Hydrophobic *BEA-Type Zeolite Membranes on Tubular Silica Supports for Alcohol/Water Separation by Pervaporation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
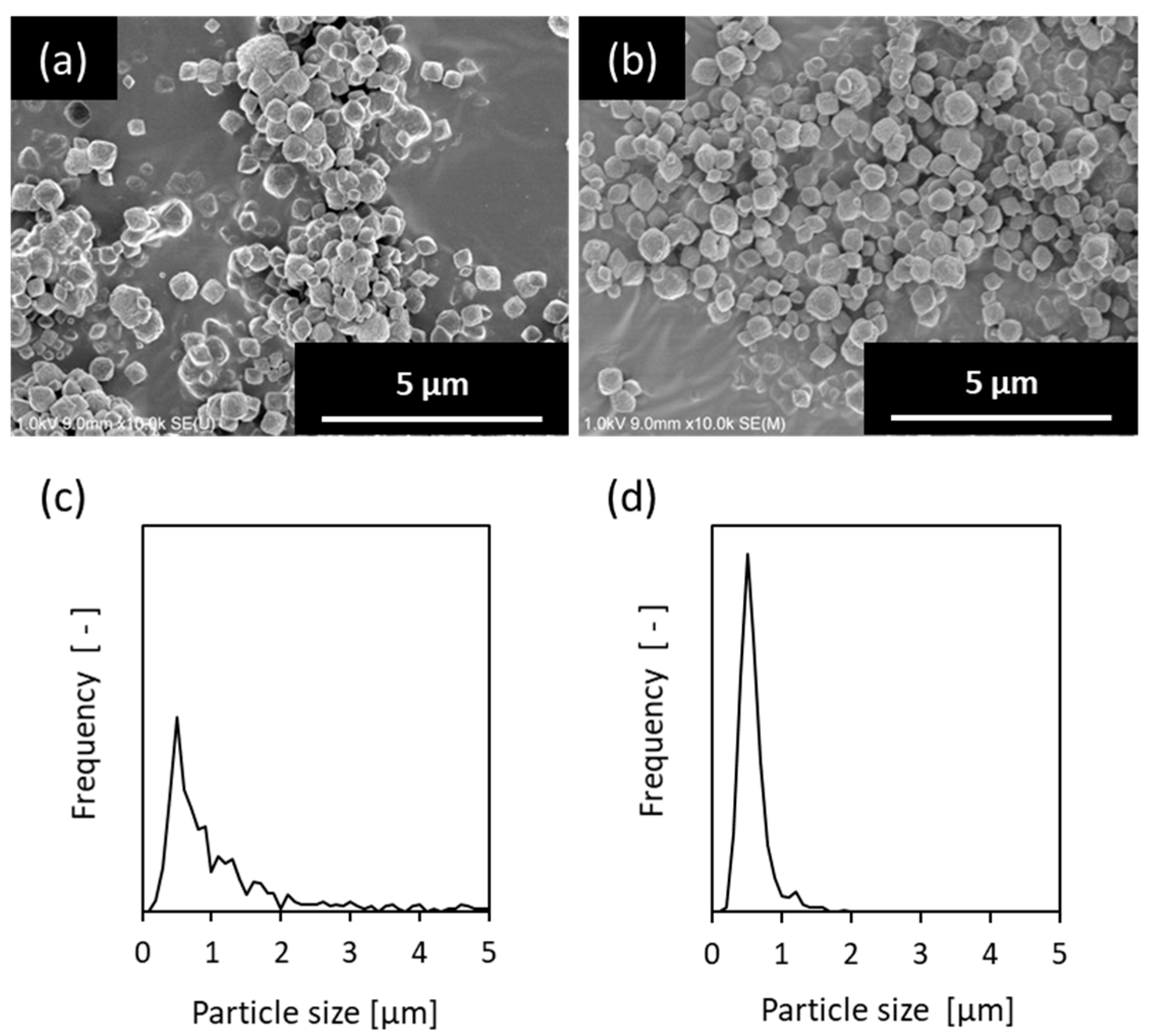
2.1. Classification of *BEA-Type Zeolite Crystals
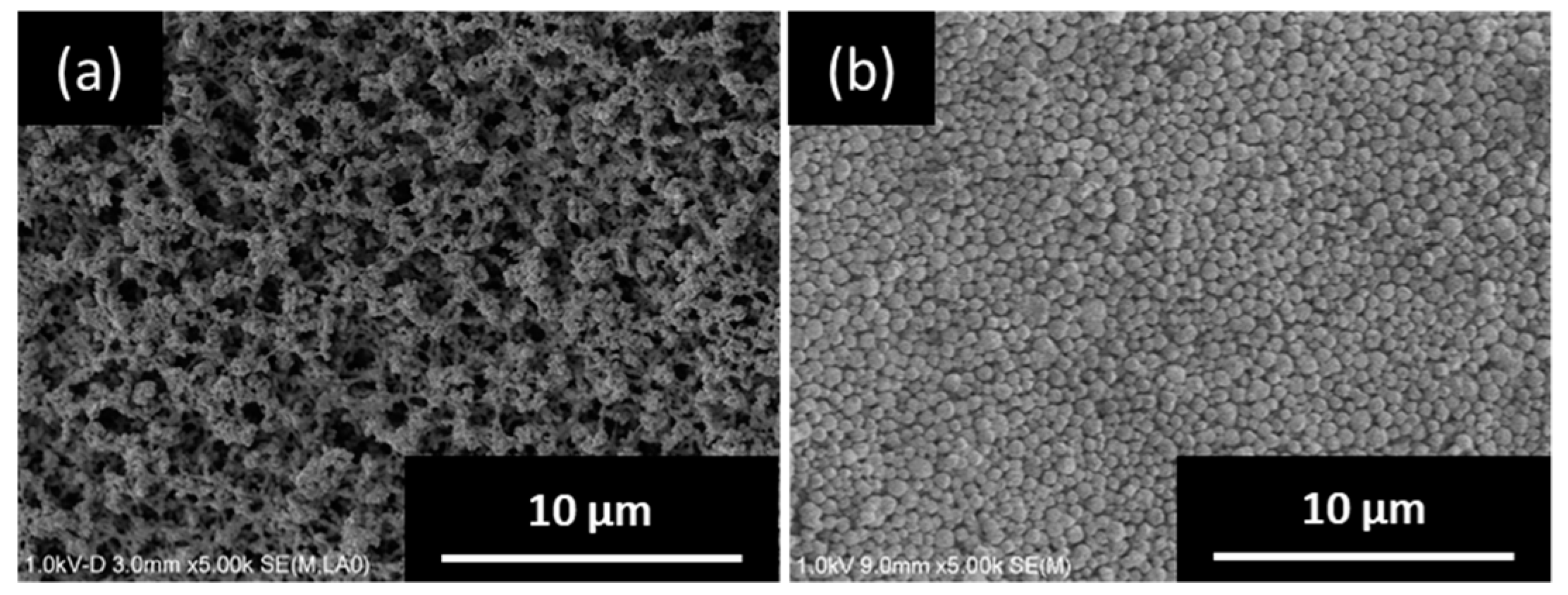
2.2. Preparation of Seeded Support by Electrophoretic Deposition (EPD)
2.3. Preparation of Pure-Silica *BEA-Type Zeolite Membranes
2.4. Characterization
3. Result and Discussion
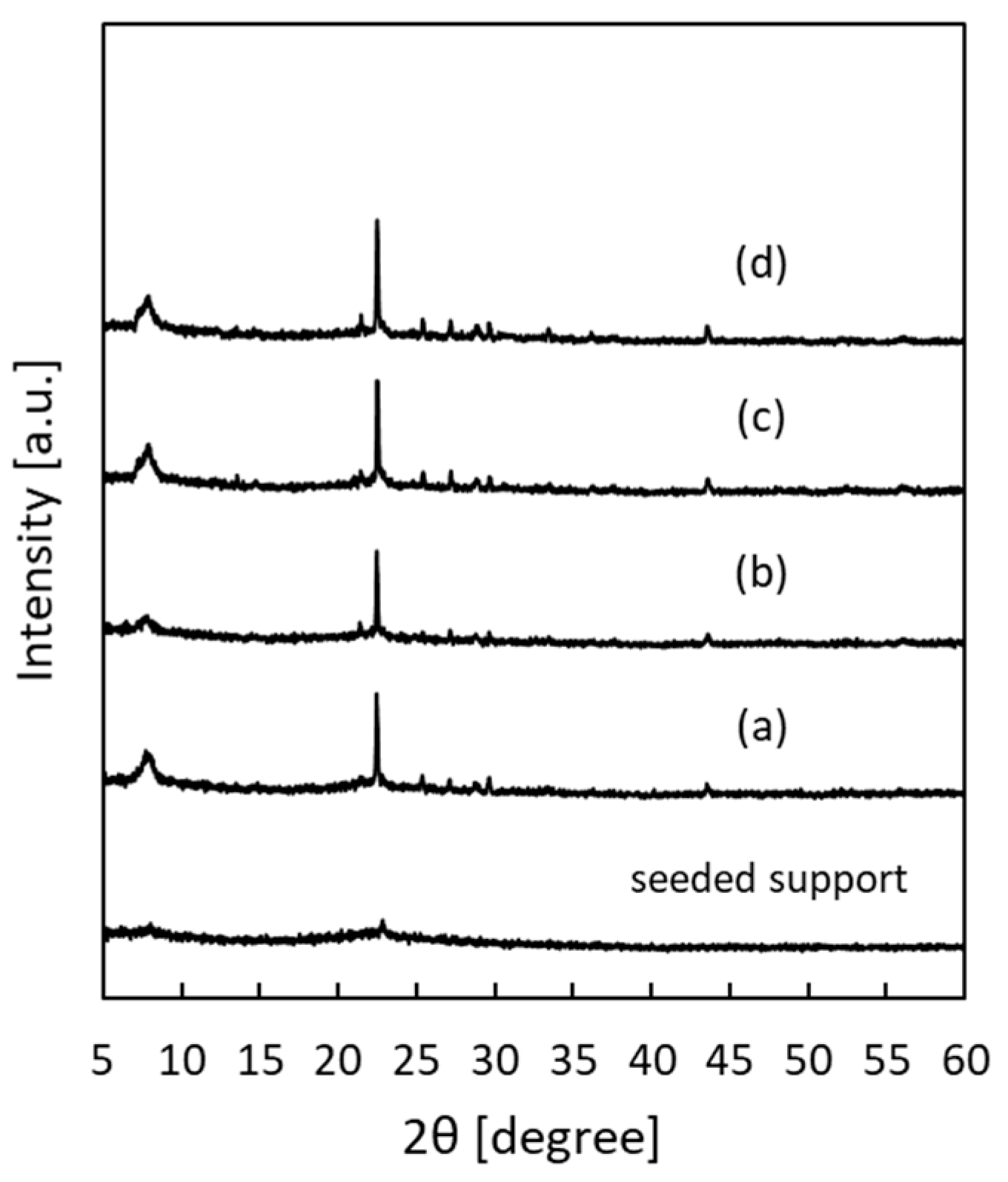
3.1. Seeded Support
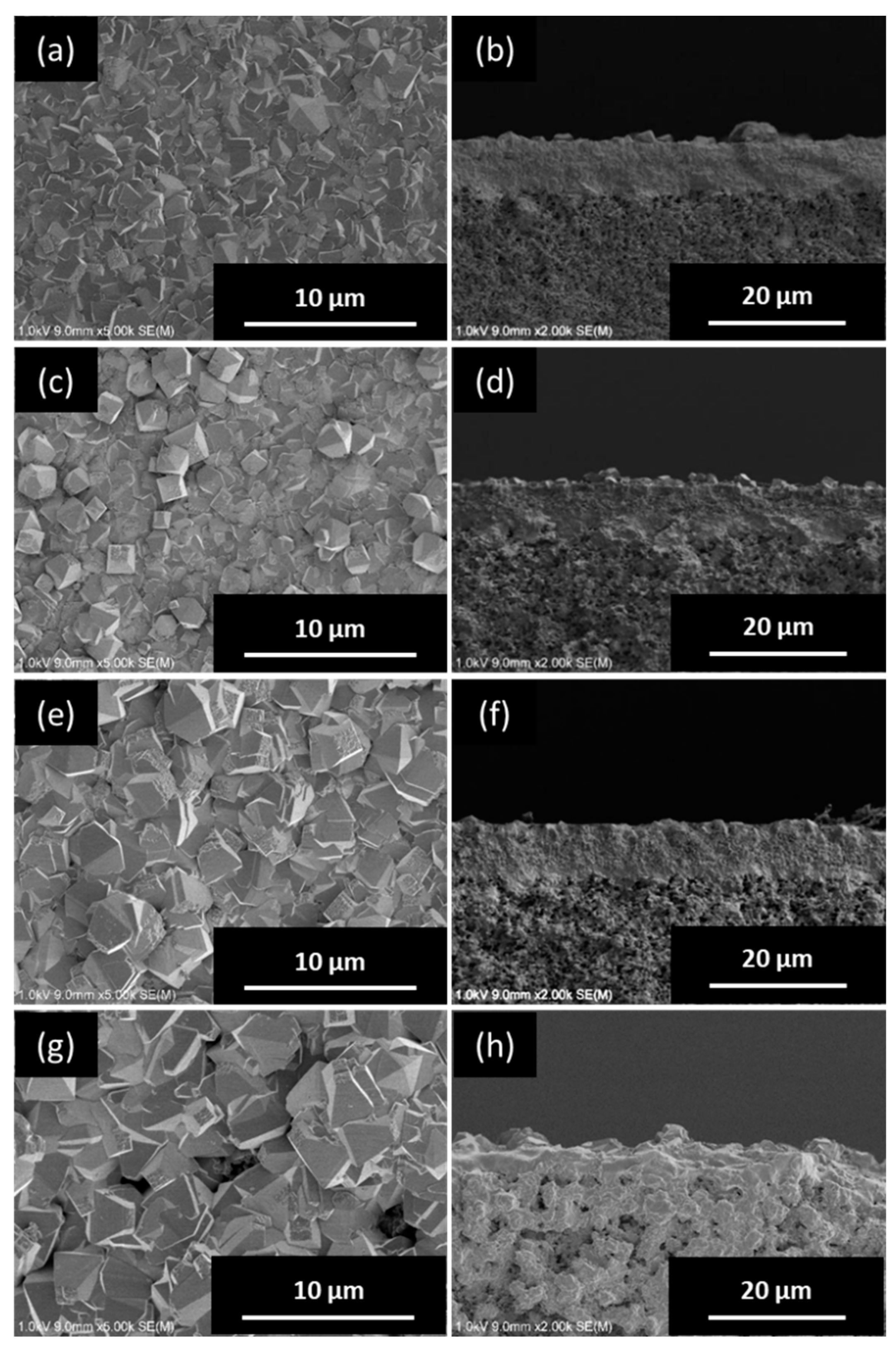
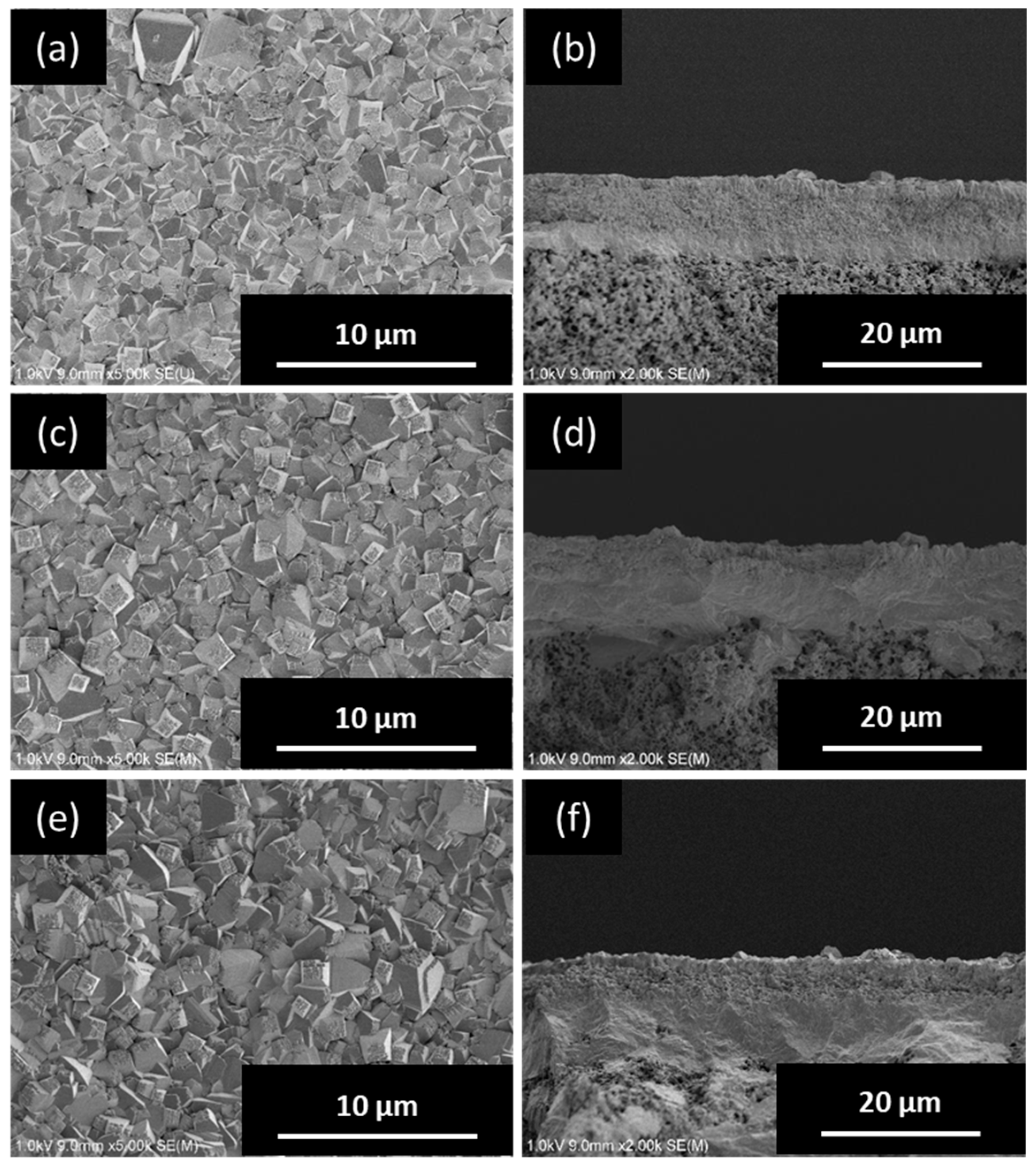
3.2. Pure-Silica *BEA-Type Zeolite Membrane
3.2.1. Effect of H2O/SiO2 Ratio of Synthesis Gel
3.2.2. Effect of NH4F/SiO2 Ratio of Synthesis Gel
3.2.3. Separation Performance of Butanol/Water Mixtures
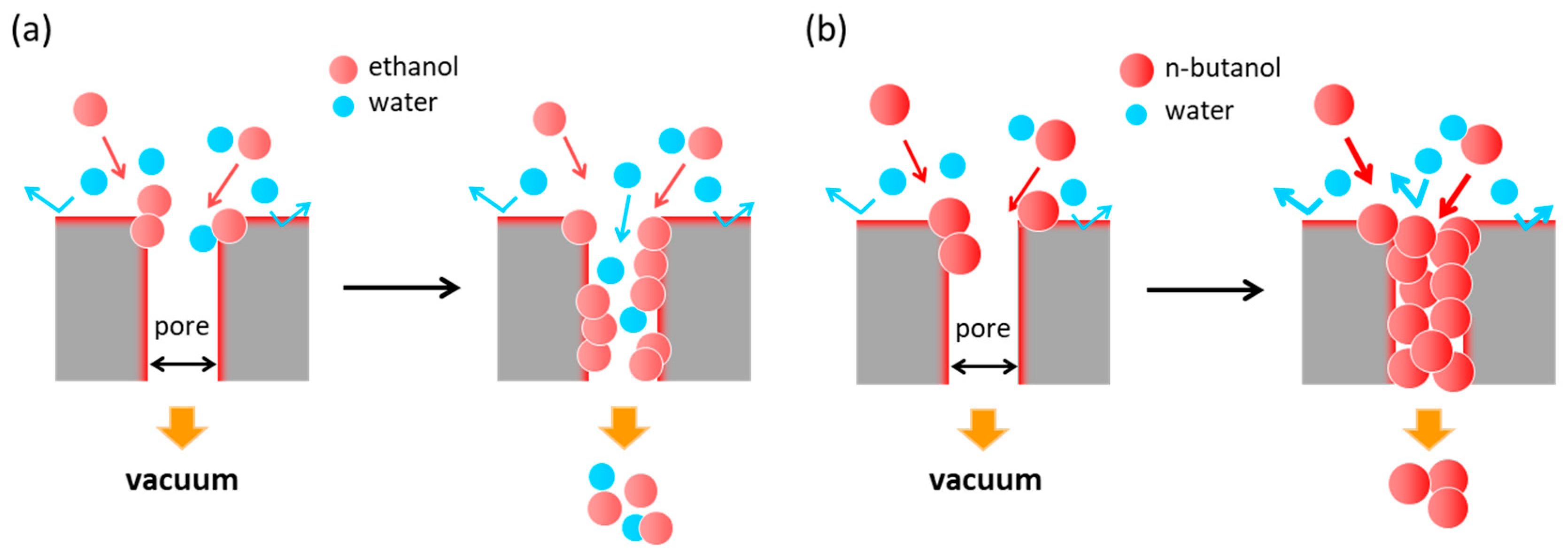
3.3. Separation Mechanism of Hydrophobic *BEA Membrane
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsapatsis, M. Toward high-throughput zeolite membranes. Science 2011, 334, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.C.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L. Fundamentals and applications of pervaporation through zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Yanagishita, H.; Kiyozumi, Y.; Mizukami, F.; Haraya, K. Separation of ethanol/water mixture by silicalite membrane on pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 95, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakao, S.I. Ethanol/water transport through silicalite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 144, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, W. Preparation of silicalite-1 membrane by solution-filling method and its alcohol extraction properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Y. Microstructural optimization of MFI-type zeolite membranes for ethanol–water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16093–16100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhu, M.H.; Zhou, R.F.; Chen, X.S.; Kita, H. Synthesis of a silicalite zeolite membrane in ultradilute solution and its highly selective separation of organic/water mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 11499–11508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z. Effects of sodium ions on the separation performance of pure-silica MFI zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.J.; Shao, J.; Wang, Z.B.; Yan, Y.S. Preparation of zeolite MFI membranes on alumina hollow fibers with high flux for pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Negishi, H.; Miyamoto, M.; Uemiya, S.; Oumi, Y. Effect of deposition seed crystal amount on the α-Al2O3 support and separation performance of silicalite-1 membranes for acetic acid/water mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Horiguchi, Y.; Negishi, H.; Miyamoto, M.; Uemiya, S.; Takeno, A.; Sawada, S.; Oumi, Y. Fabrication of high-performance silicalite-1 membrane by a novel seeding method using zeolite-dispersed polymer film. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 261, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, H.; Sakaki, K.; Ikegami, T. Silicalite pervaporation membrane exhibiting a separation factor of over 400 for butanol. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Xiao, W.; Yang, J.; Chu, N.; Lu, J.; Yin, D.; Wang, J. Synthesis of silicalite-1 membrane with two silicon source by secondary growth method and its pervaporation performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 76, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.X.; Xue, S.M.; Xu, Z.L. Preparation of MFI zeolite membranes on coarse macropore stainless steel hollow fibers for the recovery of bioalcohols. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 109936–109944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Negishi, H.; Okuno, T.; Saito, T.; Tawarayama, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Miyamoto, M.; Uemiya, S.; Sawada, Y.; Oumi, Y. High-performance silicalite-1 membranes on porous tubular silica supports for separation of ethanol/water mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 187, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Negishi, H.; Okuno, T.; Saito, T.; Tawarayama, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Miyamoto, M.; Uemiya, S.; Sawada, Y.; Oumi, Y. A simple secondary growth method for the preparation of silicalite-1 membrane on a tubular silica support via gel-free steam-assisted conversion. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Negishi, H.; Okuno, T.; Tawarayama, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Miyamoto, M.; Uemiya, S.; Oumi, Y. Effects of Silica-Particle Coating on a Silica Support for the Fabrication of High-Performance Silicalite-1 Membranes by Gel-Free Steam-Assisted Conversion. Membranes 2019, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacy, M.M.J.; Newsam, J.M. Two new three-dimensional twelve-ring zeolite frameworks of which zeolite beta is a disordered intergrowth. Nature 1988, 332, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobler, J.; Abrevaya, H.; Mintova, S.; Bein, T. High-silica zeolite-β: From stable colloidal suspensions to thin films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 14274–14280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Fujimaki, N.; Kobayashi, G.; Yasuda, N.; Oshima, Y.; Seshimo, M.; Matsukata, M. Formation process of BEA-type zeolite membrane under OSDA-free conditions and its separation property. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 284, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcia, P.S.; Ferreira, A.; Gascon, J.; Aguado, S.; Silva, J.A.C.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Kapteijn, F. Zeolite beta membranes for the separation of hexane isomers. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 128, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloncy, M.L.; van der Berg, A.W.C.; Gora, L.; Jansen, J.C. Preparation of zeolite beta membranes and their pervaporation performance in separating di-from mono-branched alkanes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 85, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jon, H.; Lu, B.; Oumi, Y.; Itabashi, K.; Sano, T. Synthesis and thermal stability of beta zeolite using ammonium fluoride. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 89, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosheva, L.; Holzl, M.; Metzger, T.H.; Valtchev, V.; Mintova, S.; Bein, T. Zeolite beta films synthesized from basic and near-neutral precursor solutions and gels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2005, 25, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, D.P.; Griken, R.V.; Sanchez, P.; Sanz, R.; Rodriguez, L. Crystallization mechanism of all-silica zeolite beta in fluoride medium. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 46, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Peng, Y.; Yao, X.; Qiu, S. Synthesis and characterization of (h0l) oriented high-silica zeolite beta membrane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 124, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B. Synthesis of (h0l)-oriented zeolite Fe-beta membrane. Mater. Lett. 2014, 131, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, Y.F.; Bhatia, S. Synthesis and characterization of pure-silicazeolite-beta membrane. AJSTD 2006, 23, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Shan, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Y. Preparation of zeolite MFI membranes on defective macroporous alumina supports by a novel wetting-rubbing seeding method: Role of wetting agent. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Negishi, H.; Miyamoto, M.; Uemiya, S.; Oumi, Y. Effect of Si/Al ratio and amount of deposited MFI-type seed crystals on the separation performance of silicalite-1 membranes for ethanol/water mixtures in the presence of succinic acid. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 267, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, J.; Paulus, M.; Hunger, M.; Weitkamp, J. Hydrophobic properties of all-silica zeolite beta. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1998, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qin, F.; Qin, P.; Karim, M.N.; Tan, T. Preparation of PDMS membrane using water as solvent for pervaporation separation of butanol–water mixture. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2180–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Chen, J.X.; Fang, M.Q.; Wang, T.; Yu, L.X.; Li, J.D. ZIF-7/PDMS mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation recovery of butanol from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 163, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Shi, Q.; Yan, H.; Ji, S.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G. Simultaneous spray self-assembly of highly loaded ZIF-8-PDMS nanohybrid membranes exhibiting exceptionally high biobutanol-permselective pervaporation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5578–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Ban, Y.; Xu, L.; Yang, W. An organophilic pervaporation membrane derived from metal–organic framework nanoparticles for efficient recovery of bio-alcohols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10636–10639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Meagher, M. Pervaporative recovery of nbutanol from aqueous solutions and ABE fermentation broth using thin-film silicalite-filled silicone composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 192, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G.; Tuan, V.A.; Falconer, J.L.; Noble, R.D. Properties and separation performance of Ge-ZSM-5 membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 58, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.Z.; Engtrakul, C.; Bischoff, B.L.; Lu, M.; Alemseghed, M. Surface-engineered inorganic nanoporous membranes for vapor and pervaporative separations of water–ethanol mixtures. Membranes 2018, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | Synthesis Gel Composition 1 | Separation Factor | Flux [kg·m−2·h−1] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | H2O/SiO2 Ratio | |||
| M1 | 1.00 | 8 | 8.7 | 8.56 |
| M2 | 0.20 | 40 | 8.7 | 7.51 |
| M3 | 0.08 | 100 | 8.5 | 7.97 |
| M4 | 0.05 | 160 | 1.5 | 20.6 |
| Support Materials | Feed Concentration [wt %] | Feed Temperature [K] | Separation Factor | Flux [kg·m−2·h−1] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Al2O3 | 3 | 353 | 33 | 0.35 | [5] |
| Silica | 3 | 333 | 68 | 0.87 | [5] |
| α-Al2O3 | 5 | 333 | 85 | 1.36 | [6] |
| Mullite | 5 | 333 | 66 | 1.91 | [7] |
| α-Al2O3 | 5 | 323 | 76 | 1.05 | [8] |
| α-Al2O3 | 10 | 323 | 88 | 0.47 | [10] |
| α-Al2O3 | 5 | 333 | 39 | 1.51 | [13] |
| Silica | 10 | 323 | 92 | 3.00 | [15] |
| Samples | Synthesis Gel Composition 2 | Separation Factor | Flux [kg·m−2·h−1] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | NH4F/SiO2 Ratio | |||
| M3 | 0.45 | 5.63 | 8.5 | 7.97 |
| M5 | 0.50 | 6.25 | 9.8 | 7.37 |
| M6 | 0.60 | 7.50 | 12.3 | 6.29 |
| M7 | 0.70 | 8.75 | 12.0 | 6.22 |
| Membrane Type | Feed Concentration [wt %] | Feed Temperature [K] | Separation Factor | Flux [kg·m−2·h−1] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDMS | 1.5 | 328 | 43 | 0.67 | [32] |
| PDMS | 1 | 333 | 51 | 1.08 | [33] |
| ZIF-7/PDMS | 1 | 333 | 66 | 1.69 | [33] |
| ZIF-8/PDMS | 1.5 | 353 | 82 | 4.85 | [34] |
| ZIF-8/PMPS | 1 | 353 | 40 | 6.40 | [35] |
| Silicalite-1/PDMS | 1 | 313 | 92 | 0.13 | [36] |
| Ge-ZSM-5 | 5 | 303 | 19 | 0.02 | [37] |
| Silicalite-1 | 1 | 343 | 150 | 0.10 | [13] |
| Silicalite-1 | 1 | 318 | 465 | 0.04 | [12] |
| Silicalite-1 | 1.5 | 353 | 207 | 0.22 | [14] |
| *BEA | 1 | 318 | 229 | 0.62 | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ueno, K.; Yamada, S.; Watanabe, T.; Negishi, H.; Okuno, T.; Tawarayama, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Miyamoto, M.; Uemiya, S.; Oumi, Y. Hydrophobic *BEA-Type Zeolite Membranes on Tubular Silica Supports for Alcohol/Water Separation by Pervaporation. Membranes 2019, 9, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070086
Ueno K, Yamada S, Watanabe T, Negishi H, Okuno T, Tawarayama H, Ishikawa S, Miyamoto M, Uemiya S, Oumi Y. Hydrophobic *BEA-Type Zeolite Membranes on Tubular Silica Supports for Alcohol/Water Separation by Pervaporation. Membranes. 2019; 9(7):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070086
Chicago/Turabian StyleUeno, Kyohei, Saki Yamada, Toshinari Watanabe, Hideyuki Negishi, Takuya Okuno, Hiromasa Tawarayama, Shinji Ishikawa, Manabu Miyamoto, Shigeyuki Uemiya, and Yasunori Oumi. 2019. "Hydrophobic *BEA-Type Zeolite Membranes on Tubular Silica Supports for Alcohol/Water Separation by Pervaporation" Membranes 9, no. 7: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070086
APA StyleUeno, K., Yamada, S., Watanabe, T., Negishi, H., Okuno, T., Tawarayama, H., Ishikawa, S., Miyamoto, M., Uemiya, S., & Oumi, Y. (2019). Hydrophobic *BEA-Type Zeolite Membranes on Tubular Silica Supports for Alcohol/Water Separation by Pervaporation. Membranes, 9(7), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070086






