Long-Term Complications after Surgical or Medical Treatment of Predominantly Forefoot Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: 1 Year Follow Up
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
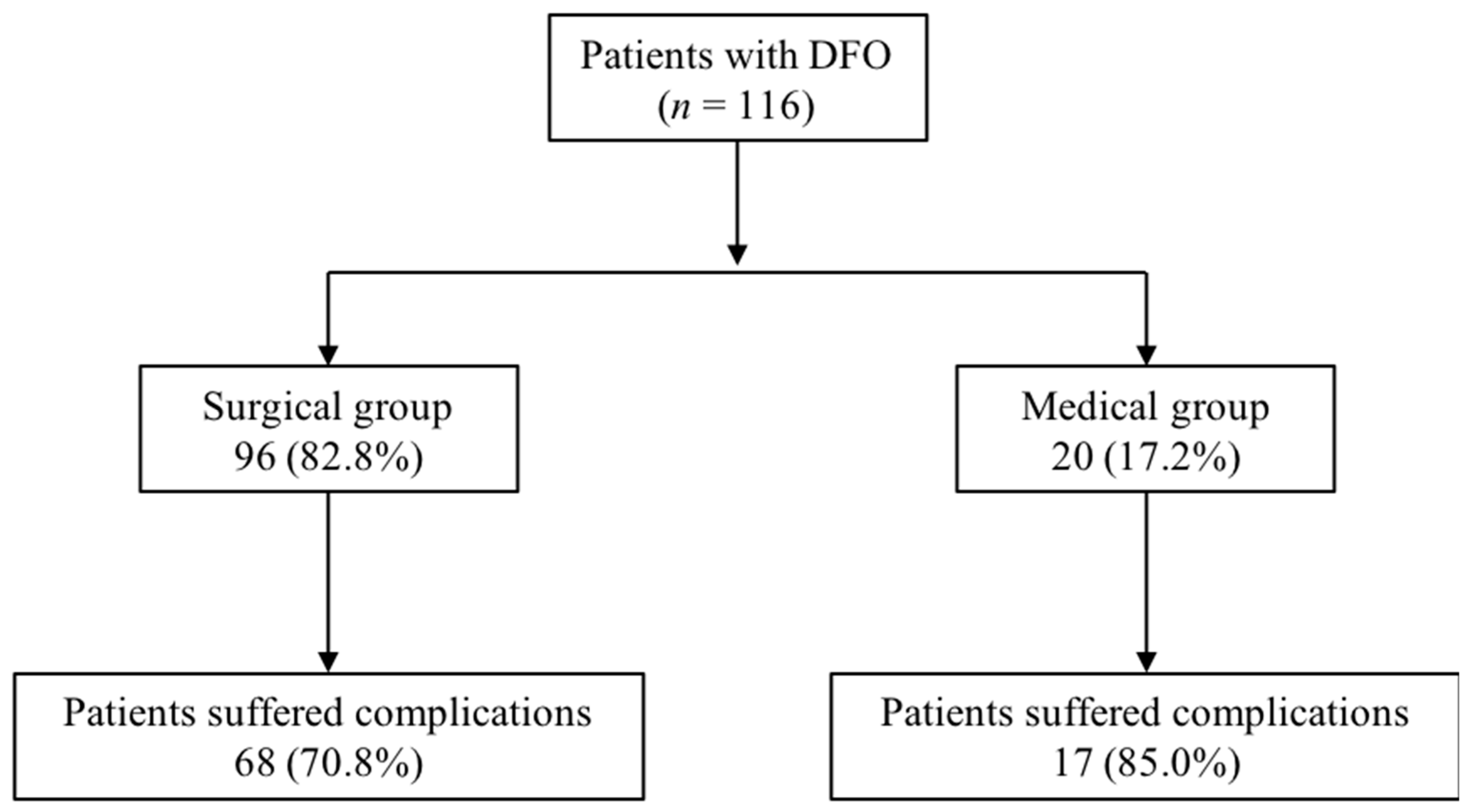
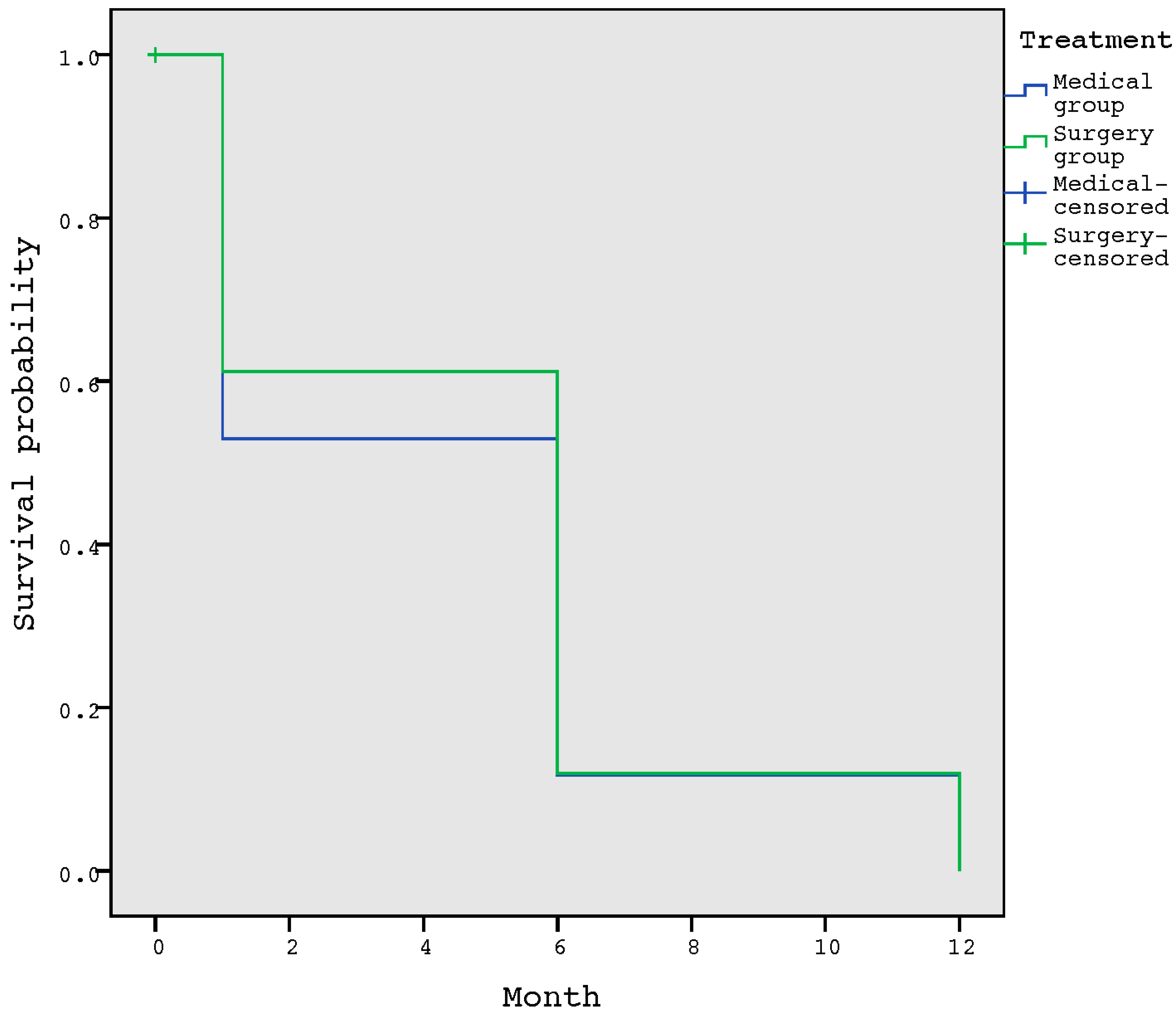
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahbazian, H.; Yazdanpanah, L.; Latifi, S.M. Risk assessment of patients with diabetes for foot ulcers according to risk classification consensus of International Working Group on Diabetic Foot (IWGDF). Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 29, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, B.A. Bone of contention: Diagnosing diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro-Martinez, J.L.; Aragon-Sanchez, J.; Garcia-Morales, E. Antibiotics versus conservative surgery for treating diabetic foot osteomyelitis: A randomized comparative trial. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon-Sanchez, J. Treatment of diabetic foot osteomyelitis: A surgical critique. Int. J. Low Extrem. Wounds 2010, 9, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Berendt, A.R.; Cornia, P.B.; Pile, J.C.; Peters, E.J.; Armstrong, D.G.; Deery, H.G.; Embil, J.M.; Joseph, W.S.; Karchmer, A.W.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, e132–e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Senneville, E.; Abbas, Z.G.; Aragon-Sanchez, J.; Diggle, M.; Embil, J.M.; Kono, S.; Lavery, L.A.; Malone, M.; van Asten, S.A.; et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of foot infection in persons with diabetes (IWGDF 2019 update). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36 (Suppl. 1), e3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Game, F.L. Osteomyelitis in the diabetic foot: Diagnosis and management. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 97, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embil, J.M.; Rose, G.; Trepman, E.; Math, M.C.; Duerksen, F.; Simonsen, J.N.; Nicolle, L.E. Oral antimicrobial therapy for diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Foot Ankle Int. 2006, 27, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senneville, E.; Lombart, A.; Beltrand, E.; Valette, M.; Legout, L.; Cazaubiel, M.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Fontaine, P. Outcome of diabetic foot osteomyelitis treated nonsurgically: A retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Game, F.L.; Jeffcoate, W.J. Primarily non-surgical management of osteomyelitis of the foot in diabetes. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon-Sanchez, F.J.; Cabrera-Galvan, J.J.; Quintana-Marrero, Y.; Hernandez-Herrero, M.J.; Lazaro-Martinez, J.L.; Garcia-Morales, E.; Beneit-Montesinos, J.V.; Armstrong, D.G. Outcomes of surgical treatment of diabetic foot osteomyelitis: A series of 185 patients with histopathological confirmation of bone involvement. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1962–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro Martinez, J.L.; Garcia Alvarez, Y.; Tardaguila-Garcia, A.; Garcia Morales, E. Optimal management of diabetic foot osteomyelitis: Challenges and solutions. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Berendt, A.R.; Deery, H.G.; Embil, J.M.; Joseph, W.S.; Karchmer, A.W.; LeFrock, J.K.; Lew, D.P.; Mader, J.T.; Norden, C.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117 (Suppl. 7), 212S–238S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitocco, D.; Spanu, T.; Di Leo, M.; Vitiello, R.; Rizzi, A.; Tartaglione, L.; Fiori, B.; Caputo, S.; Tinelli, G.; Zaccardi, C.; et al. Diabetic foot infections: A comprehensive overview. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23 (Suppl. 2), 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky, B.A. Treating diabetic foot osteomyelitis primarily with surgery or antibiotics: Have we answered the question? Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Peters, E.J.; Senneville, E.; Berendt, A.R.; Embil, J.M.; Lavery, L.A.; Urbančič-Rovan, V.; Jeffcoate, W.J. Expert opinion on the management of infections in the diabetic foot. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2012, 28 (Suppl. 1), 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutluoglu, M.; Lipsky, B.A. Non-surgical treatment of diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardaguila-Garcia, A.; Garcia Alvarez, Y.; Garcia-Morales, E.; Alvaro-Afonso, F.J.; Sanz-Corbalan, I.; Lazaro-Martinez, J.L. Utility of Blood Parameters to Detect Complications during Long-Term Follow-Up in Patients with Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragon-Sanchez, J.; Lipsky, B.A.; Lazaro-Martinez, J.L. Diagnosing diabetic foot osteomyelitis: Is the combination of probe-to-bone test and plain radiography sufficient for high-risk inpatients? Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardaguila-Garcia, A.; Sanz-Corbalan, I.; Garcia-Morales, E.; Garcia-Alvarez, Y.; Molines-Barroso, R.J.; Lazaro-Martinez, J.L. Diagnostic Accuracy of Bone Culture versus Biopsy in Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2021, 34, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalani, M.; Brismar, K.; Fagrell, B.; Ostergren, J.; Jorneskog, G. Transcutaneous oxygen tension and toe blood pressure as predictors for outcome of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norgren, L.; Hiatt, W.R.; Dormandy, J.A.; Nehler, M.R.; Harris, K.A.; Fowkes, F.G. Inter-Society Consensus for the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease (TASC II). J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 45 (Suppl. S), S5–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchliffe, R.J.; Forsythe, R.O.; Apelqvist, J.; Boyko, E.J.; Fitridge, R.; Hong, J.P.; Katsanos, K.; Mills, J.L.; Nikol, S.; Reekers, J.; et al. Guidelines on diagnosis, prognosis, and management of peripheral artery disease in patients with foot ulcers and diabetes (IWGDF 2019 update). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36 (Suppl. 1), e3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanas, N.; Ziegler, D. New diagnostic tests for diabetic distal symmetric polyneuropathy. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2011, 25, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardaguila-Garcia, A.; Lazaro-Martinez, J.L.; Sanz-Corbalan, I.; Garcia-Alvarez, Y.; Alvaro-Afonso, F.J.; Garcia-Morales, E. Correlation between Empirical Antibiotic Therapy and Bone Culture Results in Patients with Osteomyelitis. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2019, 32, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, A.; Nguyen, S.; Devemy, F.; Topolinski, H.; Valette, M.; Cazaubiel, M.; Fayard, A.; Beltrand, E.; Lemaire, C.; Senneville, E. Six-week versus twelve-week antibiotic therapy for nonsurgically treated diabetic foot osteomyelitis: A multicenter open-label controlled randomized study. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 302–307, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Netten, J.J.; Bus, S.A.; Apelqvist, J.; Lipsky, B.A.; Hinchliffe, R.J.; Game, F.; Rayman, G.; Lazzarini, P.A.; Forsythe, R.O.; Peters, E.J.G.; et al. Definitions and criteria for diabetic foot disease. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36 (Suppl. 1), e3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bus, S.A.; Lavery, L.A.; Monteiro-Soares, M.; Rasmussen, A.; Raspovic, A.; Sacco, I.C.N.; van Netten, J.J. Guidelines on the prevention of foot ulcers in persons with diabetes (IWGDF 2019 update). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36 (Suppl. 1), e3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical, A. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Tardaguila-Garcia, A.; Garcia-Alvarez, Y.; Sanz-Corbalan, I.; Alvaro-Afonso, F.J.; Molines-Barroso, R.J.; Lazaro-Martinez, J.L. Role of inflammatory markers in the healing time of diabetic foot osteomyelitis treated by surgery or antibiotics. J. Wound Care 2020, 29, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro-Martinez, J.L.; Tardaguila-Garcia, A.; Garcia-Klepzig, J.L. Diagnostic and therapeutic update on diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2017, 64, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardaguila-Garcia, A.; Sanz-Corbalan, I.; Garcia-Alamino, J.M.; Ahluwalia, R.; Uccioli, L.; Lazaro-Martinez, J.L. Medical versus Surgical Treatment for the Management of Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bus, S.A.; van Netten, J.J.; Lavery, L.A.; Monteiro-Soares, M.; Rasmussen, A.; Jubiz, Y.; Price, P.E. IWGDF guidance on the prevention of foot ulcers in at-risk patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32 (Suppl. 1), 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Game, F.; Jeffcoate, W. MRSA and osteomyelitis of the foot in diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2004, 21 (Suppl. 4), 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesens, O.; Desbiez, F.; Theis, C.; Ferry, T.; Bensalem, M.; Laurichesse, H.; Tauveron, I.; Beytout, J.; Sánchez, J.A.; The Working Group on Diabetic Osteomyelitis. Staphylococcus aureus-Related Diabetic Osteomyelitis: Medical or Surgical Management? A French and Spanish Retrospective Cohort. Int. J. Low Extrem. Wounds 2015, 14, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardaguila-Garcia, A.; Sanz-Corbalan, I.; Molines-Barroso, R.J.; Alvaro-Afonso, F.J.; Garcia-Alvarez, Y.; Lazaro-Martinez, J.L. Complications associated with the approach to metatarsal head resection in diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Int. Wound J. 2019, 16, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Surgery Group n (%) | Medical Group n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male: 79 (82.3) Female: 17 (17.7) | Male: 17 (85.0) Female: 3 (15.0) |
| Type of DM | Type 1: 11 (11.5) Type 2: 85 (88.6) | Type 1: 1 (5.0) Type 2: 19 (95.0) |
| PAD (mild and moderate ischemia) | 39 (40.6) | 9 (45.0) |
| Neuropathy | 96 (100.0) | 20 (100.0) |
| Location of the ulcer | Forefoot: 89 (92.7) Mindfoot: 5 (5.2) Hindfoot: 2 (2.1) | Forefoot: 18 (90.0) Mindfoot: none Hindfoot: 2 (10.0) |
| Variable | Surgery Group Mean ± SD | Medical Group Mean ± SD |
| Age (years) | 63.1 ± 10.1 | 62.0 ± 10.3 |
| DM duration (years) | 17.8 ± 12.7 | 15.8 ± 10.0 |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.2 ± 6.5 | 7.8 ± 1.7 |
| Body mass index (Kg/cm2) | 28.3 ± 4.6 | 28.4 ± 8.8 |
| Ulcer duration (weeks) | 15.8 ± 34.6 | 15.0 ± 16.4 |
| Surgical Group n = 96 | Medical Group n = 20 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visit 2 | Visit 3 | Visit 4 | Total | Visit 2 | Visit 3 | Visit 4 | Total | |
| n = 26 | n = 48 | n = 47 | n = 8 | n = 14 | n = 8 | |||
| Re-ulceration | 14 | 31 | 20 | 65 | 4 | 8 | 3 | 15 |
| n (%) | (53.8) | (64.6) | (42.6) | (67.7) | (50) | (57.1) | (37.5) | (75) |
| New case DFO | 5 | 9 | 17 | 31 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| n (%) | (19.2) | (18.7) | (36.2) | (32.2) | (12.5) | (7.1) | (37.5) | (25) |
| DFO recurrence | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | none | 2 | none | 2 |
| n (%) | (11.5) | (4.2) | (6.4) | (8.4) | (14.3) | (10) | ||
| Ulcer recurrence | 2 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 1 | none | 3 |
| n (%) | (7.7) | (6.2) | (6.4) | (8.4) | (25) | (7.1) | (15) | |
| Other | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 1 | none | none | 1 |
| n (%) | (7.7) | (4.2) | (2.1) | (5.2) | (12.5) | (5) | ||
| Soft tissue infection | none | 1 | none | 1 | none | none | none | none |
| n (%) | (2.1) | (1.1) | ||||||
| Major amputation | none | none | 2 | 2 | none | none | 1 | 1 |
| n (%) | (4.3) | (2.1) | (12.5) | (5) | ||||
| Death | none | none | 1 | 1 | none | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| n (%) | (2.1) | (1.1) | (14.3) | (12.5) | (15) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tardáguila-García, A.; García-Álvarez, Y.; García-Morales, E.; López-Moral, M.; Sanz-Corbalán, I.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.L. Long-Term Complications after Surgical or Medical Treatment of Predominantly Forefoot Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: 1 Year Follow Up. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091943
Tardáguila-García A, García-Álvarez Y, García-Morales E, López-Moral M, Sanz-Corbalán I, Lázaro-Martínez JL. Long-Term Complications after Surgical or Medical Treatment of Predominantly Forefoot Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: 1 Year Follow Up. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(9):1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091943
Chicago/Turabian StyleTardáguila-García, Aroa, Yolanda García-Álvarez, Esther García-Morales, Mateo López-Moral, Irene Sanz-Corbalán, and José Luis Lázaro-Martínez. 2021. "Long-Term Complications after Surgical or Medical Treatment of Predominantly Forefoot Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: 1 Year Follow Up" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 9: 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091943
APA StyleTardáguila-García, A., García-Álvarez, Y., García-Morales, E., López-Moral, M., Sanz-Corbalán, I., & Lázaro-Martínez, J. L. (2021). Long-Term Complications after Surgical or Medical Treatment of Predominantly Forefoot Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: 1 Year Follow Up. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(9), 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091943










