The Tacrolimus Metabolism Rate and Dyslipidemia after Kidney Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
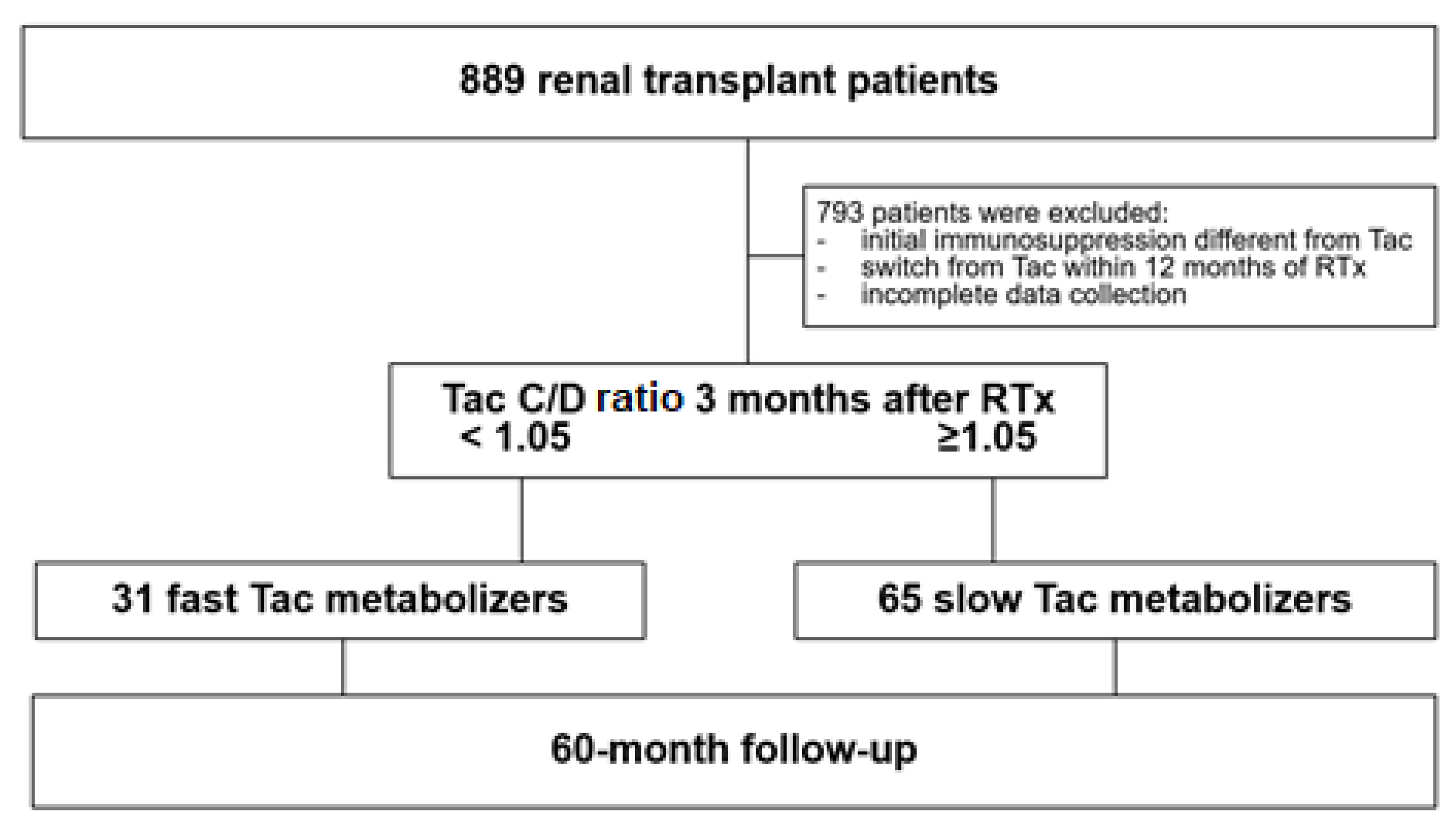
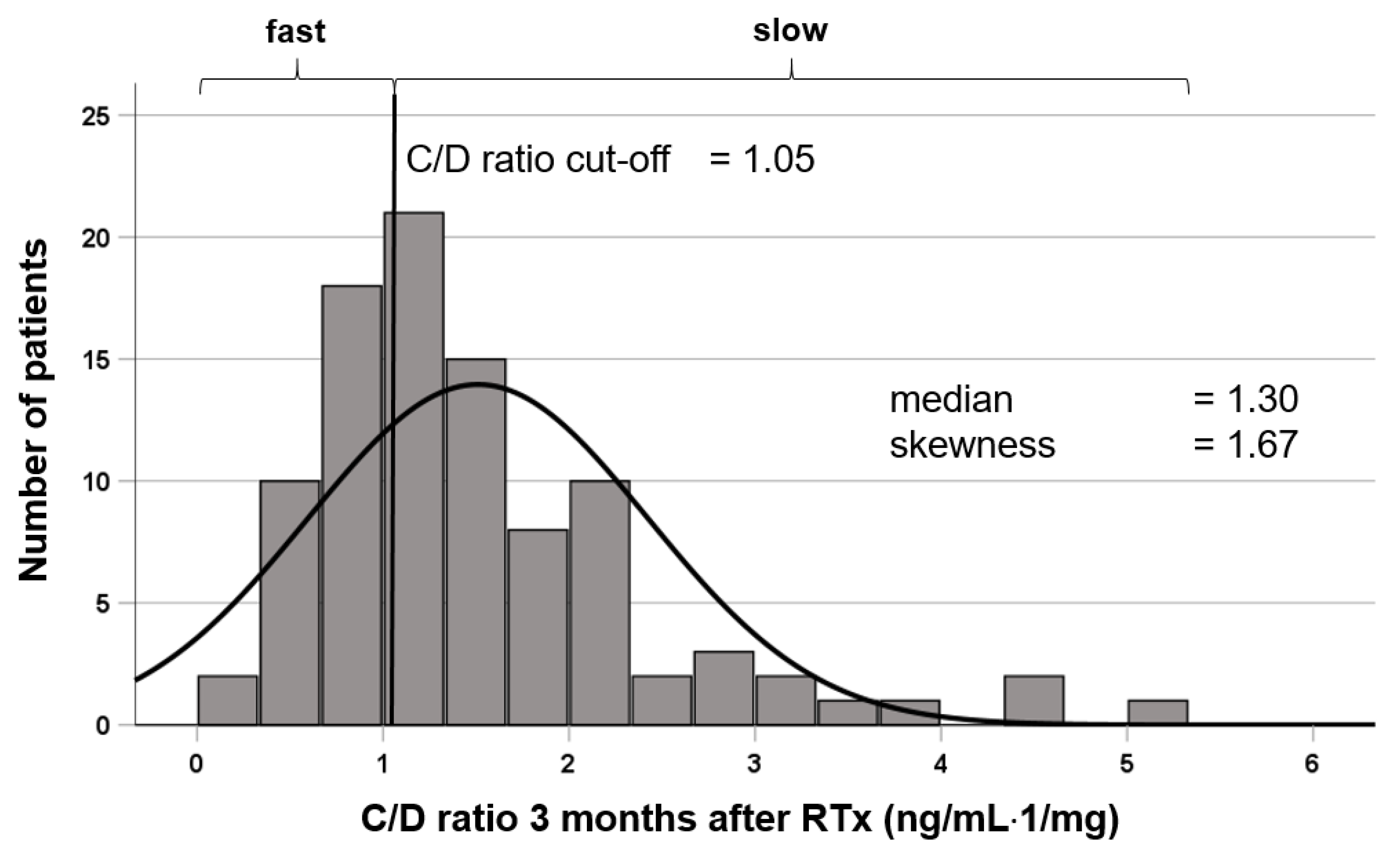
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
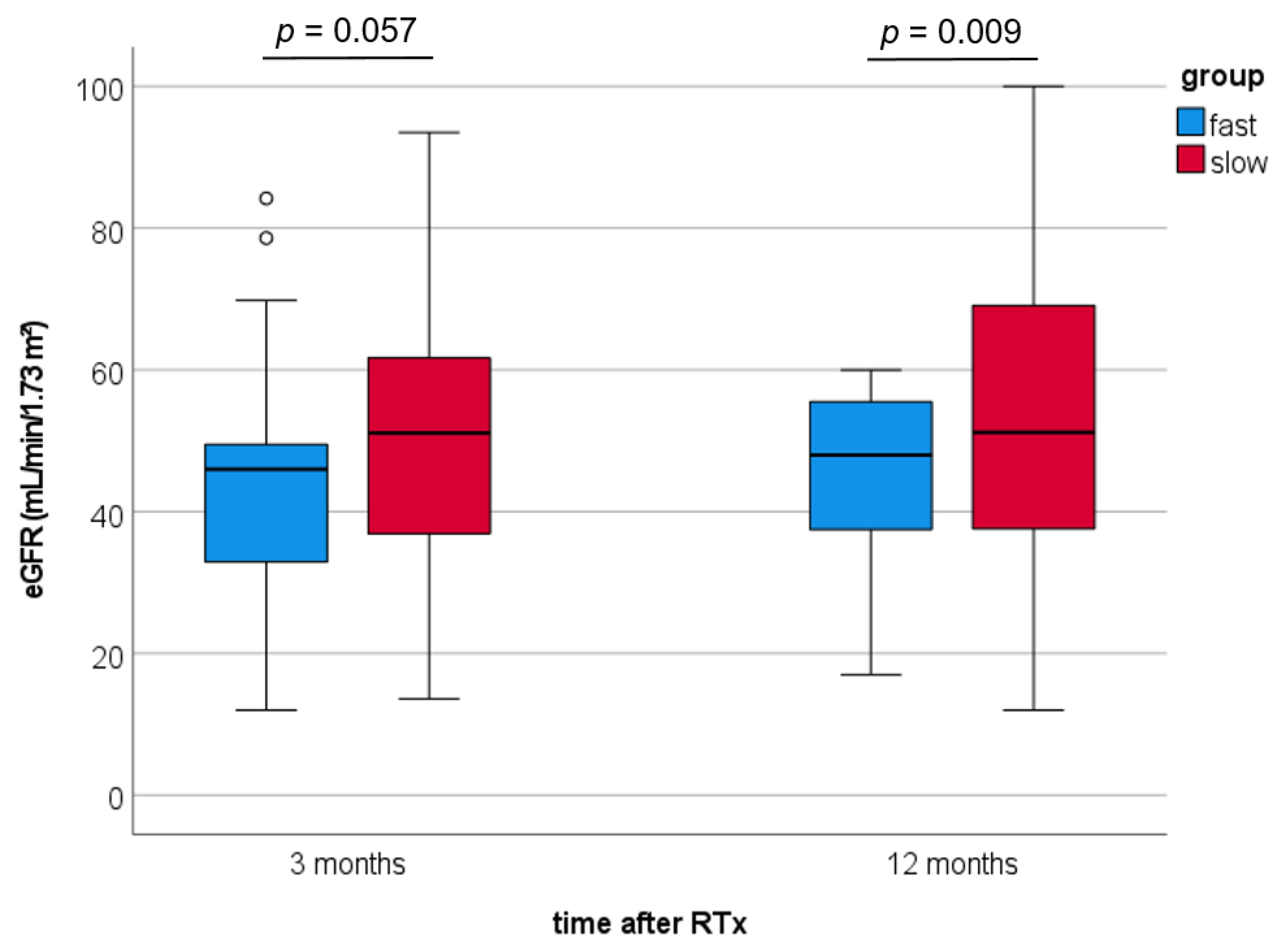
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfe, R.A.; Ashby, V.B.; Milford, E.L.; Ojo, A.O.; Ettenger, R.E.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Held, P.J.; Port, F.K. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Task Force Members; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG); ESC National Cardiac Societies. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Atherosclerosis 2019, 290, 140–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium; Matsushita, K.; van der Velde, M.; Astor, B.C.; Woodward, M.; Levey, A.S.; de Jong, P.E.; Coresh, J.; Gansevoort, R.T. Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: A collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiske, B.L.; Chakkera, H.A.; Roel, J. Explained and unexplained ischemic heart disease risk after renal transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massy, Z.A.; Ferrieres, J.; Bruckert, E.; Lange, C.; Liabeuf, S.; Velkovski-Rouyer, M.; Stengel, B.; Collaborators, C.-R. Achievement of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Targets in CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte-Nutgen, K.; Tholking, G.; Steinke, J.; Pavenstadt, H.; Schmidt, R.; Suwelack, B.; Reuter, S. Fast Tac Metabolizers at Risk—It is Time for a C/D Ratio Calculation. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouve, T.; Fonrose, X.; Noble, J.; Janbon, B.; Fiard, G.; Malvezzi, P.; Stanke-Labesque, F.; Rostaing, L. The TOMATO study (TacrOlimus MetabolizAtion in kidney TransplantatiOn): Impact of the concentration-dose ratio on death-censored graft survival. Transplantation 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tholking, G.; Fortmann, C.; Koch, R.; Gerth, H.U.; Pabst, D.; Pavenstadt, H.; Kabar, I.; Husing, A.; Wolters, H.; Reuter, S.; et al. The tacrolimus metabolism rate influences renal function after kidney transplantation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Hansrivijit, P.; Kovvuru, K.; Kanduri, S.R.; Bathini, T.; Pivovarova, A.; Smith, J.R.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Impacts of High Intra- and Inter-Individual Variability in Tacrolimus Pharmacokinetics and Fast Tacrolimus Metabolism on Outcomes of Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiske, B.; Zeier, M.; Craig, J.; Ekberg, H.; Garvey, C.; Green, M.; Abariga, S. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Transplant Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9 (Suppl. 3), S1–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou, F.N.; Guillaud, O.; Erard-Poinsot, D.; Chambon-Augoyard, C.; Thimonier, E.; Vallin, M.; Boillot, O.; Dumortier, J. Tacrolimus exposure after liver transplantation for alcohol-related liver disease: Impact on complications. Transpl. Immunol. 2019, 56, 101227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matas, A.J.; Gillingham, K.J.; Humar, A.; Kandaswamy, R.; Sutherland, D.E.; Payne, W.D.; Dunn, T.B.; Najarian, J.S. 2202 kidney transplant recipients with 10 years of graft function: What happens next? Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 2410–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte-Nutgen, K.; Tholking, G.; Suwelack, B.; Reuter, S. Tacrolimus—Pharmacokinetic Considerations for Clinicians. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholking, G.; Schutte-Nutgen, K.; Schmitz, J.; Rovas, A.; Dahmen, M.; Bautz, J.; Jehn, U.; Pavenstadt, H.; Heitplatz, B.; Van Marck, V.; et al. A Low Tacrolimus Concentration/Dose Ratio Increases the Risk for the Development of Acute Calcineurin Inhibitor-Induced Nephrotoxicity. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholking, G.; Schmidt, C.; Koch, R.; Schuette-Nuetgen, K.; Pabst, D.; Wolters, H.; Kabar, I.; Husing, A.; Pavenstadt, H.; Reuter, S.; et al. Influence of tacrolimus metabolism rate on BKV infection after kidney transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, M.; Gorska, M.; Nowicka, Z.; Edyko, K.; Edyko, P.; Wislicki, S.; Zawiasa-Bryszewska, A.; Strzelczyk, J.; Matych, J.; Kurnatowska, I. Tacrolimus: Influence of the Posttransplant Concentration/Dose Ratio on Kidney Graft Function in a Two-Year Follow-Up. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2019, 44, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeland, E.J.; Robertsen, I.; Hermann, M.; Midtvedt, K.; Storset, E.; Gustavsen, M.T.; Reisaeter, A.V.; Klaasen, R.; Bergan, S.; Holdaas, H.; et al. High Tacrolimus Clearance Is a Risk Factor for Acute Rejection in the Early Phase After Renal Transplantation. Transplantation 2017, 101, e273–e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzler, M.A.; Johnston, K.; Axelrod, D.; Gheorghian, A.; Lentine, K.L. Associations of renal function at 1-year after kidney transplantation with subsequent return to dialysis, mortality, and healthcare costs. Transplantation 2011, 91, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehn, U.; Schutte-Nutgen, K.; Strauss, M.; Kunert, J.; Pavenstadt, H.; Tholking, G.; Suwelack, B.; Reuter, S. Antihypertensive Treatment in Kidney Transplant Recipients-A Current Single Center Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, M.R.; Burgess, E.D.; Cooper, J.E.; Fenves, A.Z.; Goldsmith, D.; McKay, D.; Mehrotra, A.; Mitsnefes, M.M.; Sica, D.A.; Taler, S.J. Assessment and management of hypertension in transplant patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, Z.; Catapano, A.L.; De Backer, G.; Graham, I.; Taskinen, M.R.; Wiklund, O.; Agewall, S.; Alegria, E.; Chapman, M.J.; Durrington, P.; et al. ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: The Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 1769–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, P.; Navalesi, R. The metabolic effects of cyclosporin and tacrolimus. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2000, 23, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artz, M.A.; Boots, J.M.; Ligtenberg, G.; Roodnat, J.I.; Christiaans, M.H.; Vos, P.F.; Blom, H.J.; Sweep, F.C.; Demacker, P.N.; Hilbrands, L.B. Improved cardiovascular risk profile and renal function in renal transplant patients after randomized conversion from cyclosporine to tacrolimus. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCune, T.R.; Thacker, L.R., II; Peters, T.G.; Mulloy, L.; Rohr, M.S.; Adams, P.A.; Yium, J.; Light, J.A.; Pruett, T.; Gaber, A.O.; et al. Effects of tacrolimus on hyperlipidemia after successful renal transplantation: A Southeastern Organ Procurement Foundation multicenter clinical study. Transplantation 1998, 65, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, K.; Meier-Kriesche, H.U.; Schold, J.D.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Halloran, P.F.; Ekberg, H. Effect of different immunosuppressive regimens on the evolution of distinct metabolic parameters: Evidence from the Symphony study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, J.M.; van Duijnhoven, E.M.; Christiaans, M.H.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.; van Hooff, J.P. Glucose metabolism in renal transplant recipients on tacrolimus: The effect of steroid withdrawal and tacrolimus trough level reduction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciftci, H.S.; Ayna, T.K.; Caliskan, Y.K.; Turkmen, A.; Gurtekin, M. Lipid parameters, doses and blood levels of calcineurin inhibitors in renal transplant patients. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 28, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuypers, D.R.; Claes, K.; Evenepoel, P.; Maes, B.; Vanrenterghem, Y. Clinical efficacy and toxicity profile of tacrolimus and mycophenolic acid in relation to combined long-term pharmacokinetics in de novo renal allograft recipients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 75, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, D.R.; Naesens, M.; de Jonge, H.; Lerut, E.; Verbeke, K.; Vanrenterghem, Y. Tacrolimus dose requirements and CYP3A5 genotype and the development of calcineurin inhibitor-associated nephrotoxicity in renal allograft recipients. Ther. Drug Monit. 2010, 32, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartmann, I.; Schutte-Nutgen, K.; Suwelack, B.; Reuter, S. Early postoperative calculation of the tacrolimus concentration-to-dose ratio does not predict outcomes after kidney transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2020, 33, 689–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostaing, L.; Bunnapradist, S.; Grinyo, J.M.; Ciechanowski, K.; Denny, J.E.; Silva, H.T., Jr.; Budde, K.; Envarsus Study, G. Novel Once-Daily Extended-Release Tacrolimus Versus Twice-Daily Tacrolimus in De Novo Kidney Transplant Recipients: Two-Year Results of Phase 3, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholking, G.; Reuter, S. Alternative Viewpoint on Tacrolimus Concentration-to-Dose Ratios in Kidney Transplant Recipients and Relationship to Clinical Outcomes. Pharmacotherapy 2019, 39, 1036–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, F.E.; Carthon, C.E.; Hagopian, J.C.; Horwedel, T.A.; January, S.E.; Malone, A. Tacrolimus Concentration-to-Dose Ratios in Kidney Transplant Recipients and Relationship to Clinical Outcomes. Pharmacotherapy 2019, 39, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Fast Metabolizers (n = 31) | Slow Metabolizers (n = 65) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 51.9 ± 12.6 | 51.0 ± 14.8 | 0.770 a |
| Sex (m/f) | 22 (71%)/9 (29%) | 45 (69%)/20 (31%) | 1 b |
| Weight (kg) | 79.7 ± 19.2 | 74.1 ± 14.7 | 0.158 a |
| Height (cm) | 176 ± 11 | 172 ± 9 | 0.108 a |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.4 ± 4.4 | 24.7 ± 4.2 | 0.503 a |
| Living donor transplantation | 10 (32%) | 16 (25%) | 0.467 b |
| ESP | 4 (13%) | 9 (14%) | 1 b |
| Cold ischemic time (h) | 8.1 ± 5.8 | 8.6 ± 4.7 | 0.698 a |
| Warm ischemic time (min) | 31.6 ± 5.9 | 32.6 ± 7.5 | 0.483 a |
| DGF | 2 (7%) | 9 (14%) | 0.494 b |
| Time on dialysis | 47.5 ± 42.0 | 59.5 ± 44.6 | 0.206 a |
| Previous transplantation | 5 | 5 | 0.284 b |
| One previous transplantation | 3 | 5 | 0.168 b |
| Two previous transplantations | 2 | 0 | |
| Combined liver transplantation | 1 | 2 | 1 b |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (16%) | 2 (3%) | 0.034 b |
| Arterial hypertension | 25 (81%) | 59 (91%) | 0.193 b |
| BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 | 18 (58%) | 36 (55%) | 0.830 b |
| Donor Characteristics | |||
| Donor age | 51.0 ± 15.3 | 53.4 ± 14.5 | 0.475 a |
| Donor sex (m/f) | 10 (32%)/21 (68%) | 30 (46%)/35 (54%) | 0.269 b |
| Fast Metabolizers (n = 31) | Slow Metabolizers (n = 65) | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tac trough level M3 (ng/mL) | 6.8 ± 2.4 | 8.4 ± 2.8 | 0.004 a |
| Tac daily dose M3 (mg) | 9.0 (3–20) | 5 (2–12) | <0.001 b |
| Tac C/D ratio M3 (ng/mL/mg) | 0.79 (0.28–1.00) | 1.57 (1.05–5.15) | <0.001 b |
| Tac daily dose M12 (mg) | 7 (2–18) | 3.75 (1–11) | <0.001 b |
| Tac trough level M12 (ng/mL) | 6.8 ± 2.1 | 6.3 ± 2.1 | 0.401 a |
| Tac C/D ratio M12 (ng/mL/mg) | 0.96 (0.28–2.85) | 1.59 (0.24–7.60) | <0.001 b |
| Prednisolone M3 (mg) | 7.5 (0–50) | 10 (5–30) | 0.015 b |
| Prednisolone M12 (mg) | 5 (0–20) | 5 (3–20) | 0.594 b |
| Statin at discharge | 8 (26%) | 5 (8%) | 0.024 c |
| Statin M3 | 10 (32%) | 18 (28%) | 0.640 c |
| Statin M12 | 18 (58%) | 39 (60%) | 1 c |
| Complications | |||
| CNIT until M12 | 4 (12.9%) | 4 (6.2%) | 0.268 c |
| BKVN until M12 | 3 (9.7%) | 1 (1.5%) | 0.097 c |
| AR until M12 | 6 (19.4%) | 6 (9.2%) | 0.193 c |
| NODAT until M3 | 4 (12.9%) | 7 (10.8%) | 0.743 c |
| NODAT between M3 and M12 | 5 (16.1%) | 10 (15.4%) | 1 c |
| TC | |||
| At RTx | 195 (85–455) | 200 (119–395) | 0.422 b |
| 3 months | 215 (119–284) | 224 (125–353) | 0.285 b |
| 12 months | 209 (109–353) | 202 (121–378) | 0.443 b |
| LDL-C | |||
| At RTx | 102 (11–372) | 111 (39–274) | 0.565 b |
| 3 months | 117 (57–194) | 122 (56–229) | 0.347 b |
| 12 months | 116 (43–269) | 114 (47–266) | 0.919 b |
| HDL-C | |||
| At RTx | 45 (25–87) | 48 (22–119) | 0.464 b |
| 3 months | 49 (31–91) | 52 (28–91) | 0.426 b |
| 12 months | 46 (31–108) | 51 (24–104) | 0.148 b |
| TG | |||
| At RTx | 158 (57–469) | 159 (67–885) | 0.763 b |
| 3 months | 221 (90–545) | 186 (46–1326) | 0.283 b |
| 12 months | 206 (68–774) | 160 (77–663) | 0.138 b |
| Fast Metabolizers (n = 31) | Slow Metabolizers (n = 65) | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CV risk level according to the ESC guidelines | |||
| Moderate-risk | 4 (12.9%) | 7 (10.8%) | 0.259 |
| High-risk | 17 (54.8%) | 34 (52.3%) | |
| Very-high-risk | 10 (32.3%) | 14 (21.5%) | |
| LDL-C target level achieved * | |||
| Individual level achieved | 2 (6.5%) | 3 (4.6%) | 0.657 |
| Moderate-risk achieved | 8 (25.8%) | 12 (18.5%) | 0.342 |
| High-risk level achieved | 2 (6.5%) | 1 (1.5%) | |
| Very-high-risk level achieved | 0 | 0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thölking, G.; Schulte, C.; Jehn, U.; Schütte-Nütgen, K.; Pavenstädt, H.; Suwelack, B.; Reuter, S. The Tacrolimus Metabolism Rate and Dyslipidemia after Kidney Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143066
Thölking G, Schulte C, Jehn U, Schütte-Nütgen K, Pavenstädt H, Suwelack B, Reuter S. The Tacrolimus Metabolism Rate and Dyslipidemia after Kidney Transplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(14):3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143066
Chicago/Turabian StyleThölking, Gerold, Christian Schulte, Ulrich Jehn, Katharina Schütte-Nütgen, Hermann Pavenstädt, Barbara Suwelack, and Stefan Reuter. 2021. "The Tacrolimus Metabolism Rate and Dyslipidemia after Kidney Transplantation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 14: 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143066
APA StyleThölking, G., Schulte, C., Jehn, U., Schütte-Nütgen, K., Pavenstädt, H., Suwelack, B., & Reuter, S. (2021). The Tacrolimus Metabolism Rate and Dyslipidemia after Kidney Transplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(14), 3066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143066






