Frailty Assessed with FRAIL Scale and G8 Questionnaire Predicts Severe Postoperative Complications in Patients Receiving Major Head and Neck Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Statistical Considerations and Sample Size
2.2. Study Cohort
2.3. Assessment of Frailty and Postoperative Complications
2.4. Demographic Parameters and Existing Medical Conditions
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Parameters and Study Cohort
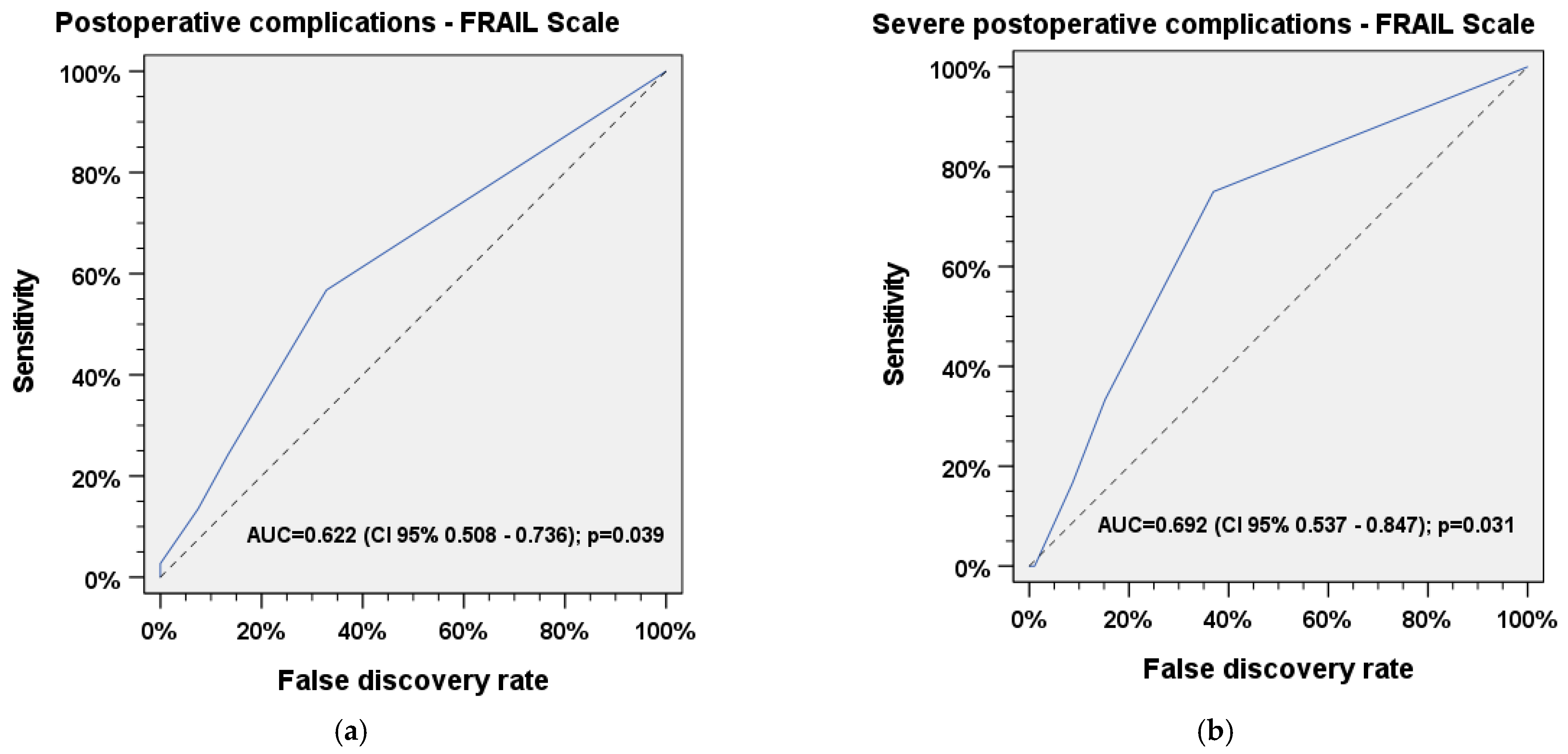
3.2. ROC Analysis
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| Clavien–Dindo | Classification system for postoperative complications |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| FRAIL Scale | Screening instrument for the assessment of frailty |
| G8 | Geriatric eight (screening instrument for the assessment of frailty) |
| HNC | Head and neck cancer |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| IBM | International Business Machines Corporation |
| n | Sample size |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| p | p value |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic (used to assess the accuracy of tests in predictive models) |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SPSS | Statistical package for the Social Sciences |
| φ | Cramer’s phi (measure of effect size in χ² test) |
References
- Clegg, A.; Young, J.; Iliffe, S.; Rikkert, M.O.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet 2013, 381, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcotte, L.A.; Zalucky, A.A.; Stall, N.M.; Downar, J.; Rockwood, K.; Theou, O.; McArthur, C.; Heckman, G. Baseline Frailty as a Predictor of Survival After Critical Care: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Older Adults Receiving Home Care in Ontario, Canada. Chest 2021, 160, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppenstall, C.P.; Wilkinson, T.J.; Hanger, H.C.; Keeling, S.; Pearson, J. Factors related to care home admission in the year following hospitalisation in frail older adults. Age Ageing 2011, 40, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handforth, C.; Clegg, A.; Young, C.; Simpkins, S.; Seymour, M.T.; Selby, P.J.; Young, J. The prevalence and outcomes of frailty in older cancer patients. A systematic review. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, W.B.; Rosenthal, R.A.; Merkow, R.P.; Ko, C.Y.; Esnaola, N.F. Optimal preoperative assessment of the geriatric surgical patient. A best practices guideline from the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program and the American Geriatrics Society. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2012, 215, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bras, L.; Driessen, D.A.J.J.; de Vries, J.; Festen, S.; van der Laan, B.F.A.M.; van Leeuwen, B.L.; de Bock, G.H.; Halmos, G.B. Patients with head and neck cancer. Are they frailer than patients with other solid malignancies? Eur. J. Cancer Care 2020, 29, e13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, D.P.; Sklar, M.C.; de Almeida, J.R.; Gilbert, R.; Gullane, P.; Irish, J.; Brown, D.; Higgins, K.; Enepikedes, D.; Xu, W.; et al. Frailty as a predictor of outcomes in patients undergoing head and neck cancer surgery. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, E340–E345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fancy, T.; Huang, A.T.; Kass, J.I.; Lamarre, E.D.; Tassone, P.; Mantravadi, A.V.; Alwani, M.M.; Subbarayan, R.S.; Bur, A.M.; Worley, M.L.; et al. Complications, Mortality, and Functional Decline in Patients 80 Years or Older Undergoing Major Head and Neck Ablation and Reconstruction. JAMA Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.; Kim, S.-A.; Roh, J.-L.; Lee, S.-W.; Kim, S.-B.; Choi, S.-H.; Ham, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y. An Introduction to a Head and Neck Cancer-Specific Frailty Index and Its Clinical Implications in Elderly Patients. A Prospective Observational Study Focusing on Respiratory and Swallowing Functions. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.M.; Sklar, M.C.; Su, J.; Xu, W.; de Almeida, J.R.; Gullane, P.; Gillbert, R.; Brown, D.; Irish, J.; Alibhai, S.M.H.; et al. Evaluation of Older Age and Frailty as Factors Associated with Depression and Postoperative Decision Regret in Patients Undergoing Major Head and Neck Surgery. JAMA Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, A.N.; Lee, J.T.; Gurrola, J.G.; Wang, M.B.; Suh, J.D. The impact of frailty on perioperative outcomes and resource utilization in sinonasal cancer surgery. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleere, E.F.; Davey, M.G.; O’Neill, J.P. “Age is just a number”; frailty as a marker of peri-operative risk in head and neck surgery: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2022, 44, 1927–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Kitzman, D.; Whellan, D.J.; Duncan, P.W.; Mentz, R.J.; Pastva, A.M.; Nelson, M.B.; Upadhya, B.; Chen, H.; Reeves, G.R. Frailty Among Older Decompensated Heart Failure Patients: Prevalence, Association with Patient-Centered Outcomes, and Efficient Detection Methods. JACC Heart Fail. 2019, 7, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, N.; Locke, E.R.; Pike, K.C.; Chen, Z.; Lee, J.; Huang, J.C.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Fan, V.S. Frailty in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Risk of Exacerbations and Hospitalizations. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2020, 15, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| All Patients | HNSCC | Other | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | n | 104 | 36 | 68 | |
| Minimum | 65 | 65 | 65 | ||
| Maximum | 88 | 84 | 88 | ||
| Mean | 73.41 | 72.69 | 73.79 | n.s. | |
| SD | 6.07 | 5.31 | 6.44 | ||
| Weight | n | 104 | 36 | 68 | |
| Minimum | 47 | 47 | 54 | ||
| Maximum | 169 | 104 | 169 | ||
| Median | 77.0 | 75 | 78 | ||
| Mean | 78.94 | 75.47 | 80.78 | n.s. | |
| SD | 17.23 | 15.67 | 17.84 | ||
| Sex | n | 104 | 36 | 68 | |
| Male (%) | 68 (65.4%) | 23 (63.9%) | 45 (66.2%) | n.s. | |
| Female (%) | 36 (34.6%) | 13 (36.1%) | 23 (33.8%) | n.s. |
| Frailty | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| G8 | 56 | 53.8 |
| FRAIL Scale | 42 | 40.4 |
| Existing medical conditions | ||
| Asthma | 2 | 1.9 |
| COPD | 10 | 9.6 |
| Cardiac arrhythmia | 22 | 21.2 |
| Hypertension | 62 | 59.6 |
| Heart insufficiency | 6 | 5.8 |
| Myocardial infarction in medical history | 2 | 1.9 |
| Coronary heart disease | 8 | 7.7 |
| Diabetes type 1 and 2 | 32 | 30.8 |
| Dementia | 1 | 0.96 |
| BMI | ||
| <19 | 6 | 5.8 |
| 19–21 | 4 | 3.8 |
| 21–23 | 6 | 5.8 |
| ≥23 | 88 | 84.6 |
| Diagnoses with indication for major surgery | ||
| HNSCC (larynx, pharynx, oral cavity, neck) | 36 | 34.6 |
| Benign lesions of the larynx | 13 | 12.5 |
| Benign lesions of the lymphatic nodes (neck) | 6 | 5.8 |
| Skin lesions/skin tumors (benign and malignant) | 5 | 4.8 |
| Subglottic/tracheal stenosis | 2 | 1.9 |
| Benign tumors or lesions of the salivary glands | 10 | 9.6 |
| Septum deviation, chronic sinusitis | 12 | 11.5 |
| Hearing loss, chronic mesotympanal/epitympanal otitis media | 11 | 10.6 |
| Benign lesions of the pharynx/oral cavity, chronic tonsillitis | 4 | 3.8 |
| Esophageal stenosis, Zenker’s diverticulum | 5 | 4.8 |
| Postoperative complications | ||
| Any | 37 | 35.6 |
| Mild (Clavien–Dindo ≤ 2) | 25 | 24.0 |
| Severe (Clavien–Dindo ≥ 3) | 12 | 11.5 |
| Grouped surgical procedures | n | Mean time (min) |
| Cancer surgery in HNSCC (pharynx, larynx, oral cavity, neck dissection) | 36 | 298.25 |
| Without reconstruction | 25 | 204.56 |
| With reconstruction (radial forearm flap, anterior lateral thigh flap, pectoralis major flap) | 11 | 511.18 |
| Septoplasty/FESS/pansinus surgery | 12 | 64.92 |
| Mikrolaryngoscopy for benign lesions with laser | 13 | 34.07 |
| Excision of skin lesions (benign and malignant) | 5 | 99.68 |
| Laryngotracheal reconstruction | 2 | 100.06 |
| Partial parotidectomy/submandibulectomy | 10 | 101.0 |
| Cochlear implant/tympanoplasty | 11 | 78.09 |
| Excision of lesion (benign) pharynx/oral cavity, tonsillectomy | 4 | 31.5 |
| Esophageal bougienage (three sessions), endoscopic laser diverticulotomy | 5 | 32.6 |
| Lymphatic node extirpation (neck) | 6 | 42.46 |
| Postoperative Complications | χ2 | p | φ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNSCC vs. other | Any | 7.11 | 0.008 | 0.26 |
| Mild | 0.099 | 0.752 | 0.03 | |
| Severe | 19.51 | <0.001 | 0.43 | |
| Any postoperative complications and frailty | ||||
| FRAIL Scale | All patients | 4.46 | 0.035 | 0.21 |
| HNSCC | 3.95 | 0.047 | 0.33 | |
| Other | 0.281 | 0.596 | 0.06 | |
| G8 | All patients | 1.59 | 0.206 | 0.12 |
| HNSCC | 0.892 | 0.345 | 0.16 | |
| Other | 0.085 | 0.771 | 0.04 | |
| Mild postoperative complications and frailty | ||||
| FRAIL Scale | All patients | 0.179 | 0.673 | 0.04 |
| HNSCC | 0.390 | 0.532 | 0.10 | |
| Other | 0.022 | 0.882 | 0.02 | |
| G8 | All patients | 0.045 | 0.832 | 0.02 |
| HNSCC | 0.080 | 0.778 | 0.05 | |
| Other | 0.000 | 01.00 | 0.00 | |
| Severe postoperative complications and frailty | ||||
| FRAIL Scale | All patients | 6.75 | 0.009 | 0.26 |
| HNSCC | 2.53 | 0.112 | 0.27 | |
| Other | 1.97 | 0.159 | 0.17 | |
| G8 | All patients | 4.75 | 0.029 | 0.21 |
| HNSCC | 1.64 | 0.201 | 0.21 | |
| Other | 1.14 | 0.285 | 0.13 |
| Frailty | Existing Medical Conditions | χ2 | p | φ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FRAIL Scale | Asthma | 0.078 | 0.780 | 0.03 |
| COPD | 7.27 | 0.007 | 0.26 | |
| Cardiac arrhythmia | 0.298 | 0.585 | 0.05 | |
| Hypertension | 0.153 | 0.695 | 0.04 | |
| Heart insufficiency | 0.245 | 0.621 | 0.05 | |
| Myocardial infarction in medical history | 1.38 | 0.240 | 0.12 | |
| Coronary heart disease | 0.030 | 0.863 | 0.02 | |
| Diabetes type 1 and 2 | 1.76 | 0.183 | 0.13 | |
| G8 | Asthma | 0.012 | 0.912 | 0.01 |
| COPD | 1.16 | 0.281 | 0.11 | |
| Cardiac arrhythmia | 0.309 | 0.578 | 0.05 | |
| Hypertension | 9.32 | 0.002 | 0.30 | |
| Heart insufficiency | 2.23 | 0.136 | 0.15 | |
| Myocardial infarction in medical history | 2.38 | 0.123 | 0.15 | |
| Coronary heart disease | 1.56 | 0.212 | 0.12 | |
| Diabetes type 1 and 2 | 8.32 | 0.004 | 0.28 |
| Frailty (HNSCC vs. Other) | χ 2 | p | φ |
|---|---|---|---|
| G8 | 3.64 | 0.056 | 0.19 |
| FRAIL Scale | 3.51 | 0.061 | 0.18 |
| Existing medical conditions (HNSCC vs. other) | |||
| Asthma | 1.08 | 0.299 | 0.10 |
| COPD | 3.15 | 0.076 | 0.17 |
| Cardiac arrhythmia | 5.42 | 0.020 | 0.22 |
| Hypertension | 0.418 | 0.518 | 0.06 |
| Heart insufficiency | 3.37 | 0.066 | 0.18 |
| Myocardial infarction in medical history | 0.213 | 0.644 | 0.04 |
| Coronary heart disease | 1.87 | 0.171 | 0.13 |
| Diabetes type 1 and 2 | 0.860 | 0.354 | 0.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kunz, V.; Wichmann, G.; Wald, T.; Pirlich, M.; Zebralla, V.; Dietz, A.; Wiegand, S. Frailty Assessed with FRAIL Scale and G8 Questionnaire Predicts Severe Postoperative Complications in Patients Receiving Major Head and Neck Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164714
Kunz V, Wichmann G, Wald T, Pirlich M, Zebralla V, Dietz A, Wiegand S. Frailty Assessed with FRAIL Scale and G8 Questionnaire Predicts Severe Postoperative Complications in Patients Receiving Major Head and Neck Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(16):4714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164714
Chicago/Turabian StyleKunz, Viktor, Gunnar Wichmann, Theresa Wald, Markus Pirlich, Veit Zebralla, Andreas Dietz, and Susanne Wiegand. 2022. "Frailty Assessed with FRAIL Scale and G8 Questionnaire Predicts Severe Postoperative Complications in Patients Receiving Major Head and Neck Surgery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 16: 4714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164714
APA StyleKunz, V., Wichmann, G., Wald, T., Pirlich, M., Zebralla, V., Dietz, A., & Wiegand, S. (2022). Frailty Assessed with FRAIL Scale and G8 Questionnaire Predicts Severe Postoperative Complications in Patients Receiving Major Head and Neck Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(16), 4714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11164714






