The Association of the One-Abutment at One-Time Concept with Marginal Bone Loss around the SLA and Platform Switch and Conical Abutment Implants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Age of at least 21 years.
- Good oral hygiene was defined as a full mouth plaque score <25% [21].
- Partial edentulism with the need for two adjacent implant-supported fixed restorations.
- Treated and stable periodontal disease of the remaining dentition.
- Availability of native healed bone to accommodate at least two adjacent implants of ≥8 mm length and ≥3.75 mm width without bone augmentation and a minimum of buccal/lingual or palatal wall of 2 mm after implant installation.
- Existence of a sufficient amount of (≥2 mm) keratinized gingiva for transgingival healing.
- The presence of opposing dentition (natural or restored).
- Uncontrolled diabetes, untreated malignancies, pregnancy, previous/current bisphosphonate therapy, immune diseases.
- Previous radiation therapy to the head and neck area.
- Untreated pathology in the jaws.
- Psychological problems.
- Oral mucosal diseases, such as lichen planus.
- Poor oral hygiene (defined as full mouth plaque score >25% at re-evaluation) or lack of compliance with treatment visits or protocol.
- Active periodontal disease involving the residual dentition.
- Need for bone augmentation.
- Light/heavy smokers.
3. Treatment Protocol
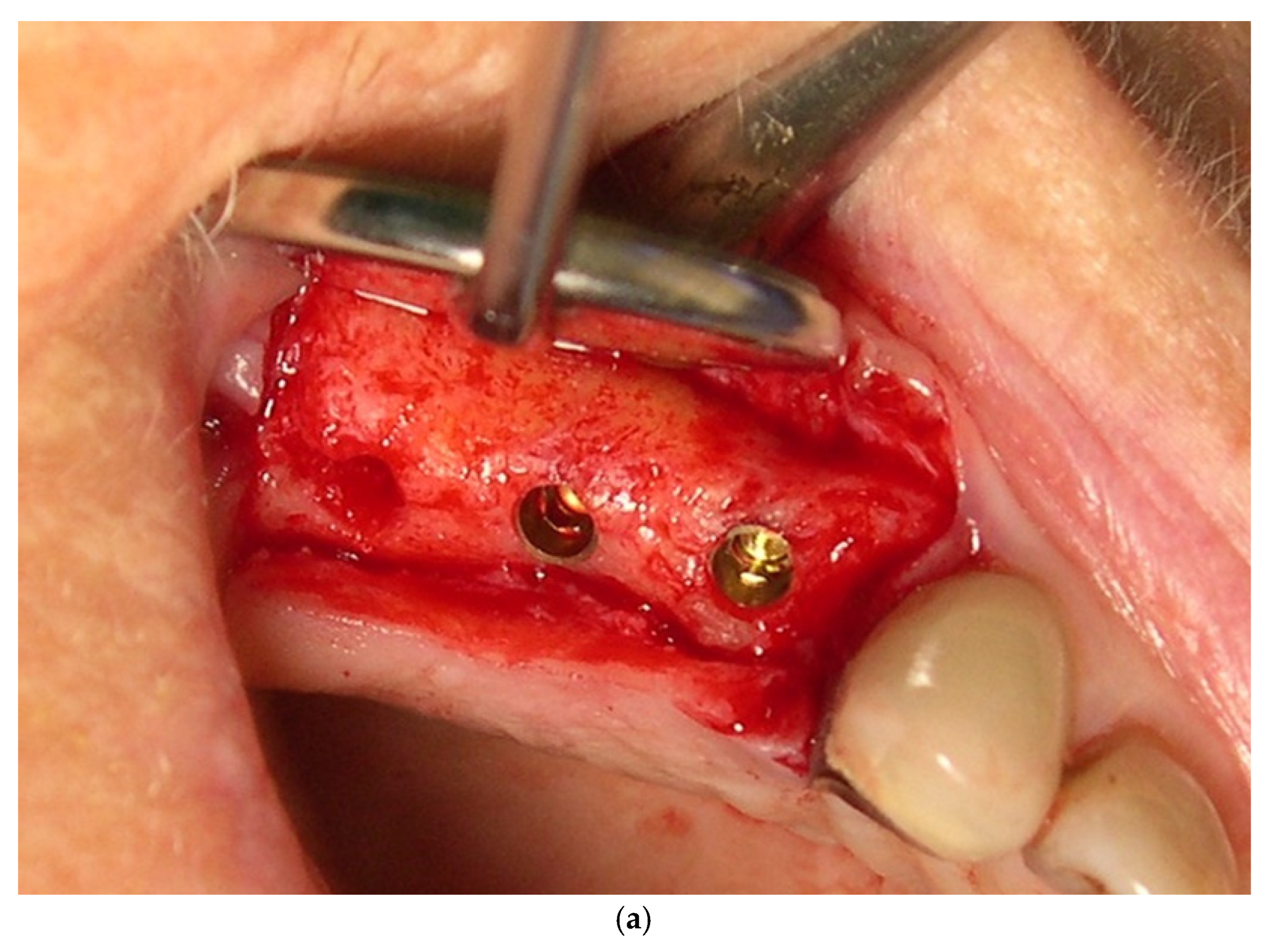
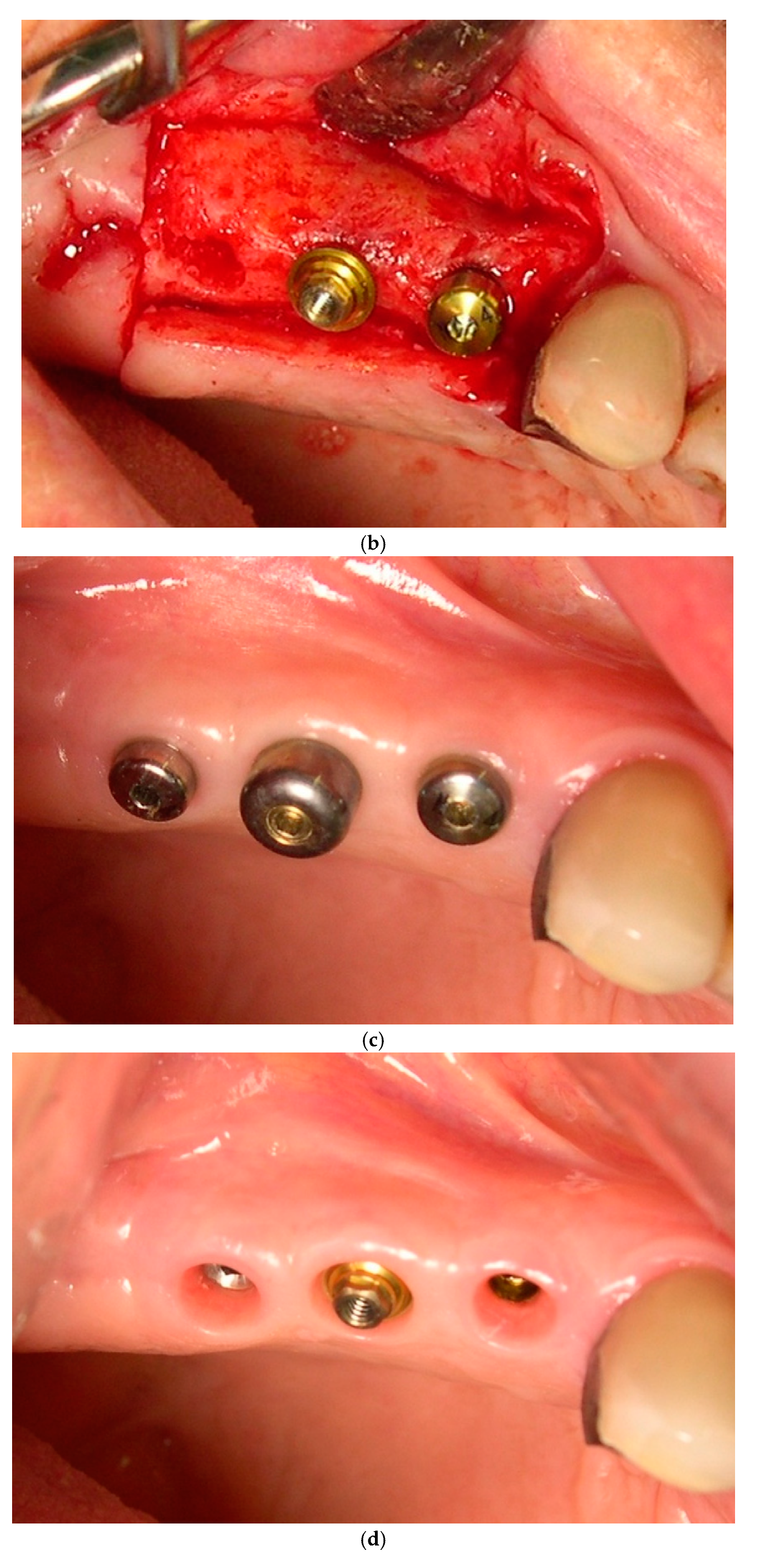
3.1. Surgical Technique and Postoperative Management
3.2. Prosthetic Procedures
3.3. Postoperative Follow-Ups and Treatment
3.4. Outcome Measurements
- -
- Implant crowns bucco–palatal/lingual and mesiodistal diameter in mm measured using a caliper and a 1 mm periodontal probe.
- -
- Multiunit gingival and transmucosal individual abutment height (in mm).
- ▪
- Plaque index (PI)—percentage of visible plaque measured at four sites per implant and tooth (mesial, midfacial, distal, and palatal) at the soft tissue margin [21]. The plaque was stained with a disclosing solution.
- ▪
- Bleeding index—consisting of a dichotomous recording of the absence or presence of bleeding after probing the implant sulcus/pocket within 10 s after probing per site (mesial, midfacial, distal, and palatal).
- ▪
- PD—measured using a light probing force (approximately 25 g) to the nearest mm using a periodontal probe (UNC 15, Hu-Friedy, Chicago, IL, USA). The probing depth was calculated per implant.
- ▪
- Keratinized mucosal width (KMW) was measured using a 1 mm probe to the nearest mm (Hu-Friedy, Chicago, IL, USA).
- ▪
- Gingival biotype (thin or thick) reflected by the transparency of the periodontal probe through the gingival margin.
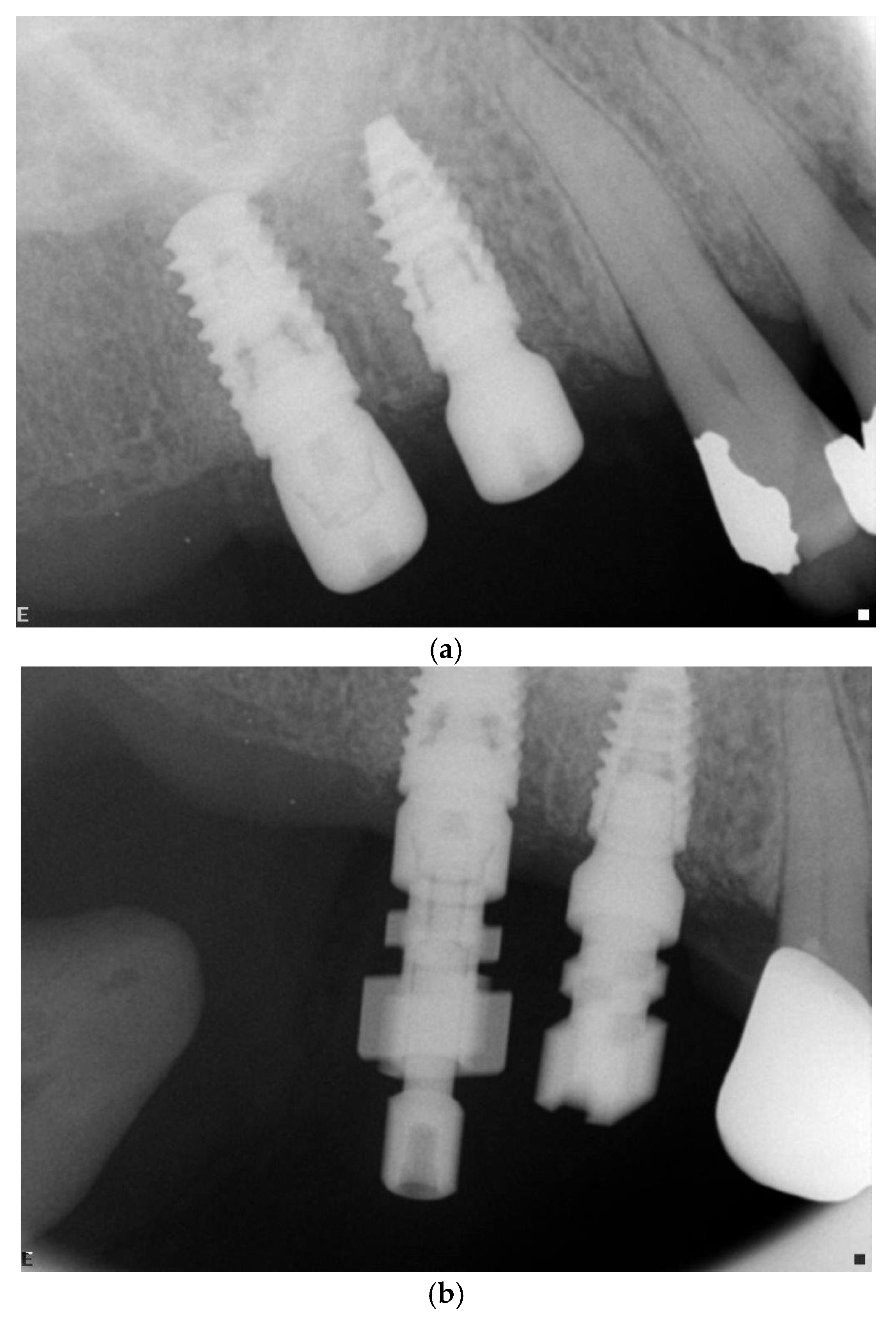
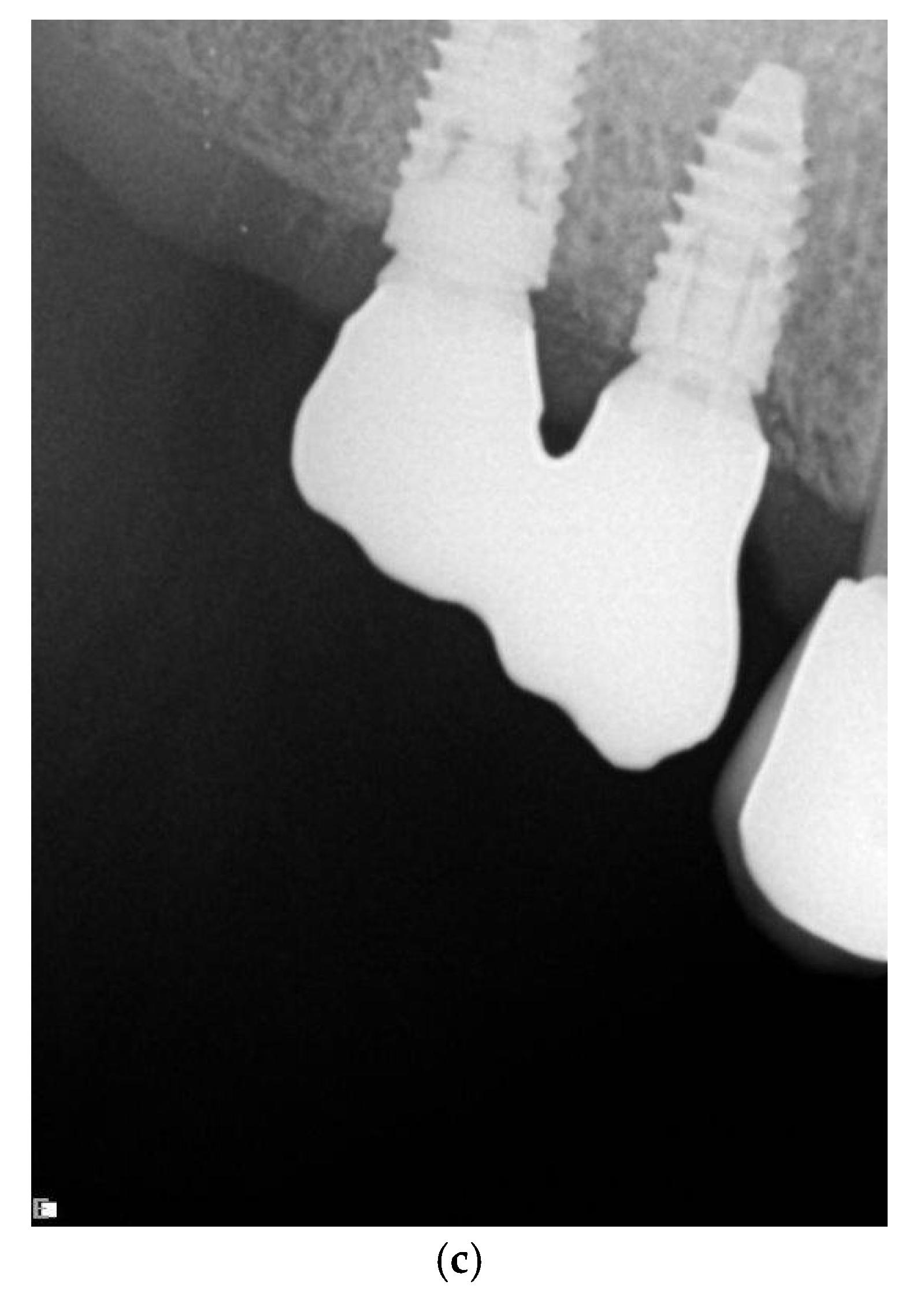
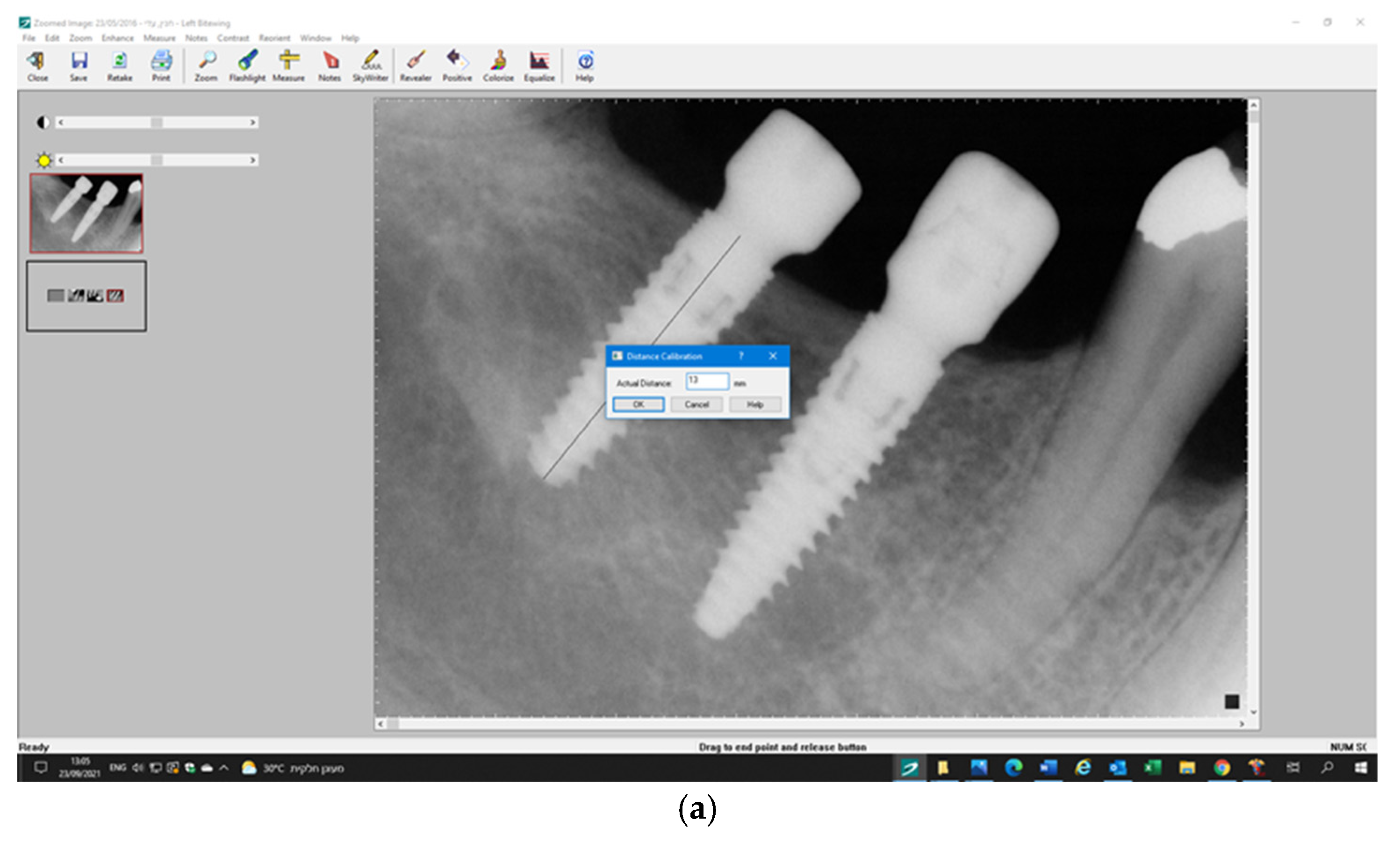
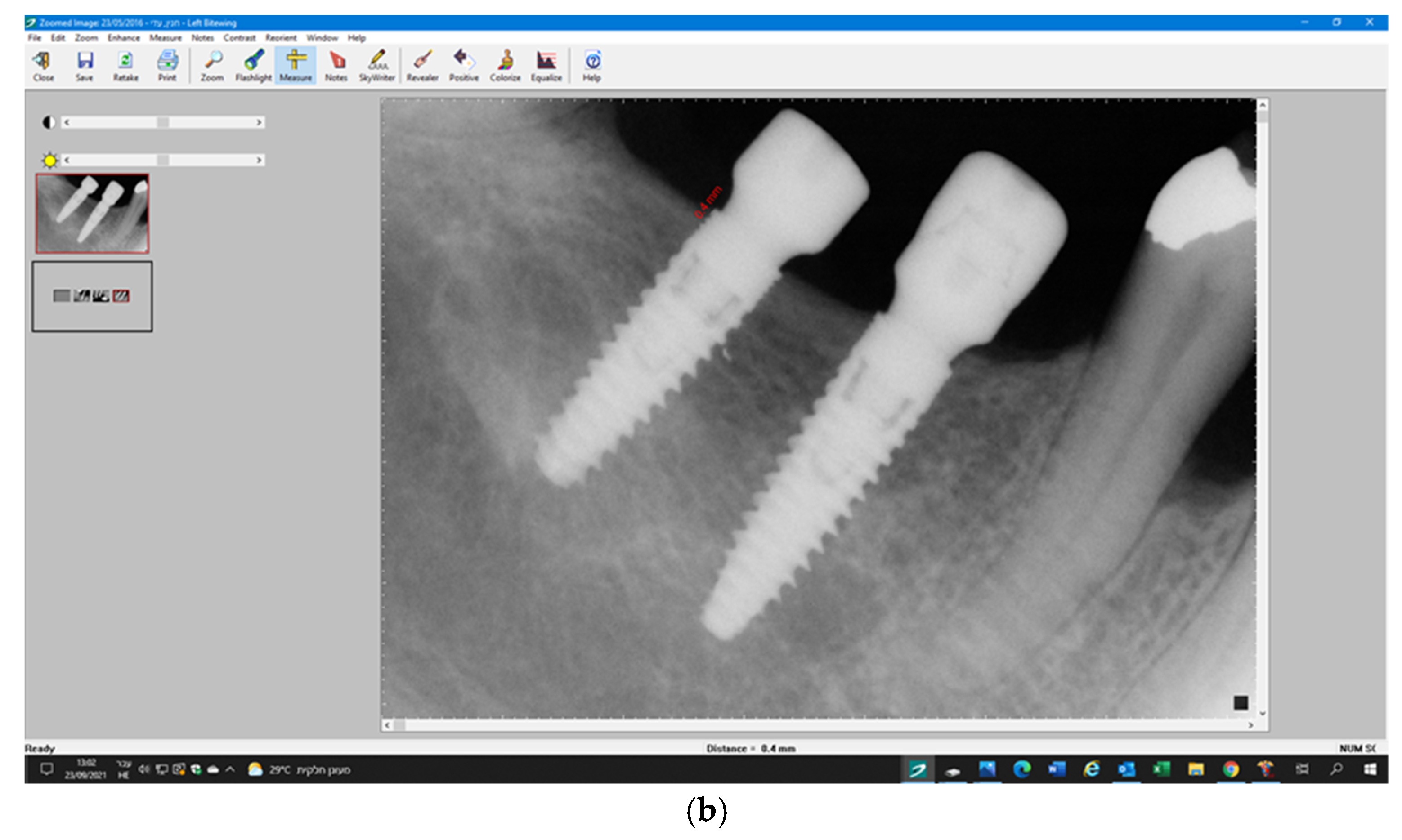
3.5. Radiographic Measurements
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Results
5.1. Implant Survival and Success Rate
5.2. Marginal Bone Level
5.3. Mechanical Complications
6. Discussion
6.1. Present Study Results
6.2. RCT—Similar Clinical Studies HEAs (Healing Abutments) vs. DEFs (Definitive Abutments)
6.3. Implant Neck Position Related to Crestal Bone
6.4. Platform Switch Design
6.5. Abutment Type
6.6. Time of Prosthetic Loading
6.7. Abutment Height and Emergence Profile
6.8. Cementation vs. Screw Retained
6.9. Smoking
6.10. Splinted Implants and Internal vs. External Connection
6.11. Clinical Relevance of the Study
6.12. Limitation of this Study
6.13. Strengths of the Study
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ericsson, I.; Persson, L.G.; Berglundh, T.; Marinello, C.P.; Lindhe, J.; Klinge, B. Different types of inflammatory reactions in peri-implant soft tissues. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1995, 22, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J. Dimension of the periimplant mucosa. Biological width revisited. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1996, 23, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J.; Ericsson, I.; Marinello, C.P.; Liljenberg, B.; Thornsen, P. The soft tissue barrier at implants and teeth. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1991, 2, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Annunziata, M.; Pesce, P.; Tommasato, G.; Nastri, L.; Guida, L. Influence of abutment material and modifications on peri-implant soft-tissue attachment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of histological animal studies. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, C.; Mangano, F.G.; Shibli, J.A.; Roth, L.A.; Addazio, G.D.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Peri-Implant Soft Tissues around Machined and Direct Metal Laser Sintered (DMLS) Healing Abutments in Humans. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leong, A.; De Kok, I.; Mendonça, D.; Cooper, L.F. Molecular Assessment of Human Peri-implant Mucosal Healing at Laser-Modified and Machined Titanium Abutments. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, J.-B.; Rheu, G.-B.; Kim, Y.-S.; Jeong, C.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Shin, S.-W. Influence of Implant transmucosal design on early peri-implant tissue responses in beagle dogs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.C.; Munoz, F.; Cantalapiedra, A.G.; Ramos, I.; Neves, M.; Blanco, J. Marginal bone and soft tissue behavior following platform switching abutment connection/disconnection- a dog model study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piattelli, A.; Vrespa, G.; Petrone, G.; Iezzi, G.; Annibali, S.; Scarano, A. Role of the Microgap Between Implant and Abutment: A Retrospective Histologic Evaluation in Monkeys. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degidi, M.; Nardi, D.; Piattelli, A. One abutment at one time: Non-removal of an immediate abutment and its effect on bone healing around subcrestal tapered implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, T.; Guazzi, P.; Samarani, R.; Maghaireh, H.; Grandi, G. Immediate positioning of definitive abutments versus repeated abutment replacements in immediately loaded implants: Effects on bone healing at the 1-year follow-up of a multicenter randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 5, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Canullo, L.; Bignozzi, I.; Cocchetto, R.; Cristalli, M.P.; Iannello, G. Immediate positioning of a definitive abutment versus repeated abutment replacements in post-extractive implants: 3-year follow-up of a randomized multicenter clinical trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2010, 3, 285–296. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsson, I.; Berglundh, T.; Wennström, J.; Lindhe, J. The peri-implant hard and soft tissues at different implant systems. A comparative study in the dog. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1996, 7, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, I.; Berglundh, T.; Moon, I.-S.; Lindhe, J. Peri-implant tissues at submerged and non-submerged titanium implants. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1999, 26, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.; Ferrari, D.; Herten, M.; Kirsch, A.; Schaer, A.; Schwarz, F. Influence of platform switching on crestal bone changes at non-submerged titanium implants: A histomorphometrical study in dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2007, 34, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.; Ferrari, D.; Mihatovic, I.; Sahm, N.; Schaer, A.; Schwarz, F. Stability of crestal bone level at platform-switched non-submerged titanium implants: A histomorphometrical study in dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atieh, M.A.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Atieh, A.H. Platform Switching for Marginal Bone Preservation Around Dental Implants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 1350–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, I.; Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J. The mucosal barrier following abutment dis/reconnection. An experimental study in dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1997, 24, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, T.; Guazzi, P.; Samarani, R.; Maghaireh, H.; Grandi, G. One abutment-one time versus a provisional abutment in immediately loaded post-extractive single implants: A 1-year follow-up of a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral Implant. 2014, 7, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Koutouzis, T.; Koutouzis, G.; Gadella, H.; Neiva, R. The Effect of Healing Abutment Reconnection and Disconnection on Soft and Hard Peri-implant Tissues: A Short-Term Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Leary, T.J.; Drake, R.B.; Naylor, J.E. The Plaque Control Record. J. Periodontol. 1972, 43, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Zarb, G.; Worthington, P.; Eriksson, A.R. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1986, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E. Peri-implant mucositis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S257–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.L. Peri-implantitis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S267–S290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Sanz-Sánchez, I.; Martín, C.; Blanco, J.; Sanz, M. The effect of one-time abutment placement on interproximal bone levels and peri-implant soft tissues: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 28, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Tello-González, G.; Lázaro-Calvo, P.; Gil Mur, F.J.; Ríos-Carrasco, B.; Fernández-Palacín, A.; Herrero-Climent, M. One Abutment One Time: A Multicenter, Prospective, Controlled, Randomized Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praça, L.D.F.G.; Teixeira, R.C.; Rego, R. Influence of abutment disconnection on peri-implant marginal bone loss: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2020, 31, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, G.; Bressan, E.; Grusovin, M.G.; d’Avenia, F.; Neumann, K.; Sbricoli, L.; Esposito, M. Do repeated changes of abutments have any influence on the stability of peri-implant tissues? Four-month post-loading preliminary results from a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 8, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, M.; Bressan, E.; Grusovin, M.G.; D’Avenia, F.; Neumann, K.; Sbricoli, L.; Luongo, G. Do repeated changes of abutments have any influence on the stability of peri-implant tissues? One-year post-loading results from a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bressan, E.; Grusovin, M.G.; D’Avenia, F.; Neumann, K.; Sbricoli, L.; Luongo, G.; Esposito, M. The influence of repeated abutment changes on peri-implant tissue stability: 3-year post-loading results from a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 373–390. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann, J.S.; Cochran, D.L.; Buser, D.; Schenk, R.K.; Schoolfield, J.D. Biologic Width around one- and two-piece titanium implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualini, F.; Salina, S.; Rigotti, F.; Mazzarini, C.; Longhin, D.; Grigoletto, M.; Trullenque-Eriksson, A.; Sbricoli, L.; Esposito, M. Subcrestal placement of dental implants with an internal conical connection of 0.5 mm versus 1.5 mm: Outcome of a multicentre randomised controlled trial 1 year after loading. Eur. J. Oral Implant. 2017, 10, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Degidi, M.; Nardi, D.; Daprile, G.; Piattelli, A. Nonremoval of Immediate Abutments in Cases Involving Subcrestally Placed Postextractive Tapered Single Implants: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 16, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricasulo, R.; Malchiodi, L.; Ghensi, P.; Fantozzi, G.; Cucchi, A. The influence of implant-abutment connection to peri-implant bone loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaska, I.; Tsaousoglou, P.; Vouros, I.; Konstantinidis, A.; Menexes, G. Influence of placement depth and abutment connection pattern on bone remodeling around 1-stage implants: A prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 27, e47–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göthberg, C.; Gröndahl, K.; Omar, O.; Thomsen, P.; Slotte, C. Bone and soft tissue outcomes, risk factors, and complications of implant-supported prostheses: 5-Years RCT with different abutment types and loading protocols. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; León-Cano, A.; Monje, A.; Ortega-Oller, I.; O′valle, F.; Catena, A. Abutment height influences the effect of platform switching on peri-implant marginal bone loss. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 27, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Pico, A.; Caneiro, L.; Nóvoa, L.; Batalla, P.; Martín-Lancharro, P. Effect of abutment height on interproximal implant bone level in the early healing: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 29, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóvoa, L.; Batalla, P.; Caneiro, L.; Pico, A.; Liñares, A.; Blanco, J. Influence of Abutment Height on Maintenance of Peri-implant Crestal Bone at Bone-Level Implants: A 3-Year Follow-up Study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2017, 37, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinato, S.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Bernardello, F.; Zaffe, D. Minimum Abutment Height to Eliminate Bone Loss: Influence of Implant Neck Design and Platform Switching. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borges, T.; Leitão, B.; Pereira, M.; Carvalho, Á.; Galindo-Moreno, P. Influence of the abutment height and connection timing in early peri-implant marginal bone changes: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, A.B.; Alshihri, A.; Kämmerer, P.W.; Araújo, M.G.; Gallucci, G.O. Histological and micro-CT analysis of peri-implant soft and hard tissue healing on implants with different healing abutments configurations. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkevicius, T.; Puisys, A.; Vindasiute, E.; Linkeviciene, L.; Apse, P. Does residual cement around implant-supported restorations cause peri-implant disease? A retrospective caseanalysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Souza Batista, V.E.; Verri, F.R.; Lemos, C.A.A.; Cruz, R.S.; Oliveira, H.F.F.; Gomes, J.M.L.; Pellizzer, E.P. Should the restoration of adjacent implants be splinted or nonsplinted? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Amri, M.D.; Kellesarian, S.V. Crestal Bone Loss Around Adjacent Dental Implants Restored with Splinted and Nonsplinted Fixed Restorations: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 26, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
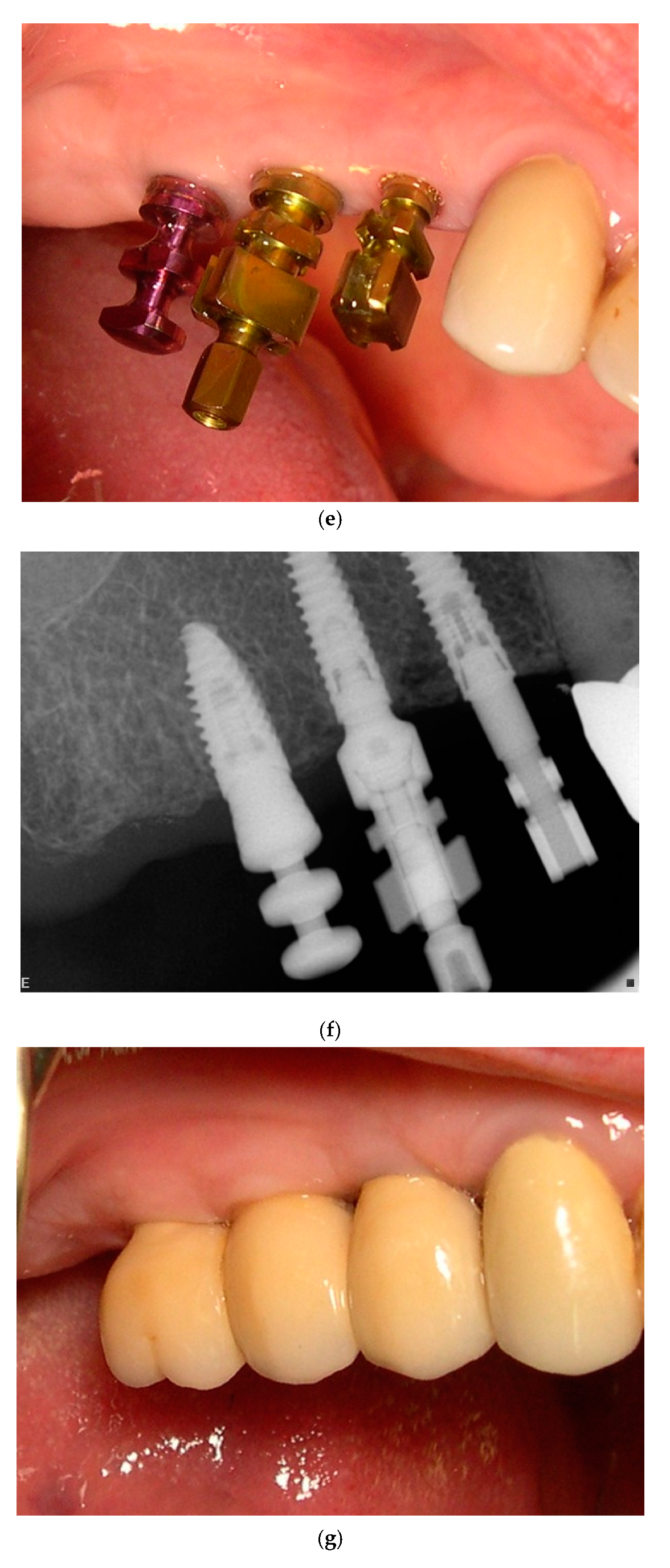
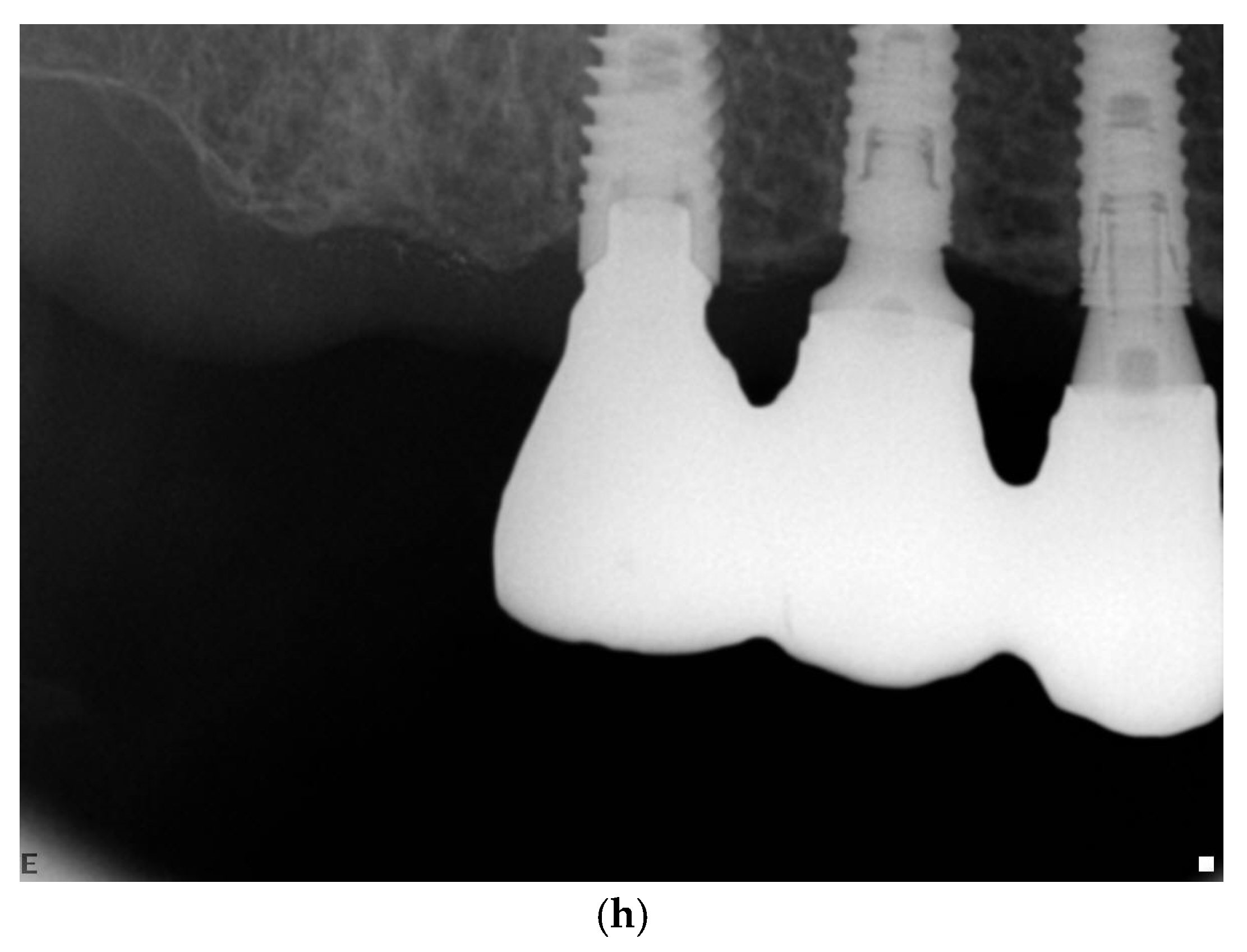
| Timeline | Preliminary Visit | Baseline Visit | 12 Weeks | 14–16 Weeks | 24 Weeks | 26–28 Weeks | 1 Year | 3 Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screen | x | |||||||
| Admission criteria | x | |||||||
| Informed consent | x | |||||||
| Demographics | x | |||||||
| Medical history | x | |||||||
| Periodontal examination | x | x | x | |||||
| Parallel periapical X-ray | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| SRP–hygiene reinforcement | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Implant placement | x | |||||||
| Impressions–maxilla | x | |||||||
| Impressions–mandible | x | |||||||
| Prosthetic delivery | x | x |
| No | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Female | 15 | 71 | |
| Male | 6 | 29 | |
| Implant position | |||
| Maxilla | 9 | 43 | |
| Mandible | 12 | 57 | |
| Diabetes | |||
| No | 18 | 86 | |
| HbA1c < 7 | 3 | 14 | |
| Periodontal diagnosis | |||
| Stage 1 | 2 | 10 | |
| (Tonetti 2018) | |||
| Stage 2 | 6 | 29 | |
| Stage 3 | 13 | 61 | |
| Bone Quality (Lekholm and Zarb 1985) | |||
| Type 1 | 2 | 10 | |
| Type 2 | 12 | 57 | |
| Type 3 | 7 | 33 | |
| Gingival biotype | |||
| Thick | 17 | 81 | |
| Thin | 4 | 19 | |
| Implant site, maxilla | |||
| First premolar | 4 | 9.5 | |
| Second premolar | 4 | 9.5 | |
| First molar | 7 | 16.5 | |
| Second molar | 3 | 7 | |
| Implant site, mandible | |||
| Central incisor | 2 | 5 | |
| First premolar | 2 | 5 | |
| Second premolar | 3 | 7 | |
| First molar | 8 | 19 | |
| Second molar | 9 | 21.5 |
| Abutment Type | Implant Diameter(mm) | 8 | 10 | 11.5 | 13 | 16 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiunit | |||||||
| 3.75 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 9 | |
| 4.2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 9 | |
| 5 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | |
| Healing cap | |||||||
| 3.75 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 8 | |
| 4.2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 7 | |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | |
| Total | 42 |
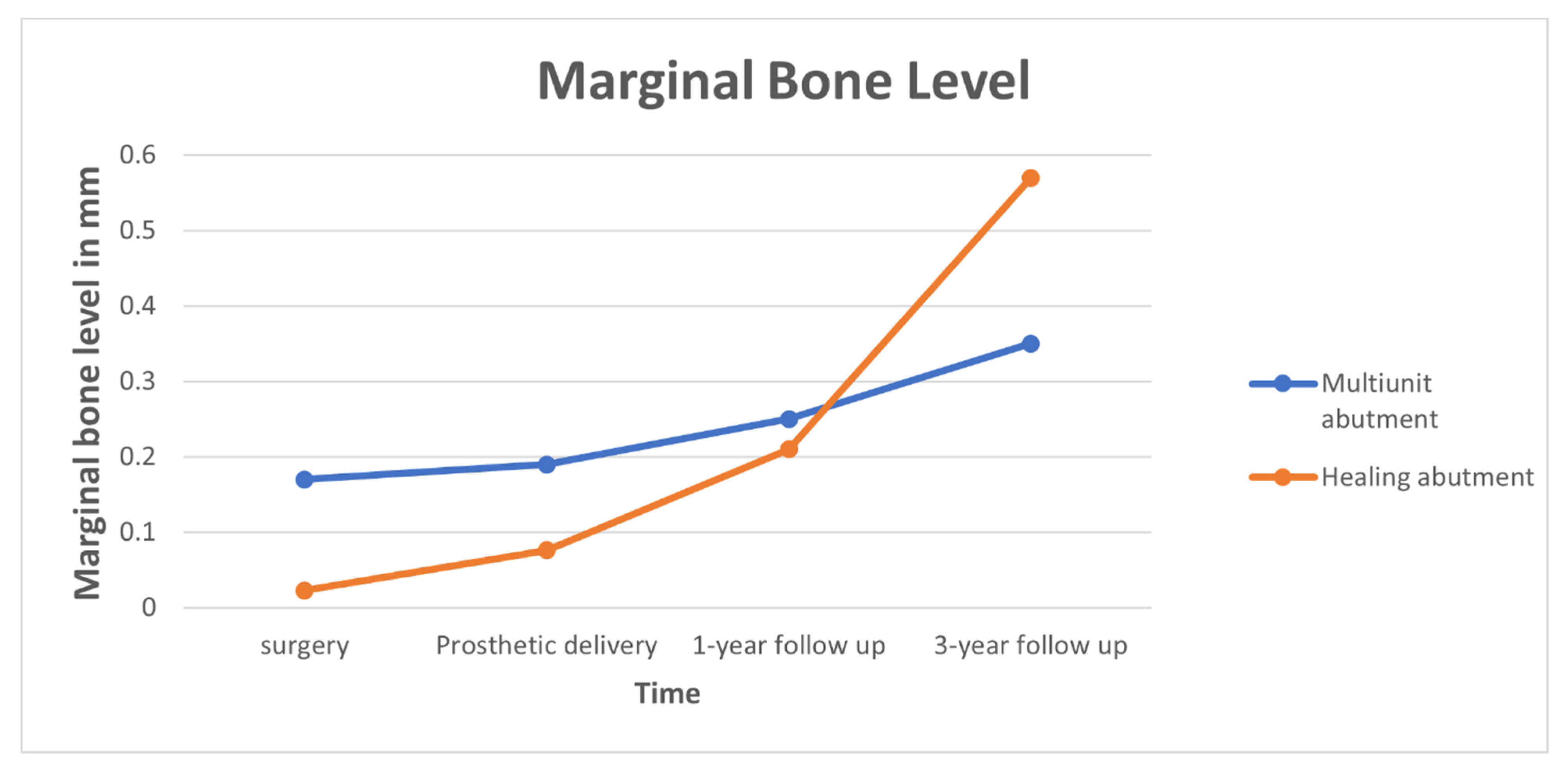
| Multiunit Abutment (Test) | Healing Abutment (Control) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD, mm | Range, mm | Mean ± SD, mm | Range, mm | |
| Surgery | 0.17 ± 0.41 | 0–0.9 | 0.023 ± 0.076 | 0–0.3 |
| Prosthetic delivery | 0.19 ± 0.45 | 0–1.0 | 0.076 ± 0.17 | 0–0.5 |
| 1-year follow-up | 0.52 ± 0.25 | 0–1.2 | 0.21 ± 0.41 | 0–1.0 |
| 3-year follow-up | 0.35 ± 0.69 | 0–1.7 | 0.57 ± 0.80 * | 0–1.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamudi, N.; Barnea, E.; Weinberg, E.; Laviv, A.; Mijiritsky, E.; Matalon, S.; Chaushu, L.; Kolerman, R. The Association of the One-Abutment at One-Time Concept with Marginal Bone Loss around the SLA and Platform Switch and Conical Abutment Implants. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010074
Hamudi N, Barnea E, Weinberg E, Laviv A, Mijiritsky E, Matalon S, Chaushu L, Kolerman R. The Association of the One-Abutment at One-Time Concept with Marginal Bone Loss around the SLA and Platform Switch and Conical Abutment Implants. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(1):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010074
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamudi, Nasreen, Eitan Barnea, Evgeny Weinberg, Amir Laviv, Eitan Mijiritsky, Shlomo Matalon, Liat Chaushu, and Roni Kolerman. 2022. "The Association of the One-Abutment at One-Time Concept with Marginal Bone Loss around the SLA and Platform Switch and Conical Abutment Implants" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 1: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010074
APA StyleHamudi, N., Barnea, E., Weinberg, E., Laviv, A., Mijiritsky, E., Matalon, S., Chaushu, L., & Kolerman, R. (2022). The Association of the One-Abutment at One-Time Concept with Marginal Bone Loss around the SLA and Platform Switch and Conical Abutment Implants. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(1), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010074







