Silica-Based RO Membranes for Separation of Acidic Solution
Abstract
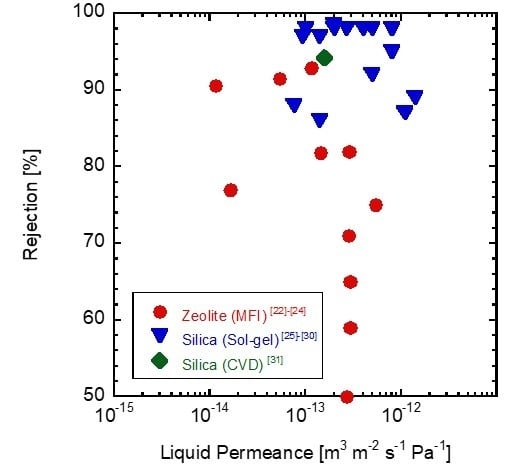
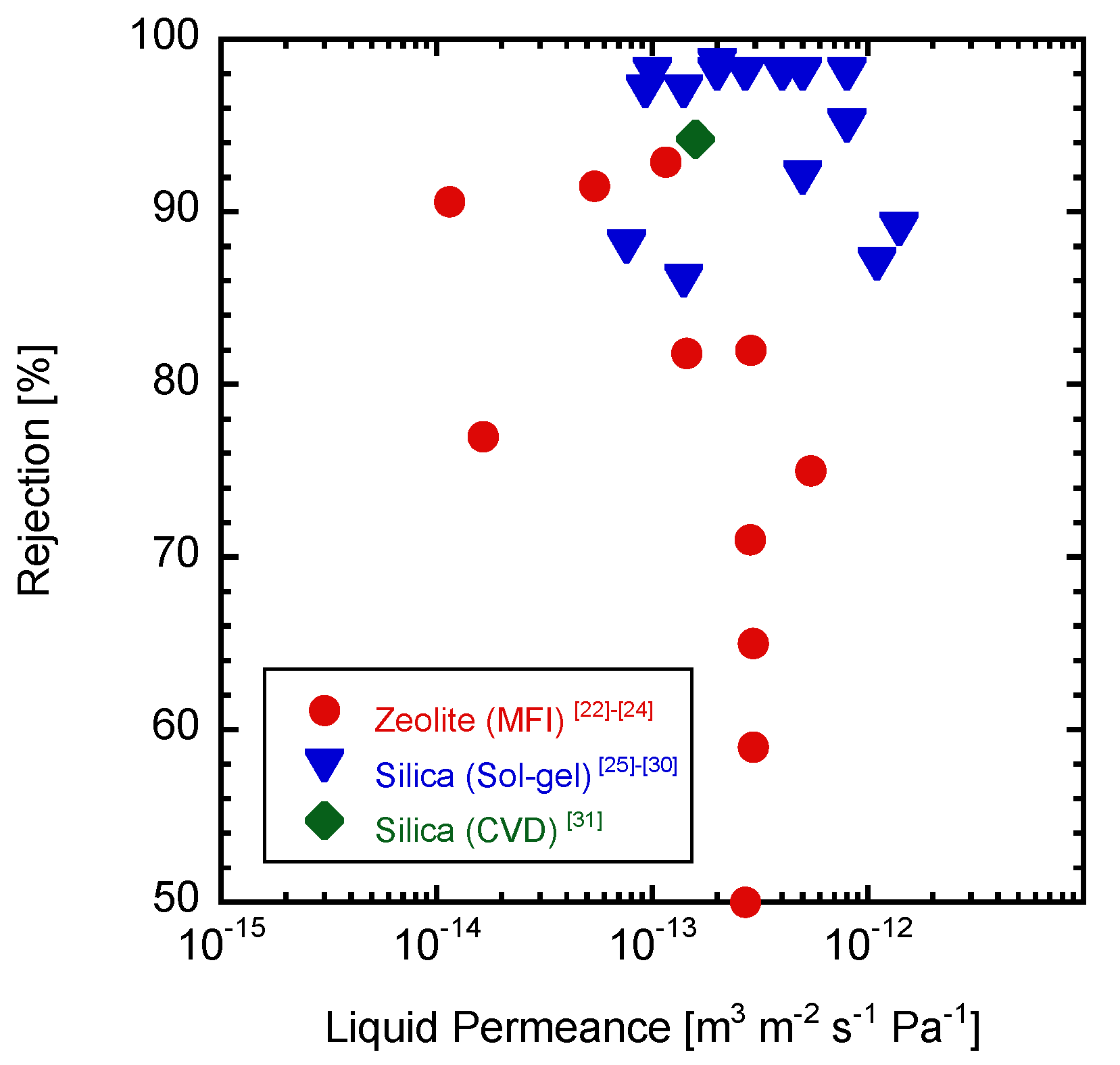
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Porous Support
2.1.1. γ-alumina Coating
2.1.2. Silica Coating
2.2. Characterization
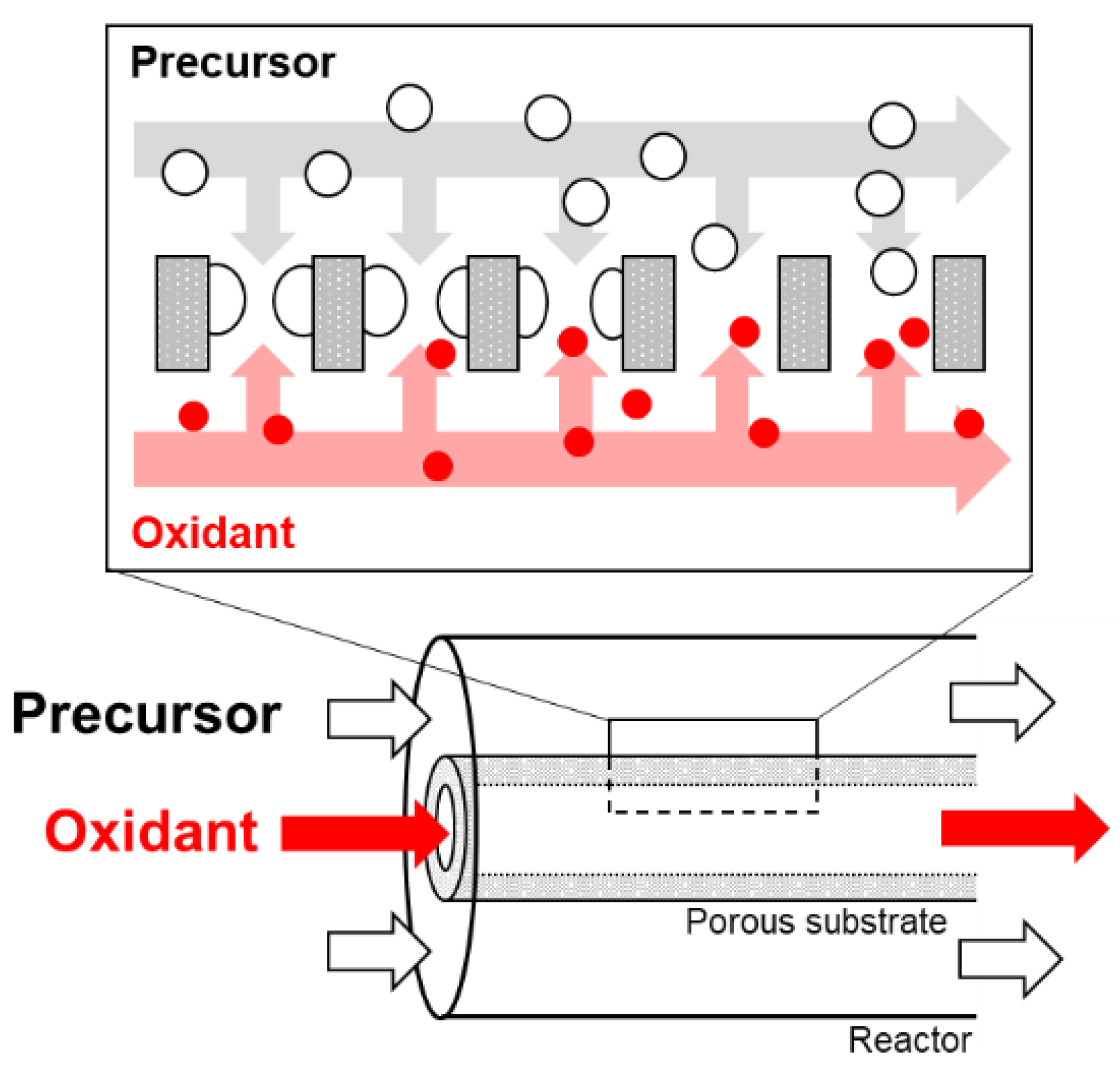
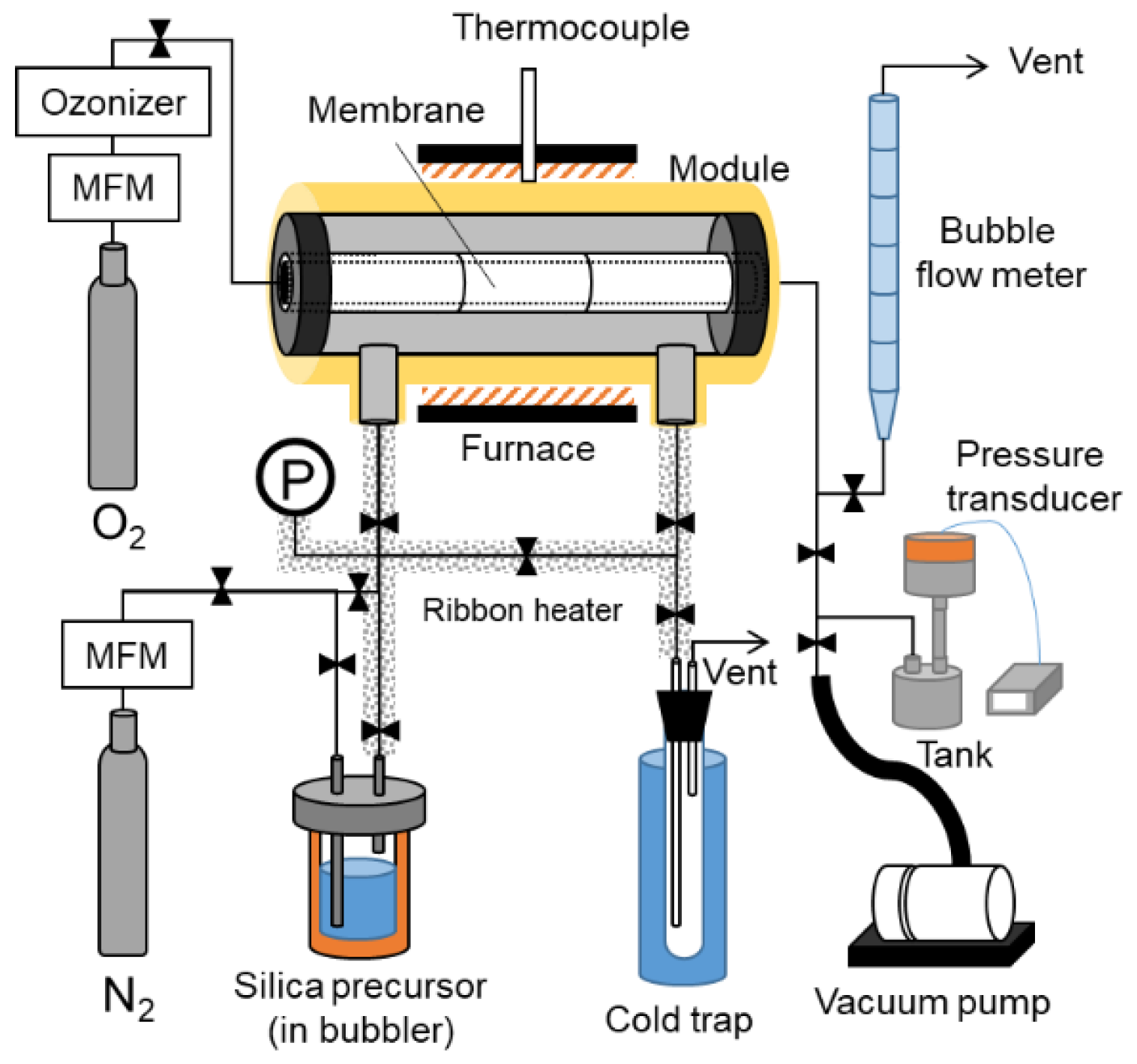
2.3. CVD Procedures
2.4. Membrane Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
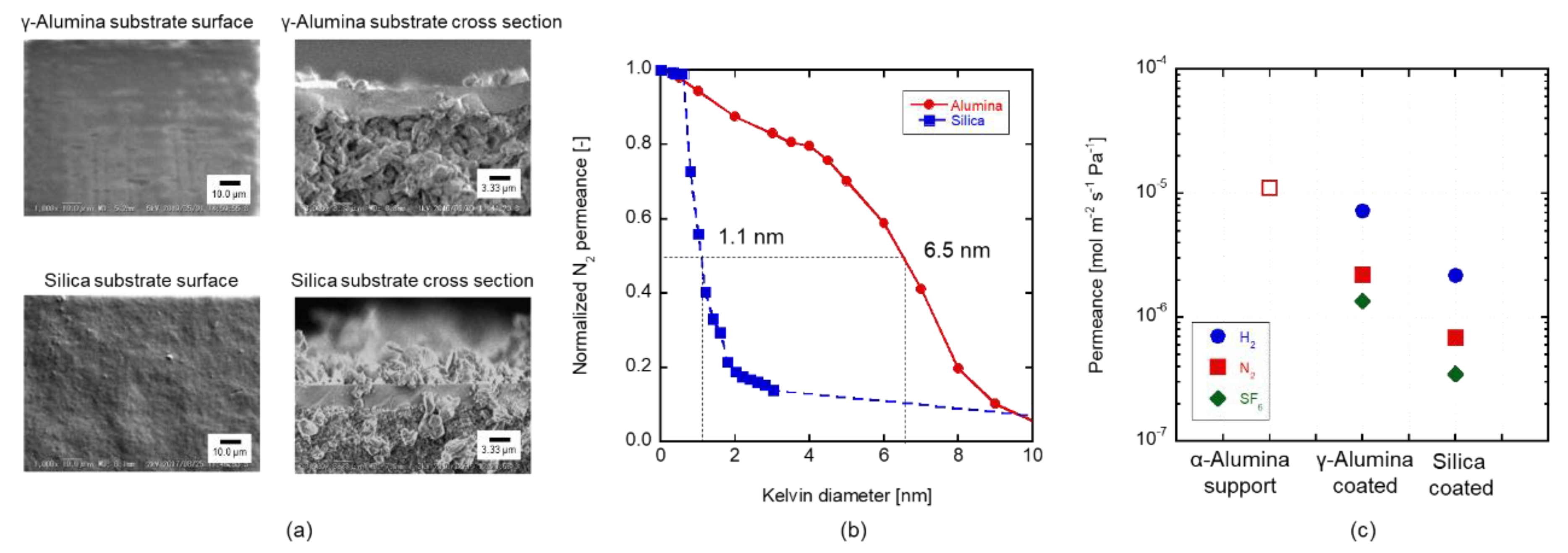
3.1. Pore Size Evaluation
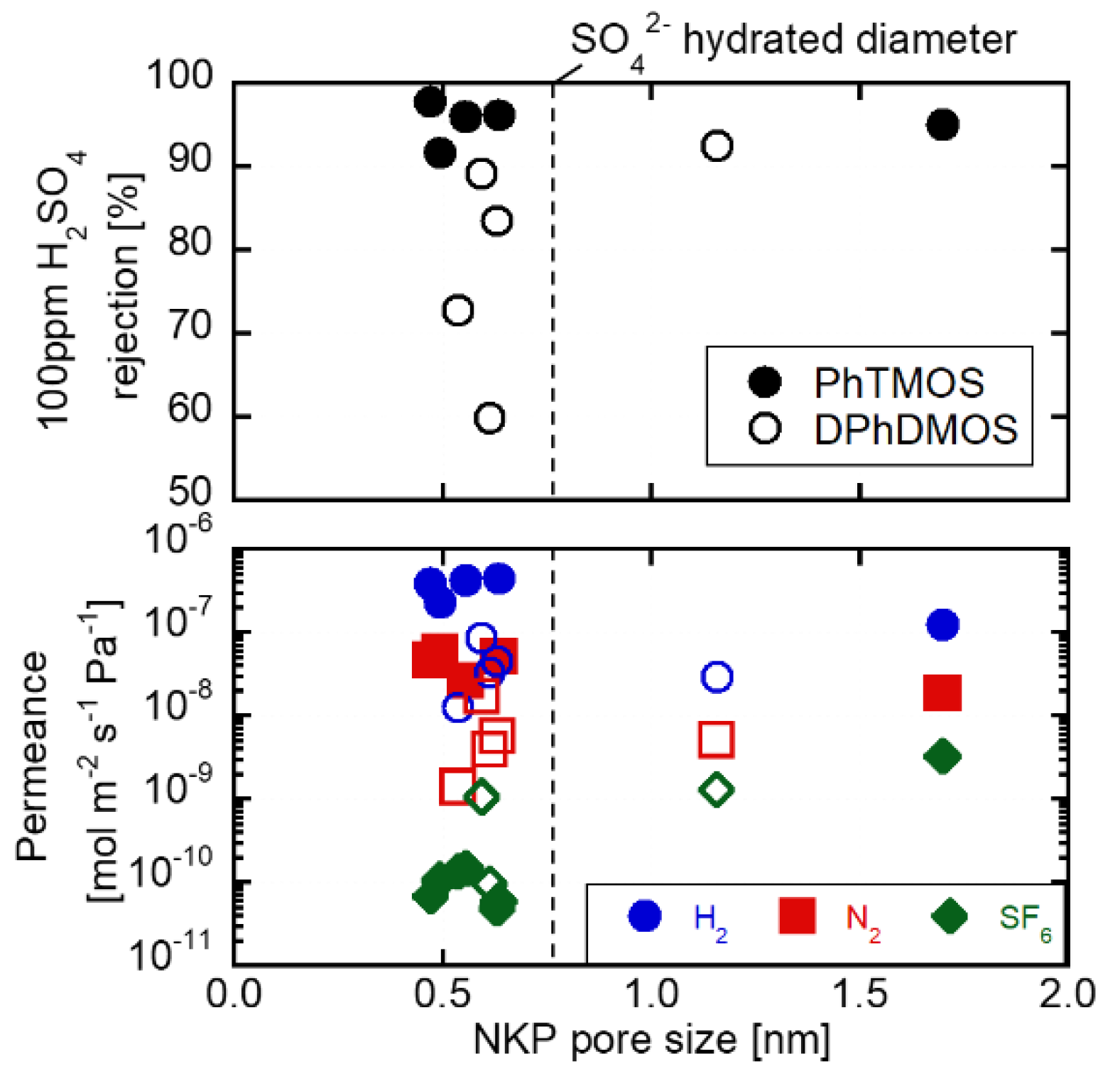
3.2. H2SO4 Permeation through the Membranes Deposited on the γ-alumina Substrates
3.3. Silica Substrates
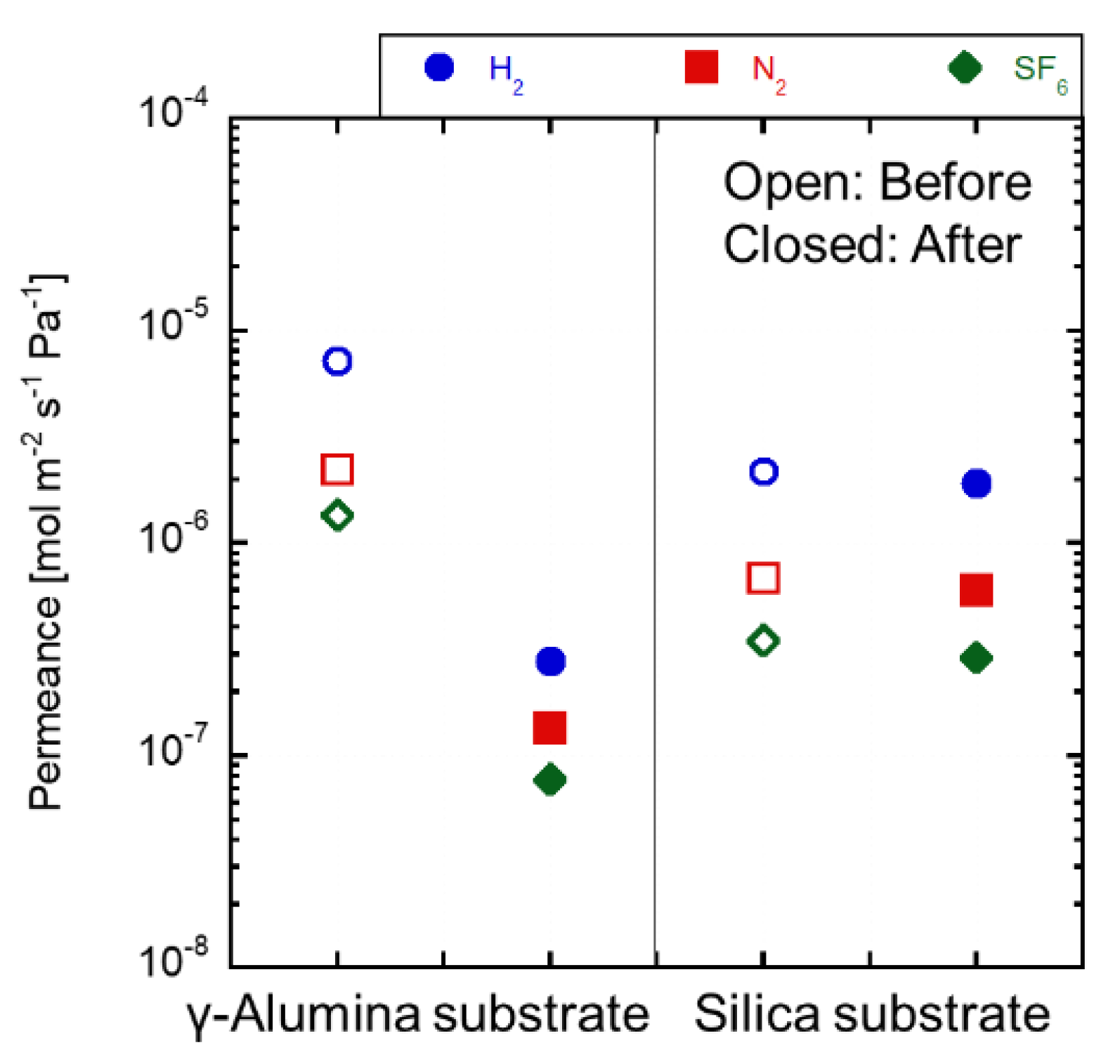
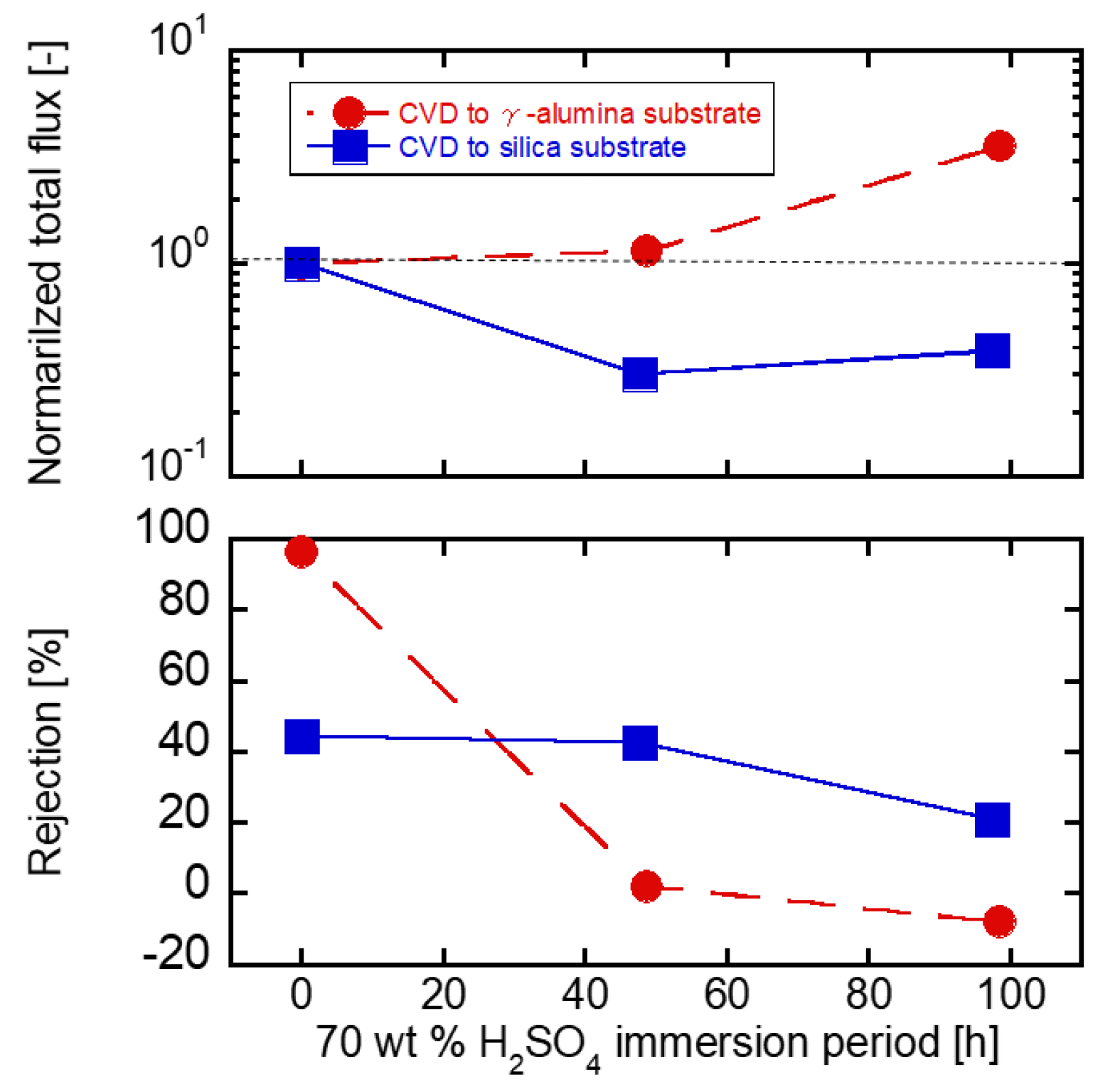
3.4. Acid Stability of the Substrates
3.5. CVD Treatment on the Silica Substrates
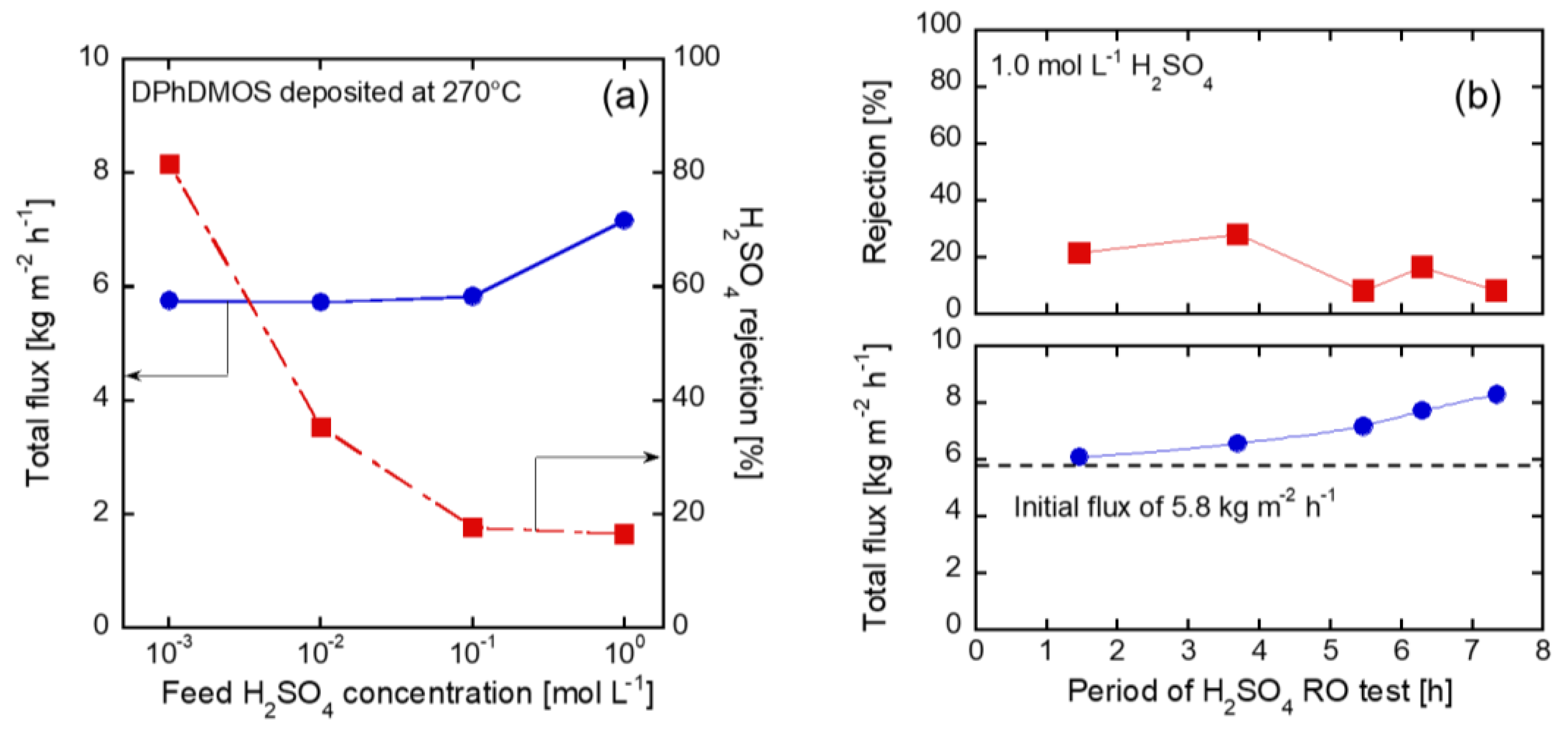
3.6. RO Tests through the Membrane on the Silica Substrates
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasahara, S.; Hwang, G.J.; Nakajima, H.; Choi, H.S.; Onuki, K.; Nomura, M. Effects of process parameters of the IS process on total thermal efficiency to produce hydrogen from water. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2003, 36, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, S.; Kubo, S.; Hino, R.; Onuki, K.; Nomura, M.; Nakao, S. Flowsheet study of the thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process for effective hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Lee, K.; Kim, Y.; Chang, J.; Cho, W.; Bae, K. A sulfur-iodine flowsheet using precipitation electro dialysis and membrane separation to produce hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 16604–16614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Chang, J.; Lee, T.; Lee, K.; Kim, Y. Start-up behaviors of a H2SO4–H2O distillation column for the 50 NL H2/H sulfur–iodine cycle. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 14172–14177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, N.; Nomura, M.; Kubo, S. Hydrogen production tests by hydrogen iodide decomposition membrane reactor equipped with silica-based ceramics membrane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 29091–29100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myagmarjav, O.; Ikeda, A.; Tanaka, N.; Kubo, S.; Nomura, M. Preparation of an H2-permselective silica membrane for the separation of H2 from the hydrogen iodide decomposition reaction in the iodine – sulfur process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 6012–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, N.; Nomura, M.; Kubo, S. Module design of silica membrane reactor for hydrogen production via thermochemical IS process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 10207–10217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myagmarjav, O.; Iwatsuki, J.; Tanaka, N.; Kubo, S.; Inagaki, Y.; Nomura, M.; Sawada, S.; Yamaki, T.; Yu, X.; Kanezashi, M.; et al. Research and development on membrane IS process for hydrogen production using solar heat. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 19141–19152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simate, G.S.; Ndlovu, S. Acid mine drainage: Challenges and opportunities. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1785–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.S.; Cheryan, M. Nanofiltration of model acetate solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, C.K.; Lee, K.H. Pervaporation separation of water-acetic acid mixtures through poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 109, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L.; Funke, H.H. Organics/ water separation by pervaporation with zeolite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 117, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariduraganavar, M.Y.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Kittur, A.A. Pervaporation separation of water-acetic acid mixtures through poly (vinyl alcohol)-silicone based hybrid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 246, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuru, T.; Shibata, T.; Wang, J.; Lee, H.R.; Kanezashi, M.; Yoshioka, T. Pervaporation of acetic acid aqueous solutions by organosilica membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 421–422, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shameli, A.; Ameri, E. Synthesis of cross-linked PVA membranes embedded with multi-wall carbon nanotubes and their application to esterification of acetic acid with methanol. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, C.; Wei, J. Separation of acetic acid from monosaccharides by NF and RO membranes: Performance comparison. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 429, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, J.P.; Benyamin, M.S.; Sumner, J.J.; Mackie, D.M. Using Reverse Osmosis Membranes to Couple Direct Ethanol Fuel Cells with Ongoing Fermentations. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 2016, 55, 12091–12098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, T.J.K.; Modise, S.J.; Krieg, H.M.; Keizer, K. The removal of acid sulphate pollution by nanofiltration. Desalination 2001, 140, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Reig, M.; Gibert, O.; Valderrama, C.; Cortina, J.L. Evaluation of NF membranes as treatment technology of acid mine drainage: Metals and sulfate removal. Desalination 2018, 440, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Reig, M.; Gibert, O.; Cortina, J.L. Recovery of sulphric acid and added value metals (Zn Cu and rare earths) from acidic mine waters using nanofiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumakiri, I.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakao, S. Application of a Zeolite A Membrane to Reverse Osmosis Process. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2000, 33, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, J.; Nenoff, T.M.; Lee, R. Desalination by reverse osmosis using MFI zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, N.; McPherson, B.; Lee, R. Enhanced Water Permeation of Reverse Osmosis through MFI-Type Zeolite Membranes with High Aluminum Contents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Kim, J.H.; Na, Y.H.; Moon, I.S.; Connor, G.; Maeda, S.; Morris, G.; Gray, S.; Duke, M. Temperature and Pressure Effects of Desalination Using a MFI-Type Zeolite Membrane. Membranes 2013, 3, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, J.; Kanezashi, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Tsuru, T. Development of Robust Organosilica Membranes for Reverse Osmosis. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13996–13999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Kanezashi, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Okuda, T.; Ohshita, J.; Tsuru, T. Tailoring the affinity of organosilica membranes by introducing polarizable ethenylene bridges and aqueous ozone modification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6147–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Kanezashi, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Ito, K.; Ohshita, J.; Tsuru, T. New insights into the microstructure-separation properties of organosilica membranes with ethane, ethylene, and acetylene bridges. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9357–9364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshita, J.; Muragishi, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Mizumo, T.; Kanezashi, M.; Tsuru, T. Preparation and separation properties of porous norbornane-bridged silica membrane. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 73, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Lin, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, J.; Tsuru, T. Development of ethylene-bridged organosilica membranes for desalination applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Koge, S.; Gunji, T.; Kanezashi, M.; Tsuru, T.; Ohshita, J. Preparation of POSS-derived robust RO membranes for water desalination. Desalination 2017, 404, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Matsuyama, E.; Komatsuzaki, M.; Sasaki, M.; Nomura, M. Development of Inorganic Silica Reverse Osmosis Membranes by Using a Counter-Diffusion Chemical Vapor Deposition Method. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2014, 47, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Ying, X.; Tokimasa, Y.; Nair, B.N.; Sugawara, T.; Nakao, S. Reaction control of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS)/O3 and tetramethyl orthosilicate (TMOS)/O3 counter diffusion chemical vapor deposition for preparation of molecular-sieve membranes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 4465–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Ono, K.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Sugawara, T.; Nakao, S. Preparation of a stable silica membrane by a counter diffusion chemical vapor deposition method. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 251, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Nagayo, T.; Monma, K. Pore size control of a molecular sieve silica membrane prepared by counter diffusion CVD method. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2007, 40, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Nomura, M. Preparation of Amorphous Silica Based Membranes for Separation of Hydrocarbons. J. Jpn. Petrol. Inst. 2016, 59, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsuyama, E.; Ikeda, A.; Komatsuzaki, M.; Sasaki, M.; Nomura, M. High-temperature propylene/propane separation through silica hybrid membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, S.; Bai, Y.; Shao, L. Ultra-facile aqueous synthesis of nanoporous zeolitic imidazolate framework membranes for hydrogen purification and olefin/paraffin separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 10898–10904. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Jiang, X.; Sun, H.; He, S.; Zhang, L.; Shao, L. Mesoporous dendric fibrous nanosilica (DFNS) stimulation mix matrix membranes towards superior CO2 capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 586, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Sadam, H.; Liu, Y.; Shao, L. Supramolecular chemistry assisted contribution of ultra-stable solvent-resistant membrane for angstrom-sized molecular separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.R.; Kanezashi, M.; Shimomura, Y.; Yoshioka, T.; Tsuru, T. Evaluation and fabrication of pore-size tuned silica membranes with tetraethoxydimethyl disiloxane for gas separation. AlChE J. 2011, 57, 2755–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, E.R., Jr. Phenomenological theory of ion solvation. Effective radii of hydrated ions. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| c [mol L−1] | α2 | [SO42−] | [HSO4−] | [H+] | Total Ionized Concentration [mol L−1] | π [MPa] | Δp [MPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−3 | 0.847 | 0.000847 | 0.0002 | 0.00185 | 0.002847 | 0.007 | 3.9929 |
| 10−2 | 0.418 | 0.004183 | 0.0058 | 0.01418 | 0.024183 | 0.060 | 3.9400 |
| 10−1 | 0.086 | 0.008587 | 0.0914 | 0.10859 | 0.208587 | 0.517 | 3.4829 |
| 100 | 0.010 | 0.009998 | 0.9900 | 1.01000 | 2.009998 | 4.983 | −0.9827 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishii, K.; Ikeda, A.; Takeuchi, T.; Yoshiura, J.; Nomura, M. Silica-Based RO Membranes for Separation of Acidic Solution. Membranes 2019, 9, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9080094
Ishii K, Ikeda A, Takeuchi T, Yoshiura J, Nomura M. Silica-Based RO Membranes for Separation of Acidic Solution. Membranes. 2019; 9(8):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9080094
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshii, Katsunori, Ayumi Ikeda, Toshichika Takeuchi, Junko Yoshiura, and Mikihiro Nomura. 2019. "Silica-Based RO Membranes for Separation of Acidic Solution" Membranes 9, no. 8: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9080094
APA StyleIshii, K., Ikeda, A., Takeuchi, T., Yoshiura, J., & Nomura, M. (2019). Silica-Based RO Membranes for Separation of Acidic Solution. Membranes, 9(8), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9080094