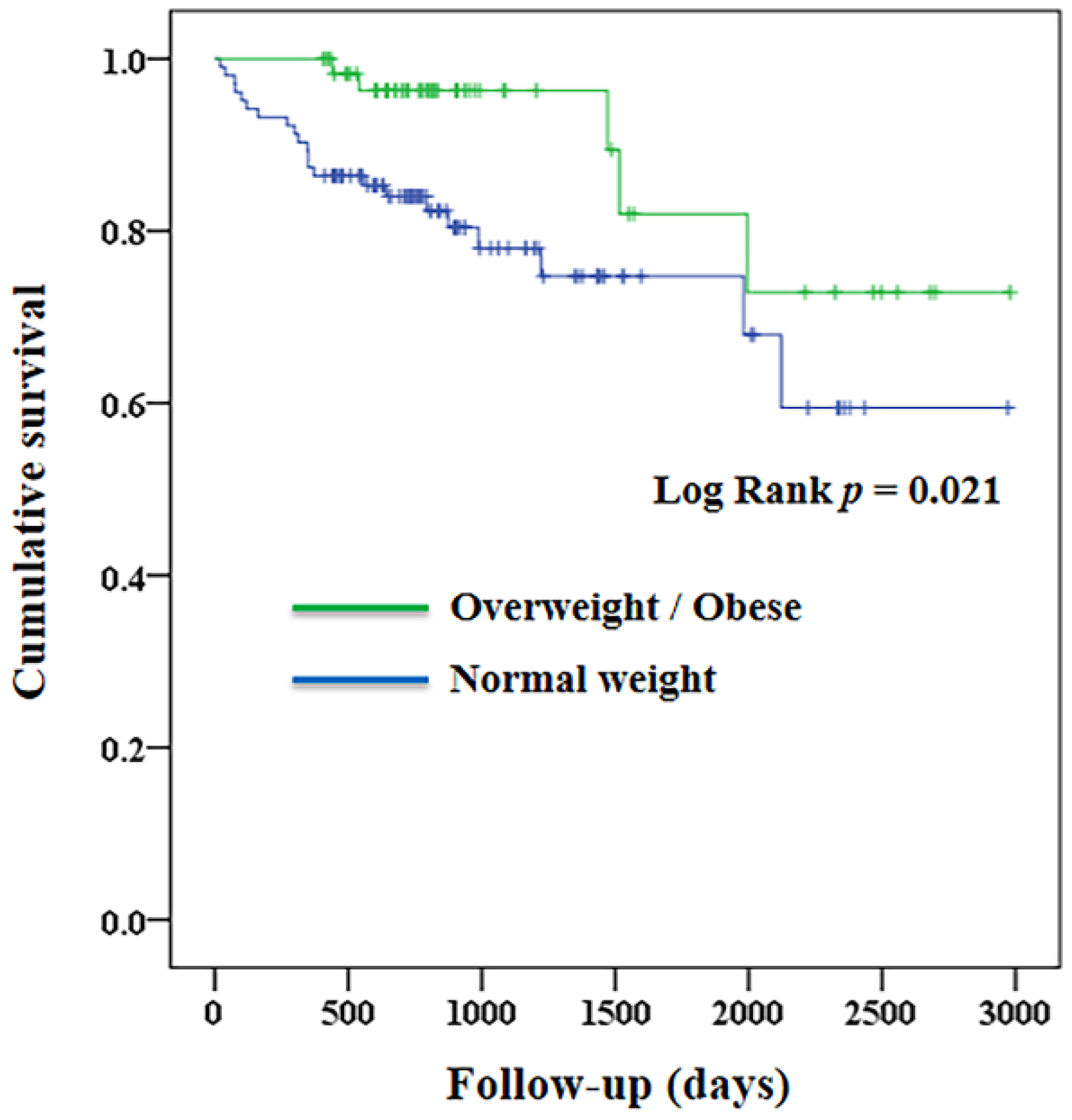
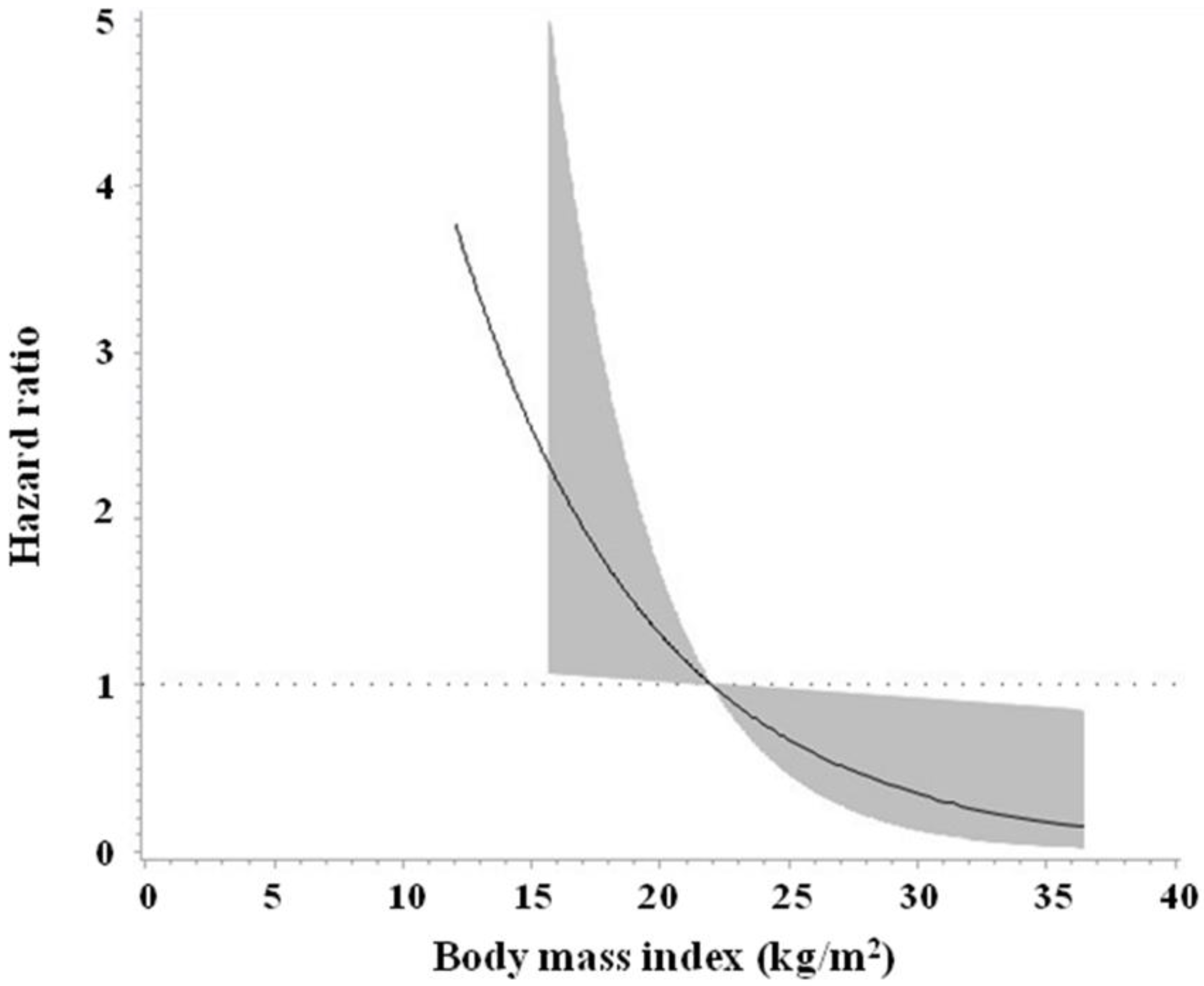
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19·2 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global BMI Mortality Collaboration; Di Angelantonio, E.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Wormser, D.; Gao, P.; Kaptoge, S.; Berrington de Gonzalez, A. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: Individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet 2016, 388, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospective Studies Collaboration. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900,000 adults: Collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet 2009, 373, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Hartge, P.; Cerhan, J.R.; Flint, A.J.; Hannan, L.; MacInnis, R.J.; Thun, M.J. Body-mass index and mortality among 1.46 million white adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Sen, A.; Prasad, M.; Norat, T.; Janszky, I.; Tonstad, S.; Vatten, L.J. BMI and all cause mortality: Systematic review and non-linear dose-response meta-analysis of 230 cohort studies with 3.74 million deaths among 30.3 million participants. BMJ 2016, 353, i2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerrakalva, D.; Mullis, R.; Mant, J. The associations of “fatness”, “fitness”, and physical activity with all-cause mortality in older adults, a systematic review. Obesity 2015, 23, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.A.; Aljied, R.; Allison, D.J.; Anderson, L.N.; Ma, J.; Raina, P. Body mass index and all-cause mortality in older adults, A scoping review of observational studies. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, R.; Osborne, R.H.; Ebeling, P.R.; Wark, J.D.; Mitchell, P.; Wriedt, C.; Murphy, B. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallmes, D.F.; Comstock, B.A.; Heagerty, P.J.; Turner, J.A.; Wilson, D.J.; Diamond, T.H.; Jarvik, J.G. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spinal fractures. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staples, M.P.; Kallmes, D.F.; Comstock, B.A.; Jarvik, J.G.; Osborne, R.H.; Heagerty, P.J.; Buchbinder, R. Effectiveness of vertebroplasty using individual patient data from two randomised placebo controlled trials: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2011, 343, d3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.L.; Jiang, J.M.; Chen, J.T.; Wang, J.X. Risk factors of new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures in osteoporotic patients undergone percutaneous vertebroplasty. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.G.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Choi, W.R.; Lee, S.G.; Kang, C.N. Risk factors for newly developed osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures following treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine J. 2019, 19, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Dos-Santos-Silva, I.; Leon, D.A.; Douglas, I.J.; Smeeth, L. Association of BMI with overall and cause-specific mortality: A population-based cohort study of 3·6 million adults in the UK. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Kit, B.K.; Orpana, H.; Graubard, B.I. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2013, 309, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toy, J.O.; Basques, B.A.; Grauer, J.N. Morbidity, mortality, and readmission after vertebral augmentation: Analysis of 850 patients from the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database. Spine 2014, 39, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Zuckerman, S.L.; Cerpa, M.; Yeom, J.S.; Lehman, R.A., Jr.; Lenke, L.G. Incidence and Risk Factors for Complications and Mortality After Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty in the Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture-Analysis of 1,932 Cases From the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement. Glob. Spine J. 2022, 12, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumholz, H.M.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.T.; Wang, Y.; Radford, M.J. Predicting one-year mortality among elderly survivors of hospitalization for an acute myocardial infarction: Results from the Cooperative Cardiovascular Project. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 38, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Montori, V.M.; Somers, V.K.; Korinek, J.; Thomas, R.J.; Allison, T.G.; Mookadam, F.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Association of bodyweight with total mortality and with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease: A systematic review of cohort studies. Lancet 2006, 368, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenchaiah, S.; Pocock, S.J.; Wang, D.; Finn, P.V.; Zornoff, L.A.; Skali, H.; Solomon, S.D. CHARM Investigators. Body mass index and prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure: Insights from the Candesartan in Heart failure, Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM) program. Circulation 2007, 116, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Lavie, C.J.; Borer, J.S.; Vallakati, A.; Goel, S.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Arbab-Zadeh, A.; Mukherjee, D.; Lazar, J.M. Meta-analysis of the relation of body mass index to all-cause and cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization in patients with chronic heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, K.; Peter, R.S.; Concin, H.; Nagel, G. Associations of pre-diagnostic body mass index with overall and cancer-specific mortality in a large Austrian cohort. Cancer Causes Control 2015, 26, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, S.; Siegert, S.; Koch, M.; Walter, J.; Heits, N.; Hinz, S.; Jacobs, G.; Hampe, J.; Schafmayer, C.; Nöthlings, U. Postdiagnosis body mass index and risk of mortality in colorectal cancer survivors: A prospective study and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 2014, 25, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casas-Vara, A.; Santolaria, F.; Fernández-Bereciartúa, A.; González-Reimers, E.; García-Ochoa, A.; Martínez-Riera, A. The obesity paradox in elderly patients with heart failure: Analysis of nutritional status. Nutrition 2012, 28, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakuyama, A.; Saitoh, M.; Hori, K.; Adachi, Y.; Iwai, K.; Nagayama, M. Associations of body mass index and hospital-acquired disability with post-discharge mortality in older patients with acute heart failure. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Tapia, C.; Diot, T.; Oubaya, N.; Paillaud, E.; Poisson, J.; Gisselbrecht, M.; Morisset, L.; Caillet, P.; Baudin, A.; Pamoukdjian, F.; et al. The obesity paradox for mid- and long-term mortality in older cancer patients: A prospective multicenter cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 113, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- El Moheb, M.; Jia, Z.; Qin, H.; El Hechi, M.W.; Nordestgaard, A.T.; Lee, J.M.; Han, K.; Kaafarani, H.M. The Obesity Paradox in Elderly Patients Undergoing Emergency Surgery, A Nationwide Analysis. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 265, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Sood, A.; Abdollah, F.; Sammon, J.D.; Majumder, K.; Schmid, M.; Peabody, J.O.; Preston, M.A.; Kibel, A.S.; Menon, M.; Trinh, Q.D. The Effect of Body Mass Index on Perioperative Outcomes After Major Surgery, Results from the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS-NSQIP) 2005–2011. World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 2376–2385. [Google Scholar]
- Hennrikus, M.; Hennrikus, W.P.; Lehman, E.; Skolka, M.; Hennrikus, E. The obesity paradox and orthopedic surgery. Medicine 2021, 100, e26936. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.I.; Chen, Y.H.; Chiang, M.H.; Kuo, Y.J.; Chen, Y.P. Inverse relation of body weight with short-term and long-term mortality following hip fracture surgery: A meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 249. [Google Scholar]
- Modig, K.; Erdefelt, A.; Mellner, C.; Cederholm, T.; Talbäck, M.; Hedström, M. “Obesity Paradox” Holds True for Patients with Hip Fracture, A Registry-Based Cohort Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2019, 101, 888–895. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, Y.J.; Choe, W.J.; Chun, Y.I. Risk factors predicting the new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Eur. Spine J. 2012, 21, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buchbinder, R.; Johnston, R.V.; Rischin, K.J.; Homik, J.; Jones, C.A.; Golmohammadi, K.; Kallmes, D.F. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 4, CD006349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eminovic, S.; Vincze, G.; Eglseer, D.; Riedl, R.; Sadoghi, P.; Leithner, A.; Bernhardt, G.A. Malnutrition as predictor of poor outcome after total hip arthroplasty. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raad, M.; Amin, R.; Puvanesarajah, V.; Musharbash, F.; Rao, S.; Best, M.J.; Amanatullah, D.F. The CARDE-B Scoring System Predicts 30-Day Mortality After Revision Total Joint Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2021, 103, 424–431. [Google Scholar]
- Valentijn, T.M.; Galal, W.; Tjeertes, E.K.; Hoeks, S.E.; Verhagen, H.J.; Stolker, R.J. The obesity paradox in the surgical population. Surgeon 2013, 11, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.M.; Al-Jaouni, R.; Pivot, X.; Braulio, V.B.; Rampal, P.; Hebuterne, X. Lack of adaptation to severe malnutrition in elderly patients. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 21, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coin, A.; Sergi, G.; Beninca, P.; Lupoli, L.; Cinti, G.; Ferrara, L.; Benedetti, G.; Tomasi, G.; Pisent, C.; Enzi, G. Bone mineral density and body composition in underweight and normal elderly subjects. Osteoporos. Int. 2000, 11, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Tonial, P.C.; Colussi, E.L.; Alves, A.L.S.; Stürmer, J.; Bettinelli, L.A. Prevalence of sarcopenia in elderly users of the primary health care system. Nutr. Hosp. 2020, 34, 450–455. [Google Scholar]
- Meesters, D.M.; Wijnands, K.A.P.; Brink, P.R.G.; Poeze, M. Malnutrition and Fracture Healing: Are Specific Deficiencies in Amino Acids Important in Nonunion Development? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1597. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, M.H.; Kuo, Y.J.; Chen, Y.P. The Association between Sarcopenia and Postoperative Outcomes among Older Adults with Hip Fracture, a Systematic Review. J. Appl. Gerontol. 2021, 40, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | <25 kg/m2 | ≥25 kg/m2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 103 | 61 | |
| Age, years | 77.2 ± 9.4 | 73.5 ± 8.6 | 0.013 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 30 (29.1) | 12 (19.7) | 0.180 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 21.5 ± 2.5 | 28.2 ± 2.8 | <0.001 |
| <18.5 kg/m2, n (%) | 14 (13.6) | --- | --- |
| Smoking, n (%) | 10 (9.7) | 2 (3.3) | 0.126 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 15 (14.6) | 18 (29.5) | 0.021 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 52 (50.5) | 35 (57.4) | 0.393 |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) | 36 (35.0) | 20 (32.8) | 0.778 |
| Osteoporosis, n (%) | 83 (80.6) | 38 (62.3) | 0.010 |
| Medication for osteoporosis, n (%) a | 68 (66.0) | 36 (59.0) | 0.368 |
| Level of vertebral fracture, n (%) | 0.847 | ||
| T-spine | 44 (42.7) | 27 (44.3) | |
| L-spine | 59 (57.3) | 34 (55.7) |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age, year | 1.052 (1.003, 1.104) | 0.037 | 1.028 (0.979, 1.079) | 0.265 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 1.018 (0.430, 2.409) | 0.968 | 0.297 (0.088, 1.008) | 0.052 |
| BMI (≥25 vs. <25 kg/m2) | 0.336 (0.127, 0.890) | 0.028 | 0.297 (0.101, 0.878) | 0.028 |
| Smoking (yes vs. no) | 2.844 (1.075, 7.524) | 0.035 | 9.012 (2.166, 37.495) | 0.003 |
| Diabetes (yes vs. no) | 1.453 (0.614, 3.439) | 0.396 | 1.518 (0.578, 3.986) | 0.397 |
| Hypertension (yes vs. no) | 2.016 (0.881, 4.617) | 0.097 | 2.216 (0.903, 5.441) | 0.082 |
| CKD (yes vs. no) | 2.601 (1.211, 5.587) | 0.014 | 3.137 (1.375, 7.157) | 0.007 |
| Osteoporosis (yes vs. no) | 2.368 (0.815, 6.879) | 0.113 | 1.326 (0.420, 4.188) | 0.631 |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | ||
| Model 1 | 0.889 (0.808, 0.977) | 0.015 |
| Model 2 | 0.896 (0.810, 0.990) | 0.031 |
| Model 3 | 0.874 (0.773, 0.988) | 0.031 |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Body mass index ≥25 vs. <25 kg/m2 | ||
| Model 1 | 0.570 (0.377, 0.861) | 0.008 |
| Model 2 | 0.588 (0.387, 0.891) | 0.012 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | ||
| Model 1 | 0.941 (0.893, 0.992) | 0.025 |
| Model 2 | 0.945 (0.895, 0.998) | 0.041 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.-C.; Wu, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chen, K.-H.; Pan, C.-C.; Wang, J.-S.; Lee, C.-H. Association of Body Mass Index with Long-Term All-Cause Mortality in Patients Who Had Undergone a Vertebroplasty for a Vertebral Compression Fracture. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216519
Wang W-C, Wu Y-C, Lin Y-H, Lin Y-T, Chen K-H, Pan C-C, Wang J-S, Lee C-H. Association of Body Mass Index with Long-Term All-Cause Mortality in Patients Who Had Undergone a Vertebroplasty for a Vertebral Compression Fracture. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(21):6519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216519
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wen-Chien, Yun-Che Wu, Yu-Hsien Lin, Yu-Tsung Lin, Kun-Hui Chen, Chien-Chou Pan, Jun-Sing Wang, and Cheng-Hung Lee. 2022. "Association of Body Mass Index with Long-Term All-Cause Mortality in Patients Who Had Undergone a Vertebroplasty for a Vertebral Compression Fracture" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 21: 6519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216519
APA StyleWang, W.-C., Wu, Y.-C., Lin, Y.-H., Lin, Y.-T., Chen, K.-H., Pan, C.-C., Wang, J.-S., & Lee, C.-H. (2022). Association of Body Mass Index with Long-Term All-Cause Mortality in Patients Who Had Undergone a Vertebroplasty for a Vertebral Compression Fracture. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(21), 6519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216519





