Comparison of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients’ 2-Year Infliximab, Abatacept, and Tocilizumab Persistence Rates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Data Recorded
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
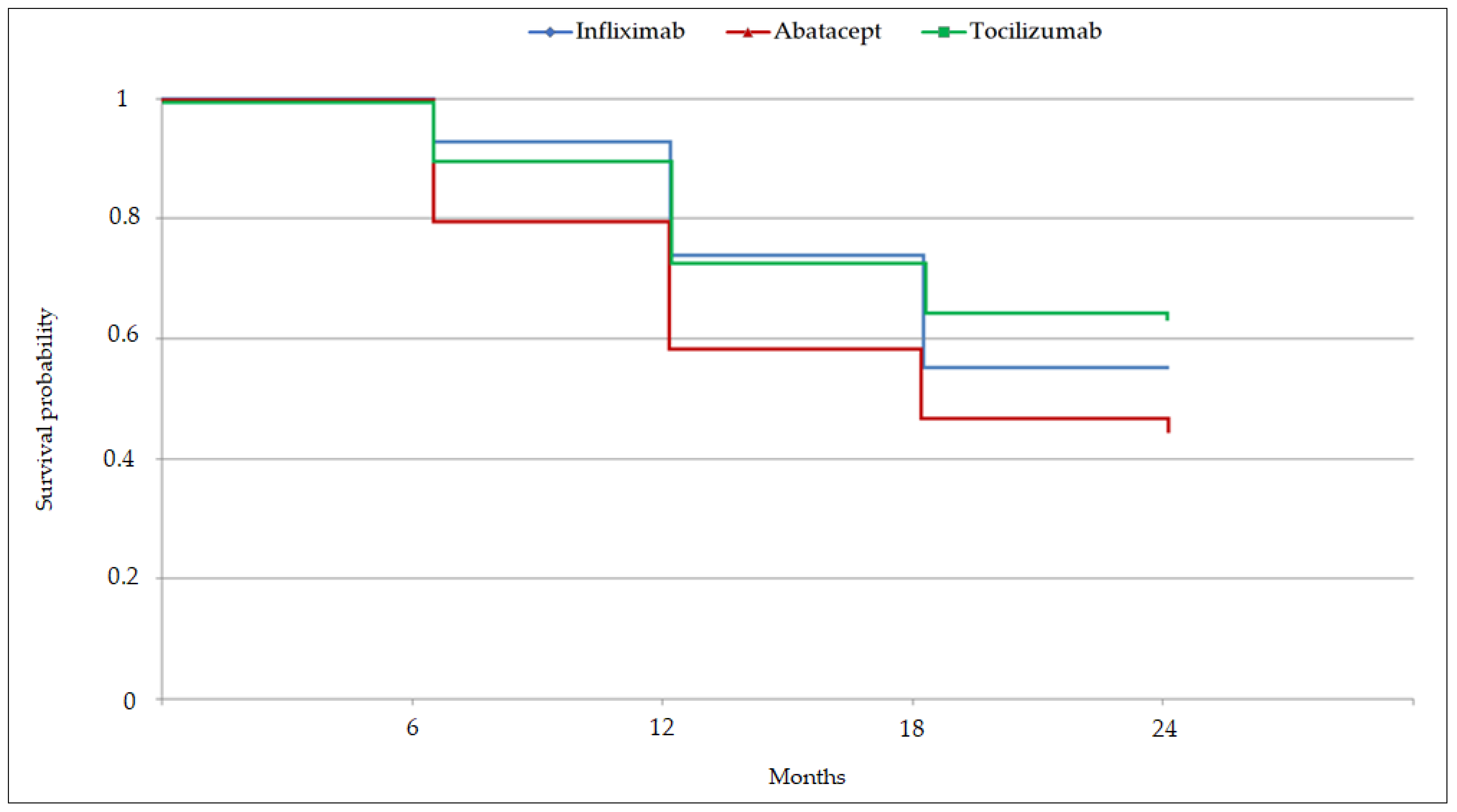
3.2. Drug-persistence Comparisons
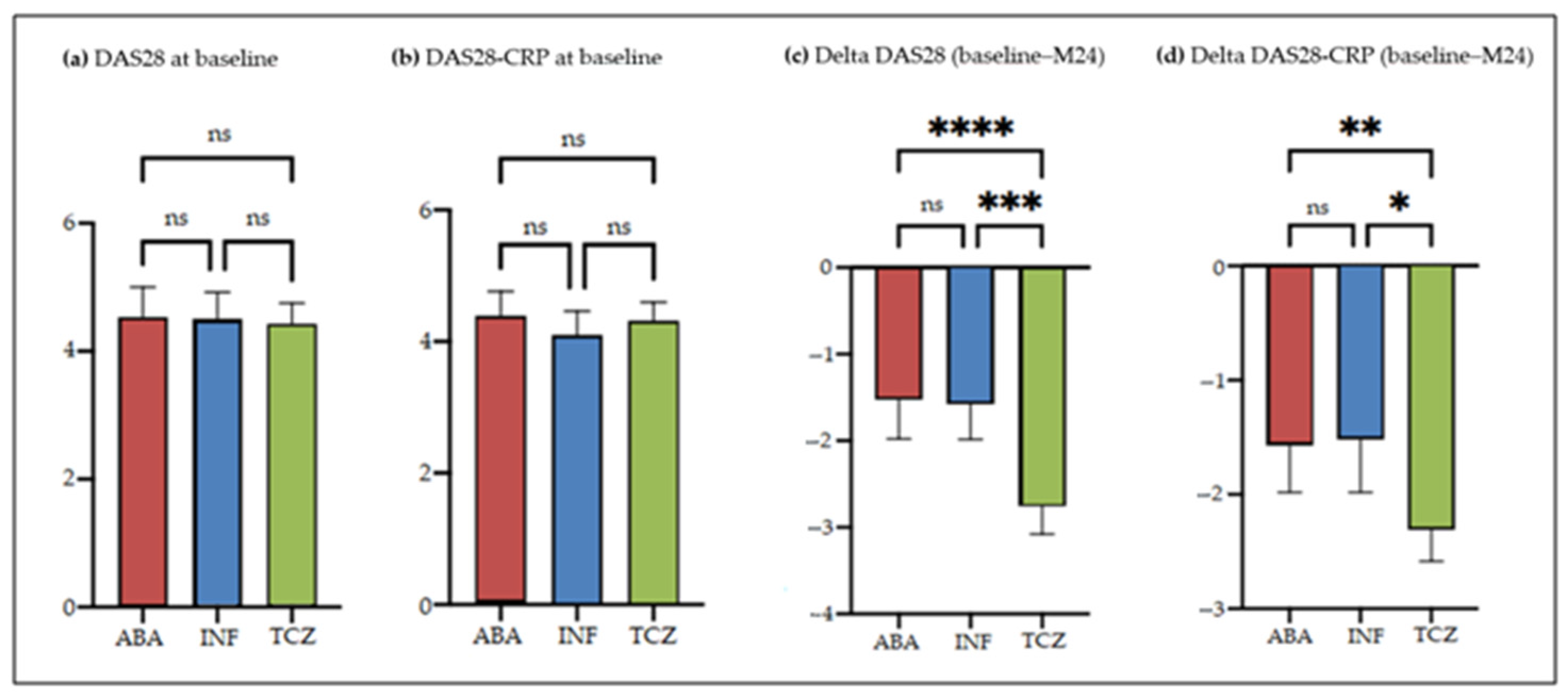
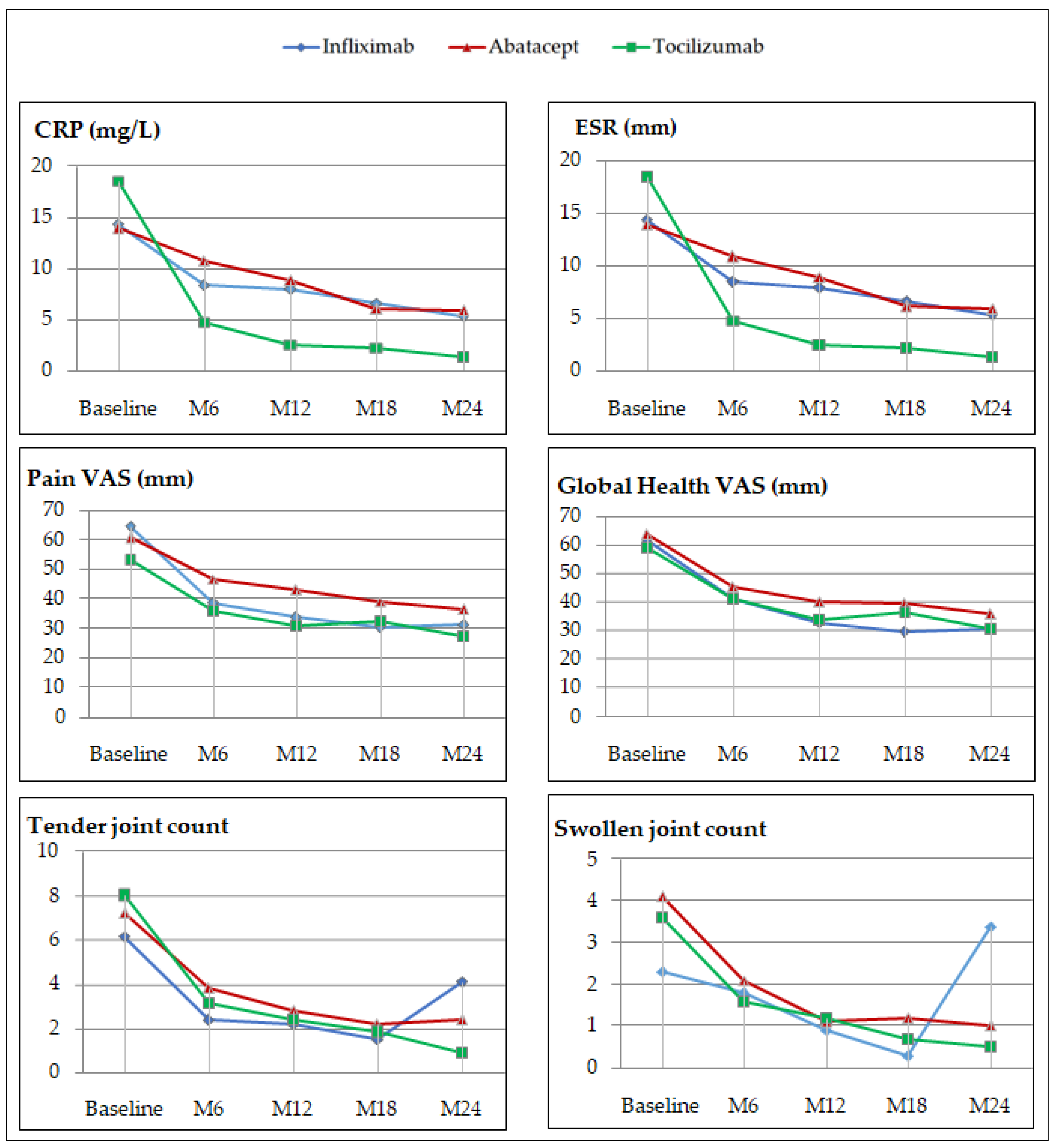
3.3. Effectiveness Profile
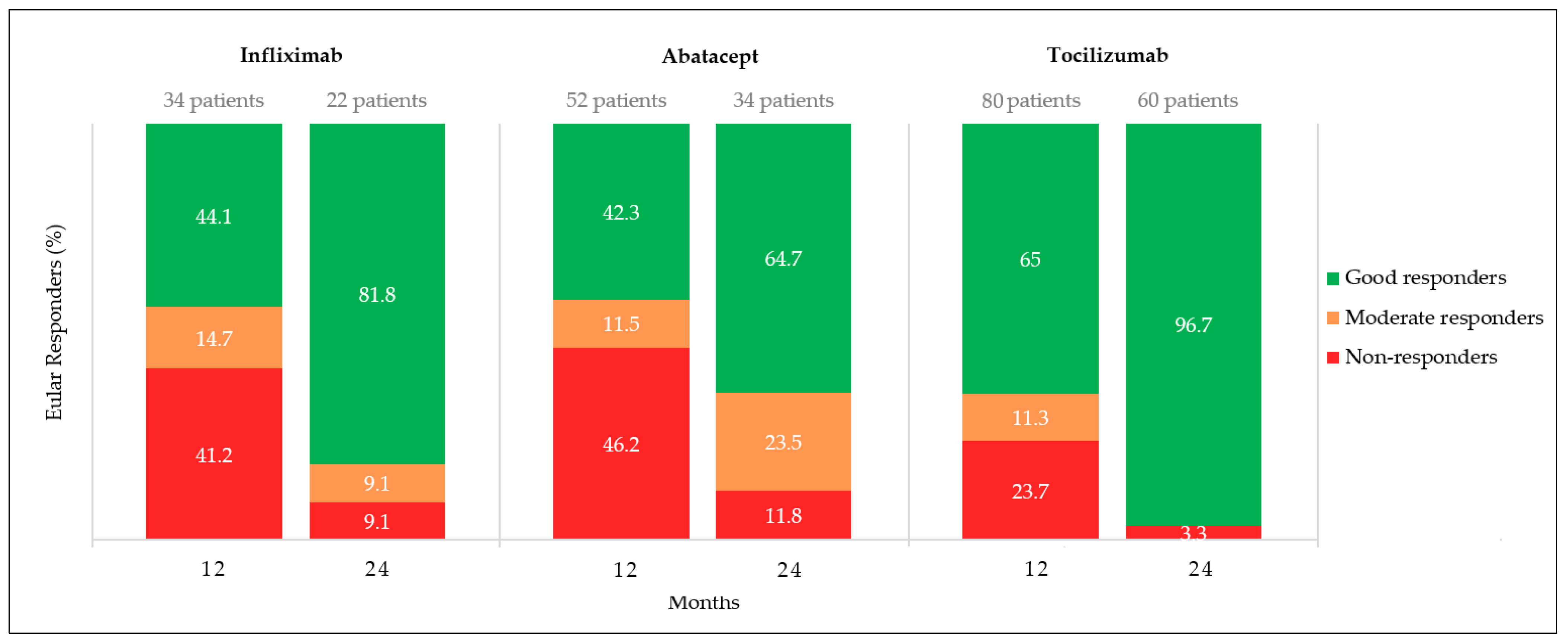
3.4. EULAR responses
3.5. Tolerance Profiles
4. Discussion
4.1. Drug Persistence
4.2. Effectiveness Profile
4.3. Tolerance Profile
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenauer, B.; Judd, M.; Wells, G.; Burls, A.; Cranney, A.; Hochberg, M.; Tugwell, P. Infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2002, 3, CD003785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L.J. Tocilizumab: A Review in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drugs 2017, 77, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, G.M. Abatacept: A review of its use in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs 2013, 73, 1095–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, J.A.; Roy, A.; Burrell, A.; Fairchild, C.J.; Fuldeore, M.J.; Ollendorf, D.A.; Wong, P.K. Medication compliance and persistence: Terminology and definitions. Value Health 2008, 11, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottenberg, J.E.; Morel, J.; Constantin, A.; Bardin, T.; Cantagrel, A.G.; Combe, B.; Dougados, M.; Flipo, R.M.; Saraux, A.; Schaeverbeke, T.; et al. Long-Term Registry Data in 4498 Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Indicate a Similar Safety but a Different Drug Retention between Abatacept, Rituximab and Tocilizumab. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsblad-d’Elia, H.; Bengtsson, K.; Kristensen, L.E.; Jacobsson, L.T. Drug adherence, response and predictors thereof for tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the Swedish biologics register. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alten, R.; Mariette, X.; Lorenz, H.M.; Nüßlein, H.; Galeazzi, M.; Navarro, F.; Chartier, M.; Heitzmann, J.; Poncet, C.; Rauch, C.; et al. Predictors of abatacept retention over 2 years in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the real-world ACTION study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batteux, B.; Devauchelle, A.; Boyard, P.L.; Sejourné, A.; Fardellone, P.; Goëb, V. Comparison of continuation rates with three TNFα antagonists (adalimumab, infliximab, etanercept) in rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis: Retrospective 10-year study. Jt. Bone Spine 2016, 83, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leffers, H.C.; Ostergaard, M.; Glintborg, B.; Krogh, N.S.; Foged, H.; Tarp, U.; Lorenzen, T.; Hansen, A.; Hansen, M.S.; Jacobsen, M.S.; et al. Efficacy of abatacept and tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in clinical practice: Results from the nationwide Danish DANBIO registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottenberg, J.E.; Morel, J.; Perrodeau, E.; Bardin, T.; Combe, B.; Dougados, M.; Flipo, R.M.; Saraux, A.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Sibilia, J.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of rituximab, abatacept, and tocilizumab in adults with rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to TNF inhibitors: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2019, 364, l67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choquette, D.; Bessette, L.; Alemao, E.; Haraoui, B.; Postema, R.; Raynauld, J.P.; Coupal, L. Persistence rates of abatacept and TNF inhibitors used as first or second biologic DMARDs in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: 9 years of experience from the Rhumadata® clinical database and registry. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, M.C.; McKay, J.D.; Nasonov, E.L.; Mysler, E.F.; Da Silva, N.A.; Alecock, E.; Woodworth, T.; Gomez-Reino, J.J. Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab reduces disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: The tocilizumab in combination with traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2968–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazici, Y.; Curtis, J.R.; Ince, A.; Baraf, H.; Malamet, R.L.; Teng, L.L.; Kavanaugh, A. Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients with moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis and a previous inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: The ROSE study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maini, R.; St Clair, E.W.; Breedveld, F.; Furst, D.; Kalden, J.; Weisman, M.; Smolen, J.; Emery, P.; Harriman, G.; Feldmann, M.; et al. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: A randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet 1999, 354, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, M.F.; Crowson, C.S.; Pond, G.R.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Frequency of infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with controls: A population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2287–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rempenault, C.; Lukas, C.; Combe, B.; Herrero, A.; Pane, I.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Wendling, D.; Pham, T.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Mariette, X.; et al. Risk of Diverticulitis and Gastrointestinal Perforation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Tocilizumab Compared to Rituximab or Abatacept. Rheumatology 2021, 59, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Infliximab (n = 40) | Abatacept (n = 72) | Tocilizumab (n = 93) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female sex | 34 (85) | 54 (75) | 71 (76.3) | 0.472 |
| Age (years) | 53.8 ± 15.6 | 58.2 ±13.0 | 55.6 ±13.2 | 0.215 |
| Body mass index (kg/m²) | 28.5 ± 6.5 | 27.8 ± 5.6 | 28.1 ± 6.5 | 0.855 |
| Smokers | 17 (42.5) | 30 (41.7) | 34 (36.6) | 0.734 |
| Disease duration (years) | 8.1 ± 5.8 | 13.1 ± 10.7 | 10.9 ± 8.6 | 0.007 |
| RF positive | 25 (62.5) | 47 (65.3) | 61 (65.6) | 0.962 |
| ACPA positive | 30 (75) | 49 (68.1) | 70 (75.3) | 0.578 |
| RF and ACPA negative | 9 (22.5) | 19 (26.4) | 16 (17.2) | 0.384 |
| Erosion | 28 (70) | 57 (79.2) | 73 (78.5) | 0.527 |
| Extra-articular manifestations | 8 (20) | 13 (18.1) | 16 (17.2) | 0.971 |
| DAS28 | ||||
| Mean | 4.7 ± 1.1 | 4.7 ± 1.2 | 4.6 ± 1.3 | 0.987 |
| Median | 4.5 (2.8–7.6) | 4.8 (2.3–8.0) | 4.6 (1.5–7.5) | |
| DAS28-CRP | ||||
| Mean | 4.4 ± 1.0 | 4.5 ± 1.0 | 4.5 ± 1.1 | 0.899 |
| Median | 4.2 (2.7–6.8) | 4.5 (2.7–7.6) | 4.5 (2.2–7.0) | |
| Pain VAS | 61.8 ± 23.0 | 60.1 ± 19.8 | 57.4 ± 21.6 | 0.431 |
| Patient global health VAS | 59.8 ± 25.5 | 63.0 ± 19.6 | 60.8 ± 19.0 | 0.713 |
| Tender joint count | 8.3 ± 7.0 | 8.4 ± 7.0 | 9.0 ± 10.0 | 0.861 |
| Swollen joint count | 3.2 ± 3.2 | 4.1 ± 3.9 | 3.9 ± 4.0 | 0.524 |
| ESR (mm) | 26.6 ± 20.7 | 22.3 ± 22.2 | 23.3 ± 21.4 | 0.595 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 14.6 ± 17.6 | 14.0 ± 25.6 | 18.5 ± 25.7 | 0.455 |
| Monotherapy | 5 (12.5) | 25 (34.7) | 23 (24.7) | 0.034 |
| Methotrexate at baseline | 28 (70) | 39 (54.2) | 59 (63.4) | 0.224 |
| Methotrexate dose (mg/week) | 16.8 ± 3.2 | 13.9 ± 3.6 | 15.4 ± 4.1 | 0.785 |
| Corticosteroids at baseline | 25 (62.5) | 38 (52.8) | 53 (57) | 0.598 |
| Corticosteroids dose (mg/d) | 9.0 ± 9.3 | 10.7 ± 4.6 | 9.9 ± 6.4 | 0.850 |
| Number of prior bDMARDs | 2.07 ± 1.73 | 3.15 ± 1.32 | 2.56 ± 1.28 |
| Infliximab (n = 40) | Abatacept (n = 72) | Tocilizumab (n = 93) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop/Censure | 18/22 | 39/33 | 35/58 | 0.106 |
| Number of patients, n (%) | ||||
| 6 months | 37 (92.5) | 57 (79.2) | 82 (88.2) | |
| 12 months | 30 (75) | 42 (58.3) | 68 (73.1) | |
| 18 months | 22 (55) | 34 (47.2) | 60 (64.5) | |
| 24 months | 22 (55) | 33 (45.8) | 58 (62.4) | |
| Mean Persistence Duration, months (CI 95%) | ||||
| 19.3 (17.5–21.2) | 17.0 (15.2–18.7) | 19.6 (17.7–19.6) | 0.064 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diep, L.; Barbier, V.; Doussière, M.; Touboul, E.; Jesson, C.; Deprez, V.; Sobhy-Danial, J.-M.; Fardellone, P.; Goëb, V. Comparison of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients’ 2-Year Infliximab, Abatacept, and Tocilizumab Persistence Rates. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11205978
Diep L, Barbier V, Doussière M, Touboul E, Jesson C, Deprez V, Sobhy-Danial J-M, Fardellone P, Goëb V. Comparison of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients’ 2-Year Infliximab, Abatacept, and Tocilizumab Persistence Rates. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(20):5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11205978
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiep, Laetitia, Vincent Barbier, Marie Doussière, Estelle Touboul, Claire Jesson, Valentine Deprez, Jean-Marc Sobhy-Danial, Patrice Fardellone, and Vincent Goëb. 2022. "Comparison of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients’ 2-Year Infliximab, Abatacept, and Tocilizumab Persistence Rates" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 20: 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11205978
APA StyleDiep, L., Barbier, V., Doussière, M., Touboul, E., Jesson, C., Deprez, V., Sobhy-Danial, J.-M., Fardellone, P., & Goëb, V. (2022). Comparison of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients’ 2-Year Infliximab, Abatacept, and Tocilizumab Persistence Rates. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(20), 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11205978







