Impact of Kidney Failure on the Severity of COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
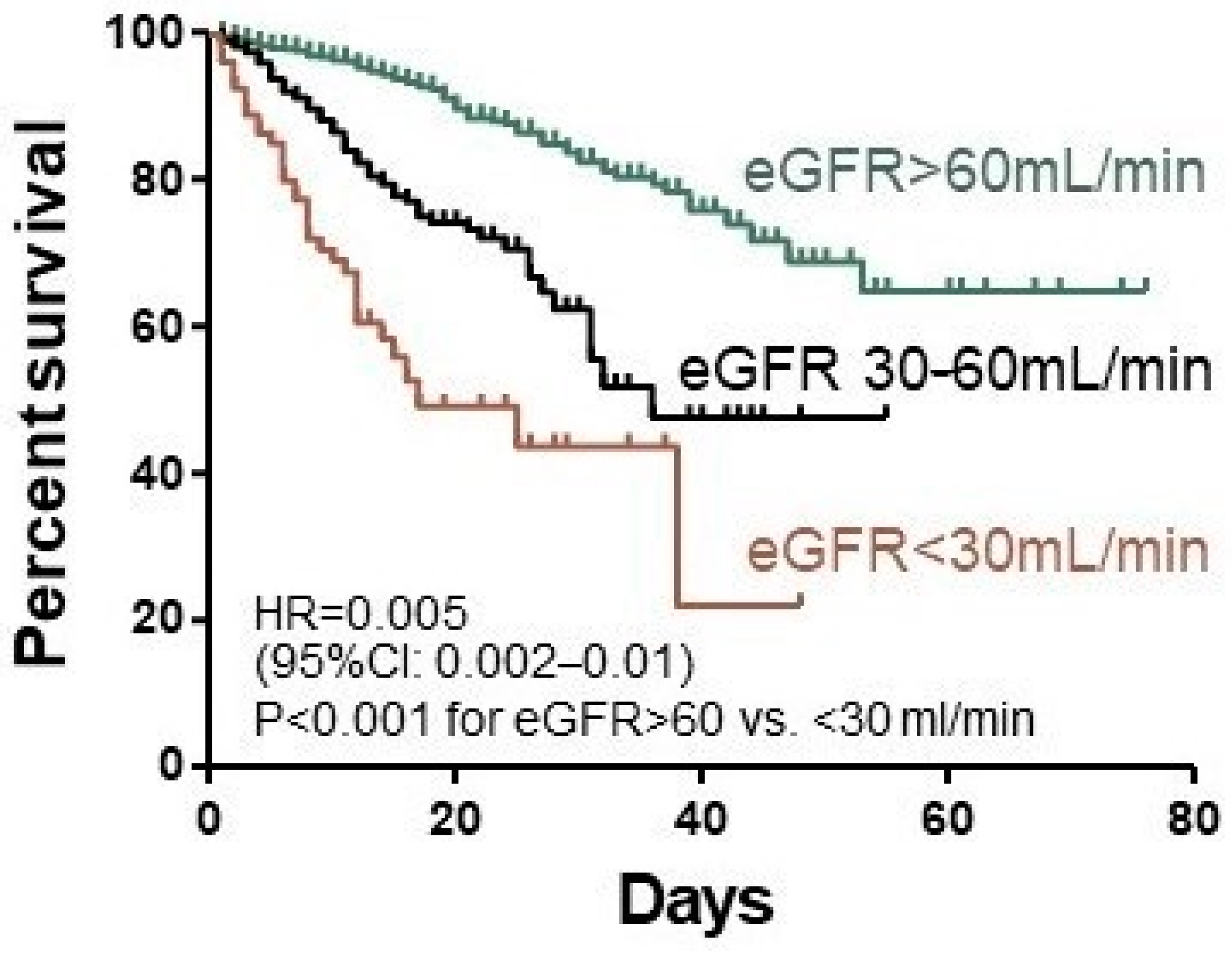
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/.WorldHealthOrganizationwebsite (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.H.; Liang, L.R.; Yang, C.Q.; Wang, W.; Cao, T.Z.; Li, M.; Guo, G.Y.; Du, J.; Zheng, C.L.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Predictors of mortality for patients with COVID-19 pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2: A prospective cohort study. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.; Hirsch, J.S.; Narasimhan, M.; Crawford, J.M.; McGinn, T.; Davidson, K.W.; the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium; Barnaby, D.P.; Becker, L.B.; Chelico, J.D.; et al. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA 2020, 323, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girndt, M.; Sester, M.; Sester, U.; Kaul, H.; Köhler, H. Molecular aspects of T- and B-cell function in uremia. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2001, 78, S206–S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed-Ahmed, M.; Narayanan, M. Immune Dysfunction and Risk of Infection in Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019, 26, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Clinical Management of Severe Acute Respiratory Infection (SARI) When COVID-19 Disease Is Suspected: Interim Guidance; Version 1.2; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 13 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Flisiak, R.; Horban, A.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Kozielewicz, D.; Pawłowska, M.; Parczewski, M.; Piekarska, A.; Simon, K.; Tomasiewicz, K.; Zarębska-Michaluk, D. Management of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Recommendations of the Polish Association of Epidemiologists and Infectiologists as of 31 March 2020. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020, 130, 352–357. [Google Scholar]
- Flisiak, R.; Horban, A.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Kozielewicz, D.; Pawłowska, M.; Parczewski, M.; Piekarska, A.; Simon, K.; Tomasiewicz, K.; Zarębska-Michaluk, D. Management of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Recommendations of the Polish Association of Epidemiologists and Infectiologists. Annex no. 1 as of 8 June 2020. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020, 130, 557–558. [Google Scholar]
- Flisiak, R.; Parczewski, M.; Horban, A.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Kozielewicz, D.; Pawłowska, M.; Piekarska, A.; Simon, K.; Tomasiewicz, K.; Zarębska-Michaluk, D. Management of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Recommendations of the Polish Association of Epidemiologists and Infectiologists. Annex no. 2 as of 13 October 2020. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020, 130, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.K.; Knicely, D.H.; Grams, M.E. Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and Management: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; He, Q. Mortality in chronic kidney disease patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Gu, J.; Hou, P.; Zhang, L.; Bai, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, P.; Zhao, X. Incidence, clinical characteristics and prognostic factor of patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERA-EDTA Council; ERACODA Working Group. Chronic kidney disease is a key risk factor for severe COVID-19: A call to action by the ERA-EDTA. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Gillies, C.L.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.; Chudasama, Y.; Coles, B.; Seidu, S.; Zaccardi, F.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K. Prevalence of co-morbidities and their association with mortality in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, B.M.; Lippi, G. Chronic kidney disease is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1193–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Esposito, P.; Taramasso, L.; Magnasco, L.; Saio, M.; Briano, F.; Russo, C.; Dettori, S.; Vena, A.; Di Biagio, A.; et al. GECOVID working group. Kidney disease and all-cause mortality in patients with COVID-19 hospitalized in Genoa, Northern Italy. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askari, H.; Sanadgol, N.; Azarnezhad, A.; Tajbakhsh, A.; Rafiei, H.; Safarpour, A.R.; Gheibihayat, S.M.; Raeis-Abdollahi, E.; Savardashtaki, A.; Ghanbariasad, A.; et al. Kidney diseases and COVID-19 infection: Causes and effect, supportive therapeutics and nutritional perspectives. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, A.; Javanmardi, F.; Pirbonyeh, N.; Akbari, A. Prevalence of Underlying Diseases in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 8, e35. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, S.; Turgutalp, K.; Arici, M.; Odabas, A.R.; Altiparmak, M.R.; Aydin, Z.; Cebeci, E.; Basturk, T.; Soypacaci, Z.; Sahin, G.; et al. Mortality analysis of COVID-19 infection in chronic kidney disease, haemodialysis and renal transplant patients compared with patients without kidney disease: A nationwide analysis from Turkey. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flythe, J.E.; Assimon, M.M.; Tugman, M.J.; Chang, E.H.; Gupta, S.; Shah, J.; Sosa, M.A.; Renaghan, A.D.; Melamed, M.L.; Wilson, F.P.; et al. STOP-COVID Investigators. Characteristics and Outcomes of Individuals With Pre-existing Kidney Disease and COVID-19 Admitted to Intensive Care Units in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 190–203.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coca, A.; Burballa, C.; Centellas-Pérez, F.J.; Pérez-Sáez, M.J.; Bustamante-Munguira, E.; Ortega, A.; Dueñas, C.; Arenas, M.D.; Pérez-Martínez, J.; Ruiz, G.; et al. Outcomes of COVID-19 among Hospitalized Patients with Non-dialysis CKD. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 615312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Luo, P.; Liu, Q.; Yang, C.; Xiong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. COVID-19 and chronic renal disease: Clinical characteristics and prognosis. QJM 2020, 113, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirjalili, H.; Dastgheib, S.A.; Shaker, S.H.; Bahrami, R.; Mazaheri, M.; Sadr-Bafghi, S.M.H.; Sadeghizadeh-Yazdi, J.; Neamatzadeh, H. Proportion and mortality of Iranian diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, hypertension and cardiovascular disease patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Jit, M.; Warren-Gash, C.; Guthrie, B.; Wang, H.H.X.; Mercer, S.W.; Sanderson, C.; McKee, M.; Troeger, C.; Ong, K.L.; et al. Centre for the Mathematical Modelling of Infectious Diseases COVID-19 working group. Global, regional, and national estimates of the population at increased risk of severe COVID-19 due to underlying health conditions in 2020: A modelling study. Lancet Glob. Health. 2020, 8, e1003–e1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Covassin, N.; Fan, Z.; Singh, P.; Gao, W.; Li, G.; Kara, T.; Somers, V.K. Association between Hypoxemia and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020, 95, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, B.; Li, L.; Ye, T.; Li, L.; Liu, D.; Gui, S.; Hu, Y.; et al. Factors associated with death outcome in patients with severe coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): A case-control study. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.M.; Weiner, D.E.; Aweh, G.; Miskulin, D.C.; Manley, H.J.; Stewart, C.; Ladik, V.; Hosford, J.; Lacson, E.C.; Johnson, D.S.; et al. COVID-19 Infection among US Dialysis Patients: Risk Factors and Outcomes from a National Dialysis Provider. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhard, C.; Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Neuhauser, H.K.; Morgan, R.; Klein, S.L. Impact of sex and gender on COVID-19 outcomes in Europe. Biol. Sex Differ. 2020, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tao, Z.W.; Wang, L.; Yuan, M.L.; Liu, K.; Zhou, L.; Wei, S.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.G.; et al. Analysis of factors associated with disease outcomes in hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus disease. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, A.M.; Robbins-Juarez, S.Y.; Stevens, J.S.; Ahn, W.; Rao, M.K.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Gharavi, A.G.; Mohan, S.; Husain, S.A. Presentation and Outcomes of Patients with ESKD and COVID-19. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.E.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H.K.; Kim, H.N.; Jang, S.Y.; Bae, M.H.; Yang, D.H.; Park, H.S.; Cho, Y.; Lee, B.Y.; et al. Daegu COVID-19 Research Project. Impact of Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Cardiovascular Diseases on Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 in Daegu Metropolitan City. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Nayan, N.; Nair, R.; Kumar, K.; Joshi, A.; Sharma, S.; Singh, J.; Kapoor, R. Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension Increase Risk of Death in Novel Corona Virus Patients Irrespective of Age: A Prospective Observational Study of Co-morbidities and COVID-19 from India. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2021, 3, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liang, W.; Jiang, M.; Guan, W.; Zhan, C.; Wang, T.; Tang, C.; Sang, L.; Liu, J.; Ni, Z.; et al. Medical Treatment Expert Group for COVID-19. Risk Factors of Fatal Outcome in Hospitalized Subjects with Coronavirus Disease 2019 from a Nationwide Analysis in China. Chest 2020, 158, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veklury—Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/veklury-epar-product-information_pl.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Pettit, N.N.; Pisano, J.; Nguyen, C.T.; Lew, A.K.; Hazra, A.; Sherer, R.; Mullane, K. Remdesivir Use in the Setting of Severe Renal Impairment: A Theoretical Concern or Real Risk? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, ciaa1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, S.; Menez, S.P.; Hanouneh, M.; Fine, D.M.; Crews, D.C.; Brennan, D.C.; Sperati, C.J.; Jaar, B.G. The COVID-19 nephrology compendium: AKI, CKD, ESKD and transplantation. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adapa, S.; Chenna, A.; Balla, M.; Merugu, G.P.; Koduri, N.M.; Daggubati, S.R.; Gayam, V.; Naramala, S.; Konala, V.M. COVID-19 Pandemic Causing Acute Kidney Injury and Impact on Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Renal Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2020, 12, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egbi, O.G.; Adejumo, O.A.; Akinbodewa, A.A. Coronavirus infection and kidney disease: A review of current and emerging evidence. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 37, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | eGFR > 60 mL/min n = 1867 | eGFR 30–60 mL/min n = 373 | eGFR < 30 mL/min n = 82 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 57.1 (16.5) | 73.4 (12.5) | 76.5 (12.9) | <0.001 |
| >70 years (%) | 397 (21.3) | 240 (64.3) | 57 (69.5) | <0.001 |
| Gender | ||||
| Female, n (%) | 869 (46.5) | 177 (47.5) | 44 (53.7) | 0.44 |
| Male, n (%) | 998 (53.5) | 196 (52.5) | 38 (46.3) | |
| Body mass index, mean (SD) | 27.8 (5.1) | 28.5 (5.3) | 29.2 (6.9) | 0.03 |
| Disease severity at the baseline, n (%) | ||||
| Oxygen saturation 91–95% | 596 (31.9) | 129 (34.6) | 24 (29.3) | 0.51 |
| Oxygen saturation ≤ 90% | 526 (28.2) | 169 (45.3) | 43 (52.4) | <0.001 |
| Score on ordinal scale, n (%) | ||||
| 3. Hospitalized, does not require oxygen supplementation and does not require medical care | 131 (7%) | 3 (1.9%) | 1 (1.2%) | <0.001 |
| 4. Hospitalized, requiring no oxygen supplementation, but requiring medical care | 833 (44.6) | 108 (29) | 21 (25.6) | <0.001 |
| 5. Hospitalized, requiring normal oxygen supplementation | 835 (44.7) | 244 (65.4) | 54 (65.9) | <0.001 |
| 6. Hospitalized, on non-invasive ventilation with high-flow oxygen equipment | 61 (3.3) | 14 (3.7) | 3 (3.7) | 0.88 |
| 7. Hospitalized, for invasive mechanical ventilation or ECMO | 6 (0.3) | 0 | 3 (3.7) | - |
| Concomitant medications, n (%) | 1071 (57.4) | 331 (88.7) | 69 (84.1) | <0.001 |
| Coexisting conditions, n (%) | 1285 (68.9) | 354 (94.9) | 77 (93.9) | <0.001 |
| Arterial hypertension | 719 (38.5) | 268 (71.8) | 53 (64.6) | <0.001 |
| Coronary artery disease | 155 (8.3) | 92 (24.7) | 27 (32.9) | <0.001 |
| Heart failure | 58 (3.1) | 51 (13.7) | 20 (24.4) | <0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 88 (4.7) | 59 (15.8) | 11 (13.4) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 268 (14.4) | 53 (14.2) | 30 (36.6) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 48 (2.6) | 23 (6.2) | 4 (4.9) | 0.001 |
| Malignancy | 99 (5.3) | 42 (11.3) | 9 (11) | <0.001 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 46 (2.5) | 29 (7.8) | 2 (2.4) | <0.001 |
| Bronchial asthma | 91 (4.9) | 20 (5.4) | 6 (7.3) | 0.58 |
| Chronic liver disease | 49 (2.6) | 7 (1.9) | 1 (1.2) | 0.53 |
| Dementia | 47 (2.5) | 21 (5.6) | 6 (7.3) | 0.001 |
| Hypothyroidism | 136 (7.3) | 28 (7.5) | 1 (1.2) | 0.10 |
| Characteristic | eGFR > 60 mL/min n = 1867 | eGFR 30–60 mL/min n = 373 | eGFR < 30 mL/min n = 82 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP mg/L, mean (SD) | 65.5 (73.8) | 91.7 (85.2) | 107 (85.2) | <0.001 |
| Procalcitonin ng/mL, mean (SD) | 0.28 (1.82) | 1.30 (6.8) | 2.83 (6.6) | <0.001 |
| Leukocytes 1/μL, mean (SD) | 6405 (3079) | 8962 (15028) | 8700 (4563) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocytes 1/μL, mean (SD) | 1311 (909) | 1532 (4064) | 1026 (630) | <0.001 |
| Neutrocytes 1/μL, mean (SD) | 4446 (2767) | 5717 (4575) | 7050 (4136) | <0.001 |
| Platelets 1000/μL, mean (SD) | 221 (90.5) | 202 (96) | 208.5 (125.1) | <0.001 |
| IL-6 pg/mL, mean (SD) | 47.0 (94.2) | 108.7 (209.1) | 211.2 (600.3) | <0.001 |
| D-dimers ng/mL, mean (SD) | 1638 (5448) | 2127 (3628) | 5113 (11612) | <0.001 |
| ALT IU/L, mean (SD) | 41 (39) | 36 (29) | 52 (223) | 0.001 |
| Medications | eGFR > 60 mL/min n = 1867 | eGFR 30–60 mL/min n = 373 | eGFR < 30 mL/min n = 82 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Related to COVID-19, n (%) | ||||
| Remdesivir | 454 (24.3) | 81 (21.7) | 5 (6.1) | <0.001 |
| Tocilizumab | 186 (9.9) | 79 (21.1) | 14 (17.1) | <0.001 |
| Dexamethason | 492 (26.3) | 137 (36.7) | 35 (42.7) | <0.001 |
| Convalescent plasma | 216 (11.6) | 44 (11.8) | 16 (19.5) | 0.09 |
| Low molecular weight heparin | 1306 (70) * | 299 (80.2) ** | 69 (84.1) *** | <0.001 |
| A eGFR > 60 mL/min | B eGFR 30–60 mL/min | C eGFR < 30 mL/min | Odds Ratio A vs. B | Odds Ratio B vs. C | Odds Ratio A vs. C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n = 1867 | n = 373 | n = 82 | |||
| Death, n (%) | 132 (7.1) | 82 (22) | 35 (42.7) | 0.27 (0.20–0.36) p < 0.001 | 0.38 (0.23–0.62) p < 0.001 | 0.10 (0.06–0.17) p < 0.001 |
| Death time, mean (SD), days | 14.4 (10.8) | 10.8 (8.2) | 8 (6.6) | <0.001 | p = 0.01 | p = 0.48 |
| Mechanical ventilation, n (%) | 86 (4.6) | 35 (9.4) | 10 (12.2) | 0.47 (0.31–0.70) p < 0.001 | 0.74 (0.35–1.57) p = 0.42 | 0.35 (0.17–0.70) p = 0.006 |
| Clinical improvement 14th day, n (%) | 1068 (57.2) | 158 (42.4) | 21 (25.6) | 1.81 (1.45–2.28) p < 0.001 | 2.13 (1.25–3.65) p = 0.006 | 3.89 (2.34–6.43) p < 0.001 |
| Clinical improvement 21st day, n (%) | 1467 (78.6) | 222 (59.5) | 34 (41.5) | 2.45 (1.97–3.15) p < 0.001 | 2.07 (1.28–3.37) p = 0.003 | 5.18 (3.29–8.14) p < 0.001 |
| Clinical improvement 28th day, n (%) | 1601 (85.8) | 262 (70.2) | 40 (48.8) | 2.55 (1.97–3.30) p < 0.001 | 2.47 (1.52–4.03) <0.001 | 6.32 (4.02–9.93) <0.001 |
| Characteristic | Died N = 249 | 28-Day Survive N = 2073 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| Mean (SD) | 74.2 (11.9) | 58.7 (16.9) | <0.001 |
| >70 years (%) | 158 (63.5) | 536 (25.9) | <0.001 |
| Gender | |||
| Female, n (%) | 95 (38.2) | 995 (48) | 0.04 |
| Male, n (%) | 154 (61.8) | 1078 (52) | 0.04 |
| Body mass index, mean (SD) | 27.9 (6.1) | 28 (5.1) | 0.47 |
| Disease severity at the baseline, n (%) | |||
| Oxygen saturation 91–95% | 51 (20.5) | 698 (33.7) | <0.001 |
| Oxygen saturation ≤ 90% | 169 (67.9) | 569 (27.5) | <0.001 |
| Score on ordinal scale, n (%) | |||
| 3. Hospitalized, does not require oxygen supplementation and does not require medical care | 1 (0.4) | 138 (6.7) | <0.001 |
| 4. Hospitalized, requiring no oxygen supplementation, but requiring medical care | 36 (14.5) | 926 (44.7) | |
| 5. Hospitalized, requiring normal oxygen supplementation | 174 (69.9) | 959 (46.3) | |
| 6. Hospitalized, on non-invasive ventilation with high-flow oxygen equipment | 30 (12) | 48 (2.3) | |
| 7. Hospitalized, for invasive mechanical ventilation or ECMO | 8 (3.2) | 1 (0.05) | |
| Concomitant medications, n (%) | 205 (82.3) | 1266 (61.1) | <0.001 |
| Coexisting conditions, n (%) | 233 (93.6) | 1483 (71.5) | <0.001 |
| Medication related to COVID-19, n (%) | |||
| Remdesivir | 61 (24.5) | 479 (23.1) | 0.68 |
| Tocilizumab | 55 (22.1) | 224 (10.8) | <0.001 |
| Dexamethason | 135 (54.2) | 529 (25.5) | <0.001 |
| Convalescent plasma | 50 (20.1) | 226 (10.9) | <0.001 |
| Low molecular weight heparin | 203 (81.5) | 1471 (71) | <0.001 |
| Antibiotics | 183 (73.5) | 1045 (50.4) | <0.001 |
| CRP mg/L, mean (SD) | 128.5 (91.7) | 64.2 (72.1) | <0.001 |
| Procalcitonin ng/mL, mean (SD) | 2.0 (6.2) | 0.36 (2.98) | <0.001 |
| Leukocytes 1/μL, mean (SD) | 10,622 (16,729) | 6450 (3963) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocytes 1/μL, mean (SD) | 1186 (2122) | 1354 (1798) | <0.001 |
| Neutrocytes 1/μL, mean (SD) | 7354 (5150) | 4441 (2796) | <0.001 |
| Platelets 1000/μL, mean (SD) | 210 (109) | 219 (91) | 0.008 |
| IL-6 pg/mL, mean (SD) | 192.4 (399.7) | 50.2 (107.4) | <0.001 |
| D-dimers ng/mL, mean (SD) | 4654 (9820) | 1507 (4722) | <0.001 |
| ALT IU/L, mean (SD) | 51 (133) | 39 (37) | 0.06 |
| eGFR < 30 mL/min/1,73 m2, n(%) | 35 (14.1) | 47 (2.3) | <0.001 |
| eGFR 30–60 mL/min/1,73 m2, n(%) | 82 (32.9) | 291 (13.7) | |
| eGFR > 60 mL/min/1,73 m2, n(%) | 132 (53.0) | 1735 (84.0) |
| Characteristic | Died N = 35 | 28-Day Survive N = 47 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| Mean (SD) | 80.7 (9.4) | 73.4 (14.2) | 0.02 |
| >70 years (%) | 30 (85.7) | 27 (57.4) | 0.007 |
| Gender | |||
| Female, n (%) | 19 (54.3) | 25 (53.2) | 1.00 |
| Male, n (%) | 16 (45.7) | 22 (46.8) | 1.00 |
| Body mass index, mean (SD) | 28.2 (7.7) | 29.6 (6.5) | 0.36 |
| Disease severity at the baseline, n (%) | |||
| Oxygen saturation 91–95% | 7 (20) | 17 (36.2) | 0.14 |
| Oxygen saturation ≤ 90% | 24 (68.6) | 19 (40.4) | 0.01 |
| Score on ordinal scale, n (%) | |||
| 3. Hospitalized, does not require oxygen supplementation and does not require medical care | 0 | 1 (2.1) | 1.00 |
| 4. Hospitalized, requiring no oxygen supplementation, but requiring medical care | 7 (20) | 14 (29.8) | 0.44 |
| 5. Hospitalized, requiring normal oxygen supplementation | 23 (65.7) | 31 (66) | 1.00 |
| 6. Hospitalized, on non-invasive ventilation with high-flow oxygen equipment | 2 (5.7) | 1 (2.1) | 0.57 |
| 7. Hospitalized, for invasive mechanical ventilation or ECMO | 3 (8.6) | 0 | 0.07 |
| Concomitant medications, n (%) | 27 (77.1) | 30 (63.8) | 0.23 |
| Coexisting conditions, n (%) | 33 (94.3) | 31 (66) | 0.002 |
| Medication related to COVID-19, n (%) | |||
| Remdesivir | 1 (2.9) | 4 (8.5) | 0.39 |
| Tocilizumab | 3 (8.6) | 11 (23.4) | 0.13 |
| Dexamethason | 15 (42.9) | 20 (42.6) | 1.00 |
| Convalescent plasma | 4 (11.4) | 12 (25.6) | 0.16 |
| Low molecular weight heparin | 28 (80) | 41 (87.2) | 0.54 |
| Antibiotics | 28 (65.1) | 27 (57.5) | 0.04 |
| CRP mg/l, mean (SD) | 120.1 (93) | 97.3 (78.6) | 0.28 |
| Procalcitonin ng/mL, mean (SD) | 4.75 (9.2) | 1.45 (3.3) | 0.07 |
| Leukocytes 1/μL, mean (SD) | 9351 (4540) | 8214 (4568) | 0.13 |
| Lymphocytes 1/μL, mean (SD) | 1042 (643) | 1014 (628) | 0.78 |
| Neutrocytes 1/μL, mean (SD) | 7803 (3871) | 6527 (4274) | 0.08 |
| Platelets 1000/μL, mean (SD) | 200 (103) | 215 (141) | 0.70 |
| IL-6 pg/mL, mean (SD) | 470.9 (1036.5) | 95.8 (164.8) | 0.24 |
| D-dimers ng/mL, mean (SD) | 4360 (4845) | 5696 (14,940) | 0.25 |
| ALT IU/L, mean (SD) | 86 (333) | 26 (19) | 0.43 |
| AST IU/L, mean (SD) | 72 (83) | 38 (33) | 0.03 |
| GGTP IU/L, mean (SD) | 33 (14) | 69 (76) | 0.60 |
| LDH IU/L, mean (SD) | 406 (205) | 414 (192) | 0.89 |
| INR, mean (SD) | 1.46 (0.83) | 1.16 (0.14) | 0.38 |
| Fibrinogen mg/dL, mean (SD) | 567 (150) | 553.7 (216.1) | 0.54 |
| Ferritin mcg/L, mean (SD) | 1828.2 (1507.3) | 1244 (1533.7) | 0.13 |
| Estimate of β | SE | tStat | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 854,282 | <0.001 | ||
| Age (per year) | 0.139 | 0.023 | 5991 | <0.001 |
| SpO2 (%) | −0.213 | 0.025 | −8578 | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils | 0.153 | 0.022 | 6915 | <0.001 |
| Platelets | −0.073 | 0.020 | −3655 | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.048 | 0.022 | 2123 | 0.034 |
| Ordinal scale (2) | −0.038 | 0.044 | −0.857 | 0.391 |
| Ordinal scale (3) | −0.055 | 0.042 | −1302 | 0.193 |
| Ordinal scale (4) | −0.160 | 0.081 | −1987 | 0.047 |
| Ordinal scale (5) | −0.195 | 0.080 | −2429 | 0.015 |
| Ordinal scale (6) | 0.027 | 0.033 | 0.821 | 0.411 |
| Arterial hypertension (no) | 0.069 | 0.021 | 3260 | 0.001 |
| Iscehmic heart disease (no) | −0.053 | 0.020 | −2637 | 0.008 |
| Malignancy (No) | −0.120 | 0.019 | −6384 | <0.001 |
| eGFR < 30 mL/min | 0.195 | 0.034 | 5649 | <0.001 |
| eGFR 30–60 mL/min | −0.090 | 0.034 | −2592 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarębska-Michaluk, D.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Rogalska, M.; Lorenc, B.; Rorat, M.; Szymanek-Pasternak, A.; Piekarska, A.; Berkan-Kawińska, A.; Sikorska, K.; Tudrujek-Zdunek, M.; et al. Impact of Kidney Failure on the Severity of COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10092042
Zarębska-Michaluk D, Jaroszewicz J, Rogalska M, Lorenc B, Rorat M, Szymanek-Pasternak A, Piekarska A, Berkan-Kawińska A, Sikorska K, Tudrujek-Zdunek M, et al. Impact of Kidney Failure on the Severity of COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(9):2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10092042
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarębska-Michaluk, Dorota, Jerzy Jaroszewicz, Magdalena Rogalska, Beata Lorenc, Marta Rorat, Anna Szymanek-Pasternak, Anna Piekarska, Aleksandra Berkan-Kawińska, Katarzyna Sikorska, Magdalena Tudrujek-Zdunek, and et al. 2021. "Impact of Kidney Failure on the Severity of COVID-19" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 9: 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10092042
APA StyleZarębska-Michaluk, D., Jaroszewicz, J., Rogalska, M., Lorenc, B., Rorat, M., Szymanek-Pasternak, A., Piekarska, A., Berkan-Kawińska, A., Sikorska, K., Tudrujek-Zdunek, M., Oczko-Grzesik, B., Bolewska, B., Czupryna, P., Kozielewicz, D., Kowalska, J., Podlasin, R., Kłos, K., Mazur, W., Leszczyński, P., ... Flisiak, R. (2021). Impact of Kidney Failure on the Severity of COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(9), 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10092042









